
The psychological and physiological effects of meditation have been studied. In recent years, studies of
meditation
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique – such as mindfulness, or focusing the mind on a particular object, thought, or activity – to train attention and awareness, and achieve a mentally clear and emotionally cal ...
have increasingly involved the use of modern instruments, such as
fMRI
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area o ...
and
EEG
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex ...
, which are able to observe brain physiology and neural activity in living subjects, either during the act of
meditation
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique – such as mindfulness, or focusing the mind on a particular object, thought, or activity – to train attention and awareness, and achieve a mentally clear and emotionally cal ...
itself or before and after meditation. Correlations can thus be established between meditative practices and
brain structure or function.
Since the 1950s hundreds of studies on meditation have been conducted, but many of the early studies were flawed and thus yielded unreliable results.
Contemporary studies have attempted to address many of these flaws with the hope of guiding current research into a more fruitful path.
In 2013, researchers found moderate evidence that meditation ca
reduce anxiety depression, and pain, but no evidence that it is more effective than active treatments such as drugs or exercise.
Another major review article also cautioned about possible misinformation and
misinterpretation
Interpreting is a translational activity in which one produces a first and final target-language output on the basis of a one-time exposure to an expression in a source language.
The most common two modes of interpreting are simultaneous interp ...
of data related to the subject.
Effects of mindfulness meditation
A previous study commissioned by the
US Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality found that meditation interventions reduce multiple negative dimensions of psychological stress.
Other systematic reviews and meta-analyses show that
mindfulness
Mindfulness is the practice of purposely bringing one's attention to the present-moment experience without evaluation, a skill one develops through meditation or other training. Mindfulness derives from ''sati'', a significant element of Hind ...
meditation has several mental health benefits such as bringing about reductions in depression symptoms,
improvements in mood,
stress-resilience
and attentional control.
Mindfulness interventions also appear to be a promising intervention for managing depression in youth.
Mindfulness meditation is useful for managing stress,
anxiety
and also appears to be effective in treating substance use disorders.
A recent meta analysis by Hilton et al. (2016) including 30 randomized controlled trials found high quality evidence for improvement in depressive symptoms.
Other review studies have shown that mindfulness meditation can enhance the psychological functioning of breast cancer survivors,
is effective for people with eating disorders
and may also be effective in treating psychosis.
Studies have also shown that rumination and worry contribute to mental illnesses such as depression and anxiety,
and mindfulness-based interventions are effective in the reduction of worry.
Some studies suggest that mindfulness meditation contributes to a more coherent and healthy sense of self and identity, when considering aspects such as sense of responsibility, authenticity, compassion, self-acceptance and character.
Brain mechanisms
The
analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It ...
effect of
mindfulness
Mindfulness is the practice of purposely bringing one's attention to the present-moment experience without evaluation, a skill one develops through meditation or other training. Mindfulness derives from ''sati'', a significant element of Hind ...
meditation may involve multiple brain
mechanisms, but there are too few studies to allow conclusions about its effects on
chronic pain
Chronic pain is classified as pain that lasts longer than three to six months. In medicine, the distinction between Acute (medicine), acute and Chronic condition, chronic pain is sometimes determined by the amount of time since onset. Two commonly ...
.
Changes in the brain
Mindfulness meditation is under study for whether structural changes in the brain may occur, but most studies have weak methodology.
A meta-analysis found preliminary evidence for effects in the prefrontal cortex and other brain regions associated with body awareness. However, the results should be interpreted with caution because
funnel plot
A funnel plot is a graph designed to check for the existence of publication bias; funnel plots are commonly used in systematic reviews and meta-analyses. In the absence of publication bias, it assumes that studies with high precision will be plotte ...
s indicate that publication bias is an issue in meditation research.
A 2016 review using 78 functional
neuroimaging
Neuroimaging is the use of quantitative (computational) techniques to study the structure and function of the central nervous system, developed as an objective way of scientifically studying the healthy human brain in a non-invasive manner. Incre ...
studies suggests that different meditation styles are associated with different brain activity.
Attention and mindfulness
Attention networks and mindfulness meditation
Psychological and Buddhist conceptualizations of
mindfulness
Mindfulness is the practice of purposely bringing one's attention to the present-moment experience without evaluation, a skill one develops through meditation or other training. Mindfulness derives from ''sati'', a significant element of Hind ...
both highlight awareness and attention training as key components, in which levels of mindfulness can be cultivated with practise of mindfulness meditation.
Focused attention meditation (FAM) and open monitoring meditation (OMM) are distinct types of mindfulness meditation; FAM refers to the practice of intently maintaining focus on one object, whereas OMM is the progression of general awareness of one's surroundings while regulating thoughts.
Focused attention meditation is typically practiced first to increase the ability to enhance attentional stability, and awareness of mental states with the goal being to transition to open monitoring meditation practise that emphasizes the ability to monitor moment-by-moment changes in experience, without a focus of attention to maintain. Mindfulness meditation may lead to greater
cognitive flexibility
Cognitive flexibility is an intrinsic property of a cognitive system often associated with the mental ability to adjust its activity and content, switch between different task rules and corresponding behavioral responses, maintain multiple con ...
.
In an active randomized controlled study completed in 2019, participants who practiced mindfulness meditation demonstrated a greater improvement in awareness and attention than participants in the active control condition.
Alpha wave
Alpha waves, or the alpha rhythm, are neural oscillations in the frequency range of 8–12 Hz likely originating from the synchronous and coherent (in phase or constructive) electrical activity of thalamic pacemaker cells in humans. Historica ...
neural oscillation
Neural oscillations, or brainwaves, are rhythmic or repetitive patterns of neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by ...
power
Power most often refers to:
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
** Abusive power
Power may a ...
