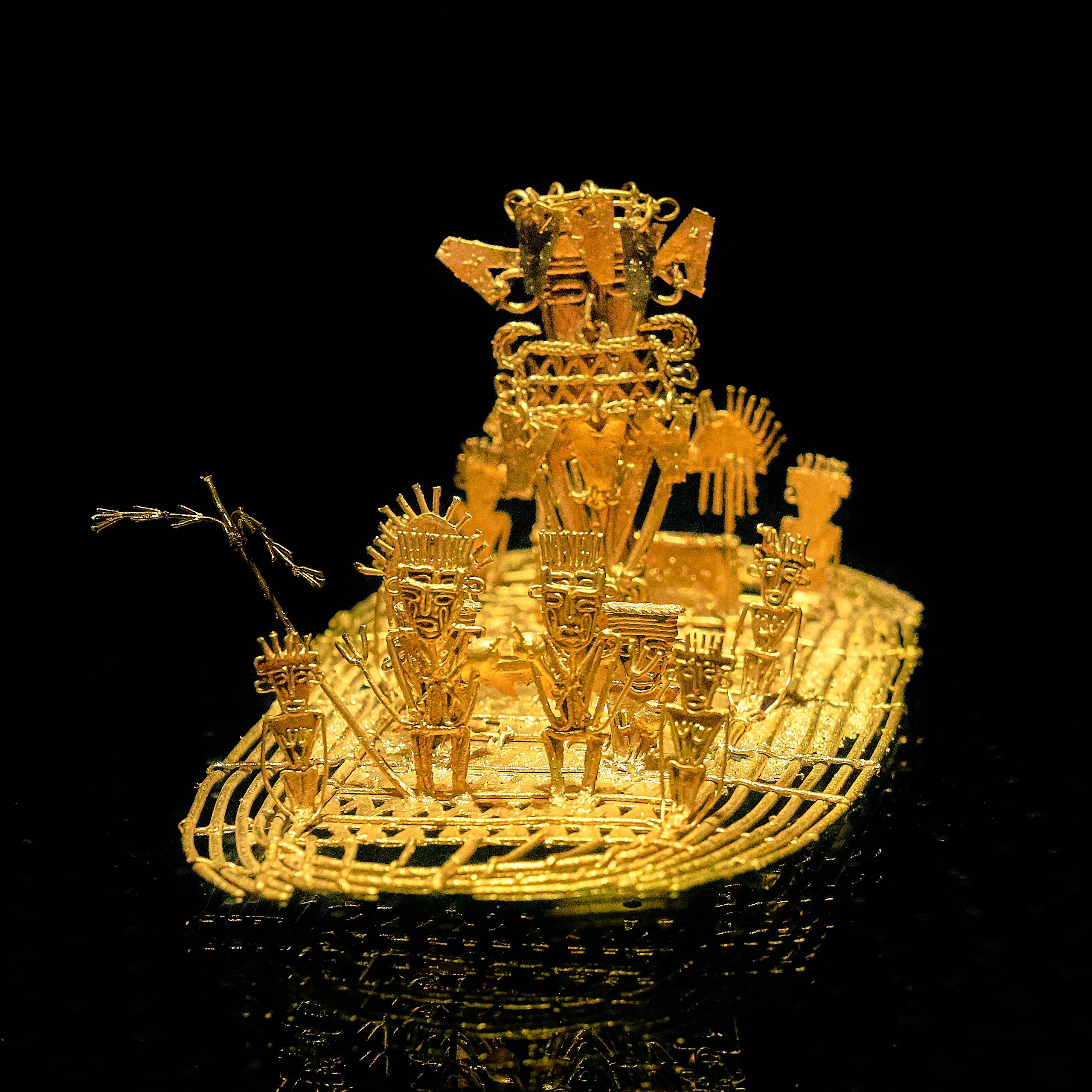

El Dorado (, ;
Spanish for "the
gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
en"), originally ''El Hombre Dorado'' ("The Golden Man") or ''El Rey Dorado'' ("The Golden King"), was the term used by the Spanish in the 16th century to describe a
mythical tribal chief (''zipa'') or king of the
Muisca people
The Muisca (also called Chibcha) are an indigenous people and culture of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Colombia, that formed the Muisca Confederation before the Spanish conquest. The people spoke Muysccubun, a language of the Chibchan lang ...
, an
indigenous people
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
of the
Altiplano Cundiboyacense of
Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
, who as an initiation rite, covered himself with
gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
dust and submerged in
Lake Guatavita
Lake Guatavita (Spanish: ''Laguna Guatavita'') is located in the Cordillera Oriental of the Colombian Andes in the municipality of Sesquilé in the Almeidas Province, Cundinamarca department of Colombia, northeast of Bogotá, the capital of ...
. The legends surrounding El Dorado changed over time, as it went from being a man, to a city, to a kingdom, and then finally to an empire.
A second location for El Dorado was inferred from rumors, which inspired several unsuccessful expeditions in the late 1500s in search of a city called Manoa on the shores of
Lake Parime
Lake Parime or Lake Parima is a legendary lake located in South America. It was reputedly the location of the fabled city of El Dorado, also known as Manoa, much sought-after by European explorers. Repeated attempts to find the lake failed to conf ...
or Parima. Two of the most famous of these expeditions were led by
Sir Walter Raleigh
Sir Walter Raleigh (; – 29 October 1618) was an English statesman, soldier, writer and explorer. One of the most notable figures of the Elizabethan era, he played a leading part in English colonisation of North America, suppressed rebellion ...
. In pursuit of the legend, Spanish
conquistadors and numerous others searched what is today Colombia,
Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
, and parts of
Guyana
Guyana ( or ), officially the Cooperative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. Guyana is an indigenous word which means "Land of Many Waters". The capital city is Georgetown. Guyana is bordered by the ...
and northern
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, for the city and its fabulous king. In the course of these explorations, much of northern South America, including the
Amazon River
The Amazon River (, ; es, Río Amazonas, pt, Rio Amazonas) in South America is the largest river by discharge volume of water in the world, and the disputed longest river system in the world in comparison to the Nile.
The headwaters of t ...
, was mapped. By the beginning of the 19th century, most people dismissed the existence of the city as a myth.
The legend of the
Seven Cities of Gold (Seven Cities of Cibola) led to
Francisco Vázquez de Coronado
Francisco Vázquez de Coronado y Luján (; 1510 – 22 September 1554) was a Spanish conquistador and explorer who led a large expedition from what is now Mexico to present-day Kansas through parts of the southwestern United States between 15 ...
's expedition of 1540 across the New Mexico territory. This became mixed with the stories of El Dorado, which was sometimes said to be one of the seven cities.
