Durham Light Infantry on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
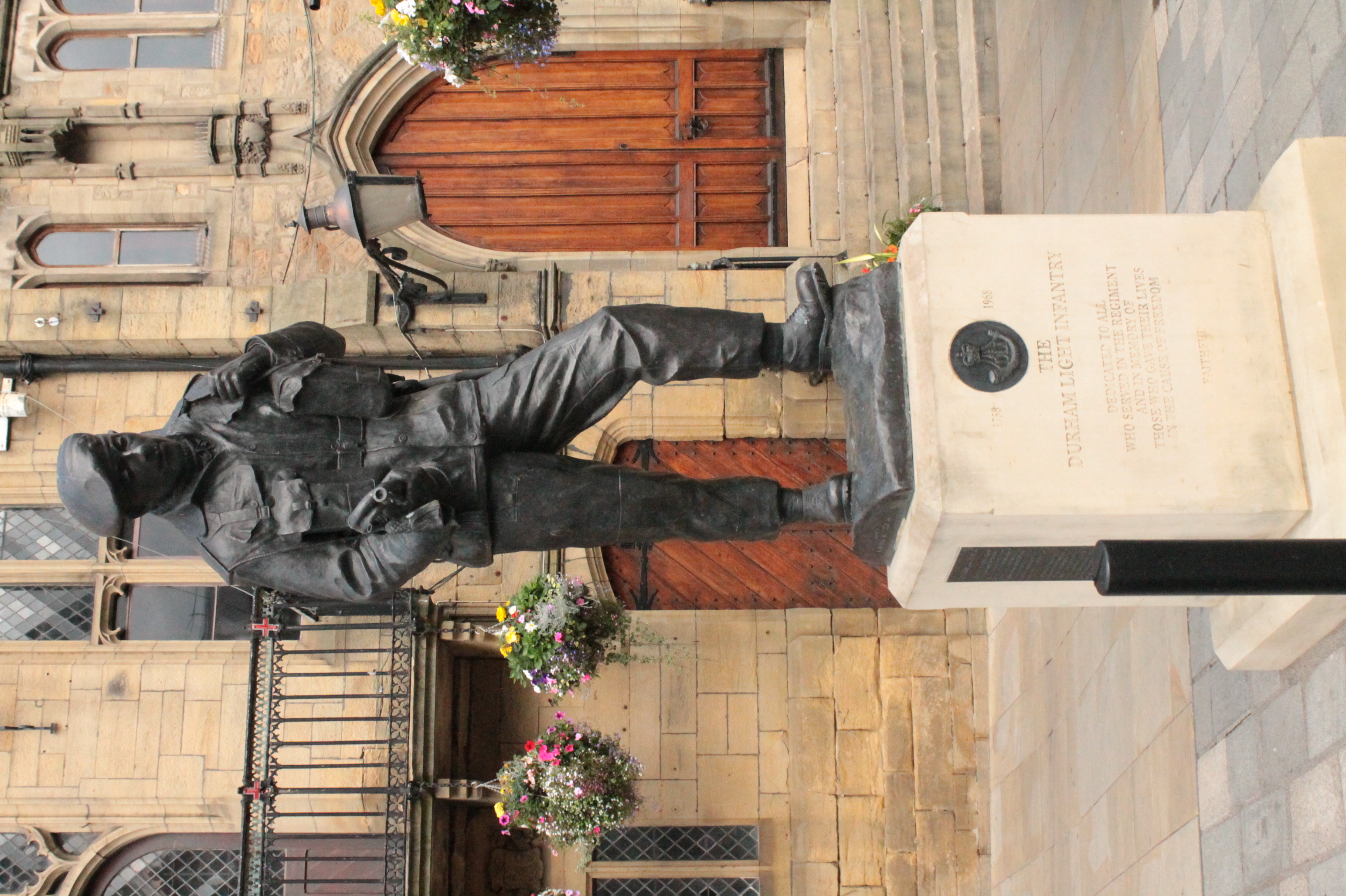 The Durham Light Infantry (DLI) was a
The Durham Light Infantry (DLI) was a
 The 1st battalion was dispatched from Britain to South Africa to take part in the Second Anglo-Boer War, arriving in November 1899, after local forces had been besieged in Mafeking, and the British forces stationed there had been surrounded in the town of
The 1st battalion was dispatched from Britain to South Africa to take part in the Second Anglo-Boer War, arriving in November 1899, after local forces had been besieged in Mafeking, and the British forces stationed there had been surrounded in the town of
 The 1st battalion and the company from the 2nd left South Africa for India on the SS ''Assaye'' at the end of October 1902, and on 15 November both battalions met at Calicut, before the 2nd battalion, which had been guarding Boer prisoners, left for Britain. The 1st battalion was stationed at
The 1st battalion and the company from the 2nd left South Africa for India on the SS ''Assaye'' at the end of October 1902, and on 15 November both battalions met at Calicut, before the 2nd battalion, which had been guarding Boer prisoners, left for Britain. The 1st battalion was stationed at
 The Somme offensive was originally planned, earlier in the year, as a joint British-French offensive but due to the increasing pressure on the French at
The Somme offensive was originally planned, earlier in the year, as a joint British-French offensive but due to the increasing pressure on the French at
 The next battle around the Ypres salient was to clear the Germans from the remaining high ground to the East of the city. The 20th battalion was involved in the first day's attacks on 31 July, advancing alongside the Ypres-Comines canal for the loss of 8 officers and 431 other ranks.Ward p. 386 The next advance was held up until near the end of August by heavy rains and was directed along the Menin Road, here the 10th battalion attempted to take and hold Inverness Copse losing over half its original strength by 25 August. General Plumer's methodical advance began on 20 September on the Menin Road ridge. The 20th battalion's advance on 21 September was checked after 200 yards, the 13th battalion reached their objective with both battalions losing around 300 men. The third of General Plumer's steps, the
The next battle around the Ypres salient was to clear the Germans from the remaining high ground to the East of the city. The 20th battalion was involved in the first day's attacks on 31 July, advancing alongside the Ypres-Comines canal for the loss of 8 officers and 431 other ranks.Ward p. 386 The next advance was held up until near the end of August by heavy rains and was directed along the Menin Road, here the 10th battalion attempted to take and hold Inverness Copse losing over half its original strength by 25 August. General Plumer's methodical advance began on 20 September on the Menin Road ridge. The 20th battalion's advance on 21 September was checked after 200 yards, the 13th battalion reached their objective with both battalions losing around 300 men. The third of General Plumer's steps, the 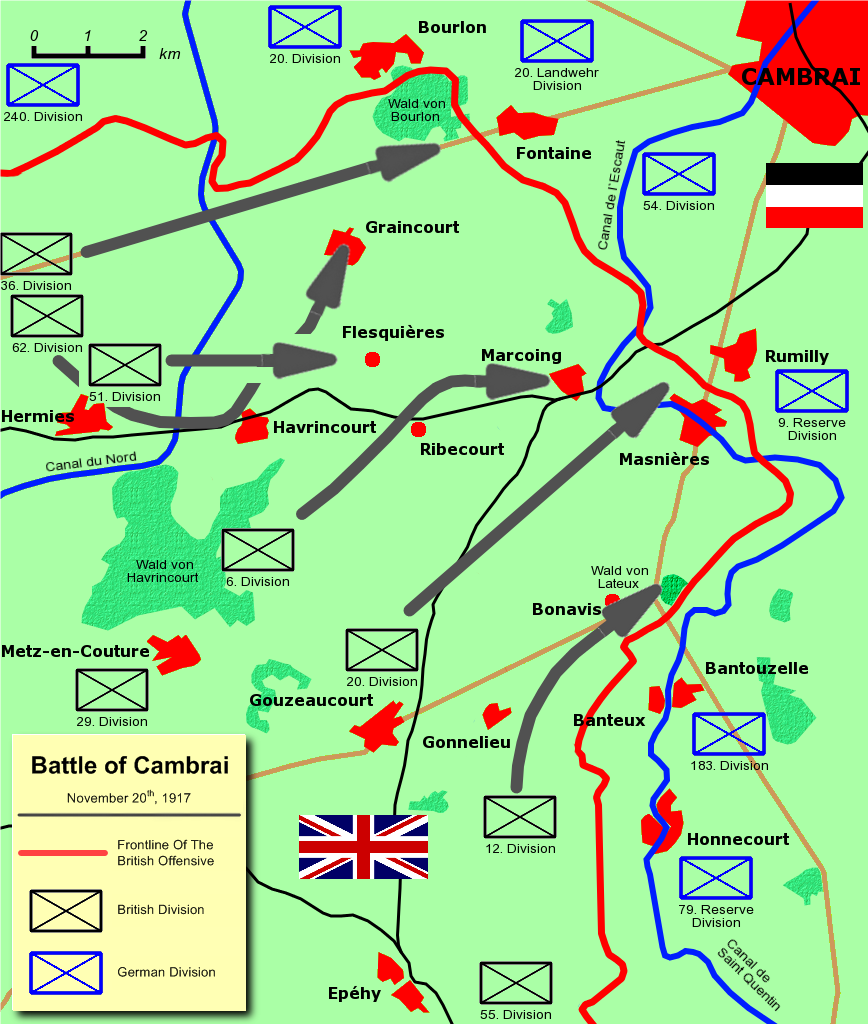 The Battle of Cambrai was the first successful use of maturing
The Battle of Cambrai was the first successful use of maturing
 The British Divisions were deployed between
The British Divisions were deployed between
 By 1920, the service battalions had been disbanded with their King's colours laid up in Durham Cathedral except for the 20th battalion's at the parish church of Bishopwearmouth.
The 1st battalion was reformed with drafts from the 3rd (the last act of the Militia) and left for Germany, still understrength, in March 1921 for duty in Upper
By 1920, the service battalions had been disbanded with their King's colours laid up in Durham Cathedral except for the 20th battalion's at the parish church of Bishopwearmouth.
The 1st battalion was reformed with drafts from the 3rd (the last act of the Militia) and left for Germany, still understrength, in March 1921 for duty in Upper
 The 50th Division returned to the front line when the Eighth Army reached the
The 50th Division returned to the front line when the Eighth Army reached the
 The 2nd battalion was sent to India in April 1942 with the 2nd Division, arriving in June. For some months it was trained in Jungle fighting and in amphibious assault methods. Later in that year the 6th brigade was made an independent formation. The brigade fought in the
The 2nd battalion was sent to India in April 1942 with the 2nd Division, arriving in June. For some months it was trained in Jungle fighting and in amphibious assault methods. Later in that year the 6th brigade was made an independent formation. The brigade fought in the
 The 151st brigade was chosen as an assault brigade for the
The 151st brigade was chosen as an assault brigade for the
 The 50th Division with its 151st brigade was withdrawn to Britain in October 1943 to be trained for the
The 50th Division with its 151st brigade was withdrawn to Britain in October 1943 to be trained for the  The 9th battalion was reinforced and transferred to 7th Armoured Division, 131st Infantry Brigade, as a motorised battalion fighting at the
The 9th battalion was reinforced and transferred to 7th Armoured Division, 131st Infantry Brigade, as a motorised battalion fighting at the
 The Durham Light Infantry (DLI) was a
The Durham Light Infantry (DLI) was a light infantry
Light infantry refers to certain types of lightly equipped infantry throughout history. They have a more mobile or fluid function than other types of infantry, such as heavy infantry or line infantry. Historically, light infantry often fought ...
regiment
A regiment is a military unit. Its role and size varies markedly, depending on the country, service and/or a specialisation.
In Medieval Europe, the term "regiment" denoted any large body of front-line soldiers, recruited or conscript ...
of the British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurk ...
in existence from 1881 to 1968. It was formed in 1881 under the Childers Reforms by the amalgamation of the 68th (Durham) Regiment of Foot (Light Infantry)
The 68th (Durham) Regiment of Foot (Light Infantry) was an infantry regiment of the British Army, raised in 1758. Under the Childers Reforms it amalgamated with the 106th Regiment of Foot (Bombay Light Infantry), 106th Bombay Light Infantry to ...
and the 106th Regiment of Foot (Bombay Light Infantry)
The 106th Regiment of Foot (Bombay Light Infantry) was an infantry regiment of the British Army from 1862 to 1881, the third to bear the number after the Black Musqueteers (1761–1763) and a regiment raised briefly in 1794. It was formed by r ...
along with the Militia and Volunteers of County Durham
The Militia and Volunteers of County Durham are those military units raised in the County independent of the regular Army. The "modern" militia dates from legislation enacted during the Seven Years' War. The volunteers had several forms and separa ...
.
The regiment served notably in the Second Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the South ...
, World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the Korean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
and the Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation. During times of peace it had duty in India, China, West Germany and Cyprus.
In 1968, the regiment was amalgamated with the Somerset and Cornwall Light Infantry
The Somerset and Cornwall Light Infantry (SCLI) was a light infantry regiment of the British Army. It was formed in October 1959 by the merger of the Somerset Light Infantry and the Duke of Cornwall's Light Infantry, and was itself merged with ...
, the King's Own Yorkshire Light Infantry and the King's Shropshire Light Infantry
The King's Shropshire Light Infantry (KSLI) was a light infantry regiment of the British Army, formed in the Childers Reforms of 1881, but with antecedents dating back to 1755. It served in the Second Boer War, World War I and World War II. In 19 ...
to form The Light Infantry
The Light Infantry was an infantry regiment of the British Army, part of the Light Division. The regiment was one of four 'large' regiments formed after the 1966 Defence White Paper through the amalgamation of units of the Light Infantry Brig ...
, which again amalgamated in 2007 with the Devonshire and Dorset Regiment
The Devonshire and Dorset Regiment (11th, 39th and 54th), usually just known as the Devon and Dorsets, was an infantry regiment of the British Army formed in 1958 by the amalgamation of two county regiments, the Devonshire Regiment and the Dorset ...
, the Royal Gloucestershire, Berkshire and Wiltshire Regiment
The Royal Gloucestershire, Berkshire and Wiltshire Regiment was a short-lived infantry regiment of the British Army.
History
The regiment was formed in 1994 by the amalgamation of the Gloucestershire Regiment and the Duke of Edinburgh's Royal Re ...
and the Royal Green Jackets
The Royal Green Jackets (RGJ) was an infantry regiment of the British Army, one of two "large regiments" within the Light Division (the other being The Light Infantry).
History
The Royal Green Jackets was formed on 1 January 1966 by the amalgama ...
to form a new large regiment A large regiment is a multi-battalion infantry formation of the British Army. First formed in the 1960s, large regiments are the result of the amalgamation of a number of existing single-battalion regiments, and perpetuate the traditions of each of ...
, The Rifles
The Rifles is an infantry regiment of the British Army. Formed in 2007, it consists of four Regular battalions and three Reserve battalions, plus a number of companies in other Army Reserve battalions. Each battalion of The Rifles was formerl ...
, which continues the lineage of the regiment.
Formation
As part of the Cardwell and Childers Reforms of the British Army's regiments, in 1881 the68th (Durham) Regiment of Foot (Light Infantry)
The 68th (Durham) Regiment of Foot (Light Infantry) was an infantry regiment of the British Army, raised in 1758. Under the Childers Reforms it amalgamated with the 106th Regiment of Foot (Bombay Light Infantry), 106th Bombay Light Infantry to ...
and the 106th Regiment of Foot (Bombay Light Infantry)
The 106th Regiment of Foot (Bombay Light Infantry) was an infantry regiment of the British Army from 1862 to 1881, the third to bear the number after the Black Musqueteers (1761–1763) and a regiment raised briefly in 1794. It was formed by r ...
became the 1st and 2nd battalions of the Durham Light Infantry. Both already had their depots at Sunderland Barracks in Sunderland, as was the Brigade Depot (No. 3). The militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of r ...
battalionsthe 1st Durham Fusiliers and 2nd North Durham Militiabecame the 3rd and 4th battalions of the new regiment, with their depots in Barnard Castle
Barnard Castle (, ) is a market town on the north bank of the River Tees, in County Durham, Northern England. The town is named after and built around a medieval castle ruin. The town's Bowes Museum's has an 18th-century Silver Swan automato ...
and Durham City. The five Volunteer Force
The Volunteer Force was a citizen army of part-time rifle, artillery and engineer corps, created as a popular movement throughout the British Empire in 1859. Originally highly autonomous, the units of volunteers became increasingly integrated ...
battalions of Durham Rifle Volunteersthe 1st to 4th Administrative battalions of the Durham Rifle Volunteers and the 3rd Durham Rifle Volunteer Corpsbecame the 1st to 5th Volunteer battalions.
