East Fork Russian River on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
East Fork Russian River is a long tributary of the Russian River in
 Tributaries in the Potter Valley include Adobe Creek, Burright Creek and Mewhinney Creek from the left and Busch Creek, Williams Creek, Bevans Creek and White Creek from the right.
Today the river's primary source of water is the Powerhouse Canal from the Potter Valley Project.
The project began to transfer water from the Eel River into the East Fork Russian River in 1908 to generate electricity and support irrigation.
The water has been used in the Potter Valley for alfafa, grapes and rice.
The river flows south through the valley, then runs southwest through mountainous territory to
Tributaries in the Potter Valley include Adobe Creek, Burright Creek and Mewhinney Creek from the left and Busch Creek, Williams Creek, Bevans Creek and White Creek from the right.
Today the river's primary source of water is the Powerhouse Canal from the Potter Valley Project.
The project began to transfer water from the Eel River into the East Fork Russian River in 1908 to generate electricity and support irrigation.
The water has been used in the Potter Valley for alfafa, grapes and rice.
The river flows south through the valley, then runs southwest through mountainous territory to
 The upper Eel River runs to the north of the ridge at the north end of Potter Valley, and in this section is higher than the headwaters of East Fork Russian River.
The
The upper Eel River runs to the north of the ridge at the north end of Potter Valley, and in this section is higher than the headwaters of East Fork Russian River.
The
 The East Fork Russian River is impounded near its mouth to form
The East Fork Russian River is impounded near its mouth to form
 The alternation of the Clear Lake drainage route in the past explains why there are many fish species common to the Russian River and the Sacramento River.
Native fish species that currently inhabit, or that have historically inhabited the East Fork of the Russian River, include
The alternation of the Clear Lake drainage route in the past explains why there are many fish species common to the Russian River and the Sacramento River.
Native fish species that currently inhabit, or that have historically inhabited the East Fork of the Russian River, include
Mendocino County, California
Mendocino County (; ''Mendocino'', Spanish language, Spanish for "of Antonio de Mendoza, Mendoza) is a County (United States), county located on the North Coast (California), North Coast of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 United Sta ...
artificially connected to the Eel River via an interbasin diversion at the Potter Valley Project hydroelectric facility.
It forms in the north of Potter Valley
Potter Valley is a census-designated place in Mendocino County, California, United States. It is located north-northeast of Ukiah, at an elevation of at the headwaters of the East Fork Russian River. The CDP population was 665 at the 2020 cens ...
, flows south through this valley, then southwest through a mountain pass to Lake Mendocino
Lake Mendocino is a large reservoir in Mendocino County, California, northeast of Ukiah. It covers and was formed by the construction of Coyote Valley Dam in 1958. The lake and dam provide flood control, water conservation, hydroelectric powe ...
, an artificial reservoir that empties into Russian River.
At one time Clear Lake to the east drained through Cold Creek then along the lower part of East Fork Russian River through Coyote Valley to the Russian River proper.
A few hundred years ago a massive landslide blocked this channel, and Clear Lake found a new outlet to the Sacramento River
The Sacramento River ( es, Río Sacramento) is the principal river of Northern California in the United States and is the largest river in California. Rising in the Klamath Mountains, the river flows south for before reaching the Sacramento–S ...
.
Cold Creek flows year round, while the upper part of East Fork Russian River used to dry up in the summer leaving isolated pools along its course.