Several literary works have used the name in their titles, sometimes as "El Dorado", and other times as "Eldorado".
Muisca
The Muisca occupied the highlands of
Cundinamarca and
Boyacá departments of Colombia in two migrations from outlying lowland areas, one starting c. 1270 BC, and a second between 800 BC and 500 BC. At those times, other more ancient civilizations also flourished in the highlands. The
Muisca Confederation
The Muisca Confederation was a loose confederation of different Muisca rulers (''zaques'', ''zipas'', '' iraca'', and ''tundama'') in the central Andean highlands of present-day Colombia before the Spanish conquest of northern South America. The ...
was as advanced as the
Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those g ...
,
Maya and
Inca
The Inca Empire (also known as the Incan Empire and the Inka Empire), called ''Tawantinsuyu'' by its subjects, (Quechua for the "Realm of the Four Parts", "four parts together" ) was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The admin ...
civilizations.
In the
mythology of the Muisca, Mnya the Gold or golden color, represents the energy contained in the trinity of
Chiminigagua, which constitutes the creative power of everything that exists. Chiminigagua is related to
Bachué
The goddess Bachué (in Chibcha language: "the one with the naked breast"), is a mother goddess that according to the Muisca religion is the mother of humanity. She emerged of the waters in the Iguaque Lake with a baby in her arms, who grew to ...
, Cuza,
Chibchacum,
Bochica, and
Nencatacoa
Nencatacoa or Nem-catacoa was the god and protector of the mantle makers, artists and festivities in the religion of the Muisca. The Muisca and their confederation were one of the advanced civilizations of the Americas; as much as the Aztec, May ...
.
The tribal ceremony
The original narrative can be found in the rambling chronicle ''
El Carnero
''El Carnero'' ( en, The Sheep) is the colloquial name of a Spanish language colonial chronicle whose title was ''Conquista i descubrimiento del nuevo reino de Granada de las Indias Occidentales del mar oceano, i fundacion de la ciudad de San ...
'' of
Juan Rodriguez Freyle
''Juan'' is a given name, the Spanish and Manx versions of '' John''. It is very common in Spain and in other Spanish-speaking communities around the world and in the Philippines, and also (pronounced differently) in the Isle of Man. In Spanish, ...
. According to Freyle, the ''zipa'' of the Muisca, in a ritual at
Lake Guatavita
Lake Guatavita (Spanish: ''Laguna Guatavita'') is located in the Cordillera Oriental of the Colombian Andes in the municipality of Sesquilé in the Almeidas Province, Cundinamarca department of Colombia, northeast of Bogotá, the capital of ...
near present-day
Bogotá
Bogotá (, also , , ), officially Bogotá, Distrito Capital, abbreviated Bogotá, D.C., and formerly known as Santa Fe de Bogotá (; ) during the Spanish period and between 1991 and 2000, is the capital city of Colombia, and one of the larges ...
, was said to be covered with gold dust, which he then washed off in the lake while his attendants threw objects made of gold, emeralds, and precious stones into the lake - such as
tunjo
A ''tunjo'' (from Muysccubun: ''chunso'') is a small anthropomorh or zoomorph figure elaborated by the Muisca as part of their art. ''Tunjos'' were made of gold or ''tumbaga''; a gold-silver-copper alloy. The Muisca used their ''tunjos'' ...
s.
In 1638, Freyle wrote this account of the ceremony, addressed to the ''
cacique
A ''cacique'' (Latin American ; ; feminine form: ''cacica'') was a tribal chieftain of the Taíno people, the indigenous inhabitants at European contact of the Bahamas, the Greater Antilles, and the northern Lesser Antilles. The term is a Spa ...
'' or governor of
Guatavita:
There is also an account, titled ''The Quest of El Dorado'', by poet-priest and historian of the Conquest
, who had served under Jiménez de Quesada in his campaign against the Muisca, written in the mid-16th century but not published until 1850:
In his ''Historia general y natural de las Indias'' (1535, expanded in 1851 from his previously unpublished papers),
Gonzalo Fernández de Oviedo y Valdés noted:
In the Muisca territories, there were a number of natural locations considered sacred, including lakes, rivers, forests and large rocks. People gathered here to perform rituals and sacrifices mostly with gold and emeralds. Important lakes were
Lake Guatavita
Lake Guatavita (Spanish: ''Laguna Guatavita'') is located in the Cordillera Oriental of the Colombian Andes in the municipality of Sesquilé in the Almeidas Province, Cundinamarca department of Colombia, northeast of Bogotá, the capital of ...
,
Lake Iguaque
Lake Iguaque is a lake located in the Boyacá Department of Colombia. The lake and the surrounding area was declared a Flora and Fauna Sanctuary in 1977.
Geography and climate
Lake Iguaque is located northeast of Villa de Leyva and is part of th ...
,
Lake Fúquene
Lake Fúquene is a heart-shaped lake located in the Ubaté-Chiquinquirá Valley, part of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, in the north of Cundinamarca, Colombia, at the border with Boyacá. The Andean lake, at an average altitude of , was consider ...
,
Lake Tota
Lake Tota ( es, Lago de Tota) is the largest lake in Colombia, located in the east of Boyacá department, inside the Sugamuxi Province, it is the source of the Upia River which flows into the Orinoco River basin.
The major town on the lake is ...
, the
Siecha Lakes
The Siecha Lakes are three glacial lakes located in the Chingaza Natural National Park in Cundinamarca, Colombia. The Andean lakes are considered sacred in the religion of the Muisca who inhabited the area before the Spanish conquest of the Muis ...
, Lake Teusacá and
Lake Ubaque.
From ritual to myth and metaphor
El Dorado is applied to a legendary story in which precious stones were found in fabulous abundance along with gold coins. The concept of El Dorado underwent several transformations, and eventually accounts of the previous myth were also combined with those of a legendary lost city. The resulting El Dorado myth enticed European explorers for two centuries. Among the earliest stories was the one told on his deathbed by Juan Martinez, a captain of munitions for Spanish adventurer
Diego de Ordaz, who claimed to have visited the city of Manoa. Martinez had allowed a store of gunpowder to catch fire and was condemned to death, however his friends let him escape downriver in a canoe. Martinez then met with some local people who took him to the city:
The fable of Juan Martinez was founded on the adventures of Juan Martin de Albujar, well known to the Spanish historians of the Conquest; and who, in the expedition of Pedro de Silva (1570), fell into the hands of the Caribs of the Lower Orinoco.
