enact legislation in justice and home affairs; and maintain common policies on trade, agriculture,
History
Origins
Initial years and the Paris Treaty (19481957)
The year 1948 marked the beginning of the institutionalised modern European integration. In March 1948 the Treaty of Brussels was signed, establishing the Western Union (alliance), Western Union (WU), followed by the International Authority for the Ruhr. Furthermore, the Organization for European Economic Co-operation (OEEC), the predecessor of the OECD, was also founded in 1948 to manage the Marshall Plan, triggering as a Soviet response formation of the Comecon. The ensuing Hague Congress (1948), Hague Congress of May 1948 was a pivotal moment in European integration, as it led to the creation of the European Movement International, the College of Europe and most importantly to the foundation of the Council of Europe on 5 May 1949 (today its Europe day). The Council of Europe was one of the first institutions to bring the sovereign nations of (then only Western) Europe together, raising great hopes and fevered debates in the following two years for further European integration. It has since been a broad forum to further cooperation and shared issues, achieving for example the European Convention on Human Rights in 1950. Essential for the actual birth of the institutions of the EU was the Schuman Declaration on 9 May 1950 (the day after the fifth Victory in Europe Day) and the decision by six nations (France, Belgium, Netherlands, Luxembourg, West Germany and Italy) to follow Schuman and draft the Treaty of Paris (1951), Treaty of Paris. This treaty created in 1952 the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC), which was built on the International Authority for the Ruhr, installed by the Western Allies in 1949 to regulate the coal and steel industries of the Ruhr area in West Germany. Backed by the Marshall Plan with large funds coming from the United States since 1948, the ECSC became a milestone organization, enabling European economic development and integration and being the origin of the main institutions of the EU such as the European Commission and European Parliament, Parliament. Founding fathers of the European Union understood that coal and steel were the two industries essential for waging war, and believed that by tying their national industries together, a future war between their nations became much less likely. In parallel with Schuman, the Pleven Plan of 1951 tried but failed to tie the institutions of the developing European community under the European Political Community (1952), European Political Community, which was to include the also proposed Treaty establishing the European Defence Community, European Defence Community, an alternative to West Germany joining NATO which was established in 1949 under the Truman Doctrine. In 1954 the Modified Brussels Treaty transformed the Western Union into the Western European Union (WEU). West Germany eventually joined in 1955 both WEU and NATO, prompting the Soviet Union to form the Warsaw Pact in 1955 as an institutional framework for its military dominatin in the countries of Central and Eastern Europe. Assessing the progress of European integration the Messina Conference was held in 1955, ordering the Spaak report, which in 1956 recommended the next significant steps of European integration.Treaty of Rome (19581972)
 In 1957, Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and West Germany signed the Treaty of Rome, which created the European Economic Community (EEC) and established a European Union Customs Union, customs union. They also signed another pact creating the European Atomic Energy Community (Euratom) for co-operation in developing nuclear power. Both treaties came into force in 1958. Although the EEC and Euratom were created separately from the ECSC, they shared the same courts, and the Common Assembly. The EEC was headed by Walter Hallstein (Hallstein Commission) and Euratom was headed by Louis Armand (Armand Commission) and then Étienne Hirsch (Hirsch Commission). The OEEC was in turn reformed in 1961 into the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and its membership was extended to non-European states, the US and Canada. During the 1960s, tensions began to show, with France seeking to limit supranational power. Nevertheless, in 1965 an agreement was reached, and on 1 July 1967 the Merger Treaty created a single set of institutions for the three communities, which were collectively referred to as the ''European Communities''. Jean Rey (politician), Jean Rey President of the European Commission, presided over the first merged commission (Rey Commission).
In 1957, Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and West Germany signed the Treaty of Rome, which created the European Economic Community (EEC) and established a European Union Customs Union, customs union. They also signed another pact creating the European Atomic Energy Community (Euratom) for co-operation in developing nuclear power. Both treaties came into force in 1958. Although the EEC and Euratom were created separately from the ECSC, they shared the same courts, and the Common Assembly. The EEC was headed by Walter Hallstein (Hallstein Commission) and Euratom was headed by Louis Armand (Armand Commission) and then Étienne Hirsch (Hirsch Commission). The OEEC was in turn reformed in 1961 into the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and its membership was extended to non-European states, the US and Canada. During the 1960s, tensions began to show, with France seeking to limit supranational power. Nevertheless, in 1965 an agreement was reached, and on 1 July 1967 the Merger Treaty created a single set of institutions for the three communities, which were collectively referred to as the ''European Communities''. Jean Rey (politician), Jean Rey President of the European Commission, presided over the first merged commission (Rey Commission).
First enlargement, and European co-operation (19731993)
In 1973, the communities were enlarged to include Denmark (including Greenland), Republic of Ireland, Ireland, and the Accession of the United Kingdom to the European Communities, United Kingdom. Norway had negotiated to join at the same time, but Norwegian voters rejected membership in a 1972 Norwegian European Communities membership referendum, referendum. The ''Ostpolitik'' and the ensuing détente led to establishment of a first truly pan-European body, the Conference on Security and Co-operation in Europe (CSCE), predecessor of the modern Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE). In 1979, the 1979 European Parliament election, first direct elections to the European Parliament were held. Greece joined in 1981. In 1985, Greenland 1982 Greenlandic European Communities membership referendum, left the Communities, following a dispute over fishing rights. During the same year, the Schengen Agreement paved the way for the creation of open borders without passport controls between most member states and some non-member states. In 1986, the Flag of Europe, European flag began to be used by the EEC and the Single European Act was signed. Portugal and Spain joined in 1986. In 1990, after revolutions of 1989, the fall of the Eastern Bloc, the former East Germany became part of the communities as part of a German reunification, reunified Germany.Treaties of Maastricht, Amsterdam and Nice (19932004)
The European Union was formally established when the Maastricht Treaty—whose main architects were Horst Köhler, Helmut Kohl and François Mitterrand—came into force on 1 November 1993. The treaty also gave the name ''European Community'' to the EEC, even if it was referred to as such before the treaty. With further enlargement planned to include the former communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, as well as Cyprus and Malta, the Copenhagen criteria for candidate members to join the EU were agreed upon in June 1993. The expansion of the EU introduced a new level of complexity and discord. In 1995, Austria, Finland, and Sweden 1995 enlargement of the European Union, joined the EU. In 2002, euro banknotes and coins replaced national currencies in 12 of the member states. Since then, the eurozone has increased to encompass 19 countries. The euro currency became the second-largest reserve currency in the world. In 2004, the EU saw 2004 enlargement of the European Union, its biggest enlargement to date when Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Slovakia, and Slovenia joined the union.Treaty of Lisbon, and Brexit (2004present)
 In 2007, Bulgaria and Romania became EU members. Later that year, Slovenia adopted the euro, followed by Cyprus and Malta in 2008, Slovakia in 2009, Estonia in 2011, Latvia in 2014, and Lithuania in 2015.
On 1 December 2009, the Treaty of Lisbon, Lisbon Treaty entered into force and reformed many aspects of the EU. In particular, it changed the legal structure of the European Union, merging the Three pillars of the European Union, EU three pillars system into a single legal entity provisioned with a legal personality, created a permanent president of the European Council, the first of which was Herman Van Rompuy, and strengthened the position of the High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy, high representative of the union for foreign affairs and security policy.
In 2012, the EU received the 2012 Nobel Peace Prize, Nobel Peace Prize for having "contributed to the advancement of peace and reconciliation, democracy, and human rights in Europe". In 2013, Croatia became the 28th EU member.
From the beginning of the 2010s, the cohesion of the European Union has been tested by several issues, including European debt crisis, a debt crisis in some of the Eurozone countries, European migrant crisis, increasing migration from Africa and Asia, and the Brexit, United Kingdom's withdrawal from the EU. A 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum, referendum in the UK on its membership of the European Union was held in 2016, with 51.9 per cent of participants voting to leave. The UK formally notified the European Council of its decision to leave on 29 March 2017, initiating the Article 50 of the Treaty on European Union, formal withdrawal procedure for leaving the EU; following extensions to the process, the UK left the European Union on 31 January 2020, though most areas of EU law continued to apply to the UK for a transition period which lasted until 31 December 2020.
In 2007, Bulgaria and Romania became EU members. Later that year, Slovenia adopted the euro, followed by Cyprus and Malta in 2008, Slovakia in 2009, Estonia in 2011, Latvia in 2014, and Lithuania in 2015.
On 1 December 2009, the Treaty of Lisbon, Lisbon Treaty entered into force and reformed many aspects of the EU. In particular, it changed the legal structure of the European Union, merging the Three pillars of the European Union, EU three pillars system into a single legal entity provisioned with a legal personality, created a permanent president of the European Council, the first of which was Herman Van Rompuy, and strengthened the position of the High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy, high representative of the union for foreign affairs and security policy.
In 2012, the EU received the 2012 Nobel Peace Prize, Nobel Peace Prize for having "contributed to the advancement of peace and reconciliation, democracy, and human rights in Europe". In 2013, Croatia became the 28th EU member.
From the beginning of the 2010s, the cohesion of the European Union has been tested by several issues, including European debt crisis, a debt crisis in some of the Eurozone countries, European migrant crisis, increasing migration from Africa and Asia, and the Brexit, United Kingdom's withdrawal from the EU. A 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum, referendum in the UK on its membership of the European Union was held in 2016, with 51.9 per cent of participants voting to leave. The UK formally notified the European Council of its decision to leave on 29 March 2017, initiating the Article 50 of the Treaty on European Union, formal withdrawal procedure for leaving the EU; following extensions to the process, the UK left the European Union on 31 January 2020, though most areas of EU law continued to apply to the UK for a transition period which lasted until 31 December 2020.
