The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a
chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the
States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first
joint-stock company in the world, granting it a 21-year
monopoly to carry out trade activities in Asia. Shares in the company could be bought by any resident of the
United Provinces and then subsequently bought and sold in open-air secondary markets (one of which became the
Amsterdam Stock Exchange
Euronext Amsterdam is a stock exchange based in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. Formerly known as the Amsterdam Stock Exchange, it merged on 22 September 2000 with the Brussels Stock Exchange and the Paris Stock Exchange to form Euronext. The r ...
). It is sometimes considered to have been the first
multinational corporation. It was a powerful company, possessing quasi-governmental powers, including the ability to wage war, imprison and execute convicts, negotiate treaties, strike
its own coins, and establish colonies. They are also known for their international slave trade.
Statistically, the VOC eclipsed all of its rivals in the Asia trade. Between 1602 and 1796 the VOC sent almost a million Europeans to work in the Asia trade on 4,785 ships, and netted for their efforts more than 2.5 million tons of Asian trade goods. By contrast, the rest of Europe combined sent only 882,412 people from 1500 to 1795, and the fleet of the
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
(later
British)
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Sou ...
, the VOC's nearest competitor, was a distant second to its total traffic with 2,690 ships and a mere one-fifth the tonnage of goods carried by the VOC. The VOC enjoyed huge profits from its spice monopoly through most of the 17th century.
Having been set up in 1602 to profit from the
Malukan spice trade, the VOC established a capital in the port city of
Jayakarta in 1609 and changed the city name into
Batavia (now
Jakarta). Over the next two centuries the company acquired additional ports as trading bases and safeguarded their interests by taking over surrounding territory. It remained an important trading concern and paid an 18% annual
dividend
A dividend is a distribution of profits by a corporation to its shareholders. When a corporation earns a profit or surplus, it is able to pay a portion of the profit as a dividend to shareholders. Any amount not distributed is taken to be re-i ...
for almost 200 years.
Weighed down by smuggling, corruption and growing administrative costs in the late 18th century, the company went bankrupt and was formally dissolved in 1799. Its possessions and debt were taken over by the government of the Dutch
Batavian Republic. The former territories owned by the VOC went on to become the
Dutch East Indies and were expanded over the course of the 19th century to include the entirety of the Indonesian archipelago. In the 20th century, these islands would form the
Republic of Indonesia.
Company name, logo, and flag


In Dutch, the name of the company was the Vereenigde Nederlandsche Geoctroyeerde Oostindische Compagnie (abbreviated as the VOC), literally the 'United Dutch Chartered East India Company' (the United East India Company). The company's
monogram logo consisted of a large
capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used fo ...
'V' with an O on the left and a C on the right half and was possibly the first globally recognised
corporate logo
A logo (abbreviation of logotype; ) is a graphic mark, emblem, or symbol used to aid and promote public identification and recognition. It may be of an abstract or figurative design or include the text of the name it represents as in a wordma ...
.
[ Brook, Timothy: '' Vermeer's Hat: The Seventeenth Century and the Dawn of the Global World''. (London: ]Profile Books
Profile Books is a British independent book publishing firm founded in 1996. It publishes non-fiction subjects including history, biography, memoir, politics, current affairs, travel and popular science.
Profile Books is distributed in the UK ...
, 2008) It appeared on various corporate items, such as
cannon
A cannon is a large- caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder ...
s and coins. The first letter of the hometown of the chamber conducting the operation was placed on top. The monogram, versatility, flexibility, clarity, simplicity, symmetry, timelessness, and symbolism are considered notable characteristics of the VOC's professionally designed logo. Those elements ensured its success at a time when the concept of the
corporate identity was virtually unknown.
An Australian
vintner has used the VOC logo since the late 20th century, having re-registered the company's name for the purpose. The flag of the company was red, white, and blue, with the company logo embroidered on it.
Around the world, and especially in English-speaking countries, the VOC is widely known as the 'Dutch East India Company'. The name 'Dutch East India Company' is used to make a distinction from the
ritishEast India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Sou ...
(EIC) and
other East Indian companies (such as the
Danish East India Company,
French East India Company,
Portuguese East India Company
The Portuguese East India Company ( pt, Companhia do commércio da Índia or ) was a short-lived and ill-fated attempt by Philip III of Portugal, to create a chartered company to ensure the security of their interests in India, in the face of t ...
, and the
Swedish East India Company). The company's alternative names that have been used include the 'Dutch East Indies Company', 'United East India Company', 'Jan Company', or 'Jan Compagnie'.
History
Origins
Before the
Dutch Revolt, which started in 1566/68, the Dutch city of
Antwerp had played an important role as a distribution center in northern Europe. After 1591, however, the Portuguese used an international syndicate of the German
Fugger family and
Welser family
Welser was a German banking and merchant family, originally a patrician family based in Augsburg and Nuremberg, that rose to great prominence in international high finance in the 16th century as bankers to the Habsburgs and financiers of Char ...
, as well as Spanish and Italian firms, which operated out of
Hamburg as the northern staple port to distribute their goods, thereby cutting Dutch merchants out of the trade. At the same time, the Portuguese trade system was unable to increase supply to satisfy growing demand, in particular the demand for pepper. Demand for spices was relatively
inelastic; therefore, each lag in the supply of pepper caused a sharp rise in pepper prices.
In 1580, the
Portuguese crown was
united in a
personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interli ...
with the
Spanish crown (called the
Iberian Union), of which the
Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiograph ...
was at war. The
Portuguese Empire thenceforward became an appropriate target for Dutch military incursions. These factors motivated Dutch merchants to enter the intercontinental spice trade themselves. Further, a number of Dutch merchants and explorers, such as
Jan Huyghen van Linschoten and
Cornelis de Houtman, went on to obtain first hand knowledge of the "secret" Portuguese trade routes and practices that were already in place, thereby providing further opportunity for the Dutch to enter the trade.

The stage was thus set for Dutch expeditions to the
Indonesian islands, beginning with
James Lancaster in 1591,
Cornelis de Houtman in 1595 and again in 1598,
Jacob Van Neck
Jacob Corneliszoon van Neck (often anglicized to Jacob Cornelius van Neck) (1564–1638) was a Dutch naval officer and explorer who led the second Dutch expedition to Indonesia from 1598 to 1599.
Early life
Van Neck was from an Amsterdam famil ...
in 1598, Lancaster again in 1601, among others. During the four-ship exploratory expedition by
Frederick de Houtman
Frederick de Houtman ( – 21 October 1627) was a Dutch explorer, navigator, and colonial governor who sailed on the first Dutch expedition to the East Indies from 1595 until 1597, during which time he made observations of the southern ce ...
in 1595 to
Banten, the main pepper port of West Java, the crew clashed with both Portuguese and indigenous Javanese. Houtman's expedition then sailed east along the north coast of
Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
, losing twelve crew members to a Javanese attack at Sidayu and killing a local ruler in
Madura. Half the crew were lost before the expedition made it back to the Netherlands the following year, but with enough spices to make a considerable profit.

In 1598, an increasing number of fleets were sent out by competing merchant groups from around the Netherlands. Some fleets were lost, but most were successful, with some voyages producing high profits. In 1598, a
fleet of eight ships under
Jacob van Neck
Jacob Corneliszoon van Neck (often anglicized to Jacob Cornelius van Neck) (1564–1638) was a Dutch naval officer and explorer who led the second Dutch expedition to Indonesia from 1598 to 1599.
Early life
Van Neck was from an Amsterdam famil ...
had been the first Dutch fleet to reach the 'Spice Islands' of Maluku (also known as the Moluccas), cutting out the Javanese middlemen. The ships returned to Europe in 1599 and 1600 and the expedition made a 400 percent profit.
In 1600, the Dutch joined forces with the Muslim Hituese on
Ambon Island in an anti-Portuguese alliance, in return for which the Dutch were given the sole right to purchase spices from Hitu.
Dutch control of Ambon was achieved when the Portuguese surrendered their fort in Ambon to the Dutch-Hituese alliance. In 1613, the Dutch expelled the Portuguese from their
Solor fort, but a subsequent Portuguese attack led to a second change of hands; following this second reoccupation, the Dutch once again captured Solor in 1636.
East of
Solor, on the island of
Timor, Dutch advances were halted by an autonomous and powerful group of Portuguese Eurasians called the
Topasses. They remained in control of the
Sandalwood
Sandalwood is a class of woods from trees in the genus '' Santalum''. The woods are heavy, yellow, and fine-grained, and, unlike many other aromatic woods, they retain their fragrance for decades. Sandalwood oil is extracted from the woods for ...
trade and their resistance lasted throughout the 17th and 18th centuries, causing
Portuguese Timor
Portuguese Timor ( pt, Timor Português) was a colonial possession of Portugal that existed between 1702 and 1975. During most of this period, Portugal shared the island of Timor with the Dutch East Indies.
The first Europeans to arrive in th ...
to remain under the Portuguese sphere of control.
Formative years


At the time, it was customary for a company to be funded only for the duration of a single voyage and to be liquidated upon the return of the fleet. Investment in these expeditions was a very high-risk venture, not only because of the usual dangers of piracy, disease and shipwreck, but also because the interplay of inelastic demand and relatively elastic supply of spices could make prices tumble, thereby ruining prospects of profitability. To manage such risk, the forming of a
cartel to control supply would seem logical. In 1600, the English were the first to adopt this approach by bundling their resources into a monopoly enterprise, the
English East India Company, thereby threatening their Dutch competitors with ruin.
[De Vries and Van der Woude, p. 384–385]
In 1602, the Dutch government followed suit, sponsoring the creation of a single "United East Indies Company" that was also granted monopoly over the Asian trade. For a time in the seventeenth century, it was able to monopolise the trade in nutmeg, mace, and cloves and to sell these spices across European kingdoms and Emperor
Akbar the Great's
Mughal Empire at 14-17 times the price it paid in
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
; while Dutch profits soared, the local economy of the Spice Islands was destroyed. With a capital of 6,440,200
guilders, the new company's charter empowered it to build forts, maintain armies, and conclude treaties with Asian rulers. It provided for a venture that would continue for 21 years, with a financial accounting only at the end of each decade.
In February 1603, the company seized the
''Santa Catarina'', a 1500-ton Portuguese merchant
carrack, off the coast of Singapore. She was such a rich prize that her sale proceeds increased the capital of the VOC by more than 50%.
Also in 1603, the first permanent Dutch trading post in Indonesia was established in
Banten,
West Java, and in 1611, another was established at
Jayakarta (later "Batavia" and then "Jakarta").
In 1610, the VOC established the post of
governor-general to more firmly control their affairs in Asia. To advise and control the risk of
despotic governors-general, a
Council of the Indies (''Raad van Indië'') was created. The governor-general effectively became the main administrator of the VOC's activities in Asia, although the ''Heeren XVII'', a body of 17 shareholders representing different chambers, continued to officially have overall control.

VOC headquarters were located in
Ambon during the tenures of the first three governors-general (1610–1619), but it was not a satisfactory location. Although it was at the centre of the spice production areas, it was far from the Asian trade routes and other VOC areas of activity ranging from Africa to India to Japan. A location in the west of the archipelago was thus sought. The Straits of Malacca were strategic but became dangerous following the Portuguese conquest, and the first permanent VOC settlement in Banten was controlled by a powerful local ruler and subject to stiff competition from Chinese and English traders.
In 1604, a second English
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Sou ...
voyage commanded by
Sir Henry Middleton reached the islands of
Ternate,
Tidore,
Ambon and
Banda
Banda may refer to:
People
* Banda (surname)
* Banda Prakash (born 1954), Indian politician
* Banda Kanakalingeshwara Rao (1907–1968), Indian actor
* Banda Karthika Reddy (born 1977), Indian politician
*Banda Singh Bahadur (1670–1716), Sikh ...
. In Banda, they encountered severe VOC hostility, sparking Anglo-Dutch competition for access to spices.
From 1611 to 1617, the English established trading posts at
Sukadana (southwest
Kalimantan),
Makassar,
Jayakarta and
Jepara in
Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
, and Aceh,
Pariaman and
Jambi in
Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
, which threatened Dutch ambitions for a monopoly on East Indies trade.
In 1620, diplomatic agreements in Europe ushered in a period of co-operation between the Dutch and the English over the spice trade.
This ended with a notorious but disputed incident known as the '
Amboyna massacre', where ten Englishmen were arrested, tried and beheaded for conspiracy against the Dutch government.
Although this caused outrage in Europe and a diplomatic crisis, the English quietly withdrew from most of their Indonesian activities (except trading in Banten) and focused on other Asian interests.
Growth


