EDCI on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (EDC, EDAC or EDCI) is a water-soluble carbodiimide usually handled as the hydrochloride. It is typically employed in the 4.0-6.0 pH range. It is generally used as a carboxyl activating agent for the coupling of primary amines to yield amide bonds. While other carbodiimides like dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) or diisopropylcarbodiimide (DIC) are also employed for this purpose, EDC has the advantage that the urea byproduct formed (often challenging to remove in the case of DCC or DIC) can be washed away from the amide product using dilute acid. Additionally, EDC can also be used to activate
phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
groups in order to form phosphomonoesters and phosphodiesters. Common uses for this carbodiimide include peptide synthesis, protein crosslinking to nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main cl ...
s, but also in the preparation of immunoconjugate Immunoconjugates are antibodies conjugated (joined) to a second molecule, usually a toxin, radioisotope or label.
These conjugates are used in immunotherapy and to develop monoclonal antibody therapy as a targeted form of chemotherapy when they ar ...
s. EDC is often used in combination with ''N''-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) for the immobilisation of large biomolecules. Recent work has also used EDC to assess the structure state of uracil nucleobases in RNA.
Preparation
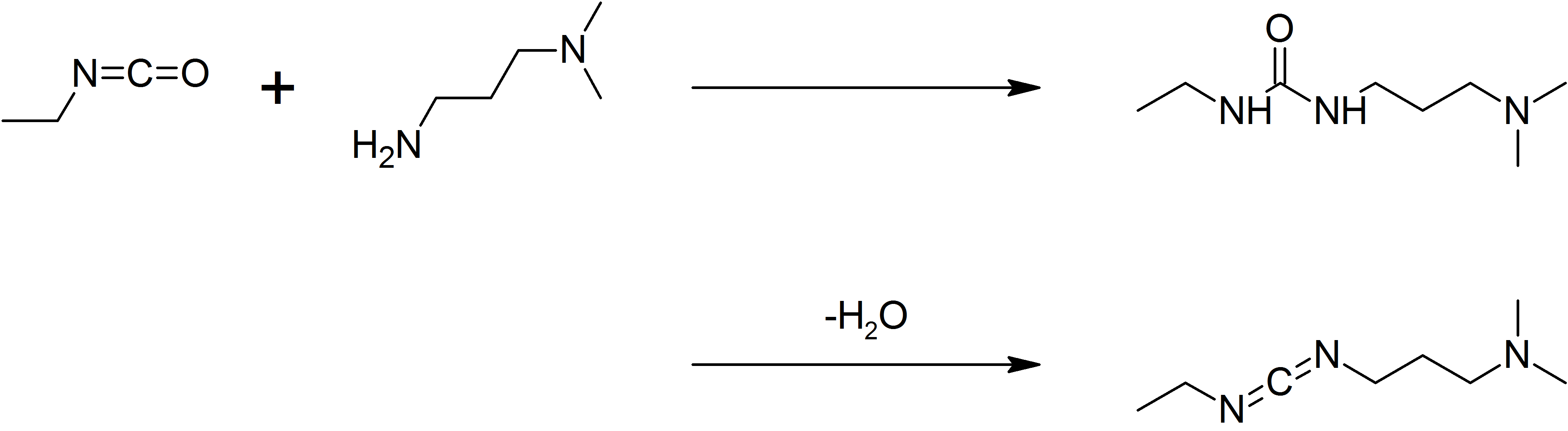
EDC is commercially available. It may be prepared by coupling ethyl isocyanate to ''N'',''N''-dimethylpropane-1,3-diamine to give aurea
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid.
Urea serves an important r ...
, followed by dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water, with an accompanying disruption of metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds free water intake, usually due to exercise, disease, or high environmental temperature. Mil ...
:
:
Mechanism
EDC couples primary amines, and other nucleophiles, to carboxylic acids by creating an activated ester leaving group. First, the carbonyl of the acid attacks the carbodiimide of EDC, and there is a subsequent proton transfer. The primary amine then attacks the carbonyl carbon of the acid which forms a tetrahedral intermediate before collapsing and discharging the urea byproduct. The desired amide is obtained.References
Further reading
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide, 1- Carbodiimides Reagents for biochemistry