Energy Use In California on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Energy in California is a major area of the economy of California. California is the state with the largest population and the largest economy in the United States. It is second in energy consumption after Texas. , per capita consumption was the fourth-lowest in the United States partially because of the mild climate and energy efficiency programs.
Energy consumption in California is dominated by transportation, due to the high number of motor vehicles and long commutes. California also is responsible for about 20% of total jet fuel consumption in the United States. The second largest energy sector is industry. Energy consumption of the state's residential sector per capita is lower than that of any other state except Hawaii thanks to a relatively mild climate.
California has large energy resources, being among the top producers of oil, hydroelectricity, solar, biomass, and geothermal energy in the United States.
Energy in California is a major area of the economy of California. California is the state with the largest population and the largest economy in the United States. It is second in energy consumption after Texas. , per capita consumption was the fourth-lowest in the United States partially because of the mild climate and energy efficiency programs.
Energy consumption in California is dominated by transportation, due to the high number of motor vehicles and long commutes. California also is responsible for about 20% of total jet fuel consumption in the United States. The second largest energy sector is industry. Energy consumption of the state's residential sector per capita is lower than that of any other state except Hawaii thanks to a relatively mild climate.
California has large energy resources, being among the top producers of oil, hydroelectricity, solar, biomass, and geothermal energy in the United States.
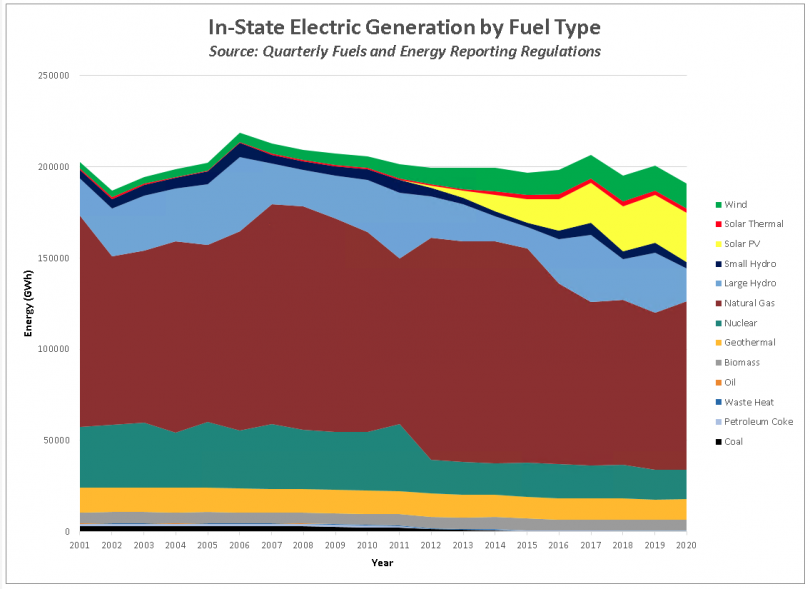
 Natural gas-fired power plants typically account for almost one-half of in-state electricity generation. California is one of the largest
Natural gas-fired power plants typically account for almost one-half of in-state electricity generation. California is one of the largest
Solar Trough Systems
Retrieved December 18, 2008. Other large solar plants in the Mojave Desert include the 392 MW
Assembly Bill 2514
directed the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) to adopt an energy storage program and procurement target. As a result, the CPUC established an energy storage target of 1,325 MW by 2020. In 2014, Southern California Edison commissioned the 8MW/32MWh
Today's Outlook
California ISO
Yesterday's Renewables Production
California ISO
Energy Flow Chart
(2000) *Grid maps
SouthCentralNorth
{{United states topic, prefix=Energy in Environmental issues in California

 Energy in California is a major area of the economy of California. California is the state with the largest population and the largest economy in the United States. It is second in energy consumption after Texas. , per capita consumption was the fourth-lowest in the United States partially because of the mild climate and energy efficiency programs.
Energy consumption in California is dominated by transportation, due to the high number of motor vehicles and long commutes. California also is responsible for about 20% of total jet fuel consumption in the United States. The second largest energy sector is industry. Energy consumption of the state's residential sector per capita is lower than that of any other state except Hawaii thanks to a relatively mild climate.