This changed when the Potter Valley Project
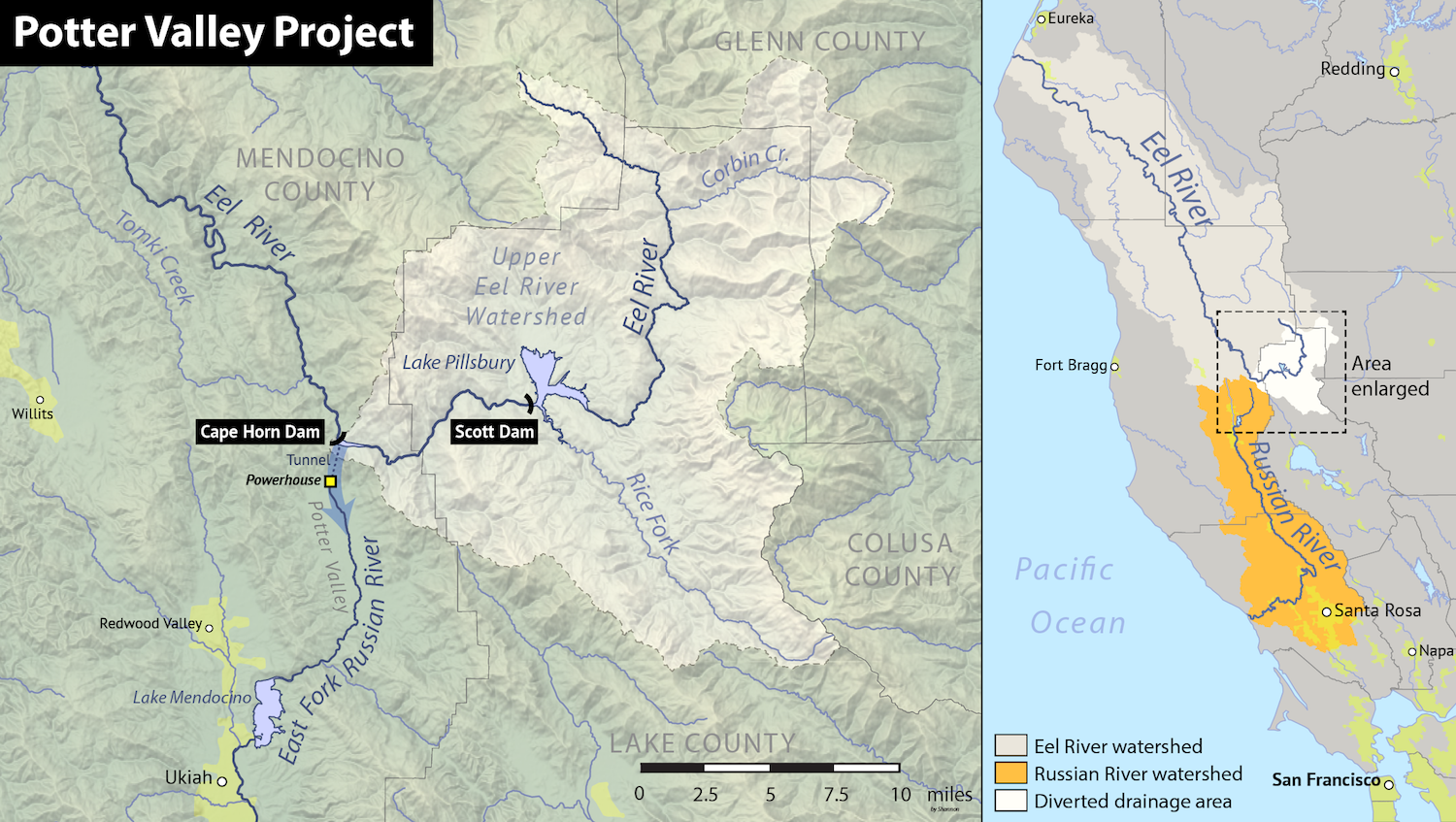
The Potter Valley Project is an hydroelectric project in Northern California in the United States, delivering water from the Eel River basin to turbines in the headwaters of the Russian River. The project is owned and operated by Pacific Gas and ...
was completed in 1908.
The project involved construction of two reservoirs on Eel River to the north of the Russian River basin, and a tunnel to the head of Potter Valley that carried water from Eel River to a hydroelectric station that discharged into East Fork Russian River.
The Eel River water was used to irrigate Potter Valley, and supplied water to Ukiah below the convergence with Russian River.
In 1958 Coyote Dam was built on East Fork Russian River just above its mouth on Russian River, flooding Coyote Valley to form Lake Mendocino.
The lake provides additional water storage as well as flood control.
The continuous flow from the Potter Valley Project changed the fish ecosystem in the Russian River by eliminating the warm, still pools that had been used for breeding by native fish.
In the 1950s the state introduced poison to the river to eliminate "useless" fish species in favor of game species.
The Coyote Dam prevented steelhead trout
Steelhead, or occasionally steelhead trout, is the common name of the anadromous form of the coastal rainbow trout or redband trout (O. m. gairdneri). Steelhead are native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific basin in Northeast Asia and N ...
from returning upstream, so today the East Fork Russian River is dominated by rainbow trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. The steelhead (sometimes called "steelhead trout") is an anadromous (sea-run) form of the coasta ...
.
