Diurnal parallax on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Parallax is a displacement or difference in the
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the
 As the eyes of humans and other animals are in different positions on the head, they present different views simultaneously. This is the basis of
As the eyes of humans and other animals are in different positions on the head, they present different views simultaneously. This is the basis of
 Parallax arises due to a change in viewpoint occurring due to the motion of the observer, of the observed, or both. What is essential is relative motion. By observing parallax, measuring
Parallax arises due to a change in viewpoint occurring due to the motion of the observer, of the observed, or both. What is essential is relative motion. By observing parallax, measuring
 The fact that stellar parallax was so small that it was unobservable at the time was used as the main scientific argument against heliocentrism during the early modern age. It is clear from
The fact that stellar parallax was so small that it was unobservable at the time was used as the main scientific argument against heliocentrism during the early modern age. It is clear from
 Distance measurement by parallax is a special case of the principle of triangulation, which states that one can solve for all the sides and angles in a network of triangles if, in addition to all the angles in the network, the length of at least one side has been measured. Thus, the careful measurement of the length of one baseline can fix the scale of an entire triangulation network. In parallax, the triangle is extremely long and narrow, and by measuring both its shortest side (the motion of the observer) and the small top angle (always less than 1 arcsecond, leaving the other two close to 90 degrees), the length of the long sides (in practice considered to be equal) can be determined.
Assuming the angle is small (see
Distance measurement by parallax is a special case of the principle of triangulation, which states that one can solve for all the sides and angles in a network of triangles if, in addition to all the angles in the network, the length of at least one side has been measured. Thus, the careful measurement of the length of one baseline can fix the scale of an entire triangulation network. In parallax, the triangle is extremely long and narrow, and by measuring both its shortest side (the motion of the observer) and the small top angle (always less than 1 arcsecond, leaving the other two close to 90 degrees), the length of the long sides (in practice considered to be equal) can be determined.
Assuming the angle is small (see
 Parallax can also be used to determine the distance to the Moon.
One way to determine the lunar parallax from one location is by using a lunar eclipse. A full shadow of the Earth on the Moon has an apparent
Parallax can also be used to determine the distance to the Moon.
One way to determine the lunar parallax from one location is by using a lunar eclipse. A full shadow of the Earth on the Moon has an apparent 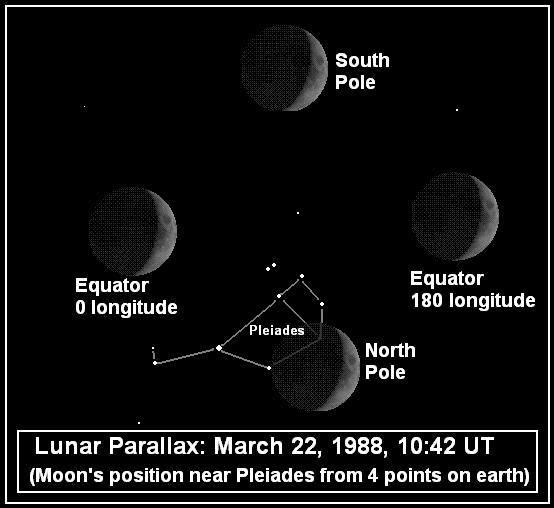 This is the method referred to by Jules Verne in ''
This is the method referred to by Jules Verne in ''
 Although Aristarchus' results were incorrect due to observational errors, they were based on correct geometric principles of parallax, and became the basis for estimates of the size of the Solar System for almost 2000 years, until the
Although Aristarchus' results were incorrect due to observational errors, they were based on correct geometric principles of parallax, and became the basis for estimates of the size of the Solar System for almost 2000 years, until the
 Measurements made by viewing the position of some marker relative to something to be measured are subject to parallax error if the marker is some distance away from the object of measurement and not viewed from the correct position. For example, if measuring the distance between two ticks on a line with a ruler marked on its top surface, the thickness of the ruler will separate its markings from the ticks. If viewed from a position not exactly perpendicular to the ruler, the apparent position will shift and the reading will be less accurate than the ruler is capable of.
A similar error occurs when reading the position of a pointer against a scale in an instrument such as an analog
Measurements made by viewing the position of some marker relative to something to be measured are subject to parallax error if the marker is some distance away from the object of measurement and not viewed from the correct position. For example, if measuring the distance between two ticks on a line with a ruler marked on its top surface, the thickness of the ruler will separate its markings from the ticks. If viewed from a position not exactly perpendicular to the ruler, the apparent position will shift and the reading will be less accurate than the ruler is capable of.