A new regimental badge was to be worn, a Tudor rose
The Tudor rose (sometimes called the Union rose) is the traditional floral heraldic badge, heraldic emblem of England and takes its name and origins from the House of Tudor, which united the House of Lancaster and the House of York. The Tudor ...
, this was never worn on any article of clothing, but did appear on the colours until 1934. Instead the light infantry bugle horn was modified with a crown and the regiment's abbreviation.
The system was designed to permit one regular battalion of a regiment to be stationed at home, providing trained recruits for the other on overseas service.
History
1881–99
On formation of the regiment the 1st Battalion was in India atMeerut
Meerut (, IAST: ''Meraṭh'') is a city in Meerut district of the western part of the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The city lies northeast of the national capital New Delhi, within the National Capital Region and west of the state capital ...
and the 2nd Battalion was in Ireland at Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of th ...
.Vane p. 121 The elements of the new regiment still maintained a separate and independent existence, as they had since being grouped together in 1873, however the introduction of shorter service (six years, then another six in the reserves) and the increase in cross posting of officers in the linked regular and Militia battalions, increased the assimilation into a single regiment.
In August 1882 the 2nd Battalion was sent to the garrison the Mediterranean, being split between Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
and Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
, it was reunited in March 1883 at Gibraltar.
In 1884, the Depot moved from Sunderland to Fenham Barracks
Fenham Barracks is a military installation in Barrack Road, Newcastle upon Tyne.
History
The site was acquired by the War Office from Newcastle Corporation in 1804 and, following the construction of three barrack blocks, became the home of units ...
in Newcastle upon Tyne
Newcastle upon Tyne ( RP: , ), or simply Newcastle, is a city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England. The city is located on the River Tyne's northern bank and forms the largest part of the Tyneside built-up area. Newcastle is ...
which it shared with the Northumberland Fusiliers
The Royal Northumberland Fusiliers was an infantry regiment of the British Army. Raised in 1674 as one of three 'English' units in the Dutch Anglo-Scots Brigade, it accompanied William III to England in the November 1688 Glorious Revolution ...
as there was no suitable site near Durham City "which could not be relied upon as not being undermined". The move was not popular as it took the Depot out of the County, it was not to return until 1939, when it was transferred to Brancepeth Castle.
In 1885 the 2nd Battalion was transferred to Egypt to take part in the Mahdist War and was employed with the force under General Stephenson to repel attacks on the railway between Wadi Halfa and Akasha, fighting at the Battle of Ginnis. After the battle, while securing one of the Arab's nuggers (supply boats), an Arab child of about two years was found by the battalion's mounted infantry. Brought back and baptised as James Francis Durham (Jimmy Durham) he would enlist with the regiment and become a corporal of buglers before dying in August 1910. In January 1887, the 2nd Battalion sailed from Suez
Suez ( ar, السويس '; ) is a seaport city (population of about 750,000 ) in north-eastern Egypt, located on the north coast of the Gulf of Suez (a branch of the Red Sea), near the southern terminus of the Suez Canal, having the same boun ...
to India, while in March, the 1st Battalion returned from there to Britain.
While in India, the 2nd Battalion came to dominate the Indian polo scene, winning 17 tournaments against "rich men's regiments" and cavalry regiments. In 1897 and 1898, it assisted in combating outbreaks of the plague in Poona
Pune (; ; also known as Poona, (List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name from 1818 until 1978) is one of the most important industrial and educational hubs of India, with an estimated population of 7.4 million ...
and Bombay
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the second- ...
.
Second Boer War
 The 1st battalion was dispatched from Britain to South Africa to take part in the Second Anglo-Boer War, arriving in November 1899, after local forces had been besieged in Mafeking, and the British forces stationed there had been surrounded in the town of
The 1st battalion was dispatched from Britain to South Africa to take part in the Second Anglo-Boer War, arriving in November 1899, after local forces had been besieged in Mafeking, and the British forces stationed there had been surrounded in the town of Ladysmith Ladysmith may refer to:
* Ladysmith, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa
* Ladysmith, British Columbia, Canada
* Ladysmith, Wisconsin, United States
* Ladysmith, New South Wales, Australia
* Ladysmith, Virginia, United States
* Ladysmith Island, Queenslan ...
. The battalion was involved in General Redvers Buller
General Sir Redvers Henry Buller, (7 December 1839 – 2 June 1908) was a British Army officer and a recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth forc ...
's unsuccessful attempts to approach Ladysmith across the Teluga river, in reserve for the Battle of Colenso, launching diversionary attacks to the east of Spion Kop, and in early February attacked Vaal Krantz
The Battle of Vaal Krantz (5 February to 7 February 1900) was the third failed attempt by General Redvers Buller's British army to fight its way past Louis Botha's army of Boer irregulars and lift the Siege of Ladysmith. The battle occurred durin ...
with the battalion taking two hills of the ridge, before the position was abandoned. The battalion was in a supporting role for the Relief of Ladysmith
When the Second Boer War broke out on 11 October 1899, the Boers had a numeric superiority within Southern Africa. They quickly invaded the British territory and laid siege to Ladysmith, Kimberley and Mafeking. Britain meanwhile transported th ...
Vane ch10 and took little part in the offensive that ended with the annexation of the Transvaal in September 1900.
The war now became one of guerilla raids by the Boers against the British forces and their lines of communication. The battalion was deployed guarding a section of railway line in the Transvaal, while sending two platoon sized units to the mounted infantry. During this time the battalion was joined or reinforced by other units from the regiment. One company from the 2nd battalion came from India in January 1900 and formed part of the Burmah Mounted Infantry, seeing action at Sanna's Post
Sanna's Post (a.k.a. Korn Spruit) was an engagement fought during the Second Boer War (1899-1902) between the British Empire and the Boers of the two independent republics of the Orange Free State and the South African Republic.
Background
In e ...
.
The 3rd and 4th battalions were embodied and also served in South Africa. The 3rd arriving in February 1900, where it guarded lines of communications in the Cape Colony and the Orange Free State, escorted convoys and garrisoned Dewetsdorp for 6 months.Vane p. 299 The 4th arrived in February 1902 and was split into detachments serving in many places, and a mounted infantry company, which escorted convoys. Almost 800 officers and men of the 4th battalion returned to the United Kingdom on the SS ''Roslin Castle'' in September 1902, following the end of the war, and returned to Newcastle for disembodiment.
The volunteer battalions supplied contingents to form three special service companies, reinforcing the 1st battalion, which served individually from March 1900 to April 1902.
Pre First World War
 The 1st battalion and the company from the 2nd left South Africa for India on the SS ''Assaye'' at the end of October 1902, and on 15 November both battalions met at Calicut, before the 2nd battalion, which had been guarding Boer prisoners, left for Britain. The 1st battalion was stationed at
The 1st battalion and the company from the 2nd left South Africa for India on the SS ''Assaye'' at the end of October 1902, and on 15 November both battalions met at Calicut, before the 2nd battalion, which had been guarding Boer prisoners, left for Britain. The 1st battalion was stationed at Wellington
Wellington ( mi, Te Whanganui-a-Tara or ) is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the second-largest city in New Zealand by me ...
in Madras Presidency.
In 1908, as part of the Territorial Forces Act, the 3rd and 4th battalions exchanged numbers and were recast as the 3rd (Reserve) and 4th (Extra Reserve) battalions in a draft finding role. The 1st to 5th Volunteer battalions were renumbered as the 5th to 9th battalions Durham Light Infantry of the Territorial Force
The Territorial Force was a part-time volunteer component of the British Army, created in 1908 to augment British land forces without resorting to conscription. The new organisation consolidated the 19th-century Volunteer Force and yeomanry ...
. The 5th formed part of the York and Durham Brigade and the 6th–9th battalions formed the Durham Light Infantry Brigade of the Northumbrian Division (eventually the 150th (York and Durham) Brigade and 151st (Durham Light Infantry) Brigade respectively of the 50th (Northumbrian) Division when the territorial formations were given numbers in May 1915). The 5th Battalion was based at Paradise Row in Stockton-on-Tees, while the 6th Battalion was based at Union Street in Bishop Auckland, the 7th Battalion was based at Livingstone Road in Sunderland, the 8th Battalion was based at Gilesgate in Durham Durham most commonly refers to:
*Durham, England, a cathedral city and the county town of County Durham
*County Durham, an English county
* Durham County, North Carolina, a county in North Carolina, United States
*Durham, North Carolina, a city in N ...
and the 9th Battalion was based Burt Terrance in Gateshead (all since demolished). In 1911, the 1st battalion took part in the Delhi Durbar, receiving new colours from the King.
First World War
During theFirst World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the D.L.I. expanded to 42 battalions, comprising two Regular, two Militia, 17 Territorial (1st, 2nd and 3rd line, some never completed) and 21 service and other types (some short lived), with 22 seeing active service overseas – on the Western Front (at Ypres
Ypres ( , ; nl, Ieper ; vls, Yper; german: Ypern ) is a Belgian city and municipality in the province of West Flanders. Though
the Dutch name is the official one, the city's French name is most commonly used in English. The municipality c ...
, Loos, Arras
Arras ( , ; pcd, Aro; historical nl, Atrecht ) is the prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais Departments of France, department, which forms part of the regions of France, region of Hauts-de-France; before the regions of France#Reform and mergers of ...
, Messines, Cambrai, the Somme and Passchendaele), in Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
, Salonika
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
and India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. Some battalions were part of the Army of occupation in Germany after the War. In addition, ten battalions of County Volunteers were raised under the terms of the 1859 Volunteer act.Ward p. 334
The regiment earned 59 battle honour
A battle honour is an award of a right by a government or sovereign to a military unit to emblazon the name of a battle or operation on its flags ("colours"), uniforms or other accessories where ornamentation is possible.
In European military t ...
s and won six Victoria Cross
The Victoria Cross (VC) is the highest and most prestigious award of the British honours system. It is awarded for valour "in the presence of the enemy" to members of the British Armed Forces and may be awarded posthumously. It was previously ...
es, but at the cost of 12,006 dead NCOs
A non-commissioned officer (NCO) is a military officer who has not pursued a commission. Non-commissioned officers usually earn their position of authority by promotion through the enlisted ranks. (Non-officers, which includes most or all enli ...
and other ranks. When officers are included this rises to approximately 12,530the 10th highest of any of the infantry regiments of the British Army.
When War was declared, the 1st battalion was in India part of the Nowshera Brigade, 1st (Peshawar) Division, and was one of only eight of 52 British Army regular infantry battalions to remain in India. When volunteers for drafts to fight in France were called for, 880 out of 900 responded.Ward p. 438 The 2nd battalion was in Whittington Barracks
DMS Whittington, otherwise known as Defence Medical Services Whittington (formerly Whittington Barracks), is a military base in Whittington, Staffordshire, near Lichfield in England. It is home to the Staffordshire Regiment Museum, the Headquarte ...
, assigned to the 18th Brigade of the 6th Division.Ward p. 337 The Territorial battalions had been withdrawn early from their summer training camp to their home mobilisation stations.
1914
The 6th Division reached France on 10–11 September as part of the British Expeditionary Force. By this time the German Army's advance had been halted on the Marne and pushed back to beyond the Ainse. The 6th Division was dispersed among the units of the BEF holding the line on the ridge of the Chemin des Dames, with 2nd battalion the penultimate battalion on the right of the line. On 20 September the Germans attacked the junction of the British and French forces but were held; in this introduction to the war the 2nd battalion lost in one day almost as many men as the 1st battalion lost in the whole of the Boer War. The Allies and the Germans now began a series of moves to try and outflank each other resulting in a northwards movement called theRace to the Sea
The Race to the Sea (; , ) took place from about 1914 during the First World War, after the Battle of the Frontiers () and the German advance into France. The invasion had been stopped at the First Battle of the Marne and was followed by the ...
. Rejoining the rest of the division in early October during this northward movement the 2nd battalion fought at the Battle of Armentières
The Battle of Armentières (also Battle of Lille) was fought by German and Franco-British forces in northern France in October 1914, during reciprocal attempts by the armies to envelop the northern flank of their opponent, which has been called ...
, dispersed in companies to reinforce other units to the south-east of Armentiers. By the end of October when it was withdrawn from the front, the 2nd battalion had lost over 80% of its original complement killed or wounded.
On 16 December, the 18th battalion (a Pals battalion
The Pals battalions of World War I were specially constituted battalions of the British Army comprising men who had enlisted together in local recruiting drives, with the promise that they would be able to serve alongside their friends, neighbour ...
) became the first New Army
The New Armies ( Traditional Chinese: 新軍, Simplified Chinese: 新军; Pinyin: Xīnjūn, Manchu: ''Ice cooha''), more fully called the Newly Created Army ( ''Xinjian Lujun''Also translated as "Newly Established Army" ()), was the modernised ...
battalion to come under enemy fire when two companies on coastal defence duty at Hartlepool suffered five dead and 11 wounded when the town came under fire from the battlecruisers SMS Derfflinger
SMS was a battlecruiser of the German Empire, German (Imperial Navy) built in the early 1910s during the Anglo-German naval arms race. She was the lead ship of her ship class, class of three ships; her sister ships were and . The s were larg ...
, SMS Von der Tann
SMS was the first battlecruiser built for the German Kaiserliche Marine, as well as Germany's first major turbine-powered warship. At the time of her construction, was the fastest dreadnought-type warship afloat, capable of reaching speeds i ...
and SMS Blucher.
1915
After the failure of British attacks atNeuve Chapelle
Neuve-Chapelle ( vls, Nieuwkappel) is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region of France. It was the site of a First World War battle in 1915.
Geography
Neuve-Chapelle is situated some northeast of Béthune and ...
and the French in Champagne
Champagne (, ) is a sparkling wine originated and produced in the Champagne wine region of France under the rules of the appellation, that demand specific vineyard practices, sourcing of grapes exclusively from designated places within it, ...
, the Germans attacked at the Second Battle of Ypres
During the First World War, the Second Battle of Ypres was fought from for control of the tactically important high ground to the east and south of the Flemish town of Ypres in western Belgium. The First Battle of Ypres had been fought the pr ...
on 22 April. By this time the territorial battalions of the regiment had just landed in France with the 50th (Northumbrian) Division on 17–18 April. Without any 'nursery' period the brigades of the Division were deployed as needed in the northern part of the salient around St Julian and the Gravenstafl Ridge. Repeated German attacks throughout late April and May forced a withdrawal toward Ypres. Between 25 and 27 April, the 8th battalion was reduced to the effective strength of one company after being enfiladed at Boetleer's Farm with the 8th Canadian battalion and is credited with saving the flank of the 85th Brigade. In late May, the 5th, 7th, 8th and 9th battalions were part of the forces that slowed the German assault on the Bellewaarde Ridge the last battle of Second Ypres. Due to its losses, in June, the 8th battalion was merged with the 6th battalion to form the 6th/8th Composite battalion, which separated back into its components in August after reinforcement.Ward p. 353
The first of the service battalions of the New Army, the 10th battalion of the 43rd Brigade, 14th (Light) Division and the 11th battalion which were pioneers of the 20th (Light) Division, arrived in France in May and July respectively. The 7th battalion was converted to the (50th) Division pioneer battalion on 16 May 1915.
