Domain coloring on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
.
Another desirable property is such that
the inverse of a function is exactly as light as the original function is dark (and the other way around). Possible choices include
* and
* (with some parameter ). With , this corresponds to the stereographic projection onto the Riemann sphere.
A widespread choice which does not have this property is the function (with some parameter ) which for and is very close to .
This approach uses the HSL (hue, saturation, lightness) color model. Saturation is always set at the maximum of 100%. Vivid colors of the rainbow are rotating in a continuous way on the complex unit circle, so the sixth
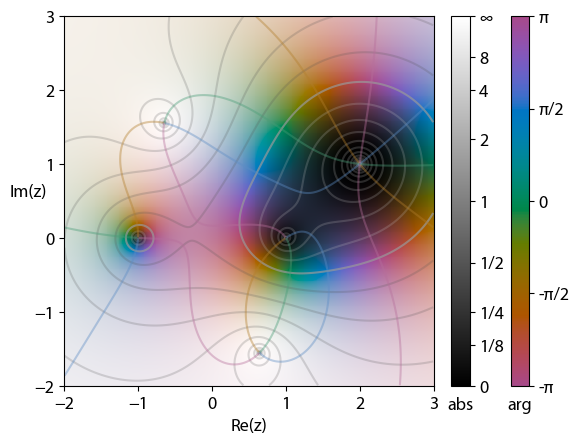
 Unlike the argument, which has finite range, the magnitude of a complex number can range from to . Therefore, in functions that have large ranges of magnitude, changes in magnitude can sometimes be hard to differentiate when a very large change is also pictured in the graph. This can be remedied with a discontinuous color function which shows a repeating brightness pattern for the magnitude based on a given equation. This allows smaller changes to be easily seen as well as larger changes that "discontinuously jump" to a higher magnitude. In the graph on the right, these discontinuities occur in circles around the center, and show a dimming of the graph that can then start becoming brighter again. A similar color function has been used for the graph on top of the article.
Equations that determine the discontinuities may be linear, such as for every
Unlike the argument, which has finite range, the magnitude of a complex number can range from to . Therefore, in functions that have large ranges of magnitude, changes in magnitude can sometimes be hard to differentiate when a very large change is also pictured in the graph. This can be remedied with a discontinuous color function which shows a repeating brightness pattern for the magnitude based on a given equation. This allows smaller changes to be easily seen as well as larger changes that "discontinuously jump" to a higher magnitude. In the graph on the right, these discontinuities occur in circles around the center, and show a dimming of the graph that can then start becoming brighter again. A similar color function has been used for the graph on top of the article.
Equations that determine the discontinuities may be linear, such as for every
Samuel Li's function plotter
High-quality, browser-based interactive complex function plotter by Ricky Reusseur
Complex Mapper
by Alessandro Rosa
John Davis software
−
Open source C and Python domain coloring softwareEnhanced 3D Domain coloringDomain Coloring Method on GPUJava domain coloring software (In development)
*
Python script for GIMP by Michael J. Gruber
*
*
*
Color wheel method
Real-Time Zooming Math Engine
Fractal Zoomer : Software that utilizes domain coloring
cplot, a domain-coloring package for Python
{{DEFAULTSORT:Domain Coloring Complex analysis Numerical function drawing
 In
In complex analysis
Complex analysis, traditionally known as the theory of functions of a complex variable, is the branch of mathematical analysis that investigates Function (mathematics), functions of complex numbers. It is helpful in many branches of mathemati ...
, domain coloring or a color wheel graph is a technique for visualizing complex functions by assigning a color
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associ ...
to each point of the complex plane
In mathematics, the complex plane is the plane formed by the complex numbers, with a Cartesian coordinate system such that the -axis, called the real axis, is formed by the real numbers, and the -axis, called the imaginary axis, is formed by the ...
. By assigning points on the complex plane to different colors and brightness, domain coloring allows for a function from the complex plane to itself — whose graph would normally require four space dimensions — to be easily represented and understood. This provides insight to the fluidity of complex functions and shows natural geometric extensions of real function
In mathematical analysis, and applications in geometry, applied mathematics, engineering, and natural sciences, a function of a real variable is a function whose domain is the real numbers \mathbb, or a subset of \mathbb that contains an interv ...
s.