A similar error occurs when reading the position of a pointer against a scale in an instrument such as an analog
 Parallax error can be seen when taking photos with many types of cameras, such as
Parallax error can be seen when taking photos with many types of cameras, such as
 In some
In some
 A
A
Instructions for having background images on a web page use parallax effects
* BBC's ttp://www.bbc.co.uk/science/space/universe/questions_and_ideas/astronomical_distances/#p00bf0l7 Sky at Nightprogram: Patrick Moore demonstrates Parallax using Cricket. (Requires RealPlayer) * Berkeley Center for Cosmological Physic
Parallax
on an educational website, including a quick estimate of distance based on parallax using eyes and a thumb only * {{Portal bar, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System Optics Vision Angle Astrometry Geometry in computer vision Trigonometry
 Parallax is a displacement or difference in the
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position The apparent place of an object is its position in space as seen by an observer. Because of physical and geometrical effects it may differ from the "true" or "geometric" position.
Astronomy
In astronomy, a distinction is made between the ''mean ...
of an object viewed along two different lines of sight and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to foreshortening
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, ...
, nearby objects show a larger parallax than farther objects when observed from different positions, so parallax can be used to determine distances.
To measure large distances, such as the distance of a planet or a star from Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
, astronomers use the principle of parallax. Here, the term ''parallax'' is the semi-angle of inclination between two sight-lines to the star, as observed when Earth is on opposite sides of the Sun in its orbit. These distances form the lowest rung of what is called "the cosmic distance ladder
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A ''direct'' distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible o ...
", the first in a succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects, serving as a basis for other distance measurements in astronomy forming the higher rungs of the ladder.
Parallax also affects optical instruments such as rifle scopes, binoculars, microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisi ...
s, and twin-lens reflex camera
A twin-lens reflex camera (TLR) is a type of camera with two objective lenses of the same focal length. One of the lenses is the photographic objective or "taking lens" (the lens that takes the picture), while the other is used for the viewfind ...
s that view objects from slightly different angles. Many animals, along with humans, have two eyes
Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide living organisms with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and con ...
with overlapping visual fields that use parallax to gain depth perception; this process is known as stereopsis
Stereopsis () is the component of depth perception retrieved through binocular vision.
Stereopsis is not the only contributor to depth perception, but it is a major one. Binocular vision happens because each eye receives a different image becaus ...
. In computer vision the effect is used for computer stereo vision
Computer stereo vision is the extraction of 3D information from digital images, such as those obtained by a CCD camera. By comparing information about a scene from two vantage points, 3D information can be extracted by examining the relative positi ...
, and there is a device called a parallax rangefinder that uses it to find the range, and in some variations also altitude to a target.
A simple everyday example of parallax can be seen in the dashboards of motor vehicles that use a needle-style mechanical speedometer. When viewed from directly in front, the speed may show exactly 60, but when viewed from the passenger seat, the needle may appear to show a slightly different speed due to the angle of viewing combined with the displacement of the needle from the plane of the numerical dial.
Visual perception
 As the eyes of humans and other animals are in different positions on the head, they present different views simultaneously. This is the basis of
As the eyes of humans and other animals are in different positions on the head, they present different views simultaneously. This is the basis of stereopsis
Stereopsis () is the component of depth perception retrieved through binocular vision.
Stereopsis is not the only contributor to depth perception, but it is a major one. Binocular vision happens because each eye receives a different image becaus ...
, the process by which the brain exploits the parallax due to the different views from the eye to gain depth perception and estimate distances to objects. Animals also use ''motion parallax'', in which the animals (or just the head) move to gain different viewpoints. For example, pigeon
Columbidae () is a bird family consisting of doves and pigeons. It is the only family in the order Columbiformes. These are stout-bodied birds with short necks and short slender bills that in some species feature fleshy ceres. They primarily ...
s (whose eyes do not have overlapping fields of view and thus cannot use stereopsis) bob their heads up and down to see depth.
The motion parallax is exploited also in wiggle stereoscopy, computer graphics that provide depth cues through viewpoint-shifting animation rather than through binocular vision.
Astronomy
angle
In Euclidean geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two rays, called the '' sides'' of the angle, sharing a common endpoint, called the '' vertex'' of the angle.
Angles formed by two rays lie in the plane that contains the rays. Angles a ...
s, and using geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is ...