(which is normally associated with an alert resting state) has been shown to be increased by mindfulness in both healthy subjects and patients.
Areas of attention
=Sustained attention
=
Tasks of sustained attention relate to vigilance and the preparedness that aids completing a particular task goal. Psychological research into the relationship between mindfulness meditation and the sustained attention network have revealed the following:
* In a
continuous performance task
A continuous performance task, continuous performance test, or CPT, is any of several kinds of neuropsychological test that measures a person's sustained and selective attention. Sustained attention is the ability to maintain a consistent focus on ...
an association was found between higher dispositional mindfulness and more stable maintenance of sustained attention.
* In an
EEG
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex ...
study, the
attentional blink
Attentional blink (AB) is a phenomenon that reflects temporal limitations in the ability to deploy visual attention. When people must identify two visual stimuli in quick succession, accuracy for the second stimulus is poor if it occurs within 20 ...
effect was reduced, and
P3b
The P3b is a subcomponent of the P300, an event-related potential (ERP) component that can be observed in human scalp recordings of brain electrical activity. The P3b is a positive-going amplitude (usually relative to a reference behind the ear ...
ERP amplitude decreased in a group of participants who completed a mindfulness retreat. The incidence of reduced attentional blink effect relates to an increase in detectability of a second target.
* A greater degree of attentional resources may also be reflected in faster response times in task performance, as was found for participants with higher levels of mindfulness experience.
=Selective attention
=
* Selective attention as linked with the orientation network, is involved in selecting the relevant stimuli to attend to.
* Performance in the ability to limit attention to potentially sensory inputs (i.e. selective attention) was found to be higher following the completion of an eight-week MBSR course, compared to a one-month retreat and control group (with no mindfulness training).
The ANT task is a general applicable task designed to test the three attention networks, in which participants are required to determine the direction of a central arrow on a computer screen.
Efficiency in orienting that represent the capacity to selectively attend to stimuli was calculated by examining changes in the reaction time that accompanied cues indicating where the target occurred relative to the aid of no cues.
* Meditation experience was found to correlate negatively with reaction times on an
Eriksen flanker task
In cognitive psychology, the Eriksen flanker task is a set of response inhibition tests used to assess the ability to suppress responses that are inappropriate in a particular context. The target is flanked by non-target stimuli which correspond ei ...
measuring responses to global and local figures. Similar findings have been observed for correlations between mindfulness experience in an orienting score of response times taken from Attention Network Task performance.
* Participants who engaged in the Meditation Breath Attention Score exercise performed better on anagram tasks and reported greater focused attention on this task compared to those who did not undergo this exercise.
=Executive control attention
=
* Executive control attention include functions of inhibiting the conscious processing of distracting information. In the context of mindful meditation, distracting information relates to attention grabbing mental events such as thoughts related to the future or past.
* More than one study have reported findings of a reduced
Stroop effect
----
----
Naming the font color of a printed word is an easier and quicker task if word meaning and font color are congruent. If two words are both printed in red, the average time to say "red" in response to the written word "green" is ...
following mindfulness meditation training.
The Stroop effect indexes interference created by having words printed in colour that differ to the read semantic meaning e.g. green printed in red. However findings for this task are not consistently found.
For instance the MBSR may differ to how mindful one becomes relative to a person who is already high in trait mindfulness.
* Using the Attention Network Task (a version of
Eriksen flanker task
In cognitive psychology, the Eriksen flanker task is a set of response inhibition tests used to assess the ability to suppress responses that are inappropriate in a particular context. The target is flanked by non-target stimuli which correspond ei ...
) it was found that error scores that indicate executive control performance were reduced in experienced meditators
and following a brief five-session mindfulness training program.
* A neuroimaging study supports behavioural research findings that higher levels of mindfulness are associated with greater proficiency to inhibit distracting information. As greater activation of the rostral anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) was shown for mindfulness meditators than matched controls.
* Participants with at least 6 years of experience meditating performed better on the Stroop Test compared to participants who had not had experience meditating.
The group of meditators also had lower reaction times during this test than the group of non-meditators.
* Following a
Stroop test
----
----
Naming the font color of a printed word is an easier and quicker task if word meaning and font color are congruent. If two words are both printed in red, the average time to say "red" in response to the written word "green" is ...
, reduced amplitude of the
P3 ERP component was found for a meditation group relative to control participants. This was taken to signify that mindfulness meditation improves executive control functions of attention. An increased amplitude in the
N2 ERP component was also observed in the mindfulness meditation group, thought to reflect more efficient perceptual discrimination in earlier stages of perceptual processing.
Emotion regulation and mindfulness
Research shows meditation practices lead to greater emotional regulation abilities. Mindfulness can help people become more aware of thoughts in the present moment, and this increased self-awareness leads to better processing and control over one's responses to surroundings or circumstances.
Positive effects of this heightened awareness include a greater sense of empathy for others, an increase in positive patterns of thinking, and a reduction in anxiety.
Reductions in
rumination also have been found following mindfulness meditation practice, contributing to the development of positive thinking and emotional well-being.
Evidence of mindfulness and emotion regulation outcomes
Emotional reactivity can be measured and reflected in brain regions related to the production of emotions. It can also be reflected in tests of attentional performance, indexed in poorer performance in attention related tasks. The regulation of emotional reactivity as initiated by attentional control capacities can be taxing to performance, as attentional resources are limited.