During the 16th and 17th centuries, Europeans, still fascinated by the New World, believed that a hidden city of immense wealth existed. Numerous expeditions were mounted to search for this treasure, all of which ended in failure. The illustration of El Dorado's location on maps only made matters worse, as it made some people think that the city of El Dorado's existence had been confirmed. The mythical city of El Dorado on
Lake Parime
Lake Parime or Lake Parima is a legendary lake located in South America. It was reputedly the location of the fabled city of El Dorado, also known as Manoa, much sought-after by European explorers. Repeated attempts to find the lake failed to conf ...
was marked on numerous maps until its existence was disproved by
Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 17696 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, naturalist, explorer, and proponent of Romantic philosophy and science. He was the younger brother of the Prussian minister, p ...
during his Latin America expedition (1799–1804).
Meanwhile, the name of ''El Dorado'' came to be used metaphorically of any place where wealth could be rapidly acquired. It was given to
El Dorado County, California
El Dorado County (), officially the County of El Dorado, is a county located in the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 191,185. The county seat is Placerville. The County is part of the Sacramento- Roseville-A ...
, and to towns and cities in various states. It has also been anglicized to the single word ''Eldorado'', and is sometimes used in product titles to suggest great wealth and fortune, such as the
Cadillac Eldorado line of
luxury automobiles.

El Dorado is also sometimes used as a metaphor to represent an ultimate prize or "
Holy Grail
The Holy Grail (french: Saint Graal, br, Graal Santel, cy, Greal Sanctaidd, kw, Gral) is a treasure that serves as an important motif in Arthurian literature. Various traditions describe the Holy Grail as a cup, dish, or stone with miracul ...
" that one might spend one's life seeking. It could represent true love, heaven, happiness, or success. It is used sometimes as a figure of speech to represent something much sought after that may not even exist, or, at least, may not ever be found. Such use is evident in
Edgar Allan Poe
Edgar Allan Poe (; Edgar Poe; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, editor, and literary critic. Poe is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales of mystery and the macabre. He is wide ...
's poem "
El Dorado
El Dorado (, ; Spanish for "the golden"), originally ''El Hombre Dorado'' ("The Golden Man") or ''El Rey Dorado'' ("The Golden King"), was the term used by the Spanish in the 16th century to describe a mythical tribal chief (''zipa'') or king o ...
." In this context, El Dorado bears similarity to other myths such as the
Fountain of Youth and
Shangri-la
Shangri-La is a fictional place in Asia's Kunlun Mountains (昆仑山), Uses the spelling 'Kuen-Lun'. described in the 1933 novel ''Lost Horizon'' by English author James Hilton. Hilton portrays Shangri-La as a mystical, harmonious valley, ge ...
. The other side of the ideal quest metaphor may be represented by ''Helldorado'', a satirical nickname given to
Tombstone, Arizona
Tombstone is a historic city in Cochise County, Arizona, United States, founded in 1877 by prospector Ed Schieffelin in what was then Pima County, Arizona Territory. It became one of the last boomtowns in the American frontier. The town grew si ...
(United States) in the 1880s by a disgruntled miner who complained that many of his profession had traveled far to find El Dorado, only to wind up washing dishes in restaurants. The South African city
Johannesburg
Johannesburg ( , , ; Zulu and xh, eGoli ), colloquially known as Jozi, Joburg, or "The City of Gold", is the largest city in South Africa, classified as a megacity, and is one of the 100 largest urban areas in the world. According to Demo ...
is commonly interpreted as a modern-day El Dorado, due to the extremely large gold deposit found along the
Witwatersrand
The Witwatersrand () (locally the Rand or, less commonly, the Reef) is a , north-facing scarp in South Africa. It consists of a hard, erosion-resistant quartzite metamorphic rock, over which several north-flowing rivers form waterfalls, which ...
on which it is situated.
Early search for gold in northern South America
Spanish conquistadores had noticed the native people's fine artifacts of gold and silver long before any legend of "golden men" or "lost cities" had appeared. The prevalence of such valuable artifacts, and the natives' apparent ignorance of their value, inspired speculation as to a plentiful source for them.
Prior to the time of the
Spanish conquest of the Muisca
The Spanish conquest of the Muisca took place from 1537 to 1540. The Muisca were the inhabitants of the central Andean highlands of Colombia before the arrival of the Spanish conquistadors. They were organised in a loose confederation of differe ...
and discovery of Lake Guatavita, a handful of expeditions had set out to explore the lowlands to the east of the Andes in search of gold, cinnamon, precious stones, and anything else of value. During the Klein-Venedig period in Venezuela (1528–1546), agents of the German Welser banking family (which had received a concession from Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles I of Spain) launched repeated expeditions into the interior of the country in Klein-Venedig#The search for El Dorado, search of gold, starting with Ambrosius Ehinger's first expedition in July 1529.
Spanish explorer
Diego de Ordaz, then governor of the eastern part of Venezuela known as Paria (named after Paria Peninsula), was the first European to explore the Orinoco river in 1531–32 in search of gold. A veteran of Hernán Cortés's campaign in Mexico, Ordaz followed the Orinoco beyond the mouth of the Meta River but was blocked by the rapids at Atures Municipality, Atures. After his return he died, possibly poisoned, on a voyage back to Spain.
[John Hemming, ''Red Gold: The Conquest of the Brazilian Indians, 1500-1760,'' Harvard University Press, 1978.](_blank)
After the death of Ordaz while returning from his expedition, the Crown appointed a new Governor of Paria, Jerónimo de Ortal, who diligently explored the interior along the Meta River between 1532 and 1537. In 1535, he ordered captain Alonso de Herrera to move inland by the waters of the Uyapari River (today the town of Barrancas del Orinoco). Herrera, who had accompanied Ordaz three years before, explored the Meta River but was killed by the indigenous Achagua people, Achagua near its banks, while waiting out the winter rains in Casanare Department, Casanare.
The search for El Dorado
Even before the conquest of the Aztec Empire, Aztec and
Inca
The Inca Empire (also known as the Incan Empire and the Inka Empire), called ''Tawantinsuyu'' by its subjects, (Quechua for the "Realm of the Four Parts", "four parts together" ) was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The admin ...
empires and the
Muisca Confederation
The Muisca Confederation was a loose confederation of different Muisca rulers (''zaques'', ''zipas'', '' iraca'', and ''tundama'') in the central Andean highlands of present-day Colombia before the Spanish conquest of northern South America. The ...
the Spanish collected vague hearsay about these polities and their riches. After the Inca Empire in Peru Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire, was conquered by Francisco Pizarro and its riches proved real, new rumours of riches reached the Spanish.
The earliest reference to an El Dorado-like kingdom occurred in 1531 during Ordaz's expedition when he was told of a kingdom called Meta that was said to exist beyond a mountain on the left bank of the Orinoco River. Meta was supposedly abundant in gold and ruled by a chief that only had one intact eye.

