Electrical Double Layer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
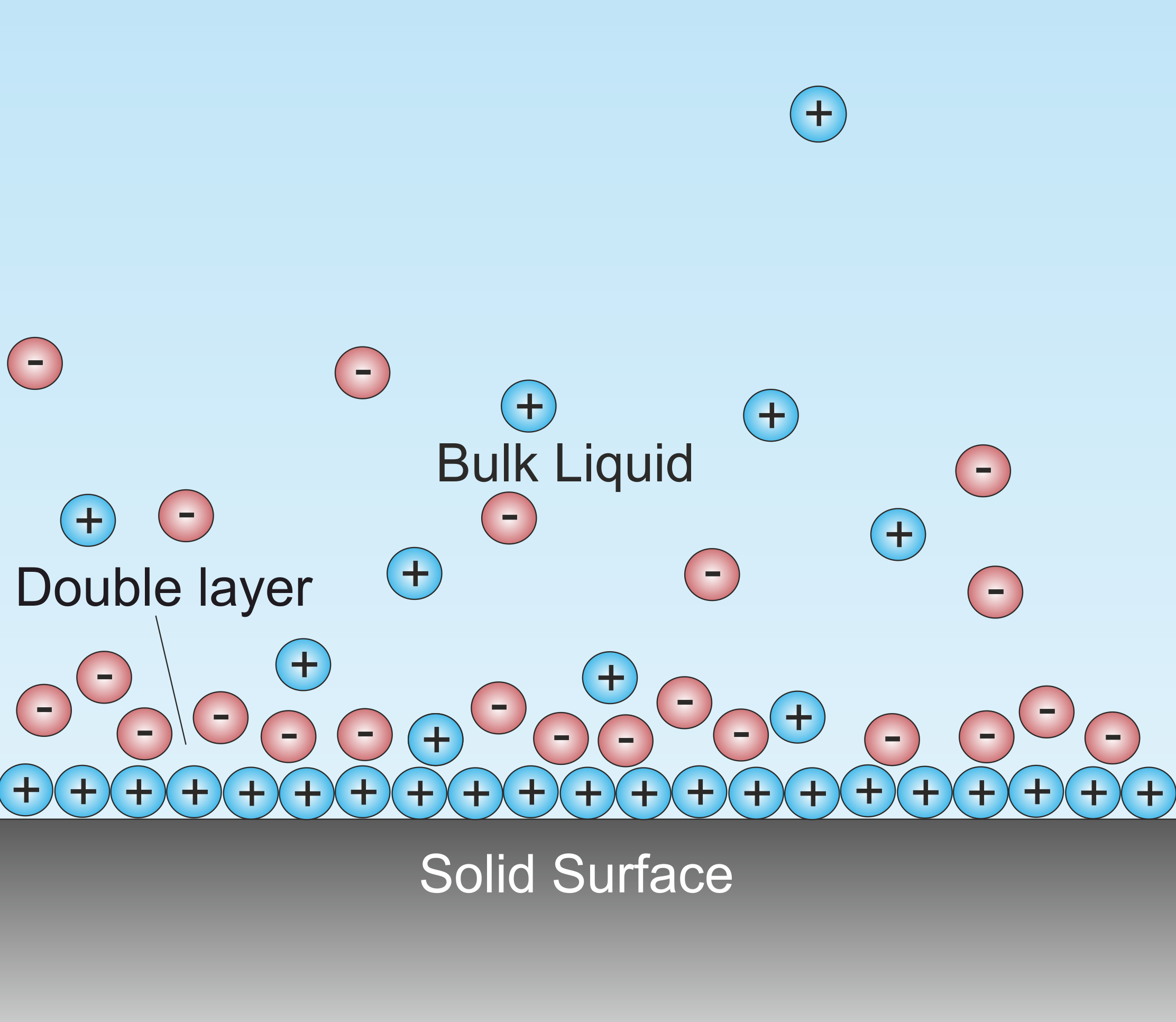 A double layer (DL, also called an electrical double layer, EDL) is a structure that appears on the surface of an object when it is exposed to a fluid. The object might be a solid particle, a gas bubble, a liquid
A double layer (DL, also called an electrical double layer, EDL) is a structure that appears on the surface of an object when it is exposed to a fluid. The object might be a solid particle, a gas bubble, a liquid
 When an ''electronic'' conductor is brought in contact with a solid or liquid ''ionic'' conductor (electrolyte), a common boundary (
When an ''electronic'' conductor is brought in contact with a solid or liquid ''ionic'' conductor (electrolyte), a common boundary (
Chapter 2, Electrode/electrolyte interfaces: Structure and kinetics of charge transfer.
