Earth's Location on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Knowledge of the location of Earth has been shaped by 400 years of telescopic observations, and has expanded radically since the start of the 20th century. Initially, Earth was believed to be the center of the Universe,
which consisted only of those planets visible with the naked eye and an outlying sphere of
fixed stars
In astronomy, fixed stars ( la, stellae fixae) is a term to name the full set of glowing points, astronomical objects actually and mainly stars, that appear not to move relative to one another against the darkness of the night sky in the backgro ...
. After the acceptance of the heliocentric model in the 17th century, observations by William Herschel and others showed that the Sun lay within a vast, disc-shaped galaxy
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. ...
of stars. By the 20th century, observations of spiral nebula
Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae''Milky Way galaxy was one of billions in an expanding universe, grouped into clusters and
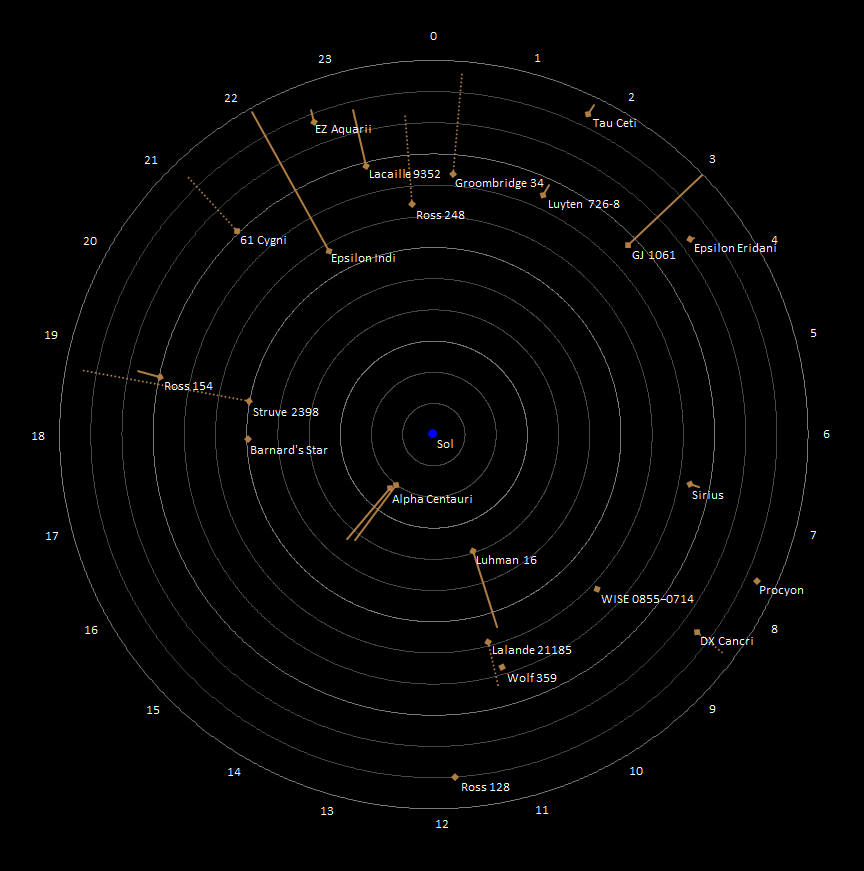
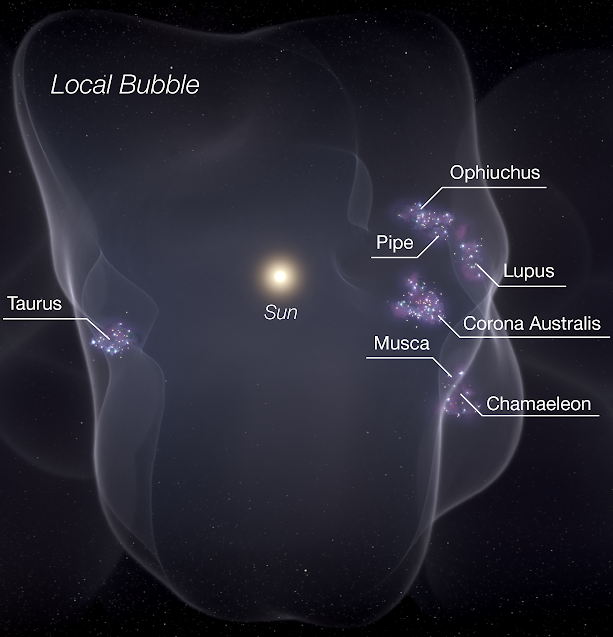 Earth is the third planet from the Sun with an approximate distance of , and is traveling nearly through outer space.