Timeline
Politics
The European Union operates through a hybrid system of Supranational union, supranational and intergovernmentalism, intergovernmental decision-making, and according to the principles of Principle of conferral, conferral (which says that it should act only within the limits of the competences conferred on it by the Treaties of the European Union, treaties) and of Subsidiarity (European Union), subsidiarity (which says that it should act only where an objective cannot be sufficiently achieved by the member states acting alone). European Union law, Laws made by the EU institutions are passed in a variety of forms. Generally speaking, they can be classified into two groups: those which come into force without the necessity for national implementation measures (regulations) and those which specifically require national implementation measures (directives).These legislative instruments are dealt with in more detail #Acts, below. EU policy is in general promulgated by Directive (European Union), EU directives, which are then implemented in the Sovereignty, domestic legislation of its Member state of the European Union, member states, and Regulation (European Union), EU regulations, which are immediately enforceable in all member states. Lobbying#European Union, Lobbying at EU level by special interest groups is regulated to try to balance the aspirations of private initiatives with public interest decision-making process.Budget
The European Union had an agreed budget of billion for the year 2007 and billion for the period 2007–2013, representing 1.10 per cent and 1.05 per cent of the EU-27's Gross national income, GNI forecast for the respective periods. In 1960, the budget of the European Economic Community, European Community was 0.03 per cent of GDP. In the 2010 budget of billion, the largest single expenditure item was "''European Structural and Investment Funds, cohesion & competitiveness''" with around 45 per cent of the total budget. Next was "'' agriculture''" with approximately 31 per cent of the total. "''Rural development, environment andGovernance
Member states retain in principle all powers not conferred by them on the European Union, though the exact delimitation has on many occasions become a subject of scholarly or legal disputes. Inspired by the famous Commerce Clause and the huge impact that its interpretation and mode of application by the Supreme Court of the United States had on shaping the American federal government, the Court of Justice of the European Union has sometimes managed to expand through its case law the powers of the EU, including those related to areas other than only the ones explicitly conferred on it in the founding treaties. In certain fields the EU has been awarded exclusive competence and exclusive mandate, mandate. These are areas in which member states have entirely renounced their own capacity to enact legislation. In other areas the EU and its member states share the competence to legislate. While both can legislate, the member states can only legislate to the extent to which the EU has not. In other policy areas the EU can only co-ordinate, support and supplement member state action but cannot enact legislation with the aim of harmonising national laws. That a particular policy area falls into a certain category of competence is not necessarily indicative of what Legislature of the European Union, legislative procedure is used for enacting legislation within that policy area. Different legislative procedures are used within the same category of competence, and even with the same policy area. The distribution of competences in various policy areas between member states and the union is divided in the following three categories: The European Union has seven principal decision-making bodies, its Institutions of the European Union, institutions: the European Parliament, the European Council, the Council of the European Union, the European Commission, the Court of Justice of the European Union, the European Central Bank and the European Court of Auditors. Competence in scrutinising and amending legislation is shared between the Council of the European Union and the European Parliament, while executive tasks are performed by the European Commission and in a limited capacity by the European Council (not to be confused with the aforementioned Council of the European Union). The monetary policy of the eurozone is determined by the European Central Bank. The interpretation and the application of EU law and the treaties are ensured by the Court of Justice of the European Union. The EU budget is scrutinised by the European Court of Auditors. There are also a number of ancillary bodies which advise the EU or operate in a specific area.Branches of power
Executive branch
The European Council sets the broad political direction to the EU. It convenes at least four times a year and comprises the president of the European Council (presently Charles Michel), the president of the European Commission and one representative per member state of the European Union, member state (either its head of state or head of government). The High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy, high representative of the union for foreign affairs and security policy (presently Josep Borrell) also takes part in its meetings. Described by some as the union's "supreme political leadership", it is actively involved in the negotiation of Treaties of the European Union, treaty changes and defines the EU's policy agenda and strategies. Its leadership role involves solving disputes between member states and the institutions, and to resolving any political crises or disagreements over controversial issues and policies. It acts as a "head of state, collective head of state" and ratification, ratifies important documents (for example, international agreements and treaties). Tasks for the president of the European Council are ensuring the external representation of the EU, driving consensus and resolving divergences among member states, both during meetings of the European Council and over the periods between them. The European Council should not be mistaken for the Council of Europe, an international organisation independent of the EU and based in Strasbourg. The European Commission acts both as the EU's executive (government), executive arm, responsible for the day-to-day running of the EU, and also the Right of initiative (legislative), legislative initiator, with the sole power to propose laws for debate. The commission is 'guardian of the Treaties' and is responsible for their efficient operation and policing. It has 27 European Commissioner, European commissioners for different areas of policy, one from each member state, though commissioners are bound to represent the interests of the EU as a whole rather than their home state. The leader of the 27 is the president of the European Commission (presently Ursula von der Leyen for 20192024), President of the European Commission#Appointment, proposed by the European Council, following and taking into account the result of the European elections, and is then elected by the European Parliament. The President retains, as the leader responsible for the entire cabinet, the final say in accepting or rejecting a candidate submitted for a given portfolio by a member state, and oversees the commission's permanent civil service. After the President, the most prominent commissioner is the high representative of the union for foreign affairs and security policy, who is ''ex-officio'' a Vice-President of the European Commission, vice-president of the European Commission and is also chosen by the European Council. The other 26 commissioners are subsequently appointed by the Council of the European Union in agreement with the nominated president. The 27 commissioners as a single body are subject to approval (or otherwise) by vote of the European Parliament. All commissioners are first nominated by the government of the respective member state.Legislative branch
 The Council of the European Union (also called the Council and the "Council of Ministers", its former title) forms one half of the EU's legislature. It consists of a representative from each member state's government and meets in Council of the European Union#Configurations, different compositions depending on the policy area being addressed. Notwithstanding its different configurations, it is considered to be one single body. In addition to the legislative functions, members of the council also have Executive (government), executive responsibilities, such as the development of a Common Foreign and Security Policy and the coordination of broad economic policies within the Union. The Presidency of the Council of the European Union, Presidency of the council rotates between member states, with each holding it for six months. Beginning on 1 July 2022, the position is held by the Czech Republic.
The European Parliament is one of three Legislature of the European Union, legislative institutions of the EU, which together with the Council of the European Union is tasked with amending and approving the European Commission's proposals. 705 Member of the European Parliament, members of the European Parliament (MEPs) are directly Elections in the European Union, elected by Citizenship of the European Union, EU citizens every five years on the basis of proportional representation. MEPs are elected on a national basis and they sit according to Political groups of the European Parliament, political groups rather than their nationality. Each country has a set number of seats and is divided into European Parliament constituency, sub-national constituencies where this does not affect the proportional nature of the voting system. In the ordinary legislative procedure, the European Commission proposes legislation, which requires the joint approval of the European Parliament and the Council of the European Union to pass. This process applies to nearly all areas, including the budget of the European Union, EU budget. The parliament is the final body to approve or reject the proposed membership of the commission, and can attempt motions of censure on the commission by appeal to the European Court of Justice, Court of Justice. The president of the European Parliament carries out the role of speaker in Parliament and represents it externally. The president and Vice President of the European Parliament, vice-presidents are elected by MEPs every two and a half years.
The Council of the European Union (also called the Council and the "Council of Ministers", its former title) forms one half of the EU's legislature. It consists of a representative from each member state's government and meets in Council of the European Union#Configurations, different compositions depending on the policy area being addressed. Notwithstanding its different configurations, it is considered to be one single body. In addition to the legislative functions, members of the council also have Executive (government), executive responsibilities, such as the development of a Common Foreign and Security Policy and the coordination of broad economic policies within the Union. The Presidency of the Council of the European Union, Presidency of the council rotates between member states, with each holding it for six months. Beginning on 1 July 2022, the position is held by the Czech Republic.
The European Parliament is one of three Legislature of the European Union, legislative institutions of the EU, which together with the Council of the European Union is tasked with amending and approving the European Commission's proposals. 705 Member of the European Parliament, members of the European Parliament (MEPs) are directly Elections in the European Union, elected by Citizenship of the European Union, EU citizens every five years on the basis of proportional representation. MEPs are elected on a national basis and they sit according to Political groups of the European Parliament, political groups rather than their nationality. Each country has a set number of seats and is divided into European Parliament constituency, sub-national constituencies where this does not affect the proportional nature of the voting system. In the ordinary legislative procedure, the European Commission proposes legislation, which requires the joint approval of the European Parliament and the Council of the European Union to pass. This process applies to nearly all areas, including the budget of the European Union, EU budget. The parliament is the final body to approve or reject the proposed membership of the commission, and can attempt motions of censure on the commission by appeal to the European Court of Justice, Court of Justice. The president of the European Parliament carries out the role of speaker in Parliament and represents it externally. The president and Vice President of the European Parliament, vice-presidents are elected by MEPs every two and a half years.
Judicial branch
 The judicial branch of the European Union is formally called the Court of Justice of the European Union and consists of two courts: the European Court of Justice, Court of Justice and the General Court (European Union), General Court. The European Court of Justice, Court of Justice is the supreme court of the European Union in matters of European Union law. As a part of the Court of Justice of the European Union, it is tasked with interpreting EU law and ensuring its uniform application across all Member state of the European Union, EU member states under Article 263 of the Treaty of the Functioning of the European Union (TFEU). The Court was established in 1952, and is based in Luxembourg City, Luxembourg. It is composed of one judge per Member state of the European Union, member state – currently 27 – although it normally hears cases in panels of three, five or fifteen judges. The Court has been led by president Koen Lenaerts since 2015. The ECJ is the highest court of the European Union in matters of European Union law, Union law, but not national law. It is not possible to appeal against the decisions of national courts in the ECJ, but rather national courts refer questions of EU law to the ECJ. However, it is ultimately for the national court to apply the resulting interpretation to the facts of any given case. Although, only courts of final appeal are bound to refer a question of EU law when one is addressed. The treaties give the ECJ the power for consistent application of EU law across the EU as a whole. The court also acts as an administrative and constitutional court between the other EU institutions and the Member States and can annul or invalidate unlawful acts of EU institutions, bodies, offices and agencies.
The General Court (European Union), General Court is a constituent court of the European Union. It hears actions taken against the institutions of the European Union by individuals and member states, although certain matters are reserved for the Court of Justice. Decisions of the General Court can be appealed to the Court of Justice, but only on a point of law. Prior to the coming into force of the Lisbon Treaty on 1 December 2009, it was known as the Court of First Instance.
The judicial branch of the European Union is formally called the Court of Justice of the European Union and consists of two courts: the European Court of Justice, Court of Justice and the General Court (European Union), General Court. The European Court of Justice, Court of Justice is the supreme court of the European Union in matters of European Union law. As a part of the Court of Justice of the European Union, it is tasked with interpreting EU law and ensuring its uniform application across all Member state of the European Union, EU member states under Article 263 of the Treaty of the Functioning of the European Union (TFEU). The Court was established in 1952, and is based in Luxembourg City, Luxembourg. It is composed of one judge per Member state of the European Union, member state – currently 27 – although it normally hears cases in panels of three, five or fifteen judges. The Court has been led by president Koen Lenaerts since 2015. The ECJ is the highest court of the European Union in matters of European Union law, Union law, but not national law. It is not possible to appeal against the decisions of national courts in the ECJ, but rather national courts refer questions of EU law to the ECJ. However, it is ultimately for the national court to apply the resulting interpretation to the facts of any given case. Although, only courts of final appeal are bound to refer a question of EU law when one is addressed. The treaties give the ECJ the power for consistent application of EU law across the EU as a whole. The court also acts as an administrative and constitutional court between the other EU institutions and the Member States and can annul or invalidate unlawful acts of EU institutions, bodies, offices and agencies.