(769 kB) This model, with a good foundation for the description of the interface, does not consider important factors including diffusion/mixing of ions in solution, the possibility of
 D. C. Grahame modified the Stern model in 1947. He proposed that some ionic or uncharged species can penetrate the Stern layer, although the closest approach to the electrode is normally occupied by solvent molecules. This could occur if ions lose their
D. C. Grahame modified the Stern model in 1947. He proposed that some ionic or uncharged species can penetrate the Stern layer, although the closest approach to the electrode is normally occupied by solvent molecules. This could occur if ions lose their
/ref>
The Electrical Double Layer
{{DEFAULTSORT:Double Layer (Interfacial) Chemical mixtures Colloidal chemistry Surface science Electrochemistry Matter Soft matter
 A double layer (DL, also called an electrical double layer, EDL) is a structure that appears on the surface of an object when it is exposed to a fluid. The object might be a solid particle, a gas bubble, a liquid
A double layer (DL, also called an electrical double layer, EDL) is a structure that appears on the surface of an object when it is exposed to a fluid. The object might be a solid particle, a gas bubble, a liquid droplet
A drop or droplet is a small column of liquid, bounded completely or almost completely by free surfaces. A drop may form when liquid accumulates at the lower end of a tube or other surface boundary, producing a hanging drop called a pendant ...
, or a porous body. The DL refers to two parallel layers of charge surrounding the object. The first layer, the surface charge
Surface charge is a two-dimensional surface with non-zero electric charge. These electric charges are constrained on this 2-D surface, and surface charge density, measured in coulombs per square meter (C•m−2), is used to describe the charge di ...
(either positive or negative), consists of ions adsorbed
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. This process creates a film of the ''adsorbate'' on the surface of the ''adsorbent''. This process differs from absorption, in which a ...
onto the object due to chemical interactions. The second layer is composed of ions attracted to the surface charge via the Coulomb force
Coulomb's inverse-square law, or simply Coulomb's law, is an experimental law of physics that quantifies the amount of force between two stationary, electrically charged particles. The electric force between charged bodies at rest is conventiona ...
, electrically screening
Screening may refer to:
* Screening cultures, a type a medical test that is done to find an infection
* Screening (economics), a strategy of combating adverse selection (includes sorting resumes to select employees)
* Screening (environmental), a ...
the first layer. This second layer is loosely associated with the object. It is made of free ions that move in the fluid under the influence of electric attraction and thermal motion
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example ...
rather than being firmly anchored. It is thus called the "diffuse layer".
Interfacial DLs are most apparent in systems with a large surface area to volume ratio, such as a colloid
A colloid is a mixture in which one substance consisting of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Some definitions specify that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, while others extend ...
or porous bodies with particles or pores (respectively) on the scale of micrometres to nanometres. However, DLs are important to other phenomena, such as the electrochemical
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between electrical potential difference, as a measurable and quantitative phenomenon, and identifiable chemical change, with the potential difference as an outco ...
behaviour of electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials de ...
s.