California has large energy resources, being among the top producers of oil, hydroelectricity, solar, biomass, and geothermal energy in the United States.
Energy in California is a major area of the economy of California. California is the state with the largest population and the largest economy in the United States. It is second in energy consumption after Texas. , per capita consumption was the fourth-lowest in the United States partially because of the mild climate and energy efficiency programs.
Energy consumption in California is dominated by transportation, due to the high number of motor vehicles and long commutes. California also is responsible for about 20% of total jet fuel consumption in the United States. The second largest energy sector is industry. Energy consumption of the state's residential sector per capita is lower than that of any other state except Hawaii thanks to a relatively mild climate.
California has large energy resources, being among the top producers of oil, hydroelectricity, solar, biomass, and geothermal energy in the United States.
Electricity
 Natural gas-fired power plants typically account for almost one-half of in-state electricity generation. California is one of the largest
Natural gas-fired power plants typically account for almost one-half of in-state electricity generation. California is one of the largest hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
power producers in the United States, and with adequate rainfall, hydroelectric power typically accounts for close to one-fifth of State electricity generation. Due to strict emission laws, only one coal-fired power plant remains operating in California, the 63-megawatt Argus Cogeneration Plant in Trona ( San Bernardino County).
California's peak electricity demand
World energy supply and consumption is global production and preparation of fuel, generation of electricity, energy transport, and energy consumption. It is a basic part of economic activity. It includes heat, but not energy from food.
This a ...
of 52,061 megawatts occurred on September 6, 2022, during one of the longest and hottest September heatwaves on record, which encompassed multiple Western states. Widespread rolling blackouts were narrowly avoided due to conservation efforts, though several thousand customers in Palo Alto and Alameda had their power cut when the California Independent System Operator told those cities' municipal power companies to shed load. The CEO of CAISO stated that the 3,300 megawatts of grid storage batteries added since the August 2020 rolling blackouts were definitely helpful during this event. The previous peak was on July 24, 2006, at 2:44 pm, with 50,270 MW. After the 2006 record, measures to reduce peak load resulted in decreased peak demand, even as the state's population continued to grow. On September 1, 2017, the peak load was 50,116 MW.
Although California's population increased by 13% during the 1990s, the state did not build any new major power plants during that time, although existing in-state power plants were expanded and power output was increased nearly 30% from 1990 to 2001. However, between 2000 and 2015, California built nearly 500 new power plants to supplement the 700 operating in 2000, boosting power supplies by 43%.
In 2016, California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) announced new rules for connecting coming generation sources to grid. Connection costs must be estimated by the utility, and the developer is limited to paying within ±25% change of the estimate. CPUC expects the rules to lower overall costs for ratepayers. California requires 1.3 GW of utility storage and studies long duration bulk energy storage. The state allocated US$83 million per year during 2017-2019 for behind-the-meter storage. The plan was amended in 2020 to a combined $613 million by 2024.
California's electricity rates are among the highest in the United States as a result of the changing energy mix within the state, including aggressive construction of new natural gas power plants. California's electricity costs were 17.4 cents per kWh for residential customers and 14.8 cents per kWh for commercial. Due to high electricity demand, California imports more electricity than any other state, (32% of its consumption in 2018) primarily wind and hydroelectric power from states in the Pacific Northwest (via Path 15 and Path 66) and nuclear, coal, and natural gas-fired production from the desert Southwest via Path 46
Path 46, also called West of Colorado River, Arizona-California West-of-the-River Path (WOR), is a set of fourteen high voltage (500 kV & 230 kV) alternating-current transmission lines that are located in southeast California and Nevada up to ...
. Imported coal-fired electricity is expected to decline as power agreements expire and the city of Los Angeles phases out its use of such electricity by 2025. In 2018, curtailment was 460 GWh, or 0.2% of generation, but has increased since.
Blackouts
Major blackouts in California include: * 1996 Western North America blackouts, caused by a summer heat wave *2000–01 California electricity crisis
The 2000–01 California electricity crisis, also known as the Western U.S. energy crisis of 2000 and 2001, was a situation in which the U.S. state of California had a shortage of electricity supply caused by market manipulations and capped reta ...