In July, the 41st Division was in the line in the Ypres salient at the chateau of Hooge, where the Germans held the house and the allies the stable block, just north of the Menin road. On 30 July, the Germans used Flamethrowers, which threw back the 41st Brigade and pushed the front line south back to Zouave and Sanctuary Woods. The 6th Division was tasked to retake the old line of late July. The now reinforced 2nd battalion had to face a 500-yard advance paralleling the German line before reaching its objective. In the early hours of 9 August, together with the 1st K.S.L.I. on its left, the battalion overran the German trenches at bayonet point and re-established the British line on the north of the Menin road at a cost of nearly 200 dead and 270 wounded.Ward p. 358 Praise was received from the brigade, Division, corps and Army commanders and Sir John French
Field Marshal John Denton Pinkstone French, 1st Earl of Ypres, (28 September 1852 – 22 May 1925), known as Sir John French from 1901 to 1916, and as The Viscount French between 1916 and 1922, was a senior British Army officer. Born in Kent t ...
commander of the BEF said of the assault it was "...one of the best conducted of the smaller operations of the campaign".
Four more service battalions arrived in France, the 12th and 13th of the 68th Brigade of the 23rd Division in late August and the 14th and 15th of the 64th Brigade of the 21st Division in early September.
The 21st and 24th Divisions were chosen as part of the reserve for the Battle of Loos
The Battle of Loos took place from 1915 in France on the Western Front, during the First World War. It was the biggest British attack of 1915, the first time that the British used poison gas and the first mass engagement of New Army units. Th ...
despite being newly arrived in France and having had comparatively little training. After a long night march,Ward p. 361 dawn found the battalions between Loos and Hulluch with a German redoubt on Hill 70 to their right. Over the course of the day, both essentially untrained battalions attacked a total of five times unsupported by artillery but were beaten back. The 14th battalion lost 294 killed and wounded, the 15th 642. In late November, the 14th battalion joined the 2nd in the 18th Brigade of 6th Division.
On 4 November, the regiment won its first VC of the war when Pte Thomas Kenny of the 13th battalion rescued a wounded officer.
1916
The arrival of service battalions of the regiment continued: the 19th battalion (Bantams) in the 106th Brigade of the 35th Division on 29 February, the 20th battalion (Wearsiders) in the 123rd Brigade of the 41st Division and the 22nd battalion which landed on 16 June attached to the 19th (Western) Division, but quickly transferred to the8th Division 8th Division, 8th Infantry Division or 8th Armored Division may refer to:
Infantry divisions
* 8th Division (Australia)
* 8th Canadian Infantry Division
* 8th Air Division (People's Republic of China)
* 8th Division (1st Formation) (People's Repu ...
as Division pioneers. The 18th battalion (Pals) had arrived in March from Egypt where it had garrisoned the Suez Canal at Qantara as part of 93rd Brigade of the 31st Division.
;The Somme
 The Somme offensive was originally planned, earlier in the year, as a joint British-French offensive but due to the increasing pressure on the French at
The Somme offensive was originally planned, earlier in the year, as a joint British-French offensive but due to the increasing pressure on the French at Verdun
Verdun (, , , ; official name before 1970 ''Verdun-sur-Meuse'') is a large city in the Meuse department in Grand Est, northeastern France. It is an arrondissement of the department.
Verdun is the biggest city in Meuse, although the capital ...
was fought in part to relieve that pressure without much of the expected French support. General Haig felt that he lacked sufficient artillery and that many of the New Army Divisions were not yet fully trained but was pressured into starting the offensive at the start of July.
The regiment had two battalions in action on the first day of the Somme, 1 July, the 18th (31st Division) opposite Serre and the 15th (21st Division) north of Fricourt. The 15th battalion, aided by its Division artillery's used of a rolling barrage, captured the German front line trenches and pressed on, until by the afternoon the battalion advanced an additional 600 yards to the edge of Shelter Wood, beating off a counterattack until relieved that night. Casualties amounted to 440 officers and other ranks.
The planned advance of D company of the 18th battalion that morning was overlooked by German forces in the ruins of Serre and together with the other assaulting troops of the first wave suffered grievous losses and gained no ground. The retaliatory German shelling virtually destroyed the front line and communication trenches and the remaining companies of the 18th and other battalions were ordered to prepare a defence in case of counterattack. They remained in these shattered trenches, attempting to repair them and rescuing the wounded from no-mans land, under at times intense bombardment, until relieved during the night of 4 July. When reassembled the battalion had 14 officers and 357 men, having lost 58% of its strength killed and wounded.
British tactics now changed; instead of attacks aiming for deep penetrations, smaller objectives were set, the first at Bezatin Ridge on 14 July. The 12th and 13th battalions fought between Poiziers and Martinpuich up to the end of July, the 19th although only in a supporting role, had still lost more than 250 officers and men near Guillemont at the end of July, the 10th fought in Delville Wood in August, and the 11th, a pioneer battalion, was fighting in the trenches near Ginchy in early September.
The next objective was on a 10-mile front between the villages of Flers and Courcelette in mid September. The 2nd and 14th battalions were part of the attack that took the Quadrilateral strong point near Ginchy. The territorials and the 10th, 15th and 20th battalions were also involved in this phase, with the 5th battalion having only 92 officers and men fit by 19 September. Le Transloy ridge was the next target in the increasingly wet autumn, this involved the 2nd battalion, the 6th, 8th (temporarily joined with the 1/5th Borderers) and 9th territorials and the 12th and 13th service battalions. These last two captured the village of Le Sars in what the Official History called "...the striking success of the day." The territorials were again involved in the last assault of the Somme offensive, on the Butte de Warlencourt
The Attacks on the Butte de Warlencourt (7 October – 16 November 1916) describe a tactical incident during the Battle of the Somme. The Butte de Warlencourt is an ancient burial mound off the Albert–Bapaume road, north-east of Le Sars in th ...
, the 1/6th, 1/8th and 1/9th losing between them nearly 940 officers and men killed, wounded or missing for no gain.
In early November the 2/5th and the 2/9th battalions consisting of category B fitness men separately embarked for Salonika and the front against Bulgaria.
1917
;Arras The attack along the line atArras
Arras ( , ; pcd, Aro; historical nl, Atrecht ) is the prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais Departments of France, department, which forms part of the regions of France, region of Hauts-de-France; before the regions of France#Reform and mergers of ...
, starting on 9 April was intended as a diversion for the French attack at Nivelle. In the first phase of the attack, the 10th battalion had advanced ~4000 yards through the Hindenburg trench system until relieved on the night of 10 April. The 15th battalion also fought on the first day taking the front line trench (at ~1,000 yards) but being held up afterwards. The territorial battalions were in action in mid and late April south of the village of Guemappe.
In the coalfields of Lens the 2nd and 14th battalions fought the Germans over a feature called 'Hill 70' between April and July, adding it as a battle honour to the regiment.
;Messines
The set piece battle of Messines was intended to take high ground to the south of Ypres prior to the northern offensive. After an intense bombardment, the explosion of underground mines and following a creeping barrage the 12th and 13th battalions near Hill 60 advanced ~1,000 yards and the 20th battalion starting from St Eloi advanced nearly 4000 yards with fewer losses than previous operations.
;Third Ypres
 The next battle around the Ypres salient was to clear the Germans from the remaining high ground to the East of the city. The 20th battalion was involved in the first day's attacks on 31 July, advancing alongside the Ypres-Comines canal for the loss of 8 officers and 431 other ranks.Ward p. 386 The next advance was held up until near the end of August by heavy rains and was directed along the Menin Road, here the 10th battalion attempted to take and hold Inverness Copse losing over half its original strength by 25 August. General Plumer's methodical advance began on 20 September on the Menin Road ridge. The 20th battalion's advance on 21 September was checked after 200 yards, the 13th battalion reached their objective with both battalions losing around 300 men. The third of General Plumer's steps, the
The next battle around the Ypres salient was to clear the Germans from the remaining high ground to the East of the city. The 20th battalion was involved in the first day's attacks on 31 July, advancing alongside the Ypres-Comines canal for the loss of 8 officers and 431 other ranks.Ward p. 386 The next advance was held up until near the end of August by heavy rains and was directed along the Menin Road, here the 10th battalion attempted to take and hold Inverness Copse losing over half its original strength by 25 August. General Plumer's methodical advance began on 20 September on the Menin Road ridge. The 20th battalion's advance on 21 September was checked after 200 yards, the 13th battalion reached their objective with both battalions losing around 300 men. The third of General Plumer's steps, the Battle of Broodseinde
The Battle of Broodseinde was fought on 4 October 1917 near Ypres in Belgium, at the east end of the Gheluvelt plateau, by the British Second and Fifth armies against the German 4th Army. The battle was the most successful Allied attack of t ...
on 4 October involved the 15th battalion on the extreme right of 21st Division, despite being reduced to two composite companies by German heavy bombardment, they advanced south of Polygon Wood achieving the objective of the village of Reutel. When the battalion was relieved on 6 October it was commanded by a Lieutenant and had lost 430 officers and men.
For the remainder of the Third Ypres the regiment's battalions were in reserve positions, the Territorials during Second Battle of Passchendaele
The Second Battle of Passchendaele was the culminating attack during the Third Battle of Ypres of the First World War. The battle took place in the Ypres Salient area of the Western Front, in and around the Belgian village of Passchendaele, bet ...
, or holding the line, and the 19th battalion (which had ceased to be a 'Bantam' unit in January) at Weidendreft in early November and the 10th battalion at Passchendaele in December. The Pioneer battalions, 11th and 22nd, also served with their respective Divisions (20th and 8th) during the Battle.
;Italy
When the Central Powers forced a retreat on the Italian Front at the Battle of Caporetto
The Battle of Caporetto (also known as the Twelfth Battle of the Isonzo, the Battle of Kobarid or the Battle of Karfreit) was a battle on the Italian front of World War I.
The battle was fought between the Kingdom of Italy and the Central ...
, 5 British and 2 French Divisions were sent to Italy. The British Divisions contained the 12th and 13th battalions (23rd Division) and the 20th battalion (41st Division) leaving the Ypres Salient between the end of October and mid November and arriving in at the Italian front between the end of November and early December.
;Cambrai
 The Battle of Cambrai was the first successful use of maturing
The Battle of Cambrai was the first successful use of maturing combined arms
Combined arms is an approach to warfare that seeks to integrate different combat arms of a military to achieve mutually complementary effects (for example by using infantry and armour in an urban environment in which each supports the other) ...
tactics by the British. On 20 November, the 2nd and 14th battalions of the 6th Division were to pass through the assaulting forces and take the Hindenburg Line support trench; both battalions reached their objective with a total loss of 30 killed or wounded. On the next day, 3 companies from 14th battalion assisted tanks and squadron of cavalry in taking the village of Cantaing (north-west of Marcoing). The advance came to a halt as the Germans brought their reserves into the battle. The 11th battalion had been consolidating the ground behind the 4 mile advance of 20th Division but on 29 November its scattered companies were involved in fighting the German counter-attack on the ridges north of Gouzeacourt. The 14th battalion (together with the 1st battalion Shropshire Light Infantry
The King's Shropshire Light Infantry (KSLI) was a light infantry regiment of the British Army, formed in the Childers Reforms of 1881, but with antecedents dating back to 1755. It served in the Second Boer War, World War I and World War II. In 196 ...
) was ordered across the Canal du Nord on the night of 2 December to trenches facing Masniere, one of which was only 2–3 feet deep. After beating off one attack they were forced to withdraw back over the canal and over the next few days withdrew to the "Flesquires Line" and, for the British the disappointing end of the Battle.
1918–19
With the Russians out of the war, Germany was able to transfer forces and at last outnumber the Allies on the Western Front before the arrival of theAmericans
Americans are the Citizenship of the United States, citizens and United States nationality law, nationals of the United States, United States of America.; ; Although direct citizens and nationals make up the majority of Americans, many Multi ...
in force. Large numbers of stormtroopers were to be used, together with new artillery tactics. The Allies knew what was in store and began to prepare a defence in depth with varying degrees of effectiveness. As a result of manpower shortages (some politically induced), in February the British Army was reorganised from a four battalion to a three battalion infantry brigade structure, with many infantry battalions being disbanded to strengthen remaining battalions. In this way the 10th and 14th battalions were disbanded, reinforcing the other battalions of the regiment while the 9th was converted to a pioneer battalion and joined the 62nd (2nd West Riding) Division
The 62nd (2nd West Riding) Division was an infantry division of the British Army that saw active service on the Western Front during the First World War.
History
During the First World War the division fought on the Western Front at Bulle ...
. The 20th battalion returned from Italy to the Western Front with its Division in early March.
; German spring offensive
On the first day of the German "Operation Michael
Operation Michael was a major German military offensive during the First World War that began the German Spring Offensive on 21 March 1918. It was launched from the Hindenburg Line, in the vicinity of Saint-Quentin, France. Its goal was t ...
" the 2nd battalion was in the front line north of the Bapume-Cambrai road. After losing the two forward companies, the infantry withdrew in the evening mist with the remains of the 1st battalion West Yorkshire Regiment
)
, march = ''Ça Ira''
, battles = Namur FontenoyFalkirk Culloden Brandywine
, anniversaries = Imphal (22 June)
The West Yorkshire Regiment (Prince of Wales's Own) (14th Foot) wa ...
. At dusk on the 22nd, out of an original strength of 30 officers and 639 other ranks, the battalion had two officers and 58 men unwounded with six officers and 286 other ranks wounded. The 11th pioneer battalion was building a supply railway in the 20th Division's rear, in the Saint-Quentin area around Ham. It was scattered during the week long battle, and only a few men regrouped in Amiens at its conclusion.
All the regiment's battalions on the Western Front suffered heavy losses as a result of the weight of numbers and new tactics of the Germans. The 18th, 19th and 20th battalions also fought on the Somme. The 9th battalion fought before Bucquoy at the end of March where Pte Young won the V.C. for rescuing 9 men under fire. When relieved on 1 April, the battalion had lost 492 officers and men,Ward p. 405 and the 15th battalion reduced to one company.Ward p. 403
The territorials of the 50th Division, the 5th, 6th and 8th battalions and 7th (Pioneer) battalion were particularly unfortunate, forced into the long retreat on the Somme, they were reinforced by drafts from the graduated battalions and sent to the Ypres salient
The Ypres Salient around Ypres in Belgium was the scene of several battles and an extremely important part of the Western front during the First World War.
Ypres district
Ypres lies at the junction of the Ypres–Comines Canal and the Ieperlee ...
in April where, after the initial assault they were only saved by the German looting:
Reduced to a total of a battalion in strength, The 151st Brigade was then sent to the Aisne to recuperate where a third German attack found them on 26 May, 21 days after arriving. The scattered parties were forced back to south of the Marne where eventually the Durham battalions of the 151st Brigade could only muster 103 men of all ranks.
Also on the Lys, the 18th battalion fought in retreat south and west around Bailleul and, when taken out of the line on 14 April was formed into a composite battalion with the 15th West Yorkshire Regiment
)
, march = ''Ça Ira''
, battles = Namur FontenoyFalkirk Culloden Brandywine
, anniversaries = Imphal (22 June)
The West Yorkshire Regiment (Prince of Wales's Own) (14th Foot) wa ...
which totalled around 450 men.
The 22nd (Pioneer) battalion fought as infantry on the Aisne on 27 May; after losing 513 officers and men in continual withdrawal, it was absorbed into the 8th Division Composite Battalion.
In June, the remains of the 5th, 6th and 8th battalions were reduced to cadre strength and were sent to the Dieppe area while the 7th (Pioneer) Battalion joined 8th Division and absorbed 22nd (Pioneer) Battalion.
The 62nd Division arrived on the eastern flank of the new salient 2 days after the start of the German attack on 17 July. The 9th battalion was used as infantry for the counter-offensive along the Ardre river, and on 20 July fought through thick woods and captured the village of Cuitron on 22 July at a cost of 294 officers and men killed wounded and missing.