DLs play a fundamental role in many everyday substances. For instance, homogenized milk exists only because fat droplets are covered with a DL that prevents their coagulation
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanism o ...
into butter. DLs exist in practically all heterogeneous
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts often used in the sciences and statistics relating to the uniformity of a substance or organism. A material or image that is homogeneous is uniform in composition or character (i.e. color, shape, siz ...
fluid-based systems, such as blood, paint, ink and ceramic and cement slurry
A slurry is a mixture of denser solids suspended in liquid, usually water. The most common use of slurry is as a means of transporting solids or separating minerals, the liquid being a carrier that is pumped on a device such as a centrifugal pu ...
.
The DL is closely related to electrokinetic phenomena Electrokinetic phenomena are a family of several different effects that occur in heterogeneous fluids, or in porous bodies filled with fluid, or in a fast flow over a flat surface. The term heterogeneous here means a fluid containing particles. Part ...
and electroacoustic phenomena Electroacoustic phenomena arise when ultrasound propagates through a fluid containing ions. The associated particle motion generates electric signals because ions have electric charge. This coupling between ultrasound and electric field is called el ...
.
Development of the (interfacial) double layer
Helmholtz
 When an ''electronic'' conductor is brought in contact with a solid or liquid ''ionic'' conductor (electrolyte), a common boundary (
When an ''electronic'' conductor is brought in contact with a solid or liquid ''ionic'' conductor (electrolyte), a common boundary (interface
Interface or interfacing may refer to:
Academic journals
* ''Interface'' (journal), by the Electrochemical Society
* '' Interface, Journal of Applied Linguistics'', now merged with ''ITL International Journal of Applied Linguistics''
* '' Int ...
) among the two phases appears. Hermann von Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz (31 August 1821 – 8 September 1894) was a German physicist and physician who made significant contributions in several scientific fields, particularly hydrodynamic stability. The Helmholtz Association, ...
was the first to realize that charged electrodes immersed in electrolyte solutions repel the co-ions of the charge while attracting counterions to their surfaces. Two layers of opposite polarity
Polarity may refer to:
Science
*Electrical polarity, direction of electrical current
*Polarity (mutual inductance), the relationship between components such as transformer windings
* Polarity (projective geometry), in mathematics, a duality of ord ...
form at the interface between electrode and electrolyte. In 1853 he showed that an electrical double layer (DL) is essentially a molecular
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
dielectric and stores charge electrostatically. Below the electrolyte's decomposition voltage, the stored charge is linearly dependent on the voltage applied.
This early model predicted a constant differential capacitance Differential capacitance in physics, electronics, and electrochemistry is a measure of the voltage-dependent capacitance of a nonlinear capacitor, such as an electrical double layer or a semiconductor diode. It is defined as the derivative of cha ...
independent from the charge density depending on the dielectric constant
The relative permittivity (in older texts, dielectric constant) is the permittivity of a material expressed as a ratio with the electric permittivity of a vacuum. A dielectric is an insulating material, and the dielectric constant of an insulat ...
of the electrolyte solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for ...
and the thickness of the double-layer.Srinivasan S. (2006) Fuel cells, from Fundamentals to Applications, Springer eBooks, Chapter 2, Electrode/electrolyte interfaces: Structure and kinetics of charge transfer.
(769 kB) This model, with a good foundation for the description of the interface, does not consider important factors including diffusion/mixing of ions in solution, the possibility of
adsorption
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. This process creates a film of the ''adsorbate'' on the surface of the ''adsorbent''. This process differs from absorption, in which a f ...
onto the surface, and the interaction between solvent dipole moments and the electrode.
Gouy–Chapman
Louis Georges Gouy
Louis Georges Gouy (February 19, 1854 – January 27, 1926) was a French physicist. He is the namesake of the Gouy balance, the Gouy–Chapman electric double layer model (which is a relatively successful albeit limited model that describes the ...
in 1910 and David Leonard Chapman in 1913 both observed that capacitance was not a constant and that it depended on the applied potential and the ionic concentration. The "Gouy–Chapman model" made significant improvements by introducing a diffuse
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
model of the DL. In this model, the charge distribution of ions as a function of distance from the metal surface allows Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics
In statistical mechanics, Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics describes the distribution of Classical physics, classical material particles over various energy states in thermal equilibrium. It is applicable when the temperature is high enough or the ...
to be applied. Thus the electric potential
The electric potential (also called the ''electric field potential'', potential drop, the electrostatic potential) is defined as the amount of work energy needed to move a unit of electric charge from a reference point to the specific point in ...
decreases exponentially away from the surface of the fluid bulk.