, caused by market manipulation
* 2011 Southwest blackout
The 2011 Southwest blackout, also known as the Great Blackout of 2011, was a widespread power outage that affected
the San Diego–Tijuana area, southern Orange County, Imperial Valley, Mexicali Valley, Coachella Valley, and parts of Arizona. I ...
, caused by operator error
* 2019 California power shutoffs
The 2019 California power shutoffs, known as public safety power shutoff (PSPS) events, were massive preemptive power shutoffs that occurred in approximately 30 counties in Northern California and several areas in Southern California from Octob ...
to prevent wildfires, caused by lack of maintenance
In August 2020, during a heat wave which affected the entire West coast, air conditioning usage caused the peak load to hit 47 GW, and CAISO issued rolling blackouts to avoid a larger system shutdown. The state did not have enough generation ready to fulfill demand, and it was unable to import sufficient electricity from neighboring states who had no surplus themselves. A 4 GW demand reduction alleviated the grid shortfall in the days after the blackouts.
State agencies identified three main causes: inadequate preparation for heat waves made worse by climate change, insufficient power in the early evening due to sequencing errors in the shift to renewable energy, and market mechanisms that allowed power to be exported during the shortage.
Transmission grid
The electric grid is made of up electric transmission andelectric distribution
Electric power distribution is the final stage in the Power delivery, delivery of electric power; it carries electricity from the Electric power transmission, transmission system to individual consumers. Distribution Electrical substation, substa ...
, with electric production by itself averaging about 44% of the cost nationally. As of 2019, transmission costs are the fastest-growing part of the bill, and Transmission Access Charges (TAC) are applied regardless of how far electricity travels across the grid.
California is part of the Western Interconnection, with transmission lines connecting to the Pacific Northwest including the California Oregon Intertie (with a capacity of almost 5 GW) as well as the Pacific DC Intertie, an HVDC line with a capacity of 3.1 GW which brings (predominantly hydroelectric) power from the Pacific Northwest to the Los Angeles area. From Utah, another HVDC line, Path 27
Path 27, also called the Intermountain or the Southern Transmission System (STS), is a high-voltage direct current (HVDC) electrical transmission line running from the coal-fired Intermountain Power Plant near Delta, Utah to the Adelanto Conv ...
, provides coal generated electricity to Los Angeles. From the Southeast, Path 46
Path 46, also called West of Colorado River, Arizona-California West-of-the-River Path (WOR), is a set of fourteen high voltage (500 kV & 230 kV) alternating-current transmission lines that are located in southeast California and Nevada up to ...
brings up to 10.6 GW of electricity from sources including hydroelectric, fossil fuels, nuclear, and solar from generating stations in Nevada and Arizona.
Transmission lines under construction as of 2019 include the TransWest Express, which would connect Wyoming to Nevada, which is already connected to Southern California via Path 46
Path 46, also called West of Colorado River, Arizona-California West-of-the-River Path (WOR), is a set of fourteen high voltage (500 kV & 230 kV) alternating-current transmission lines that are located in southeast California and Nevada up to ...
.
While experts have stated that more grid connections to other states would allow California to export its excess solar and wind generated electricity to other states during sunny times of the day, and to import wind generated electricity when wind is blowing in other Western states but not in California, the legislature has resisted allowing more connections for fear of losing sovereignty over the state's electricity supply.
Generation
, California had 80 GW of installed generation capacity encompassing more than 1,500 power plants; with 41 GW of natural gas, 26.5 GW of renewable (12 GW solar, 6 GW wind), 12 GW large hydroelectric, and 2.4 GW nuclear.Legal renewables requirement
In 2006, the California legislature passed the Global Warming Solutions Act of 2006 which set a goal for 33% of electricity consumption in California to be generated by renewable sources by 2020. In 2015, SB350 mandated that electric utilities purchase 50% of their electricity from renewable sources by 2030. Then in 2018, Senate Bill 100 was passed which increased the renewables requirement for electric utilities to 50% by 2026, 60% by 2030, and 100% by 2045.Natural gas
, California natural gas plants supplied a third of the state's total demand for electricity, (almost half of the state's in-state generation) and supply the state with 41,000 megawatts of installed capacity. Because renewables cannot generate power 24/7, and it is cost prohibitive to install enough solar panels, wind turbines and batteries to supply sufficient electricity to ensure resource adequacy during extended cloudy or windless periods, researchers have estimated that the state will still need between 17,000 and 35,000 megawatts of natural gas fueled generation in 2050.Renewables
California leads the nation in electricity generation from non-hydroelectricrenewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
sources, including geothermal power
Geothermal power is electrical power generated from geothermal energy. Technologies in use include dry steam power stations, flash steam power stations and binary cycle power stations. Geothermal electricity generation is currently used in 2 ...
