Elton's quadrant on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An Elton's quadrant is a derivative of the
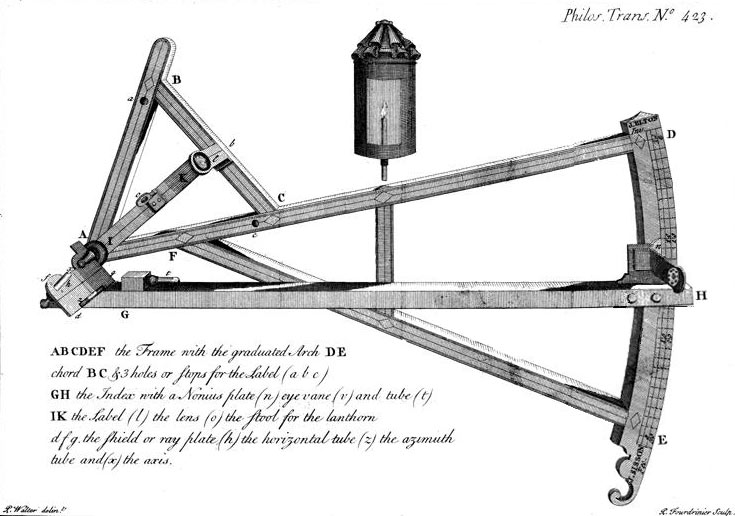 This instrument clearly reflects the shape and features of the
This instrument clearly reflects the shape and features of the
Maritime Art Greenwich, at the National Maritime Museum, London
Painting of a captain holding an Elton's Quadrant. Navigational equipment Measuring instruments Astronomical instruments Celestial navigation Historical scientific instruments
Davis quadrant
The backstaff is a navigational instrument that was used to measure the altitude of a celestial body, in particular the Sun or Moon. When observing the Sun, users kept the Sun to their back (hence the name) and observed the shadow cast by the u ...
. It adds an index arm and artificial horizon to the instrument. It was invented by John Elton a sea captain who patented his design in 1728Bennett, Jim, "Catadioptrics and commerce in eighteenth-century London", in History of Science, vol xliv, 2006, pages 247-277. and published details of the instrument in the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society in 1732.Elton, John, ''The Description of a New Quadrant for Taking Altitudes Without an Horizon, Either at Sea or Land'', Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, Vol 37, No. 423, 1731-1732.
Construction
 This instrument clearly reflects the shape and features of the
This instrument clearly reflects the shape and features of the Davis quadrant
The backstaff is a navigational instrument that was used to measure the altitude of a celestial body, in particular the Sun or Moon. When observing the Sun, users kept the Sun to their back (hence the name) and observed the shadow cast by the u ...
. The significant differences are the change in the upper arc to a simple triangular frame and the addition of an index arm. The triangular frame at the top spans 60° as did the arc on the backstaff. The main graduated arc subtends 30° as in the backstaff. The 30° arc is graduated in degrees and sixths of a degree, that is, at ten- minute intervals.
The sighting vane of the backstaff is replaced with a sight (called an ''eye vane'') mounted on the end of the index arm.
The index arm includes a noniusDaumas, Maurice, ''Scientific Instruments of the Seventeenth and Eighteenth Centuries and Their Makers'', Portman Books, London 1989 {{ISBN, 978-0-7134-0727-3 - Daumas points out that the name ''nonius'' continued to be used instead of ''vernier'' until the beginning of the 19th century. to allow reading the large scale with ten divisions between the graduations on the scale. This provides the navigator with the ability to read the scale to the nearest minute of arc. The index arm has a spirit level
A spirit level, bubble level, or simply a level, is an instrument designed to indicate whether a surface is horizontal (level) or vertical ( plumb). Different types of spirit levels may be used by carpenters, stonemasons, bricklayers, ...
to allow the navigator to ensure that the index is horizontal even when he cannot see the horizon.
The instrument has a horizon vane like a Davis quadrant, but Elton refers to it as the ''shield'' or ''ray vane''. The shield is attached to the ''label''.''Label
A label (as distinct from signage) is a piece of paper, plastic film, cloth, metal, or other material affixed to a container or product, on which is written or printed information or symbols about the product or item. Information printed dir ...