The section of the river that flows through the mountains between Potter Valley and Lake Mendocino includes stretches of white water that are challenging for kayakers and rafters.
Watershed
The East Fork Russian River is a long tributary of the Russian River in Mendocino County. It drains the northeastern part of the Russian River basin. The region has aMediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
.
The fork's watershed covers .
The mouth elevation is about above sea level.
East Fork Russian River forms in the north end of Potter Valley
Potter Valley is a census-designated place in Mendocino County, California, United States. It is located north-northeast of Ukiah, at an elevation of at the headwaters of the East Fork Russian River. The CDP population was 665 at the 2020 cens ...
and flows south through a canyon to Coyote Valley, now filled by Lake Mendocino
Lake Mendocino is a large reservoir in Mendocino County, California, northeast of Ukiah. It covers and was formed by the construction of Coyote Valley Dam in 1958. The lake and dam provide flood control, water conservation, hydroelectric powe ...
.
Potter Valley is an alluvial valley, a depression created by movement of parallel faults that has filled with gravel, boulders and cobble eroded from the surrounding mountains.
The basement rock is Franciscan Complex
The Franciscan Complex or Franciscan Assemblage is a geologic term for a late Mesozoic terrane of heterogeneous rocks found throughout the California Coast Ranges, and particularly on the San Francisco Peninsula. It was named by geologist Andrew ...
, a jumbled mixture of different types of rock that is very prone to erosion and landslides.
Coyote Valley is a southerly trending valley about wide by long that is underlain primarily by metamorphic rocks from the Franciscan formation.
Most of the recreation areas located within the Lake Mendocino boundary have 6 to 12 inches of silt, or sandy silt, overlying the gravelly phase, Older Alluvium.
Coyote Valley is flanked by rolling hills that rise about the valley floor to the west of Lake Mendocino and steeper Franciscan bedrock hills to the east.
Elevations above mean sea level in the surrounding region range from about in the valleys near Ukiah to about on top of Cow Mountain to the east.
The hills to the east of Lake Mendocino are very rugged and continue for many miles.
To the west and northwest, the hills are more rounded with benches that were once planted with vineyards.
In a period of very low water in September 1905 the East Fork Russian River had a discharge of .
A discharge measurement station is located upstream from the Russian River and downstream from the Coyote Dam, which impounds Lake Mendocino.
At this point the maximum discharge of the East Fork Russian River before regulation by Lake Mendocino was , recorded on 21 December 1955.
Since then the maximum discharge was , recorded on 24 January 1970.
Course
 Tributaries in the Potter Valley include Adobe Creek, Burright Creek and Mewhinney Creek from the left and Busch Creek, Williams Creek, Bevans Creek and White Creek from the right.
Today the river's primary source of water is the Powerhouse Canal from the Potter Valley Project.
The project began to transfer water from the Eel River into the East Fork Russian River in 1908 to generate electricity and support irrigation.
The water has been used in the Potter Valley for alfafa, grapes and rice.
The river flows south through the valley, then runs southwest through mountainous territory to
Tributaries in the Potter Valley include Adobe Creek, Burright Creek and Mewhinney Creek from the left and Busch Creek, Williams Creek, Bevans Creek and White Creek from the right.
Today the river's primary source of water is the Powerhouse Canal from the Potter Valley Project.
The project began to transfer water from the Eel River into the East Fork Russian River in 1908 to generate electricity and support irrigation.
The water has been used in the Potter Valley for alfafa, grapes and rice.
The river flows south through the valley, then runs southwest through mountainous territory to Lake Mendocino
Lake Mendocino is a large reservoir in Mendocino County, California, northeast of Ukiah. It covers and was formed by the construction of Coyote Valley Dam in 1958. The lake and dam provide flood control, water conservation, hydroelectric powe ...
, formed by the Coyote Dam near the point where East Fork enters the main Russian River.
In the canyon between Potter Valley and Lake Mendocino, the East Fork receives the left tributary Cold Creek, which flows from Lake County to the east.
A 1914 survey of the Ukiah Area said the Cold Creek Valley was small and not very important agriculturally.
It was interesting because it belonged to a middle-aged stream that was now tributary to a very youthful stream.
The East Fork of the Russian River has a youthful topography in this section, flowing with a high gradient through a V-shaped gorge.
Cold Creek flows at a much lower gradient, as is shown by the size of stones in its bed, and has a distinct flood plain and also a terrace.