Between 1531 and 1538, the German conquistadors Nikolaus Federmann and Georg von Speyer searched the Venezuelan lowlands, Colombian plateaus, Orinoco Basin and Orinoquía Region, Llanos Orientales for El Dorado. Subsequently, Philipp von Hutten accompanied Von Speyer on a journey (1536–38) in which they reached the headwaters of the Rio Japura, near the equator. In 1541 Hutten led an exploring party of about 150 men, mostly horsemen, from Santa Ana de Coro, Coro on the coast of
Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
in search of the Golden City. After several years of wandering, harassed by the natives and weakened by hunger and fever, he crossed the Rio Bermejo, and went on with a small group of around 40 men on horseback into Llanos, Los Llanos, where they engaged in battle with a large number of Omaguas and Hutten was severely wounded. He led those of his followers who survived back to Coro in 1546. On Hutten's return, he and a traveling companion, Bartholomeus VI. Welser, were executed in El Tocuyo by the Spanish authorities.
In 1535, Sebastian de Benalcazar, a lieutenant of Francisco Pizarro, interrogated an Indian that had been captured at Quito. Luis Daza recorded that the Indian was a warrior while Antonio de Herrera y Tordesillas wrote that the Indian was an ambassador who had come to request military assistance from the Inca, unaware that they had already been conquered. The Indian told Benalcazar that he was from a kingdom of riches known as Cundinamarca far to the north where a zipa, or chief, covered himself in gold dust during ceremonies. Benalcazar set out to find the chief, reportedly saying "Lets go find that golden Indian!" ( es, ¡Vámos a buscar a este indio dorado!), eventually the chief became known to the Spaniards came to know as El Dorado. Benalcazar failed however to find El Dorado and eventually joined up with Federmann and Gonzalo Jimenez de Quesada and returned to Spain. It has been speculated that the land of wealth spoken of by the Indian was Arma, a kingdom whose inhabitants wore gold ornaments, which was eventually conquered by Pedro Cieza de Leon.
In 1536 Gonzalo Díaz de Pineda led an expedition to the lowlands to the east of Quito and found cinnamon trees but no rich empire.
Quesada brothers' expeditions
In 1536, stories of El Dorado drew the Spanish conquistador Gonzalo Jimenez de Quesada and his army of 800 men away from their mission to find an overland route to Peru and up into the Andean homeland of the Muisca for the first time. The southern Muisca settlements and their treasures quickly fell to the conquistadors in 1537 and 1538. On the Bogotá savanna, Quesada received reports from captured natives about a kingdom called Metza whose inhabitants built a temple dedicated to the sun and "keep in it an infinite quantity of gold and jewels, and live in stone houses, go about dressed and booted, and fight with lances and maces". Quesada believed this might have been El Dorado and decided to postpone his return to Santa Marta and continue his expedition for another year. After his brother Gonzalo had left for Spain in May 1539, Spanish conquistador Hernán Pérez de Quesada set out a new expedition in September 1540, leaving with 270 Spanish soldiers and countless indigenous porters to explore the Orinoquía Region, Llanos Orientales. One of his main captains on this journey was Baltasar Maldonado. Their expedition was unsuccessful and after reaching Quito, the troops returned to Santafe de Bogotá.
Pizarro and Orellana's discovery of the Amazon
In December of 1540, Gonzalo Pizarro, the younger half-brother of Francisco Pizarro, the Spanish conquistador who toppled the Incan Empire in Peru, as vice governor of the province of Quito (current Ecuador) prepared in Cusco an expedition of 170 spaniards and 3,000 natives and depart to Quito to explore it lands at the east, where many natives talked of the existence of a valley far to the east rich in both cinnamon and gold. When he arrived to Quito, he banded together 220 soldiers and about 4,000 natives and depart in February of 1541. He led them eastward down the Coca River, Rio Coca and Napo River, Rio Napo. Francisco de Orellana a relative of Pizarro, accompanied him on the expedition as his second in command. Gonzalo quit after many of the soldiers and natives had died from hunger, disease, and periodic attacks by hostile natives. He ordered Orellana to continue downstream, where he eventually made it to the Atlantic Ocean. The expedition found neither cinnamon nor gold, but Orellana is credited with discovering the
Amazon River
The Amazon River (, ; es, Río Amazonas, pt, Rio Amazonas) in South America is the largest river by discharge volume of water in the world, and the disputed longest river system in the world in comparison to the Nile.
The headwaters of t ...
(so named because of a Amazons, tribe of female warriors that attacked Orellana's men while on their voyage).
Expeditions of Pedro de Ursúa and Lope de Aguirre
In 1560, Basque ''conquistadors'' Pedro de Ursúa and Lope de Aguirre journeyed down the Marañón River (Peru), Marañón and
Amazon River
The Amazon River (, ; es, Río Amazonas, pt, Rio Amazonas) in South America is the largest river by discharge volume of water in the world, and the disputed longest river system in the world in comparison to the Nile.
The headwaters of t ...
s, in search of El Dorado, with 300 Spaniards and hundreds of natives;
the actual goal of Ursúa was to send idle veterans from the Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire away, to keep them from trouble-making, using the El Dorado myth as a lure. A year later, Aguirre participated in the overthrow and killing of Ursúa and his successor, Fernando de Guzmán, whom he ultimately succeeded.
He and his men reached the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic (probably by the Orinoco River), destroying native villages of Margarita island and actual Venezuela.
In 1561 Aguirre's expedition ended with his death in Barquisimeto, and in the years since then he has been treated by historians as a symbol of cruelty and treachery in the early history of Spanish colonization of the Americas, colonial Spanish America.
Lake Guatavita gold
While the existence of a sacred lake in the Cordillera Oriental (Colombia), Eastern Ranges of the Andes, associated with Indian rituals involving gold, was known to the Spaniards possibly as early as 1531, its location was only discovered in 1537 by conquistador Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada while on an expedition to the highlands of the Cordillera Oriental (Colombia), Eastern Ranges of the Andes in search of gold.
Conquistadores Lázaro Fonte and Hernán Perez de Quesada attempted (unsuccessfully) to drain the lake in 1545 using a "bucket chain" of labourers. After 3 months, the water level had been reduced by 3 metres, and only a small amount of gold was recovered, with a value of 3000–4000 pesos (approx. US$100,000 today; a peso or Spanish dollar, piece of eight of the 15th century weighs 0.88 oz of 93% pure silver).
