Duplicate code on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
Duplicate code detection using anti-unification
" Proceedings of the Spring/Summer Young Researchers’ Colloquium on Software Engineering. No. 2. Федеральное государственное бюджетное учреждение науки Институт системного программирования Российской академии наук, 2008.
extern int array_a[];
extern int array_b[];
int sum_a = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
sum_a += array_a[i];
int average_a = sum_a / 4;
int sum_b = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
sum_b += array_b[i];
int average_b = sum_b / 4;
The two loops can be rewritten as the single function:
int calc_average_of_four(int* array)
or, usually preferably, by parameterising the number of elements in the array.
Using the above function will give source code that has no loop duplication:
extern int array1[];
extern int array2[];
int average1 = calc_average_of_four(array1);
int average2 = calc_average_of_four(array2);
Note that in this trivial case, the compiler may choose to inline expansion, inline both calls to the function, such that the resulting machine code is identical for both the duplicated and non-duplicated examples above. If the function is not inlined, then the Subroutine#Disadvantages, additional overhead of the function calls will probably take longer to run (on the order of 10 processor instructions for most high-performance languages). Theoretically, this additional time to run could matter.
The University of Alabama at Birmingham: Code Clones Literature
Finding duplicate code in C#, VB.Net, ASPX, Ruby, Python, Java, C, C++, ActionScript, or XAML
Anti-patterns Articles with example C code Software metrics Source code
computer programming
Computer programming is the process of performing a particular computation (or more generally, accomplishing a specific computing result), usually by designing and building an executable computer program. Programming involves tasks such as anal ...
, duplicate code is a sequence of source code
In computing, source code, or simply code, is any collection of code, with or without comments, written using a human-readable programming language, usually as plain text. The source code of a program is specially designed to facilitate the ...
that occurs more than once, either within a program or across different programs owned or maintained by the same entity. Duplicate code is generally considered undesirable for a number of reasons. A minimum requirement is usually applied to the quantity of code that must appear in a sequence for it to be considered duplicate rather than coincidentally similar. Sequences of duplicate code are sometimes known as code clones or just clones, the automated process of finding duplications in source code is called clone detection.
Two code sequences may be duplicates of each other without being character-for-character identical, for example by being character-for-character identical only when white space characters and comments are ignored, or by being token-for-token identical, or token-for-token identical with occasional variation. Even code sequences that are only functionally identical may be considered duplicate code.
Emergence
Some of the ways in which duplicate code may be created are: * copy and paste programming, which in academic settings may be done as part ofplagiarism
Plagiarism is the fraudulent representation of another person's language, thoughts, ideas, or expressions as one's own original work.From the 1995 '' Random House Compact Unabridged Dictionary'': use or close imitation of the language and though ...
* scrounging, in which a section of code is copied "because it works". In most cases this operation involves slight modifications in the cloned code, such as renaming variables or inserting/deleting code. The language nearly always allows one to call one copy of the code from different places, so that it can serve multiple purposes, but instead the programmer creates another copy, perhaps because they
** do not understand the language properly
** do not have the time to do it properly, or
** do not care about the increased active software rot.
It may also happen that functionality is required that is very similar to that in another part of a program, and a developer independently writes code that is very similar to what exists elsewhere. Studies suggest that such independently rewritten code is typically not syntactically similar.
Automatically generated code, where having duplicate code may be desired to increase speed or ease of development, is another reason for duplication. Note that the actual generator will not contain duplicates in its source code, only the output it produces.
Fixing
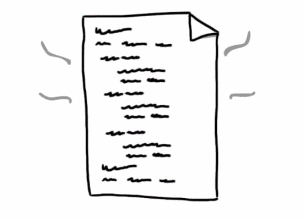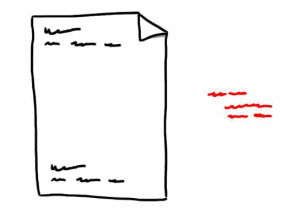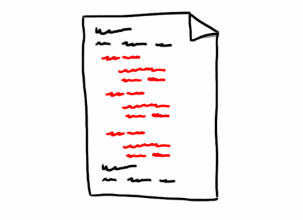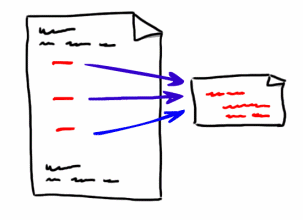
Duplicate code is most commonly fixed by moving the code into its own unit (function or module) and calling that unit from all of the places where it was originally used. Using a more open-source style of development, in which components are in centralized locations, may also help with duplication.Costs and benefits
Code which includes duplicate functionality is more difficult to support because, * it is simply longer, and * if it needs updating, there is a danger that one copy of the code will be updated without further checking for the presence of other instances of the same code. On the other hand, if one copy of the code is being used for different purposes, and it is not properly documented, there is a danger that it will be updated for one purpose, but this update will not be required or appropriate to its other purposes. These considerations are not relevant for automatically generated code, if there is just one copy of the functionality in the source code. In the past, when memory space was more limited, duplicate code had the additional disadvantage of taking up more space, but nowadays this is unlikely to be an issue. When code with a software vulnerability is copied, the vulnerability may continue to exist in the copied code if the developer is not aware of such copies.Refactoring
In computer programming and software design, code refactoring is the process of restructuring existing computer code—changing the '' factoring''—without changing its external behavior. Refactoring is intended to improve the design, structu ...