; Hundred Days Offensive
The German offensive had petered out without the decisive breakthrough that was desired and the German high command knew that the allies would respond, knowing of the German losses, and bolstered by the arrival of the Americans and the reinforcement of the British and French making up for some of the losses from the spring offensive. The first blow fell on 8 August at Amiens
Amiens (English: or ; ; pcd, Anmien, or ) is a city and commune in northern France, located north of Paris and south-west of Lille. It is the capital of the Somme department in the region of Hauts-de-France. In 2021, the population of ...
in which the regiment had no part. This signalled the beginning of a general advance of the five British Armies through Picardy on 21 August and Flanders on 28 September, four of which contained battalions from the regiment.
The remaining battalions of the regiment participated in this advance being joined in France by the 2/6th battalion in May as part of the 177th brigade of the 59th Division, the 29th battalion reinforcing the 41st Brigade of the 14th Division and the 13th battalion returning from Italy in September to join the 74th brigade in the 25th Division.
On the Somme with the Third Army the 15th battalion made a night advance of over 3,000 yards on 23/24 August and fought again on the Hindengurg Line in mid September. In the Fourth Army the 2nd battalion attacked the Hindenburg Line near St Quentin over terrain that was "...a bare, glacis-like slope devoid of cover..." and lost over 300 men for only 200 yards gained. The 13th battalion attacked the reserve line of the Hindenburg system on 6 October near Villers-Outreaux, with the 15th battalion attacking the same day a few miles to the North. In Flanders, the clearing of the German's spring salient and subsequent advance over the battlefields of the last four years at Ypres was shared by the 18th, 19th, 20th, 2/6th and 29th battalions. The 29th battalion's only battle was the crossing of the Lys near Comines on 15 October. The 2/6th fought on the Premesques ridge and went on with the Division to cross the Scheldt. The 2nd, 13th and 15th battalions took part in the final advance across the Selle and Sambre rivers, the 15th having to drive out the Germans at Limont-Fontaine at bayonet point losing 127 men on 7 November.
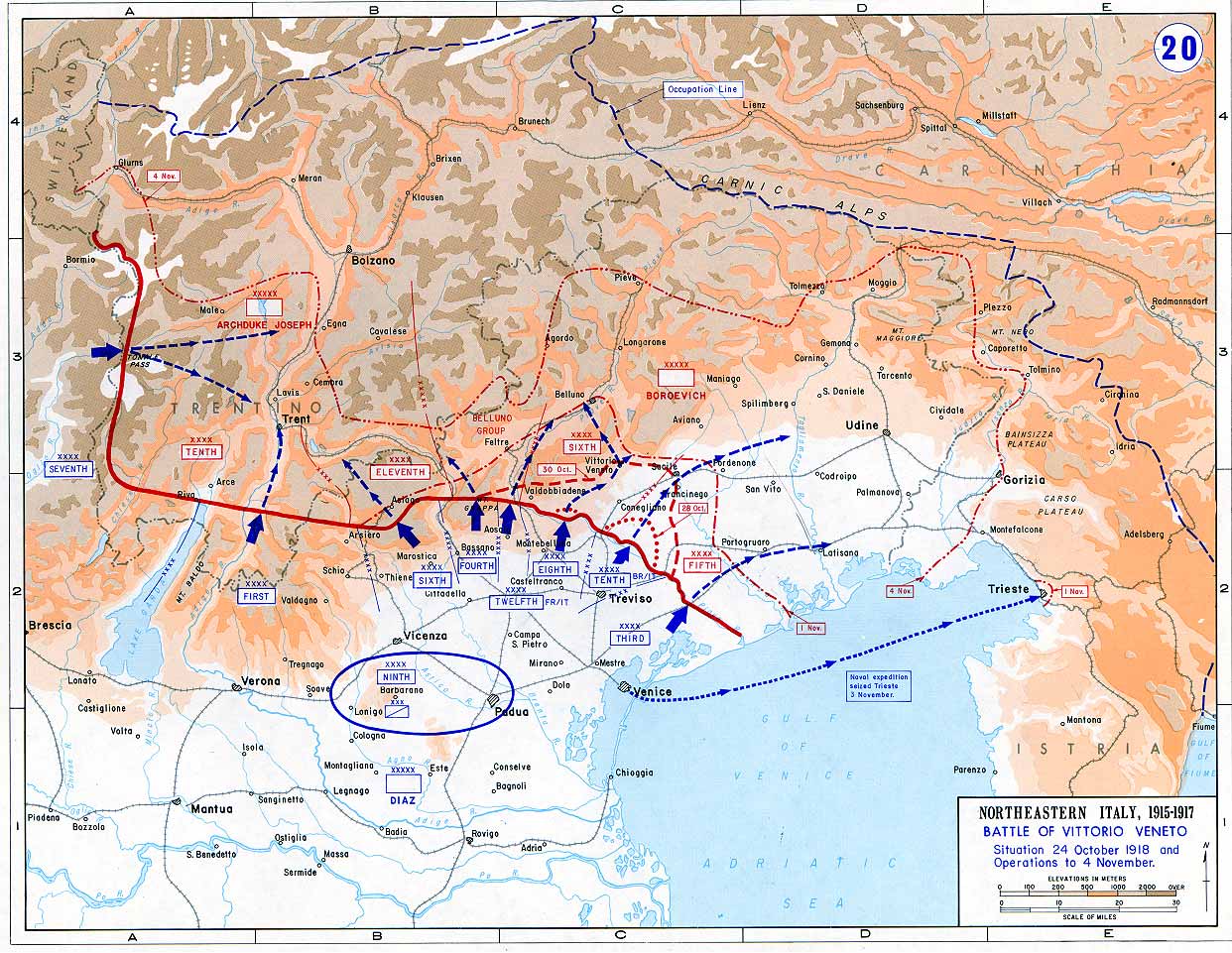
;Italy
 The British Divisions were deployed between
The British Divisions were deployed between Lake Garda
Lake Garda ( it, Lago di Garda or ; lmo, label= Eastern Lombard, Lach de Garda; vec, Ƚago de Garda; la, Benacus; grc, Βήνακος) is the largest lake in Italy.
It is a popular holiday location in northern Italy, about halfway between ...
and the Piave River, however in February, the 41st Division with the 20th battalion was returned to the Western Front. In June the Austrians launched the Battle of the Piave River
The Second Battle of the Piave River, fought between 15 and 23 June 1918, was a decisive victory for the Italian Army against the Austro-Hungarian Empire during World War I. Though the battle proved to be a decisive blow to the Austro-Hungaria ...
with the 12th and 13th battalions facing the northern pincer which made no progress against the British, the two battalions losing six dead and 61 wounded during the day. The 13th battalion returned to the Western Front in September. At the end of October, the 12th battalion took part in the Battle of Vittorio Veneto
The Battle of Vittorio Veneto was fought from 24 October to 3 November 1918 (with an armistice taking effect 24 hours later) near Vittorio Veneto on the Italian Front during World War I. After having thoroughly defeated Austro-Hungarian troop ...
assaulting across the Piave River before being relieved on 30 October.
;Macedonia
Initially both 2/5th and 2/9th battalions were employed on guard duties in and around Salonika where the 2/9th battalion remained until the end of the War. In March 1917 the 2/5th battalion was brigaded into the independent 228th Brigade and sent into the line west of Lake Butkovo. There it stayed until the Bulgarian armistice on 1 October 1918 when it began to advance with the brigade under Greek command. When the Turkish armistice was signed on 31 October the battalion was sent with the 2/5th battalion Seaforth Highlanders to occupy the ports of Varna and Burgas. While overseas the battalion lost two men from wounds but 21 from disease.
;Russia
The 2/7th battalion joined the Allied Intervention in Russia in Archangel, Northern Russia as a garrison battalion, arriving on 7 October 1918. It did not see action and was withdrawn in January 1920.
; Army of Occupation
In November and December, the 2nd and 9th battalions were among the British forces that marched to the Rhine as part of the Army of Occupation. In early 1919 the 51st and 52nd (Graduated) battalions together with the 20th battalion formed the 3rd Northern Brigade of the Northern Division with the 53rd battalion, reduced to cadre, supplying reinforcements; all were based in Cologne.
India
The 1st battalion remained in India throughout the First World War, suffering a continual drain of drafts for the Western Front. In August 1914 it was part of the Nowshera Brigade of thePeshawar Division
Peshawar (; ps, پېښور ; hnd, ; ; ur, ) is the sixth most populous city in Pakistan, with a population of over 2.3 million. It is situated in the north-west of the country, close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is ...
, and served on the North West Frontier in 1915, and 1916–17 in campaigns against the Mohmands
The Mohmand ( ps, مومند) or Mohmand is a prominent tribe of Pashtun people. They are based primarily in the Mohmand territory, which is located in Nangarhar, Afghanistan and Mohmand Agency, Pakistan.
Most people of the Mohmand tribe sp ...
. The battalion was in Rawalpindi in 1919 at the outbreak of the Third Anglo-Afghan War
The Third Anglo-Afghan War; fa, جنگ سوم افغان-انگلیس), also known as the Third Afghan War, the British-Afghan War of 1919, or in Afghanistan as the War of Independence, began on 6 May 1919 when the Emirate of Afghanistan inv ...
in which it played a mostly supporting role. Demobilising its time expired men, a cadre of the battalion returned to Britain in February 1920.
Inter-war
 By 1920, the service battalions had been disbanded with their King's colours laid up in Durham Cathedral except for the 20th battalion's at the parish church of Bishopwearmouth.
The 1st battalion was reformed with drafts from the 3rd (the last act of the Militia) and left for Germany, still understrength, in March 1921 for duty in Upper
By 1920, the service battalions had been disbanded with their King's colours laid up in Durham Cathedral except for the 20th battalion's at the parish church of Bishopwearmouth.
The 1st battalion was reformed with drafts from the 3rd (the last act of the Militia) and left for Germany, still understrength, in March 1921 for duty in Upper Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
, returning to Britain in July 1922. The battalion spent 3 years in Egypt again returning to Britain in April 1930. Joining the 6th Brigade of the 2nd Infantry Division it took part in experiments in infantry mechanisation. It was then sent to Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flow ...
arriving in November 1937, reinforced by personnel from the 2nd battalion at Port Sudan. In October 1938 the battalion moved to Tientsin and was there when Britain declared war against Germany.
The 2nd battalion returned to Britain from Germany in April 1919 as a cadre; the battalion reformed and was sent to Batoum in South Russia in October 1919 to police territorial terms of the Armistice. In July 1920 it was sent to the Izmit in Turkey to police the terms of the Turkish armistice until November. From here they went to India and in February 1927 were deployed to Shanghai to protect the International Settlement. Returning to India in August, it fought against the Mahsuds, relieving the post of Datta Khel
Datakhel () or Datta Khel is a town in North Waziristan district of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.
It is part of Datta Khel Tehsil of North Waziristan district.
Overview and history
Datakhel is located around 41 km South West of near by to ...
in May 1930. The battalion arrived back in Britain in November 1937 after a few months in Egypt, replacing the 1st battalion in the 6th Infantry Brigade, 2nd Infantry Division.
In February 1920 the Territorial Force was re-raised and later in the year renamed the Territorial Army. In the 1930s as part of the growing realisation of the threat of air power, numbers of territorial battalions were converted to an air defence role, either as Anti-Aircraft gunners or search light regiments, in this way the D.L.I. lost the 5th and 7th battalions. These units were no longer a part of the Regiment.
Second World War
During theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
the D.L.I. raised 15 battalions, two Regular, six 1st and 2nd line Territorial (one renamed and transferred to another regiment), and the remainder war formed (mostly so called 'Dunkirk' battalions), with 10 seeing active service overseas in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
, North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
, and France and Germany. The low number of battalions raised compared to the First World War was due to the increasing specialisation of a more mechanised army and its associated support requirements. Additionally, twenty six battalions of the Home Guard
Home guard is a title given to various military organizations at various times, with the implication of an emergency or reserve force raised for local defense.
The term "home guard" was first officially used in the American Civil War, starting w ...
wore the D.L.I. cap badge.
After the war Field Marshal Montgomery
Field Marshal Bernard Law Montgomery, 1st Viscount Montgomery of Alamein, (; 17 November 1887 – 24 March 1976), nicknamed "Monty", was a senior British Army officer who served in the First World War, the Irish War of Independence and ...
was to write,
The remaining first line territorial battalions once again formed the 151st Infantry Brigade of the 50th (Northumbrian) Infantry Division, initially a two brigade motorised Division. The territorials again raised second line battalions now numbering them sequentially, 10th, 11th and 12th battalions, these were now part of 70th Infantry Brigade of the 23rd (Northumbrian) Division the 2nd line copy of the 50th Division. The 12th battalion was named as a Tyneside Scottish unit and on 31 January 1940 the battalion left the regiment to become 1st battalion, Tyneside Scottish
Tyneside Scottish is an honour title which has been held by a variety of British Army units since 1914. The Regiments which have held the title are the Northumberland Fusiliers, Durham Light Infantry, Black Watch and Royal Artillery. The Tynesid ...
of the Black Watch (Royal Highland Regiment)
The Black Watch, 3rd Battalion, Royal Regiment of Scotland (3 SCOTS) is an infantry battalion of the Royal Regiment of Scotland. The regiment was created as part of the Childers Reforms in 1881, when the 42nd Regiment of Foot, 42nd (Roy ...
.Ward p. 461
When the War broke out the 1st battalion was in China at Tientsin, the 2nd battalion at Woking in the 2nd Infantry Division and the territorial battalions had already begun to form their 2nd line.
France 1940
The 2nd battalion arrived in France with the 2nd Infantry Division as part of the BEF in late September 1939 and was quickly deployed on the border with Belgium. The 151st brigade arrived in late January 1940 with 50th Division, with training still to be completed for some men, and moved up to the border at the end of March. The second line battalions (and the Tyneside Scottish) arrived in the part trained 23rd Division in early April, with no artillery or mortars and a reduced rear echelon with orders to complete their training and construct airfields. In the 70th brigade, 1400 men had not fired a Bren gun and 400 had not completed the war course with therifle
A rifle is a long-barreled firearm designed for accurate shooting, with a barrel that has a helical pattern of grooves ( rifling) cut into the bore wall. In keeping with their focus on accuracy, rifles are typically designed to be held with ...
.
When the Germans attacked on 10 May the 2nd battalion had moved into Belgium to the River Dyle by late on the 11th, 151st brigade was to be held in reserve. On the Dyle, the 2nd battalion held the Germans for two days until ordered to withdraw on 16 May, with Lt Annand winning the Army's first V.C. of the War. The 151st brigade was ordered to move forward to the River Dendre on 16 May, only to begin to fall back on the 18th.
In an attempt to delay the German armoured thrust, the rear echelon, including 70th brigade, was ordered into its path. After a series of marches and counter marches that began on 13 May the brigade, on 20 May, was spread along the roads south of Arras travelling west. Here they were ambushed by German armour, without heavy weapons their defence became a series of isolated and confused company actions. At St Pol the next day the brigade headquarters, the survivors of the three battalions and some engineers amounted to 14 officers and 219 other ranks, joined by other stragglers in the next few days they total ~800 men. On the claim that the action south of Arras delayed the German advance by five hours, the official history states:
The remains were formed into "Marleyforce" and as such it reached Dunkirk to be evacuated on 31 May.
On 20 May, 151st brigade, after a series of marches west and south, was chosen as part of the Arras counter-attack. The 6th and 8th battalions were to support the 4th and 7th Royal Tank Regiments respectively, with the 9th battalion in reserve. After initial successes to the west of Arras the Germans counter-attacked, and the British forces were withdrawn to Vimy Ridge. The brigade was then ordered north on 25 May to plug the gap of the impending Belgian surrender. To do this it had to extract itself from fighting on the Le Bassee Canal, the 8th battalion having to recapture the village of Carvin north of the canal, and only on the 27th could the brigade move north following the rest of 50th Division to Ypres.
