Edmontosaurus Regalis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Edmontosaurus regalis'' is a species of comb-crested
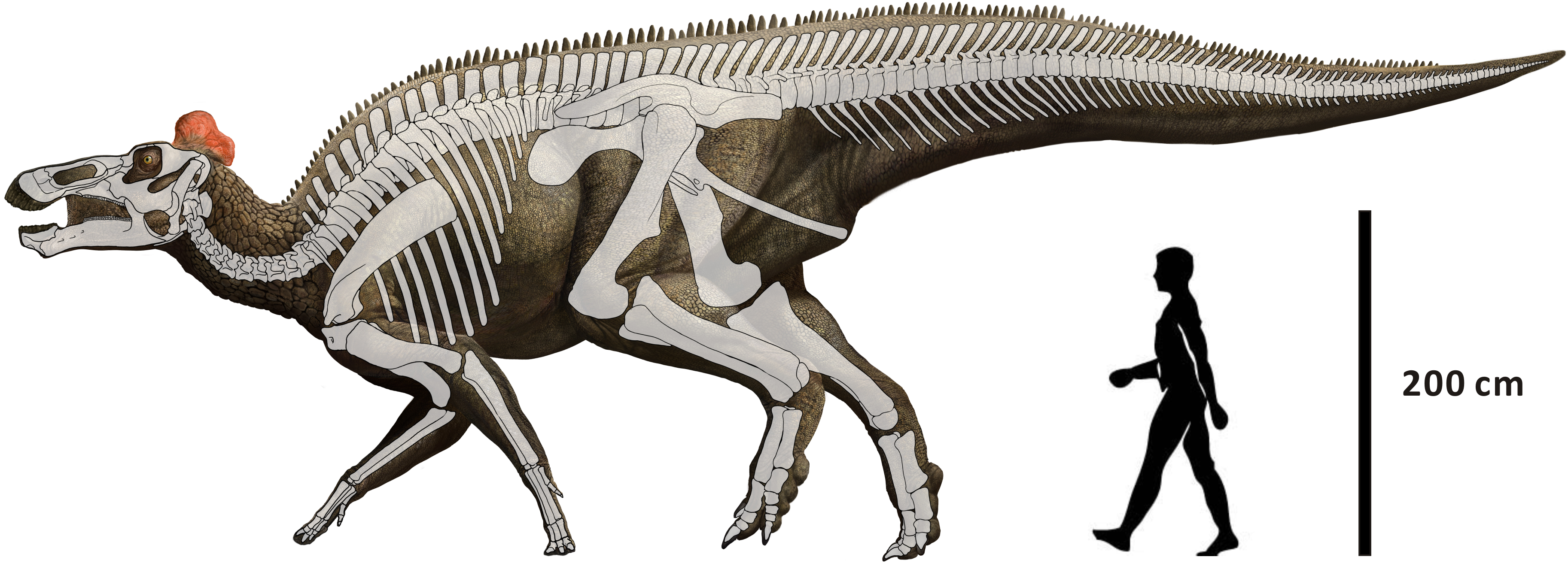
 ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' is known from several fossil specimens. ''E. regalis'' was among the largest hadrosaurids. A fully grown adult could have been long, and some of the larger specimens reached the range of to long. Its weight was on the order of . The
''Edmontosaurus regalis'' is known from several fossil specimens. ''E. regalis'' was among the largest hadrosaurids. A fully grown adult could have been long, and some of the larger specimens reached the range of to long. Its weight was on the order of . The  ''E. regalis'' had thirteen neck vertebrae, eighteen back vertebrae, nine hip vertebrae, and an unknown number of tail vertebrae. The fore legs were shorter and less heavily built than the hind legs. Each hand had four fingers, with no thumb (first finger). The index second, third, and fourth fingers were approximately the same length and were united in life within a fleshy covering. Although the second and third finger had hoof-like claws, these bones were also within the skin and not apparent from the outside. The little finger was separate from the other three and was much shorter.Lull, Richard Swann; and Wright, Nelda E. (1942). ''Hadrosaurian Dinosaurs of North America''. pp. 98–110. Each foot had three toes, with no big toe or little toe. The toes had hoof-like tips.
''E. regalis'' had thirteen neck vertebrae, eighteen back vertebrae, nine hip vertebrae, and an unknown number of tail vertebrae. The fore legs were shorter and less heavily built than the hind legs. Each hand had four fingers, with no thumb (first finger). The index second, third, and fourth fingers were approximately the same length and were united in life within a fleshy covering. Although the second and third finger had hoof-like claws, these bones were also within the skin and not apparent from the outside. The little finger was separate from the other three and was much shorter.Lull, Richard Swann; and Wright, Nelda E. (1942). ''Hadrosaurian Dinosaurs of North America''. pp. 98–110. Each foot had three toes, with no big toe or little toe. The toes had hoof-like tips.