California State Route 20
State Route 20 (SR 20) is a state highway in the northern-central region of the state of California, running east–west north of Sacramento from the North Coast to the Sierra Nevada. Its west end is at SR 1 in Fort Bragg, from where it heads e ...
runs east from Route 101 to the north of Ukiah.
It skirts the north shore of Lake Mendocino and then crosses East Fork Russian River near the northeast corner of the lake.
It follows the river for about two miles, then turns to the southeast along Cold Creek.
Potter Valley Road continues from Highway 20 along East Fork Russian River, which it crosses twice before reaching Potter Valley.
McKee Park is in the south of Potter Valley beside the Potter Valley Road and stretches along the East Fork Russian River for about .
This section of the river is shaded by various types of native oaks and bay trees.
The waters may be dangerous, and there are no attendants, but visitors may wade, swim or fish along the river.
Geological changes
Clear Lake, to the east of the Russian River, formed about 600,000 years ago as the land in the region began to subside when theClear Lake Volcanic Field
The Clear Lake Volcanic Field is a volcanic field beside Clear Lake in California's northern Coast Ranges. The site of late-Pliocene to early Holocene activity, the volcanic field consists of lava domes, cinder cones, and maars with eruptive p ...
erupted.
The Clear Lake basin lies between the watersheds of the Sacramento River
The Sacramento River ( es, Río Sacramento) is the principal river of Northern California in the United States and is the largest river in California. Rising in the Klamath Mountains, the river flows south for before reaching the Sacramento–S ...
and the Russian River.
When it was formed it drained east into the Sacramento Valley.
About 200,000 years ago the Clear Lake Volcanic Field blocked the lake's outlet.
The lake rose until it found a new outlet, draining west through the Blue Lakes into Cold Creek and the Russian River.
This could account for the relatively mature profile of Cold Creek.
At some time in the last 10,000 years a landslide at the west end of the Blue Lakes blocked Clear Lake's outlet to the Russian River watershed.
The lake rose again, and created its present outlet via Cache Creek to the Sacramento River.
At one time the lower part of what is now East Fork Russian River from the present mouth of Cold Creek down through Coyote Valley to Russian River proper was also called Cold Creek.
In 1908 the Potter Valley Project
The Potter Valley Project is an interbasin water transfer project in Northern California in the United States, delivering water from the Eel River basin to turbines in the headwaters of the Russian River. The project is owned and operated by Pa ...
transferred water from the Eel River to the powerhouse in Potter Valley
Potter Valley is a census-designated place in Mendocino County, California, United States. It is located north-northeast of Ukiah, at an elevation of at the headwaters of the East Fork Russian River. The CDP population was 665 at the 2020 cens ...
, and its discharge flowed out through the East Fork Russian River, to which Cold Creek is a tributary.
Before the Eel River water was diverted, the East Fork would nearly dry up in July, August and September.
A flour mill in Coyote Valley had water to drive its wheel carried from Cold Creek, which runs year round, along of flume.
Potter Valley Project
 The upper Eel River runs to the north of the ridge at the north end of Potter Valley, and in this section is higher than the headwaters of East Fork Russian River.
The
The upper Eel River runs to the north of the ridge at the north end of Potter Valley, and in this section is higher than the headwaters of East Fork Russian River.
The Potter Valley Project
The Potter Valley Project is an hydroelectric project in Northern California in the United States, delivering water from the Eel River basin to turbines in the headwaters of the Russian River. The project is owned and operated by Pacific Gas and ...
was begun in 1900 to exploit the hydroelectric potential.
The concrete gravity and earth filled Cape Horn Dam was built to impound a reservoir called Lake Van Arsdale
Lake Van Arsdale, also known as Van Arsdale Reservoir, is a reservoir on the Eel River in California, part of the Potter Valley Project. Located in Mendocino County, north of the town of Potter Valley, California, the reservoir supplies water to ...
on the Eel River.
A tunnel in diameter lined with redwood timbers was excavated for more than south to emerge above the northern end of Potter Valley.
The water then fell through a penstock with vertical elevation of more than to the Potter Valley Powerhouse, which came online in April 1908 to deliver 4 MW.
It was upgraded to 7 MW in 1910, a second penstock was built in 1912, and in 1917 the powerhouse was upgraded to 9.4 MW.