The General Court (European Union), General Court is a constituent court of the European Union. It hears actions taken against the institutions of the European Union by individuals and member states, although certain matters are reserved for the Court of Justice. Decisions of the General Court can be appealed to the Court of Justice, but only on a point of law. Prior to the coming into force of the Lisbon Treaty on 1 December 2009, it was known as the Court of First Instance.
Additional branches
 The European Central Bank (ECB) is one of the institutions of the central bank, monetary branch of the European Union, prime component of the Eurosystem and the European System of Central Banks. It is one of the world's Big Four (banking)#International use, most important central banks. The Governing Council of the European Central Bank, ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy for the Eurozone and the European Union, administers the foreign exchange reserves of EU member states, engages in foreign exchange operations, and defines the intermediate monetary objectives and key interest rate of the EU. The Executive Board of the European Central Bank, ECB Executive Board enforces the policies and decisions of the Governing Council, and may direct the national central banks when doing so. The ECB has the exclusive right to authorise the issuance of euro banknotes. Member states can issue euro coins, but the volume must be approved by the ECB beforehand. The bank also operates the TARGET2 payments system. The European System of Central Banks (ESCB) consists of the ECB and the national central banks (NCBs) of all 27 member states of the European Union. The ESCB is not the monetary authority of the eurozone, because not all EU member states have joined the euro. The ESCB's objective is price stability throughout the European Union. Secondarily, the ESCB's goal is to improve monetary and financial cooperation between the Eurosystem and member states outside the eurozone.
The European Court of Auditors (ECA) is the supreme audit institution, auditory branch of the European Union. It was established in 1975 in Luxembourg City, Luxembourg in order to improve EU financial management. It has 27 members (1 from each EU member-state) supported by approximately 800 civil servants. The European Personnel Selection Office (EPSO) is the civil service commission, civil service branch of the European Union, and is responsible for selecting staff to work for the institutions and agencies of the European Union including the European Parliament, the European Council, the Council of the European Union, the European Commission, the European Court of Justice, the Court of Auditors, the European External Action Service, the Economic and Social Committee, the Committee of the Regions and the European Ombudsman. Each institution is then able to recruit staff from among the pool of candidates selected by EPSO. On average, EPSO receives around 60,000-70,000 applications a year with around 1,500-2,000 candidates recruited by the European Union institutions. The European Ombudsman is the ombudsman, ombudsman branch of the European Union that holds the institutions, bodies and agencies of the EU to account, and promotes good administration. The Ombudsman helps people, businesses and organisations facing problems with the EU administration by investigating complaints, as well as by proactively looking into broader systemic issues. The current Ombudsman is Emily O'Reilly. The European Public Prosecutor's Office (EPPO) is the attorney general, prosecutory branch of the European Union with juridical personality, established under the Treaty of Lisbon between 22 of the 27 states of the EU following the method of enhanced cooperation. It is based in Kirchberg, Luxembourg City alongside the Court of Justice of the European Union and the European Court of Auditors.
The European Central Bank (ECB) is one of the institutions of the central bank, monetary branch of the European Union, prime component of the Eurosystem and the European System of Central Banks. It is one of the world's Big Four (banking)#International use, most important central banks. The Governing Council of the European Central Bank, ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy for the Eurozone and the European Union, administers the foreign exchange reserves of EU member states, engages in foreign exchange operations, and defines the intermediate monetary objectives and key interest rate of the EU. The Executive Board of the European Central Bank, ECB Executive Board enforces the policies and decisions of the Governing Council, and may direct the national central banks when doing so. The ECB has the exclusive right to authorise the issuance of euro banknotes. Member states can issue euro coins, but the volume must be approved by the ECB beforehand. The bank also operates the TARGET2 payments system. The European System of Central Banks (ESCB) consists of the ECB and the national central banks (NCBs) of all 27 member states of the European Union. The ESCB is not the monetary authority of the eurozone, because not all EU member states have joined the euro. The ESCB's objective is price stability throughout the European Union. Secondarily, the ESCB's goal is to improve monetary and financial cooperation between the Eurosystem and member states outside the eurozone.
The European Court of Auditors (ECA) is the supreme audit institution, auditory branch of the European Union. It was established in 1975 in Luxembourg City, Luxembourg in order to improve EU financial management. It has 27 members (1 from each EU member-state) supported by approximately 800 civil servants. The European Personnel Selection Office (EPSO) is the civil service commission, civil service branch of the European Union, and is responsible for selecting staff to work for the institutions and agencies of the European Union including the European Parliament, the European Council, the Council of the European Union, the European Commission, the European Court of Justice, the Court of Auditors, the European External Action Service, the Economic and Social Committee, the Committee of the Regions and the European Ombudsman. Each institution is then able to recruit staff from among the pool of candidates selected by EPSO. On average, EPSO receives around 60,000-70,000 applications a year with around 1,500-2,000 candidates recruited by the European Union institutions. The European Ombudsman is the ombudsman, ombudsman branch of the European Union that holds the institutions, bodies and agencies of the EU to account, and promotes good administration. The Ombudsman helps people, businesses and organisations facing problems with the EU administration by investigating complaints, as well as by proactively looking into broader systemic issues. The current Ombudsman is Emily O'Reilly. The European Public Prosecutor's Office (EPPO) is the attorney general, prosecutory branch of the European Union with juridical personality, established under the Treaty of Lisbon between 22 of the 27 states of the EU following the method of enhanced cooperation. It is based in Kirchberg, Luxembourg City alongside the Court of Justice of the European Union and the European Court of Auditors.
Law
Primary law
The European Union is based on a series of Treaties of the European Union, treaties. These first established the European Community and the EU, and then made amendments to those founding treaties. These are power-giving treaties which set broad policy goals and establish institutions with the necessary legal powers to implement those goals. These legal powers include the ability to enact legislation which can directly affect all member states and their inhabitants.According to the principle of Direct Effect first invoked in the Court of Justice's decision in See: Craig and de Búrca, ch. 5. The EU has legal personality, with the right to sign agreements and international treaties.Secondary law
The main legal acts of the European Union come in three forms: Regulation (European Union), regulations, Directive (European Union), directives, and Decision (European Union), decisions. Regulations become law in all member states the moment they come into force, without the requirement for any implementing measures, and automatically override conflicting domestic provisions. Directives require member states to achieve a certain result while leaving them discretion as to how to achieve the result. The details of how they are to be implemented are left to member states.To do otherwise would require the drafting of legislation which would have to cope with the frequently divergent legal systems and administrative systems of all of the now 28 member states. See Craig and de Búrca, p. 115 When the time limit for implementing directives passes, they may, under certain conditions, have direct effect in national law against member states. Decisions offer an alternative to the two above modes of legislation. They are legal acts which only apply to specified individuals, companies or a particular member state. They are most often used in competition law, or on rulings on State Aid, but are also frequently used for procedural or administrative matters within the institutions. Regulations, directives, and decisions are of equal legal value and apply without any formal hierarchy.Foreign relations
 Foreign policy co-operation between member states dates from the establishment of the community in 1957, when member states negotiated as a bloc in international trade negotiations under the EU's common commercial policy. Steps for a more wide-ranging co-ordination in foreign relations began in 1970 with the establishment of European Political Cooperation which created an informal consultation process between member states with the aim of forming common foreign policies. In 1987 the European Political Cooperation was introduced on a formal basis by the Single European Act. EPC was renamed as the Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP) by the Maastricht Treaty.
The aims of the CFSP are to promote both the EU's own interests and those of the international community as a whole, including the furtherance of international co-operation, respect for human rights, democracy, and the rule of law. The CFSP requires unanimity among the member states on the appropriate policy to follow on any particular issue. The unanimity and difficult issues treated under the CFSP sometimes lead to disagreements, such as those which occurred over the Iraq War, war in Iraq.
The coordinator and representative of the CFSP within the EU is the High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy, high representative of the union for foreign affairs and security policy who speaks on behalf of the EU in foreign policy and defence matters, and has the task of articulating the positions expressed by the member states on these fields of policy into a common alignment. The high representative heads up the European External Action Service (EEAS), a unique EU department that has been officially implemented and operational since 1 December 2010 on the occasion of the first anniversary of the entry into force of the Treaty of Lisbon. The EEAS will serve as a foreign ministry and diplomatic corps for the European Union.
Besides the emerging international policy of the European Union, the international influence of the EU is also felt through Enlargement of the European Union, enlargement. The perceived benefits of becoming a member of the EU act as an incentive for both political and economic reform in states wishing to fulfil the EU's accession criteria, and are considered an important factor contributing to the reform of European formerly Communist countries. This influence on the internal affairs of other countries is generally referred to as "soft power", as opposed to military "hard power".
Foreign policy co-operation between member states dates from the establishment of the community in 1957, when member states negotiated as a bloc in international trade negotiations under the EU's common commercial policy. Steps for a more wide-ranging co-ordination in foreign relations began in 1970 with the establishment of European Political Cooperation which created an informal consultation process between member states with the aim of forming common foreign policies. In 1987 the European Political Cooperation was introduced on a formal basis by the Single European Act. EPC was renamed as the Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP) by the Maastricht Treaty.
The aims of the CFSP are to promote both the EU's own interests and those of the international community as a whole, including the furtherance of international co-operation, respect for human rights, democracy, and the rule of law. The CFSP requires unanimity among the member states on the appropriate policy to follow on any particular issue. The unanimity and difficult issues treated under the CFSP sometimes lead to disagreements, such as those which occurred over the Iraq War, war in Iraq.
The coordinator and representative of the CFSP within the EU is the High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy, high representative of the union for foreign affairs and security policy who speaks on behalf of the EU in foreign policy and defence matters, and has the task of articulating the positions expressed by the member states on these fields of policy into a common alignment. The high representative heads up the European External Action Service (EEAS), a unique EU department that has been officially implemented and operational since 1 December 2010 on the occasion of the first anniversary of the entry into force of the Treaty of Lisbon. The EEAS will serve as a foreign ministry and diplomatic corps for the European Union.
Besides the emerging international policy of the European Union, the international influence of the EU is also felt through Enlargement of the European Union, enlargement. The perceived benefits of becoming a member of the EU act as an incentive for both political and economic reform in states wishing to fulfil the EU's accession criteria, and are considered an important factor contributing to the reform of European formerly Communist countries. This influence on the internal affairs of other countries is generally referred to as "soft power", as opposed to military "hard power".