, wind power, and solar power. California has some of the most aggressive renewable energy goals in the United States. The state is required to obtain at least 33% of its electricity from renewable resources by 2020, and 50% by 2030, excluding large hydro. On May 13, 2017, the California Independent System Operator (ISO) reported that the state had broken a new instantaneous renewable energy record, with non-hydro renewables providing 67.2% of the total electricity on the ISO's grid, with another 13.5% being provided by hydro. Intermittent solar power has led to a peak demand and peak production imbalance creating a " duck curve", where traditional power plants produce little generation at noon, ramping fast to high generation at dusk.
Solar Energy Generating Systems (SEGS) is the name given to nine solar power plants in the Mojave Desert which were built in the 1980s. These plants have a combined capacity of 354 megawatts (MW) making them at one time the largest solar power installation in the world.SunLab (1998Solar Trough Systems
Retrieved December 18, 2008. Other large solar plants in the Mojave Desert include the 392 MW
Ivanpah Solar Power Facility
The Ivanpah Solar Electric Generating System is a concentrated solar thermal plant in the Mojave Desert. It is located at the base of Clark Mountain in California, across the state line from Primm, Nevada. The plant has a gross capacity of 392&n ...
, opened in 2014, and the 550 MW Desert Sunlight Solar Farm
The Desert Sunlight Solar Farm is a 550 megawatt (MW AC) photovoltaic power station approximately six miles north of Desert Center, California, United States, in the Mojave Desert. It uses approximately 8.8 million cadmium telluride mod ...
and 579 MW Solar Star
Solar Star is a 579-megawatt ( MWAC) photovoltaic power station near Rosamond, California, United States, that is operated and maintained by SunPower Services. When completed in June 2015, it was the world's largest solar farm in terms of instal ...
, both completed in 2015. The Beacon Solar Project
The Beacon Solar Project is a photovoltaic power station in the northwestern Mojave Desert, near California City in eastern Kern County, California. Split into five phases, the combined Beacon solar facilities generate 250 MW of renewable ener ...
, which generates 250 MW for the LADWP, was completed in 2017 in the northwestern Mojave Desert.
The Alta Wind Energy Center
Alta Wind Energy Center (AWEC), also known as Mojave Wind Farm, is the third largest onshore wind energy project in the world. The Alta Wind Energy Center is a wind farm located in Tehachapi Pass of the Tehachapi Mountains, in Kern County, Californ ...
in the Tehachapi Mountains is the largest wind power plant in the United States with 1,548 MW installed capacity. A facility known as " The Geysers," located in the Mayacamas Mountains north of San Francisco, is the largest group of geothermal power plants in the world, with more than 750 MW of installed capacity. California's hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
power potential ranks second in the United States (behind Washington State), and substantial geothermal and wind power resources are found along the coastal mountain ranges and the eastern border with Nevada. High solar power potential is found in southeastern California's deserts.
Energy storage
California has several large pumped-storage hydroelectric powerplants.Assembly Bill 2514
directed the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) to adopt an energy storage program and procurement target. As a result, the CPUC established an energy storage target of 1,325 MW by 2020. In 2014, Southern California Edison commissioned the 8MW/32MWh
Tehachapi Energy Storage Project
The Tehachapi Energy Storage Project (TSP) is a 8 MW/32 MWh lithium-ion battery-based grid energy storage system at the Monolith Substation of Southern California Edison (SCE) in Tehachapi, California, sufficient to power between 1,600 and 2,400 ...