At first the powerhouse only ran at full capacity in the winter, and had to shut down completely in summer due to lack of water.
In 1920 work started on Scott Dam, a large concrete ogee
An ogee ( ) is the name given to objects, elements, and curves—often seen in architecture and building trades—that have been variously described as serpentine-, extended S-, or sigmoid-shaped. Ogees consist of a "double curve", the combinatio ...
gravity structure upstream from Van Arsdale which collects water from the upper 7.3% of the Eel River watershed.
It was completed in 1922 and began to fill Lake Pillsbury
Lake Pillsbury is a lake in the Mendocino National Forest of Lake County, California, created from the Eel River and Hull Mountain watershed by Scott Dam. Elevation is with of shoreline and covering . Activities in the Lake Pillsbury Recreat ...
, which has a storage capacity of and releases water for the powerhouse throughout the year.
The Pacific Gas and Electric Company
The Pacific Gas and Electric Company (PG&E) is an American investor-owned utility (IOU). The company is headquartered in the Pacific Gas & Electric Building, in San Francisco, California. PG&E provides natural gas and electricity to 5.2 milli ...
(PG&E) acquired the project in 1930.
The Potter Valley Project maintains minimum instream flow in the East Fork Russian River and in the Eel River.
Some of the water from the generating station is used by the Potter Valley Irrigation District, while the remainder flows to Lake Mendocino.
In 1969 water diversion from the Eel River into the Russian River basin ranged from .
Spent water from the power station averaged and allowed for more croplands in the Potter and Ukiah valleys to be irrigated, as well as allowing more urban and industrial development along the river.
The power meets the needs of the city of Ukiah, and the water is valuable for agriculture, fish and recreation.
Lake Mendocino
 The East Fork Russian River is impounded near its mouth to form
The East Fork Russian River is impounded near its mouth to form Lake Mendocino
Lake Mendocino is a large reservoir in Mendocino County, California, northeast of Ukiah. It covers and was formed by the construction of Coyote Valley Dam in 1958. The lake and dam provide flood control, water conservation, hydroelectric powe ...
by the Coyote Dam, a rolled earth embankment built by the United States Army Corps of Engineers
, colors =
, anniversaries = 16 June (Organization Day)
, battles =
, battles_label = Wars
, website =
, commander1 = ...
(USACE).
The reservoir's catchment area is about and holds a water supply pool of .
The embankment is high and has a crest length of .
Construction of the Coyote Dam began in July 1956.
The USACE proposed to only clear a strip of land around the reservoir from the elevations.
Residents were concerned that underwater trees, stumps and debris would be dangerous to swimmers, boaters and fisherment, and in the summer of 1958 volunteers cleared most of the basin, cutting down and burning the trees.
Highway 20, which had crossed Coyote Valley, was rerouted around the new reservoir.
The dam began to store water in 1959.
It serves the dual purpose of protecting against floods and supplying water.
The USACE is responsible for flood control and Sonoma Water
Sonoma Water, formerly known as the Sonoma County Water Agency, maintains a water transmission system that provides naturally filtered Russian River water to more than 600,000 residents in portions of Sonoma County, California and Marin County, ...
controls water release.
Operations are not coordinated with the Potter Valley Project.
A 3.5 MW hydroelectric power plant operated by the City of Ukiah came into operation in 1986.
Lake Mendocino is used for recreational purposes such as camping, swimming, hiking, fishing, and boating.
All the facilities are operated by the USACE.
A large amount of fine sediment is transported through the water diversion on Eel River, causing turbidity in Lake Mendocino during the first heavy runoff of the year and for several months afterwards.
Normally sediment migrates steadily down the river.
The Coyote Dam impounds bedload, and the sediment-poor water it releases erodes the bed and banks of the river downstream in the Ukiah Valley.
After a major storm, flood releases from the Coyote Dam may also cause erosion of the river banks.
In February 2019 torrential rains caused serious floods on the lower Russian River.
In June 2021 the river's tributaries were almost dry due to a severe drought.
Lake Mendocino and Lake Sonoma
Lake Sonoma is a reservoir west of Cloverdale in northern Sonoma County, California, created by the construction of Warm Springs Dam. Access from U.S. Route 101 is by way of Canyon Road (from the south) from Geyserville, or Dutcher Creek Road (fr ...
, further downstream, were only releasing the minimum amount of water needed for fish and wildlife to survive.