duplicate code can improve many software metrics, such as lines of code, cyclomatic complexity, and coupling
A coupling is a device used to connect two shafts together at their ends for the purpose of transmitting power. The primary purpose of couplings is to join two pieces of rotating equipment while permitting some degree of misalignment or end mov ...
. This may lead to shorter compilation times, lower cognitive load
In cognitive psychology, cognitive load refers to the amount of working memory resources used. There are three types of cognitive load: ''intrinsic'' cognitive load is the effort associated with a specific topic; ''extraneous'' cognitive load refe ...
, less human error
Human error refers to something having been done that was " not intended by the actor; not desired by a set of rules or an external observer; or that led the task or system outside its acceptable limits".Senders, J.W. and Moray, N.P. (1991) Human ...
, and fewer forgotten or overlooked pieces of code. However, not all code duplication can be refactored.
Clones may be the most effective solution if the programming language provides inadequate or overly complex abstractions, particularly if supported with user interface techniques such as simultaneous editing. Furthermore, the risks of breaking code when refactoring may outweigh any maintenance benefits.
A study by Wagner, Abdulkhaleq, and Kaya concluded that while additional work must be done to keep duplicates in sync, if the programmers involved are aware of the duplicate code there weren't significantly more faults caused than in unduplicated code.
Detecting duplicate code
A number of different algorithms have been proposed to detect duplicate code. For example: *Baker
A baker is a tradesperson who baking, bakes and sometimes Sales, sells breads and other products made of flour by using an oven or other concentrated heat source. The place where a baker works is called a bakery.
History
Ancient history
Si ...
's algorithm.
* Rabin–Karp string search algorithm.
* Using Abstract Syntax Trees.
* Visual clone detection.
* Count Matrix Clone Detection.
* Locality-sensitive hashing
* Anti-unificationBulychev, Peter, and Marius Minea.Duplicate code detection using anti-unification
" Proceedings of the Spring/Summer Young Researchers’ Colloquium on Software Engineering. No. 2. Федеральное государственное бюджетное учреждение науки Институт системного программирования Российской академии наук, 2008.
Example of functionally duplicate code
Consider the following code snippet for calculating theaverage
In ordinary language, an average is a single number taken as representative of a list of numbers, usually the sum of the numbers divided by how many numbers are in the list (the arithmetic mean). For example, the average of the numbers 2, 3, 4, 7 ...
of an array
An array is a systematic arrangement of similar objects, usually in rows and columns.
Things called an array include:
{{TOC right
Music
* In twelve-tone and serial composition, the presentation of simultaneous twelve-tone sets such that the ...
of integer
An integer is the number zero (), a positive natural number (, , , etc.) or a negative integer with a minus sign ( −1, −2, −3, etc.). The negative numbers are the additive inverses of the corresponding positive numbers. In the languag ...
s

See also
* Abstraction principle (programming) * Anti-pattern *Data deduplication
In computing, data deduplication is a technique for eliminating duplicate copies of repeating data. Successful implementation of the technique can improve storage utilization, which may in turn lower capital expenditure by reducing the overall amou ...
*Don't repeat yourself
"Don't repeat yourself" (DRY) is a principle of software development aimed at reducing repetition of software patterns, replacing it with abstractions or using data normalization to avoid redundancy.
The DRY principle is stated as "Every piece of ...
(DRY)
* List of tools for static code analysis
* Redundant code
*Rule of three (computer programming)
Rule of three (''"Three strikes and you refactor"'') is a code refactoring rule of thumb to decide when similar pieces of code should be refactored to avoid duplication. It states that two instances of similar code do not require refactoring, but ...
References
{{reflistExternal links
The University of Alabama at Birmingham: Code Clones Literature
Finding duplicate code in C#, VB.Net, ASPX, Ruby, Python, Java, C, C++, ActionScript, or XAML
Anti-patterns Articles with example C code Software metrics Source code