Drain-waste-vent system on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
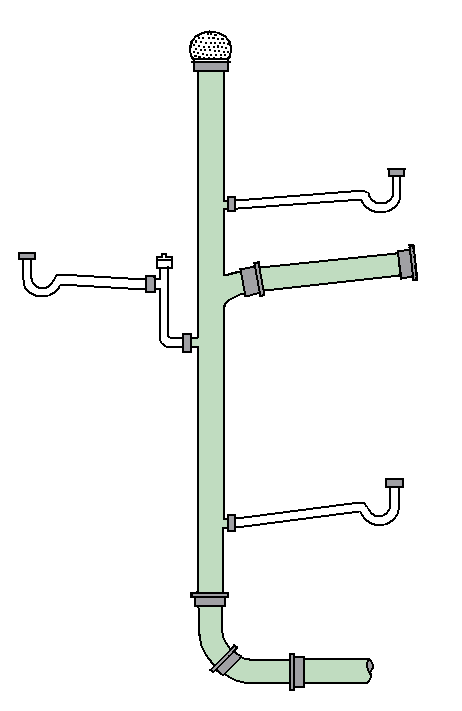 In modern
In modern
plumbing
Plumbing is any system that conveys fluids for a wide range of applications. Plumbing uses pipes, valves, plumbing fixtures, tanks, and other apparatuses to convey fluids. Heating and cooling (HVAC), waste removal, and potable water delive ...
, a drain-waste-vent (or DWV) is a system that allows air to enter the plumbing system to maintain proper air pressure to enable the removal of sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged from reside ...
and greywater
Greywater (or grey water, sullage, also spelled gray water in the United States) refers to domestic wastewater generated in households or office buildings from streams without fecal contamination, i.e., all streams except for the wastewater fro ...
from a dwelling. Drain refers to water produced at fixtures such as sinks, and showers; waste refers to water from toilets. As the water runs down, proper venting is required to allow water to flow freely, and avoid a vacuum from being created. As the water runs down air must be allowed into the waste pipe either through a roof vent (external), or an internal vent.
Overview
DWV systems maintain neutral air pressure in the drains, allowing free flow ofwater
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
and sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged from reside ...
down drains and through waste pipes by gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stro ...
. It is critical that a sufficient downward slope be maintained throughout the drain pipes, to keep liquids and entrained solids flowing freely towards the main drain from the building. In some situations, a downward slope out of a building to the sewer cannot be created, and a special collection pit and grinding lift "sewage ejector" pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic energy. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they ...
are needed. By contrast, potable water
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, ...
supply systems operate under pressure to distribute water up through buildings, and do not require a continuous downward slope in their piping.
Every fixture is required to have an internal or external trap; double trapping is prohibited by plumbing code A plumbing code is a code that provides regulations for the design, installation and inspection of building plumbing and sanitary systems. In the United States, jurisdictions enact their own codes, some of which are based upon model plumbing codes ...
s due to its susceptibility to clogging. Every plumbing fixture must also have an attached vent. Without a vent, negative pressure from water leaving the system can cause a siphon which empties the trap. The top of stacks must be vented too, via a stack vent, which is sometimes called a stink pipe.
All plumbing waste fixtures use traps to prevent sewer gas
Sewer gas is a complex, generally obnoxious smelling mixture of toxic and nontoxic gases produced and collected in sewage systems by the decomposition of organic household or industrial wastes, typical components of sewage.
Sewer gases may inclu ...
es from leaking into the house. Through traps, all fixtures are connected to waste lines, which in turn take the waste to a "soil stack", a.k.a. "soil stack pipe", "soil vent pipe" or "main". At the building drain system's highest point, the drain-waste vent is attached, and rises (usually inside a wall) to and out of the roof. Waste exits from the building through the building's main drain and flows through a sewage line, which leads to a septic system or a public sewer. Cesspit
A cesspit (or cesspool or soak pit in some contexts) is a term with various meanings: it is used to describe either an underground holding tank (sealed at the bottom) or a soak pit (not sealed at the bottom). It can be used for the temporary co ...
s are generally prohibited in developed areas. In the US, fixtures must have a vent (discharging into the "main stack" is not viewed as enough).