'' is an older term for a long, thin device, in particular the rule on an astrolabe, circumferentor
A circumferentor, or surveyor's compass, is an instrument used in surveying to measure horizontal angles. It was superseded by the theodolite in the early 19th century.
A circumferentor consists of a circular brass box containing a magnetic n ...
or similar instrument. It differs from an alidade
An alidade () (archaic forms include alhidade, alhidad, alidad) or a turning board is a device that allows one to sight a distant object and use the line of sight to perform a task. This task can be, for example, to triangulate a scale map on site ...
in that it has no sighting vanes on it. In this latter detail, Elton's use of the term may be inappropriate. The label is an arm that extends from the centre of the arc to the outside of the upper triangle and can be set to one of the three positions in the triangle (in the diagram, it appears to bisect the triangle as it is set to the centre or 30° position). At the upper end of the label is a ''Flamsteed
John Flamsteed (19 August 1646 – 31 December 1719) was an English astronomer and the first Astronomer Royal. His main achievements were the preparation of a 3,000-star catalogue, ''Catalogus Britannicus'', and a star atlas called ''Atlas Coe ...
glass'' or lens.
The three set positions allow the instrument to read 0° to 30°, 30° to 60° or 60° to 90°. The lens projects an image of the sun rather than a shadow of the sun on the shield. This provides an image even when the sky is hazy or lightly overcast. In addition, at the mid-span of the label there is a mounting point for a lantern to be used during nocturnal observations.
There are two spirit levels on the shield. One, called the ''azimuth tube'', ensures that the plane of the instrument is vertical. The other is perpendicular
In elementary geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at a right angle (90 degrees or π/2 radians). The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the ''perpendicular symbol'', ⟂. It can ...
to the shield and will indicate when the plane of the shield is vertical and the label is horizontal.
Usage
Solar altitude by backsight
For measuring thealtitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context ...
of the sun, the Elton's quadrant can be used in the same manner as a Davis quadrant. However, with the artificial horizon, the eye vane is not required to be used.
Hold the instrument in a comfortable manner with the arc towards the sun. Set the label so that the sun's image is projected on the shield at the hole with the index arm roughly horizontal. Move the index arm so that the index's spirit level shows the arm is precisely horizontal. This sets the instrument and the angle can be read with the scale and nonius.
Stellar altitude by foresight
This is a means of measuring altitude of acelestial object
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are often u ...
that is very different from what can be done with a Davis quadrant. It reveals one of the significant improvements of the Elton's quadrant over the former instrument.
Set the label to a position that will put the object to be measured within the range of the instrument. Observe the object through the eye vane so that the object touches the upper edge of the shield while using the azimuth tube to ensure that the frame is vertical. Move the index arm so that the shield's horizontal tube indicates that the shield is precisely vertical. This sets the instrument and the angle can be read on the arc.
Significance to navigation
The Elton's quadrant is not very well known as a navigation instrument. It was used, though to what degree is not known. Elton had the misfortune to invent his instrument in the same period of time as the octant. In fact,John Hadley
John Hadley (16 April 1682 – 14 February 1744) was an English mathematician, and laid claim to the invention of the octant, two years after Thomas Godfrey claimed the same.
Biography
He was born in Bloomsbury, London the eldest son of ...
published details on his octant prior to Elton's article in the same volume of the Philosophical Transactions (article 37 vs 48).
Given that Elton's quadrant was roughly as complex as an octant in construction, there would not likely be a significant advantage in price. The octant was an easier instrument to use and Hadley had supported the use of artificial horizons on the octant in the form of spirit levels. This would have given no advantage to Elton's instrument. In addition, there were many other instruments competing for the attention of navigators in this period. In the end, the Hadley octant and later sextant took precedence as instruments for navigators.
References
External links
Maritime Art Greenwich, at the National Maritime Museum, London
Painting of a captain holding an Elton's Quadrant. Navigational equipment Measuring instruments Astronomical instruments Celestial navigation Historical scientific instruments