The 2nd Division had been sent to man 21 miles of the western side of the Dunkirk corridor with the 2nd battalion positioned near St. Venant. From 24 to 27 May the Division held off attacks by four Panzer Divisions (3rd
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Numbers
* 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3
* , a fraction of one third
* Second#Sexagesimal divisions of calendar time and day, 1⁄60 of a ''second'', or 1⁄3600 of a ''minute''
Places
* 3rd Street (d ...
, 4th, 7th
7 (seven) is the natural number following 6 and preceding 8. It is the only prime number preceding a cube (algebra), cube.
As an early prime number in the series of positive integers, the number seven has greatly symbolic associations in religion ...
and S.S. Totenkopf
''Totenkopf'' (, i.e. ''skull'', literally "dead person's head") is the German word for the skull and crossbones symbol. The "skull and crossbones" symbol is an old international symbol for death, the defiance of death, danger, or the dead, as ...
), ending with over 70% of the Division becoming casualties and the massacre of 97 men of the 2nd battalion, Royal Norfolk Regiment
The Royal Norfolk Regiment was a line infantry regiment of the British Army until 1959. Its predecessor regiment was raised in 1685 as Henry Cornwall's Regiment of Foot. In 1751, it was numbered like most other British Army regiments and named ...
at La Paradis. When the 2nd battalion reformed in Britain after evacuation from Dunkirk on the night of 29 May it consisted of the remains of D company and the battalion's B echelon, stragglers and convalescents, some 180 men.
Arriving at Ypres 151st brigade was almost immediately forced back, and the retreat to the Dunkirk perimeter began. By 30 May the brigade was entrenched between the Bergues and Ringsloot canals and reinforced by some remnants from 70th Brigade, after repulsing German attacks on the 31st, the brigade embarked for Britain from the Dunkirk mole late on 1 June.
Iceland
British forces had invaded Iceland in May 1940, and in October, the 10th Battalion arrived followed by the rest of 70th Brigade a month later replacing 148th Brigade in 49th (West Riding) Infantry Division. While there the division used the empty terrain of the island to train using live ammunition, the 70th brigade left in December 1941.North Africa, the Middle East and the Mediterranean 1940–43
The 1st battalion left China and arrived inNorth Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
in January 1940 The battalion played a supporting role in Lieutenant-General O'Connor's offensive in December except for a composite company which advanced as far as Sidi Barani. It joined the 22nd Guards Brigade
The 22nd Guards Brigade was an infantry brigade of the British Army that saw distinguished active service during the Second World War.
History
The 22nd Infantry Brigade was formed by the redesignation of the 29th Infantry Brigade on 3 Septemb ...
in January 1941 and trained for amphibious operations at Qassassin, only to be returned to the desert in March when Erwin Rommel counter-attacked. Counter attacking at Halfaya Pass
Halfaya Pass ( ar, ممر حلفيا, translit=Mamarr Ḥalfayā ) is in northwest Egypt, 11.5 kilometres east of the border with Libya and 7.5 kilometres south of the other, more major pass in the ridge today. A high, narrow escarpment extends ...
the battalion used primitive motorised tactics and communications (flag signals), the attack failed and the battalion lost more than half its strength including the whole of D company. In June the reinforced battalion was deployed as part of the take-over of Vichy controlled Syria, but in October 1941 it moved back to North Africa as part of the rotation of forces in the besieged Tobruk garrison. Here they patrolled and raided the German and Italian lines, and in early December extended the perimeter near El-Adem as part of the lifting of the siege.
Meanwhile, 50th Division with 151st Brigade had been sent to the Middle-east arriving early July 1941 and at the end of the month deployed to Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geo ...
to improve the islands defences. From there the 50th Division was sent to Palestine in November and then on to Irbil in Iraq to be part of the forces to meet an anticipated German advance from southern Russia.
In January 1942 the 1st Battalion was moved to garrison Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
, returning to North Africa in June 1943 after losing only a few men to air attack.
In February 1942 the 50th Division was recalled to the Western Desert and the British Eighth Army
The Eighth Army was an Allied field army formation of the British Army during the Second World War, fighting in the North African and Italian campaigns. Units came from Australia, British India, Canada, Czechoslovakia, Free French Forces ...
and found itself on the Gazala line. For some months the Durham battalions patrolled no mans land disrupting and stealing German and Italian supply lines in front of them, 'commerce raiding' and then attacking the supply columns for Rommel's armoured thrust which began the Gazala
Gazala, or ʿAyn al-Ġazāla ( ), is a small Libyan village near the coast in the northeastern portion of the country. It is located west of Tobruk.
History
In the late 1930s (during the Italian occupation of Libya), the village was the site of ...
on 27 May. The Division's 150th brigade was forced to surrender on 1 June and Axis forces were now west, south and east of the remaining brigades. Forming columns most of the 6th and 8th battalions broke out west through Italian then German lines on the night of 14/15 June, then travelled south past the German armoured thrust and east to the Egyptian border. The 9th battalion and a party from the 6th were forced to take the coastal route after the Italians and Germans had been alerted to the western breakout and fought through German positions west of Tobruk, they were reunited with the rest of the division on 16 June. After the fall of Tobruk the division was now placed on an escarpment south of the town of Mersa Matruh
Mersa Matruh ( ar, مرسى مطروح, translit=Marsā Maṭrūḥ, ), also transliterated as ''Marsa Matruh'', is a port in Egypt and the capital of Matrouh Governorate. It is located west of Alexandria and east of Sallum on the main highway ...
and on 27 June held attacks by the German 90th Light Division during which Pte A H Wakenshaw won a posthumous V.C. but after which the 9th battalion positions were isolated and overrun with only the headquarters company escaping. The division was ordered to withdraw on 28 June again in column formation but this time over ground broken by wadi
Wadi ( ar, وَادِي, wādī), alternatively ''wād'' ( ar, وَاد), North African Arabic Oued, is the Arabic term traditionally referring to a valley. In some instances, it may refer to a wet (ephemeral) riverbed that contains water ...
s. In one of these the 8th battalion lost its D company to a German ambush and the rendezvous point, Fuka, was in German hands leading to the capture of some un-diverted columns. When reassembled the 50th Division was withdrawn behind the Alamein line to rest and reorganise after suffering over 8000 casualties since the start of the Gazala battle.
While behind the lines the 6th, 8th and 9th battalions each contributed a company to a composite battalion for an attack on the southern part of Ruin Ridge on 27/28 July, while the Australians
Australians, colloquially known as Aussies, are the citizens, nationals and individuals associated with the country of Australia. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or ethno-cultural. For most Australians, several (or all) ...
attacked the northern part. Although the position was taken, almost the entire composite battalion was killed or captured by the German counterattack.
The 50th Division returned to the front line on 4 September, and during the first days of the Second Battle of El Alamein
The Second Battle of El Alamein (23 October – 11 November 1942) was a battle of the Second World War that took place near the Egyptian Railway station, railway halt of El Alamein. The First Battle of El Alamein and the Battle of Alam el Halfa ...
stayed in reserve in the southern part of the line. On 28 October, the 151st Brigade was moved north and with the 152nd Brigade came under command of the 2nd New Zealand Division for Operation Supercharge. Early on 2 November the three battalions advanced through the smoke and dust of the bombardment which reduced visibility to 50 yards and facing scattered German resistance reached their objective by the dawn. Here they witnessed the destruction of 9th Armoured Brigade and were subject to German shelling before being relieved on the evening of 3 November, having lost nearly 400 men.
 The 50th Division returned to the front line when the Eighth Army reached the
The 50th Division returned to the front line when the Eighth Army reached the Mareth Line
The Mareth Line was a system of fortifications built by France in southern Tunisia in the late 1930s. The line was intended to protect Tunisia against an Italian invasion from its colony in Libya. The line occupied a point where the routes into T ...
in February 1943. On the night of 20/21 March, the 8th and 9th battalions attacked, crossing the wadi and fighting the dug in Italians of the Young Fascist Division, with the 6th battalion the tanks of 50th R.T.R. following The tanks were unable to cross the wadi that night, however the next night after the 6th battalion and the 5th battalion East Yorkshire Regiment
The East Yorkshire Regiment was a line infantry regiment of the British Army, first raised in 1685 as Sir William Clifton's Regiment of Foot and later renamed the 15th Regiment of Foot. It saw service for three centuries, before eventually being ...
reinforced the penetration, some 40 tanks were able to cross. On 22 March the Germans counterattacked with the 15th Panzer Division and the infantry battalions were forced to withdraw, crossing back over the wadi at first light on 23 March. The 6th battalion, which started the battle with a strength of only ~300 of all ranks, was reduced to 65 unwounded men by the end of the battle, the 8th and 9th were in a similar condition. Shortly after the division was withdrawn from the front and sent to Alexandria.
On 3 January 1943 the 16th Battalion landed at Algiers with the 139th Brigade of the 46th Infantry Division, part of the British First Army
The First Army was a formation of the British Army that existed during the First and Second World Wars. The First Army included Indian and Portuguese forces during the First World War and American and French units during the Second World War.
F ...
. It moved into Tunisia it fought at the first battle of Sedjenane, where they were forced to withdraw by 4 March after losing nearly half their number. First Army's offensive was resumed in April and on 22 April, the 16th Battalion attacked the hill of Sidi Barka held by men of the Hermann Goering Division Hermann or Herrmann may refer to:
* Hermann (name), list of people with this name
* Arminius, chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci tribe in the 1st century, known as Hermann in the German language
* Éditions Hermann, French publisher
* Hermann, Miss ...
, after gaining a false crest instead of the summit, the battalion held on through mortar bombardment until the Germans pulled out the next night.
With the defeat of the Germans in North Africa the 6th 8th and 9th battalions were withdrawn to Alexandria, reinforced and trained in amphibious techniques for the invasion of Sicily. The 16th Battalion, after taking part in the victory parade in Tunis, was sent to Algiers for training.
In March 1943 a second incarnation of the 18th Battalion was raised at Genefia in Egypt from convalescents of the other D.L.I. battalions as the infantry component of 36th Beach Brick.
Arriving back in Africa in June 1943 the 1st battalion was moved to Syria where it was attached to the 10th Indian Infantry Division. The battalion was chosen to be sent to invade the island of Kos
Kos or Cos (; el, Κως ) is a Greek island, part of the Dodecanese island chain in the southeastern Aegean Sea. Kos is the third largest island of the Dodecanese by area, after Rhodes and Karpathos; it has a population of 36,986 (2021 census), ...
, the first company arriving on 16 September but not until the end of the month was the whole battalion on the island, during which time German bombing was increasing. After 10 days of fighting paratroopers and other German forces the remaining men of the battalion were taken off the island by the SBS on 13 October. The battalion was gradually rebuilt from the 129 officers and men who assembled at Genefia at the end of October, and retrained and reinforced until at full strength by the end of March 1944. In April the battalion was deployed to Alexandria to contain a mutiny by the Greek Brigade, but by the end of the month had set sail for Italy.Rissik p. 220
Burma 1941–45
 The 2nd battalion was sent to India in April 1942 with the 2nd Division, arriving in June. For some months it was trained in Jungle fighting and in amphibious assault methods. Later in that year the 6th brigade was made an independent formation. The brigade fought in the
The 2nd battalion was sent to India in April 1942 with the 2nd Division, arriving in June. For some months it was trained in Jungle fighting and in amphibious assault methods. Later in that year the 6th brigade was made an independent formation. The brigade fought in the Arakan
Arakan ( or ) is a historic coastal region in Southeast Asia. Its borders faced the Bay of Bengal to its west, the Indian subcontinent to its north and Burma proper to its east. The Arakan Mountains isolated the region and made it accessi ...
early 1943 at Donbiak on the Mayu peninsular with the brigade making little progress against strong Japanese positions. It was forced to withdraw when the Japanese cut off the peninsular at Indin bridge, the brigade fought its way out, arriving back in India in May. After more amphibious training in the rest of 1943 and early 1944 the 2nd Division was sent relieve Kohima
Kohima (; Angami Naga: ''Kewhira'' ()), is the capital of the Northeastern Indian state of Nagaland. With a resident population of almost 100,000, it is the second largest city in the state. Originally known as ''Kewhira'', Kohima was founded ...
in April 1944. Here the 2nd battalion fought on Garrison Hill and F.S.D. Ridge in late April and early May while overlooked by the guns of the Japanese on Kuki Piquet. Withdrawn to Diampaur in early May the battalion could only muster three companies of two platoons each. By June the battalion was taking its turn as the lead of the advance, with supporting armour, along the Imphal road, when its 'A' company made contact with the lead elements of the 5th Indian Infantry Division on 22 June and the siege of Imphal
Imphal ( Meitei pronunciation: /im.pʰal/; English pronunciation: ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Manipur. The metropolitan centre of the city contains the ruins of Kangla Palace (also known as Kangla Fort), the royal seat of the f ...
was lifted:
The Division was rested until December when it continued its advance into central Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
encountering light but continual resistance. The 6th brigade was in reserve when Mandaly was taken, after which the battalion was returned to India and reacquainted with its previous amphibious training for the attack on Rangoon, in the event they entered the undefended city on 13 May. The battalion was withdrawn back to India in September 1945 to prepare for occupation duties in Japan.
Sicily, Italy and Greece 1943–45
 The 151st brigade was chosen as an assault brigade for the
The 151st brigade was chosen as an assault brigade for the Allied invasion of Sicily
The Allied invasion of Sicily, also known as Operation Husky, was a major campaign of World War II in which the Allied forces invaded the island of Sicily in July 1943 and took it from the Axis powers ( Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany). It bega ...
on 10 July 1943 with the 6th and 9th battalions leading. Due to poor weather both landed late and in the wrong place but against light resistance. After advancing inland and breaking up attacks from the 54th (Napoli) Division on 12 July, the Durham battalions were ordered to Primosole bridge after its capture by British Paratroopers of the 1st Parachute Brigade arriving on 15 July after a forced march of 25 miles and the paratroopers had been forced from the bridge. After 2 days of ferocious battle against men of the 1st Fallschirmjager Division the bridge was retaken at a cost of 500 casualties to the brigade. After entering Catania on 5 August after the Germans withdrew the advance northward was contested in a landscape of terraced hillsides and stone walls. With the end of resistance in Sicily the brigade rested and was informed it was to return to Britain in October.
The 16th battalion landed in Italy at Salerno as part of British X Corps, attached to US Fifth Army
The United States Army North (ARNORTH) is a formation of the United States Army. An Army Service Component Command (ASCC) subordinate to United States Northern Command (NORTHCOM), ARNORTH is the joint force land component of NORTHCOM.
, on 9 September in the second wave, and defended the perimeter of the beach-head until 15 September. The 18th battalion was also part of the landings at Salerno (with two companies) in its role as a beach group. The 16th battalion fought toward, and entered Naples on 6 October, then on 12 October made a silent crossing of the River Volturno reaching its first objective before the Germans noticed. It held the bridgehead it established for 8 days until relieved. The battalion took part in the forcing of the Winter Line
The Winter Line was a series of German and Italian military fortifications in Italy, constructed during World War II by Organisation Todt and commanded by Albert Kesselring. The series of three lines was designed to defend a western section ...