Stern
The Gouy-Chapman model fails for highly charged DLs. In 1924,Otto Stern
:''Otto Stern was also the pen name of German women's rights activist Louise Otto-Peters (1819–1895)''.
Otto Stern (; 17 February 1888 – 17 August 1969) was a German-American physicist and Nobel laureate in physics. He was the second most n ...
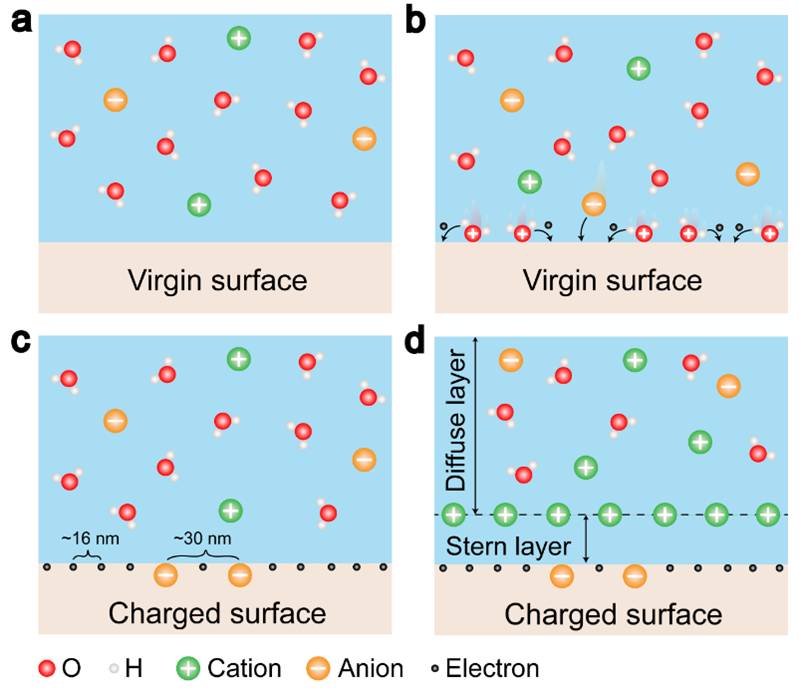
suggested combining the Helmholtz model with the Gouy-Chapman model: in Stern's model, some ions adhere to the electrode as suggested by Helmholtz, giving an internal Stern layer, while some form a Gouy-Chapman diffuse layer.
The Stern layer accounts for ions' finite size and consequently an ion's closest approach to the electrode is on the order of the ionic radius. The Stern model has its own limitations, namely that it effectively treats ions as point charges, assumes all significant interactions in the diffuse layer
A double layer (DL, also called an electrical double layer, EDL) is a structure that appears on the surface of an object when it is exposed to a fluid. The object might be a solid particle, a gas bubble, a liquid droplet, or a porous body. The D ...
are Coulomb
The coulomb (symbol: C) is the unit of electric charge in the International System of Units (SI).
In the present version of the SI it is equal to the electric charge delivered by a 1 ampere constant current in 1 second and to elementary char ...
ic, assumes dielectric permittivity
In electromagnetism, the absolute permittivity, often simply called permittivity and denoted by the Greek letter ''ε'' ( epsilon), is a measure of the electric polarizability of a dielectric. A material with high permittivity polarizes more in ...
to be constant throughout the double layer, and that fluid viscosity is constant plane.