Defence
Member states
Subdivisions
Country subdivision, Subdivisions of member-states are based on the Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics (NUTS), a geocode Standardization, standard for statistical purposes. The standard, adopted in 2003, is developed and regulated by the European Union, and thus only covers the Member State of the European Union, member states of the EU in detail. The Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics is instrumental in the European Union's Structural Funds and Cohesion Fund delivery mechanisms and for locating the area where goods and services subject to European Government procurement in the European Union, public procurement legislation are to be delivered.Schengen Area
Candidate countries
There are eight countries that are recognised as Future enlargement of the European Union, candidates for membership: Accession of Albania to the European Union, Albania, Accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to the European Union, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Accession of Moldova to the European Union, Moldova, Accession of Montenegro to the European Union, Montenegro, Accession of North Macedonia to the European Union, North Macedonia, Accession of Serbia to the European Union, Serbia, Accession of Turkey to the European Union, Turkey and Accession of Ukraine to the European Union, Ukraine. Norway–European Union relations, Norway, Switzerland–European Union relations, Switzerland and Accession of Iceland to the European Union, Iceland have submitted membership applications in the past, but subsequently frozen or withdrawn them. Additionally, Georgia–European Union relations#Proposed European Union membership, Georgia and Accession of Kosovo to the European Union, Kosovo are officially recognised as potential candidates, and have submitted membership applications.Former members
Article 50 of the Treaty on European Union, Article 50 of the Treaty of Lisbon, Lisbon Treaty provides the basis for a member to Withdrawal from the European Union, leave the EU. Two territories have left the union: Greenland (an autonomous area, autonomous province of Denmark) withdrew in 1985; the United Kingdom formally invoked Article 50 of the Consolidated Treaty on European Union in 2017, and became the only sovereign state to leave when it Brexit, withdrew from the EU in 2020.Geography
Climate
Environment
 In 1957, when the European Economic Community was founded, it had no environmental policy. Over the past 50 years, an increasingly dense network of legislation has been created, extending to all areas of environmental protection, including air pollution, water quality, waste management, nature conservation, and the control of chemicals, industrial hazards, and biotechnology. According to the Institute for European Environmental Policy, environmental law comprises over 500 Directives, Regulations and Decisions, making environmental policy a core area of European politics.Institute for European Environmental Policy (2012) Manual of European Environmental Policy, Earthscan, London.
European policy-makers originally increased the EU's capacity to act on environmental issues by defining it as a trade problem. Trade barriers and competitive distortions in the Common Market could emerge due to the different environmental standards in each member state. In subsequent years, the environment became a formal policy area, with its own policy actors, principles and procedures. The legal basis for EU environmental policy was established with the introduction of the Single European Act in 1987.
Initially, EU environmental policy focused on Europe. More recently, the EU has demonstrated leadership in global environmental governance, e.g. the role of the EU in securing the ratification and coming into force of the Kyoto Protocol despite opposition from the United States. This international dimension is reflected in the EU's Sixth Environmental Action Programme, which recognises that its objectives can only be achieved if key international agreements are actively supported and properly implemented both at EU level and worldwide. The Lisbon Treaty further strengthened the leadership ambitions. EU law has played a significant role in improving habitat and species protection in Europe, as well as contributing to improvements in air and water quality and waste management.
Mitigating climate change is one of the top priorities of EU environmental policy. In 2007, member states agreed that, in the future, 20 per cent of the energy used across the EU must be renewable energy, renewable, and carbon dioxide emissions have to be lower in 2020 by at least 20 per cent compared to 1990 levels. In 2017, the EU emitted 9.1 per cent of global greenhouse-gas emissions. The European Union claims that already in 2018, its GHG emissions were 23% lower that in 1990.
The EU has adopted an Emissions trading, emissions trading system to incorporate carbon emissions into the economy. The European Green Capital is an annual award given to cities that focuses on the environment, energy efficiency, and quality of life in urban areas to create smart city. In the 2019 European Parliament election, 2019 elections to the European Parliament, the green parties increased their power, possibly because of the rise of post materialist values. Proposals to reach a zero carbon economy in the European Union by 2050 were suggested in 2018 – 2019. Almost all member states supported that goal at an EU summit in June 2019. The Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, and Poland disagreed. In June 2021 the European Union passed a European Climate Law with targets of 55% GHG emissions reduction by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2050. In 2021 the European Union and the United States pledged to cut methane emissions by 30% by 2030. The pledge is considered as a big achievement for climate change mitigation.
In 1957, when the European Economic Community was founded, it had no environmental policy. Over the past 50 years, an increasingly dense network of legislation has been created, extending to all areas of environmental protection, including air pollution, water quality, waste management, nature conservation, and the control of chemicals, industrial hazards, and biotechnology. According to the Institute for European Environmental Policy, environmental law comprises over 500 Directives, Regulations and Decisions, making environmental policy a core area of European politics.Institute for European Environmental Policy (2012) Manual of European Environmental Policy, Earthscan, London.
European policy-makers originally increased the EU's capacity to act on environmental issues by defining it as a trade problem. Trade barriers and competitive distortions in the Common Market could emerge due to the different environmental standards in each member state. In subsequent years, the environment became a formal policy area, with its own policy actors, principles and procedures. The legal basis for EU environmental policy was established with the introduction of the Single European Act in 1987.
Initially, EU environmental policy focused on Europe. More recently, the EU has demonstrated leadership in global environmental governance, e.g. the role of the EU in securing the ratification and coming into force of the Kyoto Protocol despite opposition from the United States. This international dimension is reflected in the EU's Sixth Environmental Action Programme, which recognises that its objectives can only be achieved if key international agreements are actively supported and properly implemented both at EU level and worldwide. The Lisbon Treaty further strengthened the leadership ambitions. EU law has played a significant role in improving habitat and species protection in Europe, as well as contributing to improvements in air and water quality and waste management.
Mitigating climate change is one of the top priorities of EU environmental policy. In 2007, member states agreed that, in the future, 20 per cent of the energy used across the EU must be renewable energy, renewable, and carbon dioxide emissions have to be lower in 2020 by at least 20 per cent compared to 1990 levels. In 2017, the EU emitted 9.1 per cent of global greenhouse-gas emissions. The European Union claims that already in 2018, its GHG emissions were 23% lower that in 1990.
The EU has adopted an Emissions trading, emissions trading system to incorporate carbon emissions into the economy. The European Green Capital is an annual award given to cities that focuses on the environment, energy efficiency, and quality of life in urban areas to create smart city. In the 2019 European Parliament election, 2019 elections to the European Parliament, the green parties increased their power, possibly because of the rise of post materialist values. Proposals to reach a zero carbon economy in the European Union by 2050 were suggested in 2018 – 2019. Almost all member states supported that goal at an EU summit in June 2019. The Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, and Poland disagreed. In June 2021 the European Union passed a European Climate Law with targets of 55% GHG emissions reduction by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2050. In 2021 the European Union and the United States pledged to cut methane emissions by 30% by 2030. The pledge is considered as a big achievement for climate change mitigation.
Economy
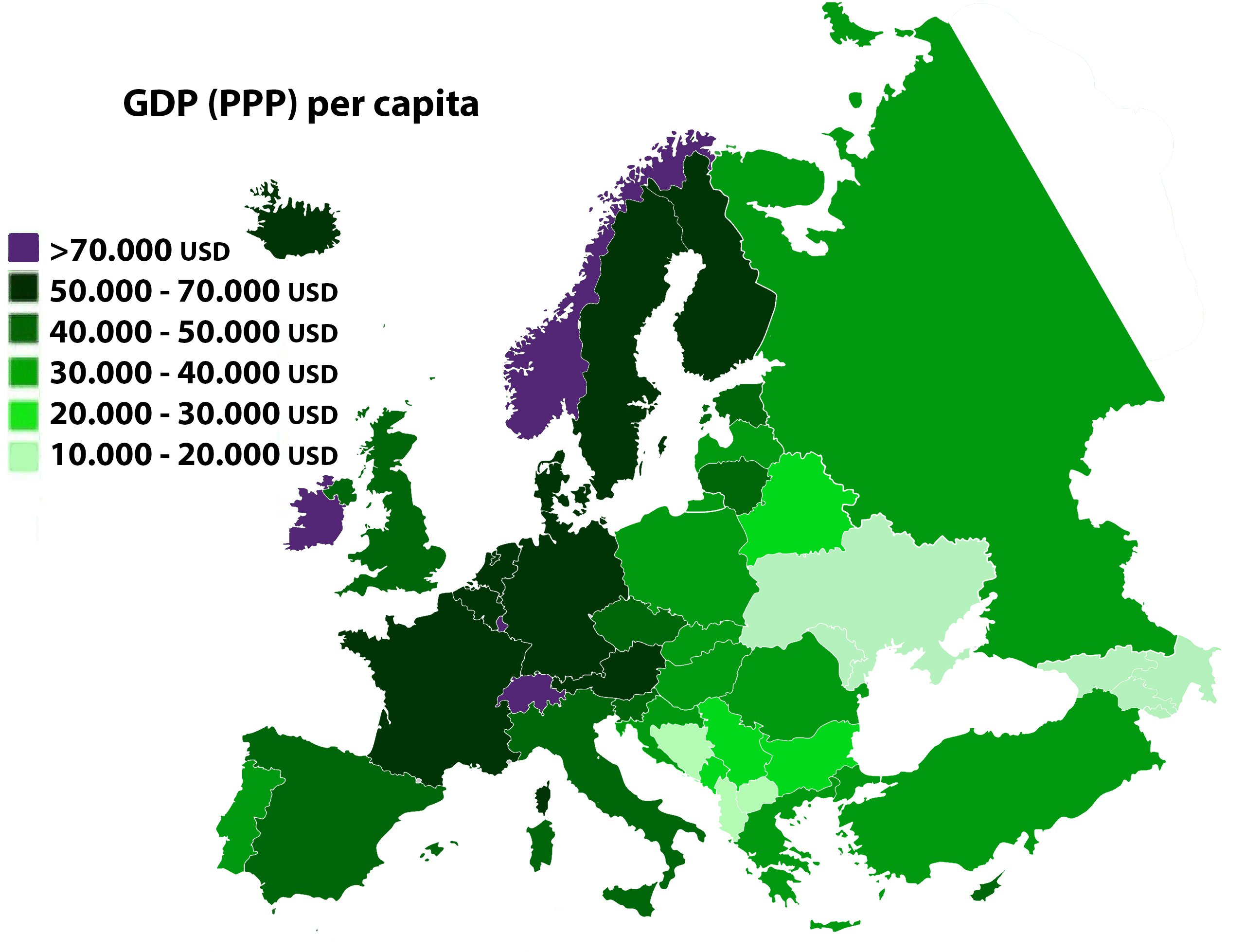 EU member states own the estimated third largest after the United States (trillion) and China (trillion) net wealth in the world, equal to around one sixth (trillion) of the trillion global wealth. Of the top Fortune Global 500, 500 largest corporations in the world measured by revenue in 2010, 161 had their headquarters in the EU. In 2016, unemployment in the EU stood at 8.9 per cent while inflation was at 2.2 per cent, and the account balance at −0.9 per cent of GDP. The average annual net earnings in the European Union was around in 2021. There is a significant variation in nominal GDP per capita within individual EU states. The difference between the richest and poorest regions (281 NUTS-2 regions of the Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics) ranged, in 2017, from 31 per cent (Severozapaden, Bulgaria) of the EU28 average () to 253 per cent (Luxembourg), or from to .