, at the end of October at the Bernhardt line, (after which it was reinforced by drafts from the regiment's 70th battalion) and in January 1944 forcing the main Gustav line. In February, the 46th Division was withdrawn for rest and retraining to Egypt and Palestine, where the battalion aided the civil authorities during a riot in Tel-Aviv. Returning to Italy in July, it fought hard on the Gothic Line advancing along the road to Gemmano in early September and crossed the Cosina Canal in November. In December the battalion was sent to Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
as part of the efforts to keep the peace and then to forestall a communist take over. Initially deployed to Athens, a platoon accidentally occupied the Acropolis
An acropolis was the settlement of an upper part of an ancient Greek city, especially a citadel, and frequently a hill with precipitous sides, mainly chosen for purposes of defense. The term is typically used to refer to the Acropolis of Athens, ...
after turning left instead of right. It became involved in fighting ELAS
The Greek People's Liberation Army ( el, Ελληνικός Λαϊκός Απελευθερωτικός Στρατός (ΕΛΑΣ), ''Ellinikós Laïkós Apeleftherotikós Stratós'' (ELAS) was the military arm of the left-wing National Liberat ...
at Phaleron and in January 1945, Patras. The battalion returned to Italy in April 1945, but did not see action.
Meanwhile, the 1st battalion had returned to Italy in May 1944 where it joined the 10th Indian Infantry Brigade
The 10th Indian Infantry Brigade was an infantry brigade formation of the Indian Army during World War II. It was formed in September 1939. In June 1940 it was assigned to the 5th Indian Infantry Division and in September 1940, sailed for East A ...
in the 10th Indian Infantry Division and by 19 May was back in the line north of Ortona. Transferred to the Tiber valley in June, it fought toward the Gustav Line until September, then was transferred once more to the Adriatic coast fighting though the Gothic Line when it was relieved in February 1945. Returning to the Adriatic coast in April it crossed the Sillaro on 15 April, the battalion heard news of the Armistice while in billets in Ferrara.
France and Germany 1944–45
 The 50th Division with its 151st brigade was withdrawn to Britain in October 1943 to be trained for the
The 50th Division with its 151st brigade was withdrawn to Britain in October 1943 to be trained for the Normandy landings
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on Tuesday, 6 June 1944 of the Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during World War II. Codenamed Operation Neptune and often referred to as ...
, General Montgomery had wanted veteran divisions to be part of the invasion. The news that it was to be an assault division was not universally well received by the other ranks. The brigade landed in the second wave on Gold Beach King sector on which the 18th battalion was also present in its capacity as the infantry of a reserve beach group. Advancing inland they faced the grenadiers of the Panzer Lehr Division
The Panzer-Lehr-Division (in the meaning of: Armoured training division) was an elite German armoured division during World War II. It was formed in 1943 onwards from training and demonstration troops (''Lehr'' = "teach") stationed in Germany, ...
in the bocage
Bocage (, ) is a terrain of mixed woodland and pasture characteristic of parts of Northern France, Southern England, Ireland, the Netherlands and Northern Germany, in regions where pastoral farming is the dominant land use.
''Bocage'' may als ...
around St Pierre, Verrieres and Tilley-sur-Seulles throughout mid June.
The 10th and 11th battalions were landed with the 49th Infantry Division on 10 June and were committed to the attempt to outflank Caen. The 70th brigade with support of the tanks of the Sherwood Rangers Yeomanry
The Sherwood Rangers Yeomanry (SRY) was a British Yeomanry regiment. In 1967 it was amalgamated with other units to form the Royal Yeomanry (RY), a light cavalry regiment of the Army Reserve. Originally raised as the Nottinghamshire Yeomanry Cav ...
captured Rauray (11th battalion) and the high ground beyond (10th battalion) on 27–28 June. The German counter-attack by troops of II SS Panzer Corps
The II SS Panzer Corps was a German Waffen-SS armoured corps which saw action on both the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern and Western Front (World War II), Western Fronts during World War II. It was commanded by Paul Hausser during the Thir ...
was held by the 11th and Tyneside Scottish battalions after such hard fighting that Lord Haw Haw
Lord Haw-Haw was a nickname applied to William Joyce, who broadcast Nazi propaganda to the UK from Germany during the Second World War. The broadcasts opened with "Germany calling, Germany calling", spoken in an affected upper-class English acc ...
called the division the ''Polar Bear Butchers'' (referencing their formation sign). After some days rest and reinforcement the five D.L.I. battalions in Normandy were briefly together when the 70th brigade relieved the 151st brigade around Tilley-Sur-Seulles on 7 July. Later in the month the brigade was transferred to the east of Caen and covered the right flank of Operation Spring
Operation Spring (July 25–27, 1944) was an offensive operation of the Second World War conducted by II Canadian Corps during the Normandy campaign in 1944. The plan was intended to create pressure on the German forces operating on the British ...
. Advancing to Mezidon on the River Dives after the German defeat at Falaise, the brigade fought its last action on 18 August, after which the brigade (as a second line formation) received news it was to be disbanded to reinforce other units of the Second Army.
The 151st brigade advanced in line with the other advances made by the allies in July and by early August was attacking hills south of St.Pierre la Vielle on what was to become the northern edge of the Falaise pocket. After the break out from Normandy the division crossed the Seine on 29 August and reached the Belgian border on 6 September. After a brief rest in Brussels the brigade was tasked to cross the Albert canal in the wake of the 69th brigade, and take the village of Gheel. After holding a series of counter-attacks the 15th Division entered the village on 12 September without a shot being fired, as the Germans had retreated.Ward p. 543 In October the division was moved to the 'Island', the low-lying ground between the Wall and the Lower Rhine north of Eindhoven. After a short operation to expand the bridgehead the brigade garrisoned the area in the early winter. In December, due to its heavy losses, the 50th Division was broken up to reinforce other formations, the 6th and 8th battalions were reduced to a training cadres of time expired men and returned to Britain.
 The 9th battalion was reinforced and transferred to 7th Armoured Division, 131st Infantry Brigade, as a motorised battalion fighting at the
The 9th battalion was reinforced and transferred to 7th Armoured Division, 131st Infantry Brigade, as a motorised battalion fighting at the Roer Triangle
The Rur or Roer (german: Rur ; Dutch and li, Roer, , ; french: Rour) is a major river that flows through portions of Belgium, Germany and the Netherlands. It is a right (eastern) tributary to the Meuse ( nl, links=no, Maas). About 90 perce ...
in January 1945 and the town of Ibbenbüren in March. The battalion ended the war near Hamburg.
The 18th battalion had been serving as lines of communications
A line of communication (or communications) is the route that connects an operating military unit with its supply base. Supplies and reinforcements are transported along the line of communication. Therefore, a secure and open line of communicat ...
troops of 21st Army Group
The 21st Army Group was a British headquarters formation formed during the Second World War. It controlled two field armies and other supporting units, consisting primarily of the British Second Army and the First Canadian Army. Established in ...
, however one company fought the Germans during an attack from besieged Calais in February 1945, the battalion was disbanded at Calais in August 1945.
Home Front 1939–45
Some battalions raised by the regiment were destined not to leave Britain. AHome Defence
A home, or domicile, is a space used as a permanent or semi-permanent residence for one or many humans, and sometimes various companion animals. It is a fully or semi sheltered space and can have both interior and exterior aspects to it. H ...
battalion, the 13th, was formed from the Durham Group (No. 41) National Defence Company in December 1939. It divided in September 1940, producing the 2/13th (Home Defence) battalion which was renamed as the 18th battalion in March 1941. The 1/13th battalion then re-joined the 18th battalion to form the 30th battalion in November 1941 applying the numbering used nationally for 'B' category fitness battalions.Ward pp. 464–465 In 1942 it was briefly organised as a field force unit (a standard army battalion with 'A' category fitness men), until it was disbanded in November 1942.
After the Army's evacuation from Dunkirk, 60 so called 'Dunkirk' infantry battalions were raised in the country that summer, three of which were D.L.I., the 14th, 16th and 17th battalions. All three were brigaded in the 206th Independent Infantry Brigade initially in Scotland, and then on the South coast of England. The 14th and 17th were used as a source of trained reinforcements to the front line. In June 1943 the 14th battalion was sent to Durham as a rehabilitation unit for convalescing troops and ex-PoWs where it stayed until the end of the war. The 17th was disbanded in September 1943.Ward p. 463
The 15th battalion was raised from the 50thRissik p. 317 (or 15th ) Holding battalion in October 1940 and took up the role of coastal defence. In November 1941 it was converted to an armoured unit as 155th Regiment of the Royal Armoured Corps
The Royal Armoured Corps is the component of the British Army, that together with the Household Cavalry provides its armour capability, with vehicles such as the Challenger 2 Tank and the Scimitar Reconnaissance Vehicle. It includes most of the ...
(RAC), retaining the D.L.I. cap badge on the black beret of the RAC.
The 70th (Young Soldiers) battalion was formed in December 1940 at School Aycliffe near Darlington, for men too young for conscription
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day un ...
(20 years at the time). Instead of disbanding when the conscription age was lowered to 18 years in 1942 it was chosen to be a demonstration battalion for the G.H.Q. Battle School at Barnard Castle
Barnard Castle (, ) is a market town on the north bank of the River Tees, in County Durham, Northern England. The town is named after and built around a medieval castle ruin. The town's Bowes Museum's has an 18th-century Silver Swan automato ...
. The battalion was disbanded in August 1943, over 400 of its men being sent overseas.
On their return from the front line in December 1944 the territorial battalion cadres of the 6th and 8th battalions were sent to Yorkshire and were given the task of training service corps soldiers as infantry until the battalions were placed into suspended animation in January 1946.
Post War
Post war, the 1st battalion was active in theGreek Civil War
The Greek Civil War ( el, ο Eμφύλιος �όλεμος}, ''o Emfýlios'' 'Pólemos'' "the Civil War") took place from 1946 to 1949. It was mainly fought against the established Kingdom of Greece, which was supported by the United Kingdom and ...
between January 1946 and June 1948, returning to Britain on 23 July 1948. The 2nd battalion was sent to Singapore from November 1945 to January 1947 when it returned to Burma. By March it was conducting operations against dacoits
Dacoity is a term used for "banditry" in the Indian subcontinent. The spelling is the anglicised version of the Hindi word ''daaku''; "dacoit" is a colloquial Indian English word with this meaning and it appears in the ''Glossary of Colloqui ...
around Maymyo
Pyin Oo Lwin or Pyin U Lwin (, ; Shan: ), formerly and colloquially referred to as Maymyo (), is a scenic hill town in the Mandalay Region, Myanmar, some east of Mandalay, and at an elevation of . The town was estimated to have a population of ...
. Demobilisation
Demobilization or demobilisation (see spelling differences) is the process of standing down a nation's armed forces from combat-ready status. This may be as a result of victory in war, or because a crisis has been peacefully resolved and milit ...
had reduced the battalion to 30 men when it returned to Singapore in November and it returned to Britain on 18 February 1948 as a cadre.Ward p. 559
The 6th, 8th and 9th territorial battalions were reformed as part of the Territorial Army in March 1947, with the 9th battalion being renamed in July 1948 as the 17th battalion, Parachute Regiment.Ward p. 564
On 25 September 1948 the remaining cadre of the 2nd battalion was absorbed into the 1st battalion. The battalion served as part of the Allied occupation forces in Germany, stationed in Dortmund in 1949 and Berlin in 1951.Ward p. 560 The 2nd battalion was reformed in 1952 and was sent to Germany, substituting for the 1st battalion which had been sent to Korea, the battalions re-amalgamated in 1955.
Korea
While in Germany the battalion learned that it was due for a tour of service inKorea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic o ...
, after leave and training in Britain it arrived in September 1952, and was made part of 28th Commonwealth Brigade of the 1st Commonwealth Division part of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
forces in Korea. During its year there up to 50% of its strength was composed of National Servicemen and resulted in a high turnover of men. After initial training in theatre the battalion was first stationed at Neachon (Point 159) in late September, to be greeted by the Chinese by name on arrival (on this and subsequent movement into the front line, as were other battalions). Here it began the never-ending process of attempting to make its trenches clean and habitable, and began patrolling to dominate no-mans-land. In November two trench raids were mounted to try and capture Chinese soldiers, but these were unsuccessful in spite of reaching the Chinese lines due to defensive fire and the extensive use of dugouts by the Chinese in their trench system.
At the end of December in the cold of a Korean winter, the battalion took over and began repairing the trenches at Point 210, and continued patrolling, they were relieved by the Americans at the end of January.
In early April 1953, after being joined by a draft of 94 Korean soldiers who wore British uniform and the D.L.I. cap badge, the battalion relieved the Americans on Point 355, also known as "little Gibraltar" for its steep sides. The battalion continued to patrol vigorously, encountering Chinese patrols on occasion. On the night of 2 July, to celebrate the Coronation of Queen Elizabeth II, a patrol from A Company staked out the Royal cypher "EIIR" in red and yellow fluorescent aircraft recognition panels about ten metres below the Chinese forward trenches.Moses p. 46
At 22:00 hours 27 July, after continued patrolling and ambushes defending the position in the closing stages of the conflict, the battalion buglers sounded "ceasefire". The battalion had lost 24 dead (including 2 attached Koreans) and three missing and 124 wounded. The battalion left Korea in September.
After the war, Patrick O'Donovan of The Observer
''The Observer'' is a British newspaper published on Sundays. It is a sister paper to ''The Guardian'' and ''The Guardian Weekly'', whose parent company Guardian Media Group Limited acquired it in 1993. First published in 1791, it is the w ...
, wrote of the soldiers of the D.L.I. he met in the trenches:
Post Korea
From Korea the 1st battalion was stationed in Egypt, where buglers from the battalion took part in the unveiling of the El-Alamein Memorial on 24 October 1954. The battalion returned to Britain in June 1955. In 1955 the 3rd and 4th battalions were finally disbanded; they had been in suspended animation since 1919. During theSuez Crisis
The Suez Crisis, or the Second Arab–Israeli war, also called the Tripartite Aggression ( ar, العدوان الثلاثي, Al-ʿUdwān aṯ-Ṯulāṯiyy) in the Arab world and the Sinai War in Israel,Also known as the Suez War or 1956 Wa ...
the battalion was flown to Aden on 4 November 1956 for possible deployment to Kuwait
Kuwait (; ar, الكويت ', or ), officially the State of Kuwait ( ar, دولة الكويت '), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to the nort ...
. Most of the battalion returned in February 1957, except for one company which assisted in repelling a Yemeni incursion in the Wadi Harib area.
On 17 May 1958 a bicentenary parade was held at Brancepeth Castle in the presence of Princess Alexandria of Kent to commemorate the raising of the regiment. Present were the 1st battalion and one company each from the 6th and 8th battalions as well as their massed bands and bugles, and detachments from the 437th Light Anti-Aircraft Regiment R.A. (D.L.I.) T.A., and 463th (7 D.L.I.) Light Anti-Aircraft/Searchlight Regiment R.A. T.A. and the 17th battalion The Parachute Regiment (9 D.L.I.) T.A.. The associated Artillery and Parachute Regiments also provided troops who lined the route from the castle gates to the parade area.
In 1958, the battalion served in Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geo ...
to provide troops in the Cyprus Emergency
The Cyprus Emergency ( gr, Απελευθερωτικός Αγώνας της Κύπρου 1955–59), also known as the Greek Cypriot War of Independence or Cypriot War of Independence, was a conflict fought in British Cyprus between November 1 ...
, returning to Britain in 1959. After this, the battalion saw service in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
in 1961 and Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China ( abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delt ...
in 1963.
Borneo
While in Hong Kong in June 1965 the battalion was informed it was to be deployed toBorneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and eas ...
as part of Britain's response to the Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation. Here they patrolled the Jungle taking part in the secret 'Claret
Bordeaux wine ( oc, vin de Bordèu, french: vin de Bordeaux) is produced in the Bordeaux region of southwest France, around the city of Bordeaux, on the Garonne River. To the north of the city the Dordogne River joins the Garonne forming the ...
' operations across the border into Indonesia alongside the Gurkha
The Gurkhas or Gorkhas (), with endonym Gorkhali ), are soldiers native to the Indian subcontinent, Indian Subcontinent, chiefly residing within Nepal and some parts of Northeast India.
The Gurkha units are composed of Nepalis and Indian Go ...
s and Australians. During one of these operations the D.L.I. suffered its last combat fatality, Pte Thomas Griffiths on 26 February 1966.
