Eparchy of Santa María del Patrocinio en Buenos Aires on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Eparchy ( gr, ἐπαρχία, la, eparchía / ''overlordship'') is an ecclesiastical unit in Eastern Christianity, that is equivalent to a

 Throughout the late antiquity and the early medieval period, within
Throughout the late antiquity and the early medieval period, within 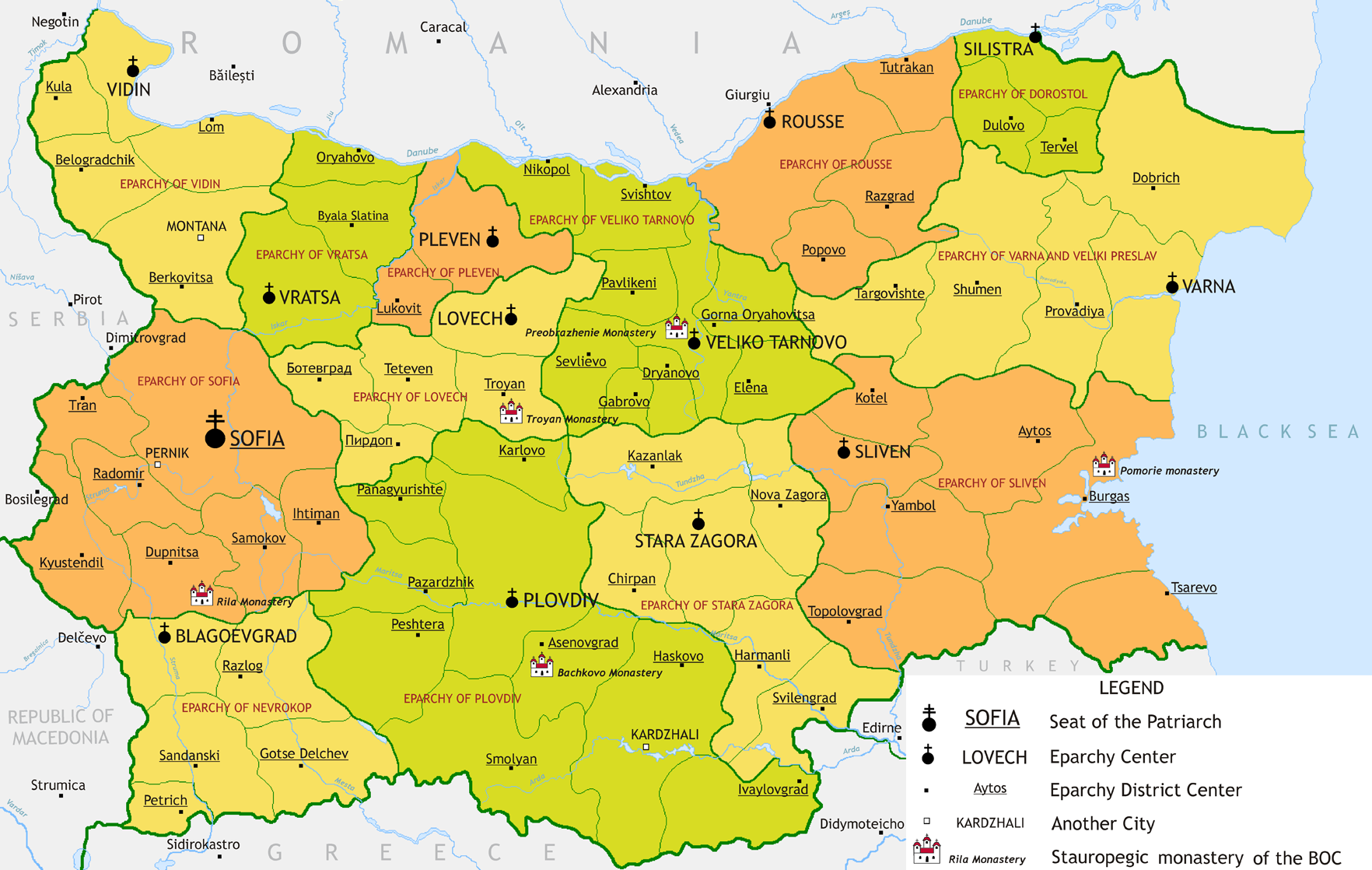
 Since the fragmentation of the original metropolitan provinces into several titular metropolises, that were also referred to as ''eparchies'', the Patriarchate of Constantinople became more centralized, and such was structure remains up to the present day. Similar ecclesiastical terminology is also employed by other
Since the fragmentation of the original metropolitan provinces into several titular metropolises, that were also referred to as ''eparchies'', the Patriarchate of Constantinople became more centralized, and such was structure remains up to the present day. Similar ecclesiastical terminology is also employed by other
Catholic Encyclopedia (1909): Adrian Fortescue: Eparchy
Map with all Dioceses of the Eastern Churches
{{Greek terms for country subdivisions Eastern Christianity Dioceses (ecclesiastical) Bishops by type Episcopacy in the Catholic Church Episcopacy in Eastern Orthodoxy Episcopacy in Oriental Orthodoxy Ecclesiastical titles Greek words and phrases
diocese
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associa ...