 Two more species that would come to be included with ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' were named from Canadian remains in the 1920s, but both would initially be assigned to the genus '' Thespesius''. Gilmore named the first, ''Thespesius edmontoni'', in 1924. ''T. edmontoni'' also came from the Horseshoe Canyon Formation. It was based on NMC 8399, another nearly complete skeleton lacking most of the tail. NMC 8399 was discovered on the Red Deer River in 1912 by a Sternberg party. Its forelimbs, ossified tendons, and skin impressions were briefly described in 1913 and 1914 by Lambe, who at first thought it was an example of a species he'd named ''Trachodon marginatus'', but then changed his mind. The specimen became the first dinosaur skeleton to be mounted for exhibition in a Canadian museum. Gilmore found that his new species compared closely to what he called '' Thespesius annectens'', but left the two apart because of details of the arms and hands. He also noted that his species had more vertebrae than Marsh's in the back and neck, but proposed that Marsh was mistaken in assuming that the ''annectens'' specimens were complete in those regions.
In 1926,
Two more species that would come to be included with ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' were named from Canadian remains in the 1920s, but both would initially be assigned to the genus '' Thespesius''. Gilmore named the first, ''Thespesius edmontoni'', in 1924. ''T. edmontoni'' also came from the Horseshoe Canyon Formation. It was based on NMC 8399, another nearly complete skeleton lacking most of the tail. NMC 8399 was discovered on the Red Deer River in 1912 by a Sternberg party. Its forelimbs, ossified tendons, and skin impressions were briefly described in 1913 and 1914 by Lambe, who at first thought it was an example of a species he'd named ''Trachodon marginatus'', but then changed his mind. The specimen became the first dinosaur skeleton to be mounted for exhibition in a Canadian museum. Gilmore found that his new species compared closely to what he called '' Thespesius annectens'', but left the two apart because of details of the arms and hands. He also noted that his species had more vertebrae than Marsh's in the back and neck, but proposed that Marsh was mistaken in assuming that the ''annectens'' specimens were complete in those regions.
In 1926,
 The
The
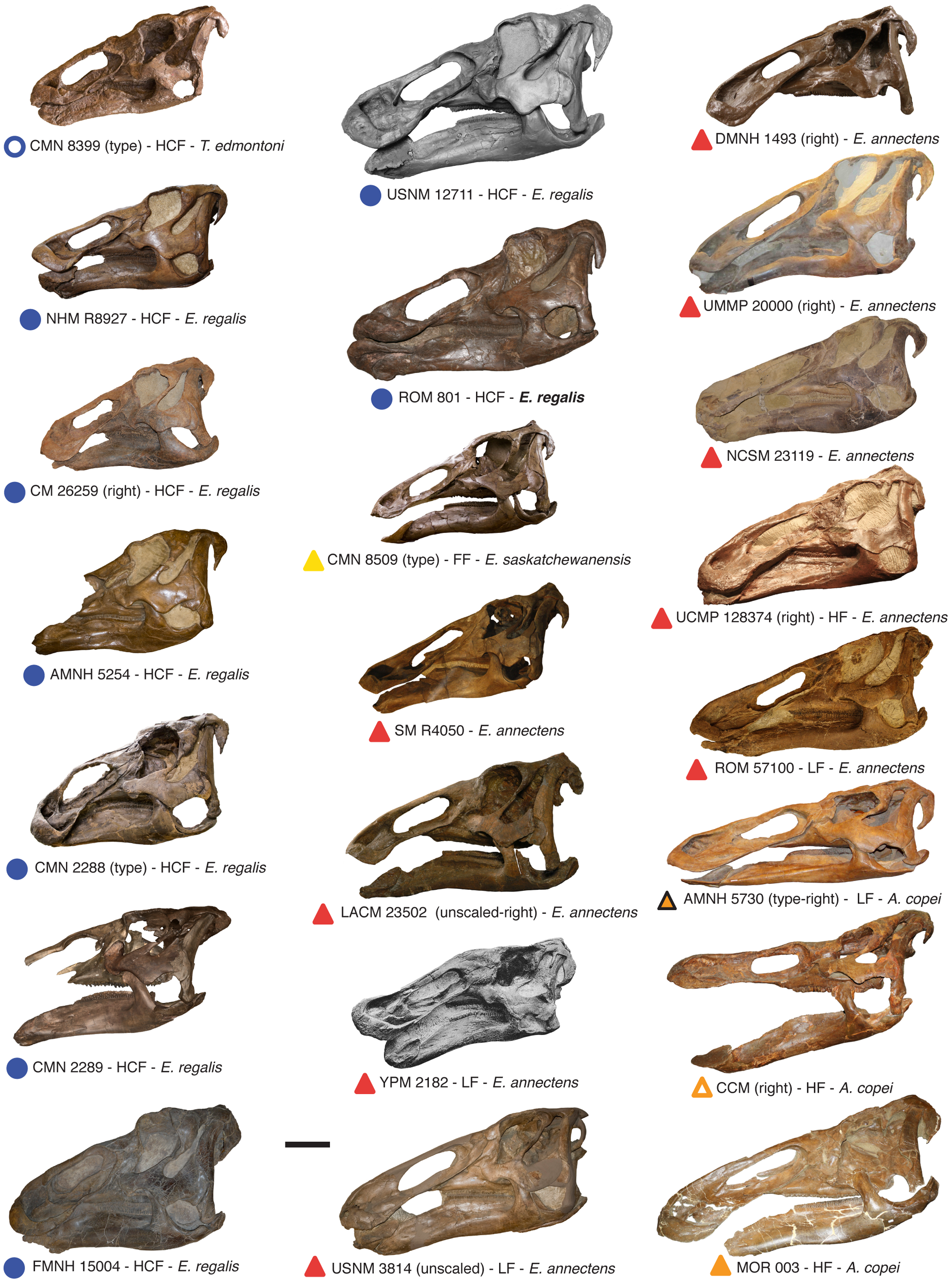
 In a 2011 study, Campione and Evans recorded data from all known edmontosaur skulls and used it to plot a ''morphometric'' graph, comparing variable features of the skull with skull size. Their results showed that within ''Edmontosaurus regalis'', many features previously used to classify additional species were directly correlated with skull size. Campione and Evans interpreted these results as strongly suggesting that the shape of ''E. regalis'' skulls changed dramatically as they grew. This has led to several apparent mistakes in classification in the past. The Campanian species ''Thespesius edmontoni'', previously considered a synonym of ''E. annectens'' due to its small size and skull shape, is more likely a subadult specimen of the contemporary ''E. regalis''. In a 2014 study, researchers proposed that ''E. regalis'' reached maturity in 10-15 years of age. A preserved
In a 2011 study, Campione and Evans recorded data from all known edmontosaur skulls and used it to plot a ''morphometric'' graph, comparing variable features of the skull with skull size. Their results showed that within ''Edmontosaurus regalis'', many features previously used to classify additional species were directly correlated with skull size. Campione and Evans interpreted these results as strongly suggesting that the shape of ''E. regalis'' skulls changed dramatically as they grew. This has led to several apparent mistakes in classification in the past. The Campanian species ''Thespesius edmontoni'', previously considered a synonym of ''E. annectens'' due to its small size and skull shape, is more likely a subadult specimen of the contemporary ''E. regalis''. In a 2014 study, researchers proposed that ''E. regalis'' reached maturity in 10-15 years of age. A preserved