, one can determine distance
Distance is a numerical or occasionally qualitative measurement of how far apart objects or points are. In physics or everyday usage, distance may refer to a physical length or an estimation based on other criteria (e.g. "two counties over"). ...
.
Stellar parallax
Stellar parallax created by the relative motion between the Earth and a star can be seen, in the Copernican model, as arising from the orbit of the Earth around the Sun: the star only ''appears'' to move relative to more distant objects in the sky. In a geostatic model, the movement of the star would have to be taken as ''real'' with the star oscillating across the sky with respect to the background stars. Stellar parallax is most often measured using annual parallax, defined as the difference in position of a star as seen from the Earth and Sun, i.e. the angle subtended at a star by the mean radius of the Earth's orbit around the Sun. Theparsec
The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System, approximately equal to or (au), i.e. . The parsec unit is obtained by the use of parallax and trigonometry, an ...
(3.26 light-years) is defined as the distance for which the annual parallax is 1 arcsecond. Annual parallax is normally measured by observing the position of a star at different times of the year
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hou ...
as the Earth moves through its orbit. Measurement of annual parallax was the first reliable way to determine the distances to the closest stars. The first successful measurements of stellar parallax were made by Friedrich Bessel
Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel (; 22 July 1784 – 17 March 1846) was a German astronomer, mathematician, physicist, and geodesist. He was the first astronomer who determined reliable values for the distance from the sun to another star by the method ...
in 1838 for the star 61 Cygni using a heliometer.. Stellar parallax remains the standard for calibrating other measurement methods. Accurate calculations of distance based on stellar parallax require a measurement of the distance from the Earth to the Sun, now based on radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
reflection off the surfaces of planets.
The angles involved in these calculations are very small and thus difficult to measure. The nearest star to the Sun (and thus the star with the largest parallax), Proxima Centauri, has a parallax of 0.7687 ± 0.0003 arcsec. This angle is approximate that subtended by an object 2 centimeters in diameter located 5.3 kilometers away.
 The fact that stellar parallax was so small that it was unobservable at the time was used as the main scientific argument against heliocentrism during the early modern age. It is clear from
The fact that stellar parallax was so small that it was unobservable at the time was used as the main scientific argument against heliocentrism during the early modern age. It is clear from Euclid
Euclid (; grc-gre, Εὐκλείδης; BC) was an ancient Greek mathematician active as a geometer and logician. Considered the "father of geometry", he is chiefly known for the '' Elements'' treatise, which established the foundations of ...
's geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is ...
that the effect would be undetectable if the stars were far enough away, but for various reasons such gigantic distances involved seemed entirely implausible: it was one of Tycho's principal objections to Copernican heliocentrism
Copernican heliocentrism is the astronomical model developed by Nicolaus Copernicus and published in 1543. This model positioned the Sun at the center of the Universe, motionless, with Earth and the other planets orbiting around it in circular ...
that for it to be compatible with the lack of observable stellar parallax, there would have to be an enormous and unlikely void between the orbit of Saturn (then the most distant known planet) and the eighth sphere
A sphere () is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is th ...
(the fixed stars).
In 1989, the satellite Hipparcos was launched primarily for obtaining improved parallaxes and proper motions for over 100,000 nearby stars, increasing the reach of the method tenfold. Even so, Hipparcos was only able to measure parallax angles for stars up to about 1,600 light-years away, a little more than one percent of the diameter of the Milky Way Galaxy
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
. The European Space Agency's Gaia mission
''Gaia'' is a space observatory of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 2013 and expected to operate until 2025. The spacecraft is designed for astrometry: measuring the positions, distances and motions of stars with unprecedented preci ...
, launched in December 2013, can measure parallax angles to an accuracy of 10 microarcseconds, thus mapping nearby stars (and potentially planets) up to a distance of tens of thousands of light-years from Earth. In April 2014, NASA astronomers reported that the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most vers ...
, by using spatial scanning, can precisely measure distances up to 10,000 light-years away, a ten-fold improvement over earlier measurements.
Distance measurement
derivation
Derivation may refer to:
Language
* Morphological derivation, a word-formation process
* Parse tree or concrete syntax tree, representing a string's syntax in formal grammars
Law
* Derivative work, in copyright law
* Derivation proceeding, a proc ...
below), the distance to an object (measured in parsec
The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System, approximately equal to or (au), i.e. . The parsec unit is obtained by the use of parallax and trigonometry, an ...
s) is the reciprocal
Reciprocal may refer to:
In mathematics
* Multiplicative inverse, in mathematics, the number 1/''x'', which multiplied by ''x'' gives the product 1, also known as a ''reciprocal''
* Reciprocal polynomial, a polynomial obtained from another pol ...
of the parallax (measured in arcseconds): For example, the distance to Proxima Centauri is 1/0.7687 = .