in Western Christianity
Western Christianity is one of two sub-divisions of Christianity ( Eastern Christianity being the other). Western Christianity is composed of the Latin Church and Western Protestantism, together with their offshoots such as the Old Catholic ...
. Eparchy is governed by an ''eparch'', who is a bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is c ...
. Depending on the administrative structure of a specific Eastern Church, eparchy can belong to an ecclesiastical province
An ecclesiastical province is one of the basic forms of jurisdiction in Christian Churches with traditional hierarchical structure, including Western Christianity and Eastern Christianity. In general, an ecclesiastical province consists of seve ...
(usually a metropolis
A metropolis () is a large city or conurbation which is a significant economic, political, and cultural center for a country or region, and an important hub for regional or international connections, commerce, and communications.
A big ci ...
), but it can also be exempt. Each eparchy is divided into parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest, often termed a parish priest, who might be assisted by one o ...
es, in the same manner as a diocese in Western Churches. Historical development of eparchies in various Eastern Churches was marked by local distinctions, that can be observed in modern ecclesiastical practices of Eastern Orthodox Churches, Oriental Orthodox Churches
The Oriental Orthodox Churches are Eastern Christian churches adhering to Miaphysite Christology, with approximately 60 million members worldwide. The Oriental Orthodox Churches are part of the Nicene Christian tradition, and represent ...
and Eastern Catholic Churches
The Eastern Catholic Churches or Oriental Catholic Churches, also called the Eastern-Rite Catholic Churches, Eastern Rite Catholicism, or simply the Eastern Churches, are 23 Eastern Christian autonomous ('' sui iuris'') particular churches of t ...
.
Terminology
TheEnglish
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
word ''eparchy'' is an anglicize
Anglicisation is the process by which a place or person becomes influenced by English culture or British culture, or a process of cultural and/or linguistic change in which something non-English becomes English. It can also refer to the influenc ...
d term, that comes from the original Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
word ( grc-koi, , eparchía, overlordship, ). It is an abstract noun, formed with an intensive
In grammar, an intensive word form is one which denotes stronger, more forceful, or more concentrated action relative to the root on which the intensive is built. Intensives are usually lexical formations, but there may be a regular process for for ...
prefix (, , + , , ). It is commonly Latinized as ''eparchia''. The term can be loosely translated as the rule over something (literally: an overlordship). The term had various meanings and multiple uses throughout history, mainly in politics and administration, starting from the Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
, and continuing throughout the Roman era
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC ...
.
In the Greco-Roman world, it was used as a Greek equivalent for the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
term ''provincia'', denoting province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
, the main administrative unit of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
. The same use was employed in the early Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, until major administrative reforms, that were undertaken between the 7th and 9th centuries, abolishing the old provincial system. In modern times, the term was also employed within administrative systems of some countries, like Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
and Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ge ...
.
Since it was commonly used as the main Greek designation for an administrative province of the Roman Empire, the term ''eparchy'' consequently gained an additional use among Greek-speaking Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
, denoting ecclesiastical structures on the provincial level of Church administration, within Eastern Christianity. Such terminological borrowing resulted from the final consolidation of the provincial (metropolitan) system in the 4th century. The First Ecumenical Council
The First Council of Nicaea (; grc, Νίκαια ) was a council of Christian bishops convened in the Bithynian city of Nicaea (now İznik, Turkey) by the Roman Emperor Constantine I in AD 325.
This ecumenical council was the first effor ...
(325) confirmed (Canon IV) that all bishops of each civil province should be grouped in one ecclesiastical province
An ecclesiastical province is one of the basic forms of jurisdiction in Christian Churches with traditional hierarchical structure, including Western Christianity and Eastern Christianity. In general, an ecclesiastical province consists of seve ...
, headed by a metropolitan (bishop of the provincial capital). Since civil provinces were called eparchies in Greek, the same term was used to define ecclesiastical provinces. Such use became customary, and metropolitan provinces came to be known as ''eparchies''.