 The Edmontonian land vertebrate age is defined by the first appearance of ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' in the fossil record. Although sometimes reported as of exclusively early Maastrichtian age, the Horseshoe Canyon Formation was of somewhat longer duration. Deposition began approximately 73 million years ago, in the late
The Edmontonian land vertebrate age is defined by the first appearance of ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' in the fossil record. Although sometimes reported as of exclusively early Maastrichtian age, the Horseshoe Canyon Formation was of somewhat longer duration. Deposition began approximately 73 million years ago, in the late
hadrosaurid
Hadrosaurids (), or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod family, which inclu ...
(duck-billed) dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
. Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s of ''E. regalis'' have been found in rocks of western North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
that date from the late Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campanian s ...
stage
Stage or stages may refer to:
Acting
* Stage (theatre), a space for the performance of theatrical productions
* Theatre, a branch of the performing arts, often referred to as "the stage"
* ''The Stage'', a weekly British theatre newspaper
* Sta ...
of the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
Period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Era, a length or span of time
* Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept ...
73 million years ago, but it may have possibly lived till the early Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the interval from ...
.
''E. regalis'' was one of the largest hadrosaurids, measuring up to long and weighing around . It is classified as a genus of saurolophine
Saurolophinae is a subfamily (biology), subfamily of hadrosaurid dinosaurs. It has since the mid-20th century generally been called the Hadrosaurinae, a group of largely non-crested hadrosaurs related to the crested sub-family Lambeosaurinae. How ...
(or hadrosaurine) hadrosaurid, a member of the group of hadrosaurids which lacked large, hollow crests, instead having smaller solid crests or fleshy combs. The distribution of ''E. regalis'' fossils suggests that it preferred coasts and coastal plain
A coastal plain is flat, low-lying land adjacent to a sea coast. A fall line commonly marks the border between a coastal plain and a piedmont area. Some of the largest coastal plains are in Alaska and the southeastern United States. The Gulf Coa ...
s. It was a herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
that could move on both two legs and four. Because it is known from several bone bed
A bone bed is any geological stratum or deposit that contains bones of whatever kind. Inevitably, such deposits are sedimentary in nature. Not a formal term, it tends to be used more to describe especially dense collections such as Lagerstätte. ...
s, ''E. regalis'' is thought to have lived in groups. The wealth of fossils has allowed researchers to study its paleobiology
Paleobiology (or palaeobiology) is an interdisciplinary field that combines the methods and findings found in both the earth sciences and the life sciences. Paleobiology is not to be confused with geobiology, which focuses more on the interactio ...
in detail, including its brain, how it may have fed, and its injuries and pathologies
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in t ...