In 1619,
Jan Pieterszoon Coen was appointed governor-general of the VOC. He saw the possibility of the VOC becoming an Asian power, both political and economic. On 30 May 1619, Coen, backed by a force of nineteen ships, stormed Jayakarta, driving out the Banten forces; and from the ashes established
Batavia as the VOC headquarters. In the 1620s almost the entire native population of the
Banda Islands was driven away, starved to death, or killed in an attempt to replace them with Dutch plantations. These plantations were used to grow
nutmeg for export. Coen hoped to settle large numbers of Dutch colonists in the East Indies, but implementation of this policy never materialised, mainly because very few Dutch were willing to emigrate to Asia.
Another of Coen's ventures was more successful. A major problem in the European trade with Asia at the time was that the Europeans could offer few goods that Asian consumers wanted, except silver and gold. European traders therefore had to pay for spices with the precious metals, which were in short supply in Europe, except for Spain and Portugal. The Dutch and English had to obtain it by creating a trade surplus with other European countries. Coen discovered the obvious solution for the problem: to start an intra-Asiatic trade system, whose profits could be used to finance the spice trade with Europe. In the long run this obviated the need for exports of precious metals from Europe, though at first it required the formation of a large trading-capital fund in the Indies. The VOC reinvested a large share of its profits to this end in the period up to 1630.
[De Vries and Van der Woude, p. 386]
The VOC traded throughout Asia, benefiting mainly from
Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
. Ships coming into Batavia from the Netherlands carried supplies for VOC settlements in Asia. Silver and copper from Japan were used to trade with the world's wealthiest empires,
Mughal India and
Qing China, for silk, cotton, porcelain, and textiles. These products were either traded within Asia for the coveted spices or brought back to Europe. The VOC was also instrumental in introducing European ideas and technology to Asia. The company supported Christian missionaries and traded modern technology with China and Japan. A more peaceful VOC trade post on
Dejima, an
artificial island off the coast of
Nagasaki
is the capital and the largest city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan.
It became the sole port used for trade with the Portuguese and Dutch during the 16th through 19th centuries. The Hidden Christian Sites in the ...
, was for more than two hundred years the only place where Europeans were permitted to trade with Japan. When the VOC tried to use military force to make
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
China open up to Dutch trade, the Chinese defeated the Dutch in
a war over the Penghu islands from 1623 to 1624, forcing the VOC to abandon
Penghu for Taiwan. The Chinese defeated the VOC again at the
Battle of Liaoluo Bay in 1633.
The Vietnamese Nguyen Lords defeated the VOC in
a 1643 battle during the
Trịnh–Nguyễn War, blowing up a Dutch ship. The Cambodians defeated the VOC in the
Cambodian–Dutch War from 1643 to 1644 on the Mekong River.
In 1640, the VOC obtained the port of
Galle,
Ceylon, from the Portuguese and broke the latter's monopoly of the
cinnamon trade. In 1658,
Gerard Pietersz Hulft
Gerard Pietersz Hulft (12 December 1621 in Amsterdam – 10 April 1656 in Colombo), was a Dutch general. In 1655 he was sent with a fleet to Ceylon and died in action.
Life
Hulft was born as the youngest son of the brewer Pieter Hulft, and me ...
laid siege to
Colombo
Colombo ( ; si, කොළඹ, translit=Koḷam̆ba, ; ta, கொழும்பு, translit=Koḻumpu, ) is the executive and judicial capital and largest city of Sri Lanka by population. According to the Brookings Institution, Colombo me ...
, which was captured with the help of King
Rajasinghe II of
Kandy
Kandy ( si, මහනුවර ''Mahanuwara'', ; ta, கண்டி Kandy, ) is a major city in Sri Lanka located in the Central Province. It was the last capital of the ancient kings' era of Sri Lanka. The city lies in the midst of hills ...
. By 1659, the Portuguese had been expelled from the coastal regions, which were then occupied by the VOC, securing for it the monopoly over cinnamon.
To prevent the Portuguese or the English from ever recapturing Sri Lanka, the VOC went on to conquer the entire
Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing ...
from the Portuguese, almost entirely driving them from the west coast of India.
In 1652,
Jan van Riebeeck established a resupply outpost at the Cape of Storms (the southwestern tip of Africa, now
Cape Town
Cape Town ( af, Kaapstad; , xh, iKapa) is one of South Africa's three capital cities, serving as the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. It is the legislative capital of the country, the oldest city in the country, and the second largest ...
, South Africa) to service company ships on their journey to and from East Asia. The cape was later renamed
Cape of Good Hope in honour of the outpost's presence. Although non-company ships were welcome to use the station, they were charged exorbitantly. This post later became a full-fledged colony, the
Cape Colony
The Cape Colony ( nl, Kaapkolonie), also known as the Cape of Good Hope, was a British colony in present-day South Africa named after the Cape of Good Hope, which existed from 1795 to 1802, and again from 1806 to 1910, when it united with ...
, when more Dutch and other Europeans started to settle there.
Through the seventeenth century VOC trading posts were also established in
Persia,
Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
,
Malacca,
Siam,
Formosa (now Taiwan), as well as the
Malabar and
Coromandel coasts in India. Direct access to mainland China came in 1729 when a
factory
A factory, manufacturing plant or a production plant is an industrial facility, often a complex consisting of several buildings filled with machinery, where workers manufacture items or operate machines which process each item into another. ...
was established in
Canton. In 1662, however,
Koxinga expelled the Dutch from Taiwan
(''see''
History of Taiwan
The history of the island of Taiwan dates back tens of thousands of years to the earliest known evidence of human habitation. The sudden appearance of a culture based on agriculture around 3000 BC is believed to reflect the arrival of the ances ...
).
In 1663, the VOC signed the "Painan Treaty" with several local lords in the
Painan area that were revolting against the
Aceh Sultanate. The treaty allowed the VOC to build a trading post in the area and eventually to monopolise the trade there, especially the gold trade.
By 1669, the VOC was the richest private company the world had ever seen, with over 150 merchant ships, 40 warships, 50,000 employees, a private army of 10,000 soldiers, and a
dividend
A dividend is a distribution of profits by a corporation to its shareholders. When a corporation earns a profit or surplus, it is able to pay a portion of the profit as a dividend to shareholders. Any amount not distributed is taken to be re-i ...
payment of 40% on the original investment.
[The share price had appreciated significantly, so in that respect the dividend was less impressive]
Many of the VOC employees inter-mixed with the indigenous peoples and expanded the population of
Indos in pre-colonial history
Indo people (short for Indo-European) are a Eurasian people of mixed Indonesian and European descent. Through the 16th and 18th century known by the name Mestiço (Dutch: Mestiezen). To this day they form one of the largest Eurasian communities in ...
.
Reorientation
Around 1670, two events caused the growth of VOC trade to stall. In the first place, the highly profitable trade with Japan started to decline. The loss of the outpost on Formosa to
Koxinga in the 1662
Siege of Fort Zeelandia and related internal turmoil in China (where the
Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
was being replaced with the China's
Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
) brought an end to the silk trade after 1666. Though the VOC substituted
Mughal Bengal's for Chinese silk, other forces affected the supply of Japanese silver and gold. The
shogunate enacted a number of measures to limit the export of these precious metals, in the process limiting VOC opportunities for trade, and severely worsening the terms of trade. Therefore, Japan ceased to function as the linchpin of the intra-Asiatic trade of the VOC by 1685.
Even more importantly, the
Third Anglo-Dutch War temporarily interrupted VOC trade with Europe. This caused a spike in the price of pepper, which enticed the English East India Company (EIC) to enter this market aggressively in the years after 1672. Previously, one of the tenets of the VOC pricing policy was to slightly over-supply the pepper market, so as to depress prices below the level where interlopers were encouraged to enter the market (instead of striving for short-term
profit maximisation). The wisdom of such a policy was illustrated when a fierce price war with the EIC ensued, as that company flooded the market with new supplies from India. In this struggle for market share, the VOC (which had much larger financial resources) could wait out the EIC. Indeed, by 1683, the latter came close to bankruptcy; its share price plummeted from 600 to 250; and its president
Josiah Child was temporarily forced from office.
However, the writing was on the wall. Other companies, like the
French East India Company and the
Danish East India Company also started to make inroads on the Dutch system. The VOC therefore closed the theretofore flourishing open pepper emporium of
Bantam by a treaty of 1684 with the Sultan. Also, on the
Coromandel Coast
The Coromandel Coast is the southeastern coastal region of the Indian subcontinent, bounded by the Utkal Plains to the north, the Bay of Bengal to the east, the Kaveri delta to the south, and the Eastern Ghats to the west, extending over an ...
, it moved its chief stronghold from
Pulicat
Pulicat or Pazhaverkadu is a historic seashore town in Chennai Metropolitan Area at Thiruvallur District, of Tamil Nadu state, India. It is about north of Chennai and from Elavur, on the southern periphery of the Pulicat Lake. Pulicat lake i ...
to
Negapatnam, so as to secure a monopoly on the pepper trade to the detriment of the French and the Danes. However, the importance of these traditional commodities in the Asian-European trade was diminishing rapidly at the time. The military outlays that the VOC needed to make to enhance its monopoly were not justified by the increased profits of this declining trade.
Nevertheless, this lesson was slow to sink in and at first the VOC made the strategic decision to improve its military position on the
Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing ...
(hoping thereby to curtail English influence in the area, and end the drain on its resources from the cost of the Malabar garrisons) by using force to compel the
Zamorin of
Calicut
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second ...
to submit to Dutch domination. In 1710, the Zamorin was made to sign a treaty with the VOC undertaking to trade exclusively with the VOC and expel other European traders. For a brief time, this appeared to improve the company's prospects. However, in 1715, with EIC encouragement, the Zamorin renounced the treaty. Though a Dutch army managed to suppress this insurrection temporarily, the Zamorin continued to trade with the English and the French, which led to an appreciable upsurge in English and French traffic. The VOC decided in 1721 that it was no longer worth the trouble to try to dominate the
Malabar pepper and spice trade. A strategic decision was taken to scale down the Dutch military presence and in effect yield the area to EIC influence.

The 1741
Battle of Colachel
The Battle of Colachel (or The Battle of Kulachal) was fought on
between the Indian kingdom of Travancore and the Dutch East India Company. During the Travancore-Dutch War, King Marthanda Varma's (1729–1758) forces defeated the Dutch East ...
by warriors of
Travancore under Raja
Marthanda Varma defeated the Dutch. The Dutch commander Captain
Eustachius De Lannoy was captured. Marthanda Varma agreed to spare the Dutch captain's life on condition that he joined his army and trained his soldiers on modern lines. This defeat in the
Travancore-Dutch War is considered the earliest example of an organised Asian power overcoming European military technology and tactics; and it signalled the decline of Dutch power in India.
The attempt to continue as before as a low volume-high profit business enterprise with its core business in the spice trade had therefore failed. The company had however already (reluctantly) followed the example of its European competitors in diversifying into other Asian commodities, like tea, coffee, cotton, textiles, and sugar. These commodities provided a lower profit margin and therefore required a larger sales volume to generate the same amount of revenue. This structural change in the commodity composition of the VOC's trade started in the early 1680s, after the temporary collapse of the EIC around 1683 offered an excellent opportunity to enter these markets. The actual cause for the change lies, however, in two structural features of this new era.
In the first place, there was a revolutionary change in the tastes affecting European demand for Asian textiles, coffee and tea, around the turn of the 18th century. Secondly, a new era of an abundant supply of capital at low interest rates suddenly opened around this time. The second factor enabled the company easily to finance its expansion in the new areas of commerce. Between the 1680s and 1720s, the VOC was therefore able to equip and man an appreciable expansion of its fleet, and acquire a large amount of precious metals to finance the purchase of large amounts of Asian commodities, for shipment to Europe. The overall effect was approximately to double the size of the company.
The tonnage of the returning ships rose by 125 percent in this period. However, the company's revenues from the sale of goods landed in Europe rose by only 78 percent. This reflects the basic change in the VOC's circumstances that had occurred: it now operated in new markets for goods with an elastic demand, in which it had to compete on an equal footing with other suppliers. This made for low profit margins. Unfortunately, the business information systems of the time made this difficult to discern for the managers of the company, which may partly explain the mistakes they made from hindsight. This lack of information might have been counteracted (as in earlier times in the VOC's history) by the business acumen of the directors. Unfortunately by this time these were almost exclusively recruited from the political ''
regent
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state '' pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy ...
'' class, which had long since lost its close relationship with merchant circles.
Low profit margins in themselves do not explain the deterioration of revenues. To a large extent the costs of the operation of the VOC had a "fixed" character (military establishments; maintenance of the fleet and such). Profit levels might therefore have been maintained if the increase in the scale of trading operations that in fact took place had resulted in
economies of scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of output produced per unit of time. A decrease in cost per unit of output enables ...
. However, though larger ships transported the growing volume of goods, labour productivity did not go up sufficiently to realise these. In general the company's overhead rose in step with the growth in trade volume; declining gross margins translated directly into a decline in profitability of the invested capital. The era of expansion was one of "profitless growth".
[De Vries and Van der Woude, p. 447]
Specifically: "
e long-term average annual profit in the VOC's 1630–70 'Golden Age' was 2.1 million guilders, of which just under half was distributed as dividends and the remainder reinvested. The long-term average annual profit in the 'Expansion Age' (1680–1730) was 2.0 million guilders, of which three-quarters was distributed as dividend and one-quarter reinvested. In the earlier period, profits averaged 18 percent of total revenues; in the latter period, 10 percent. The annual return of invested capital in the earlier period stood at approximately 6 percent; in the latter period, 3.4 percent."
Nevertheless, in the eyes of investors the VOC did not do too badly. The share price hovered consistently around the 400 mark from the mid-1680s (excepting a hiccup around the
Glorious Revolution in 1688), and they reached an all-time high of around 642 in the 1720s. VOC shares then yielded a return of 3.5 percent, only slightly less than the yield on Dutch government bonds.
Decline and fall


After 1730, the fortunes of the VOC started to decline. Five major problems, not all of equal weight, explain its decline over the next fifty years to 1780:
*There was a steady erosion of intra-Asiatic trade because of changes in the Asiatic political and economic environment that the VOC could do little about. These factors gradually squeezed the company out of Persia,
Suratte, the Malabar Coast, and Bengal. The company had to confine its operations to the belt it physically controlled, from Ceylon through the Indonesian archipelago. The volume of this intra-Asiatic trade, and its profitability, therefore had to shrink.
*The way the company was organised in Asia (centralised on its hub in Batavia), that initially had offered advantages in gathering market information, began to cause disadvantages in the 18th century because of the inefficiency of first shipping everything to this central point. This disadvantage was most keenly felt in the tea trade, where competitors like the EIC and the
Ostend Company shipped directly from China to Europe.
*The "venality" of the VOC's personnel (in the sense of corruption and non-performance of duties), though a problem for all East India Companies at the time, seems to have plagued the VOC on a larger scale than its competitors. To be sure, the company was not a "good employer". Salaries were low, and "private-account trading" was officially not allowed. Not surprisingly, it proliferated in the 18th century to the detriment of the company's performance. From about the 1790s onward, the phrase ''perished under corruption'' (''vergaan onder corruptie'', also abbreviated VOC in Dutch) came to summarise the company's future.
*A problem that the VOC shared with other companies was the high mortality and morbidity rates among its employees. This decimated the company's ranks and enervated many of the survivors.
*A self-inflicted wound was the VOC's
dividend policy. The dividends distributed by the company had exceeded the surplus it garnered in Europe in every decade from 1690 to 1760 except 1710–1720. However, in the period up to 1730 the directors shipped resources to Asia to build up the trading capital there. Consolidated bookkeeping therefore probably would have shown that total profits exceeded dividends. In addition, between 1700 and 1740 the company retired 5.4 million guilders of long-term debt. The company therefore was still on a secure financial footing in these years. This changed after 1730. While profits plummeted the ''bewindhebbers'' only slightly decreased dividends from the earlier level. Distributed dividends were therefore in excess of earnings in every decade but one (1760–1770). To accomplish this, the Asian capital stock had to be drawn down by 4 million guilders between 1730 and 1780, and the
liquid capital available in Europe was reduced by 20 million guilders in the same period. The directors were therefore constrained to replenish the company's liquidity by resorting to short-term financing from anticipatory loans, backed by expected revenues from home-bound fleets.