Relief was not expected until the winter rains, and meanwhile fish were struggling to survive in river pools.
Fish
 The alternation of the Clear Lake drainage route in the past explains why there are many fish species common to the Russian River and the Sacramento River.
Native fish species that currently inhabit, or that have historically inhabited the East Fork of the Russian River, include
The alternation of the Clear Lake drainage route in the past explains why there are many fish species common to the Russian River and the Sacramento River.
Native fish species that currently inhabit, or that have historically inhabited the East Fork of the Russian River, include steelhead trout
Steelhead, or occasionally steelhead trout, is the common name of the anadromous form of the coastal rainbow trout or redband trout (O. m. gairdneri). Steelhead are native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific basin in Northeast Asia and N ...
(''Oncorhynchus mykiss''), chinook salmon
The Chinook salmon (''Oncorhynchus tshawytscha'') is the largest and most valuable species of Pacific salmon in North America, as well as the largest in the genus ''Oncorhynchus''. Its common name is derived from the Chinookan peoples. Other ve ...
(''Oncorhynchus tshawytscha''), coho salmon
The coho salmon (''Oncorhynchus kisutch;'' Karuk: achvuun) is a species of anadromous fish in the salmon family and one of the five Pacific salmon species. Coho salmon are also known as silver salmon or "silvers". The scientific species name i ...
(''Oncorhynchus kisutch''), rainbow trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. The steelhead (sometimes called "steelhead trout") is an anadromous (sea-run) form of the coasta ...
(''oncorhynchus mykiss irideus''), hardhead ('' Mylopharodon conocephalus''), Pacific lamprey
The Pacific lamprey (''Entosphenus tridentatus'') is an anadromous parasitic lamprey from the Pacific Coast of North America and Asia. It is a member of the Petromyzontidae family. The Pacific lamprey is also known as the three-tooth lamprey and ...
(''Entosphenus tridentata''), Sacramento pikeminnow
The Sacramento pikeminnow (''Ptychocheilus grandis''), formerly known as the Sacramento squawfish, is a large cyprinid fish of California, United States. It is native to the Los Angeles River, Sacramento- San Joaquin, Pajaro- Salinas, Russian Ri ...
(''Ptychocheilus grandis''), Sacramento sucker
The Sacramento sucker (''Catostomus occidentalis'') is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Catostomidae. It is primarily found in California with some populations extending into Oregon and Nevada. They inhabit a diverse range of habitats f ...
(''Catostomas occidentalis occidentalis'') and Russian River tule perch
The tule perch ''Hysterocarpus traskii'' is a surfperch ( Embiotocidae) native to the rivers and estuaries of central California, United States of America. It is the sole member of its genus, and the only freshwater surfperch.
The tule perch is ...
(''Hysterocarpus traskii pomo'').
Numerous non-native species also inhabit the East Fork including bluegill
The bluegill (''Lepomis macrochirus''), sometimes referred to as "bream", "brim", "sunny", or "copper nose" as is common in Texas, is a species of North American freshwater fish, native to and commonly found in streams, rivers, lakes, ponds and ...
(''Lepomis macrochirus''), brown bullhead
The brown bullhead (''Ameiurus nebulosus'') is a fish of the family Ictaluridae that is widely distributed in North America. It is a species of bullhead catfish and is similar to the black bullhead (''Ameiurus melas'') and yellow bullhead (''Ame ...
(''Ameiurus nebulosis''), common carp
The Eurasian carp or European carp (''Cyprinus carpio''), widely known as the common carp, is a widespread freshwater fish of eutrophic waters in lakes and large rivers in Europe and Asia.Fishbase''Cyprinus carpio'' Linnaeus, 1758/ref>Arkive The ...
(''Cyprinus carpio''), golden shiner
The golden shiner (''Notemigonus crysoleucas'') is a cyprinid fish native to eastern North America. It is the sole member of its genus. Much used as a bait fish, it is probably the most widely pond-cultured fish in the United States. It can be fo ...
(''Notemigonus crysoleucas''), green sunfish
The green sunfish (''Lepomis cyanellus'') is a species of freshwater fish in the sunfish family (Centrarchidae) of order Perciformes. A panfish popular with anglers, the green sunfish is also kept as an aquarium fish by hobbyists. They are us ...