Motivation
Agraph
Graph may refer to:
Mathematics
*Graph (discrete mathematics), a structure made of vertices and edges
**Graph theory, the study of such graphs and their properties
*Graph (topology), a topological space resembling a graph in the sense of discre ...
of a real function
In mathematical analysis, and applications in geometry, applied mathematics, engineering, and natural sciences, a function of a real variable is a function whose domain is the real numbers \mathbb, or a subset of \mathbb that contains an interv ...
can be drawn in two dimensions because there are two represented variables, and . However, complex numbers are represented by two variables and therefore two dimensions; this means that representing a complex function (more precisely, a complex-valued function
Complex analysis, traditionally known as the theory of functions of a complex variable, is the branch of mathematical analysis that investigates functions of complex numbers. It is helpful in many branches of mathematics, including algebrai ...
of one complex variable
Complex analysis, traditionally known as the theory of functions of a complex variable, is the branch of mathematical analysis that investigates functions of complex numbers. It is helpful in many branches of mathematics, including algebra ...
) requires the visualization of four dimensions. One way to achieve that is with a Riemann surface
In mathematics, particularly in complex analysis, a Riemann surface is a connected one-dimensional complex manifold. These surfaces were first studied by and are named after Bernhard Riemann. Riemann surfaces can be thought of as deformed ver ...
, but another method is by domain coloring.
Method
Representing a four dimensional complex mapping with only two variables is undesirable, as methods like projections can result in a loss of information. However, it is possible to add variables that keep the four-dimensional process without requiring a visualization of four dimensions. In this case, the two added variables are visual inputs such as color and brightness because they are naturally two variables easily processed and distinguished by the human eye. This assignment is called a "color function". There are many different color functions used. A common practice is to represent the complex argument (also known as "phase" or "angle") with a hue following thecolor wheel
A color wheel or color circle is an abstract illustrative organization of color hues around a circle, which shows the relationships between primary colors, secondary colors, tertiary colors etc.
Some sources use the terms ''color wheel'' ...
, and the magnitude by other means, such as brightness
Brightness is an attribute of visual perception in which a source appears to be radiating or reflecting light. In other words, brightness is the perception elicited by the luminance of a visual target. The perception is not linear to luminance, ...
or saturation
Saturation, saturated, unsaturation or unsaturated may refer to:
Chemistry
* Saturation, a property of organic compounds referring to carbon-carbon bonds
**Saturated and unsaturated compounds
** Degree of unsaturation
**Saturated fat or fatty aci ...
.
Simple color function
The following example colors theorigin
Origin(s) or The Origin may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Comics and manga
* Origin (comics), ''Origin'' (comics), a Wolverine comic book mini-series published by Marvel Comics in 2002
* The Origin (Buffy comic), ''The Origin'' (Bu ...
in black, in green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a combin ...
, in magenta
Magenta () is a color that is variously defined as pinkish- purplish- red, reddish-purplish-pink or mauvish-crimson. On color wheels of the RGB (additive) and CMY (subtractive) color models, it is located exactly midway between red and blu ...
, and a point at infinity in white:
There are a number of choices for the function .
should be Monotonic function">strictly monotonic and Continuous function">continuous
Continuity or continuous may refer to:
Mathematics
* Continuity (mathematics), the opposing concept to discreteness; common examples include
** Continuous probability distribution or random variable in probability and statistics
** Continuous g ...roots of unity
In mathematics, a root of unity, occasionally called a de Moivre number, is any complex number that yields 1 when raised to some positive integer power . Roots of unity are used in many branches of mathematics, and are especially important in ...
(starting with 1) are: green, cyan, blue, magenta, red, and yellow.
Since the HSL color space is not perceptually uniform, one can see streaks of perceived brightness at yellow, cyan, and magenta (even though their absolute values are the same as red, green, and blue) and a halo around . More modern color spaces, e.g, the Lab color space
The CIELAB color space, also referred to as ''L*a*b*'' , is a color space defined by the International Commission on Illumination (abbreviated CIE) in 1976. (Referring to CIELAB as "Lab" without asterisks should be avoided to prevent confusio ...
or CIECAM02
In colorimetry, CIECAM02 is the color appearance model published in 2002 by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) Technical Committee 8-01 (''Color Appearance Modelling for Color Management Systems'') and the successor of CIECAM97s ...
, correct this, making the images more accurate and less saturated.
Discontinuous color changing
Many color graphs have discontinuities, where instead of evenly changing brightness and color, it suddenly changes, even when the function itself is still smooth. This is done for a variety of reasons such as showing more detail or highlighting certain aspects of a function, likelevel sets
In mathematics, a level set of a real-valued function of real variables is a set where the function takes on a given constant value , that is:
: L_c(f) = \left\~,
When the number of independent variables is two, a level set is calle ...
.