Despite these problems, the VOC in 1780 remained an enormous operation. Its capital in the Republic, consisting of ships and goods in inventory, totalled 28 million guilders; its capital in Asia, consisting of the liquid trading fund and goods en route to Europe, totalled 46 million guilders. Total capital, net of outstanding debt, stood at 62 million guilders. The prospects of the company at this time therefore were not hopeless, had one of the plans for reform been undertaken successfully. However, the
Fourth Anglo-Dutch War
The Fourth Anglo-Dutch War ( nl, Vierde Engels-Nederlandse Oorlog; 1780–1784) was a conflict between the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Dutch Republic. The war, contemporary with the War of American Independence (1775-1783), broke out o ...
intervened. British naval attacks in Europe and Asia reduced the VOC fleet by half; removed valuable cargo from its control; and eroded its remaining power in Asia. The direct losses of the VOC during the war can be calculated at 43 million guilders. Loans to keep the company operating reduced its net assets to zero.
From 1720 on, the market for sugar from Indonesia declined as the competition from cheap sugar from Brazil increased. European markets became saturated. Dozens of Chinese sugar traders went bankrupt, which led to massive unemployment, which in turn led to gangs of unemployed
coolies
A coolie (also spelled koelie, kuli, khuli, khulie, cooli, cooly, or quli) is a term for a low-wage labourer, typically of South Asian or East Asian descent.
The word ''coolie'' was first popularized in the 16th century by European traders acros ...
. The Dutch government in Batavia did not adequately respond to these problems. In 1740, rumours of deportation of the gangs from the Batavia area led to widespread rioting. The Dutch military searched houses of Chinese in Batavia for weapons. When a house accidentally burnt down, military and impoverished citizens started slaughtering and pillaging the Chinese community. This
massacre of the Chinese was deemed sufficiently serious for the board of the VOC to start an official investigation into the Government of the Dutch East Indies for the first time in its history.
After the
Fourth Anglo-Dutch War
The Fourth Anglo-Dutch War ( nl, Vierde Engels-Nederlandse Oorlog; 1780–1784) was a conflict between the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Dutch Republic. The war, contemporary with the War of American Independence (1775-1783), broke out o ...
, the VOC was a financial wreck. After vain attempts at reorganisation by the provincial States of Holland and Zeeland, it was nationalised by the new
Batavian Republic on 1 March 1796.
[TANAP, The end of the VOC] The VOC charter was renewed several times, but was allowed to expire on 31 December 1799.
Most of the possessions of the former VOC were subsequently occupied by Great Britain during the
Napoleonic wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
, but after the new
United Kingdom of the Netherlands
The United Kingdom of the Netherlands ( nl, Verenigd Koninkrijk der Nederlanden; french: Royaume uni des Pays-Bas) is the unofficial name given to the Kingdom of the Netherlands as it existed between 1815 and 1839. The United Netherlands was cr ...
was created by the
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon ...
, some of these were restored to this successor state of the Dutch Republic by the
Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814
The Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814 (also known as the Convention of London; nl, Verdrag van Londen) was signed by the United Kingdom and the Netherlands in London on 13 August 1814.
The treaty restored most of the territories in Java that ...
.
Organisational structure
While the VOC mainly operated in what later became the
Dutch East Indies (modern Indonesia), the company also had important operations elsewhere. It employed people from different continents and origins in the same functions and working environments. Although it was a Dutch company its employees included not only people from the Netherlands, but also many from Germany and from other countries as well. Besides the diverse north-west European
workforce recruited by the VOC in the
Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiograph ...
, the VOC made extensive use of local Asian labour markets. As a result, the personnel of the various VOC offices in Asia consisted of European and Asian employees. Asian or
Eurasian
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipela ...
workers might be employed as sailors, soldiers, writers, carpenters, smiths, or as simple unskilled workers. At the height of its existence the VOC had 25,000 employees who worked in Asia and 11,000 who were en route. Also, while most of its
shareholders were Dutch, about a quarter of the initial shareholders were Zuid-Nederlanders (people from an area that includes modern Belgium and
Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
) and there were also a few dozen Germans.
The VOC had two types of shareholders: the ''participanten'', who could be seen as non-managing members, and the 76 ''bewindhebbers'' (later reduced to 60) who acted as managing directors. This was the usual set-up for Dutch
joint-stock companies at the time. The innovation in the case of the VOC was that the liability of not just the ''participanten'' but also of the ''bewindhebbers'' was limited to the paid-in capital (usually, ''bewindhebbers'' had unlimited liability). The VOC therefore was a
limited liability company
A limited liability company (LLC for short) is the US-specific form of a private limited company. It is a business structure that can combine the pass-through taxation of a partnership or sole proprietorship with the limited liability ...
. Also, the capital would be ''permanent'' during the lifetime of the company. As a consequence, investors that wished to liquidate their interest in the interim could only do this by selling their share to others on the
Amsterdam Stock Exchange
Euronext Amsterdam is a stock exchange based in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. Formerly known as the Amsterdam Stock Exchange, it merged on 22 September 2000 with the Brussels Stock Exchange and the Paris Stock Exchange to form Euronext. The r ...
.
''Confusion of confusions'', a 1688 dialogue by the Sephardi Jew
Joseph de la Vega analysed the workings of this one-stock exchange.
The VOC consisted of six Chambers (''Kamers'') in port cities:
Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the urban ar ...
,
Delft,
Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Rotte (river), Rotte'') is the second largest List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Netherlands. It is in the Prov ...
,
Enkhuizen,
Middelburg and
Hoorn. Delegates of these chambers convened as the ''Heeren XVII'' (the Lords Seventeen). They were selected from the ''bewindhebber''-class of shareholders.
Of the ''Heeren XVII'', eight delegates were from the Chamber of Amsterdam (one short of a majority on its own), four from the Chamber of Zeeland, and one from each of the smaller Chambers, while the seventeenth seat was alternatively from the Chamber of Middelburg-Zeeland or rotated among the five small Chambers. Amsterdam had thereby the decisive voice. The Zeelanders in particular had misgivings about this arrangement at the beginning. The fear was not unfounded, because in practice it meant Amsterdam stipulated what happened.
The six chambers raised the start-up capital of the Dutch East India Company:
The raising of capital in Rotterdam did not go so smoothly. A considerable part originated from inhabitants of
Dordrecht. Although it did not raise as much capital as Amsterdam or Middelburg-Zeeland, Enkhuizen had the largest input in the
share capital of the VOC. Under the first 358 shareholders, there were many small entrepreneurs, who dared to take the
risk
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environm ...
. The minimum investment in the VOC was 3,000 guilders, which priced the company's stock within the means of many merchants.

Among the early shareholders of the VOC, immigrants played an important role. Under the 1,143 tenderers were 39
Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
and no fewer than 301 from the
Southern Netherlands (roughly present Belgium and Luxembourg, then under
Habsburg rule), of whom
Isaac le Maire was the largest subscriber with ƒ85,000. VOC's total
capitalisation was ten times that of its British rival.
The ''Heeren XVII'' (Lords Seventeen) met alternately six years in Amsterdam and two years in Middelburg-Zeeland. They defined the VOC's general policy and divided the tasks among the Chambers. The Chambers carried out all the necessary work, built their own ships and warehouses and traded the merchandise. The ''Heeren XVII'' sent the ships' masters off with extensive instructions on the route to be navigated, prevailing winds, currents, shoals and landmarks. The VOC also produced its own
charts
A chart (sometimes known as a graph) is a graphical representation for data visualization, in which "the data is represented by symbols, such as bars in a bar chart, lines in a line chart, or slices in a pie chart". A chart can represent tabu ...
.
In the context of the
Dutch-Portuguese War the company established its headquarters in Batavia,
Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
(now
Jakarta,
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
). Other colonial outposts were also established in the
East Indies, such as on the
Maluku Islands, which include the
Banda Islands, where the VOC forcibly maintained a monopoly over
nutmeg and
mace. Methods used to maintain the monopoly involved
extortion and the violent suppression of the native population, including
mass murder. In addition, VOC representatives sometimes used the tactic of burning spice trees to force indigenous populations to grow other crops, thus artificially cutting the supply of spices like nutmeg and cloves.
Shareholder activism and governance issues

The seventeenth-century Dutch businessmen, especially the VOC investors, were possibly history's first recorded investors to seriously consider the
corporate governance
Corporate governance is defined, described or delineated in diverse ways, depending on the writer's purpose. Writers focused on a disciplinary interest or context (such as accounting, finance, law, or management) often adopt narrow definitions ...
's problems.
Isaac Le Maire, who is known as history's first recorded
short seller, was also a sizeable shareholder of the VOC. In 1609, he complained of the VOC's shoddy corporate governance. On 24 January 1609, Le Maire filed a petition against the VOC, marking the first recorded expression of
shareholder activism. In what is the first recorded corporate governance dispute, Le Maire formally charged that the VOC's board of directors (the Heeren XVII) sought to "retain another's money for longer or use it ways other than the latter wishes" and petitioned for the liquidation of the VOC in accordance with standard business practice. Initially the largest single shareholder in the VOC and a ''bewindhebber'' sitting on the board of governors, Le Maire apparently attempted to divert the firm's profits to himself by undertaking 14 expeditions under his own accounts instead of those of the company. Since his large shareholdings were not accompanied by greater voting power, Le Maire was soon ousted by other governors in 1605 on charges of embezzlement, and was forced to sign an agreement not to compete with the VOC. Having retained stock in the company following this incident, in 1609 Le Maire would become the author of what is celebrated as "first recorded expression of shareholder advocacy at a publicly traded company".
In 1622, the history's first recorded
shareholder revolt
Shareholder rebellion occurs when the owners of a corporation work to throw out management or oppose their decisions. Shareholder rebellion may occur at an annual general meeting or through a proxy battle. Shareholders may also threaten to collaps ...
also happened among the VOC investors who complained that the company account books had been "smeared with bacon" so that they might be "eaten by dogs." The investors demanded a "reeckeninge," a proper financial audit. The 1622 campaign by the
shareholders of the VOC is a testimony of genesis of
corporate social responsibility (CSR) in which shareholders staged protests by distributing pamphlets and complaining about management self enrichment and secrecy.
Main trading posts, settlements, and colonies
Europe
Netherlands
*
Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the urban ar ...
(global headquarters)
*
Delft
*
Enkhuizen
*
Hoorn
*
Middelburg
*
Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Rotte (river), Rotte'') is the second largest List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Netherlands. It is in the Prov ...
Africa
Mauritius
*
Dutch Mauritius
Mauritius was an official settlement of the Dutch East India Company on the island of Mauritius between 1638 and 1710, and used as a refreshing station for passing ships. It was already frequented by Dutch ships from 1598 onwards, but only settl ...
(1638–1658; 1664–1710)
South Africa
*
Dutch Cape Colony (1652–1806)
Asia