A later more industrious attempt was made in 1580, by Bogotá business entrepreneur Antonio de Sepúlveda. A notch was cut deep into the rim of the lake, which managed to reduce the water level by 20 metres, before collapsing and killing many of the labourers. A share of the findings—consisting of various golden ornaments, jewellery and armour—was sent to Philip II of Spain, King Philip II of Spain. Sepúlveda's discovery came to approximately 12,000 pesos. He died a poor man, and is buried at the church in the small town of
Guatavita.
In 1801,
Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 17696 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, naturalist, explorer, and proponent of Romantic philosophy and science. He was the younger brother of the Prussian minister, p ...
made a visit to Guatavita, and on his return to Paris, calculated from the findings of Sepúlveda's efforts that Guatavita could offer up as much as $300 million worth of gold.
In 1898, the Company for the Exploitation of the Lagoon of Guatavita was formed and taken over by Contractors Ltd. of London, in a deal brokered by British expatriate Hartley Knowles. The lake was drained by a tunnel that emerged in the centre of the lake. The water was drained to a depth of about 4 feet of mud and slime. This made it impossible to explore, and when the mud had dried in the sun, it had set like concrete. Artifacts worth only about £500 were found, and auctioned at Sotheby's of London. Some of these were donated to the British Museum. The company filed for bankruptcy and ceased activities in 1929.
In 1965, the Colombian government designated the lake as a protected area. Private salvage operations, including attempts to drain the lake, are now illegal.
Antonio de Berrio's expeditions
The Spanish Governor of Trinidad, Antonio de Berrio (nephew of Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada), made three failed expeditions to look for El Dorado. Between 1583 and 1589 he carried out his first two expeditions, going through the wild regions of the Colombian plains and the Upper Orinoco. In 1590 he began his third expedition, ascending the Orinoco to reach the Caroní River with his own expeditionaries and another 470 men under command of Domingo de Vera. In March 1591, while he was waiting for supplies on Margarita Island, his entire force was taken captive by Walter Raleigh, who proceeded up the Orinoco in search of El Dorado, with Berrio as a guide. Berrio took them to the territories he had previously explored by himself years before. After several months Raleigh's expedition returned to Trinidad, and he released Berrio at the end of June 1595 on the coast of Cumaná in exchange for some English prisoners. His son Fernando de Berrío y Oruña (1577–1622) also made numerous expeditions in search of El Dorado.
Walter Raleigh

Walter Raleigh's 1595 journey with Antonio de Berrio had aimed to reach
Lake Parime
Lake Parime or Lake Parima is a legendary lake located in South America. It was reputedly the location of the fabled city of El Dorado, also known as Manoa, much sought-after by European explorers. Repeated attempts to find the lake failed to conf ...
in the highlands of
Guyana
Guyana ( or ), officially the Cooperative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. Guyana is an indigenous word which means "Land of Many Waters". The capital city is Georgetown. Guyana is bordered by the ...
(the supposed location of El Dorado at the time). He was encouraged by the account of Juan Martinez, believed to be Juan Martin de Albujar, who had taken part in Pedro de Silva's expedition of the area in 1570, only to fall into the hands of the Caribs of the Lower Orinoco. Martinez claimed that he was taken to the golden city in blindfold, was entertained by the natives, and then left the city and couldn't remember how to return. Raleigh had set many goals for his expedition, and believed he had a genuine chance at finding the so-called city of gold. First, he wanted to find the mythical city of El Dorado, which he suspected to be an actual Indian city named Manõa. Second, he hoped to establish an English presence in the Southern Hemisphere that could compete with that of the Spanish. His third goal was to create an English settlement in the land called Guyana, and to try to reduce commerce between the natives and Spaniards.
In 1596 Raleigh sent his lieutenant, Lawrence Kemys, back to Guyana in the area of the Orinoco River, to gather more information about the lake and the golden city. During his exploration of the coast between the Amazon and the Orinoco, Kemys mapped the location of Amerindian tribes and prepared geographical, geological and botanical reports of the country. Kemys described the coast of Guiana in detail in his ''Relation of the Second Voyage to Guiana'' (1596)
and wrote that indigenous people of Guiana traveled inland by canoe and land passages towards a large body of water on the shores of which he supposed was located Manoa, Golden City of El Dorado.
Though Raleigh never found El Dorado, he was convinced that there was some fantastic city whose riches could be discovered. Finding gold on the riverbanks and in villages only strengthened his resolve. In 1617, he returned to the New World on a second expedition, this time with Kemys and his son, Watt Raleigh, to continue his quest for El Dorado. However, Raleigh, by now an old man, stayed behind in a camp on the island of Trinidad. Watt Raleigh was killed in a battle with Spaniards and Kemys subsequently committed suicide.
Upon Raleigh's return to England, James VI and I, King James ordered him to be beheaded for disobeying orders to avoid conflict with the Spanish. He was executed in 1618.