Earth is the third planet from the Sun with an approximate distance of , and is traveling nearly through outer space.
NOTE: Estimated velocity of the Earth traveling through outer space may be between – see discussion at " Wikipedia:Reference desk/Archives/Science/2019 July 20#How fast are we moving through space?"
supercluster
A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in turn ...
s. By the end of the 20th century, the overall structure of the visible universe was becoming clearer, with superclusters forming into a vast web of filaments and voids
Void may refer to:
Science, engineering, and technology
* Void (astronomy), the spaces between galaxy filaments that contain no galaxies
* Void (composites), a pore that remains unoccupied in a composite material
* Void, synonym for vacuum, a s ...
. Superclusters, filaments and voids are the largest coherent structures in the Universe that we can observe. At still larger scales (over 1000 megaparsecs) the Universe becomes homogeneous, meaning that all its parts have on average the same density, composition and structure.
Since there is believed to be no "center" or "edge" of the Universe, there is no particular reference point with which to plot the overall location of the Earth in the universe. Because the observable universe is defined as that region of the Universe visible to terrestrial observers, Earth is, because of the constancy of the speed of light, the center of Earth's observable universe. Reference can be made to the Earth's position with respect to specific structures, which exist at various scales. It is still undetermined whether the Universe is infinite. There have been numerous hypotheses that the known universe may be only one such example within a higher multiverse
The multiverse is a hypothetical group of multiple universes. Together, these universes comprise everything that exists: the entirety of space, time, matter, energy, information, and the physical laws and constants that describe them. The di ...
; however, no direct evidence of any sort of multiverse has been observed, and some have argued that the hypothesis is not falsifiable.
Details

 Earth is the third planet from the Sun with an approximate distance of , and is traveling nearly through outer space.
Earth is the third planet from the Sun with an approximate distance of , and is traveling nearly through outer space.NOTE: Estimated velocity of the Earth traveling through outer space may be between – see discussion at " Wikipedia:Reference desk/Archives/Science/2019 July 20#How fast are we moving through space?"
Table
Gallery
See also
* ''Cosmic View
''Cosmic View: The Universe in 40 Jumps'' is a 1957 book by Dutch educator Kees Boeke that combines writing and graphics to explore many levels of size and structure, from the astronomically vast to the atomically tiny. The book begins with a ph ...
''
* ''Cosmic Zoom
''Cosmic Zoom'' is a 1968 short film directed by Robert Verrall and produced by the National Film Board of Canada. It depicts the relative size of everything in the universe in an 8-minute sequence using animation and animation camera shots.
Sy ...
''
* ''Galaxy Song
"Galaxy Song" is a Monty Python song written by Eric Idle and John Du Prez.
The song first appeared in the 1983 film ''Monty Python's The Meaning of Life'' and was later released on the album ''Monty Python Sings''. The song was released as ...
''
* History of the center of the Universe
The center of the Universe is a concept that lacks a coherent definition in modern astronomy; according to standard cosmological theories on the shape of the universe, it has no center.
Historically, different people have suggested various lo ...
* Orders of magnitude (length)
* '' Pale Blue Dot''
* ''Powers of Ten'' (film)
* List of nearest stars
Notes
References
{{Portal bar, Stars, Spaceflight, Physics, Science, Weather Location in the Universe Physical cosmology