Indonesia
*
Batavia, Dutch East Indies
Batavia was the capital of the Dutch East Indies. The area corresponds to present-day Jakarta, Indonesia. Batavia can refer to the city proper or its suburbs and hinterland, the Ommelanden, which included the much-larger area of the Residen ...
Indian subcontinent
*
Dutch Coromandel (1608–1825)
*
Dutch Suratte
Suratte or Soeratte was a directorate of the Dutch East India Company between 1616 and 1795, with its main factory in the city of Surat. Surat was an important trading city of the Mughal Empire on the river Tapti, and the Portuguese had been tradi ...
(1616–1825)
*
Dutch Bengal (1627–1825)
*
Dutch Ceylon (1640–1796)
*
Dutch Malabar (1661–1795)
Japan
*
Hirado, Nagasaki (1609–1641)
*
Dejima,
Nagasaki
is the capital and the largest city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan.
It became the sole port used for trade with the Portuguese and Dutch during the 16th through 19th centuries. The Hidden Christian Sites in the ...
(1641–1853)
Taiwan
*
Anping (
Fort Zeelandia)
*
Tainan (
Fort Provincia)
*
Wang-an, Penghu
Wangan Township / Wang-an Township () is a rural township in Penghu County (the Pescadores), Taiwan. It is the second smallest township in Penghu County after Cimei Township. The township is made up of nineteen islands, six of which are inhabit ...
,
Pescadores Islands (Fort Vlissingen; 1620–1624)
*
Keelung (
Fort Noord-Holland, Fort Victoria)
*
Tamsui (
Fort Antonio)
Malaysia
*
Dutch Malacca (1641–1795; 1818–1825)
Thailand
*
Ayutthaya (1608–1767)
Vietnam
*
Thǎng Long/Tonkin (1636–1699)
*
Hội An (1636–1741)
Conflicts and wars involving the VOC
The history of VOC commercial conflict, for example with the British
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Sou ...
(EIC), was at times closely connected to Dutch military conflicts. The commercial interests of the VOC (and more generally the Netherlands) were reflected in military objectives and the settlements agreed by treaty. In the
Treaty of Breda (1667) ending the
Second Anglo-Dutch War, the Dutch were finally able to secure a
VOC monopoly for nutmeg trade, ceding the island of
Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
to the British while gaining the last non-VOC controlled source of nutmeg, the island of Rhun in the
Banda islands. The Dutch later re-captured
Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
, but returned it along with the colony of
New Netherland
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva ...
in the
Treaty of Westminster (1674) ending the
Third Anglo-Dutch War. The British also gave up claims on
Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the nor ...
as part of the
Treaty of Westminster. There was also an effort to compensate the
war-related losses of the Dutch West India Company in the mid-17th century by the profits of the VOC, though this was ultimately blocked.
''VOC mentality''
The VOC's history (and especially its dark side) has always been a potential source of controversy. In 2006 when the
Dutch Prime Minister Jan Pieter Balkenende referred to the pioneering entrepreneurial spirit and
work ethics of the
Dutch people
The Dutch (Dutch language, Dutch: ) are an ethnic group and nation native to the Netherlands. They share a common history and culture and speak the Dutch language. Dutch people and their descendants are found in migrant communities worldwide, ...
and
Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiograph ...
in
their Golden Age, he coined the term "VOC mentality" (''
VOC-mentaliteit'' in Dutch). For Balkenende, the VOC represented Dutch
business acumen
Business acumen, also known as business savviness, business sense and business understanding, is keenness and quickness in understanding and dealing with a business situation ( risks and opportunities) in a manner that is likely to lead to a goo ...
,
entrepreneurship, adventurous spirit, and decisiveness. However, it unleashed a wave of criticism, since such romantic views about the Dutch Golden Age ignores the inherent historical associations with colonialism, exploitation and violence. Balkenende later stressed that "it had not been his intention to refer to that at all".
But in spite of criticisms, the "VOC-mentality", as a characteristic of the selective historical perspective on the Dutch Golden Age, has been considered a key feature of Dutch cultural policy for many years.
International relations
The VOC existed for almost 200 years from its founding in 1602, when the
States-General of the Netherlands granted it a 21-year monopoly over Dutch operations in Asia until its demise in 1796. During those two centuries (between 1602 and 1796), the VOC sent almost a million Europeans to work in the Asia trade on 4,785 ships, and netted for their efforts more than 2.5 million tons of Asian trade goods. By contrast, the rest of Europe combined sent only 882,412 people from 1500 to 1795, and the fleet of the
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
(later
British)
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Sou ...
, the VOC's nearest competitor, was a distant second to its total traffic with 2,690 ships and a mere one-fifth the tonnage of goods carried by the VOC. The VOC enjoyed huge profits from its spice monopoly through most of the 17th century. By 1669, the VOC was the richest company the world had ever seen, with over 150 merchant ships, 40 warships, 50,000 employees, a private army of 10,000 soldiers, and a
dividend
A dividend is a distribution of profits by a corporation to its shareholders. When a corporation earns a profit or surplus, it is able to pay a portion of the profit as a dividend to shareholders. Any amount not distributed is taken to be re-i ...
payment of 40% on the original investment.
In terms of military-political history, the VOC, along with the Dutch West India Company (WIC/GWC), was seen as the international arm of the Dutch Republic and the symbolic power of the Dutch Empire. The VOC was historically a military-political-economic complex rather than a pure
trading company (or
shipping company). The government-backed but privately financed company was effectively a state in its own right, or a
state within another state. For almost 200 years of its existence, the VOC was a key non-state geopolitical player in Eurasia.
The company was much an unofficial representative of the
States General of the United Provinces in foreign relations of the Dutch Republic with many states, especially Dutch-Asian relations. The company's territories were even larger than some countries.
File:VOC Trade Cloth with Mughal design.png, VOC Trade Cloth, 1675–1725, with Mughal tent hanging / summer carpet motif. Made in India for the Indonesian market. Fine textiles from India were a popular luxury import into Indonesia, and some still survive as treasured heirlooms.
File:The arrival of King Charles II of England in Rotterdam, may 24 1660 (Lieve Pietersz. Verschuier, 1665).jpg, ''The arrival of King Charles II of England in Rotterdam, 24 May 1660'' by Lieve Verschuier. King Charles II of England sailed from Breda to Delft in May 1660 in a yacht owned by the VOC. ''HMY Mary
HMY ''Mary'' was the first Royal Yacht of the Royal Navy. She was built in 1660 by the Dutch East India Company. Then she was purchased by the City of Amsterdam and given to King Charles II, on the restoration of the monarchy, as part of the D ...
'' and ''HMY Bezan
HMY ''Bezan'' (or ''Bezaan'') was a Royal Yacht of the Royal Navy of England. The ''Bezan'' was a Dutch pleasure yacht built in 1630 and presented to Charles II by the Dutch East India Company. The ''Bezan'' was about 15 feet long with a singl ...
'' (both were built by the VOC) were given to Charles II, on the restoration of the monarchy, as part of the Dutch Gift.
File:Kopi luwak 090910-0075 lamb.JPG, Kopi luwak, coffee seeds from faeces of palm civet, Lampung, Indonesia. Coffee cultivation in Indonesia began in the late 1600s and early 1700s, in the VOC period. Indonesia was the fourth-largest producer of coffee in the world in 2014.
Arts and culture
As information and knowledge exchange network
During the
Dutch Golden Age, the Dutch – using their expertise in doing business, cartography, shipbuilding, seafaring and navigation – traveled to the far corners of the world, leaving their language embedded in the
names of many places. Dutch exploratory voyages revealed largely unknown
landmass
A landmass, or land mass, is a large region or area of land. The term is often used to refer to lands surrounded by an ocean or sea, such as a continent or a large island. In the field of geology, a landmass is a defined section of continen ...
es to the civilised world and put their names on the
world map
A world map is a map of most or all of the surface of Earth. World maps, because of their scale, must deal with the problem of projection. Maps rendered in two dimensions by necessity distort the display of the three-dimensional surface of ...
. During the Golden Age of Dutch exploration (c. 1590s–1720s) and the
Golden Age of Netherlandish cartography (c. 1570s–1670s),
Dutch-speaking navigators, explorers, and cartographers were the undisputed firsts to chart/map many hitherto largely unknown regions of the earth
and the sky.
The Dutch came to dominate the map-making and map printing industry by virtue of their own travels, trade ventures, and widespread commercial networks. As Dutch ships reached into the unknown corners of the globe, Dutch cartographers incorporated new geographical discoveries into their work. Instead of using the information themselves secretly, they published it, so the maps multiplied freely. For almost 200 years, the Dutch dominated
world trade. Dutch ships carried goods, but they also opened up opportunities for the exchange of knowledge. The commercial networks of the Dutch transnational companies, Dutch transnational companies, e.g. the VOC and
West India Company (WIC/GWC), provided an infrastructure which was accessible to people with a scholarly interest in the exotic world. The VOC's
bookkeeper Hendrick Hamel was the first known European/Westerner to experience first-hand and write about
Joseon-era
Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic ...
. In his report (published in the Dutch Republic) in 1666 Hendrick Hamel described his adventures on the
Korean Peninsula
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic ...
and gave the first accurate description of daily life of
Koreans
Koreans ( South Korean: , , North Korean: , ; see names of Korea) are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula.
Koreans mainly live in the two Korean nation states: North Korea and South Korea (collectively and simply r ...
to the western world. The VOC trade post on
Dejima, an
artificial island off the coast of
Nagasaki
is the capital and the largest city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan.
It became the sole port used for trade with the Portuguese and Dutch during the 16th through 19th centuries. The Hidden Christian Sites in the ...
, was for more than two hundred years the only place where Europeans were permitted to trade with Japan.
Rangaku (literally 'Dutch Learning', and by extension 'Western Learning') is a body of knowledge developed by Japan through its contacts with the Dutch enclave of
Dejima, which allowed Japan to keep abreast of Western technology and medicine in the period when the country was closed to foreigners, 1641–1853, because of the
Tokugawa shogunate's policy of national isolation (
sakoku).
File:JoanNieuhof.jpg, Johan Nieuhof's '' An embassy from the East-India Company of the United Provinces'' (1665).
File:HortusMalabaricus.jpg, The cover of the '' Hortus Malabaricus'' by Hendrik Adriaan van Reede tot Drakenstein.
File:Herbarium Amboinense page titre.jpg, Title page of Rumphius's ''Herbarium Amboinense'' (1741–1750)
File:Hortus Cliffortianus 1737.jpg, Title page of '' Hortus Cliffortianus'' (1737). The work was a collaboration between Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, ...
(Carl von Linné) and Georg Dionysius Ehret, financed by George Clifford III, one of the directors of the VOC.
File:Musa Cliffortiana 1736.jpg, Title page of '' Musa Cliffortiana'' (1736), Carl Linnaeus's first botanical monograph.
File:Carl Peter Thunberg x Jacob Fredrik Ek.jpg, Swedish naturalist Carl Peter Thunberg was a VOC physician and an apostle of Linnaeus.
File:Swan River,Perth,Western Australia.jpg, Black swans on the shore of the Swan River (Western Australia), with the Perth
Perth is the capital and largest city of the Australian state of Western Australia. It is the fourth most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a population of 2.1 million (80% of the state) living in Greater Perth in 2020. Perth is ...
skyline in the background. The thousand-year-old conclusion "all swans are white" was disproved by the VOC navigator Willem de Vlamingh
Willem Hesselsz de Vlamingh (November 1640 – ) was a Dutch sea captain who explored the central west coast of New Holland ( Australia) in the late 17th century, where he landed in what is now Perth on the Swan River. The mission proved fruit ...
's 1697 discovery.
Influences on Dutch Golden Age art
From 1609 the VOC had a trading post in Japan (
Hirado, Nagasaki), which used local paper for its own administration. However, the paper was also traded to the VOC's other trading posts and even the Dutch Republic. Many impressions of the
Dutch Golden Age artist Rembrandt's prints were done on Japanese paper. From about 1647 Rembrandt sought increasingly to introduce variation into his prints by using different sorts of paper, and printed most of his plates regularly on Japanese paper. He also used the paper for
his drawings. The Japanese paper types – which was actually imported from Japan by the VOC – attracted Rembrandt with its warm, yellowish colour. They are often smooth and shiny, whilst Western paper has a more rough and matt surface. Moreover, the VOC's imported
Chinese export porcelain and
Japanese export porcelain wares are
often depicted in many Dutch Golden Age
genre paintings, especially in
Jan Vermeer's paintings.
Hansken
__NOTOC__
Hansken (1630 – Florence, 9 November 1655) was a female elephant that became famous in early 17th-century Europe. She toured many countries, demonstrating circus tricks, and influenced many artists including Stefano della Bella, ...
, a young female Asian elephant
The Asian elephant (''Elephas maximus''), also known as the Asiatic elephant, is the only living species of the genus '' Elephas'' and is distributed throughout the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, from India in the west, Nepal in t ...
from Dutch Ceylon, was brought to Amsterdam in 1637, aboard a VOC ship. Rembrandt's Hansken drawing is believed to be an early portrait of one of the first Asian elephants described by science.
File:Rembrandtselfportraitweb.jpg, Rembrandt's self-portrait as an oriental potentate with a kris/ keris, a Javanese blade weapon from the VOC era (etching, c. 1634). Also, he was one of the first known western printmakers to extensively use (the VOC-imported) Japanese paper. It's important to note that some major figures of Dutch Golden Age art like Rembrandt and Vermeer
Johannes Vermeer ( , , see below; also known as Jan Vermeer; October 1632 – 15 December 1675) was a Dutch Baroque Period painter who specialized in domestic interior scenes of middle-class life. During his lifetime, he was a moderately succe ...
never went abroad during their lifetime. More than just a for-profit corporation of the early modern world, the VOC was instrumental in 'bringing' the East ( Orient) to the West ( Occident), and vice versa.
File:Willem Kalf - Still-Life with a Late Ming Ginger Jar - WGA12080.jpg, '' Still Life with a Chinese Porcelain Jar'', by Dutch Golden Age painter Willem Kalf (c. 1660s). 17th-century Chinese export porcelain wares (imported by the VOC) are often depicted in many Dutch Golden Age genre
Genre () is any form or type of communication in any mode (written, spoken, digital, artistic, etc.) with socially-agreed-upon conventions developed over time. In popular usage, it normally describes a category of literature, music, or other f ...
and still-life paintings.
File:Delftware display.JPG, Shop window display of Delftware in the market place, Delft. East Asian–inspired Delftware, a lasting cultural and economic legacy of the VOC era.
Contributions in the Age of Exploration
The Dutch East India Company (VOC) was also a major force behind the
Golden Age of Dutch exploration and discovery (c. 1590s–1720s). The VOC-funded exploratory voyages such as those led by
Willem Janszoon (''
Duyfken''),
Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson ( 1565 – disappeared 23 June 1611) was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of the northeastern United States.
In 1607 and 16 ...
(''
Halve Maen'') and
Abel Tasman revealed largely unknown landmasses to the civilised world.
File:Nova et Accuratissima Terrarum Orbis Tabula (J.Blaeu, 1664).jpg, Blaeu's ''Atlas Maior
The ''Atlas Maior'' is the final version of Joan Blaeu's atlas, published in Amsterdam between 1662 and 1672, in Latin (11 volumes), French (12 volumes), Dutch (9 volumes), German (10 volumes) and Spanish (10 volumes), containing 594 maps and ...
'' (1662–1672), a monumental multi-volume world atlas from the Golden Age of Dutch/Netherlandish cartography (c. 1570s–1670s) and a widely recognized masterpiece in the history of mapmaking. Willem Blaeu and his son Joan Blaeu
Joan Blaeu (; 23 September 1596 – 21 December 1673) was a Dutch cartographer born in Alkmaar, the son of cartographer Willem Blaeu.
Life
In 1620, Blaeu became a doctor of law but he joined the work of his father. In 1635, they published ...
were both official cartographers to the VOC.
File:Tasmanroutes.PNG, Abel Tasman's routes of the first and second voyage
''Halve Maen''s exploratory voyage and role in the formation of New Netherland

In 1609, English sea captain and explorer
Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson ( 1565 – disappeared 23 June 1611) was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of the northeastern United States.
In 1607 and 16 ...
was hired by the VOC émigrés running the VOC located in
Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the urban ar ...
to find a
north-east passage
The Northern Sea Route (NSR) (russian: Се́верный морско́й путь, ''Severnyy morskoy put'', shortened to Севморпуть, ''Sevmorput'') is a shipping route officially defined by Russian legislation as lying east of Nov ...
to Asia, sailing around Scandinavia and Russia. He was turned back by the ice of the Arctic in his second attempt, so he sailed west to seek a
north-west passage rather than return home. He ended up exploring the waters off the
east coast of North America aboard the ''
vlieboot'' ''
Halve Maen''. His first landfall was at
Newfoundland and the second at
Cape Cod
Cape Cod is a peninsula extending into the Atlantic Ocean from the southeastern corner of mainland Massachusetts, in the northeastern United States. Its historic, maritime character and ample beaches attract heavy tourism during the summer mont ...
.
Hudson believed that the passage to the Pacific Ocean was between the
St. Lawrence River and
Chesapeake Bay, so he sailed south to the Bay then turned northward, traveling close along the shore. He first discovered Delaware Bay and began to sail upriver looking for the passage. This effort was foiled by sandy shoals, and the ''Halve Maen'' continued north. After passing
Sandy Hook
Sandy Hook is a barrier spit in Middletown Township, Monmouth County, New Jersey, United States.
The barrier spit, approximately in length and varying from wide, is located at the north end of the Jersey Shore. It encloses the southern ...
, Hudson and his crew entered the
narrows
A narrows or narrow (used interchangeably but usually in the plural form), is a restricted land or water passage. Most commonly a narrows is a strait, though it can also be a water gap.
A narrows may form where a stream passes through a tilted ...
into the Upper New York Bay. (Unbeknownst to Hudson, the narrows had already been discovered in 1524 by explorer
Giovanni da Verrazzano; today, the bridge spanning them is named after him.) Hudson believed that he had found the continental water route, so he sailed up the major river which later bore his name: the
Hudson. He found the water too shallow to proceed several days later, at the site of present-day
Troy, New York.
[''Nieuwe Wereldt ofte Beschrijvinghe van West-Indien, uit veelerhande Schriften ende Aen-teekeningen van verscheyden Natien (Leiden, Bonaventure & Abraham Elseviers, 1625)''](_blank)
p. 84.
Upon returning to the Netherlands, Hudson reported that he had found a fertile land and an amicable people willing to engage his crew in small-scale bartering of furs, trinkets, clothes, and small manufactured goods. His report was first published in 1611 by
Emanuel Van Meteren, an Antwerp émigré and the Dutch Consul at London. This stimulated interest
in exploiting this new trade resource, and it was the catalyst for Dutch merchant-traders to fund more expeditions.
In 1611–12, the
Admiralty of Amsterdam
The Admiralty of Amsterdam was the largest of the five Dutch admiralties at the time of the Dutch Republic. The administration of the various admiralties was strongly influenced by provincial interests. The territory for which Amsterdam ...
sent two covert expeditions to find a passage to China with the yachts ''Craen'' and ''Vos'', captained by Jan Cornelisz Mey and Symon Willemsz Cat, respectively. In four voyages made between 1611 and 1614, the area between present-day
Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean t ...
and
Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut Massachusett_writing_systems.html" ;"title="nowiki/> məhswatʃəwiːsət.html" ;"title="Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət">Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət'' En ...
was explored, surveyed, and charted by
Adriaen Block,
Hendrick Christiaensen
Hendrick Christiaensen (died 1619) was a Dutch explorer who was involved in the earlier exploration of what became the colony of New Netherland.
Life
Hendrick Christiaensen was a ship captain and trader employed by the Van Tweenhuysen Company of ...
, and
Cornelius Jacobsen Mey
Cornelis Jacobsen Mey (in Dutch often rendered as Cornelius Jacobsz. May) was a Dutch explorer, captain and fur trader. Cape May, Cape May County, and the city of Cape May, New Jersey, are named after him.Russell Shorto, ''The Island at the Center ...
. The results of these explorations, surveys, and charts made from 1609 through 1614 were consolidated in Block's map, which used the name ''
New Netherland
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva ...
'' for the first time.
VOC-sponsored Dutch discovery, exploration, and mapping of mainland Australia, Tasmania, New Zealand, and various islands