Grahame
solvation shell
A solvation shell or solvation sheath is the solvent interface of any chemical compound or biomolecule that constitutes the solute. When the solvent is water it is called a hydration shell or hydration sphere. The number of solvent molecules sur ...
as they approach the electrode. He called ions in direct contact with the electrode "specifically adsorbed ions". This model proposed the existence of three regions. The inner Helmholtz plane (IHP) passes through the centres of the specifically adsorbed ions. The outer Helmholtz plane (OHP) passes through the centres of solvated ions at the distance of their closest approach to the electrode. Finally the diffuse layer is the region beyond the OHP.
Bockris/Devanathan/Müller (BDM)
In 1963 J. O'M. Bockris, M. A. V. Devanathan and Klaus Müller proposed the BDM model of the double-layer that included the action of the solvent in the interface. They suggested that the attached molecules of the solvent, such as water, would have a fixed alignment to the electrode surface. This first layer of solvent molecules displays a strong orientation to the electric field depending on the charge. This orientation has great influence on thepermittivity
In electromagnetism, the absolute permittivity, often simply called permittivity and denoted by the Greek letter ''ε'' ( epsilon), is a measure of the electric polarizability of a dielectric. A material with high permittivity polarizes more in ...
of the solvent that varies with field strength. The IHP passes through the centers of these molecules. Specifically adsorbed, partially solvated ions appear in this layer. The solvated ions of the electrolyte are outside the IHP. Through the centers of these ions pass the OHP. The diffuse layer is the region beyond the OHP.
Trasatti/Buzzanca
Further research with double layers on ruthenium dioxide films in 1971 by Sergio Trasatti and Giovanni Buzzanca demonstrated that the electrochemical behavior of these electrodes at low voltages with specific adsorbed ions was like that of capacitors. The specific adsorption of the ions in this region of potential could also involve a partial charge transfer between the ion and the electrode. It was the first step towards understanding pseudocapacitance.Conway
Between 1975 and 1980 Brian Evans Conway conducted extensive fundamental and development work onruthenium oxide Ruthenium oxide may refer to either of the following:
*Ruthenium(IV) oxide
Ruthenium(IV) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Ru O2. This black solid is the most common oxide of ruthenium. It is widely used as an electrocatalyst fo ...
electrochemical capacitors. In 1991 he described the difference between 'Supercapacitor' and 'Battery' behavior in electrochemical energy storage. In 1999 he coined the term supercapacitor to explain the increased capacitance by surface redox reactions with faradaic charge transfer between electrodes and ions.
His "supercapacitor" stored electrical charge partially in the Helmholtz double-layer and partially as the result of faradaic reactions with "pseudocapacitance" charge transfer of electrons and protons between electrode and electrolyte. The working mechanisms of pseudocapacitors are redox reactions, intercalation and electrosorption.
Marcus
The physical and mathematical basics of electron charge transfer absent chemical bonds leading to pseudocapacitance was developed by Rudolph A. Marcus.Marcus Theory
In theoretical chemistry, Marcus theory is a theory originally developed by Rudolph A. Marcus, starting in 1956, to explain the rates of electron transfer reactions – the rate at which an electron can move or jump from one chemical species ( ...
explains the rates of electron transfer reactions—the rate at which an electron can move from one chemical species to another. It was originally formulated to address outer sphere electron transfer
Outer sphere refers to an electron transfer (ET) event that occurs between chemical species that remain separate and intact before, during, and after the ET event. In contrast, for inner sphere electron transfer the participating redox sites underg ...
reactions, in which two chemical species change only in their charge, with an electron jumping. For redox reactions without making or breaking bonds, Marcus theory takes the place of Henry Eyring's transition state theory
In chemistry, transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.
T ...
which was derived for reactions with structural changes. Marcus received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "M ...
in 1992 for this theory.Rudolph A. Marcus: The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1992/ref>
Mathematical description
There are detailed descriptions of the interfacial DL in many books on colloid and interface science and microscale fluid transport. There is also a recent IUPAC technical report on the subject of interfacial double layer and relatedelectrokinetic phenomena Electrokinetic phenomena are a family of several different effects that occur in heterogeneous fluids, or in porous bodies filled with fluid, or in a fast flow over a flat surface. The term heterogeneous here means a fluid containing particles. Part ...