* Patients with social anxiety disorder (SAD) exhibited reduced amygdala activation in response to negative self-beliefs following an MBSR intervention program that involves mindfulness meditation practice.
* The LPP ERP component indexes arousal and is larger in amplitude for emotionally salient stimuli relative to neutral. Individuals higher in trait mindfulness showed lower LPP responses to high arousal unpleasant images. These findings suggest that individuals with higher trait mindfulness were better able to regulate emotional reactivity to emotionally evocative stimuli.
* Participants who completed a seven-week mindfulness training program demonstrated a reduction in a measure of emotional interference (measured as slower responses times following the presentation of emotional relative to neutral pictures). This suggests a reduction in emotional interference.
* Following a MBSR intervention, decreases in social anxiety symptom severity were found, as well as increases in bilateral parietal cortex neural correlates. This is thought to reflect the increased employment of inhibitory attentional control capacities to regulate emotions.
* Participants who engaged in emotion-focus meditation and breathing meditation exhibited delayed emotional response to negatively valanced film stimuli compared to participants who did not engage in any type of meditation.
Controversies in mindful emotion regulation
It is debated as to whether top-down executive control regions such as the
dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC or DL-PFC) is an area in the prefrontal cortex of the primate brain. It is one of the most recently derived parts of the human brain. It undergoes a prolonged period of maturation which lasts until adultho ...
(DLPFC), are required
or not
to inhibit reactivity of the amygdala activation related to the production of evoked emotional responses. Arguably an initial increase in activation of executive control regions developed during mindfulness training may lessen with increasing mindfulness expertise.
Stress reduction
Research has shown
stress
Stress may refer to:
Science and medicine
* Stress (biology), an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition
* Stress (linguistics), relative emphasis or prominence given to a syllable in a word, or to a word in a phrase ...
reduction benefits from mindfulness.
A 2019 study tested the effects of meditation on the psychological well-being, work stress, and blood pressure of employees working in the United Kingdom. One group of participants were instructed to meditate once a day using a mindfulness app on their smartphones, while the control group did not engage in meditation. Measurements of well-being, stress, and perceived workplace support were taken for both groups before the intervention and then again after four months. Based on self-report questionnaires, the participants who engaged in meditation showed a significant increase in psychological well-being and perceived workplace support. The meditators also reported a significant decrease in anxiety and stress levels.
Another study conducted to understand association between mindfulness, perceived stress and work engagement indicated that mindfulness was associated with lower perceived stress and higher work engagement.
Other research shows decreased stress levels in people who engage in meditation after shorter periods of time as well. Evidence of significant stress reduction was found after only three weeks of meditation intervention.
Brief, daily meditation sessions can alter one's behavioral response to stressors, improving coping mechanisms and decreasing the adverse impact caused by stress.
A study from 2016 examined anxiety and emotional states of naive meditators before and after a seven-day meditation retreat in Thailand. Results displayed a significant reduction in perceived stress after this traditional
Buddhist meditation
Buddhist meditation is the practice of meditation in Buddhism. The closest words for meditation in the classical languages of Buddhism are '' bhāvanā'' ("mental development") and '' jhāna/dhyāna'' (mental training resulting in a calm and ...
retreat.
Insomnia and sleep
Chronic
insomnia
Insomnia, also known as sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder in which people have trouble sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by daytime sleepiness, low energy, ...
is often associated with anxious hyperarousal and frustration over inability to sleep.
Mindfulness has been shown to reduce insomnia and improve sleep quality, although self-reported measures show larger effects than objective measures.
Future directions
A large part of mindfulness research is dependent on technology. As new technology continues to be developed, new imaging techniques will become useful in this field. Real-time fMRI might give immediate feedback and guide participants through the programs. It could also be used to more easily train and evaluate mental states during meditation itself.
Effects of other types of meditation
Insight (Vipassana) meditation

Vipassana
''Samatha'' (Pāli; sa, शमथ ''śamatha''; ), "calm," "serenity," "tranquillity of awareness," and ''vipassanā'' (Pāli; Sanskrit ''vipaśyanā''), literally "special, super (''vi-''), seeing (''-passanā'')", are two qualities of the ...
meditation is a component of Buddhist practice. Phra Taweepong Inwongsakul and Sampath Kumar from the University of Mysore have been studying the effects of this meditation on 120 students by measuring the associated increase of cortical thickness in the brain. The results of this study are inconclusive. Vipassana meditation leads to more than just mindfulness, but has been found to reduce stress, increase well-being and self-kindness. These effects were found to be most powerful short-term, but still had a relatively significant impact six months later. In a study conducted by Szekeres and Wertheim (2014), they found stress to be the category that seemed to have the most regression, but the others contained higher prevalence when compared to the participants' original scores that were given before embarking on Vipassana meditation. Overall, according to self-reports, Vipassana can have short and long-term effects on an individual.
EEG studies on Vipassana meditators seemed to indicate significant increase in
parieto-
occipital
The occipital bone () is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cereb ...
gamma rhythms in experienced meditators (35–45 Hz).
In another study conducted by
NIMHANS
The National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro-Sciences is a medical institution in Bangalore, India. NIMHANS is the apex centre for mental health and neuroscience education in the country. It is an Institute of National Importance operates ...
on Vipassana meditators, researchers found readings associated with improved cognitive processing after a session of meditation, with distinct and graded difference in the readings between novice meditators and experienced meditators.
An essential component to the Vipassana mediation approach is the focus on awareness, referring to bodily sensations and psychological status. In a study conducted by Zeng et al. (2013), awareness was described as the acknowledgement of consciousness which is monitoring all aspects of the environment. This definition differentiates the concept of awareness from mindfulness. The emphasis on awareness, and the way it assists in monitoring emotion, is unique to this meditative practice.