.
Description
 ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' is known from several fossil specimens. ''E. regalis'' was among the largest hadrosaurids. A fully grown adult could have been long, and some of the larger specimens reached the range of to long. Its weight was on the order of . The
''Edmontosaurus regalis'' is known from several fossil specimens. ''E. regalis'' was among the largest hadrosaurids. A fully grown adult could have been long, and some of the larger specimens reached the range of to long. Its weight was on the order of . The type specimen
In biology, a type is a particular wiktionary:en:specimen, specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to a ...
of ''E. regalis'', NMC 2288, is estimated as long.Lull, Richard Swann; and Wright, Nelda E. (1942). ''Hadrosaurian Dinosaurs of North America''. p. 225. A 2022 study proposed that ''E. regalis'' may have been heavier than ''E. annectens'', but not enough samples exist to provide a valid estimate and examination on its osteohistology and growth, so the results for ''E. regalis'' aren't statistically significant.
The skull was roughly triangular in profile.Lull, Richard Swann; and Wright, Nelda E. (1942). ''Hadrosaurian Dinosaurs of North America''. pp. 151–164. One specimen preserved a soft tissue crest or wattle on the head. The beak was toothless, and both the upper and lower beaks were extended by keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ...
ous material. Teeth were present only in the maxillae (upper cheeks) and dentaries (main bone of the lower jaw). They grew in columns, with an observed maximum of six in each, and the number of columns varied based on the animal's size. There were 51 to 53 columns per maxilla and 48 to 49 per dentary (teeth of the upper jaw being slightly narrower than those in the lower jaw).
 ''E. regalis'' had thirteen neck vertebrae, eighteen back vertebrae, nine hip vertebrae, and an unknown number of tail vertebrae. The fore legs were shorter and less heavily built than the hind legs. Each hand had four fingers, with no thumb (first finger). The index second, third, and fourth fingers were approximately the same length and were united in life within a fleshy covering. Although the second and third finger had hoof-like claws, these bones were also within the skin and not apparent from the outside. The little finger was separate from the other three and was much shorter.Lull, Richard Swann; and Wright, Nelda E. (1942). ''Hadrosaurian Dinosaurs of North America''. pp. 98–110. Each foot had three toes, with no big toe or little toe. The toes had hoof-like tips.
''E. regalis'' had thirteen neck vertebrae, eighteen back vertebrae, nine hip vertebrae, and an unknown number of tail vertebrae. The fore legs were shorter and less heavily built than the hind legs. Each hand had four fingers, with no thumb (first finger). The index second, third, and fourth fingers were approximately the same length and were united in life within a fleshy covering. Although the second and third finger had hoof-like claws, these bones were also within the skin and not apparent from the outside. The little finger was separate from the other three and was much shorter.Lull, Richard Swann; and Wright, Nelda E. (1942). ''Hadrosaurian Dinosaurs of North America''. pp. 98–110. Each foot had three toes, with no big toe or little toe. The toes had hoof-like tips.
Discovery and history
Fossil skull ROM 801 The first known fossil remains that may belong to ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' were named ''Trachodon cavatus'' in 1871 byEdward Drinker Cope
Edward Drinker Cope (July 28, 1840 – April 12, 1897) was an American zoologist, paleontologist, comparative anatomist, herpetologist, and ichthyologist. Born to a wealthy Quaker family, Cope distinguished himself as a child prodigy interested ...
(the name is spelled in more recent sources as ''Trachodon avatus'' or even ''Trachodon atavus''). This species was assessed without comment as a synonym of ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' in two reviews, although ''atavus'' predates ''regalis'' by several decades. In 1874 Cope named but did not describe ''Agathaumas milo'' for a sacral
Sacral may refer to:
*Sacred
Sacred describes something that is dedicated or set apart for the service or worship of a deity; is considered worthy of spiritual respect or devotion; or inspires awe or reverence among believers. The property ...
vertebra and shin fragments from the late Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the interval from ...
-age Upper Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
Laramie Formation
The Laramie Formation is a geologic formation of Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) age, named by Clarence King in 1876 for exposures in northeastern Colorado, in the United States.King, C. 1876. Report of the Geological Exploration of the Fortieth P ...
of Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of t ...
. Later that same year, he described these bones under the name ''Hadrosaurus occidentalis''. The bones are now lost. As with ''Trachodon atavus'', ''Agathaumas milo'' has been assigned without comment to ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' in two reviews, although predating ''regalis'' by several decades. Neither species has attracted much attention; both are absent from Lull and Wright's 1942 monograph, for example. A third obscure early species, ''Trachodon selwyni'', described by Lawrence Lambe
Lawrence Morris Lambe (August 27, 1863 – March 12, 1919) was a Canadian geologist, palaeontologist, and ecologist from the Geological Survey of Canada (GSC).