.
As stated by Lyklema, "...the reason for the formation of a "relaxed" ("equilibrium") double layer is the non-electric affinity of charge-determining ions for a surface..."Lyklema, J. "Fundamentals of Interface and Colloid Science", vol.2, page.3.208, 1995 This process leads to the buildup of an electric surface charge
Surface charge is a two-dimensional surface with non-zero electric charge. These electric charges are constrained on this 2-D surface, and surface charge density, measured in coulombs per square meter (C•m−2), is used to describe the charge dis ...
, expressed usually in C/m2. This surface charge creates an electrostatic field that then affects the ions in the bulk of the liquid. This electrostatic field, in combination with the thermal motion of the ions, creates a counter charge, and thus screens the electric surface charge. The net electric charge in this screening diffuse layer is equal in magnitude to the net surface charge, but has the opposite polarity. As a result, the complete structure is electrically neutral.
The diffuse layer, or at least part of it, can move under the influence of tangential
In geometry, the tangent line (or simply tangent) to a plane curve at a given point is the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. Leibniz defined it as the line through a pair of infinitely close points on the curve. More ...
stress
Stress may refer to:
Science and medicine
* Stress (biology), an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition
* Stress (linguistics), relative emphasis or prominence given to a syllable in a word, or to a word in a phrase ...
. There is a conventionally introduced slipping plane that separates mobile fluid from fluid that remains attached to the surface. Electric potential at this plane is called electrokinetic potential
Zeta potential is the electrical potential at the slipping plane. This plane is the interface which separates mobile fluid from fluid that remains attached to the surface.
Zeta potential is a scientific term for electrokinetic potential in coll ...
or zeta potential
Zeta potential is the electrical potential at the slipping plane. This plane is the interface which separates mobile fluid from fluid that remains attached to the surface.
Zeta potential is a scientific term for electrokinetic potential in coll ...
(also denoted as ζ-potential).
The electric potential on the external boundary of the Stern layer versus the bulk electrolyte is referred to as Stern potential. Electric potential difference between the fluid bulk and the surface is called the electric surface potential.
Usually zeta potential
Zeta potential is the electrical potential at the slipping plane. This plane is the interface which separates mobile fluid from fluid that remains attached to the surface.
Zeta potential is a scientific term for electrokinetic potential in coll ...
is used for estimating the degree of DL charge. A characteristic value of this electric potential in the DL is 25 mV with a maximum value around 100 mV (up to several volts on electrodes). The chemical composition of the sample at which the ζ-potential is 0 is called the point of zero charge
The point of zero charge (pzc) is generally described as the pH at which the net charge of total particle surface (i.e. absorbent's surface) is equal to zero, which concept has been introduced in the studies dealt with colloidal flocculation to e ...
or the iso-electric point. It is usually determined by the solution pH value, since protons and hydroxyl ions are the charge-determining ions for most surfaces.
Zeta potential can be measured using electrophoresis
Electrophoresis, from Ancient Greek ἤλεκτρον (ḗlektron, "amber") and φόρησις (phórēsis, "the act of bearing"), is the motion of dispersed particles relative to a fluid under the influence of a spatially uniform electric fie ...
, electroacoustic phenomena Electroacoustic phenomena arise when ultrasound propagates through a fluid containing ions. The associated particle motion generates electric signals because ions have electric charge. This coupling between ultrasound and electric field is called el ...
, streaming potential
Streaming media is multimedia that is delivered and consumed in a continuous manner from a source, with little or no intermediate storage in network elements. ''Streaming'' refers to the delivery method of content, rather than the content it ...