, which was the largest lithium-ion battery system operating in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
and one of the largest in the world at the time of commissioning. The 1-hour 230 MW Gateway Energy Storage project near San Diego became the biggest Lithium-ion grid storage in 2020, and several more are under construction, such as the two at Moss Landing.
Nuclear
California used to have multiplenuclear power plant
A nuclear power plant (NPP) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power stations, heat is used to generate steam that drives a steam turbine connected to a electric generator, generato ...
s, including the Rancho Seco Nuclear Generating Station, the San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station, the Vallecitos Nuclear Center
The Vallecitos Nuclear Center is a nuclear research facility, and the site of a former GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy electricity-generating nuclear power plant in unincorporated Alameda County, California, United States. The facility is approximatel ...
, and the Humboldt Bay Nuclear Power Plant, in addition to various other smaller experimental or prototype reactors which intermittently supplied power to the grid, such as the Sodium Reactor Experiment. All of these reactors have been shut down due to both economic and social factors. California's single remaining operational facility is the Diablo Canyon Power Plant. The owner, Pacific Gas & Electric, had agreed to shut down the two reactors at the site in 2025. The plant produces about 18 TWh per year. and accounts for 9% of total in-state generation. California State Lawmakers passed Senate Bill 856 on September 1, 2022, to extend Diablo Canyon operations through 2030.
The 3937 MW Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station in Tonopah, Arizona exports power to California via Path 46
Path 46, also called West of Colorado River, Arizona-California West-of-the-River Path (WOR), is a set of fourteen high voltage (500 kV & 230 kV) alternating-current transmission lines that are located in southeast California and Nevada up to ...
and is over 27% owned by California utility companies.
Hydroelectric
* California has several large conventional and pumped-storage hydroelectric powerplants. * California receives 55.9% of the power generated by theHoover Dam
Hoover Dam is a concrete arch-gravity dam in the Black Canyon of the Colorado River, on the border between the U.S. states of Nevada and Arizona. It was constructed between 1931 and 1936 during the Great Depression and was dedicated on Se ...
, on the Arizona/ Nevada border, about 2236.38 GW⋅h on average.
Coal
* The 63 MW Argus Cogeneration Plant in San Bernardino County is the onlycoal-fired power station
A coal-fired power station or coal power plant is a thermal power station which burns coal to generate electricity. Worldwide, there are about 8,500 coal-fired power stations totaling over 2,000 gigawatts Nameplate capacity, capacity. They ...
still operating within the state of California.*
* The 1,900 MW Intermountain Power Plant in Delta, Utah
Delta is the largest city in Millard County, Utah, United States. It is located in the northeastern area of Millard County along the Sevier River and is surrounded by farmland. The population was 3,436 at the 2010 census.
History
Delta was ori ...
is operated by the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power. Power is transmitted to California via Path 27
Path 27, also called the Intermountain or the Southern Transmission System (STS), is a high-voltage direct current (HVDC) electrical transmission line running from the coal-fired Intermountain Power Plant near Delta, Utah to the Adelanto Conv ...
.
* The 1,540 MW Four Corners Generating Station in San Juan County, New Mexico is 19.2% owned by Southern California Edison.
* *[NOTE: As of Nov/2022, the 63 MW Argus Cogeneration Plant is no longer on-line and is currently being dismantled. Consequently, there are no coal-fired power stations operating within the State of California providing public electricity.]
Regulatory policy
The California Energy Commission is the primary energy policy and planning agency. As of 2017, California is a deregulated electricity market. It has a number of electric load-serving entities, including as of 2015 six investor-owned utilities (IOU), 46 publicly owned utilities, 4 electric cooperatives, 3 community choice aggregators, and 22 electric service providers. Major investor-owned utilities, regulated by the California Public Utilities Commission, include Southern California Edison, Pacific Gas & Electric, and San Diego Gas & Electric. The remaining 3 IOUs are Pacificorp, Bear Valley Electric, andLiberty Utilities
Algonquin Power & Utilities Corp. is a Canadian renewable energy and regulated utility conglomerate with assets across North America. Algonquin actively invests in hydroelectric, wind and solar power facilities, and utility businesses (water, nat ...
.