Post-Elizabethan expeditions
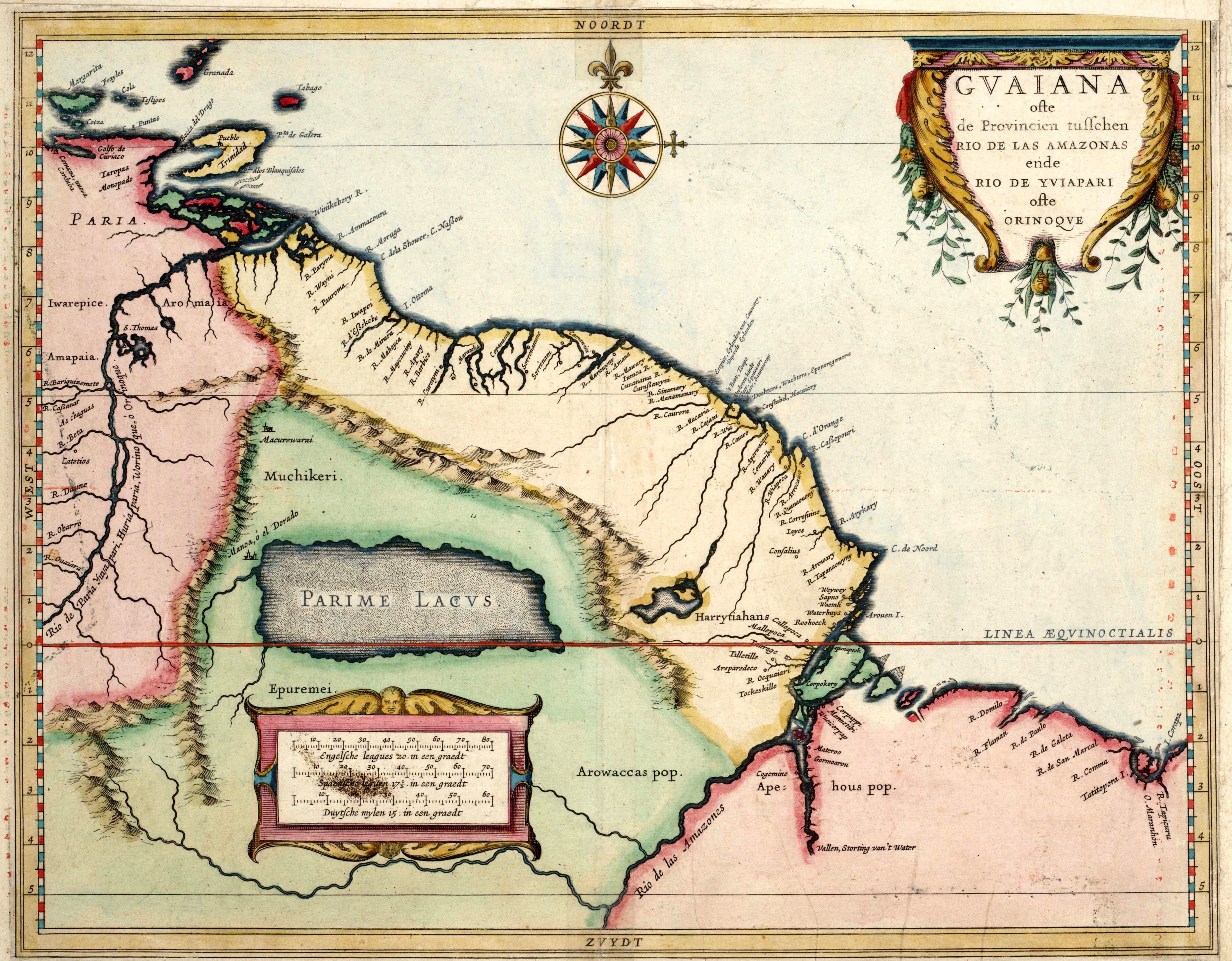
On 23 March 1609, Robert Harcourt (explorer), Robert Harcourt accompanied by his brother Michael and a company of adventurers, sailed for Guiana. On 11 May he arrived at the Oyapock River. Local people came on board, and were disappointed at the absence of
Sir Walter Raleigh
Sir Walter Raleigh (; – 29 October 1618) was an English statesman, soldier, writer and explorer. One of the most notable figures of the Elizabethan era, he played a leading part in English colonisation of North America, suppressed rebellion ...
after he had famously visited Raleigh's El Dorado Expedition, during his exploration of the area in 1595. Harcourt gave them aqua vitae. He took possession in the king's name of a tract of land lying between the River Amazon and River Essequibo on 14 August, left his brother and most of his company to colonise it, and four days later embarked for England.
In early 1611 Sir Thomas Roe, on a mission to the West Indies for Henry Frederick, Prince of Wales, sailed his 200-ton ship, the ''Lion's Claw'', some up the Amazon, then took a party of canoes up the Waipoco (probably the Oyapock River) in search of Lake Parime, negotiating thirty-two rapids and traveling about before they ran out of food and had to turn back.
In 1627 North and Harcourt, obtained letters patent under the great seal from Charles I of England, Charles I, authorising them to form a company for "the Plantation of Guiana", North being named as deputy governor of the settlement. Short of funds, this expedition was fitted out, a plantation established in 1627, and trade opened by North's endeavours.
[From Robert Harcourt (explorer): ]
In 1637-38, two monks, Acana and Fritz, undertook several journeys to the lands of the Manoas, indigenous peoples living in western Guyana and what is now Roraima in northeastern Brazil. Although they found no evidence of El Dorado, their published accounts were intended to inspire further exploration.
In November 1739, Nicholas Horstman, a German surgeon commissioned by the Dutch Governor of Guiana, traveled up the Essequibo River accompanied by two Dutch soldiers and four Indian guides. In April 1741 one of the Indian guides returned reporting that in 1740 Horstman had crossed over to the Rio Branco and descended it to its confluence with the Rio Negro. Horstman discovered Lake Amucu on the North Rupununi but found neither gold nor any evidence of a city.
In 1740, Don Manuel Centurion, Governor of Ciudad Bolívar, Santo Tomé de Guayana de Angostura del Orinoco in Venezuela, hearing a report from an Indian about Lake Parima, embarked on a journey up the Caura River (Venezuela), Caura River and the Paragua River, causing the deaths of several hundred persons. His survey of the local geography, however, provided the basis for other expeditions starting in 1775.
From 1775 to 1780, Nicholas Rodriguez and Antonio Santos, two entrepreneurs employed by the Spanish Governors, set out on foot and Santos, proceeding by the Caroní River, the Paragua River, and the Pacaraima Mountains, reached the Uraricoera River and Branco River, Rio Branco, but found nothing.
Between 1799 and 1804,
Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 17696 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, naturalist, explorer, and proponent of Romantic philosophy and science. He was the younger brother of the Prussian minister, p ...
conducted an extensive and scientific survey of the Guyana river basins and lakes, concluding that a seasonally-flooded confluence of rivers may be what inspired the notion of a mythical
Lake Parime
Lake Parime or Lake Parima is a legendary lake located in South America. It was reputedly the location of the fabled city of El Dorado, also known as Manoa, much sought-after by European explorers. Repeated attempts to find the lake failed to conf ...
, and of the supposed golden city on the shore, nothing was found.
Further exploration by Charles Waterton (1812)
and Robert Schomburgk (1840) confirmed Humboldt's findings.
Gold strikes and the extractive wealth of the rainforest
It appears today that the Muisca obtained their gold in trade, and while they possessed large quantities of it over time, no great store of the metal was ever accumulated.
By the mid-1570s, the Spanish silver strike at Potosí in Upper Peru (modern Bolivia) was producing unprecedented real wealth.
In 1603, Queen Elizabeth I of England died, bringing to an end the era of Elizabethan adventurism. In 1618, Sir Walter Raleigh, the great inspirer, was beheaded after returning from an expedition to Venezuela in search of El Dorado for an attack on a Spanish outpost.
In 1695, ''bandeirantes'' in the south struck gold along a tributary of the São Francisco River in the highlands of State of Minas Gerais, Brazil. The prospect of real gold overshadowed the illusory promise of "gold men" and "lost cities" in the vast interior of the north.
The gold mine at El Callao (Venezuela), started in 1871, a few miles at south of Orinoco River, was for a time one of the richest in the world, and the goldfields as a whole saw over a million ounces exported between 1860 and 1883. The immigrants who emigrated to the gold mines of Venezuela were mostly from the British Isles and the British West Indies.