Kundalini yoga
Kundalini yoga
Kundalini yoga () derives from ''kundalini'', defined in tantra as energy that lies within the body, frequently at the navel or the base of the spine. In normative tantric systems kundalini is considered to be dormant until it is activated (a ...
has proved to increase the prevention of cognitive decline and evaluate the response of biomarkers to treatment, thereby shedding light on the underlying mechanisms of the link between Kundalini Yoga and cognitive impairment. For the study, 81 participants aged 55 and older who had subjective memory complaints and met criteria for mild cognitive impairment, indicated by a total score of 0.5 on the Clinical Dementia Rating Scale. The results showed that at 12 weeks, both the yoga group showed significant improvements in recall memory and visual memory and showed a significant sustained improvement in memory up to the 24-week follow-up, the yoga group showed significant improvement in verbal fluency and sustained significant improvements in executive functioning at week 24. In addition, the yoga cohort showed significant improvement in depressive symptoms, apathy, and resilience from emotional stress. This research was provided by Helen Lavretsky, M.D. and colleagues. In another study, Kundalini Yoga did not show significant effectiveness in treating obsessive-compulsive disorders compared with Relaxation/Meditation.
Sahaja yoga and mental silence
Sahaja yoga
Sahaja Yoga (सहज योग) is a religion founded in 1970 by Nirmala Srivastava (1923–2011). Nirmala Srivastava is known as Shri Mataji Nirmala Devi (trans: ''Revered Immaculate Mother'') or, simply, as "Mother" by her followers, who a ...
meditation is regarded as a mental silence meditation, and has been shown to correlate with particular brain and brain wave
characteristics. One study has led to suggestions that Sahaja meditation involves 'switching off' irrelevant brain networks for the maintenance of focused internalized attention and inhibition of inappropriate information. Sahaja meditators appear to benefit from lower depression
and scored above control group for emotional well-being and mental health measures on
SF-36
The Short Form (36) Health Survey is a 36-item, patient-reported survey of patient health. The SF-36 is a measure of health status and an abbreviated variant of it, the SF-6D, is commonly used in health economics as a variable in the quality-adjus ...
ratings.
A study comparing practitioners of Sahaja Yoga meditation with a group of non-meditators doing a simple relaxation exercise, measured a drop in skin temperature in the meditators compared to a rise in skin temperature in the non-meditators as they relaxed. The researchers noted that all other meditation studies that have observed skin temperature have recorded increases and none have recorded a decrease in skin temperature. This suggests that Sahaja Yoga meditation, being a mental silence approach, may differ both experientially and physiologically from simple relaxation.
Transcendental Meditation
The first
Transcendental Meditation
Transcendental Meditation (TM) is a form of silent mantra meditation advocated by the Transcendental Meditation movement. Maharishi Mahesh Yogi created the technique in India in the mid-1950s. Advocates of TM claim that the technique promotes a ...
(TM) research studies were conducted at UCLA and Harvard University and published in ''Science'' and the ''American Journal of Physiology'' in 1970 and 1971. However, much research has been of poor quality,
[ (References the same 2004 systematic review by Canter and Ernst on TM and hypertension that is separately referenced in this article)] including a high risk for
bias
Bias is a disproportionate weight ''in favor of'' or ''against'' an idea or thing, usually in a way that is closed-minded, prejudicial, or unfair. Biases can be innate or learned. People may develop biases for or against an individual, a group, ...
due to the connection of researchers to the TM organization and the selection of subjects with a favorable opinion of TM.
Independent
systematic reviews
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on t ...
have not found health benefits for TM exceeding those of
relaxation and
health education
Health education is a profession of educating people about health. Areas within this profession encompass environmental health, physical health, social health, emotional health, intellectual health, and spiritual health, as well as sexual and r ...
.
A 2013 statement from the
American Heart Association
The American Heart Association (AHA) is a nonprofit organization in the United States that funds cardiovascular medical research, educates consumers on healthy living and fosters appropriate cardiac care in an effort to reduce disability and death ...
described the evidence supporting TM as a treatment for hypertension as Level IIB, meaning that TM "may be considered in clinical practice" but that its effectiveness is "unknown/unclear/uncertain or not well-established".
In another study, TM proved comparable with other kinds of relaxation therapies in reducing anxiety.
Practitioners of TM have demonstrated a one
Hertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that on ...
reduction in
EEG
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex ...
alpha wave
Alpha waves, or the alpha rhythm, are neural oscillations in the frequency range of 8–12 Hz likely originating from the synchronous and coherent (in phase or constructive) electrical activity of thalamic pacemaker cells in humans. Historica ...
frequency relative to controls.
Research on unspecified or multiple types of meditation
Brain activity
The medial prefrontal and posterior cingulate cortices have been found to be relatively deactivated during meditation by experienced meditators using concentration, lovingkindness and choiceless awareness meditation. In addition experienced meditators were found to have stronger coupling between the posterior cingulate, dorsal anterior cingulate, and dorsolateral prefrontal cortices both when meditating and when not meditating.
Over time meditation can actually increase the integrity of both gray and white matter. The added amount of gray matter found in the brain stem after meditation improves communication between the cortex and all other areas within the brain.
Meditation often stimulates a large network of cortical regions including the
frontal
Front may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''The Front'' (1943 film), a 1943 Soviet drama film
* ''The Front'', 1976 film
Music
*The Front (band), an American rock band signed to Columbia Records and active in the 1980s and ea ...
and
parietal regions, lateral
occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin ''ob'', "behind", and ''caput'', "head".