EU member states own the estimated third largest after the United States (trillion) and China (trillion) net wealth in the world, equal to around one sixth (trillion) of the trillion global wealth. Of the top Fortune Global 500, 500 largest corporations in the world measured by revenue in 2010, 161 had their headquarters in the EU. In 2016, unemployment in the EU stood at 8.9 per cent while inflation was at 2.2 per cent, and the account balance at −0.9 per cent of GDP. The average annual net earnings in the European Union was around in 2021. There is a significant variation in nominal GDP per capita within individual EU states. The difference between the richest and poorest regions (281 NUTS-2 regions of the Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics) ranged, in 2017, from 31 per cent (Severozapaden, Bulgaria) of the EU28 average () to 253 per cent (Luxembourg), or from to .
Economic and monetary union
Capital Markets Union and financial institutions
Free movement of capital is intended to permit movement of investments such as property purchases and buying of shares between countries. Until the drive towards economic and monetary union the development of the capital provisions had been slow. Post-Maastricht there has been a rapidly developing corpus of ECJ judgements regarding this initially neglected freedom. The free movement of capital is unique insofar as it is granted equally to non-member states. The European System of Financial Supervision is an institutional architecture of the EU's framework of financial supervision composed by three authorities: the European Banking Authority, the European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority and the European Securities and Markets Authority. To complement this framework, there is also a European Systemic Risk Board under the responsibility of the central bank. The aim of this financial control system is to ensure the economic stability of the EU.Eurozone and banking union
 In 1999, the currency union started to materialise through introducing a common accounting (virtual) currency in History of the euro, eleven of the member states. In 2002, it was turned into a fully-fledged conventible currency, when euro banknotes, euro notes and coins were issued, while the phaseout of national currencies in the eurozone (consisting by then of 12 member states) was initiated. The eurozone (constituted by the EU member states which have adopted the euro) has since grown to 19 countries.
19 member states known as the eurozone have fully implemented the currency union through supersededing their national currencies the single currency euro. The currency union represents 342million EU citizens. The euro is the second largest reserve currency as well as the second most traded currency in the world after the United States dollar.
The euro, and the monetary policies of those who have adopted it in agreement with the EU, are under the control of the ECB. The ECB is the central bank for the eurozone, and thus controls monetary policy in that area with an agenda to maintain price stability. It is at the centre of the Eurosystem, which comprehends all the Eurozone national central banks. The ECB is also the central institution of the Banking Union established within the eurozone and manages its Single Supervisory Mechanism. These is also a Single Resolution Mechanism in case of a bank default.
In 1999, the currency union started to materialise through introducing a common accounting (virtual) currency in History of the euro, eleven of the member states. In 2002, it was turned into a fully-fledged conventible currency, when euro banknotes, euro notes and coins were issued, while the phaseout of national currencies in the eurozone (consisting by then of 12 member states) was initiated. The eurozone (constituted by the EU member states which have adopted the euro) has since grown to 19 countries.
19 member states known as the eurozone have fully implemented the currency union through supersededing their national currencies the single currency euro. The currency union represents 342million EU citizens. The euro is the second largest reserve currency as well as the second most traded currency in the world after the United States dollar.
The euro, and the monetary policies of those who have adopted it in agreement with the EU, are under the control of the ECB. The ECB is the central bank for the eurozone, and thus controls monetary policy in that area with an agenda to maintain price stability. It is at the centre of the Eurosystem, which comprehends all the Eurozone national central banks. The ECB is also the central institution of the Banking Union established within the eurozone and manages its Single Supervisory Mechanism. These is also a Single Resolution Mechanism in case of a bank default.
Trade
As a political entity, the European Union is represented in the World Trade Organization (WTO). Two of the original core objectives of the European Economic Community were the development of a common market, subsequently becoming a single market, and a European Union Customs Union, customs union between its member states.Single market
Customs union
External trade
The European Union has concluded European Union free trade agreements, free trade agreements (FTAs) and other agreements with a trade component with many countries worldwide and is negotiating with many others. The European Union's services trade surplus rose from $16 billion in 2000 to more than $250 billion in 2018. In 2020, in part due to the COVID-19 pandemic, China became the EU's largest trading partner, displacing the United States. The European Union is the largest exporter in the world and in 2008 was the largest importer of goods and services. Internal trade between the member states is aided by the removal of barriers to trade such as tariffs and border controls. In the eurozone, trade is helped by not having any currency differences to deal with amongst most members.Competition and consumer protection
The EU operates a European Union competition law, competition policy intended to ensure undistorted competition within the single market.Article 3(1)(g) of the Treaty of Rome In 2001 the commission for the first time prevented a merger between two companies based in the United States (General Electric and Honeywell) which had already been approved by their national authority. Another high-profile case, European Union Microsoft competition case, against Microsoft, resulted in the commission fining Microsoft over million following nine years of legal action.Energy
Nuclear energy and renewable energy are treated differently from oil, gas, and coal in this respect. The EU has had legislative power in the area of energy policy for most of its existence; this has its roots in the original European Coal and Steel Community. The introduction of a mandatory and comprehensive European energy policy was approved at the meeting of the European Council in October 2005, and the first draft policy was published in January 2007. The EU has five key points in its energy policy: increase competition in the internal market, encourage investment and boost interconnections between electricity grids; diversify energy resources with better systems to respond to a crisis; establish a new treaty framework for energy co-operation with Russia while improving relations with energy-rich states in Central Asia and North Africa; use existing energy supplies more efficiently while increasing renewable energy commercialisation; and finally increase funding for new energy technologies. In 2007, EU countries as a whole imported 82 per cent of their oil, 57 per cent of their natural gas and 97.48 per cent of their uranium demands. The three largest suppliers of natural gas to the European Union are Russia, Norway and Algeria, that amounted for about three quarters of the imports in 2019. There is a strong Russia in the European energy sector, dependence on Russian energy that the EU has been attempting to reduce. However, in May 2022, it was reported that the European Union is preparing another sanction against Russia over its invasion of Ukraine. It is expected to target Russian oil, Russian and Belarusian banks, as well as individuals and companies. According to an article by Reuters, two diplomats stated that the European Union may impose a ban on imports of Russian oil by the end of 2022. In May 2022, the EU Commission published the 'RePowerEU' initiative, a €300 billion plan outlining the path towards the end of EU dependence on Russian fossil fuels by 2030 and the acceleration on the clean energy transition.
Transport
 The European Union manages cross-border road, railway, airport and water infrastructure through the Trans-European Transport Network (TEN-T), created in 1990, and the Trans-European Combined Transport network. TEN-T comprises two network layers: the Core Network, which is to be completed by 2030; and the Comprehensive Network, which is to be completed by 2050. The network is currently made up of 9 core corridors: the Baltic–Adriatic Corridor, the North Sea–Baltic Corridor, the Mediterranean Corridor, the Orient/East–Med Corridor, the Scandinavian–Mediterranean Corridor, the Rhine–Alpine Corridor, the Atlantic Corridor, the North Sea–Mediterranean Corridor, and the Rhine–Danube Corridor. Road transportation was organized under the TEN-T by the Trans-European road network. Bundesautobahn 7 is the longest national motorway in the EU at 963 km (598 mi).
The European Union manages cross-border road, railway, airport and water infrastructure through the Trans-European Transport Network (TEN-T), created in 1990, and the Trans-European Combined Transport network. TEN-T comprises two network layers: the Core Network, which is to be completed by 2030; and the Comprehensive Network, which is to be completed by 2050. The network is currently made up of 9 core corridors: the Baltic–Adriatic Corridor, the North Sea–Baltic Corridor, the Mediterranean Corridor, the Orient/East–Med Corridor, the Scandinavian–Mediterranean Corridor, the Rhine–Alpine Corridor, the Atlantic Corridor, the North Sea–Mediterranean Corridor, and the Rhine–Danube Corridor. Road transportation was organized under the TEN-T by the Trans-European road network. Bundesautobahn 7 is the longest national motorway in the EU at 963 km (598 mi).
 Maritime transportation is organized under the TEN-T by the Trans-European Inland Waterway network, and the Trans-European Seaport network. European seaports are categorized as international, community, or regional. The Port of Rotterdam is the busiest in the EU, and the world's largest seaport outside of East Asia, located in and near the city of Rotterdam, in the province of South Holland in the Netherlands. The European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA), founded in 2002 in Lisbon, Portugal, is charged with reducing the risk of Shipwreck, maritime accidents, marine pollution from ships and the Search and rescue, loss of human lives at sea by helping to enforce the pertinent EU legislation.
Air transportation is organized under the TEN-T by the Trans-European Airport network. European airports are categorized as international, community, or regional. The Charles de Gaulle Airport is the busiest in the EU, located in and near the city of Paris, in France. The European Common Aviation Area (ECAA) is a single market in aviation. ECAA agreements were signed on 5 May 2006 in Salzburg, Austria between the EU and some third countries. The ECAA liberalises the air transport industry by allowing any company from any ECAA member state to fly between any ECAA member states airports, thereby allowing a "foreign" airline to provide domestic flights. The Single European Sky (SES) is an initiative that seeks to reform the European air traffic management system through a series of actions carried out in four different levels (institutional, operational, technological and control and supervision) with the aim of satisfying the needs of the European airspace in terms of capacity, safety, efficiency and environmental impact. Civil aviation safety is under the responsibility of the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA). It carries out Type certificate, certification, regulation and standardisation and also performs investigation and monitoring. The idea of a European-level aviation safety authority goes back to 1996, but the agency was only legally established in 2002, and began operating in 2003.
Rail transportation is organized under the TEN-T by the Trans-European Rail network, made up of the Trans-European high-speed rail network, high-speed rail network and the Trans-European conventional rail network, conventional rail network. The Gare du Nord railway station is the busiest in the EU, located in and near the city of Paris, in France. Rail transport in Europe is being synchronised with the European Rail Traffic Management System (ERTMS) with the goal of greatly enhancing safety, increase efficiency of train transports and enhance cross-border interoperability. This is done by replacing former national Railway signal, signalling equipment and operational procedures with a single new Europe-wide standard for train control and command systems. This system is conducted by the European Union Agency for Railways (ERA).
Maritime transportation is organized under the TEN-T by the Trans-European Inland Waterway network, and the Trans-European Seaport network. European seaports are categorized as international, community, or regional. The Port of Rotterdam is the busiest in the EU, and the world's largest seaport outside of East Asia, located in and near the city of Rotterdam, in the province of South Holland in the Netherlands. The European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA), founded in 2002 in Lisbon, Portugal, is charged with reducing the risk of Shipwreck, maritime accidents, marine pollution from ships and the Search and rescue, loss of human lives at sea by helping to enforce the pertinent EU legislation.