Amalgamation
Finally in 1968, whilst the battalion was again serving in Cyprus, it was announced that the Durham Light Infantry would join with three other county light infantry regiments to form one large Regiment,The Light Infantry
The Light Infantry was an infantry regiment of the British Army, part of the Light Division. The regiment was one of four 'large' regiments formed after the 1966 Defence White Paper through the amalgamation of units of the Light Infantry Brig ...
, it was to be renamed the 4th battalion the Light Infantry. On 12 December 1968 the 1st battalion laid up its colours in a service in Durham Cathedral, attended by Princess Alexandra, the Regiment's last Colonel in Chief, who inspected the battalion and veterans of the D.L.I. Association.
Victoria Cross awards to the D.L.I.
Battle honours
The regiment inherited thebattle honours
A battle honour is an award of a right by a government or sovereign to a military unit to emblazon the name of a battle or operation on its flags ("colours"), uniforms or other accessories where ornamentation is possible.
In European military t ...
of its predecessor regiments. Due to the number of honours awarded for the First World War, in December 1922 regiments were permitted to select up to 10 honours to be emblazoned on its King's Colour, honours from other conflicts continuing to be displayed on the Regimental Colour. After the Second World War, a further 10 honours were permitted to be added the King's Colour. These are shown below in bold text below.
; Peninsular War
Salamanca
Salamanca () is a city in western Spain and is the capital of the Province of Salamanca in the autonomous community of Castile and León. The city lies on several rolling hills by the Tormes River. Its Old City was declared a UNESCO World Herit ...
, Vittoria, Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to C ...
, Nivelle
Nivelle () is a commune in the Nord department in northern France.
Heraldry
See also
*Communes of the Nord department
* Nivelle Offensive
The Nivelle offensive (16 April – 9 May 1917) was a Franco-British operation on the Western Front ...
, Orthes, Peninsula
; Crimean War
Alma
Alma or ALMA may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Alma'' (film), a 2009 Spanish short animated film
* ''Alma'' (Oswald de Andrade novel), 1922
* ''Alma'' (Le Clézio novel), 2017
* ''Alma'' (play), a 1996 drama by Joshua Sobol about Alma ...
, Inkerman
Inkerman ( uk, Інкерман, russian: Инкерман, crh, İnkerman) is a city in the Crimean peninsula. It is '' de facto'' within the federal city of Sevastopol within the Russian Federation, but '' de jure'' within Ukraine. It li ...
, Sevastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
; Anglo-Persian War
Reshire, Bushire
Bushehr, Booshehr or Bushire ( fa, بوشهر ; also romanised as ''Būshehr'', ''Bouchehr'', ''Buschir'' and ''Busehr''), also known as Bandar Bushehr ( fa, ; also romanised as ''Bandar Būshehr'' and ''Bandar-e Būshehr''), previously Antioc ...
, Koosh-Ab, Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
; New Zealand Wars
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
; Second Boer War
Relief of Ladysmith
When the Second Boer War broke out on 11 October 1899, the Boers had a numeric superiority within Southern Africa. They quickly invaded the British territory and laid siege to Ladysmith, Kimberley and Mafeking. Britain meanwhile transported th ...
, South Africa 1899–1902
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the Sout ...
; First World War
Aisne 1914
Aisne ( , ; ; pcd, Ainne) is a French department in the Hauts-de-France region of northern France. It is named after the river Aisne. In 2019, it had a population of 531,345.'18,
 * (John) William Ainsley (30 June 1898 – 23 June 1976) was a British coal miner and politician.
* General Peter de la Billière, Sir Peter de la Billière Order of the Bath, KCB, Order of the British Empire, KBE, Distinguished Service Order, DSO, Military Cross, MC & Medal bar, bar – Director Special Air Service during the Iranian Embassy Siege in 1980, Commander-in-Chief of the British forces in the 1990 Gulf War.
* George Butterworth, MC (12 July 1885 – 5 August 1916) was an England, English composer best known for his settings of A. E. Housman's poems.
* Sir John Frederick Ferguson CBE Venerable Order of Saint John, CStJ Deputy Lieutenant, DL (c.1891––27 May 1975), Chief Constable, Metropolitan Police.
* Lieutenant Colonel William Morgan Fletcher-Vane, 1st Baron Inglewood (12 April 1909 – 22 June 1989), was a British Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party politician.
* Claud Lovat Fraser (15 May 1890 London) – Artist, designer and author. Commissioned to the 14th battalion of the Durham Light Infantry. He went on to produce sketches as a record of the trenches and battlefields of Flanders.
* Peter Lewis (British Army officer), Peter Lewis MC, later a journalist and editor.
* Lieutenant William Kennett Loftus, father of the English archaeologist and traveller William Loftus (archaeologist), William Loftus.
* Sir Richard May (judge), Richard George May (12 November 1938 – 1 July 2004) – was a British judge. National service with the Durham Light Infantry.
* John Mogg (British Army officer), General Sir Herbert John Mogg, Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath, GCB, Commander of the Order of the British Empire, CBE, Distinguished Service Order, DSO & Medal bar, bar (17 February 1913 – 28 October 2001) - Commanding Officer 9th Battalion, 14 June 1944-July 1945
* Sergeant Major Bill Nicholson (footballer), Bill Nicholson OBE (26 January 1919 – 23 October 2004) was an English football (soccer), football player, coach, manager and scout who devoted his life to Tottenham Hotspur F.C., Tottenham Hotspur.
* Gilbert Norman, Gilbert Maurice Norman – received a commission in the Durham Light Infantry in 1940. Joined the Special Operations Executive (SOE). Arrested in 1943 in France by the Gestapo, he was tortured before transferred to Mauthausen concentration camp where he was executed on 6 September 1944.
* Lieutenant Harold Orton (23 October 1898 – 7 March 1975) was an English university lecturer and Dialectology, dialectologist, best remembered as co-founder of the Survey of English Dialects.
* Lieutenant Leslie Phillips, CBE, Actor
* General Sir Nigel Poett KCB, DSO (J.H.N. Poett) was a
* (John) William Ainsley (30 June 1898 – 23 June 1976) was a British coal miner and politician.
* General Peter de la Billière, Sir Peter de la Billière Order of the Bath, KCB, Order of the British Empire, KBE, Distinguished Service Order, DSO, Military Cross, MC & Medal bar, bar – Director Special Air Service during the Iranian Embassy Siege in 1980, Commander-in-Chief of the British forces in the 1990 Gulf War.
* George Butterworth, MC (12 July 1885 – 5 August 1916) was an England, English composer best known for his settings of A. E. Housman's poems.
* Sir John Frederick Ferguson CBE Venerable Order of Saint John, CStJ Deputy Lieutenant, DL (c.1891––27 May 1975), Chief Constable, Metropolitan Police.
* Lieutenant Colonel William Morgan Fletcher-Vane, 1st Baron Inglewood (12 April 1909 – 22 June 1989), was a British Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party politician.
* Claud Lovat Fraser (15 May 1890 London) – Artist, designer and author. Commissioned to the 14th battalion of the Durham Light Infantry. He went on to produce sketches as a record of the trenches and battlefields of Flanders.
* Peter Lewis (British Army officer), Peter Lewis MC, later a journalist and editor.
* Lieutenant William Kennett Loftus, father of the English archaeologist and traveller William Loftus (archaeologist), William Loftus.
* Sir Richard May (judge), Richard George May (12 November 1938 – 1 July 2004) – was a British judge. National service with the Durham Light Infantry.
* John Mogg (British Army officer), General Sir Herbert John Mogg, Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath, GCB, Commander of the Order of the British Empire, CBE, Distinguished Service Order, DSO & Medal bar, bar (17 February 1913 – 28 October 2001) - Commanding Officer 9th Battalion, 14 June 1944-July 1945
* Sergeant Major Bill Nicholson (footballer), Bill Nicholson OBE (26 January 1919 – 23 October 2004) was an English football (soccer), football player, coach, manager and scout who devoted his life to Tottenham Hotspur F.C., Tottenham Hotspur.
* Gilbert Norman, Gilbert Maurice Norman – received a commission in the Durham Light Infantry in 1940. Joined the Special Operations Executive (SOE). Arrested in 1943 in France by the Gestapo, he was tortured before transferred to Mauthausen concentration camp where he was executed on 6 September 1944.
* Lieutenant Harold Orton (23 October 1898 – 7 March 1975) was an English university lecturer and Dialectology, dialectologist, best remembered as co-founder of the Survey of English Dialects.
* Lieutenant Leslie Phillips, CBE, Actor
* General Sir Nigel Poett KCB, DSO (J.H.N. Poett) was a
 The D.L.I. Museum () (now closed) was the official museum of the Durham Light Infantry. It opened in 1966. Located in Durham, England, the museum featured displays about the regiment's history, with an emphasis on World War I and World War II activities. Exhibits included uniforms, weapons, medals, flags, hats, letters, photographs, badges, ceremonial regalia and other artefacts. The museum was located on the first two floors, with the Durham Art Gallery located on the third floor.
In October 2015 Durham County Council announced the closure of the D.L.I. Museum as a cost saving exercise. This decision sparked the formation of a campaign to see the museum saved led by John Richardson. In June 2019 Durham County Council revealed plans to move the county archives from County Hall, Durham, County Hall to a new history centre, which will also accommodate the Durham Light Infantry Collection, at Mount Oswald.
The D.L.I. Museum () (now closed) was the official museum of the Durham Light Infantry. It opened in 1966. Located in Durham, England, the museum featured displays about the regiment's history, with an emphasis on World War I and World War II activities. Exhibits included uniforms, weapons, medals, flags, hats, letters, photographs, badges, ceremonial regalia and other artefacts. The museum was located on the first two floors, with the Durham Art Gallery located on the third floor.
In October 2015 Durham County Council announced the closure of the D.L.I. Museum as a cost saving exercise. This decision sparked the formation of a campaign to see the museum saved led by John Richardson. In June 2019 Durham County Council revealed plans to move the county archives from County Hall, Durham, County Hall to a new history centre, which will also accommodate the Durham Light Infantry Collection, at Mount Oswald.
Court Circular
/ref>
Durham Light Infantry Museum and Durham Art Gallery website
Durham County Record Office, DLI Archives
*
Re-creating the 68th/Durham Light Infantry from 1758 and 1814
Project Gutenberg – The story of the 6th battalion D.L.I.; France 1915–1918
The 16th battalion Durham Light Infantry 1940–1946
{{British Infantry Regiments World War I Durham Light Infantry, The Light Infantry British light infantry Light Infantry regiments of the British Army 1881 establishments in the United Kingdom Military units and formations established in 1881 Military units and formations disestablished in 1968 Regiments of the British Army in World War I Regiments of the British Army in World War II Military units and formations of the United Kingdom in the Korean War Military units and formations in County Durham Regimental museums in England Museums in Durham, England Military units and formations in Burma in World War II, R
Armentières 1914
Armentières (; vls, Armentiers) is a commune in the Nord department in the Hauts-de-France region in northern France. It is part of the Métropole Européenne de Lille.
The motto of the town is ''Pauvre mais fière'' (Poor but proud).
Geogr ...
, Ypres 1915
Ypres ( , ; nl, Ieper ; vls, Yper; german: Ypern ) is a Belgian city and municipality in the province of West Flanders. Though
the Dutch name is the official one, the city's French name is most commonly used in English. The municipality co ...
'17 '18, Gravenstafel, St. Julien, Frezenberg, Bellewaarde, Hooge 1915
During the First World War, the Second Battle of Ypres was fought from for control of the tactically important high ground to the east and south of the Flemish town of Ypres in western Belgium. The First Battle of Ypres had been fought the pre ...
, Loos, Somme 1916, '18, Albert 1916
Albert may refer to:
Companies
* Albert (supermarket), a supermarket chain in the Czech Republic
* Albert Heijn, a supermarket chain in the Netherlands
* Albert Market, a street market in The Gambia
* Albert Productions, a record label
* Albert C ...
, '18, Bazentin
Bazentin () is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France.
Geography
Situated between Amiens to the southwest and Arras to the north, on the D73 road.
Population
History
* 1914–1918: The village, in the middle o ...
, Delville Wood
The Battle of Delville Wood was a series of engagements in the 1916 Battle of the Somme in the First World War, between the armies of the German Empire and the British Empire. Delville Wood , was a thick tangle of trees, chiefly beech and ...
, Pozières
Pozières (; ) is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France.
Geography
The commune is situated on the D929 road, northeast of Amiens between Albert and Bapaume, on the Pozières ridge.
Southwest of the village on ...
, Guillemont
Guillemont () is a commune approximately east of Albert in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France.
It, like much of the surrounding area, is primarily an agricultural community, but is known for its large Commonwealth War ...
, Flers-Courcelette, Morval, Le Transloy
Le Transloy () is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region of France.
Geography
Le Transloy is situated south of Arras, at the junction of the N17 and the D19 roads.
Population
Places of interest
* The churc ...
, Ancre Heights
The Ancre (; ) is a river of Picardy, France. Rising at Miraumont, a hamlet near the town of Albert, it flows into the Somme at Corbie. It is long. For most of its length it flows through the department of Somme. For a short stretch near P ...
, Arras 1917
Arras ( , ; pcd, Aro; historical nl, Atrecht ) is the prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais department, which forms part of the region of Hauts-de-France; before the reorganization of 2014 it was in Nord-Pas-de-Calais. The historic centre of t ...
, '18, Scarpe 1917, Arleux
Arleux () is a commune in the Nord department in northern France.
Geography
The river Sensée joins the Canal du Nord at Arleux.
Population
Heraldry
See also
*Communes of the Nord department
The following is a list of the 648 communes of ...
, Hill 70
The Battle of Hill 70 took place in the First World War between the Canadian Corps and five divisions of the German 6th Army. The battle took place along the Western Front on the outskirts of Lens in the Nord-Pas-de-Calais region of France ...
, Messines 1917
Messines may refer to:
* Mesen (in French: Messines), a village in Belgium
** Battle of Messines (disambiguation), World War I battles
* Messines, Quebec
Messines is a municipality in the Canadian province of Quebec. It includes the population ...
, Pilckem, Langemarck 1917
The Battle of Langemarck (16–18 August 1917) was the second Anglo-French general attack of the Third Battle of Ypres, during the First World War. The battle took place near Ypres in Belgian Flanders, on the Western Front against the German 4 ...
, Menin Road Menin may refer to:
*Menin, the French name for the Belgian town of Menen
*Menin, a little village in the municipality of Cesiomaggiore, Italy
*Menin or MEN1, a tumor suppressor associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1
*Měnín, villag ...
, Polygon Wood
In geometry, a polygon () is a plane figure that is described by a finite number of straight line segments connected to form a closed ''polygonal chain'' (or ''polygonal circuit''). The bounded plane region, the bounding circuit, or the two to ...
, Broodseinde, Passchendaele, Cambrai 1917
Cambrai (, ; pcd, Kimbré; nl, Kamerijk), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord department and in the Hauts-de-France region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the Esc ...
, '18, St. Quentin, Rosières, Lys, Estaires
Estaires (; vls, Stegers) is a commune in the Nord department of the Hauts-de-France region in northern France.
The town gives its name to a type of chicken bred in the area: the Estaires chicken.
Geography
Estaires is located in French Fla ...
, Hazebrouck
Hazebrouck (, nl, Hazebroek, , vls, Oazebroeke) is a commune in the Nord department, Hauts-de-France. It was a small market town in Flanders until it became an important railway junction in the 1860s. West Flemish was the usual language until 1 ...
, Bailleul, Kemmel
Heuvelland () is a municipality located in the Belgian province of West Flanders. The municipality comprises the villages of Dranouter, Kemmel, De Klijte, Loker, Nieuwkerke, Westouter, Wijtschate and Wulvergem. Heuvelland is a thinly populate ...