The occipital lobe is the vi ...
, the
insular cortex
The insular cortex (also insula and insular lobe) is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus (the fissure separating the temporal lobe from the parietal and frontal lobes) within each hemisphere of the mammalian bra ...
,
thalamic nuclei
This traditional list does not accord strictly with human thalamic anatomy.
Nuclear groups of the thalamus include:
* anterior nuclear group
** anteroventral nucleus
** anterodorsal nucleus
** anteromedial nucleus
**superficial ("lateral dorsal ...
,
basal ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG), or basal nuclei, are a group of subcortical nuclei, of varied origin, in the brains of vertebrates. In humans, and some primates, there are some differences, mainly in the division of the globus pallidus into an extern ...
, and the
cerebellum
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebel ...
region in the brain. These parts of the brain are connected with attention and the default network of the brain which is associated to day dreaming.
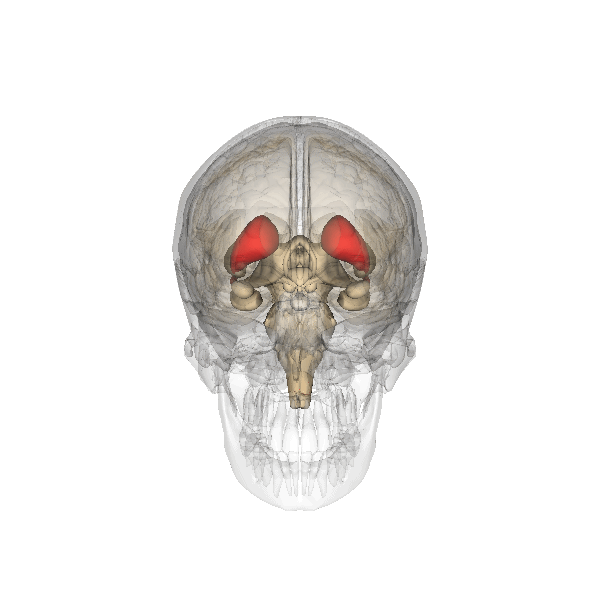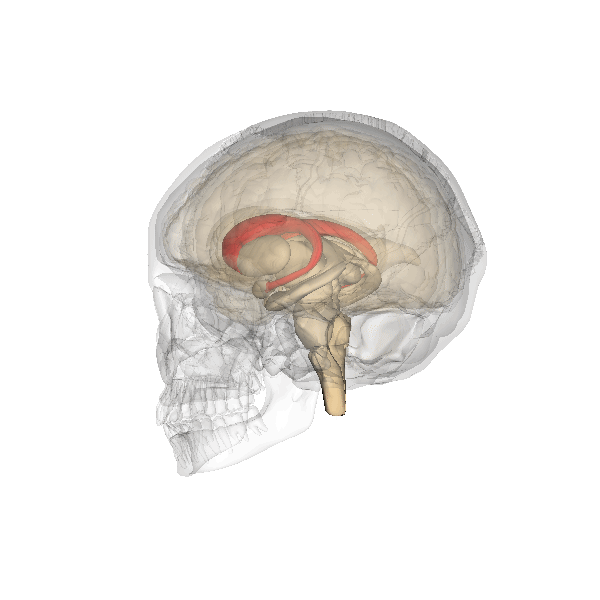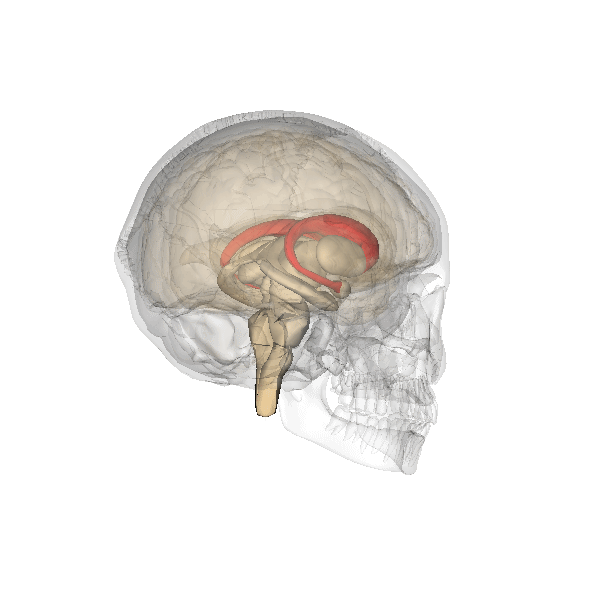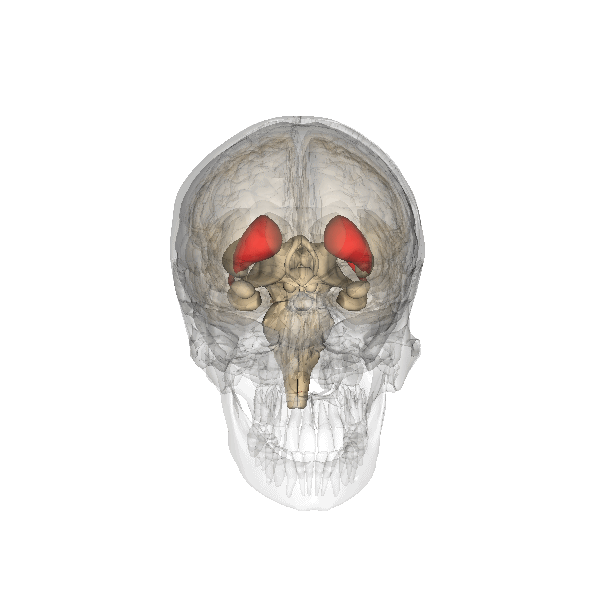
In addition, both meditation and yoga have been found to have impacts on the brain, specifically the caudate. Strengthening of the
caudate has been shown in meditators as well as yogis. The increased connectedness of the caudate has potential to be responsible for the improved well-being that is associated with yoga and meditation.