His published work, describing the diverse and plentiful dinosaur discoveries from th ...
in 1902 for a lower jaw from what is now known as the Dinosaur Park Formation
The Dinosaur Park Formation is the uppermost member of the Belly River Group (also known as the Judith River Group), a major geologic unit in southern Alberta. It was deposited during the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous, between about 76. ...
of Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
, was erroneously described by Glut (1997) as having been assigned to ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' by Lull and Wright. It was not, instead being designated "of very doubtful validity."Lull, Richard Swann; and Wright, Nelda E. (1942). ''Hadrosaurian Dinosaurs of North America''. pp. 220–221. More recent reviews of hadrosaurids have concurred.
The type specimen
In biology, a type is a particular wiktionary:en:specimen, specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to a ...
of ''E. regalis'' is NMC 2288, consisting of a skull, articulated vertebrae up to the sixth tail vertebra, ribs, partial hips, an upper arm bone, and most of a hind limb. It was discovered in 1912 by Levi Sternberg. The second specimen, paratype NMC 2289, consists of a skull and skeleton lacking the beak, most of the tail, and part of the feet. It was discovered in 1916 by George F. Sternberg. Both skeletons were found in the Horseshoe Canyon Formation
The Horseshoe Canyon Formation is a stratigraphic unit of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin in southwestern Alberta. It takes its name from Horseshoe Canyon, an area of badlands near Drumheller.
The Horseshoe Canyon Formation is part of th ...
(formerly the lower Edmonton Formation) along the Red Deer River
The Red Deer River is a river in Alberta and a small portion of Saskatchewan, Canada. It is a major tributary of the South Saskatchewan River and is part of the larger Saskatchewan-Nelson system that empties into Hudson Bay.
Red Deer River ...
of southern Alberta, Canada. The Edmonton Formation lent ''Edmontosaurus'' its name. The name ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' (meaning "regal," or, more loosely, "king-sized"), was coined in 1917 by Lawrence Lambe. Lambe found that his new dinosaur compared best to "'' Diclonius mirabilis''" specimens (now assigned to ''Edmontosaurus annectens
''Edmontosaurus annectens'' (meaning "connected lizard from Edmonton") is a species of flat-headed and duck-billed (hadrosaurid) dinosaur from the very end of the Cretaceous Period (geology), Period, in what is now North America. Remains of ''E. ...
''), and drew attention to the size and robustness of ''Edmontosaurus regalis''. Initially, Lambe only described the skulls of the two skeletons, but returned to the genus in 1920 to describe the skeleton of NMC 2289. The postcrania Postcrania (postcranium, adjective: postcranial) in zoology and vertebrate paleontology is all or part of the skeleton apart from the skull. Frequently, fossil remains, e.g. of dinosaurs or other extinct tetrapods, consist of partial or isolated sk ...
of the type specimen remains undescribed, still in its plaster jackets.
 Two more species that would come to be included with ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' were named from Canadian remains in the 1920s, but both would initially be assigned to the genus '' Thespesius''. Gilmore named the first, ''Thespesius edmontoni'', in 1924. ''T. edmontoni'' also came from the Horseshoe Canyon Formation. It was based on NMC 8399, another nearly complete skeleton lacking most of the tail. NMC 8399 was discovered on the Red Deer River in 1912 by a Sternberg party. Its forelimbs, ossified tendons, and skin impressions were briefly described in 1913 and 1914 by Lambe, who at first thought it was an example of a species he'd named ''Trachodon marginatus'', but then changed his mind. The specimen became the first dinosaur skeleton to be mounted for exhibition in a Canadian museum. Gilmore found that his new species compared closely to what he called '' Thespesius annectens'', but left the two apart because of details of the arms and hands. He also noted that his species had more vertebrae than Marsh's in the back and neck, but proposed that Marsh was mistaken in assuming that the ''annectens'' specimens were complete in those regions.
In 1926,
Two more species that would come to be included with ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' were named from Canadian remains in the 1920s, but both would initially be assigned to the genus '' Thespesius''. Gilmore named the first, ''Thespesius edmontoni'', in 1924. ''T. edmontoni'' also came from the Horseshoe Canyon Formation. It was based on NMC 8399, another nearly complete skeleton lacking most of the tail. NMC 8399 was discovered on the Red Deer River in 1912 by a Sternberg party. Its forelimbs, ossified tendons, and skin impressions were briefly described in 1913 and 1914 by Lambe, who at first thought it was an example of a species he'd named ''Trachodon marginatus'', but then changed his mind. The specimen became the first dinosaur skeleton to be mounted for exhibition in a Canadian museum. Gilmore found that his new species compared closely to what he called '' Thespesius annectens'', but left the two apart because of details of the arms and hands. He also noted that his species had more vertebrae than Marsh's in the back and neck, but proposed that Marsh was mistaken in assuming that the ''annectens'' specimens were complete in those regions.
