endurance (aeronautics) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
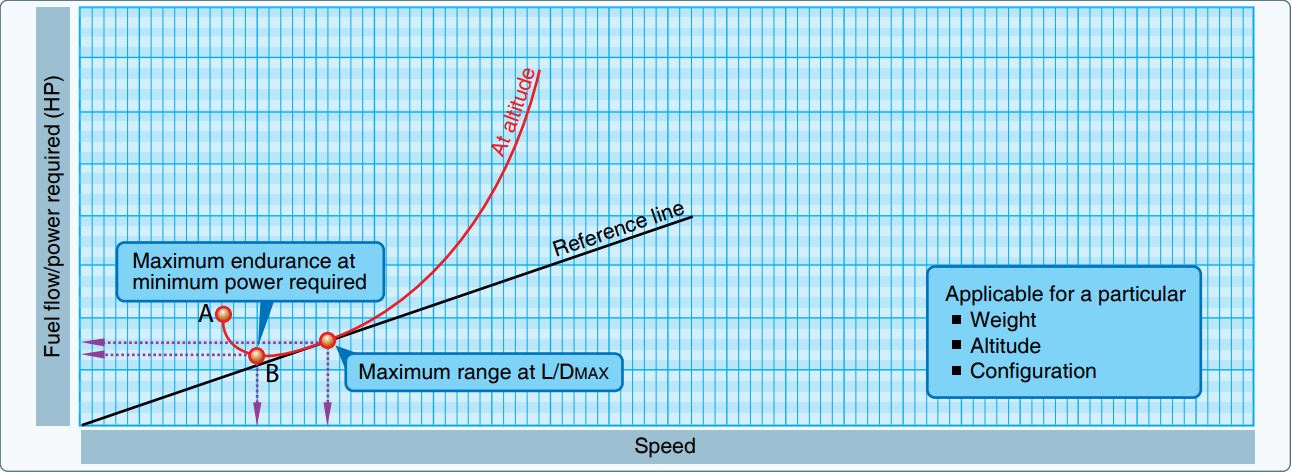 In
In
 In
In aviation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot air ...
, endurance is the maximum length of time that an aircraft can spend in cruising flight. In other words, it is the amount of time an aircraft can stay in the air with one load of fuel. Endurance is different from range
Range may refer to:
Geography
* Range (geographic), a chain of hills or mountains; a somewhat linear, complex mountainous or hilly area (cordillera, sierra)
** Mountain range, a group of mountains bordered by lowlands
* Range, a term used to i ...
, which is a measure of distance flown. For example, a typical sailplane
A glider or sailplane is a type of glider aircraft used in the leisure activity and sport of gliding (also called soaring). This unpowered aircraft can use naturally occurring currents of rising air in the atmosphere to gain altitude. Sailplan ...
exhibits high endurance characteristics but poor range characteristics.
Endurance can be defined as:
:
where W stands for fuel weight, F for fuel flow, and t for time.
Endurance can factor into aviation design in a number of ways. Some aircraft, such as the P-3 Orion
The Lockheed P-3 Orion is a four-engined, turboprop anti-submarine and maritime surveillance aircraft developed for the United States Navy and introduced in the 1960s. Lockheed based it on the L-188 Electra commercial airliner.
for an aircraft.
Endurance, like range, is also related to fuel efficiency
Fuel efficiency is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the ratio of effort to result of a process that converts chemical potential energy contained in a carrier (fuel) into kinetic energy or work. Overall fuel efficiency may vary per device, wh ...
; fuel-efficient aircraft will tend to exhibit good endurance characteristics.
References
Aeronautics {{Aviation-stub