Changes in the brain
Meditation is under preliminary research to assess possible changes in
grey matter
Grey matter is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil (dendrites and unmyelinated axons), glial cells (astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), synapses, and capillaries. Grey matter is distingui ...
concentrations.
Attention/Mind wandering
Meditation has been found to decrease
mind wandering
Mind-wandering is a broad term with no currently universal definition. According to McMillan, Kaufmann and Singer (2013) mind-wandering consists of 3 different subtypes: positive constructive daydreaming, guilty fear of failure, and poor attention ...
and allows the brain to fully focus on challenging tasks for longer periods of time without getting distracted. This is due to an increased ability to reduce activity in the
default mode network
In neuroscience, the default mode network (DMN), also known as the default network, default state network, or anatomically the medial frontoparietal network (M-FPN), is a large-scale brain network primarily composed of the dorsal medial prefro ...
when focusing on a particular task.
Non-directive forms of meditation where the meditator lets their mind wander freely can actually produce higher levels of activity in the default mode network when compared to a resting state or having the brain in a neutral place.
These Non directive forms of meditation allows the meditators to have better control over thoughts during everyday activities or when focusing on specific task due to a reduced frustration at the brains mind wandering process.
When given a specific task, meditation can allow quicker response to changing environmental stimuli. Meditation can allow the brain to decrease attention to unwanted responses of irrelevant environmental stimuli and a reduces the
Stroop effect
----
----
Naming the font color of a printed word is an easier and quicker task if word meaning and font color are congruent. If two words are both printed in red, the average time to say "red" in response to the written word "green" is ...
. Those who meditate have regularly demonstrated more control on what they focus their attention on while maintaining a mindful awareness on what is around them. Experienced meditators have been shown to have an increased ability when it comes to conflict monitoring
and find it easier to switch between competing stimuli.
Those who practice meditation experience an increase of attentional resources in the brain and steady meditation practice can lead to the reduction of the
attentional blink
Attentional blink (AB) is a phenomenon that reflects temporal limitations in the ability to deploy visual attention. When people must identify two visual stimuli in quick succession, accuracy for the second stimulus is poor if it occurs within 20 ...
due to a decreased mental exertion when identifying important stimuli.
Perception
Studies have shown that meditation has both short-term and long-term effects on various perceptual faculties. In 1984 a study showed that meditators have a significantly lower detection threshold for light stimuli of short duration. In 2000 a study of the perception of visual illusions by zen masters, novice meditators, and non-meditators showed statistically significant effects found for the
Poggendorff Illusion but not for the
Müller-Lyer Illusion
The Müller-Lyer illusion is an optical illusion consisting of three stylized arrows. When viewers are asked to place a mark on the figure at the midpoint, they tend to place it more towards the "tail" end. The illusion was devised by Franz Carl ...
. The zen masters experienced a statistically significant reduction in initial illusion (measured as error in millimeters) and a lower decrement in illusion for subsequent trials.
Tloczynski has described the theory of mechanism behind the changes in perception that accompany mindfulness meditation thus: "A person who meditates consequently perceives objects more as directly experienced stimuli and less as concepts… With the removal or minimization of cognitive stimuli and generally increasing awareness, meditation can therefore influence both the quality (accuracy) and quantity (detection) of perception."
Brown points to this as a possible explanation of the phenomenon: "
he higher rate of detection of single light flashesinvolves quieting some of the higher mental processes which normally obstruct the perception of subtle events."
In other words, the practice may temporarily or permanently alter some of the top-down processing involved in filtering subtle events usually deemed noise by the perceptual filters.
Memory
Meditation enhances memory capacity specifically in the
working memory
Working memory is a cognitive system with a limited capacity that can hold information temporarily. It is important for reasoning and the guidance of decision-making and behavior. Working memory is often used synonymously with short-term memory, ...
and increases
executive functioning
Executive ( exe., exec., execu.) may refer to:
Role or title
* Executive, a senior management role in an organization
** Chief executive officer (CEO), one of the highest-ranking corporate officers (executives) or administrators
** Executive dire ...
by helping participants better understand what is happening moment for moment. Those who meditate regularly have demonstrated the ability to better process and distinguish important information from the
working memory
Working memory is a cognitive system with a limited capacity that can hold information temporarily. It is important for reasoning and the guidance of decision-making and behavior. Working memory is often used synonymously with short-term memory, ...
and store it into
long-term memory
Long-term memory (LTM) is the stage of the Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model in which informative knowledge is held indefinitely. It is defined in contrast to short-term and working memory, which persist for only about 18 to 30 seconds. Long-t ...
with more accuracy than those who do not practice meditation techniques.
Meditation may be able to expand the amount of information that can be held within working memory and by so doing is able to improve IQ scores and increase individual intelligence.
The encoding process for both audio and visual information has been shown to be more accurate and detailed when meditation is used.
Though there are limited studies on meditation's effects on long-term memory, because of meditations ability to increase attentional awareness,
episodic long-term memory is believed to be more vivid and accurate for those who meditate regularly. Meditation has also shown to decrease memory complaints from those with Alzheimer's disease which also suggests the benefits meditation could have on episodic long-term memory which is linked to Alzheimer's.
