Domed Consonant on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
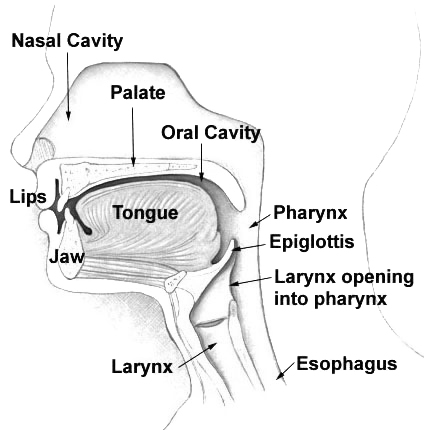 In
In
 In
In linguistics
Linguistics is the science, scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure ...
, specifically articulatory phonetics
The field of articulatory phonetics is a subfield of phonetics that studies articulation and ways that humans produce speech. Articulatory phoneticians explain how humans produce speech sounds via the interaction of different physiological stru ...
, tongue shape describes the shape that the tongue assumes when it makes a sound. Because the sibilant sounds have such a high perceptual prominence, tongue shape is particularly important; small changes in tongue shape are easily audible and can be used to produce different speech sounds, even within a given language.
For non-sibilant sounds, the relevant variations in tongue shape can be adequately described by the concept of secondary articulation, in particular palatalization (raising of the middle of the tongue), velarization
Velarization is a secondary articulation of consonants by which the back of the tongue is raised toward the velum during the articulation of the consonant.
In the International Phonetic Alphabet, velarization is transcribed by one of four di ...
(raising of the back of the tongue) and pharyngealization (retracting of the root of the tongue). Usually, only one secondary articulation can occur for a given sound.
In addition, the acoustic quality of velarization and pharyngealization is very similar so no language contrasts the two.
Shape distinctions
The following varieties of tongue shapes are defined for sibilants, from sharpest and highest-pitched to dullest and lowest-pitched: * Grooved like : with a groove running down the centerline of the tongue. The groove channels a high-velocity jet of air into the teeth, which results in a high-pitched, piercing "hissing" sound. Because of the prominence of the sounds, they are the most common and most stable of sibilants cross-linguistically. They occur inEnglish
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
and are denoted with a ''s'' or ''z'', as in ''soon'' or ''zone''.
* Grooved palatalized like : Combination of grooved shape with palatalization, the raising/bowing of the middle of the tongue.
*Alveolo-palatal
In phonetics, alveolo-palatal (or alveopalatal) consonants, sometimes synonymous with pre-palatal consonants, are intermediate in articulation between the coronal and dorsal consonants, or which have simultaneous alveolar and palatal artic ...
like , or "flat" palatalized: with a convex, V-shaped tongue and highly palatalized.
* Palato-alveolar like , or "domed:" with a "domed" tongue, convex and moderately palatalized. Such sounds occur in English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
and are denoted with ''sh'', ''ch'', ''g'', ''j'', or ''si'', as in ''shin'', ''chin'', ''gin'', and ''vision''.
*Retroflex
A retroflex (Help:IPA/English, /ˈɹɛtʃɹoːflɛks/), apico-domal (Help:IPA/English, /əpɪkoːˈdɔmɪnəl/), or cacuminal () consonant is a coronal consonant where the tongue has a flat, concave, or even curled shape, and is articulated betw ...
like : with a flat or concave (curled back) tongue and no palatalization. Such sounds occur in a large number of varieties, some of which also go by other names such as "flat postalveolar" or "apico-alveolar
An apical consonant is a phone (speech sound) produced by obstructing the air passage with the tip of the tongue (apex) in conjunction with upper articulators from lips to postalveolar, and possibly prepalatal. It contrasts with laminal cons ...
." The , or "true retroflex," sounds are the very dullest and lowest-pitched of all the sibilants, and they have the greatest amount of concavity (the most curling back) of the tongue.
The last three types of sounds are often known as "hushing" sounds and occasionally as "shibilants" because of their quality, as opposed to the "hissing" grooved sounds. Palatalization is an inherent part of the definition of the above varieties and cannot normally be varied independently.
See also
*Place of articulation
In articulatory phonetics, the place of articulation (also point of articulation) of a consonant is a location along the vocal tract where its production occurs. It is a point where a constriction is made between an active and a passive articula ...
* Manner of articulation
* Phonation
*Airstream mechanism
In phonetics, the airstream mechanism is the method by which airflow is created in the vocal tract. Along with phonation and articulation, it is one of three main components of speech production. The airstream mechanism is mandatory for sound pr ...
* Relative articulation
*List of phonetics topics
A
* Acoustic phonetics
* Active articulator
* Affricate
* Airstream mechanism
* Alexander John Ellis
* Alexander Melville Bell
* Alfred C. Gimson
* Allophone
* Alveolar approximant ()
* Alveolar click ()
* Alveolar consonant
* Alveolar ej ...
*Vocal tract
The vocal tract is the cavity in human bodies and in animals where the sound produced at the sound source ( larynx in mammals; syrinx in birds) is filtered.
In birds it consists of the trachea, the syrinx, the oral cavity, the upper part of th ...
* Human voice
* Source–filter model of speech production
References
Bibliography
* {{IPA navigation Phonetics Tongue Place of articulation