In terms of world history of geography and exploration, the VOC can be credited with putting most of Australia's coast (then Hollandia Nova and other names) on the world map, between 1606 and 1756.
While Australia's territory (originally known as
New Holland) never became an actual Dutch settlement or colony, Dutch navigators were the first to undisputedly explore and map Australian coastline. In the 17th century, the VOC's navigators and explorers charted almost three-quarters of Australia's coastline, except its east coast. The Dutch ship, ''
Duyfken'', led by
Willem Janszoon, made the first documented European landing in Australia in 1606. Although a
theory of Portuguese discovery in the 1520s exists, it lacks definitive evidence. Precedence of discovery has also been claimed for China,
France,
[Credit for the discovery of Australia was given to Frenchman Binot Paulmier de Gonneville (1504) in ] Spain,
[In the early 20th century, Lawrence Hargrave argued from archaeological evidence that Spain had established a colony in Botany Bay in the 16th century.] India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
,.
's discovery of the
Brouwer Route, that sailing east from the
Cape of Good Hope until land was sighted and then sailing north along the west coast of Australia was a much quicker route than around the coast of the Indian Ocean, made Dutch landfalls on the west coast inevitable. The first such landfall was in 1616, when
Dirk Hartog landed at Cape Inscription on what is now known as
Dirk Hartog Island
A dirk is a long bladed thrusting dagger.Chisholm, Hugh (ed.), ''Dagger'', The Encyclopædia Britannica, 11th ed., Vol. VII, New York, NY: Cambridge University Press (1910), p. 729 Historically, it gained its name from the Highland Dirk (Sco ...
, off the coast of Western Australia, and left behind an inscription on a
pewter plate. In 1697 the Dutch captain
Willem de Vlamingh
Willem Hesselsz de Vlamingh (November 1640 – ) was a Dutch sea captain who explored the central west coast of New Holland ( Australia) in the late 17th century, where he landed in what is now Perth on the Swan River. The mission proved fruit ...
landed on the island and discovered
Hartog's plate. He replaced it with one of his own, which included a copy of Hartog's inscription, and took the original plate home to
Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the urban ar ...
, where it is still kept in the
Rijksmuseum Amsterdam.
In 1627, the VOC's explorers
François Thijssen and
Pieter Nuyts discovered the south coast of Australia and charted about of it between
Cape Leeuwin
Cape Leeuwin is the most south-westerly (but not most southerly) mainland point of the Australian continent, in the state of Western Australia.
Description
A few small islands and rocks, the St Alouarn Islands, extend further in Flinders B ...
and the
Nuyts Archipelago.
[Garden 1977, p.8.] François Thijssen, captain of the ship ''
't Gulden Zeepaert'' (The Golden Seahorse), sailed to the east as far as
Ceduna in
South Australia. The first known ship to have visited the area is the ''Leeuwin'' ("Lioness"), a Dutch vessel that charted some of the nearby coastline in 1622. The log of the ''Leeuwin'' has been lost, so very little is known of the voyage. However, the land discovered by the ''Leeuwin'' was recorded on a 1627 map by
Hessel Gerritsz:
Caert van't Landt van d'Eendracht
''Caert van't Landt van d'Eendracht'' ("Chart of the Land of Eendracht") is a 1627 map by Hessel Gerritsz. One of the earliest maps of Australia, it shows what little was then known of the west coast, based on a number of voyages beginning wit ...
("Chart of the Land of Eendracht"), which appears to show the coast between present-day
Hamelin Bay and Point D'Entrecasteaux. Part of Thijssen's map shows the islands St Francis and St Peter, now known collectively with their respective groups as the
Nuyts Archipelago. Thijssen's observations were included as soon as 1628 by the VOC cartographer
Hessel Gerritsz in a chart of the Indies and New Holland. This voyage defined most of the southern coast of Australia and discouraged the notion that "
New Holland" as it was then known, was linked to Antarctica.
In 1642,
Abel Tasman sailed from
Mauritius
Mauritius ( ; french: Maurice, link=no ; mfe, label= Mauritian Creole, Moris ), officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about off the southeast coast of the African continent, east of Madagascar. It ...
and on 24 November, sighted
Tasmania. He named Tasmania
Anthoonij van Diemenslandt (Anglicised as
Van Diemen's Land), after
Anthony van Diemen
Anthony van Diemen (also ''Antonie'', ''Antonio'', ''Anton'', ''Antonius'') (1593 – 19 April 1645) was a Dutch colonial governor.
Early life
He was born in Culemborg in the Netherlands, the son of Meeus Anthonisz van Diemen and Christina Ho ...
, the VOC's governor-general, who had commissioned his voyage. It was officially renamed
Tasmania in honour of its first European discoverer on 1 January 1856.
In 1642, during the same expedition, Tasman's crew discovered and charted
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island coun ...
's coastline. They were the first Europeans known to reach New Zealand. Tasman anchored at the northern end of the
South Island in
Golden Bay / Mohua (he named it Murderers' Bay) in December 1642 and sailed northward to
Tonga following a clash with local Māori. Tasman sketched sections of the two main islands' west coasts. Tasman called them ''
Staten Landt
Staten may refer to:
;People
* Randy Staten (1944-2010), American politician and football player
* Roy N. Staten (1913–1999), American politician
;Places
*Staten Island
Staten Island ( ) is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Ri ...
'', after the ''
States General of the Netherlands'', and that name appeared on his first maps of the country. In 1645 Dutch cartographers changed the name to ''
Nova Zeelandia'' in Latin, from ''Nieuw Zeeland'', after the
Dutch province of ''
Zeeland''. It was subsequently Anglicised as ''New Zealand'' by
James Cook. Various claims have been made that New Zealand was reached by other non-
Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
n voyagers before Tasman, but these are not widely accepted.
Criticism

The company has been criticised for its quasi-absolute commercial monopoly,
colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their reli ...
,
exploitation (including use of
slave labour
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to per ...
),
slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
, use of violence,
environmental destruction (including
deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated ...
), and for its overly
bureaucratic organisational structure.
[ Shorto, Russell (2013). ''Amsterdam: A History of the World's Most Liberal City''.]
Batavia, corresponding to present day Jakarta, was the headquarters of the Dutch East India Company, and had a strict social hierarchy in the colony. According to Marsely L. Kahoe in ''The Journal of Historians of Netherlandish Art'', "it is misleading to understand Batavia, as some scholars have, as representing a pragmatic and egalitarian order that was later corrupted by the colonial situation. In fact, the social stratification and segregation of Batavia derived in certain ways directly from its Dutch plan."
There was an extraordinarily high mortality rate among employees of the VOC. Between 1602 and 1795, about one million seamen and craftsmen departed from Holland, but only 340,000 returned. J.L. van Zanden writes "the VOC 'consumed' approximately 4,000 people per year."
Colonialism, monopoly and violence
The VOC charter allowed it to act as a quasi-sovereign state, and engaged in brutal conquests.
One example is the
Dutch conquest of the Banda Islands
The Dutch conquest of the Banda Islands was a process of military conquest from 1609 to 1621 by the Dutch East India Company of the Banda Islands. The Dutch, having enforced a monopoly on the highly lucrative nutmeg production from the islands, ...
, between 1609 and 1621, after the islands resisted the nutmeg monopoly. The Dutch launched punitive expeditions that resulted in the near destruction of Bandanese society. They invaded the main
Bandanese island of
Lontor in 1621. 2,800 Bandanese were killed, mostly from famine, and 1,700 were enslaved during the attack.
The total population of the islands is estimated at 15,000 people before the conquest. Although the exact number remains uncertain, it is estimated that around 14,000 people were killed, enslaved or fled elsewhere, with only 1,000 Bandanese surviving in the islands, and were spread throughout the nutmeg groves as forced labourers. The treatment of slaves was severe—the native Bandanese population dropped to 1,000 by 1681.
200 slaves were imported annually to sustain the slave population at a total of 4,000.
Dutch slave trade and slavery under the VOC colonial rule
By the time the settlement was established at the
Cape in 1652, the VOC already had a long experience of practicing
slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
in the
East Indies.
Jan van Riebeeck concluded within two months of the establishment of the Cape settlement that
slave labor would be needed for the hardest and dirtiest work. Initially, the VOC considered enslaving men from the indigenous
Khoikhoi population, but the idea was rejected on the grounds that such a policy would be both costly and dangerous. Most Khoikhoi had chosen not to labor for the Dutch because of low wages and harsh conditions. In the beginning, the settlers traded with the Khoikhoi but the harsh working conditions and low wages imposed by the Dutch led to a series of wars. The European population remained under 200 during the settlement's first five years, and war against neighbors numbering more than 20,000 would have been foolhardy. Moreover, the Dutch feared that Khoikhoi people, if enslaved, could always escape into the local community, whereas foreigners would find it much more difficult to elude their "masters."
Between 1652 and 1657, a number of unsuccessful attempts were made to obtain men from the
Dutch East Indies and from
Mauritius
Mauritius ( ; french: Maurice, link=no ; mfe, label= Mauritian Creole, Moris ), officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about off the southeast coast of the African continent, east of Madagascar. It ...
. In 1658, however, the VOC landed two shiploads of slaves at the Cape, one containing more than 200 people brought from
Dahomey (later Benin), the second with almost 200 people, most of them children, captured from a Portuguese slaver off the coast of Angola. Except for a few individuals, these were to be the only slaves ever brought to the Cape from West Africa.
From 1658 to the end of the company's rule, many more slaves were brought regularly to the Cape in various ways, chiefly by Company-sponsored slaving voyages and slaves brought to the Cape by its return fleets. From these sources and by natural growth, the slave population increased from zero in 1652 to about 1,000 by 1700. During the 18th century, the slave population increased dramatically to 16,839 by 1795. After the slave trade was initiated, all of the slaves imported into the Cape until the British stopped the trade in 1807 were from East Africa, Mozambique, Madagascar, and South and Southeast Asia. Large numbers were brought from
Ceylon and the Indonesian archipelago. Prisoners from other countries in the VOC's empire were also enslaved. The slave population, which exceeded that of the European settlers until the first quarter of the nineteenth century, was overwhelmingly male and was thus dependent on constant imports of new slaves to maintain and to augment its size.
By the 1660s the Cape settlement was importing slaves from Ceylon, Malaya (Malaysia), and
Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Afric ...
to work on the farms.
Conflict between Dutch farmers and Khoikhoi broke out once it became clear to the latter that the Dutch were there to stay and that they intended to encroach on the lands of the pastoralists. In 1659 Doman, a Khoikhoi who had worked as a translator for the Dutch and had even traveled to Java, led an armed attempt to expel the Dutch from the Cape peninsula. The attempt was a failure, although warfare dragged on until an inconclusive peace was established a year later. During the following decade, pressure on the Khoikhoi grew as more of the Dutch became free burghers, expanded their landholdings, and sought pastureland for their growing herds. War broke out again in 1673 and continued until 1677, when Khoikhoi resistance was destroyed by a combination of superior European weapons and Dutch manipulation of divisions among the local people. Thereafter, Khoikhoi society in the western Cape disintegrated. Some people found jobs as shepherds on European farms; others rejected foreign rule and moved away from the Cape. The final blow for most came in 1713 when a Dutch ship brought smallpox to the Cape. Hitherto unknown locally, the disease ravaged the remaining Khoikhoi, killing 90 percent of the population.
Throughout the eighteenth century, the settlement continued to expand through internal growth of the European population and the continued importation of slaves. The approximately 3,000 Europeans and slaves at the Cape in 1700 had increased by the end of the century to nearly 20,000 Europeans, and approximately 25,000 slaves.
Cultural depictions
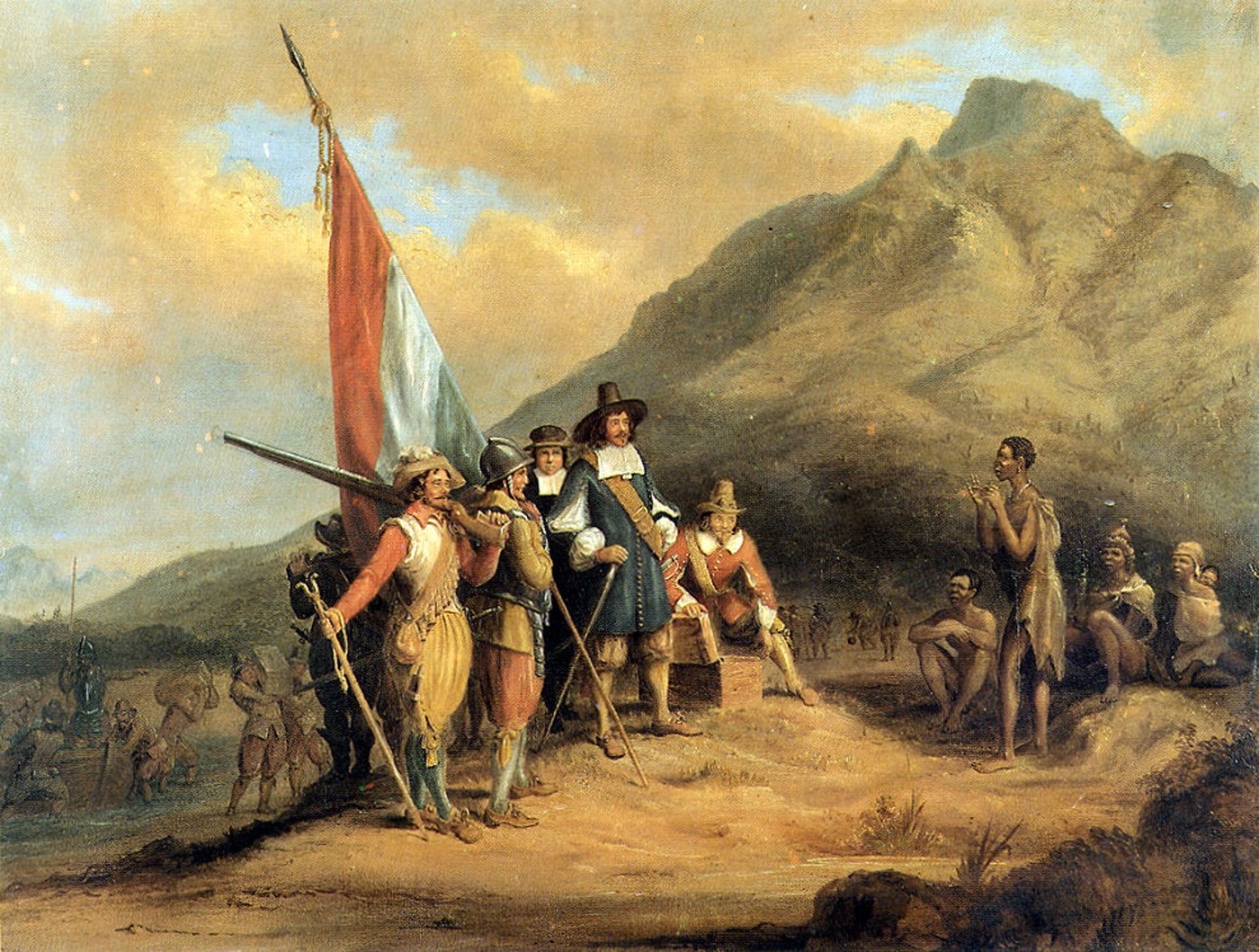