California has a regional transmission organization called CAISO covering its state, but is not merged with the rest of the Western United States; merging has been a major policy discussion with proposals considered in 2017 and 2018.
California's investor-owned utilities were transitioning to time-of-use pricing, with SD&E slated to roll it out in 2019 and the others rolling it out in 2020.
Electricity system data
, 27.81% of electricity was imported (8.62% from Northwest and 19.19% from Southwest) out of which 26.38% was of unspecified origin and 30.68% were renewables. This compares with 32.09% of in-state generated electricity which comes from renewable Peak Loads for each year in Megawatts *44,659 Wed, Aug 12, 1998 02:30 PM *45,884 Mon, Jul 12, 1999 04:52 PM *43,784 Wed, Aug 16, 2000 03:17 PM *41,419 Tue, Aug 7, 2001 04:17 PM *42,441 Wed, Jul 10, 2002 03:01 PM *42,689 Thu, Jul 17, 2003 03:22 PM *45,597 Wed, Sep 8, 2004 04:00 PM *45,431 Wed, Jul 20, 2005 03:22 PM *50,270 Mon, Jul 24, 2006 02:44 PM *48,615 Fri, Aug 31, 2007 03:27 PM *46,897 Fri, Jun 20, 2008 04:21 PM *46,042 Thu, Sep 3, 2009 04:17 PM *47,350 Wed, Aug 25, 2010 04:20 PM *45,545 Wed, Sep 7, 2011 04:30 PM *46,846 Mon, Aug 13, 2012 03:53 PM *45,097 Fri, Jun 28, 2013 04:54 PM *45,089 Mon, Sep 15, 2014 04:53 PM *46,519 Thu, Sep 10, 2015 03:38 PM *46,232 Wed, Jul 27, 2016 04:51 PM *50,116 Fri, Sep 1, 2017 03:58 PM *46,427 Wed, Jul 25, 2018 05:33 PM *44,301 Thu, Aug 15, 2019 05:50 PM *47,121 Tue, Aug 18, 2020 03:57 PMPetroleum production
California'scrude oil
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude ...
and natural gas deposits are located in six geological basins in the Central Valley and along the coast. California has more than a dozen of the United States' largest oil fields, including the Midway-Sunset Oil Field, the second largest oil field in the contiguous United States.
As of 2022, California's crude oil
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude ...
output accounted for about 3% of total U.S. production. Drilling operations are concentrated primarily in Kern County and the Los Angeles basin. With twenty seven platforms along the coast , there is substantial offshore
Offshore may refer to:
Science and technology
* Offshore (hydrocarbons)
* Offshore construction, construction out at sea
* Offshore drilling, discovery and development of oil and gas resources which lie underwater through drilling a well
* Off ...
oil and gas production. There is a permanent moratorium on new offshore oil and gas leasing in California waters and a deferral of leasing in Federal waters.
California ranks third in the United States in petroleum refining
{{Unreferenced, date=December 2009
Refining (also perhaps called by the mathematical term affining) is the process of purification of a (1) substance or a (2) form. The term is usually used of a natural resource that is almost in a usable form, b ...
capacity, behind Texas and Louisiana, and accounts for about 11% of total U.S. capacity, as of 2012. In addition to oil from California, California's refineries process crude oil from Alaska and foreign suppliers. The refineries are configured to produce cleaner fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy but ...
s, including reformulated motor gasoline and low-sulfur diesel, to meet strict Federal and State environmental regulations. As of 2017, California has 18 refineries with a capacity to process nearly per day.
Transportation
Transportation is a major use of energy, driven in part by long commuting distances. In 2017, transportation accounted for 40% of total energy use, and in 2015, transportation was estimated to be the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions. Gasoline consumption fluctuates with economic conditions and gas prices, but has generally remained flat since 2000, despite increasing population. In 2017, Texas surpassed California in gasoline consumption, despite California having 6 million more vehicles. Most California motorists are required to use a special motor gasoline blend called California Clean Burning Gasoline (CA CBG). By 2004, California completed a transition from methyl tertiary butyl-ether (MTBE) to ethanol as a gasoline oxygenate additive, making California the largest ethanol fuel market in the United States. There are four ethanol production plants in central and southern California, but most of California's ethanol supply is transported from other states or abroad. As of 2018, California is a leader in the United States inelectric vehicle
An electric vehicle (EV) is a vehicle that uses one or more electric motors for propulsion. It can be powered by a collector system, with electricity from extravehicular sources, or it can be powered autonomously by a battery (sometimes cha ...