The venting system, or plumbing vents, consists of a number of pipes leading from waste pipes to the outdoors, usually through the roof. Vents provide a means to release sewer gases outside instead of inside the house. Vents also admit oxygen to the waste system to allow aerobic
Aerobic means "requiring air," in which "air" usually means oxygen.
Aerobic may also refer to
* Aerobic exercise, prolonged exercise of moderate intensity
* Aerobics, a form of aerobic exercise
* Aerobic respiration, the aerobic process of cel ...
sewage digestion, and to discourage noxious anaerobic decomposition
Anaerobic digestion is a sequence of processes by which microorganisms break down biodegradable material in the absence of oxygen. The process is used for industrial or domestic purposes to manage waste or to produce fuels. Much of the ferment ...
. Vents provide a way to equalize the pressure on both sides of a trap, thereby allowing the trap to hold the water which is needed to maintain effectiveness of the trap, and avoiding "trap suckout" which otherwise might occur.
Operation
A sewer pipe is normally at neutral air pressure compared to the surroundingatmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A ...
. When a column of waste water
Wastewater is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of domestic, industrial ...
flows through a pipe, it compresses air ahead of it in the pipe, creating a ''positive'' pressure that must be released so it does not push back on the waste stream and downstream trap water seals. As the column of water passes, air must freely flow in behind the waste stream, or ''negative'' pressure results. The extent of these pressure fluctuations is determined by the fluid volume of the waste discharge.
Excessive negative air pressure, behind a "slug" of water that is draining, can siphon
A siphon (from grc, σίφων, síphōn, "pipe, tube", also spelled nonetymologically syphon) is any of a wide variety of devices that involve the flow of liquids through tubes. In a narrower sense, the word refers particularly to a tube in a ...
water from traps at plumbing fixtures. Generally, a toilet
A toilet is a piece of sanitary hardware that collects human urine and feces, and sometimes toilet paper, usually for disposal. Flush toilets use water, while dry or non-flush toilets do not. They can be designed for a sitting position popu ...
outlet has the shortest trap seal, making it most vulnerable to being emptied by induced siphonage. An empty trap can allow noxious sewer gas
Sewer gas is a complex, generally obnoxious smelling mixture of toxic and nontoxic gases produced and collected in sewage systems by the decomposition of organic household or industrial wastes, typical components of sewage.
Sewer gases may inclu ...
es to enter a building.
On the other hand, if the air pressure within the drain becomes suddenly higher than ambient, this positive transient could cause waste water to be pushed into the fixture, breaking the trap seal, with serious hygiene
Hygiene is a series of practices performed to preserve health.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), "Hygiene refers to conditions and practices that help to maintain health and prevent the spread of diseases." Personal hygiene refer ...
and health consequences if too forceful. Tall buildings of three or more stories are particularly susceptible to this problem. Vent stacks are installed in parallel to waste stacks to allow proper venting in tall buildings and eliminate these problems.
External venting
Most residential building drainage systems in North America are vented directly through the building roofs. The DWV pipe is typically ABS or PVC DWV-rated plastic pipe equipped with a flashing at the roof penetration to prevent rainwater from entering the buildings. Older homes may usecopper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
, iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
, lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, ...
or clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay pa ...
pipes, in rough order of increasing antiquity.
Under many older building codes, a vent stack (a pipe leading to the main roof vent) is required to be within approx. a radius of the draining fixture it serves (sink, toilet, shower stall, etc.). To allow only one vent stack, and thus one roof penetration as permitted by local building code, sub-vents may be tied together inside the building and exit via a common vent stack, frequently the "main" vent. One additional requirement for a vent stack connection occurs when there are very long horizontal drain runs with very little slope to the run. Adding a vent connection within the run will aid flow, and when used with a cleanout allows for better serviceability of the long run.