*''
Batavia'': a shipwreck on the
Houtman Abrolhos in 1629, made famous by the subsequent mutiny and massacre that took place among the survivors
*''
Flying Dutchman'': a legendary
ghost ship in several maritime myths, likely to have originated from the 17th-century golden age of the VOC.
*''
Hansken
__NOTOC__
Hansken (1630 – Florence, 9 November 1655) was a female elephant that became famous in early 17th-century Europe. She toured many countries, demonstrating circus tricks, and influenced many artists including Stefano della Bella, ...
'': a female
Asian elephant
The Asian elephant (''Elephas maximus''), also known as the Asiatic elephant, is the only living species of the genus '' Elephas'' and is distributed throughout the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, from India in the west, Nepal in t ...
from
Dutch Ceylon. The young elephant ''Hansken'' was brought to Amsterdam in 1637, aboard a VOC ship. Dutch Golden Age artist
Rembrandt made some historical drawings of ''Hansken''.
*''
Batavia, Dutch East Indies
Batavia was the capital of the Dutch East Indies. The area corresponds to present-day Jakarta, Indonesia. Batavia can refer to the city proper or its suburbs and hinterland, the Ommelanden, which included the much-larger area of the Residen ...
'': 1650s/1660s paintings of scenes from everyday life by
Dutch Golden Age painter Andries Beeckman, one of the few painters who travelled to the
Dutch East Indies in the 17th century.
*''
Cosmos: A Personal Voyage'': in the 6th episode ''
Travellers' Tales'' of the popular documentary TV series ''
Cosmos'' (1980), American astronomer
Carl Sagan, who also served as host, took a look at the voyage to Jupiter and Saturn, and compared these events with the adventuring spirit of the
Dutch Golden Age explorers (including the VOC's navigators).
*''
The Sino-Dutch War 1661
''The Sino-Dutch War 1661'' (), also known as ''Hero Zheng Chenggong'', is a 2000 Chinese historical drama film directed by Wu Ziniu, starring Vincent Zhao, Jiang Qinqin, Du Zhiguo, Yoko Shimada, Xu Min and Zhang Shan. The film is loosely base ...
'': 2000 Chinese historical drama film. The film is loosely based on the life of
Koxinga (
Zheng Chenggong) and focuses on his battle with the VOC for control of
Dutch Formosa at the Siege of
Fort Zeelandia.
*''
Ocean's Twelve
''Ocean's Twelve'' is a 2004 American heist comedy film directed by Steven Soderbergh and written by George Nolfi. The second installment in the ''Ocean's'' film trilogy franchise and the sequel to ''Ocean's Eleven'' (2001), the film features a ...
'': a 2004 American comedy heist film inspired by the historical story from the VOC's
IPO and the first shares of stock ever traded publicly in history. The VOC's
stock certificate is the focused heist by the burglars in the movie.
*''
The Thousand Autumns of Jacob de Zoet
''The Thousand Autumns of Jacob de Zoet'' is an historical fiction novel by British author David Mitchell published by Sceptre in 2010. It is set during the Dutch trading concession with Japan in the late 18th-century, during the period of Jap ...
'', 2010 historical novel by British author
David Mitchell.
*''My Father's Islands: Abel Tasman's Heroic Voyages'': a 2012
juvenile fiction
Young adult fiction (YA) is a category of fiction written for readers from 12 to 18 years of age. While the genre is primarily targeted at adolescents, approximately half of YA readers are adults.
The subject matter and genres of YA correlate ...
by
Christobel Mattingley, written from the perspective of
Tasman
Tasman most often refers to Abel Tasman (1603–1659), Dutch explorer.
Tasman may also refer to:
Animals and plants
* Tasman booby
* Tasman flax-lily
* Tasman parakeet (disambiguation)
* Tasman starling
* Tasman whale
People
* Tasman (n ...
's young daughter, Claesgen. The fictional story was inspired by a 1637 painting of the Tasman family by the Dutch Golden Age painter
Jacob Gerritsz. Cuyp
Jacob Gerritszoon Cuyp (or Jacob Gerritsz. Cuijp; 1594 – 1652) was a portrait and landscape painter, best known for his portraits.
He was born and died in Dordrecht, the son of the stained glass designer Gerrit Gerritsz Cuyp, who moved ...
, one of the treasures of the National Library of Australia.
*''
The Tsar-Carpenter'': a cultural depiction of
Tsar Peter the Great (
Peter I of Russia) in his undercover visit to the
Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiograph ...
as part of the
Grand Embassy
The Grand Embassy (russian: Вели́кое посо́льство, translit=Velíkoye posól'stvo) was a Russian diplomatic mission to Western Europe from 9 March 1697 to 25 August 1698 led by Peter the Great.
Description
In 1697 and 1698, Pete ...
mission (1697–1698). When Peter the Great wanted to learn more about the Dutch Republic's
sea power
Command of the sea (also called control of the sea or sea control) is a naval military concept regarding the strength of a particular navy to a specific naval area it controls. A navy has command of the sea when it is so strong that its rivals ...
, he came to study
seamanship
Seamanship is the art, knowledge and competence of operating a ship, boat or other craft on water. The'' Oxford Dictionary'' states that seamanship is "The skill, techniques, or practice of handling a ship or boat at sea."
It involves topics ...
,
shipbuilding industry
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befor ...
and
carpentry in Amsterdam and
Zaandam (Saardam). Through the agency of
Nicolaas Witsen, mayor of Amsterdam and an expert on Russia, Tsar Peter I worked as a
ship's carpenter in the VOC's
shipyards
A shipyard, also called a dockyard or boatyard, is a place where ships are built and repaired. These can be yachts, military vessels, cruise liners or other cargo or passenger ships. Dockyards are sometimes more associated with maintenance ...
in Holland.
*''
Megacorporation'' or ''
mega-corporation
Megacorporation, mega-corporation, or megacorp, a term originally coined by Alfred Eichner in his book ''The Megacorp and Oligopoly: Micro Foundations of Macro Dynamics'' but popularized by William Gibson, derives from the combination of the prefi ...
'': a quasi-fictional term/concept derived from the combination of the prefix ''
mega-
Mega is a unit prefix in metric systems of units denoting a factor of one million (106 or ). It has the unit symbol M. It was confirmed for use in the International System of Units (SI) in 1960. ''Mega'' comes from grc, μέγας, mégas, g ...
'' with the word ''corporation'', possibly inspired by the VOC's history. It refers to a (quasi-fictional) corporation that is a massive
conglomerate
Conglomerate or conglomeration may refer to:
* Conglomerate (company)
* Conglomerate (geology)
* Conglomerate (mathematics)
In popular culture:
* The Conglomerate (American group), a production crew and musical group founded by Busta Rhymes
** ...
, possessing quasi-governmental powers and holding
monopolistic control over markets.
*''
Black swan theory'': a
metaphor or metatheory of science popularized by
Nassim Nicholas Taleb. It was possibly inspired by
Willem de Vlamingh
Willem Hesselsz de Vlamingh (November 1640 – ) was a Dutch sea captain who explored the central west coast of New Holland ( Australia) in the late 17th century, where he landed in what is now Perth on the Swan River. The mission proved fruit ...
's 1697 discovery. De Vlamingh was the first known European/Western to observe and describe
black swans Black swan is the common name for ''Cygnus atratus'', an Australasian waterfowl.
(The) Black Swan(s) may also refer to:
Film and television
* ''The Black Swan'' (film), a 1942 swashbuckler film
* ''Black Swans'' (film), a 2005 Dutch drama film
* ' ...
and
quokkas, in
Western Australia.
VOC World etymologies
Places and things named after the VOC, its people and properties (VOC World eponyms)
*Dutch East India Company (VOC):
10649 VOC (minor planet);
VOC-mentality ("VOC-mentaliteit" in Dutch, coined in 2006 by
Jan Pieter Balkenende)
*
Arnhem (VOC ship):
Arnhem Land (Arnhems Landt),
Cape Arnhem
The Gove Peninsula is at the northeastern corner of Arnhem Land in the Northern Territory of Australia. The peninsula became strategically important during World War II when a Royal Australian Air Force base was constructed at what is now Go ...
*
Willem Blaeu:
10652 Blaeu
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. I ...
(minor planet)
*
Willem Bontekoe:
10654 Bontekoe (minor planet)
*
Hendrik Brouwer:
Brouwer Route
*
Pieter de Carpentier:
Gulf of Carpentaria,
Carpentier River
*
Jan Carstenszoon
Jan Carstenszoon or more commonly Jan Carstensz In Dutch patronyms ending in -szoon were almost universally abbreviated to -sz was a 17th-century Dutch explorer. In 1623, Carstenszoon was commissioned by the Dutch East India Company to lead an ...
:
Mount Carstensz
Puncak Jaya (; literally "Glorious Peak") or Carstensz Pyramid, Mount Jayawijaya or Mount Carstensz () on the island of New Guinea, with an elevation of , is the highest mountain peak of an island on Earth. The mountain is located in the Sud ...
;
Carstensz Pyramid;
Carstensz Glacier
The Carstensz Glacier is near the peak of Puncak Jaya (sometimes called ''Mount Carstensz'' or the ''Carstensz Pyramid'') which is a mountain in the Sudirman Range of the island of New Guinea, territorially the eastern highlands of Central Papua, ...
*
George Clifford III: ''
Musa Cliffortiana'', ''
Hortus Cliffortianus''
*
Jan Pieterszoon Coen:
Coen River
The Coen River is a river located in the Cape York Peninsula in Queensland, Australia.
The headwaters of the river rise at the confluence of Pandanus Creek and an unnamed creek near Bend along the Peninsula Developmental Road in the Great D ...
*
Anthony van Diemen
Anthony van Diemen (also ''Antonie'', ''Antonio'', ''Anton'', ''Antonius'') (1593 – 19 April 1645) was a Dutch colonial governor.
Early life
He was born in Culemborg in the Netherlands, the son of Meeus Anthonisz van Diemen and Christina Ho ...
:
Anthoonij van Diemenslandt (
Van Diemen's Land);
Van Diemen Gulf
*
Maria van Diemen:
Maria Island
Maria Island or 'wukaluwikiwayna' in alawa kani) is a mountainous island located in the Tasman Sea">island.html" ;"title="alawa kani) is a mountainous island">alawa kani) is a mountainous island located in the Tasman Sea, off the east coast of ...
;
Cape Maria van Diemen
Cape Maria van Diemen is the westernmost point of the North Island of New Zealand. A tombolo, it was originally an island composed mainly of basaltic-andesitic lava flows and dykes. Drifting sands joined it to the rest of the North Island during ...
*
Hendrik Adriaan van Rheede tot Drakenstein
Hendrik Adriaan van Rheede tot Drakenstein (Amsterdam, 13 April 1636 – at sea, 15 December 1691) was a military man and a colonial administrator of the Dutch East India Company and naturalist. Between 1669 and 1676 he served as a governor of D ...
:
Drakenstein (mountain ranges),
Drakenstein (local municipality),
Rheedia (
Rheedia aristata),
Rheedia edulis
*
Robert Jacob Gordon:
Gordon's Bay
*
Cornelis Jacob van de Graaff
Cornelis Jacob van de Graaff (also known as ''van de Graeff'') (30 March 1734 – 21 April 1812), Dutch engineer-officer and Cape Governor from 1785 to 1791.
Career
Van de Graaff followed in his father's footsteps and entered the Dutch cavalry b ...
:
Graaff-Reinet
*
Dirk Hartog:
Dirk Hartog Island
A dirk is a long bladed thrusting dagger.Chisholm, Hugh (ed.), ''Dagger'', The Encyclopædia Britannica, 11th ed., Vol. VII, New York, NY: Cambridge University Press (1910), p. 729 Historically, it gained its name from the Highland Dirk (Sco ...
;
Hartog's Plate
*
Wiebbe Hayes:
Wiebbe Hayes Stone Fort
*
Jacques l'Hermite:
Hermite Islands
*
Frederick de Houtman
Frederick de Houtman ( – 21 October 1627) was a Dutch explorer, navigator, and colonial governor who sailed on the first Dutch expedition to the East Indies from 1595 until 1597, during which time he made observations of the southern ce ...
:
Houtman Abrolhos;
10650 Houtman (minor planet)
*
Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson ( 1565 – disappeared 23 June 1611) was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of the northeastern United States.
In 1607 and 16 ...
:
Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between Ne ...
;
Hudson Valley
The Hudson Valley (also known as the Hudson River Valley) comprises the valley of the Hudson River and its adjacent communities in the U.S. state of New York. The region stretches from the Capital District including Albany and Troy south to ...
;
Hudson Bay
*
Engelbert Kaempfer
Engelbert Kaempfer (16 September 16512 November 1716) was a German naturalist, physician, explorer and writer known for his tour of Russia, Persia, India, Southeast Asia, and Japan between 1683 and 1693.
He wrote two books about his travels. '' ...
:
Kaempferia (
Kaempferia elegans,
Kaempferia galanga,
Kaempferia parviflora,
Kaempferia rotunda
''Kaempferia rotunda'' is a plant species in the ginger family. It is native to China (Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Taiwan, Yunnan), the Indian subcontinent (including Assam, Nepal and Bangladesh), Indochina, and widely cultivated elsewhere. It ...
)
*
François Levaillant:
Levaillant's cisticola
Levaillant's cisticola (''Cisticola tinniens''), also known as the tinkling cisticola, is a small passerine bird which is native to marshlands in the uplands of Africa, southwards of the equator.
Description
Levaillant's cisticola is a small, ...
,
Levaillant's cuckoo
Levaillant's cuckoo (''Clamator levaillantii'') is a cuckoo which is a resident breeding species in Africa south of the Sahara. It is found in bushy habitats. It is a brood parasite, using the nests of bulbuls and babblers. It was named in hono ...
,
Levaillant's parrot,
Levaillant's woodpecker
*
Cornelis van der Lijn:
Vanderlin Island
*
Joan Maetsuycker:
Maatsuyker Islands;
Maatsuyker Island
*
Johan Maurits Mohr thumbnail, Mohr observatory in Batavia ( Dutch East Indies).
Johan Maurits Mohr (ca. 18 August 1716, Eppingen – 25 October 1775, Batavia) was a Dutch- German pastor who studied at Groningen University from 1733 and settled in Batavia (Dutch E ...
:
5494 Johanmohr (minor planet)
*
Pieter Nuyts:
Nuyts Archipelago;
Nuyts Land District;
Nuytsia
''Nuytsia floribunda'' is a hemiparasitic tree found in Western Australia. The species is known locally as moodjar and, more recently, the Christmas tree or Western Australian Christmas tree. The display of intensely bright flowers during th ...
(
Nuytsia floribunda)
*
Francisco Pelsaert:
Pelsaert Island;
Pelsaert Group
*
Petrus Plancius
Petrus Plancius (; 1552 – 15 May 1622) was a Dutch-Flemish astronomer, cartographer and clergyman. He was born as Pieter Platevoet in Dranouter, now in Heuvelland, West Flanders. He studied theology in Germany and England. At the age of 24 he ...
:
Planciusdalen;
Planciusbukta;
10648 Plancius (minor planet)
*
Jan van Riebeeck:
Riebeeckstad;
Riebeek East;
Riebeek West
Riebeek West ( af, Riebeek-Wes) is a small town situated about 75 km north-east of Cape Town and 5 km north of its twin town Riebeek Kasteel in the Swartland area of the Western Cape, South Africa.
The Riebeek Valley would have b ...
;
Riebeek-Kasteel;
Riebeeckosaurus
*
Georg Eberhard Rumphius:
Avicennia rumphiana
''Avicennia rumphiana'' is a species of tropical mangrove in the family Acanthaceae. It is considered vulnerable by the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species in the 2008 assessment. , Plants of the World Online considered it to be only a variety ...
,
Caryota rumphiana,
Musa rumphiana,
Quadrula rumphiana
''Quadrula rumphiana'', the ridged mapleleaf, is a species of freshwater mussel, an aquatic bivalve mollusk in the family Unionidae, the river mussels.
This species is endemic to the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. o ...
*
Joost Schouten Joost Schouten (c. 1600 – 1644) was a Dutch East Indies Company figure of considerable repute, in demand as an astute administrator, diplomat, courtier and negotiator for this Dutch colonial and mercantile outpost in the South-East Asian archipel ...
:
Schouten Island
*
Willem Schouten
Willem Cornelisz Schouten ( – 1625) was a Dutch navigator for the Dutch East India Company. He was the first to sail the Cape Horn route to the Pacific Ocean.
Biography
Willem Cornelisz Schouten was born in c. 1567 in Hoorn, Holland, S ...
:
Schouten Islands (Indonesia),
Schouten Islands (Papua New Guinea),
11773 Schouten (minor planet),
Schoutenia,
Schoutenia cornerii,
Schoutenia furfuracea,
Schoutenia kunstleri
*
Leeuwin (VOC ship):
Cape Leeuwin
Cape Leeuwin is the most south-westerly (but not most southerly) mainland point of the Australian continent, in the state of Western Australia.
Description
A few small islands and rocks, the St Alouarn Islands, extend further in Flinders B ...
*
Simon van der Stel:
Simonstad
Simon's Town ( af, Simonstad), sometimes spelled Simonstown, is a town in the Western Cape, South Africa and is home to Naval Base Simon's Town, the South African Navy's largest base. It is located on the shores of False Bay, on the eastern sid ...
(
Simon's Town
Simon's Town ( af, Simonstad), sometimes spelled Simonstown, is a town in the Western Cape, South Africa and is home to Naval Base Simon's Town, the South African Navy's largest base. It is located on the shores of False Bay, on the eastern s ...
);
Stellenbosch
*
Hendrik Swellengrebel:
Swellendam
*
Salomon Sweers
Salomon Sweers (15 June 1611 in Nijmegen – 2 March 1674 in Amsterdam) was a bookkeeper and a counsel for the Dutch East India Company.
His younger brother was Admiral Isaac Sweers employed by the Admiralty of Amsterdam.
Early life
Salomon Swe ...
:
Sweers Island
Sweers Island is an island in the South Wellesley Islands in the Gulf of Carpentaria, Queensland, Australia. Privately owned via a perpetual lease and with the only residents being the owners and workers at the resort, the island is within the ...
*
Abel Tasman:
Tasmania;
Tasman Sea;
Tasman Bay / Te Tai-o-Aorere;
Tasman River;
Mount Tasman
Mount Tasman (''Horokoau'' in Māori) is New Zealand's second highest mountain, rising to a height of . It is located in the Southern Alps of the South Island, four kilometres to the north of its larger neighbour, Aoraki / Mount Cook. Unlike ...
;
Tasman Highway;
Tasman Bridge;
Abel Tasman National Park
Abel Tasman National Park is a New Zealand national park located between Golden Bay and Tasman Bay / Te Tai-o-Aorere at the north end of the South Island. It is named after Abel Tasman, who in 1642 became the first European explorer to sight Ne ...
;
Tasman District;
Tasmanian devil
*
Jacob Temminck:
Temminck's courser
*
Carl Peter Thunberg:
Thunbergia (
Thunbergia alata
''Thunbergia alata'', commonly called black-eyed Susan vine, is a herbaceous perennial climbing plant species in the family Acanthaceae. It is native to Eastern Africa, and has been naturalized in other parts of the world.
It is grown as an ...
,
Thunbergia annua,
Thunbergia erecta,
Thunbergia fragrans
''Thunbergia fragrans'', the whitelady is a perennial climbing twiner in the genus ''Thunbergia'', native to India and Southern Asia.
Distribution
It is native to India and Southern Asia where it is known as indrapushapa, it is also widesprea ...
,
Thunbergia grandiflora
''Thunbergia grandiflora'' is an evergreen vine in the family Acanthaceae. It is native to China, India, Nepal, Bangladesh, Indochina and Myanmar and widely naturalised elsewhere. Common names include Bengal clockvine, Bengal trumpet, blue skyfl ...
,
Thunbergia gregorii
''Thunbergia gregorii'', commonly known as orange clockvine or orange trumpet vine, is a herbaceous perennial climbing plant species in the family Acanthaceae, native to East Africa and sometimes cultivated as an ornamental vine. The bright, pur ...
,
Thunbergia laurifolia,
Thunbergia mysorensis,
Thunbergia natalensis);
Allium thunbergii;
Amaranthus thunbergii
''Amaranthus thunbergii'', commonly known as Thunberg's amaranthus or Thunberg's pigweed, is found in Africa.
The leaves are used as a flavouring or leafy vegetable.Grubben, G.J.H. & Denton, O.A. (2004) Plant Resources of Tropical Africa 2. Vege ...
;
Berberis thunbergii;
Geranium thunbergii;
Lespedeza thunbergii;
Pinus thunbergii;
Spiraea thunbergii
*
Maarten Gerritsz Vries:
Vries Strait
*
Nicolaes Witsen:
10653 Witsen (minor planet)
*
Wesel
Wesel () is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the capital of the Wesel district.
Geography
Wesel is situated at the confluence of the Lippe River and the Rhine.
Division of the city
Suburbs of Wesel include Lackhausen, Obrigho ...
(VOC ship):
Wessel Islands
Places and things named by VOC people
*
Arnhem Land (Australia)
*
De Witt Island
De Witt Island, also known as Big Witch, is an island located close to the south-western coast of Tasmania, Australia. The island is the largest of the Maatsuyker Islands Group, and comprises part of the Southwest National Park and the Tasma ...
(Tasmania, Australia)
*
Groote Eylandt (Australia)
*
Kaapstad / Cape Town (South Africa)
*
Moordenaers Baij / Murderers Bay (New Zealand), by Abel Tasman
*
Nova Hollandia / Nieuw Holland / New Holland (Mainland Australia), by Abel Tasman
*
Nova Zeelandia / Nieuw Zeeland / New Zealand, by VOC cartographers
*
Oranjerivier / Orange River (South Africa), by Robert Jacob Gordon
*
Pedra Branca (Tasmania), by Abel Tasman
*
Eylandt Rottenest / Rottnest Island, by Willem de Vlamingh
*
St Francis Island / Eyland St. François (South Australia), by
Pieter Nuyts and
François Thijssen
*
St Peter Island / Eyland St. Pierre (South Australia), by Pieter Nuyts and François Thijssen
*
Swarte Swaene-Revier / Zwaanenrivier / Swan River (Australia), by Willem de Vlamingh
Buildings and structures
*Forts:
Batavia Castle
Batavia Castle ( nl, Kasteel Batavia, ) was a fort located at the mouth of Ciliwung River in Jakarta. Batavia Castle was the administrative center of Dutch East India Company (VOC) in Asia.
Batavia Castle was also the residence of the Governor Ge ...
(Jakarta, Indonesia);
Fort Rotterdam (
Makassar, Indonesia);
Castle of Good Hope (Cape Town, South Africa);
Galle Fort (Galle, Sri Lanka);
Batticaloa Fort (Batticaloa, Sri Lanka);
Fort Zeelandia (
Anping District, Tainan, Taiwan)
*Others:
Oost-Indisch Huis
The Oost-Indisch Huis (Dutch for "East India House") is an early 17th-century building in the centre of Amsterdam. It was the headquarters of the Amsterdam chamber of the Dutch East India Company (''Vereenigde Oostindische Compagnie'' or VOC) ...
(Amsterdam, Netherlands);
Christ Church (Malacca City, Malaysia);
Stadthuys (Malacca City, Malaysia)
Archives and records
The VOC's operations (trading posts and colonies) produced not only warehouses packed with spices, coffee, tea, textiles, porcelain and silk, but also shiploads of documents. Data on political, economic, cultural, religious, and social conditions spread over an enormous area circulated between the VOC establishments, the administrative centre of the trade in
Batavia (modern-day
Jakarta), and the board of directors (the /Gentlemen Seventeen) in the Dutch Republic. The VOC records are included in
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international coope ...
's
Memory of the World Register.
Field of VOC World studies
The Dutch East India Company (VOC), as a historical transcontinental
company-state, is one of the best expertly researched business enterprises in history. For almost 200 years of the company's existence (1602–1800), the VOC had effectively transformed itself from a corporate entity into a state, an empire, or even a world in its own right. The VOC World (i.e. networks of people, places, things, activities, and events associated with the Dutch East India Company) has been the subject of a vast amount of literature, including works of fiction and non-fiction. VOC World studies (often included within a broader field of
early-modern Dutch global world studies) is an international
multidisciplinary field focused on social, cultural, religious, scientific, technological, economic, financial, business, maritime, military, political, legal, diplomatic activities, organization and administration of the VOC and
its colourful world. As North & Kaufmann (2014) notes, "the Dutch East India Company (VOC) has long attracted the attention of scholarship. Its lengthy history, widespread enterprises, and the survival of massive amounts of documentation – literally 1,200 meters of essays pertaining to the VOC may be found in the National Archives in The Hague, and many more documents are scattered in archives throughout Asia and in South Africa – have stimulated many works on economic and social history. Important publications have also appeared on the trade, shipping, institutional organization, and administration of the VOC. Much has also been learned about the VOC and Dutch colonial societies. Moreover, the TANAP (Towards a New Age of Partnership, 2000–2007) project has created momentum for research on the relationship between the VOC and indigenous societies. In contrast, the role of the VOC in cultural history and especially in the history of visual and material culture has not yet attracted comparable interest. To be sure, journals and other travel accounts (some even with illustrations) by soldiers, shippers, and VOC officials among others have been utilized as sources." VOC scholarship is highly specialized in general, such as archaeological studies of the VOC World. Some of the notable
VOC historians/scholars include
Sinnappah Arasaratnam,
Leonard Blussé,
Peter Borschberg,
Charles Ralph Boxer,
Jaap R. Bruijn,
Femme Gaastra
Femme Simon Gaastra (born 23 July 1945 in Leeuwarden, Netherlands) was a Dutch Professor of maritime history at the University of Leiden and a leading expert on the history of the Dutch East India Company.
Early life and education
Gaastra attende ...
,
Om Prakash
Om Prakash (born Om Prakash Chibber 19 December 1919 – 21 February 1998) was an Indian film actor. He was born in Jammu as Om Prakash Chibber and went on to become a well-known character actor of Bollywood. His most well-known movies are Na ...
,
Nigel Worden and Ian Burnet.
File:Fort Zeelandia, Anping District, Tainan City (Taiwan).jpg, Wall of Fort Zeelandia/ Fort Anping, Tainan (Taiwan)
File:Cape Town, Castle of Good Hope - panoramio.jpg, The Castle of Good Hope ( Kasteel de Goede Hoop in Dutch), Cape Town, South Africa
Gallery
File:DirectiekamerVOC.jpg, The restored conference room of the (the VOC's board of directors) in the East Indies House/Oost-Indisch Huis, Amsterdam
File:Ship Batavia 1.jpg, A replica of the VOC vessel '' Batavia'' (1620–29)
File:Half Moon in Hudson.jpg, 19th-century illustration '' Halve Maen'' ('' Half Moon'') in the Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between Ne ...
in 1609
File:Anonymous The Noord-Nieuwland in Table Bay, 1762.jpg, Anonymous painting with Table Mountain in the background, 1762
File:AMH-4802-KB The Dutch church or 'Kruiskerk' at Batavia.jpg, Dutch church at Batavia, Dutch East Indies, 1682
File:Museum Fatahillah Jakarta 2018 pas.jpg, Batavia City Hall in Kota Tua
Kota Tua Jakarta (Indonesian for "Jakarta Old Town"), officially known as Kota Tua, is a neighborhood comprising the original downtown area of Jakarta, Indonesia. It is also known as (Dutch for "Old Batavia"), ("Lower City", contrasting it wit ...
, Jakarta, Indonesia. The building was built in 1707 as administrative headquarter of the VOC.[Dinas Museum dan Sejarah (1986). ''Sejarah Singkat Gedung-Gedung Tua di Jakarta'' 'Brief History of Old Buildings in Jakarta''(in Indonesian). Jakarta: Dinas Museum dan Sejarah Pemerintah Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta.]
File:AMH-4803-KB The city hall on Batavia.jpg, ''Stadhuis van Batavia'', 1682 CE.
File:Nagasaka-Dejima-1764.jpg, A naval cannon ( Dejima, Nagasaki
is the capital and the largest city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan.
It became the sole port used for trade with the Portuguese and Dutch during the 16th through 19th centuries. The Hidden Christian Sites in the ...
, Japan). The letters "VOC" are the monogram of the "Vereenigde Oost-Indische Compagnie" and the letter "A" represents the "Amsterdam" Chamber of the company.
File:Seri-rambai-cannon-penang.jpg, The '' Seri Rambai'' at Fort Cornwallis, George Town, Penang, Malaysia
File:East Indies Company sword-J 09842-IMG 0919.JPG, Sword of the East India Company, featuring the V.O.C. monogram of the guard. On display at the Musée de l'Armée in Paris.
File:Dutch VOC ships in Chittagong or Arakan.jpg, VOC ships in Chittagong or Arakan.
File:Voyage de Levaillant1-01.jpg, Frontispiece from ''Voyage dans l'intérieur de l'Afrique'' by François Levaillant
File:Flag of the Dutch East India Company (Prinsenvlag).svg, First Flag of the Dutch East India Company
File:Flag of the Dutch East India Company.svg, Second Flag of the Dutch East India Company, adopted with red stripe around 1630 or 1663 and beyond, for the purpose of better visibility at sea against a light sky
File:Flag of the Dutch East Indies Company.svg, Flag of the Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the urban ar ...
Chamber of the Dutch East Indies Company
File:Flag of the Netherlands.svg, Later flag of the Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
), after Dutch East India Company was dissolved
File:Jingdezhen Porzellan Teller Schiffe KGM 88-571.jpg, Late 18th-century plate in European style, with Dutch/VOC ships, Canton porcelain, painted there on a "blank" from Jingdezhen.
See also
* The
Muscovy Company
* The
Levant Company
* The
British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and South ...
* The
Danish East India Company
* The
Dutch West India Company
* The
Portuguese East India Company
The Portuguese East India Company ( pt, Companhia do commércio da Índia or ) was a short-lived and ill-fated attempt by Philip III of Portugal, to create a chartered company to ensure the security of their interests in India, in the face of t ...
* The
French East India Company
* The
Danish West India Company
* The
Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business di ...
* The
Mississippi Company
The Mississippi Company (french: Compagnie du Mississippi; founded 1684, named the Company of the West from 1717, and the Company of the Indies from 1719) was a corporation holding a business monopoly in French colonies in North America and t ...
* The
South Sea Company
* The
Ostend Company
* The
Swedish East India Company
* The
Emden Company
* The
Austrian East India Company
* The
Swedish West India Company
* The
Russian-American Company
Notes
References
Bibliography
* Balk, G.L.; van Dijk, F.; Kortlang, D.J.; Gaastra, F.S.: ''The Archives of the Dutch East India Company (VOC) and the Local Institutions in Batavia (Jakarta)''. (Leiden: Brill, 2007) )
* Boxer, C.R. "The Dutch East India Company and the China Trade" ''History Today'' (Nov 1979), Vol. 29 Issue 11, p741–750; covers 1600 to 1800; online
*
Gaastra, Femme: ''De geschiedenis van de VOC''. (Zutphen: Walburg Pers, 1991)
n Dutch* Gaastra, Femme: ''The Dutch East India Company: Expansion and Decline''. (Zutphen: Walburg Pers, 2003)
* Landwehr, J.; van der Krogt, P.: ''VOC: A Bibliography of Publications Relating to the Dutch East India Company, 1602–1800''. (Utrecht: HES, 1991)
* Meilink-Roelofsz, M.A.P.; van Opstall, M.E.; Schutte, G.J. (eds.): ''Dutch Authors on Asian History: A Selection of Dutch Historiography on the Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie''. (Dordrecht: KITLV, 1988)
* Meilink-Roelofsz, M.A.P.; Raben, R.; Spijkerman, H. (eds.): ''De Archieven van de Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie (1602–1795)''
he Archives of the Dutch East India Company (1602–1795) ('s-Gravenhage: SDU Uitgeveri, 1992)
n Dutch*
Gerritsen, Rupert (ed.): ''A translation of the charter of the Dutch East Indies Company (Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie or VOC): Granted by the
States General of the United Netherlands, 20 March 1602''. Translated from the Dutch by Peter Reynders. (Canberra: Australia on the Map Division of the Australasian Hydrographic Society, 2009)
External links
VOC voyages– online database of voyages of VOC ships
Atlas of Mutual Heritage– online atlas of VOC and WIC settlements
Database of VOC crew membersVOC Historical SocietyVOC WarfareVOC archive from the Indonesian national archives
{{Authority control
1602 establishments in the Dutch Republic
1800 disestablishments in the Batavian Republic
Chartered companies
Colonial Indian companies
Companies based in Amsterdam
Companies disestablished in 1800
Companies established in 1602
Companies formerly listed on Euronext Amsterdam
Conglomerate companies
Defunct companies of the Netherlands
Former monopolies
History of the Dutch Empire
India–Netherlands relations
Maritime history of the Dutch Republic
Military history of the Dutch Empire
Multinational companies headquartered in the Netherlands
Shipping companies of the Dutch Republic
Dutch slave trade
Trading companies established in the 17th century
Trading companies of the Dutch Republic