In 1926, Charles Mortram Sternberg
Charles Mortram Sternberg (1885–1981) was an American-Canadian fossil collector and paleontologist, son of Charles Hazelius Sternberg.
Late in his career, he collected and described ''Pachyrhinosaurus'', ''Brachylophosaurus'', ''Parksosaurus ...
named ''Thespesius saskatchewanensis'' for NMC 8509, a skull and partial skeleton from the Wood Mountain plateau of southern Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada, western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on t ...
. He had collected this specimen in 1921, from rocks that were assigned to the Lance Formation, now the Frenchman Formation
The Frenchman Formation is stratigraphic unit of Late Cretaceous (late Maastrichtian) age in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin. It is present in southern Saskatchewan and the Cypress Hills of southeastern Alberta. The formation was defined by ...
. NMC 8509 included an almost complete skull, numerous vertebrae, partial shoulder and hip girdles, and partial hind limbs, representing the first substantial dinosaur specimen recovered from Saskatchewan. Sternberg opted to assign it to ''Thespesius'' because that was the only hadrosaurid genus known from the Lance Formation at the time. At the time, ''T. saskatchewanensis'' was unusual because of its small size, estimated at in length.
Classification
 The
The cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to d ...
below follows Godefroit ''et al.'' (2012) analysis.
Paleobiology
 In a 2011 study, Campione and Evans recorded data from all known edmontosaur skulls and used it to plot a ''morphometric'' graph, comparing variable features of the skull with skull size. Their results showed that within ''Edmontosaurus regalis'', many features previously used to classify additional species were directly correlated with skull size. Campione and Evans interpreted these results as strongly suggesting that the shape of ''E. regalis'' skulls changed dramatically as they grew. This has led to several apparent mistakes in classification in the past. The Campanian species ''Thespesius edmontoni'', previously considered a synonym of ''E. annectens'' due to its small size and skull shape, is more likely a subadult specimen of the contemporary ''E. regalis''. In a 2014 study, researchers proposed that ''E. regalis'' reached maturity in 10-15 years of age. A preserved
In a 2011 study, Campione and Evans recorded data from all known edmontosaur skulls and used it to plot a ''morphometric'' graph, comparing variable features of the skull with skull size. Their results showed that within ''Edmontosaurus regalis'', many features previously used to classify additional species were directly correlated with skull size. Campione and Evans interpreted these results as strongly suggesting that the shape of ''E. regalis'' skulls changed dramatically as they grew. This has led to several apparent mistakes in classification in the past. The Campanian species ''Thespesius edmontoni'', previously considered a synonym of ''E. annectens'' due to its small size and skull shape, is more likely a subadult specimen of the contemporary ''E. regalis''. In a 2014 study, researchers proposed that ''E. regalis'' reached maturity in 10-15 years of age. A preserved rhamphotheca
The beak, bill, or rostrum is an external anatomical structure found mostly in birds, but also in turtles, non-avian dinosaurs and a few mammals. A beak is used for eating, preening, manipulating objects, killing prey, fighting, probing for food, ...
present in specimen LACM 23502, housed in the Los Angeles County Museum, also indicates the beak of the related ''Edmontosaurus annectens'' was more hook-shaped and extensive than many illustrations in scientific and public media have previously depicted. Whether this was true of ''E. regalis'' as well is not known as of this time.
Extensive bone bed
A bone bed is any geological stratum or deposit that contains bones of whatever kind. Inevitably, such deposits are sedimentary in nature. Not a formal term, it tends to be used more to describe especially dense collections such as Lagerstätte. ...
s are known for ''Edmontosaurus regalis'', and such groupings of hadrosaurids are used to suggest that they were gregarious, living in groups. Two quarries containing ''E. regalis'' remains were identified in a 2007 database of fossil bone beds, from Alaska (Prince Creek Formation), and Alberta (Horseshoe Canyon Formation).
Paleoecology
 The Edmontonian land vertebrate age is defined by the first appearance of ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' in the fossil record. Although sometimes reported as of exclusively early Maastrichtian age, the Horseshoe Canyon Formation was of somewhat longer duration. Deposition began approximately 73 million years ago, in the late
The Edmontonian land vertebrate age is defined by the first appearance of ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' in the fossil record. Although sometimes reported as of exclusively early Maastrichtian age, the Horseshoe Canyon Formation was of somewhat longer duration. Deposition began approximately 73 million years ago, in the late Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campanian s ...
, and ended between 68.0 and 67.6 million years ago. ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' is known from the lowest of five units within the Horseshoe Canyon Formation, but is absent from at least the second to the top.
Because of its wide distribution, which covers a distance from Alaska to Colorado and includes polar settings that would have had little light during a significant part of the year, ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' has been considered possibly migratory. A 2008 review of dinosaur migration studies by Phil R. Bell and Eric Snively proposed that ''E. regalis'' was capable of an annual round-trip journey, provided it had the requisite metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
and fat deposition rates. Such a trip would have required speeds of about , and could have brought it from Alaska to Alberta. The possible migratory nature of ''E. regalis'' contrasts with many other dinosaurs, such as theropods
Theropoda (; ), whose members are known as theropods, is a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally ca ...