A blocked vent is a relatively common problem caused by anything from leaves, to dead animals, to ice dams in very cold weather, or a horizontal section of the venting system, sloped the wrong way and filled with water from rain or condensation. Symptoms range from bubbles in the toilet bowl when it is flushed, to slow drainage, and all the way to siphoned (empty) traps which allow sewer gases to enter the building.
When a fixture trap is venting properly, a "sucking" sound can often be heard as the fixture vigorously empties out during normal operation. This phenomenon is harmless, and is different from "trap suckout" induced by pressure variations caused by wastewater movement ''elsewhere'' in the system, which is not supposed to allow interactions from one fixture to another. Toilets are a special case, since they are usually designed to self-siphon to ensure complete evacuation of their contents; they are then automatically refilled by a special valve mechanism.
Internal venting
Mechanical vents (also called cheater vents) come in two types: Air admittance valves and check vents, the latter being a vent with acheck valve
A check valve, non-return valve, reflux valve, retention valve, foot valve, or one-way valve is a valve that normally allows fluid ( liquid or gas) to flow through it in only one direction.
Check valves are two-port valves, meaning they have ...
.
Air admittance valves (AAVs, or commonly referred to in the UK as Durgo valves and in the US as Studor vents and Sure-Vent®) are negative-pressure-activated, one-way mechanical valves, used in a plumbing or drainage venting system to eliminate the need for conventional pipe venting and roof penetrations. A discharge of wastewater
Wastewater is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of domestic, industrial ...
causes the AAV to open, releasing the vacuum and allowing air to enter the plumbing vent pipe for proper pressure equalization.
Since AAVs will only operate under negative pressure situations, they are not suitable for all venting applications, such as venting a sump, where positive pressures are created when the sump fills. Also, where positive drainage pressures are found in larger buildings or multi-story buildings, an air admittance valve could be used in conjunction with a positive pressure reduction device such as the PAPA positive air pressure attenuator to provide a complete venting solution for more complicated drainage venting systems.
Using AAVs can significantly reduce the amount of venting materials needed in a plumbing system, increase plumbing labor efficiency, allow greater flexibility in the layout of plumbing fixtures, and reduce long-term roof maintenance problems associated with conventional vent stack roofing penetrations.
While some state and local building departments prohibit AAVs, the International Residential and International Plumbing Codes allow it to be used in place of a vent through the roof. AAVs are certified to reliably open and close a minimum of 500,000 times, (approximately 30 years of use) with no release of sewer gas; some manufacturers claim their units are tested for up to 1.5 million cycles, or at least 80 years of use. AAVs have been effectively used in Europe for more than two decades.
Island fixture vent
An island fixture vent, sometimes colloquially called a "Chicago Loop", "Boston loop" or "Bow Vent", is an alternate way of venting the trap installed on an under counter islandsink
A sink is a bowl-shaped plumbing fixture for washing hands, dishwashing, and other purposes. Sinks have a tap (faucet) that supply hot and cold water and may include a spray feature to be used for faster rinsing. They also include a drain t ...
or other similar applications where a conventional vertical vent stack or air admittance valve is not feasible or allowed.
As with all drains, ventilation must be provided to allow the flowing waste water
Wastewater is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of domestic, industrial ...
to displace the sewer gas
Sewer gas is a complex, generally obnoxious smelling mixture of toxic and nontoxic gases produced and collected in sewage systems by the decomposition of organic household or industrial wastes, typical components of sewage.
Sewer gases may inclu ...
in the drain, and then to allow air (or some other fluid) to fill the vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or " void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often ...
which would otherwise form as the water flows down the pipe.
An island fixture vent provides an elegant solution for this necessity: when the drain is opened, water displaces the sewer gas up to the sanitary tee, the water flows downward while sewer gas is displaced upward and toward the vent. The vent can also provide air to fill any vacuum created.