Eastern Orthodox Churches
Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or " canonical ...
terminology, the term ''eparchy'' remained a common designation for a metropolitan province i.e. ''metropolis'' ( gr, μητρόπολις, la, metropolis).
During the later medieval period, terminology started to shift, particularly within the Patriarchate of Constantinople
The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople ( el, Οἰκουμενικὸν Πατριαρχεῖον Κωνσταντινουπόλεως, translit=Oikoumenikón Patriarkhíon Konstantinoupóleos, ; la, Patriarchatus Oecumenicus Constanti ...
. The process of title-inflation, that was affecting Byzantine bureaucracy and aristocracy
Through the 5th century Hellenistic political systems, philosophies and theocratic Christian-Eastern concepts had gained power in the eastern Greek-speaking Mediterranean due to the intervention of Important religious figures there such as ...
, also gained momentum in ecclesiastical circles. In order to promote centralization, patriarchal authorities started to multiply the numbers of metropolitans by elevating local bishops to honorary metropolitan ranks without giving them any real metropolitan powers, and making them directly appointed and thus more dependent on Constantinople. As a consequence, the use of the word ''eparchy'' was expanded to include not only proper metropolitan provinces, but also the newly created honorary metropolitan sees, that were no real provinces, and thus no different then simple bishoprics except in honorary titles and ranks. In spite of that, such honorary metropolitan sees also came to be called ''eparchies''. This process was systematically promoted, thus resulting in a major terminological shift.

autocephalous
Autocephaly (; from el, αὐτοκεφαλία, meaning "property of being self-headed") is the status of a hierarchical Christian church whose head bishop does not report to any higher-ranking bishop. The term is primarily used in Eastern O ...
and autonomous
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's ow ...
Churches within Eastern Orthodox community. In those who are non-Greek, term ''eparchy'' is used in local variants, and also has various equivalents in local languages.
Eparchies of the main Eastern Orthodox Churches:
* Eparchies of the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople
The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople ( el, Οἰκουμενικὸν Πατριαρχεῖον Κωνσταντινουπόλεως, translit=Oikoumenikón Patriarkhíon Konstantinoupóleos, ; la, Patriarchatus Oecumenicus Constanti ...
* Eparchies of the Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Alexandria
The Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Alexandria and all Africa ( grc, Πατριαρχεῖον Ἀλεξανδρείας καὶ πάσης Ἀφρικῆς, Patriarcheîon Alexandreías kaì pásēs Aphrikês, The Patriarchate of Alexandria and ...
* Eparchies of the Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Antiochia
The Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Antioch ( el, Ελληνορθόδοξο Πατριαρχείο Αντιοχείας), also known as the Antiochian Orthodox Church and legally as the Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Antioch and All the East ( ar ...
* Eparchies of the Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Jerusalem
The Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Jerusalem, el, Πατριαρχεῖον Ἱεροσολύμων, ''Patriarcheîon Hierosolýmōn;'' he, הפטריארכיה היוונית-אורתודוקסית של ירושלים; ar, كنيسة الرو� ...
* Eparchies of the Russian Orthodox Church This is the list of the metropolitanates and eparchies (dioceses) of the Russian Orthodox Church.
Russia
Eparchies and metropolitanates of the Russian Orthodox Church in the Russian Federation:Official site of the Russian Orthodox ChurchOrganizatio ...
* Eparchies of the Serbian Orthodox Church
This is the list of eparchies (dioceses) of the Serbian Orthodox Church, based on the Article No. 14 of the Constitution of Serbian Orthodox Church and subsequent decisions of the Holy assembly of SOC (seeOfficial text of the Constitution o ...
* Eparchies of the Romanian Orthodox Church
This is the list of the hierarchs of the Romanian Orthodox Church, depicting the organization of the church.
For a list of those hierarchs who are currently members of the Holy Synod, see thwebsite of the patriarchate Hierarchs
Romanian Patriar ...
* Eparchies of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church
The Bulgarian Orthodox Church ( bg, Българска православна църква, translit=Balgarska pravoslavna tsarkva), legally the Patriarchate of Bulgaria ( bg, Българска патриаршия, links=no, translit=Balgarsk ...
* Eparchies of the Georgian Orthodox Church
, the Georgian Orthodox Church is subdivided into fifty eparchies:
In Georgia
Elsewhere
See also
* Eparchies and Metropolitanates of the Russian Orthodox Church
* Eparchies of the Romanian Orthodox Church
* Eparchies of the Serbian O ...