 The stage was thus set for Dutch expeditions to the Indonesian islands, beginning with James Lancaster in 1591, Cornelis de Houtman in 1595 and again in 1598,
The stage was thus set for Dutch expeditions to the Indonesian islands, beginning with James Lancaster in 1591, Cornelis de Houtman in 1595 and again in 1598,  In 1598, an increasing number of fleets were sent out by competing merchant groups from around the Netherlands. Some fleets were lost, but most were successful, with some voyages producing high profits. In 1598, a fleet of eight ships under
In 1598, an increasing number of fleets were sent out by competing merchant groups from around the Netherlands. Some fleets were lost, but most were successful, with some voyages producing high profits. In 1598, a fleet of eight ships under  At the time, it was customary for a company to be funded only for the duration of a single voyage and to be liquidated upon the return of the fleet. Investment in these expeditions was a very high-risk venture, not only because of the usual dangers of piracy, disease and shipwreck, but also because the interplay of inelastic demand and relatively elastic supply of spices could make prices tumble, thereby ruining prospects of profitability. To manage such risk, the forming of a cartel to control supply would seem logical. In 1600, the English were the first to adopt this approach by bundling their resources into a monopoly enterprise, the English East India Company, thereby threatening their Dutch competitors with ruin.De Vries and Van der Woude, p. 384–385
In 1602, the Dutch government followed suit, sponsoring the creation of a single "United East Indies Company" that was also granted monopoly over the Asian trade. For a time in the seventeenth century, it was able to monopolise the trade in nutmeg, mace, and cloves and to sell these spices across European kingdoms and Emperor Akbar the Great's Mughal Empire at 14-17 times the price it paid in
At the time, it was customary for a company to be funded only for the duration of a single voyage and to be liquidated upon the return of the fleet. Investment in these expeditions was a very high-risk venture, not only because of the usual dangers of piracy, disease and shipwreck, but also because the interplay of inelastic demand and relatively elastic supply of spices could make prices tumble, thereby ruining prospects of profitability. To manage such risk, the forming of a cartel to control supply would seem logical. In 1600, the English were the first to adopt this approach by bundling their resources into a monopoly enterprise, the English East India Company, thereby threatening their Dutch competitors with ruin.De Vries and Van der Woude, p. 384–385
In 1602, the Dutch government followed suit, sponsoring the creation of a single "United East Indies Company" that was also granted monopoly over the Asian trade. For a time in the seventeenth century, it was able to monopolise the trade in nutmeg, mace, and cloves and to sell these spices across European kingdoms and Emperor Akbar the Great's Mughal Empire at 14-17 times the price it paid in  VOC headquarters were located in Ambon during the tenures of the first three governors-general (1610–1619), but it was not a satisfactory location. Although it was at the centre of the spice production areas, it was far from the Asian trade routes and other VOC areas of activity ranging from Africa to India to Japan. A location in the west of the archipelago was thus sought. The Straits of Malacca were strategic but became dangerous following the Portuguese conquest, and the first permanent VOC settlement in Banten was controlled by a powerful local ruler and subject to stiff competition from Chinese and English traders.
In 1604, a second English
VOC headquarters were located in Ambon during the tenures of the first three governors-general (1610–1619), but it was not a satisfactory location. Although it was at the centre of the spice production areas, it was far from the Asian trade routes and other VOC areas of activity ranging from Africa to India to Japan. A location in the west of the archipelago was thus sought. The Straits of Malacca were strategic but became dangerous following the Portuguese conquest, and the first permanent VOC settlement in Banten was controlled by a powerful local ruler and subject to stiff competition from Chinese and English traders.
In 1604, a second English 
 In 1619, Jan Pieterszoon Coen was appointed governor-general of the VOC. He saw the possibility of the VOC becoming an Asian power, both political and economic. On 30 May 1619, Coen, backed by a force of nineteen ships, stormed Jayakarta, driving out the Banten forces; and from the ashes established Batavia as the VOC headquarters. In the 1620s almost the entire native population of the Banda Islands was driven away, starved to death, or killed in an attempt to replace them with Dutch plantations. These plantations were used to grow nutmeg for export. Coen hoped to settle large numbers of Dutch colonists in the East Indies, but implementation of this policy never materialised, mainly because very few Dutch were willing to emigrate to Asia.
Another of Coen's ventures was more successful. A major problem in the European trade with Asia at the time was that the Europeans could offer few goods that Asian consumers wanted, except silver and gold. European traders therefore had to pay for spices with the precious metals, which were in short supply in Europe, except for Spain and Portugal. The Dutch and English had to obtain it by creating a trade surplus with other European countries. Coen discovered the obvious solution for the problem: to start an intra-Asiatic trade system, whose profits could be used to finance the spice trade with Europe. In the long run this obviated the need for exports of precious metals from Europe, though at first it required the formation of a large trading-capital fund in the Indies. The VOC reinvested a large share of its profits to this end in the period up to 1630.De Vries and Van der Woude, p. 386
The VOC traded throughout Asia, benefiting mainly from
In 1619, Jan Pieterszoon Coen was appointed governor-general of the VOC. He saw the possibility of the VOC becoming an Asian power, both political and economic. On 30 May 1619, Coen, backed by a force of nineteen ships, stormed Jayakarta, driving out the Banten forces; and from the ashes established Batavia as the VOC headquarters. In the 1620s almost the entire native population of the Banda Islands was driven away, starved to death, or killed in an attempt to replace them with Dutch plantations. These plantations were used to grow nutmeg for export. Coen hoped to settle large numbers of Dutch colonists in the East Indies, but implementation of this policy never materialised, mainly because very few Dutch were willing to emigrate to Asia.
Another of Coen's ventures was more successful. A major problem in the European trade with Asia at the time was that the Europeans could offer few goods that Asian consumers wanted, except silver and gold. European traders therefore had to pay for spices with the precious metals, which were in short supply in Europe, except for Spain and Portugal. The Dutch and English had to obtain it by creating a trade surplus with other European countries. Coen discovered the obvious solution for the problem: to start an intra-Asiatic trade system, whose profits could be used to finance the spice trade with Europe. In the long run this obviated the need for exports of precious metals from Europe, though at first it required the formation of a large trading-capital fund in the Indies. The VOC reinvested a large share of its profits to this end in the period up to 1630.De Vries and Van der Woude, p. 386
The VOC traded throughout Asia, benefiting mainly from  In 1640, the VOC obtained the port of Galle, Ceylon, from the Portuguese and broke the latter's monopoly of the cinnamon trade. In 1658,
In 1640, the VOC obtained the port of Galle, Ceylon, from the Portuguese and broke the latter's monopoly of the cinnamon trade. In 1658, 
 After 1730, the fortunes of the VOC started to decline. Five major problems, not all of equal weight, explain its decline over the next fifty years to 1780:
*There was a steady erosion of intra-Asiatic trade because of changes in the Asiatic political and economic environment that the VOC could do little about. These factors gradually squeezed the company out of Persia, Suratte, the Malabar Coast, and Bengal. The company had to confine its operations to the belt it physically controlled, from Ceylon through the Indonesian archipelago. The volume of this intra-Asiatic trade, and its profitability, therefore had to shrink.
*The way the company was organised in Asia (centralised on its hub in Batavia), that initially had offered advantages in gathering market information, began to cause disadvantages in the 18th century because of the inefficiency of first shipping everything to this central point. This disadvantage was most keenly felt in the tea trade, where competitors like the EIC and the Ostend Company shipped directly from China to Europe.
*The "venality" of the VOC's personnel (in the sense of corruption and non-performance of duties), though a problem for all East India Companies at the time, seems to have plagued the VOC on a larger scale than its competitors. To be sure, the company was not a "good employer". Salaries were low, and "private-account trading" was officially not allowed. Not surprisingly, it proliferated in the 18th century to the detriment of the company's performance. From about the 1790s onward, the phrase ''perished under corruption'' (''vergaan onder corruptie'', also abbreviated VOC in Dutch) came to summarise the company's future.
*A problem that the VOC shared with other companies was the high mortality and morbidity rates among its employees. This decimated the company's ranks and enervated many of the survivors.
*A self-inflicted wound was the VOC's dividend policy. The dividends distributed by the company had exceeded the surplus it garnered in Europe in every decade from 1690 to 1760 except 1710–1720. However, in the period up to 1730 the directors shipped resources to Asia to build up the trading capital there. Consolidated bookkeeping therefore probably would have shown that total profits exceeded dividends. In addition, between 1700 and 1740 the company retired 5.4 million guilders of long-term debt. The company therefore was still on a secure financial footing in these years. This changed after 1730. While profits plummeted the ''bewindhebbers'' only slightly decreased dividends from the earlier level. Distributed dividends were therefore in excess of earnings in every decade but one (1760–1770). To accomplish this, the Asian capital stock had to be drawn down by 4 million guilders between 1730 and 1780, and the liquid capital available in Europe was reduced by 20 million guilders in the same period. The directors were therefore constrained to replenish the company's liquidity by resorting to short-term financing from anticipatory loans, backed by expected revenues from home-bound fleets.
After 1730, the fortunes of the VOC started to decline. Five major problems, not all of equal weight, explain its decline over the next fifty years to 1780:
*There was a steady erosion of intra-Asiatic trade because of changes in the Asiatic political and economic environment that the VOC could do little about. These factors gradually squeezed the company out of Persia, Suratte, the Malabar Coast, and Bengal. The company had to confine its operations to the belt it physically controlled, from Ceylon through the Indonesian archipelago. The volume of this intra-Asiatic trade, and its profitability, therefore had to shrink.
*The way the company was organised in Asia (centralised on its hub in Batavia), that initially had offered advantages in gathering market information, began to cause disadvantages in the 18th century because of the inefficiency of first shipping everything to this central point. This disadvantage was most keenly felt in the tea trade, where competitors like the EIC and the Ostend Company shipped directly from China to Europe.
*The "venality" of the VOC's personnel (in the sense of corruption and non-performance of duties), though a problem for all East India Companies at the time, seems to have plagued the VOC on a larger scale than its competitors. To be sure, the company was not a "good employer". Salaries were low, and "private-account trading" was officially not allowed. Not surprisingly, it proliferated in the 18th century to the detriment of the company's performance. From about the 1790s onward, the phrase ''perished under corruption'' (''vergaan onder corruptie'', also abbreviated VOC in Dutch) came to summarise the company's future.
*A problem that the VOC shared with other companies was the high mortality and morbidity rates among its employees. This decimated the company's ranks and enervated many of the survivors.
*A self-inflicted wound was the VOC's dividend policy. The dividends distributed by the company had exceeded the surplus it garnered in Europe in every decade from 1690 to 1760 except 1710–1720. However, in the period up to 1730 the directors shipped resources to Asia to build up the trading capital there. Consolidated bookkeeping therefore probably would have shown that total profits exceeded dividends. In addition, between 1700 and 1740 the company retired 5.4 million guilders of long-term debt. The company therefore was still on a secure financial footing in these years. This changed after 1730. While profits plummeted the ''bewindhebbers'' only slightly decreased dividends from the earlier level. Distributed dividends were therefore in excess of earnings in every decade but one (1760–1770). To accomplish this, the Asian capital stock had to be drawn down by 4 million guilders between 1730 and 1780, and the liquid capital available in Europe was reduced by 20 million guilders in the same period. The directors were therefore constrained to replenish the company's liquidity by resorting to short-term financing from anticipatory loans, backed by expected revenues from home-bound fleets.
 Despite these problems, the VOC in 1780 remained an enormous operation. Its capital in the Republic, consisting of ships and goods in inventory, totalled 28 million guilders; its capital in Asia, consisting of the liquid trading fund and goods en route to Europe, totalled 46 million guilders. Total capital, net of outstanding debt, stood at 62 million guilders. The prospects of the company at this time therefore were not hopeless, had one of the plans for reform been undertaken successfully. However, the
Despite these problems, the VOC in 1780 remained an enormous operation. Its capital in the Republic, consisting of ships and goods in inventory, totalled 28 million guilders; its capital in Asia, consisting of the liquid trading fund and goods en route to Europe, totalled 46 million guilders. Total capital, net of outstanding debt, stood at 62 million guilders. The prospects of the company at this time therefore were not hopeless, had one of the plans for reform been undertaken successfully. However, the  Among the early shareholders of the VOC, immigrants played an important role. Under the 1,143 tenderers were 39
Among the early shareholders of the VOC, immigrants played an important role. Under the 1,143 tenderers were 39  The seventeenth-century Dutch businessmen, especially the VOC investors, were possibly history's first recorded investors to seriously consider the
The seventeenth-century Dutch businessmen, especially the VOC investors, were possibly history's first recorded investors to seriously consider the 