, Scherpenberg, Marne 1918, Tardenois
The Tardenois () is today a natural region (''région naturelle'') of France. It is known among archeologists for the epipaleolithic culture known as Tardenoisian after its characteristic arrowheads, originally found at Coincy in the Tardenois i ...
, Bapaume 1918
The Second Battle of Bapaume was a battle of the First World War that took place at Bapaume in France, from 21 August 1918 to 3 September 1918. It was a continuation of the Battle of Albert and is also referred to as the second phase of that ba ...
, Hindenburg Line
The Hindenburg Line (German: , Siegfried Position) was a German defensive position built during the winter of 1916–1917 on the Western Front during the First World War. The line ran from Arras to Laffaux, near Soissons on the Aisne. In 1916 ...
, Havrincourt
Havrincourt () is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in Hauts-de-France in France. The inhabitants are called ''Havrincourtois''.
Situation
The village lies about 14 kilometres south-west of Cambrai near the Havrincourt service area on ...
, Épéhy, Canal du Nord, St. Quentin Canal
The Canal de Saint-Quentin () is a canal in northern France connecting the canalised river Escaut in Cambrai to the Canal latéral à l'Oise and Canal de l'Oise à l'Aisne in Chauny.
History
The canal was built in two phases, the second much lo ...
, Beaurevoir
Beaurevoir is a commune in the department of Aisne in Hauts-de-France in northern France.
Population
See also
* Communes of the Aisne department
The following is a list of the 799 communes in the French department of Aisne.
The commu ...
, Coutrai
Kortrijk ( , ; vls, Kortryk or ''Kortrik''; french: Courtrai ; la, Cortoriacum), sometimes known in English as Courtrai or Courtray ( ), is a Belgian city and municipality in the Flemish province of West Flanders.
It is the capital and larges ...
, Selle, Sambre, France and Flanders 1914–18, Piave, Vittorio Veneto
Vittorio Veneto is a city and ''comune'' situated in the Province of Treviso, in the region of Veneto, Italy, in the northeast of Italy, between the Piave and the Livenza rivers, borders with the following municipalities:
Alpago ( BL), Bellun ...
, Italy 1917–18, Macedonia 1916–18, Egypt 1915–16, N.W. Frontier India 1915 1916–17, Archangel 1918–19
; Afghanistan
Afghanistan 1919
; Second World War
Dyle, Arras counterattack, St. Omer-La Bassée, Dunkirk 1940
Dunkirk (french: Dunkerque ; vls, label=French Flemish, Duunkerke; nl, Duinkerke(n) ; , ;) is a commune in the department of Nord in northern France.Villers Bocage, Operation Perch, Tilly sur Seulles, Operation Martlet#The Battle Continues, Defence of Rauray, Falaise Pocket, St. Pierre La Vielle, Battle of Geel, Gheel, Operation Blackcock, Roer, Western Allied invasion of Germany, Ibbenburen, Battle of France, North-West Europe 1940 Western Front (World War II)#1944–45: The Second Front, '44–45, Syria 1941, Operation Brevity, Halfaya 1941, Siege of Tobruk, Tobruk 1941, Siege of Tobruk, Relief of Tobruk,
Gazala
Gazala, or ʿAyn al-Ġazāla ( ), is a small Libyan village near the coast in the northeastern portion of the country. It is located west of Tobruk.
History
In the late 1930s (during the Italian occupation of Libya), the village was the site of ...
, Battle of Gazala, Gabr el Fachri, Battle of Gazala, Zt el Mrasses, Mersa Matruh
Mersa Matruh ( ar, مرسى مطروح, translit=Marsā Maṭrūḥ, ), also transliterated as ''Marsa Matruh'', is a port in Egypt and the capital of Matrouh Governorate. It is located west of Alexandria and east of Sallum on the main highway ...
, First Battle of El Alamein#Battle of Mersa Matruh, Point 174, Second Battle of El Alamein, El Alamein, Operation Pugilist, Mareth, Battle of Sedjenane, Sedjenane I, Tunisia Campaign, El Kourzia, North African Campaign, North Africa 1940–43, Allied invasion of Sicily, Landing in Sicily, Allied invasion of Sicily, Solarino, Operation Fustian, Primosole Bridge, Allied invasion of Sicily, Sicily 1943, Salerno, Volturno Line, Volturno Crossing, Italian Campaign (World War II)#Allied advance to Rome, Teano, Bernhardt Line, Monte Camino, Battle of Monte Cassino, Monte Tuga, Gothic Line, Gothic Line, Gemmano Ridge, Gothic Line, Cosina Canal Crossing, Gothic Line, Pergola Ridge, Gothic Line, Cesena, Spring 1945 offensive in Italy, Sillaro Crossing, Italian Campaign (World War II), Italy 1943–45, Axis occupation of Greece during World War II, Athens, Greek Civil War, Greece 1944–45, Battle of Kos, Cos, Dodecanese Campaign, Middle East 1943, Siege of Malta (World War II), Malta 1942, Arakan Campaign 1942–1943#Advance stalls, Donbaik, Kohima
Kohima (; Angami Naga: ''Kewhira'' ()), is the capital of the Northeastern Indian state of Nagaland. With a resident population of almost 100,000, it is the second largest city in the state. Originally known as ''Kewhira'', Kohima was founded ...
, Battle of Meiktila and Mandalay, Mandalay, Burma Campaign, Burma 1943–45
; Korean War
Korean War, Korea 1952–53Colonels
Colonel#Colonel of the Regiment, Colonels of the Regiment, from 1881 to 1968 * 1881–93: (1st Battalion) Lord William Paulet GCB ''(ex 68th Foot)'' * 1881–94: (2nd Battalion) John Jarvis Bisset, Sir John Bisset KCMG CB ''(ex 106th Foot)'' * 1894–95: William Augustus Fyers, Sir William Fyers KCB * 1895–97: Eyre Massey, 4th Baron Clarina, Eyre Challoner Henry Massey, 4th Baron Clarina CB * 1897–1908: Reginald Gipps, Sir Reginald Gipps G.C.B. * 1908–23: Russell Upcher C.B. * 1923–28: Frederick Robb, Sir Frederick Robb K.C.B., K.C.M.G., K.C.V.O. * 1928–34: Beauvoir De Lisle, Sir Henry de Beauvoir de Lisle K.C.B., K.C.M.G., D.S.O. * 1934–37: Charles Luard, Charles C. Luard, C.B., C.M.G. * 1937–40: Hubert Horatio Shirley Morant, DSO * 1940–47: Claude Leonard Matthews, DSO * 1947–52: John Atherton Churchill, CBE, DSO, MC * 1952–56: Terence Airey, Sir Terence Airey, KCMG, CB, CBE * 1956–65: Nigel Poett, Sir Nigel Poett, KCB, DSO * 1965–68: Abdy Ricketts CB DSO * ''1968: Regiment amalgamated with The Somerset and Cornwall Light Infantry, The King's Own Yorkshire Light Infantry and The King's Shropshire Light Infantry to formThe Light Infantry
The Light Infantry was an infantry regiment of the British Army, part of the Light Division. The regiment was one of four 'large' regiments formed after the 1966 Defence White Paper through the amalgamation of units of the Light Infantry Brig ...
''
Notable members
 * (John) William Ainsley (30 June 1898 – 23 June 1976) was a British coal miner and politician.
* General Peter de la Billière, Sir Peter de la Billière Order of the Bath, KCB, Order of the British Empire, KBE, Distinguished Service Order, DSO, Military Cross, MC & Medal bar, bar – Director Special Air Service during the Iranian Embassy Siege in 1980, Commander-in-Chief of the British forces in the 1990 Gulf War.
* George Butterworth, MC (12 July 1885 – 5 August 1916) was an England, English composer best known for his settings of A. E. Housman's poems.
* Sir John Frederick Ferguson CBE Venerable Order of Saint John, CStJ Deputy Lieutenant, DL (c.1891––27 May 1975), Chief Constable, Metropolitan Police.
* Lieutenant Colonel William Morgan Fletcher-Vane, 1st Baron Inglewood (12 April 1909 – 22 June 1989), was a British Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party politician.
* Claud Lovat Fraser (15 May 1890 London) – Artist, designer and author. Commissioned to the 14th battalion of the Durham Light Infantry. He went on to produce sketches as a record of the trenches and battlefields of Flanders.
* Peter Lewis (British Army officer), Peter Lewis MC, later a journalist and editor.
* Lieutenant William Kennett Loftus, father of the English archaeologist and traveller William Loftus (archaeologist), William Loftus.
* Sir Richard May (judge), Richard George May (12 November 1938 – 1 July 2004) – was a British judge. National service with the Durham Light Infantry.
* John Mogg (British Army officer), General Sir Herbert John Mogg, Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath, GCB, Commander of the Order of the British Empire, CBE, Distinguished Service Order, DSO & Medal bar, bar (17 February 1913 – 28 October 2001) - Commanding Officer 9th Battalion, 14 June 1944-July 1945
* Sergeant Major Bill Nicholson (footballer), Bill Nicholson OBE (26 January 1919 – 23 October 2004) was an English football (soccer), football player, coach, manager and scout who devoted his life to Tottenham Hotspur F.C., Tottenham Hotspur.
* Gilbert Norman, Gilbert Maurice Norman – received a commission in the Durham Light Infantry in 1940. Joined the Special Operations Executive (SOE). Arrested in 1943 in France by the Gestapo, he was tortured before transferred to Mauthausen concentration camp where he was executed on 6 September 1944.
* Lieutenant Harold Orton (23 October 1898 – 7 March 1975) was an English university lecturer and Dialectology, dialectologist, best remembered as co-founder of the Survey of English Dialects.
* Lieutenant Leslie Phillips, CBE, Actor
* General Sir Nigel Poett KCB, DSO (J.H.N. Poett) was a
* (John) William Ainsley (30 June 1898 – 23 June 1976) was a British coal miner and politician.
* General Peter de la Billière, Sir Peter de la Billière Order of the Bath, KCB, Order of the British Empire, KBE, Distinguished Service Order, DSO, Military Cross, MC & Medal bar, bar – Director Special Air Service during the Iranian Embassy Siege in 1980, Commander-in-Chief of the British forces in the 1990 Gulf War.
* George Butterworth, MC (12 July 1885 – 5 August 1916) was an England, English composer best known for his settings of A. E. Housman's poems.
* Sir John Frederick Ferguson CBE Venerable Order of Saint John, CStJ Deputy Lieutenant, DL (c.1891––27 May 1975), Chief Constable, Metropolitan Police.
* Lieutenant Colonel William Morgan Fletcher-Vane, 1st Baron Inglewood (12 April 1909 – 22 June 1989), was a British Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party politician.
* Claud Lovat Fraser (15 May 1890 London) – Artist, designer and author. Commissioned to the 14th battalion of the Durham Light Infantry. He went on to produce sketches as a record of the trenches and battlefields of Flanders.
* Peter Lewis (British Army officer), Peter Lewis MC, later a journalist and editor.
* Lieutenant William Kennett Loftus, father of the English archaeologist and traveller William Loftus (archaeologist), William Loftus.
* Sir Richard May (judge), Richard George May (12 November 1938 – 1 July 2004) – was a British judge. National service with the Durham Light Infantry.
* John Mogg (British Army officer), General Sir Herbert John Mogg, Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath, GCB, Commander of the Order of the British Empire, CBE, Distinguished Service Order, DSO & Medal bar, bar (17 February 1913 – 28 October 2001) - Commanding Officer 9th Battalion, 14 June 1944-July 1945
* Sergeant Major Bill Nicholson (footballer), Bill Nicholson OBE (26 January 1919 – 23 October 2004) was an English football (soccer), football player, coach, manager and scout who devoted his life to Tottenham Hotspur F.C., Tottenham Hotspur.
* Gilbert Norman, Gilbert Maurice Norman – received a commission in the Durham Light Infantry in 1940. Joined the Special Operations Executive (SOE). Arrested in 1943 in France by the Gestapo, he was tortured before transferred to Mauthausen concentration camp where he was executed on 6 September 1944.
* Lieutenant Harold Orton (23 October 1898 – 7 March 1975) was an English university lecturer and Dialectology, dialectologist, best remembered as co-founder of the Survey of English Dialects.
* Lieutenant Leslie Phillips, CBE, Actor
* General Sir Nigel Poett KCB, DSO (J.H.N. Poett) was a British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurk ...
officer best known for commanding the 5th Parachute Brigade, British 6th Airborne Division during the operation Overlord, Battle of Normandy.
* Air Vice-Marshal Adam Henry Robson CB, OBE, MC & bar, Royal Air Force – he joined the Durham Light Infantry on the outbreak of the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and served until 1919.
* Private Sir Malcolm Sargent (29 April 1895 – 3 October 1967) conducting, conductor, organist and composer
* King Vajiravudh, of Siam (Thailand) briefly commissioned after graduation from Sandhurst Royal Military College in 1889. While holding the rank of Crown Prince.
* Colonel Ernest Vaux of the Sunderland-based Vaux Breweries, Vaux family. He had won a DSO during the Boer War and commanded 7th Battalion from 1911 to 1918
* Sir Godfrey Vick, Godfrey Russell Vick King's Counsel, KC (24 December 1892 – 27 September 1958)''Who Was Who 1897–2006'' (2007) – English lawyer and judge who played a part in several important tribunals.
Regimental museum
 The D.L.I. Museum () (now closed) was the official museum of the Durham Light Infantry. It opened in 1966. Located in Durham, England, the museum featured displays about the regiment's history, with an emphasis on World War I and World War II activities. Exhibits included uniforms, weapons, medals, flags, hats, letters, photographs, badges, ceremonial regalia and other artefacts. The museum was located on the first two floors, with the Durham Art Gallery located on the third floor.
In October 2015 Durham County Council announced the closure of the D.L.I. Museum as a cost saving exercise. This decision sparked the formation of a campaign to see the museum saved led by John Richardson. In June 2019 Durham County Council revealed plans to move the county archives from County Hall, Durham, County Hall to a new history centre, which will also accommodate the Durham Light Infantry Collection, at Mount Oswald.
The D.L.I. Museum () (now closed) was the official museum of the Durham Light Infantry. It opened in 1966. Located in Durham, England, the museum featured displays about the regiment's history, with an emphasis on World War I and World War II activities. Exhibits included uniforms, weapons, medals, flags, hats, letters, photographs, badges, ceremonial regalia and other artefacts. The museum was located on the first two floors, with the Durham Art Gallery located on the third floor.
In October 2015 Durham County Council announced the closure of the D.L.I. Museum as a cost saving exercise. This decision sparked the formation of a campaign to see the museum saved led by John Richardson. In June 2019 Durham County Council revealed plans to move the county archives from County Hall, Durham, County Hall to a new history centre, which will also accommodate the Durham Light Infantry Collection, at Mount Oswald.
D.L.I. Memorial
In July 2012, the Durham Light Infantry Association Memorial was dedicated at the National Memorial Arboretum. The service was attended by Princess Alexandra, the regiment's former Colonel-in-Chief./ref>
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * Dunn, Clive (2015) ''The Fighting Pioneers: the Story of the 7th Durham Light Infantry'', Barnsley: Pen & Sword, . * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * *External links
Durham Light Infantry Museum and Durham Art Gallery website
Durham County Record Office, DLI Archives
*
Re-creating the 68th/Durham Light Infantry from 1758 and 1814
Project Gutenberg – The story of the 6th battalion D.L.I.; France 1915–1918
The 16th battalion Durham Light Infantry 1940–1946
{{British Infantry Regiments World War I Durham Light Infantry, The Light Infantry British light infantry Light Infantry regiments of the British Army 1881 establishments in the United Kingdom Military units and formations established in 1881 Military units and formations disestablished in 1968 Regiments of the British Army in World War I Regiments of the British Army in World War II Military units and formations of the United Kingdom in the Korean War Military units and formations in County Durham Regimental museums in England Museums in Durham, England Military units and formations in Burma in World War II, R