, sauropods
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their b ...
, and ankylosauria
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the order Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs. ...
ns, which Bell and Snively found were more likely to have overwinter
Overwintering is the process by which some organisms pass through or wait out the winter season, or pass through that period of the year when "winter" conditions (cold or sub-zero temperatures, ice, snow, limited food supplies) make normal activi ...
ed. In contrast to Bell and Snively, Anusuya Chinsamy and colleagues concluded from a study of bone microstructure that polar edmontosaurs overwintered.
Contemporary fauna
As many as three quarters of the dinosaur specimens frombadlands
Badlands are a type of dry terrain where softer sedimentary rocks and clay-rich soils have been extensively eroded."Badlands" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 2, p. 47. They are characterized by steep slopes, m ...
near Drumheller
Drumheller is a town on the Red Deer River in the badlands of Central Alberta, east-central Alberta, Canada. It is northeast of Calgary and south of Stettler, Alberta, Stettler. The Drumheller portion of the Red Deer River valley, often ref ...
, Alberta may pertain to ''Edmontosaurus regalis''. The Horseshoe Canyon Formation is interpreted as having a significant marine influence, due to an encroaching Western Interior Seaway
The Western Interior Seaway (also called the Cretaceous Seaway, the Niobraran Sea, the North American Inland Sea, and the Western Interior Sea) was a large inland sea that split the continent of North America into two landmasses. The ancient sea, ...
, the shallow sea
An inland sea (also known as an epeiric sea or an epicontinental sea) is a continental body of water which is very large and is either completely surrounded by dry land or connected to an ocean by a river, strait, or "arm of the sea". An inland s ...
that covered the midsection of North America through much of the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
. ''E. regalis'' shared the setting with fellow hadrosaurids ''Hypacrosaurus
''Hypacrosaurus'' (meaning "near the highest lizard" reek υπο-, ''hypo-'' = less + ακρος, ''akros'', high because it was almost but not quite as large as ''Tyrannosaurus'') was a genus of duckbill dinosaur similar in appearance to ''Co ...
'' and ''Saurolophus
''Saurolophus'' (; meaning "lizard crest") is a genus of large hadrosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period of Asia and North America, that lived in what is now the Horseshoe Canyon and Nemegt formations about 70 million to 68 million ...
'', parksosaurid ''Parksosaurus
''Parksosaurus'' (meaning " William Parks's lizard") is a genus of neornithischian dinosaur from the early Maastrichtian-age Upper Cretaceous Horseshoe Canyon Formation of Alberta, Canada. It is based on most of a partially articulated skeleton a ...
'', ceratopsids ''Montanoceratops
''Montanoceratops'' is an extinct genus of small ceratopsian dinosaur that lived approximately 70 million years ago during the latter part of the Cretaceous Period in what is now Montana and Alberta. ''Montanoceratops'' was a small sized, modera ...
'', ''Anchiceratops
''Anchiceratops'' ( ) is an extinct genus of chasmosaurine ceratopsid dinosaur that lived approximately 72 to 71 million years ago during the latter part of the Cretaceous Period in what is now Alberta, Canada.
''Anchiceratops'' was a medium-si ...
'', ''Arrhinoceratops
''Arrhinoceratops'' (meaning "no nose-horn face", derived from the Ancient Greek "a-/α-" "no", rhis/ῥίς "nose" "keras/κέρας" "horn", "-ops/ὤψ" "face") is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaur. The name was coined as its origina ...
'', and ''Pachyrhinosaurus
''Pachyrhinosaurus'' (meaning in Greek "thick-nosed lizard", from ' (), thick; ' (), nose; and (), lizard) is an extinct genus of centrosaurine ceratopsid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period of North America. The first examples were discove ...
'', pachycephalosaurid
Pachycephalosauria (; from Greek παχυκεφαλόσαυρος for 'thick headed lizards') is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs. Along with Ceratopsia, it makes up the clade Marginocephalia. With the exception of two species, most pachycephal ...
''Stegoceras
''Stegoceras'' is a genus of pachycephalosaurid (dome-headed) dinosaur that lived in what is now North America during the Late Cretaceous period, about 77.5 to 74 million years ago (mya). The first specimens from Alberta, Canada, were descri ...
'', ankylosaurid
Ankylosauridae () is a family of armored dinosaurs within Ankylosauria, and is the sister group to Nodosauridae. The oldest known Ankylosaurids date to around 122 million years ago and went extinct 66 million years ago during the Cretaceous–Pal ...
''Euoplocephalus
''Euoplocephalus'' ( ) is a genus of very large, herbivorous ankylosaurid dinosaurs, living during the Late Cretaceous of Canada. It has only one named species, ''Euoplocephalus tutus''.