, and electroosmotic flow Electroosmotic flow (or electro-osmotic flow, often abbreviated EOF; synonymous with electroosmosis or electroendosmosis) is the motion of liquid induced by an applied potential across a porous material, capillary tube, membrane, microchannel, or an ...
.
The characteristic thickness of the DL is the Debye length
In plasmas and electrolytes, the Debye length \lambda_ (also called Debye radius), is a measure of a charge carrier's net electrostatic effect in a solution and how far its electrostatic effect persists. With each Debye length the charges are in ...
, κ−1. It is reciprocally proportional to the square root of the ion concentration ''C''. In aqueous solutions it is typically on the scale of a few nanometers and the thickness decreases with increasing concentration of the electrolyte.
The electric field strength inside the DL can be anywhere from zero to over 109 V/m. These steep electric potential gradients are the reason for the importance of the DLs.
The theory for a flat surface and a symmetrical electrolyte is usually referred to as the Gouy-Chapman theory. It yields a simple relationship between electric charge in the diffuse layer σd and the Stern potential Ψd:
There is no general analytical solution for mixed electrolytes, curved surfaces or even spherical particles. There is an asymptotic solution for spherical particles with low charged DLs. In the case when electric potential over DL is less than 25 mV, the so-called Debye-Huckel approximation holds. It yields the following expression for electric potential'' Ψ'' in the spherical DL as a function of the distance ''r'' from the particle center:
There are several asymptotic models which play important roles in theoretical developments associated with the interfacial DL.
The first one is "thin DL". This model assumes that DL is much thinner than the colloidal particle or capillary radius. This restricts the value of the Debye length and particle radius as following:
This model offers tremendous simplifications for many subsequent applications. Theory of electrophoresis
Electrophoresis, from Ancient Greek ἤλεκτρον (ḗlektron, "amber") and φόρησις (phórēsis, "the act of bearing"), is the motion of dispersed particles relative to a fluid under the influence of a spatially uniform electric fie ...
is just one example. The theory of electroacoustic phenomena Electroacoustic phenomena arise when ultrasound propagates through a fluid containing ions. The associated particle motion generates electric signals because ions have electric charge. This coupling between ultrasound and electric field is called el ...
is another example.Dukhin, A. S. and Goetz, P. J. ''Characterization of liquids, nano- and micro- particulates and porous bodies using Ultrasound'', Elsevier, 2017
The thin DL model is valid for most aqueous systems because the Debye length is only a few nanometers in such cases. It breaks down only for nano-colloids in solution with ionic strengths close to water.
The opposing "thick DL" model assumes that the Debye length is larger than particle radius:
:
This model can be useful for some nano-colloids and non-polar fluids, where the Debye length is much larger.
The last model introduces "overlapped DLs". This is important in concentrated dispersions and emulsions when distances between particles become comparable with the Debye length.
Electrical double layers
The electrical double layer (EDL) is the result of the variation ofelectric potential
The electric potential (also called the ''electric field potential'', potential drop, the electrostatic potential) is defined as the amount of work energy needed to move a unit of electric charge from a reference point to the specific point in ...
near a surface, and has a significant influence on the behaviour of colloid
A colloid is a mixture in which one substance consisting of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Some definitions specify that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, while others extend ...
s and other surfaces in contact with solution
Solution may refer to:
* Solution (chemistry), a mixture where one substance is dissolved in another
* Solution (equation), in mathematics
** Numerical solution, in numerical analysis, approximate solutions within specified error bounds
* Soluti ...
s or solid-state fast ion conductor
In materials science, fast ion conductors are solid conductors with highly mobile ions. These materials are important in the area of solid state ionics, and are also known as solid electrolytes and superionic conductors. These materials are usef ...
s.
The primary difference between a double layer on an electrode and one on an interface is the mechanisms of surface charge
Surface charge is a two-dimensional surface with non-zero electric charge. These electric charges are constrained on this 2-D surface, and surface charge density, measured in coulombs per square meter (C•m−2), is used to describe the charge di ...
formation. With an electrode, it is possible to regulate the surface charge by applying an external electric potential. This application, however, is impossible in colloidal and porous double layers, because for colloidal particles, one does not have access to the interior of the particle to apply a potential difference.