Calming and relaxation
According to an article in ''Psychological Bulletin'', EEG activity slows as a result of meditation. Some types of meditation may lead to a calming effect by reducing
sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of th ...
activity while increasing
parasympathetic nervous system
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of ...
activity. Or, equivalently, that meditation produces a reduction in arousal and increase in relaxation.
Herbert Benson
Herbert Benson (April 24, 1935 – February 3, 2022) was an American medical doctor, cardiologist, and founder of the Mind/Body Medical Institute at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) in Boston. He was a professor of mind/body medicine at Harv ...
, founder of the Mind-Body Medical Institute, which is affiliated with
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
and several Boston hospitals, reports that meditation induces a host of biochemical and physical changes in the body collectively referred to as the "relaxation response". The relaxation response includes changes in metabolism, heart rate, respiration, blood pressure and brain chemistry. Benson and his team have also done clinical studies at Buddhist monasteries in the
Himalaya
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 ...
n Mountains. Benson wrote ''
The Relaxation Response
''The Relaxation Response'' is a book written in 1975 by Herbert Benson, a Harvard physician, and Miriam Z. Klipper. The response described in the book is an autonomic reaction elicited by a mental device and a passive attitude that has been use ...
'' to document the benefits of meditation, which in 1975 were not yet widely known.
Aging
There is no good evidence to indicate that meditation affects the brain in aging.
Happiness and emotional well-being
Studies have shown meditators to have higher happiness than control groups, although this may be due to non-specific factors such as meditators having better general self-care.
Positive relationships have been found between the volume of gray matter in the right
precuneus
In neuroanatomy, the precuneus is the portion of the superior parietal lobule on the medial surface of each brain hemisphere. It is located in front of the cuneus (the upper portion of the occipital lobe). The precuneus is bounded in front by th ...
area of the brain and both meditation and the subject's subjective
happiness
Happiness, in the context of Mental health, mental or emotional states, is positive or Pleasure, pleasant emotions ranging from contentment to intense joy. Other forms include life satisfaction, well-being, subjective well-being, flourishin ...
score.
A recent study found that participants who engaged in a body-scan meditation for about 20 minutes self-reported higher levels of happiness and decrease in anxiety compared to participants who just rested during the 20-minute time span. These results suggest that an increase in awareness of one's body through meditation causes a state of selflessness and a feeling of connectedness. This result then leads to reports of positive emotions.
A technique known as
mindfulness-based stress reduction
Mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) is an eight-week evidence-based program that offers secular, intensive mindfulness training to assist people with stress, anxiety, depression and pain. Developed at the University of Massachusetts Medica ...
(MBSR) displays significant benefits for mental health and coping behaviors. Participants who had no prior experience with MBSR reported a significant increase in happiness after eight weeks of MBSR practice. Focus on the present moment and increased awareness of one's thoughts can help monitor and reduce judgment or negative thoughts, causing a report of higher emotional well-being.
The MBSR program and evidence for its effectiveness is described in
Jon Kabat-Zinn's book ''
Full Catastrophe Living
''Full Catastrophe Living: Using the Wisdom of Your Body and Mind to Face Stress, Pain, and Illness'' is a book by Jon Kabat-Zinn, first published in 1990, revised in 2013, which describes the mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) program de ...
''.
Potential adverse effects and limits of meditation
The following is an official statement from the
US government
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a feder ...
-run
National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health
The National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH) is a United States government agency which explores complementary and alternative medicine (CAM). It was initially created in 1991 as the Office of Alternative Medicine (OAM), ...
:
Meditation is considered to be safe for healthy people. There have been rare reports that meditation could cause or worsen symptoms in people who have certain psychiatric problems, but this question has not been fully researched. People with physical limitations may not be able to participate in certain meditative practices involving physical movement. Individuals with existing mental or physical health conditions should speak with their health care providers prior to starting a meditative practice and make their meditation instructor aware of their condition.
Adverse effects have been reported, and may, in some cases, be the result of "improper use of meditation".
The NIH advises prospective meditators to "ask about the training and experience of the meditation instructor…
hey
Hey or Hey! may refer to:
Music
* Hey (band), a Polish rock band
Albums
* ''Hey'' (Andreas Bourani album) or the title song (see below), 2014
* ''Hey!'' (Julio Iglesias album) or the title song, 1980
* ''Hey!'' (Jullie album) or the title s ...
are considering."
As with any practice, meditation may also be used to avoid facing ongoing problems or emerging crises in the meditator's life. In such situations, it may instead be helpful to apply
mindful attitudes acquired in meditation while actively engaging with current problems. According to the
NIH
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late ...
, meditation should not be used as a replacement for conventional health care or as a reason to postpone seeing a
doctor
Doctor or The Doctor may refer to:
Personal titles
* Doctor (title), the holder of an accredited academic degree
* A medical practitioner, including:
** Physician
** Surgeon
** Dentist
** Veterinary physician
** Optometrist
*Other roles
** ...
.
Pain
Meditation has been show to reduce
pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
perception.
An intervention known as
mindfulness-based pain management
Mindfulness-based pain management (MBPM) is a mindfulness-based intervention (MBI) providing specific applications for people living with chronic pain and illness. Adapting the core concepts and practices of mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBS ...
(MBPM) has been subject to a range of studies demonstrating its effectiveness.
Difficulties in the scientific study of meditation
Weaknesses in historic meditation and mindfulness research

In June 2007, the United States
National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health
The National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH) is a United States government agency which explores complementary and alternative medicine (CAM). It was initially created in 1991 as the Office of Alternative Medicine (OAM), ...