The first fossil of ''Euoplocephalus'' was found in 1897 i ...
'', nodosaurid
Nodosauridae is a family of ankylosaurian dinosaurs, from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous period in what is now North America, South America, Europe, and Asia.
Description
Nodosaurids, like their close relatives the ankylosaurids, wer ...
''Edmontonia
''Edmontonia'' is a genus of panoplosaurin nodosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period. It is part of the Nodosauridae, a family within Ankylosauria. It is named after the Edmonton Formation (now the Horseshoe Canyon Formation in Ca ...
'', ornithomimids
Ornithomimidae (meaning "bird-mimics") is a family of theropod dinosaurs which bore a superficial resemblance to modern ostriches. Ornithomimids were fast, omnivorous or herbivorous dinosaurs known mainly from the Late Cretaceous Period of Lauras ...
''Ornithomimus
''Ornithomimus'' (; "bird mimic") is a genus of ornithomimid dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now North America. ''Ornithomimus'' was a swift bipedal theropod which fossil evidence indicates was covered in feathers, equippe ...
'' and ''Struthiomimus
''Struthiomimus'' (meaning "ostrich mimic", from the Ancient Greek, Greek στρούθειος/''stroutheios'' meaning "of the ostrich" and μῖμος/''mimos'' meaning "mimic" or "imitator") is a genus of Ornithomimidae, ornithomimid dinosaurs ...
'', a variety of poorly known small theropods
Theropoda (; ), whose members are known as theropods, is a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally ca ...
including troodontids
Troodontidae is a clade of bird-like theropod dinosaurs. During most of the 20th century, troodontid fossils were few and incomplete and they have therefore been allied, at various times, with many dinosaurian lineages. More recent fossil discov ...
and dromaeosaurids
Dromaeosauridae () is a family of feathered theropod dinosaurs. They were generally small to medium-sized feathered carnivores that flourished in the Cretaceous Period. The name Dromaeosauridae means 'running lizards', from Greek ('), meaning ...
, and the tyrannosaurids
Tyrannosauridae (or tyrannosaurids, meaning "tyrant lizards") is a family (biology), family of coelurosaurian Theropoda, theropod dinosaurs that comprises two subfamilies containing up to thirteen genus, genera, including the eponymous ''Tyrannos ...
''Albertosaurus
''Albertosaurus'' (; meaning "Alberta lizard") is a genus of tyrannosaurid theropod dinosaurs that lived in western North America during the Late Cretaceous Period, about 71 million years ago. The type species, ''A. sarcophagus'', was app ...
'' and ''Daspletosaurus
''Daspletosaurus'' ( ; meaning "frightful lizard") is a genus of tyrannosaurid dinosaur that lived in Laramidia between about 79.5 and 74 million years ago, during the Late Cretaceous Period. The genus ''Daspletosaurus'' contains three species ...
''.
''Edmontosaurus'' is found in coastal, near-marine settings, while ''Hypacrosaurus'' and ''Saurolophus'' are found in more continental lowlands. ''Edmontosaurus'' and ''Saurolophus'' are not usually found together. The typical edmontosaur habitat of this formation has been described as the back regions of bald cypress
''Taxodium distichum'' (bald cypress, swamp cypress; french: cyprès chauve;
''cipre'' in Louisiana) is a deciduous conifer in the family Cupressaceae. It is native to the southeastern United States. Hardy and tough, this tree adapts to a wide r ...
swamp
A swamp is a forested wetland.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water play a role in ...
s and peat bogs
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and muskeg; a ...
on delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), a letter of the Greek alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* D ( NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta")
* Delta Air Lines, US
* Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 that causes COVID-19
Delta may also ...
coasts. ''Pachyrhinosaurus'' also preferred this habitat to the floodplain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river which stretches from the banks of its channel to the base of the enclosing valley walls, and which experiences flooding during periods of high discharge.Goudi ...
s dominated by ''Hypacrosaurus'', ''Saurolophus'', ''Anchiceratops'' and ''Arrhinoceratops''. The Edmontonian-age coastal ''Pachyrhinosaurus''-''Edmontosaurus'' association is recognized as far north as Alaska.
See also
*Timeline of hadrosaur research
A timeline is a display of a list of events in chronological order. It is typically a graphic design showing a long bar labelled with dates paralleling it, and usually contemporaneous events.
Timelines can use any suitable scale represent ...
*Edmontosaurus annectens
''Edmontosaurus annectens'' (meaning "connected lizard from Edmonton") is a species of flat-headed and duck-billed (hadrosaurid) dinosaur from the very end of the Cretaceous Period (geology), Period, in what is now North America. Remains of ''E. ...
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q20717881 Late Cretaceous dinosaurs of North America Saurolophines Horseshoe Canyon fauna Paleontology in Alberta Paleontology in Colorado Paleontology in Saskatchewan Campanian species first appearances