Air transportation is organized under the TEN-T by the Trans-European Airport network. European airports are categorized as international, community, or regional. The Charles de Gaulle Airport is the busiest in the EU, located in and near the city of Paris, in France. The European Common Aviation Area (ECAA) is a single market in aviation. ECAA agreements were signed on 5 May 2006 in Salzburg, Austria between the EU and some third countries. The ECAA liberalises the air transport industry by allowing any company from any ECAA member state to fly between any ECAA member states airports, thereby allowing a "foreign" airline to provide domestic flights. The Single European Sky (SES) is an initiative that seeks to reform the European air traffic management system through a series of actions carried out in four different levels (institutional, operational, technological and control and supervision) with the aim of satisfying the needs of the European airspace in terms of capacity, safety, efficiency and environmental impact. Civil aviation safety is under the responsibility of the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA). It carries out Type certificate, certification, regulation and standardisation and also performs investigation and monitoring. The idea of a European-level aviation safety authority goes back to 1996, but the agency was only legally established in 2002, and began operating in 2003.
Rail transportation is organized under the TEN-T by the Trans-European Rail network, made up of the Trans-European high-speed rail network, high-speed rail network and the Trans-European conventional rail network, conventional rail network. The Gare du Nord railway station is the busiest in the EU, located in and near the city of Paris, in France. Rail transport in Europe is being synchronised with the European Rail Traffic Management System (ERTMS) with the goal of greatly enhancing safety, increase efficiency of train transports and enhance cross-border interoperability. This is done by replacing former national Railway signal, signalling equipment and operational procedures with a single new Europe-wide standard for train control and command systems. This system is conducted by the European Union Agency for Railways (ERA).
Telecommunications and space
Mobile communication European Union roaming regulations, roaming charges are abolished throughout the EU, Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway.
 The European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA), headquartered in Prague, Czech Republic, was established in 2021 to manage the European Union Space Programme in order to implement the pre-existing ''European Space Policy'', established on 22 May 2007 between the EU and the European Space Agency (ESA), known collectively as the ''European Space Council''. This was the first common political framework for space activities established by the EU. Each member state has pursued to some extent their own national space policy, though often co-ordinating through the ESA. Günter Verheugen, the European Commissioner for Enterprise and Industry, has stated that even though the EU is "a world leader in the technology, it is being put on the defensive by the United States and Russia and that it only has about a 10 year technological advantage on China and India, which are racing to catch up."
Galileo (satellite navigation), Galileo is a Satellite navigation, global navigation satellite system (GNSS) that went live in 2016, created by the EU through the ESA, operated by the EUSPA, with two ground operations centres in Fucine Lake, Fucino, Italy, and Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany. The €10 billion project is named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei. One of the aims of Galileo is to provide an independent high-precision positioning system so European political and military authorities do not have to rely on the US Global Positioning System, GPS, or the Russian GLONASS systems, which could be disabled or degraded by their operators at any time. The European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS) is a satellite-based augmentation system (SBAS) developed by the ESA and EUROCONTROL. Currently, it supplements the GPS by reporting on the reliability and accuracy of their positioning data and sending out corrections. The system will supplement Galileo in a future version. The Copernicus Programme is the EU's Earth observation programme coordinated and managed by EUSPA in partnership with ESA. It aims at achieving a global, continuous, autonomous, high quality, wide range Earth observation capacity, providing accurate, timely and easily accessible information to, among other things, improve the management of the environment, understand and Climate change mitigation, mitigate the effects of climate change, and ensure civil security.
The European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA), headquartered in Prague, Czech Republic, was established in 2021 to manage the European Union Space Programme in order to implement the pre-existing ''European Space Policy'', established on 22 May 2007 between the EU and the European Space Agency (ESA), known collectively as the ''European Space Council''. This was the first common political framework for space activities established by the EU. Each member state has pursued to some extent their own national space policy, though often co-ordinating through the ESA. Günter Verheugen, the European Commissioner for Enterprise and Industry, has stated that even though the EU is "a world leader in the technology, it is being put on the defensive by the United States and Russia and that it only has about a 10 year technological advantage on China and India, which are racing to catch up."
Galileo (satellite navigation), Galileo is a Satellite navigation, global navigation satellite system (GNSS) that went live in 2016, created by the EU through the ESA, operated by the EUSPA, with two ground operations centres in Fucine Lake, Fucino, Italy, and Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany. The €10 billion project is named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei. One of the aims of Galileo is to provide an independent high-precision positioning system so European political and military authorities do not have to rely on the US Global Positioning System, GPS, or the Russian GLONASS systems, which could be disabled or degraded by their operators at any time. The European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS) is a satellite-based augmentation system (SBAS) developed by the ESA and EUROCONTROL. Currently, it supplements the GPS by reporting on the reliability and accuracy of their positioning data and sending out corrections. The system will supplement Galileo in a future version. The Copernicus Programme is the EU's Earth observation programme coordinated and managed by EUSPA in partnership with ESA. It aims at achieving a global, continuous, autonomous, high quality, wide range Earth observation capacity, providing accurate, timely and easily accessible information to, among other things, improve the management of the environment, understand and Climate change mitigation, mitigate the effects of climate change, and ensure civil security.
Agriculture and fisheries
Regional development
Labour
The free movement of persons means that Citizenship of the European Union, EU citizens can move freely between member states to live, work, study or retire in another country. This required the lowering of administrative formalities and recognition of professional qualifications of other states. The EU seasonally adjusted unemployment rate was 6.7 per cent in September 2018. The euro area unemployment rate was 8.1 per cent. Among the member states, the lowest unemployment rates were recorded in the Czech Republic (2.3 per cent), Germany and Poland (both 3.4 per cent), and the highest in Spain (14.9 per cent) and Greece (19.0 in July 2018).Freedom, security and justice
 Since the creation of the European Union in 1993, it has developed its competencies in the area of justice and home affairs; initially at an intergovernmental level and later by supranationalism. Accordingly, the union has legislated in areas such as European Arrest Warrant, extradition, family law, asylum law, and criminal justice.
The EU has also established agencies to co-ordinate police, prosecution and civil litigations across the member states: Europol for police co-operation, CEPOL for training of police forces and the Eurojust for co-operation between prosecutors and courts. It also operates the EUCARIS database of vehicles and drivers, the Eurodac, the European Criminal Records Information System, the European Cybercrime Centre, FADO, Public Register of Travel and Identity Documents Online, PRADO and others.
Prohibitions against discrimination have a long standing in the treaties. In more recent years, these have been supplemented by powers to legislate against discrimination based on race, religion, disability, age, and sexual orientation.See Article 2(7) of the Amsterdam Treaty o
Since the creation of the European Union in 1993, it has developed its competencies in the area of justice and home affairs; initially at an intergovernmental level and later by supranationalism. Accordingly, the union has legislated in areas such as European Arrest Warrant, extradition, family law, asylum law, and criminal justice.
The EU has also established agencies to co-ordinate police, prosecution and civil litigations across the member states: Europol for police co-operation, CEPOL for training of police forces and the Eurojust for co-operation between prosecutors and courts. It also operates the EUCARIS database of vehicles and drivers, the Eurodac, the European Criminal Records Information System, the European Cybercrime Centre, FADO, Public Register of Travel and Identity Documents Online, PRADO and others.
Prohibitions against discrimination have a long standing in the treaties. In more recent years, these have been supplemented by powers to legislate against discrimination based on race, religion, disability, age, and sexual orientation.See Article 2(7) of the Amsterdam Treaty oeur-lex.europa.eu
The treaties declare that the European Union itself is "founded on the values of respect for human dignity, liberty, freedom, democracy, equality before the law, equality, the rule of law and respect for human rights, including the rights of persons belonging to minority group, minorities ... in a society in which pluralism, non-discrimination, tolerance, justice, solidarity and equality between women and men prevail." By virtue of these powers, the EU has enacted legislation on sexism in the work-place, ageism, age discrimination, and racism, racial discrimination.Council Directive 2000/43/EC of 29 June 2000 implementing the principle of equal treatment between persons irrespective of racial or ethnic origin (OJ L 180, 19 July 2000, pp. 22–26); Council Directive 2000/78/EC of 27 November 2000 establishing a general framework for equal treatment in employment and occupation (OJ L 303, 2 December 2000, pp. 16–22). In 2009, the Lisbon Treaty gave legal effect to the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union. The charter is a codified catalogue of fundamental rights against which the EU's legal acts can be judged. It consolidates many rights which were previously recognised by the Court of Justice and derived from the "constitutional traditions common to the member states." The Court of Justice has long recognised fundamental rights and has, on occasion, invalidated EU legislation based on its failure to adhere to those fundamental rights. Signing the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR) is a condition for EU membership.and is effectively treated as one of the Copenhagen criteri
Assembly.coe.int.
This is a political and not a legal requirement for membership. Previously, the EU itself could not accede to the convention as it is neither a state nor had the competence to accede. The Lisbon Treaty and Protocol 14 to the ECHR have changed this: the former binds the EU to accede to the convention while the latter formally permits it. The EU is independent from the Council of Europe, although they share purpose and ideas, especially on the rule of law, human rights and democracy. Furthermore, the European Convention on Human Rights and European Social Charter, as well as the source of law for the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union, Charter of Fundamental Rights are created by the Council of Europe. The EU has also promoted human rights issues in the wider world. The EU opposes the death penalty and has proposed its worldwide abolition. Abolition of the death penalty is a condition for EU membership. On 19 October 2020, the European Union revealed new plans to create a legal structure to act against human rights violations worldwide. The new plan was expected to provide the European Union with greater flexibility to target and sanction those responsible for serious human rights violations and abuses around the world.
Foreign relations
Humanitarian aid
The ECHO (European Commission), European Commission's Humanitarian Aid and Civil Protection department, or "ECHO", provides humanitarian aid from the EU to developing country, developing countries. In 2012, its budget amounted to million, 51 per cent of the budget went to Africa and 20 per cent to Asia, Latin America, the Caribbean and Pacific, and 20 per cent to the Middle East and Mediterranean. Humanitarian aid is financed directly by the budget (70 per cent) as part of the financial instruments for external action and also by the European Development Fund (30 per cent).Mikaela Gavas 2010Financing European development cooperation: the Financial Perspectives 2014–2020.
London: Overseas Development Institute The EU's external action financing is divided into 'geographic' instruments and 'thematic' instruments. The 'geographic' instruments provide aid through the Development Cooperation Instrument (DCI, billion, 2007–2013), which must spend 95 per cent of its budget on official development assistance (ODA), and from the European Neighbourhood and Partnership Instrument (ENPI), which contains some relevant programmes. The European Development Fund (EDF, billion for the period 2008–2013 and billion for the period 2014–2020) is made up of voluntary contributions by member states, but there is pressure to merge the EDF into the budget-financed instruments to encourage increased contributions to match the 0.7 per cent target and allow the European Parliament greater oversight. In 2016, the average among EU countries was 0.4 per cent and five had met or exceeded the 0.7 per cent target: Denmark, Germany, Luxembourg, Sweden and the United Kingdom. If considered collectively, EU member states are the largest contributor of List of development aid country donors, foreign aid in the world.