(NCCIH) published an independent, peer-reviewed, meta-analysis of the state of meditation research, conducted by researchers at the
University of Alberta
The University of Alberta, also known as U of A or UAlberta, is a public research university located in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. It was founded in 1908 by Alexander Cameron Rutherford,"A Gentleman of Strathcona – Alexander Cameron Rutherfor ...
Evidence-based Practice Center. The report reviewed 813 studies involving five broad categories of meditation:
mantra
A mantra (Pali: ''manta'') or mantram (मन्त्रम्) is a sacred utterance, a numinous sound, a syllable, word or phonemes, or group of words in Sanskrit, Pali and other languages believed by practitioners to have religious, ma ...
meditation,
mindfulness meditation
Mindfulness is the practice of purposely bringing one's attention to the present-moment experience without evaluation, a skill one develops through meditation or other training. Mindfulness derives from ''sati'', a significant element of Hind ...
,
yoga
Yoga (; sa, योग, lit=yoke' or 'union ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines which originated in ancient India and aim to control (yoke) and still the mind, recognizing a detached witness-consciou ...
,
T'ai chi
Tai chi (), short for Tai chi ch'üan ( zh, s=太极拳, t=太極拳, first=t, p=Tàijíquán, labels=no), sometimes called " shadowboxing", is an internal Chinese martial art practiced for defense training, health benefits and meditation. ...
, and
Qigong
''Qigong'' (), ''qi gong'', ''chi kung'', ''chi 'ung'', or ''chi gung'' () is a system of coordinated body-posture and movement, breathing, and meditation
used for the purposes of health, spirituality, and martial-arts training. With roots in ...
, and included all studies on adults through September 2005, with a particular focus on research pertaining to
hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
,
cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, h ...
, and
substance abuse
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods which are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, ...
. The report concluded:
It noted that there is no theoretical explanation of health effects from meditation common to all meditation techniques.
A version of this report subsequently published in the ''
Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine
The ''Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine'' is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal covering alternative medicine published by Mary Ann Liebert. It was established in 1995 and is the official journal of the Society for Acupuncture ...
'' in 2008 stated: "Most clinical trials on meditation practices are generally characterized by poor methodological quality with significant threats to
validity
Validity or Valid may refer to:
Science/mathematics/statistics:
* Validity (logic), a property of a logical argument
* Scientific:
** Internal validity, the validity of causal inferences within scientific studies, usually based on experiments
** ...
in every major quality domain assessed." This was despite a
statistically significant
In statistical hypothesis testing, a result has statistical significance when it is very unlikely to have occurred given the null hypothesis (simply by chance alone). More precisely, a study's defined significance level, denoted by \alpha, is the p ...
increase in quality of all reviewed meditation research, in general, over time between 1956 and 2005. Of the 400 clinical studies, 10% were found to be good quality. A call was made for rigorous study of meditation.
These authors also noted that this finding is not unique to the area of meditation research and that the quality of reporting is a frequent problem in other areas of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) research and related therapy research domains.
Of more than 3,000 scientific studies that were found in a comprehensive search of 17 relevant databases, only about 4% had
randomised controlled trial
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical t ...
s (RCTs), which are designed to exclude the
placebo
A placebo ( ) is a substance or treatment which is designed to have no therapeutic value. Common placebos include inert tablets (like sugar pills), inert injections (like Saline (medicine), saline), sham surgery, and other procedures.
In general ...
effect.
In a 2013 meta-analysis, Awasthi argued that meditation is defined poorly and despite the research studies showing clinical efficacy, exact mechanisms of action remain unclear.
A 2017 commentary was similarly mixed,
[ with concerns including the particular characteristics of individuals who tend to participate in mindfulness and meditation research.
]
Position statements
A 2013 statement from the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association (AHA) is a nonprofit organization in the United States that funds cardiovascular medical research, educates consumers on healthy living and fosters appropriate cardiac care in an effort to reduce disability and death ...
(AHA) evaluated the evidence for the effectiveness of TM as a treatment for hypertension as "unknown/unclear/uncertain or not well-established", and stated: "Because of many negative studies or mixed results and a paucity of available trials... other meditation techniques are not recommended in clinical practice to lower BP at this time."
Methodological obstacles
The term ''meditation'' encompasses a wide range of practices and interventions rooted in different traditions, but research literature has sometimes failed to adequately specify the nature of the particular meditation practice(s) being studied.
See also
* Buddhism and psychology
Buddhism includes an analysis of human psychology, emotion, cognition, behavior and motivation along with therapeutic practices. Buddhist psychology is embedded within the greater Buddhist ethical and philosophical system, and its psychologi ...
* Neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity, also known as neural plasticity, or brain plasticity, is the ability of Neural circuit, neural networks in the brain to change through growth and reorganization. It is when the brain is rewired to function in some way that diffe ...
References
External links
*
{{Meditation
Alternative medicine
Meditation
Mindfulness (psychology)
 The psychological and physiological effects of meditation have been studied. In recent years, studies of
The psychological and physiological effects of meditation have been studied. In recent years, studies of 
 In addition, both meditation and yoga have been found to have impacts on the brain, specifically the caudate. Strengthening of the caudate has been shown in meditators as well as yogis. The increased connectedness of the caudate has potential to be responsible for the improved well-being that is associated with yoga and meditation.
In addition, both meditation and yoga have been found to have impacts on the brain, specifically the caudate. Strengthening of the caudate has been shown in meditators as well as yogis. The increased connectedness of the caudate has potential to be responsible for the improved well-being that is associated with yoga and meditation.
 In June 2007, the United States
In June 2007, the United States