EDLs are analogous to the double layer in plasma
Plasma or plasm may refer to:
Science
* Plasma (physics), one of the four fundamental states of matter
* Plasma (mineral), a green translucent silica mineral
* Quark–gluon plasma, a state of matter in quantum chromodynamics
Biology
* Blood pla ...
.
Differential capacitance
EDLs have an additional parameter defining their characterization:differential capacitance Differential capacitance in physics, electronics, and electrochemistry is a measure of the voltage-dependent capacitance of a nonlinear capacitor, such as an electrical double layer or a semiconductor diode. It is defined as the derivative of cha ...
. Differential capacitance, denoted as ''C'', is described by the equation below:
:
where σ is the surface charge
Surface charge is a two-dimensional surface with non-zero electric charge. These electric charges are constrained on this 2-D surface, and surface charge density, measured in coulombs per square meter (C•m−2), is used to describe the charge di ...
and ψ is the electric surface potential
A double layer (DL, also called an electrical double layer, EDL) is a structure that appears on the surface of an object when it is exposed to a fluid. The object might be a solid particle, a gas bubble, a liquid droplet, or a porous body. The D ...
.
Electron transfer in electrical double layer
The formation of electrical double layer (EDL) has been traditionally assumed to be entirely dominated by ion adsorption and redistribution. With considering the fact that the contact electrification between solid-solid is dominated by electron transfer, it is suggested by Wang that the EDL is formed by a two-step process. In the first step, when the molecules in the solution first approach a virgin surface that has no pre-existing surface charges, it may be possible that the atoms/molecules in the solution directly interact with the atoms on the solid surface to form strong overlap of electron clouds. Electron transfer occurs first to make the “neutral” atoms on solid surface become charged, i.e., the formation of ions. In the second step, if there are ions existing in the liquid, such as H+ and OH-, the loosely distributed negative ions in the solution would be attracted to migrate toward the surface bonded ions due to electrostatic interactions, forming an EDL. Both electron transfer and ion transfer co-exist at liquid-solid interface.
See also
*Depletion region
In semiconductor physics, the depletion region, also called depletion layer, depletion zone, junction region, space charge region or space charge layer, is an insulating region within a conductive, doped semiconductor material where the mobile ...
(structure of semiconductor junction)
*DLVO theory
The DLVO theory (named after Boris Derjaguin and Lev Landau, Evert Verwey and Theodoor Overbeek) explains the aggregation of aqueous dispersions quantitatively and describes the force between charged surfaces interacting through a liquid medium ...
*Electroosmotic pump An electroosmotic pump (EOP), or EO pump, is used for generating flow or pressure by use of an electric field. One application of this is removing liquid flooding water from channels and gas diffusion layers and direct hydration of the proton excha ...
*Interface and colloid science
Interface and colloid science is an interdisciplinary intersection of branches of chemistry, physics, nanoscience and other fields dealing with colloids, heterogeneous systems consisting of a mechanical mixture of particles between 1 nm and ...
*Nanofluidics
Nanofluidics is the study of the behavior, manipulation, and control of fluids that are confined to structures of nanometer (typically 1–100 nm) characteristic dimensions (1 nm = 10−9 m). Fluids confined in these structures exhibit p ...
* Poisson-Boltzmann equation
*Supercapacitor
A supercapacitor (SC), also called an ultracapacitor, is a high-capacity capacitor, with a capacitance value much higher than other capacitors but with lower voltage limits. It bridges the gap between electrolytic capacitors and rechargeable ba ...
References
Further reading
* * *External links
The Electrical Double Layer
{{DEFAULTSORT:Double Layer (Interfacial) Chemical mixtures Colloidal chemistry Surface science Electrochemistry Matter Soft matter