The Orinoco Mining Arc (OMA), officially created on February 24, 2016 as the Arco Mining Orinoco National Strategic Development Zone, is an area rich in mineral resources that the Republic of Venezuela has been operating since 2017;
occupies mostly the north of the Bolivar state and to a lesser extent the northeast of the Amazonas state and part of the Delta Amacuro state. It has 7,000 tons of reserves of gold, copper, diamond, coltan, iron, bauxite and other minerals.
A photograph taken from the International Space Station (ISS) in 2021 showed golden areas near the
Amazon River
The Amazon River (, ; es, Río Amazonas, pt, Rio Amazonas) in South America is the largest river by discharge volume of water in the world, and the disputed longest river system in the world in comparison to the Nile.
The headwaters of t ...
. These were determined to be extensive illegal gold mining operations. Such photography and, especially, satellite surveys, have revealed the extent of the impact of these operations. They suggest the rate of forest loss more than tripled as gold prices rose in 2008, largely driven by small, illegal mining operations that now account for most activity in the region. A team from the Carnegie Institution for Science#Department of Global Ecology, Stanford, California, Carnegie Institution for Science in Stanford, California, has estimated, using satellite data and field surveys together, that mining covered fewer than 10,000 hectares in 1999 but had spread beyond 50,000 hectares by September 2012.
Recent research
In 1987–1988, an expedition led by John Hemming (historian), John Hemming of the Royal Geographical Society failed to uncover any evidence of the ancient city of Manoa on the :pt:Reserva Biológica Ilha de Maracá, island of Maracá in north-central Roraima. Members of the expedition were accused of looting historic artifacts but an official report of the expedition described it as "an ecological survey."
Evidence for the existence of Lake Parime
Although it was dismissed in the 19th century as a myth, some evidence for the existence of a lake in northern Brazil has been uncovered. In 1977 Brazilian geologists Gert Woeltje and Frederico Guimarães Cruz along with Roland Stevenson, found that on all the surrounding hillsides a horizontal line appears at a uniform level approximately above sea level. This line registers the water level of an extinct lake which existed until relatively recent times. Researchers who studied it found that the lake's previous diameter measured and its area was about . About 700 years ago this giant lake began to drain due to tectonic movement. In June 1690, a massive earthquake opened a bedrock Fault (geology), fault, forming a rift or a graben that permitted the water to flow into the Rio Branco. By the early 19th century it had dried up completely.
Roraima's well-known Pedra Pintada, Roraima, Pedra Pintada is the site of numerous pictographs dating to the pre-Columbian era. Designs on the sheer exterior face of the rock were most likely painted by people standing in canoes on the surface of the now-vanished lake. Gold, which was reported to be washed up on the shores of the lake, was most likely carried by streams and rivers out of the mountains where it can be found today.
21st-Century Explorations
Since 2007 a team of international and multidisciplinary researchers, led by Venezuelan archaeologist and explorer Jose Miguel Perez-Gomez, has conducted several expeditions into southeast Venezuela’s unexplored jungle areas in search of storied Lake Parime. The team presented its results in October 2019 at the TerraSAR-X / TanDEM-X Science Team Meeting held at the DLR’s (Deutschen Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt’s, i.e., the German Aerospace Center) Microwave and Radar Institute in Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany (1). These results derived from a large amount of data collected from multiple expeditions. They were based on analysis of historical sources; indigenous oral traditions; archaeological and geological studies; digital elevation models (DEM); and aerial, along with satellite, remote sensing surveys obtained from NASA's Shuttle Radar Topography Missions (SRTM), the Landsat Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+) instrument, and TanDEM-X synthetic aperture radar (SAR) sensors from the DLR’s Microwave and Radar Institute in Germany. By using these advanced remote sensing technologies, the researchers were able to reconstruct a fossil lake and also identify the place where it emptied. Based on a GIS flood projection model, the flooding computations for the proposed lake area revealed a body of water much longer than it was wide. In fact, an elongated rift lake emerged, markedly similar to Sir Walter Raleigh’s original map of 1595.
El Dorado in popular culture
Music
* ''Eldorado (EP), Eldorado'', by Neil Young (1989)
* "El Dorado" by Ravi (rapper), Ravi (2020)
* ''El Dorado'', by The Jayhawks (2018)
* ''El Dorado (Shakira album), El Dorado'', album by Shakira (2017)
**El Dorado World Tour, concert tour by Shakira (2018)
* ''El Dorado'', by Marillion (2016)
* ''El Dorado'', by Exo (group) (2015) album "EXODUS"
* ''ElDorado'', a Japanese Visual Kei band
* ''El Dorado'', by Death Cab for Cutie (2015)
* ''El Dorado'', by Every Time I Die (2014)
* ''El Dorado'', by Two Steps From Hell (2012)
* ''El Dorado'', by Iron Maiden (2010)
* ''Eldorado'', by Dave Rodgers (2007)
* ''El Dorado (Aterciopelados album), El Dorado'', by Aterciopelados (1995)
* ''Eldorado'', by The Tragically Hip (1992)
* ''El Dorado'', by John Adams (1991)
* ''Eldorado'', by Komu Vnyz (1990)
* ''Eldorado'', by Patrick O'Hearn (1989)
* ''El Dorado'', by Prince Daddy & The Hyena (2022)
* ''El Dorado'', by Restless Heart (1988)
*''El Dorado'', by Seikima-II (1986)
*''El Dorado'', by the March Violets (1986)
* ''El Dorado'', by Agent Orange (band) (1981)
* ''Eldorado'', by Goombay Dance Band (1980)
* ''Eldorado (Electric Light Orchestra album), Eldorado'', album by Electric Light Orchestra (1974)
* ''Eldorado'', by Sopor Aeternus & the Ensemble of Shadows (2000)
* ''Curse of Eldorado'', album by Ghoultown (2020)
* ''El Dorado'', by Stellar (musical artist) (Sid Banerjee) (2021)
* ''El Dorado (24kGoldn album), El Dorado'' by 24kGoldn (2021)
* ''Eldorado'' by Sanah (singer) (2022)
* El Dorado by Dirty Heads (2022)
Games
Pinball
* ''El Dorado City of Gold (pinball)'' (1984)
* Zen Studios' ''Zen Pinball#Tables, El Dorado'' (2009)