* Eparchies of the Cypriot Orthodox Church
The Church of Cyprus ( el, Ἐκκλησία τῆς Κύπρου, translit=Ekklisia tis Kyprou; tr, Kıbrıs Kilisesi) is one of the autocephaly, autocephalous Greek Orthodox Church, Greek Orthodox churches that together with other Eastern O ...
* Eparchies of the Orthodox Church of Greece
The Church of Greece ( el, Ἐκκλησία τῆς Ἑλλάδος, Ekklēsía tē̂s Helládos, ), part of the wider Greek Orthodox Church, is one of the autocephaly, autocephalous churches which make up the communion of Eastern Orthodox Chur ...
* Eparchies of the Polish Orthodox Church
The Polish Autocephalous Orthodox Church ( pl, Polski Autokefaliczny Kościół Prawosławny), commonly known as the Polish Orthodox Church, or Orthodox Church of Poland, is one of the autocephalous Eastern Orthodox churches in full communion. Th ...
* Eparchies of the Albanian Orthodox Church
The Autocephalous Orthodox Church of Albania ( sq, Kisha Ortodokse Autoqefale e Shqipërisë), commonly known as the Albanian Orthodox Church or the Orthodox Church of Albania, is an autocephaly, autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern O ...
* Eparchies of the Czech and Slovak Orthodox Church
The Orthodox Church of the Czech Lands and Slovakia ( cs, Pravoslavná církev v Českých zemích a na Slovensku; sk, Pravoslávna cirkev v českých krajinách a na Slovensku) is a autocephaly, self-governing body of the Eastern Orthodox Church ...
Eastern Catholic Churches
In theEastern Catholic Churches
The Eastern Catholic Churches or Oriental Catholic Churches, also called the Eastern-Rite Catholic Churches, Eastern Rite Catholicism, or simply the Eastern Churches, are 23 Eastern Christian autonomous ('' sui iuris'') particular churches of t ...
, eparchy is equivalent to a diocese
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associa ...
of the Roman Rite, and its bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is c ...
is called an eparch (equivalent to a diocesan of the Roman Rite). At the same time, archeparchy is equivalent to an archdiocese of the Roman Rite, and its bishop is called an archeparch (equivalent to an archbishop of the Roman Rite).
Individual eparchies of some Eastern Catholic Churches may be suffragan to Latin-rite metropolitans. For example, the Greek Catholic Eparchy of Križevci
The Eparchy of Križevci is a Greek Catholic Church of Croatia and Serbia eparchy of the Catholic Church in Croatia, Slovenia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina. Its current eparch is Milan Stipić. The cathedra is in the Cathedral of the Holy Trinit ...
is suffragan to the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Zagreb
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Zagreb ( hr, Zagrebačka nadbiskupija, la, Archidioecesis Zagrebiensis) is the central archdiocese of the Catholic Church in Croatia, centered in the capital city Zagreb. It is the metropolitan see of Croatia, an ...
. Also, some minor Eastern Catholic churches have Latin prelates. For example, the Macedonian Greek Catholic Church
The Macedonian Greek Catholic Church ( la, Ecclesiae Graecae Catholico Macedonica; mk, Македонска грчка католичка црква), sometimes called, in reference to its Byzantine Rite, the Macedonian Byzantine Catholic Churc ...
is organized as a single Eparchy of Strumica-Skopje, whose present ordinary is the Roman Catholic bishop of Skopje.
See also
*Eparchy (Roman province)
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
* Eparchy (Byzantine province) Subdivisions of the Byzantine Empire were administrative units of the Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire (330–1453). The Empire had a developed administrative system, which can be divided into three major periods: the late Roman/early Byzantine, w ...
* Eparchy (modern Greece)
The provinces of Greece ( el, επαρχία, "eparchy") were sub-divisions of some the country's prefectures. From 1887, the provinces were abolished as actual administrative units, but were retained for some state services, especially financi ...
* Eparchy (modern Cyprus)
Cyprus is divided into six districts ( gr, επαρχίες; tr, kaza), whose capitals share the same name. The districts are subdivided into municipalities and communities. The districts of Cyprus are listed in the table below.
Note: No ...
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * *External links
*Catholic Encyclopedia (1909): Adrian Fortescue: Eparchy
Map with all Dioceses of the Eastern Churches
{{Greek terms for country subdivisions Eastern Christianity Dioceses (ecclesiastical) Bishops by type Episcopacy in the Catholic Church Episcopacy in Eastern Orthodoxy Episcopacy in Oriental Orthodoxy Ecclesiastical titles Greek words and phrases