The key to a functional island fixture vent is that the top elbow must be at least as high as the "flood level" (the peak possible drain water level in the sink). This is to ensure that the vent does not become a de facto drain should the actual drain get clogged.
Cost
The cost of installation is high because of the number of elbows and small pieces of pipe required. The largest cost outlay with modern plastic drain pipes is labor. Use ofstreet elbow
A street elbow (sometimes called a street ell or service ell) is a type of plumbing or piping fitting intended to join a piece of pipe and another fitting at an angle. The difference between a street elbow and a regular elbow is the gender of its ...
s is helpful.
Alternately if moving sink to an island sink, install the P-trap below the floor of the island and vent off the top of the drain. Attach toward the trap and reverse 180 degrees so any water in the vent flows down the drain. Slope drain down, slope vent up, and attach to existing vent from previous existing fixture that is now abandoned. Patch previously existing drain to become vent. In Canada, the national plumbing code requires that the minimum trap arm be at least 2 times the pipe diameter, (e.g., 1.25 inch pipe needs a 2.5-inch trap arm, 1.5 pipe needs a 3-inch trap arm, etc.) and that the vent pipe be one size larger than the drain that it serves, also a cleanout is required on both the vent and the drain. The reason for this is in the event of a plugged sink, the waste water will back up and go down the vent, possibly plugging the vent (as it is under the countertop), and a clean-out would permit the cleaning of the pipes.
Fittings
All DWV systems require various sized fittings and pipes which are measured by their internal diameter of both the pipes and the fittings which, and in most cases are schedule 40 PVC wye's, tee's, elbows ranging from 90 degrees to 22.5 degrees for both inside diameter fitment (street) as well as outer diameter fitment (hub), repair and slip couplings, reducer couplings, and pipe which is typically ten feet in length. All DWV system fittings sizes are based on the inside diameter of the pipe that goes into the fittings. These are known as hub fittings. Sizes for hub fittings such as wye's and tee's and crosses are based on the inside diameter of the pipe that goes into the hub of the fittings. Items such as washer boxes and Studor vents are also measured by the internal diameter of the fittings. Schedule 40 PVC DWV systems are ideal for several different reasons and are replacing cast iron DWV systems in many municipalities in the US because of issues that cast iron systems present. Parts are no longer available for cast iron plumbing repairs or for installation due to being phased out for lighter and more sanitary materials. Since the advent of PVC and solvent weld adhesives, which is what holds the fittings together by melting the material into itself, along with the proper placement of support throughout the dwv system using strapping and jhooks as well as knowledge of boring holes in structural framing without comprising the integrity, a pvc dwv system can typically be installed by one individual experienced plumber as opposed to cast iron, which requires several people in order to install and remove. Most pvc dwv systems that replace cast iron systems require the complete removal of the cast iron in order to provide a proper functioning dwv system leaving only enough cast iron pipe (at the lowest point to the ground in which it tyes into the sewage) in order for a specialized rubber boot coupling, known as a fernco, to be installed in order to join the pvc system to waste drainage. A special fitting known as a test tee should immediately follow the installation of the fernco in order to adequately test the system to make sure no leaks are present and that adequate vent pressure is draining the waste water correctly. The means to properly test any dwv system is done with an inflatable apparatus known as a test ball which is placed in a test tee which should be located at the bottom most point of the system before going into the ground.See also
* Fuel gas piping *Plumber
A plumber is a tradesperson who specializes in installing and maintaining systems used for potable (drinking) water, and for sewage and drainage in plumbing systems.
* Potable cold and hot water supply
* Rainwater, surface, and subsurface water drainage
References
Further reading
* {{cite journal, last1=Fink, first1=Justin, title=Drain-Waste-Vent Systems, url=http://www.finehomebuilding.com/how-to/departments/how-it-works/drain-waste-vent-systems.aspx, website=Fine Homebuilding, publisher=Taunton Press, access-date=2015-09-25, volume=154, pages=18–19, date=16 September 2015 Building engineering