Video games
*''Monster Hunter: World'' (2018)
* ''Civilization VI'' (2017)
*''Europa Universalis IV#El Dorado, Europa Universalis IV – El Dorado DLC'' (2015)
* ''Age of Empires II: The Forgotten#Campaigns, Age of Empires II: The Forgotten HD'' (2013)
* ''Pirate101'' (2012)
* ''The Secret World'' (2012)
* ''Sid Meier's Civilization V'' (2010)
* ''Uncharted: Drake's Fortune'' (2007)
* ''Pitfall: The Lost Expedition'' (2004)
* ''The Journeyman Project 3: Legacy of Time'' (1998)
* ''Sid Meier's Colonization'' (1994)
* ''Inca (video game), Inca'' (1992)
Mobile games
* ''Monster Strike'' (2013)
Tabletop (Board) Games
* ''Reiner_Knizia, The Quest for El Dorado'' (2017)
Movies
* ''Aguirre, the Wrath of God'' (1972)
* ''El Dorado (1988 film), El Dorado'' (1988)
* ''The Mask of Zorro'' (1998)
* ''The Road to El Dorado'' (2000)
* ''National Treasure: Book of Secrets'' (2007)
* ''Indiana Jones and the Kingdom of the Crystal Skull'' (2008)
*'' El Dorado Temple of the Sun'' (2010)
* ''Entranced Earth'' (1967)
* ''The Lost City of Z (film), The Lost City of Z'' (2016)
* ''Amazon Obhijaan'' (2017)
* ''Gold (2017 film), Gold'' (2017)
* ''K.G.F: Chapter 1'' (2018)
* ''K.G.F: Chapter 2'' (2022)
* ''Black Panther (film), Black Panther'' (2018) (mentioned)
* ''Professor Shonku O El Dorado'' (2019)
* ''Dora and the Lost City of Gold'' (2019)
Television
* ''The Mysterious Cities of Gold'' (1982-1983, 2012-2016)
* ''James Bond Jr'' (1991, ''Earth Cracker'' episode)
* ''Eldorado (TV series), Eldorado'' (1992-1993)
Anime
* ''Garo: Vanishing Line'' (2017-2018)
Comics
* ''The Gilded Man (comics)'' (1952 in comics, 1952 Donald Duck's story by Carl Barks based on the legend)
* ''Beyond the Windy Isles'', album of Corto Maltese's adventures by Hugo Pratt (1970 in comics, 1970–1971 in comics, 1971)
* ''Celtic Tales (Corto Maltese), Celtic Tales'', album of Corto Maltese's adventures by Hugo Pratt (1971–1972 in comics, 1972)
* ''The Last Lord of Eldorado'' (1998 in comics, 1998 Donald Duck's story by Don Rosa)
Poems
* "Eldorado (poem), Eldorado" (1849)
Literature
* ''El Camino de El Dorado'' novel of Arturo Uslar Pietri published in 1947
* ''Candide'' satire of Voltaire published in 1759 describes a place called El Dorado, a geographically isolated utopia where the streets are covered with precious stones, there exist no priests, and all of the king's jokes are funny.
* ''The Language of Eldorado'' by Mark McWatt
Cars
*
Cadillac Eldorado
See also
*
Spanish conquest of the Muisca
The Spanish conquest of the Muisca took place from 1537 to 1540. The Muisca were the inhabitants of the central Andean highlands of Colombia before the arrival of the Spanish conquistadors. They were organised in a loose confederation of differe ...
, the main expedition in the quest for ''El Dorado''
* La Canela, the "Valley of Cinnamon," a legendary location in South America that grew out of expectations aroused by the voyage of Columbus
* ''Darkness in El Dorado''
* Liborio Zerda
*
Lake Parime
Lake Parime or Lake Parima is a legendary lake located in South America. It was reputedly the location of the fabled city of El Dorado, also known as Manoa, much sought-after by European explorers. Repeated attempts to find the lake failed to conf ...
* List of mythological places
* Lost City of Z
* Montezuma's treasure, a somewhat similar Mexico, Mexican/Southwestern United States, southwestern American legend
* Paititi
*
Seven Cities of Gold, mythological locations in New Mexico, United States (some accounts call El Dorado one of the seven)
* ''The Narrative of Robert Adams'' (1816), which dispelled a then-prevalent European misconception that Timbuktu was an African El Dorado
* Witwatersrand Gold Rush
Notes
References
Bibliography
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
*
Analysis of maps from 1570 to 1842, showing El Dorado in various locations around South AmericaEl Dorado raft– Gold Museum, Bogotá, Gold Museum,
Bogotá
Bogotá (, also , , ), officially Bogotá, Distrito Capital, abbreviated Bogotá, D.C., and formerly known as Santa Fe de Bogotá (; ) during the Spanish period and between 1991 and 2000, is the capital city of Colombia, and one of the larges ...
,
Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
El Dorado– Ancient History Encyclopedia
The Legend of ''El Dorado''– Tairona Heritage Trust
{{DEFAULTSORT:Dorado
Exploration of South America
Gold
History of South America
Muisca mythology and religion
Pre-Columbian mythology and religion
Mythological populated places
Mythological kingdoms, empires, and countries
Mythical utopias
Fictional locations in South America
Legendary treasures
 El Dorado (, ; Spanish for "the
El Dorado (, ; Spanish for "the  El Dorado is also sometimes used as a metaphor to represent an ultimate prize or "
El Dorado is also sometimes used as a metaphor to represent an ultimate prize or " Between 1531 and 1538, the German conquistadors Nikolaus Federmann and Georg von Speyer searched the Venezuelan lowlands, Colombian plateaus, Orinoco Basin and Orinoquía Region, Llanos Orientales for El Dorado. Subsequently, Philipp von Hutten accompanied Von Speyer on a journey (1536–38) in which they reached the headwaters of the Rio Japura, near the equator. In 1541 Hutten led an exploring party of about 150 men, mostly horsemen, from Santa Ana de Coro, Coro on the coast of
Between 1531 and 1538, the German conquistadors Nikolaus Federmann and Georg von Speyer searched the Venezuelan lowlands, Colombian plateaus, Orinoco Basin and Orinoquía Region, Llanos Orientales for El Dorado. Subsequently, Philipp von Hutten accompanied Von Speyer on a journey (1536–38) in which they reached the headwaters of the Rio Japura, near the equator. In 1541 Hutten led an exploring party of about 150 men, mostly horsemen, from Santa Ana de Coro, Coro on the coast of  Walter Raleigh's 1595 journey with Antonio de Berrio had aimed to reach
Walter Raleigh's 1595 journey with Antonio de Berrio had aimed to reach  On 23 March 1609, Robert Harcourt (explorer), Robert Harcourt accompanied by his brother Michael and a company of adventurers, sailed for Guiana. On 11 May he arrived at the Oyapock River. Local people came on board, and were disappointed at the absence of
On 23 March 1609, Robert Harcourt (explorer), Robert Harcourt accompanied by his brother Michael and a company of adventurers, sailed for Guiana. On 11 May he arrived at the Oyapock River. Local people came on board, and were disappointed at the absence of