International cooperation and development partnerships
 The European Union uses foreign relations instruments like the European Neighbourhood Policy which seeks to tie those countries to the east and south of the European territory of the EU to the union. These countries, primarily developing countries, include some who seek to one day become either a member state of the European Union, or more closely integrated with the European Union. The EU offers financial assistance to countries within the European Neighbourhood, so long as they meet the strict conditions of government reform, economic reform and other issues surrounding positive transformation. This process is normally underpinned by an Action Plan, as agreed by both Brussels and the target country.
The European Union uses foreign relations instruments like the European Neighbourhood Policy which seeks to tie those countries to the east and south of the European territory of the EU to the union. These countries, primarily developing countries, include some who seek to one day become either a member state of the European Union, or more closely integrated with the European Union. The EU offers financial assistance to countries within the European Neighbourhood, so long as they meet the strict conditions of government reform, economic reform and other issues surrounding positive transformation. This process is normally underpinned by an Action Plan, as agreed by both Brussels and the target country.
 There is also the worldwide European Union Global Strategy. International recognition of sustainable development as a key element is growing steadily. Its role was recognised in three major UN summits on sustainable development: the 1992 Earth Summit, UN Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; the 2002 World Summit on Sustainable Development (WSSD) in Johannesburg, South Africa; and the 2012 United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development, UN Conference on Sustainable Development (UNCSD) in Rio de Janeiro. Other key global agreements are the Paris Agreement and the Sustainable Development Goals, 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development (United Nations, 2015). The SDGs recognise that all countries must stimulate action in the following key areas – people, planet, prosperity, peace and partnership – in order to tackle the global challenges that are crucial for the survival of humanity.
EU development action is based on the European Consensus on Development, which was endorsed on 20 December 2005 by EU Member States, the council, the European Parliament and the commission. It is applied from the principles of Capability approach and Rights-based approach to development. Funding is provided by the Instrument for Pre-Accession Assistance and the Global Europe programmes.
Partnership and cooperation agreements are bilateral agreements with non-member nations.
There is also the worldwide European Union Global Strategy. International recognition of sustainable development as a key element is growing steadily. Its role was recognised in three major UN summits on sustainable development: the 1992 Earth Summit, UN Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; the 2002 World Summit on Sustainable Development (WSSD) in Johannesburg, South Africa; and the 2012 United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development, UN Conference on Sustainable Development (UNCSD) in Rio de Janeiro. Other key global agreements are the Paris Agreement and the Sustainable Development Goals, 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development (United Nations, 2015). The SDGs recognise that all countries must stimulate action in the following key areas – people, planet, prosperity, peace and partnership – in order to tackle the global challenges that are crucial for the survival of humanity.
EU development action is based on the European Consensus on Development, which was endorsed on 20 December 2005 by EU Member States, the council, the European Parliament and the commission. It is applied from the principles of Capability approach and Rights-based approach to development. Funding is provided by the Instrument for Pre-Accession Assistance and the Global Europe programmes.
Partnership and cooperation agreements are bilateral agreements with non-member nations.
Sustainability, territorial and social cohesion
The European Union has long sought to mitigate the effects of free markets by protecting workers' rights and preventing Social dumping, social and environmental dumping. To this end it has adopted laws establishing minimum employment and environmental standards. These included the Working Time Directive and the Environmental Impact Assessment Directive 2011, Environmental Impact Assessment Directive.Social rights and equality
The EU has also sought to coordinate the social security and health systems of member states to facilitate individuals exercising free movement rights and to ensure they maintain their ability to access social security and health services in other member states. Social security main legislation is found in the Equal Treatment in Occupational Social Security Directive 86/378, the Equal Treatment in Social Security Directive 79/7/EEC, the Social Security Regulation 1408/71/EC and 883/2004/EC and the Directive 2005/36/EC. The European Directive about Minimum Wage, which looks to lift minimum wages and strengthen collective bargaining was approved by the European Parliament in September 2022 Since 2019 there has been a European commissioner for equality and the European Institute for Gender Equality has existed since 2007. A Directive on countering gender-based violence has been proposed. In September 2022, a European Care strategy was approved in order to provide "quality, affordable and accessible care services". In 2020, the first ever European Union Strategy on LGBTIQ equality was approved under Helena Dalli mandate. In December 2021, the commission announced the intention of codifying a union-wide law against LGBT hate crimes. The European Social Charter is the main body that recognises the social rights of European citizens. Housing, youth, childhood, Functional diversity or elderly care are supportive competencies of the European Union and can be financed by the European Social Fund. The European Pillar of Social Rights contains a preamble and 3 chapters with target values for 20 fields: Chapter I: Equal opportunities and access to the labour market (general education, professional training and lifelong learning, gender equality, equal opportunities, active support for employment) Chapter II: Fair working conditions (secure and adaptable employment, wages, information about employment conditions and protection in the event of dismissals, social dialogue and involvement of workers, work-life balance, healthy, safe and well-adapted working environments and data protection) Chapter III: Social protection and inclusion (childcare and support for children, social protection, unemployment benefits, minimum income, old age income and pensions, healthcare, inclusion of people with disabilities, long-term care, housing and assistance for the homeless, access to essential services) The EPSR is intended to act as a reference document of sorts, by means of which the labour markets and social standards in the Member States may approach the standards defined in the Pillar in the long term.Demographics
Urbanisation
The EU's population is highly urbanised: some 75 per cent of inhabitants lived in urban areas in 2006. Cities are largely spread out across the EU with a large grouping in and around the Benelux. The EU contains about 40 urban areas with populations of over 1million. With a population of over 13 million, Paris is the largest metropolitan area and the only megacity in the EU. Paris is followed by Madrid, Barcelona, Berlin, the Ruhr, Milan, and Rome, all with a metropolitan population of over 4million. The EU also has numerous Conurbation, polycentric urbanised regions like Rhine-Ruhr (Cologne, Dortmund, Düsseldorf et al.), Randstad (Amsterdam, Rotterdam, The Hague, Utrecht et al.), Frankfurt Rhine-Main (Frankfurt, Wiesbaden, Mainz et al.), the Flemish Diamond (Antwerp, Brussels, Leuven, Ghent et al.) and Upper Silesian metropolitan area, Upper Silesian area (Katowice, Ostrava et al.).Languages
The EU has 24 official languages: Bulgarian language, Bulgarian, Croatian language, Croatian, Czech language, Czech, Danish language, Danish, Dutch language, Dutch, English language, English, Estonian language, Estonian, Finnish language, Finnish, French language, French, German language, German, Greek language, Greek, Hungarian language, Hungarian, Italian language, Italian, Irish language, Irish, Latvian language, Latvian, Lithuanian language, Lithuanian, Maltese language, Maltese, Polish language, Polish, Portuguese language, Portuguese, Romanian language, Romanian, Slovak language, Slovak, Slovene language, Slovene, Spanish language, Spanish, and Swedish language, Swedish. Important documents, such as legislation, are translated into every official language and the European Parliament provides translation for documents and plenary sessions. In 2020, the EU stated that translation and interpreting costs were less than 1% of its annual budget of €148 billion. Due to the high number of official languages, most of the institutions use only a handful of working languages. The European Commission conducts its internal business in three ''procedural languages'': English, French, and German Similarly, the Court of Justice of the European Union uses French as the working language, while the European Central Bank conducts its business primarily in English. Even though language policy is the responsibility of member states, EU institutions promote multilingualism among its citizens. In 2012, English was the most widely spoken language in the EU, being understood by 51 per cent of the EU population when counting both native and non-native speakers. However, following the UK's exit from the bloc in early 2020, the percentage of the EU population who spoke English as their native language fell from 13 per cent to 1 per cent. German is the most widely spoken mother tongue (18 per cent of the EU population), and the second most widely understood foreign language, followed by French (13 per cent of the EU population). In addition, both are official languages of several EU member states. More than half (56 per cent) of EU citizens are able to engage in a conversation in a language other than their mother tongue. A total of twenty official languages of the EU belong to the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, represented by the Balto-Slavic,Slavic: Bulgarian language, Bulgarian, Croatian language, Croatian, Czech language, Czech, Polish language, Polish, Slovak language, Slovak and Slovene language, Slovene. Baltic: Latvian language, Latvian and Lithuanian language, Lithuanian. the Italic languages, Italic,French language, French, Italian language, Italian, Portuguese language, Portuguese, Romanian language, Romanian and Spanish language, Spanish. the Germanic Europe, Germanic,Danish language, Danish, Dutch language, Dutch, English language, English, German language, German and Swedish language, Swedish. the Hellenic languages, Hellenic,Greek language, Greek and the Celtic languages, CelticIrish language, Irish branches. Only four languages, namely Hungarian language, Hungarian, Finnish language, Finnish, Estonian language, Estonian (all three Uralic languages, Uralic), and Maltese language, Maltese (Semitic languages, Semitic), are not Indo-European languages. The three official alphabets of the EU (Cyrillic script, Cyrillic, Latin alphabet, Latin, and Greek alphabet, modern Greek) all derive from the Archaic Greek alphabets, Archaic Greek scripts. Luxembourgish (in Luxembourg) and Turkish language, Turkish (in Cyprus) are the only two national languages that are not official languages of the EU. On 26 February 2016, it was made public that Cyprus has asked to make Turkish an official EU language, in a "gesture" that could help solve the Cyprus dispute, division of the country. Besides the 24 official languages, there are about 150 regional language, regional and minority languages, spoken by up to 50 million people. Catalan language, Catalan, Galician language, Galician and Basque language, Basque are not recognised official languages of the EU but have official status in one member state (Spain): therefore, official translations of the treaties are made into them and citizens have the right to correspond with the institutions in these languages. The European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages ratified by most EU states provides general guidelines that states can follow to protect their linguistic heritage. The European Day of Languages is held annually on 26 September and is aimed at encouraging language learning across Europe.Religion
Education and research
 Basic education is an area where the EU's role is limited to supporting national governments. In higher education, the policy was developed in the 1980s in programmes supporting exchanges and mobility. The most visible of these has been the Erasmus Programme, a university exchange programme which began in 1987. In its first 20 years, it supported international exchange opportunities for well over 1.5 million university and college students and became a symbol of European student life.
There are similar programmes for school pupils and teachers, for trainees in vocational education, vocational education and training, and for adult learners in the Lifelong Learning Programme 2007–2013. These programmes are designed to encourage a wider knowledge of other countries and to spread good practices in the education and training fields across the EU. Through its support of the Bologna Process, the EU is supporting comparable standards and compatible degrees across Europe.