 In 1609, English sea captain and explorer
In 1609, English sea captain and explorer  In terms of world history of geography and exploration, the VOC can be credited with putting most of Australia's coast (then Hollandia Nova and other names) on the world map, between 1606 and 1756.
While Australia's territory (originally known as New Holland) never became an actual Dutch settlement or colony, Dutch navigators were the first to undisputedly explore and map Australian coastline. In the 17th century, the VOC's navigators and explorers charted almost three-quarters of Australia's coastline, except its east coast. The Dutch ship, '' Duyfken'', led by Willem Janszoon, made the first documented European landing in Australia in 1606. Although a theory of Portuguese discovery in the 1520s exists, it lacks definitive evidence. Precedence of discovery has also been claimed for China, France,Credit for the discovery of Australia was given to Frenchman Binot Paulmier de Gonneville (1504) in Spain,In the early 20th century, Lawrence Hargrave argued from archaeological evidence that Spain had established a colony in Botany Bay in the 16th century.
In terms of world history of geography and exploration, the VOC can be credited with putting most of Australia's coast (then Hollandia Nova and other names) on the world map, between 1606 and 1756.
While Australia's territory (originally known as New Holland) never became an actual Dutch settlement or colony, Dutch navigators were the first to undisputedly explore and map Australian coastline. In the 17th century, the VOC's navigators and explorers charted almost three-quarters of Australia's coastline, except its east coast. The Dutch ship, '' Duyfken'', led by Willem Janszoon, made the first documented European landing in Australia in 1606. Although a theory of Portuguese discovery in the 1520s exists, it lacks definitive evidence. Precedence of discovery has also been claimed for China, France,Credit for the discovery of Australia was given to Frenchman Binot Paulmier de Gonneville (1504) in Spain,In the early 20th century, Lawrence Hargrave argued from archaeological evidence that Spain had established a colony in Botany Bay in the 16th century.  The company has been criticised for its quasi-absolute commercial monopoly,
The company has been criticised for its quasi-absolute commercial monopoly, 

 *'' Batavia'': a shipwreck on the Houtman Abrolhos in 1629, made famous by the subsequent mutiny and massacre that took place among the survivors
*'' Flying Dutchman'': a legendary ghost ship in several maritime myths, likely to have originated from the 17th-century golden age of the VOC.
*''
*'' Batavia'': a shipwreck on the Houtman Abrolhos in 1629, made famous by the subsequent mutiny and massacre that took place among the survivors
*'' Flying Dutchman'': a legendary ghost ship in several maritime myths, likely to have originated from the 17th-century golden age of the VOC.
*''