Magnitude growth
 Unlike the argument, which has finite range, the magnitude of a complex number can range from to . Therefore, in functions that have large ranges of magnitude, changes in magnitude can sometimes be hard to differentiate when a very large change is also pictured in the graph. This can be remedied with a discontinuous color function which shows a repeating brightness pattern for the magnitude based on a given equation. This allows smaller changes to be easily seen as well as larger changes that "discontinuously jump" to a higher magnitude. In the graph on the right, these discontinuities occur in circles around the center, and show a dimming of the graph that can then start becoming brighter again. A similar color function has been used for the graph on top of the article.
Equations that determine the discontinuities may be linear, such as for every
Unlike the argument, which has finite range, the magnitude of a complex number can range from to . Therefore, in functions that have large ranges of magnitude, changes in magnitude can sometimes be hard to differentiate when a very large change is also pictured in the graph. This can be remedied with a discontinuous color function which shows a repeating brightness pattern for the magnitude based on a given equation. This allows smaller changes to be easily seen as well as larger changes that "discontinuously jump" to a higher magnitude. In the graph on the right, these discontinuities occur in circles around the center, and show a dimming of the graph that can then start becoming brighter again. A similar color function has been used for the graph on top of the article.
Equations that determine the discontinuities may be linear, such as for every integer
An integer is the number zero (), a positive natural number (, , , etc.) or a negative integer with a minus sign ( −1, −2, −3, etc.). The negative numbers are the additive inverses of the corresponding positive numbers. In the languag ...
magnitude, exponential equations such as every magnitude where ''n'' is an integer, or any other equation.
Highlighting properties
Discontinuities may be placed where outputs have a certain property to highlight which parts of the graph have that property. For instance, a graph may instead of showing the color cyan jump from green to blue. This causes a discontinuity that is easy to spot, and can highlight lines such as where the argument is zero. Discontinuities may also affect large portions of a graph, such as a graph where the color wheel divides the graph into quadrants. In this way, it is easy to show where each quadrant ends up with relations to others.History
The term "domain coloring" was coined by Frank Farris, possibly around 1998. Lundmark refers to Farris' coining the term "domain coloring" in this 2004 article. There were many earlier uses of color to visualize complex functions, typically mappingargument
An argument is a statement or group of statements called premises intended to determine the degree of truth or acceptability of another statement called conclusion. Arguments can be studied from three main perspectives: the logical, the dialecti ...
( phase) to hue.
Larry Crone used the method in the late 1980s.
Dan Kucerovsky used it in 1990. The technique of using continuous color to map points from domain to codomain or image plane was used in 1999 by George Abdo and Paul Godfrey and colored grids were used in graphics by Doug Arnold that he dates to 1997.
Limitations
People who experiencecolor blindness
Color blindness or color vision deficiency (CVD) is the decreased ability to see color or differences in color. It can impair tasks such as selecting ripe fruit, choosing clothing, and reading traffic lights. Color blindness may make some aca ...
may have trouble interpreting such graphs when they are made with standard color maps. This issue can possibly be ameliorated by creating alternate versions using color maps that fit within the color space discernible to those with color blindness. For example, for use by those with total deuteranopia, a color map based on blue/grey/yellow may be more readable than the conventional map based on blue/green/red.
References
External links
Samuel Li's function plotter
High-quality, browser-based interactive complex function plotter by Ricky Reusseur
by Alessandro Rosa
John Davis software
−
S-Lang
The S-Lang programming library is a software library for Unix, Windows, VMS, OS/2, and Mac OS X. It provides routines for embedding an interpreter for the S-Lang scripting language, and components to facilitate the creation of text-based appl ...
script for Domain ColoringOpen source C and Python domain coloring software
*
MATLAB
MATLAB (an abbreviation of "MATrix LABoratory") is a proprietary multi-paradigm programming language and numeric computing environment developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementat ...
routinePython script for GIMP by Michael J. Gruber
*
Matplotlib
Matplotlib is a plotting library for the Python programming language and its numerical mathematics extension NumPy. It provides an object-oriented API for embedding plots into applications using general-purpose GUI toolkits like Tkinter, wxPy ...
and MayaVi implementation of domain coloring by E. Petriso*
MATLAB
MATLAB (an abbreviation of "MATrix LABoratory") is a proprietary multi-paradigm programming language and numeric computing environment developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementat ...
br>routines with user interface and various color schemes*
MATLAB
MATLAB (an abbreviation of "MATrix LABoratory") is a proprietary multi-paradigm programming language and numeric computing environment developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementat ...
br>routines for 3D-visualization of complex functionsColor wheel method
Real-Time Zooming Math Engine
Fractal Zoomer : Software that utilizes domain coloring
cplot, a domain-coloring package for Python
{{DEFAULTSORT:Domain Coloring Complex analysis Numerical function drawing