Scientific development is facilitated through the EU's Framework Programmes for Research and Technological Development, Framework Programmes, the first of which started in 1984. The aims of EU policy in this area are to co-ordinate and stimulate research. The independent European Research Council allocates EU funds to European or national research projects. EU Framework Programmes for Research and Technological Development, research and technological framework programmes deal in a number of areas, for example energy where the aim is to develop a diverse mix of renewable energy to help the environment and to reduce dependence on imported fuels.
Basic education is an area where the EU's role is limited to supporting national governments. In higher education, the policy was developed in the 1980s in programmes supporting exchanges and mobility. The most visible of these has been the Erasmus Programme, a university exchange programme which began in 1987. In its first 20 years, it supported international exchange opportunities for well over 1.5 million university and college students and became a symbol of European student life.
There are similar programmes for school pupils and teachers, for trainees in vocational education, vocational education and training, and for adult learners in the Lifelong Learning Programme 2007–2013. These programmes are designed to encourage a wider knowledge of other countries and to spread good practices in the education and training fields across the EU. Through its support of the Bologna Process, the EU is supporting comparable standards and compatible degrees across Europe.
Scientific development is facilitated through the EU's Framework Programmes for Research and Technological Development, Framework Programmes, the first of which started in 1984. The aims of EU policy in this area are to co-ordinate and stimulate research. The independent European Research Council allocates EU funds to European or national research projects. EU Framework Programmes for Research and Technological Development, research and technological framework programmes deal in a number of areas, for example energy where the aim is to develop a diverse mix of renewable energy to help the environment and to reduce dependence on imported fuels.
Health
Culture
Cultural co-operation between member states has been an interest of the European Union since its inclusion as a community competency in the Maastricht Treaty. Actions taken in the cultural area by the EU include the Culture 2000 seven-year programme, the European Cultural Month event, and orchestras such as the European Union Youth Orchestra. The European Capital of Culture programme selects one or more cities in every year to assist the Sociocultural evolution, cultural development of that city.Sport
 Sport is mainly the responsibility of the member states or other international organisations, rather than of the EU. There are some EU policies that have affected sport, such as the free movement of workers, which was at the core of the Bosman ruling that prohibited national football leagues from imposing quotas on foreign players with EU member state citizenship.
The Treaty of Lisbon requires any application of economic rules to take into account the specific nature of sport and its structures based on voluntary activity. This followed lobbying by governing organisations such as the International Olympic Committee and FIFA, due to objections over the application of free market principles to sport, which led to an increasing gap between rich and poor clubs. The EU does fund a programme for Israeli, Jordanian, Irish, and British football coaches, as part of the Football 4 Peace project.
Sport is mainly the responsibility of the member states or other international organisations, rather than of the EU. There are some EU policies that have affected sport, such as the free movement of workers, which was at the core of the Bosman ruling that prohibited national football leagues from imposing quotas on foreign players with EU member state citizenship.
The Treaty of Lisbon requires any application of economic rules to take into account the specific nature of sport and its structures based on voluntary activity. This followed lobbying by governing organisations such as the International Olympic Committee and FIFA, due to objections over the application of free market principles to sport, which led to an increasing gap between rich and poor clubs. The EU does fund a programme for Israeli, Jordanian, Irish, and British football coaches, as part of the Football 4 Peace project.
Symbols
 The flag of Europe consists of a Circle of stars, circle of 12 golden stars on a blue background. Originally designed in 1955 for the Council of Europe, the flag was adopted by the European Communities, the predecessors of the present European Union, in 1986. The Council of Europe gave the flag a symbolic description in the following terms, though the official symbolic description adopted by the EU omits the reference to the "Western world":
The flag of Europe consists of a Circle of stars, circle of 12 golden stars on a blue background. Originally designed in 1955 for the Council of Europe, the flag was adopted by the European Communities, the predecessors of the present European Union, in 1986. The Council of Europe gave the flag a symbolic description in the following terms, though the official symbolic description adopted by the EU omits the reference to the "Western world": Guide graphique relatif à l'emblème européen
' (1996), p. 3: ''Description symbolique: Sur le fond bleu du ciel, les étoiles figurant les peuples d'Europe forment un cercle en signe d'union. Elles sont au nombre invariable de douze, symbole de la perfection et de la plénitude''...''Description héraldique: Sur fond azur, un cercle composé de douze étoiles d'or à cinq rais, dont les pointes ne se touchent pas''. c.f. ''Motto of the European Union, United in Diversity'' was adopted as the motto of the union in 2000, having been selected from A motto for Europe, proposals submitted by school pupils. Since 1985, the flag day of the union has been Europe Day, on 9 May (the date of the 1950 Schuman declaration). The Anthem of Europe, anthem of the EU is an instrumental version of the prelude to the ''Ode to Joy'', the 4th movement of Ludwig van Beethoven's Symphony No. 9 (Beethoven), ninth symphony. The anthem was adopted by European Community leaders in 1985 and has since been played on official occasions. Besides naming the continent, the Greek mythology, Greek mythological figure of Europa (mythology), Europa has frequently been employed as a National personification, personification of Europe. Known from the myth in which Zeus seduces her in the guise of a white bull, Europa has also been referred to in relation to the present union. Statues of Europa and the bull decorate several of the EU's institutions and a portrait of her is seen on the 2013 series of euro banknotes. The bull is, for its part, depicted on all residence permit cards. Charlemagne, Charles the Great, also known as Charlemagne ( la, Carolus Magnus) and later recognised as ''Pater Europae'' ("Father of Europe"),Riché, Preface xviii, Pierre Riché reflects: "[H]e enjoyed an exceptional destiny, and by the length of his reign, by his conquests, legislation and legendary stature, he also profoundly marked the history of Western Europe." has a symbolic relevance to Europe. The commission has named Charlemagne building, one of its central buildings in Brussels after Charlemagne and the city of Aachen has since 1949 awarded the Charlemagne Prize to champions of European unification. Since 2008, the organisers of this prize, in conjunction with the European Parliament, have awarded the European Charlemagne Youth Prize, Charlemagne Youth Prize in recognition of similar efforts led by young people.
Media
 Media freedom is a Fundamental rights, fundamental right that applies to all Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union and its EU citizens, citizens, as defined in the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights as well as the European Convention on Human Rights.Maria Poptcheva
Media freedom is a Fundamental rights, fundamental right that applies to all Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union and its EU citizens, citizens, as defined in the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights as well as the European Convention on Human Rights.Maria PoptchevaPress freedom in the EU Legal framework and challenges
EPRS , European Parliamentary Research Service, Briefing April 2015 Within the EU enlargement process, guaranteeing media freedom is named a "key indicator of a country's readiness to become part of the EU". The majority of media in the European Union are national-orientated, although some EU-wide media focusing on European affairs have emerged since the early 1990s, such as Euronews, Eurosport, EUobserver, EURACTIV or Politico Europe. Arte, ARTE is a public Franco-German TV network that promotes programming in the areas of culture and the arts. 80 per cent of its programming are provided in equal proportion by the two member companies, while the remainder is being provided by the European Economic Interest Grouping ''ARTE GEIE'' and the channel's European partners. The MEDIA Programme of the European Union has supported the European popular film and audiovisual industries since 1991. It provides support for the development, promotion and distribution of European works within Europe and beyond.
Influence
 The European Union has had a significant positive economic effect on most member states. According to a 2019 study of the member states who joined from 1973 to 2004, "without European integration, per capita incomes would have been, on average, approximately 10 per cent lower in the first ten years after joining the EU." Greece was the exception reported by the study, which analysed up to 2008, "to avoid confounding effects from the global financial crisis". A 2021 study in the ''Journal of Political Economy'' found that the 2004 enlargement had aggregate beneficial economic effects on all groups in both the old and new member states. The largest winners were the new member states, in particular unskilled labour in the new member states.
The European Union has contributed to peace in Europe, in particular by pacifying border disputes, and to the spread of democracy, especially by encouraging democratic reforms in aspiring Eastern European member states after the collapse of the USSR. Scholar Thomas Risse wrote in 2009, "there is a consensus in the literature on Eastern Europe that the EU membership perspective had a huge anchoring effects for the new democracies." However, R. Daniel Kelemen argues that the EU has proved beneficial to leaders who are overseeing democratic backsliding, as the EU is reluctant to intervene in domestic politics, gives authoritarian governments funds which they can use to strengthen their regimes, and because freedom of movement within the EU allows dissenting citizens to leave their backsliding countries. At the same time, the union provides an external constraint that prevents soft authoritarian regimes from progressing into hard dictatorships.
The European Union has had a significant positive economic effect on most member states. According to a 2019 study of the member states who joined from 1973 to 2004, "without European integration, per capita incomes would have been, on average, approximately 10 per cent lower in the first ten years after joining the EU." Greece was the exception reported by the study, which analysed up to 2008, "to avoid confounding effects from the global financial crisis". A 2021 study in the ''Journal of Political Economy'' found that the 2004 enlargement had aggregate beneficial economic effects on all groups in both the old and new member states. The largest winners were the new member states, in particular unskilled labour in the new member states.
The European Union has contributed to peace in Europe, in particular by pacifying border disputes, and to the spread of democracy, especially by encouraging democratic reforms in aspiring Eastern European member states after the collapse of the USSR. Scholar Thomas Risse wrote in 2009, "there is a consensus in the literature on Eastern Europe that the EU membership perspective had a huge anchoring effects for the new democracies." However, R. Daniel Kelemen argues that the EU has proved beneficial to leaders who are overseeing democratic backsliding, as the EU is reluctant to intervene in domestic politics, gives authoritarian governments funds which they can use to strengthen their regimes, and because freedom of movement within the EU allows dissenting citizens to leave their backsliding countries. At the same time, the union provides an external constraint that prevents soft authoritarian regimes from progressing into hard dictatorships.
See also
* Outline of the European Union * Special territories of members of the European Economic Area * List of country groupings * List of multilateral free-trade agreements * Euroscepticism * Pan-European nationalism * Brexit withdrawal agreement * EU–UK Trade and Cooperation Agreement * African UnionNotes
References
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * *Excerpt and text search
* * *
External links
– Europa (web portal), official web portal
Historical Archives of the European Union
Eurostat – European Union Statistics Explained
CIA World Factbook: European Union
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
The European Union: Questions and Answers
Congressional Research Service. * * * {{Authority control European Union, European Economic Area 1993 establishments in Europe Articles containing video clips Confederations G20 nations G7 nations International organizations based in Europe International political organizations Organisations based in Brussels Organizations awarded Nobel Peace Prizes Organizations established in 1993 Political organizations based in Europe Political systems Supranational unions Trade blocs United Nations General Assembly observers