s. California has the second highest rate of plug-in cars in the world, trailing behind Norway, and making up half of the electric car market in the US. The Alternative and Renewable Fuel and Vehicle Technology Program, also called the Clean Transportation Program, arose out of 2007 law and is intended to drive growth in electric vehicles. California faces a potential shortage in charging stations, and setup California Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Project (CALeVIP) program to build more chargers. In September 2020, California Gov. Gavin Newsom issued an executive order requiring all passenger cars and trucks (not delivery, long-haul, or construction vehicles) sold after 2035 be fully electric. Experts have estimated that this will increase California's consumption of electric energy by 25%. California operates Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) programs to let electric vehicles supply power to the grid when feasible, and to increase consumption when supply is ample. , California's EVs have a combined charging capacity of 4.67 GW.
Building energy
Buildings use energy for lighting,heating, ventilation, and air conditioning
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HV ...
(HVAC) systems, escalators, elevators and water heating
Water heating is a heat transfer process that uses an energy source to heat water above its initial temperature. Typical domestic uses of hot water include cooking, cleaning, bathing, and space heating. In industry, hot water and water heated t ...
. In addition, municipalities pump water which requires energy; by one estimate, about 19% of electricity is used to treat, pump, and discharge water. About 2/3 of California's home heating is supplied by natural gas, and most new homes are constructed with both natural gas and electric heating.
The California Building Standards Code has targeted residential energy efficiency since 1978; Part 11 of the code is the California Green Building Standards Code.
Natural gas
California natural gas production typically is less than 2 percent of total annual U.S. production and satisfies less than one-sixth of state demand. California receives most of its natural gas by pipeline from production regions in the Rocky Mountains, the Southwest, and western Canada. Some of this is seasonally stored in the Aliso Canyon Oil Field, and its 2015 leak caused California to installgrid batteries
A battery storage power station is a type of energy storage power station that uses a group of batteries to store electrical energy. Battery storage is the fastest responding dispatchable source of power on electric grids, and it is used to stab ...
to compensate.
Sustainable
California has led the United States from 2010 to 2013 with itssustainable energy
Energy is sustainable if it "meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs". Most definitions of sustainable energy include considerations of environmental aspects such as greenh ...
plans (also known as "clean energy"), with Clean Edge's Clean Energy Index for 2013 rating it at 91.7, with the second ranked state being Massachusetts, at 77.8, and Mississippi the lowest at 4.2. California is the only state with extensive deployment of wind, solar, and geothermal energy. California's venture capital investments in sustainable energy are greater than the other 49 states combined, at $2.2 billion in 2012. In August 2018, California's legislature passed legislation that mandates completely carbon-free electricity generation by 2045.
Energy-efficient lighting regulations
In September 2019, the Energy Department announced the reversal of a 2014 regulation that would have taken effect on January 1, 2020 and implemented the last round of energy-saving light bulb regulations outlined by the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007. The ruling would allow some types ofincandescent bulbs
An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a wire filament heated until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb with a vacuum or inert gas to protect the filament from oxida ...
to remain in service. California, along with Colorado, Nevada, Washington, and Vermont, adopted its own energy standards. The California regulations were challenged in court by light bulb manufacturers but a judge ruled it was proper under the congressional exemption previously granted.
See also
* Solar power in California * Wind power in California * Offshore oil and gas in California *California oil and gas industry
The California oil and gas industry has been a major industry for over a century. Oil production was a minor factor in the 19th century, with kerosene replacing whale oil and lubricants becoming essential to the machine age. Oil became a major Cal ...
* California independent system operator
* List of power stations in California
* California Electricity Crisis
* List of articles associated with nuclear issues in California
References
External links
Today's Outlook
California ISO
Yesterday's Renewables Production
California ISO
Energy Flow Chart
(2000) *Grid maps
South
{{United states topic, prefix=Energy in Environmental issues in California