(''Lepomis cyanellus''), largemouth bass
The largemouth bass (''Micropterus salmoides'') is a carnivorous freshwater gamefish in the Centrarchidae ( sunfish) family, a species of black bass native to the eastern and central United States, southeastern Canada and northern Mexico, but ...
(''Micropterus salmoides''), redear sunfish
The redear sunfish (''Lepomis microlophus''), also known as the shellcracker, Georgia bream, cherry gill, chinquapin, improved bream, rouge ear sunfish and sun perch) is a freshwater fish in the family Centrarchidae and is native to the southeast ...
(''Lepomis microlophus''), smallmouth bass (''Micropterus dolomieu'') and western mosquitofish
The western Mosquitofish (''Gambusia affinis'') is a North American freshwater fish, also known commonly, if ambiguously, as simply Mosquitofish or by its generic name, ''Gambusia'', or by the common name gambezi. Its sister species, the easte ...
(''Gambusia affinis'').
Before 1908 the Russian River was reduced in the summer to a series of deep pools that hosted many small fish.
The constant flow of cooler water changed the summer conditions in East Fork Russian River and downstream in Russian River, degrading the spawning habitat.
In 1954 the Department of Fish and Game began a program to eradicate "trash" fish in the Russian River below East Fork.
The rotenone
Rotenone is an odorless, colorless, crystalline isoflavone used as a broad-spectrum insecticide, piscicide, and pesticide. It occurs naturally in the seeds and stems of several plants, such as the jicama vine plant, and the roots of several member ...
poison was sprayed into the river, which had the effect of suffocating resident fish such as squawfish, suckers, roach, carp, hardhead minnows, green sunfish and lampreys, as well as smallmouth bass, and steelhead trout.
Some migratory game fish were also killed.
Since 1959 the Coyote Dam has blocked steelhead trout from returning to the river, so the valley's streams are dominated by rainbow trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. The steelhead (sometimes called "steelhead trout") is an anadromous (sea-run) form of the coasta ...
.
The state regularly restocks the East Fork with rainbow trout.
Common species in Lake Mendocino now include largemouth bass, smallmouth bass, striped bass
The striped bass (''Morone saxatilis''), also called the Atlantic striped bass, striper, linesider, rock, or rockfish, is an anadromous perciform fish of the family Moronidae found primarily along the Atlantic coast of North America. It has al ...
(''Morone saxatilis''), bluegill, black crappie
The black crappie (''Pomoxis nigromaculatus'') is a freshwater fish found in North America, one of the two types of crappies. It is very similar to the white crappie in size, shape, and habits, except that it is darker, with a pattern of black sp ...
(''Pomoxis nigromaculatus''), white crappie
The white crappie (''Pomoxis annularis'') is a freshwater fish found in North America, one of the two species of crappies. Alternate common names for the species include goldring and silver perch. is named for the fish. The genus name ''Pomoxis ...
(''Pomoxis annularis''), channel catfish
The channel catfish (''Ictalurus punctatus'') is North America's most numerous catfish species. It is the official fish of Kansas, Missouri, Iowa, Nebraska, and Tennessee, and is informally referred to as a "channel cat". In the United States, the ...
(''Ictalurus punctatus''), white bullhead
The white bullhead (''Ameiurus catus''), also known as the white catfish, is a member of the family Ictaluridae of the order Siluriformes.
Distribution
Originally native to the coastal river systems of the Eastern United States, the catfish spr ...
(''Ictalurus catus''), brown bullhead
The brown bullhead (''Ameiurus nebulosus'') is a fish of the family Ictaluridae that is widely distributed in North America. It is a species of bullhead catfish and is similar to the black bullhead (''Ameiurus melas'') and yellow bullhead (''Ame ...
(''Ameiurus nebulosis'') and a variety of non-game species. Rainbow trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. The steelhead (sometimes called "steelhead trout") is an anadromous (sea-run) form of the coasta ...
stocked in the river above the lake occasionally migrate downstream for brief periods in the spring and fall, when dissolved oxygen levels in the lake are higher.
Kayaking
A stretch of the river between Three Rocks Falls below Potter Valley down to Lake Mendocino is a class II+ run for kayakers. Its gradient is about and flow is about . Flow is good all year round due to controlled release from the upstream reservoirs, but best in the autumn. The Three Rock Falls itself is a class V–VI rapid where several inner tubers have died, and should be avoided by most kayakers in most water conditions.Notes
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * () {{authority control Rivers of Mendocino County, California