Diurnal parallax
''Diurnal parallax'' is a parallax that varies with the rotation of the Earth or with a difference in location on the Earth. The Moon and to a smaller extent theterrestrial planet
A terrestrial planet, telluric planet, or rocky planet, is a planet that is composed primarily of silicate rocks or metals. Within the Solar System, the terrestrial planets accepted by the IAU are the inner planets closest to the Sun: Mercury, ...
s or asteroids seen from different viewing positions on the Earth (at one given moment) can appear differently placed against the background of fixed stars.
The diurnal parallax has been used by John Flamsteed
John Flamsteed (19 August 1646 – 31 December 1719) was an English astronomer and the first Astronomer Royal. His main achievements were the preparation of a 3,000-star catalogue, ''Catalogus Britannicus'', and a star atlas called '' Atlas C ...
in 1672 to measure the distance to Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
at its opposition and through that to estimate the astronomical unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au, or or AU) is a unit of length, roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun and approximately equal to or 8.3 light-minutes. The actual distance from Earth to the Sun varies by about 3% as Earth orbits ...
and the size of the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
.
Lunar parallax
''Lunar parallax'' (often short for ''lunar horizontal parallax'' or ''lunar equatorial horizontal parallax''), is a special case of (diurnal) parallax: the Moon, being the nearest celestial body, has by far the largest maximum parallax of any celestial body, at times exceeding 1 degree. The diagram for stellar parallax can illustrate lunar parallax as well if the diagram is taken to be scaled right down and slightly modified. Instead of 'near star', read 'Moon', and instead of taking the circle at the bottom of the diagram to represent the size of the Earth's orbit around the Sun, take it to be the size of the Earth's globe, and a circle around the Earth's surface. Then, the lunar (horizontal) parallax amounts to the difference in angular position, relative to the background of distant stars, of the Moon as seen from two different viewing positions on the Earth: one of the viewing positions is the place from which the Moon can be seen directly overhead at a given moment (that is, viewed along the vertical line in the diagram); and the other viewing position is a place from which the Moon can be seen on the horizon at the same moment (that is, viewed along one of the diagonal lines, from an Earth-surface position corresponding roughly to one of the blue dots on the modified diagram). The lunar (horizontal) parallax can alternatively be defined as the angle subtended at the distance of the Moon by the radius of the Earth—equal to angle p in the diagram when scaled-down and modified as mentioned above. The lunar horizontal parallax at any time depends on the linear distance of the Moon from the Earth. The Earth-Moon linear distance varies continuously as the Moon follows its perturbed and approximately elliptical orbit around the Earth. The range of the variation in linear distance is from about 56 to 63.7 Earth radii, corresponding to a horizontal parallax of about a degree of arc, but ranging from about 61.4' to about 54'. The ''Astronomical Almanac
''The Astronomical Almanac''The ''Astronomical Almanac'' for the Year 2015, (United States Naval Observatory/Nautical Almanac Office, 2014) . is an almanac published by the United States Naval Observatory (USNO) and His Majesty's Nautical Almanac ...
'' and similar publications tabulate the lunar horizontal parallax and/or the linear distance of the Moon from the Earth on a periodical e.g. daily basis for the convenience of astronomers (and of celestial navigators), and the study of how this coordinate varies with time forms part of lunar theory.
 Parallax can also be used to determine the distance to the Moon.
One way to determine the lunar parallax from one location is by using a lunar eclipse. A full shadow of the Earth on the Moon has an apparent
Parallax can also be used to determine the distance to the Moon.
One way to determine the lunar parallax from one location is by using a lunar eclipse. A full shadow of the Earth on the Moon has an apparent radius of curvature
In differential geometry, the radius of curvature, , is the reciprocal of the curvature. For a curve, it equals the radius of the circular arc which best approximates the curve at that point. For surfaces, the radius of curvature is the radius o ...
equal to the difference between the apparent radii of the Earth and the Sun as seen from the Moon. This radius can be seen to be equal to 0.75 degrees, from which (with the solar apparent radius of 0.25 degrees) we get an Earth apparent radius of 1 degree. This yields for the Earth-Moon distance 60.27 Earth radii or This procedure was first used by Aristarchus of Samos and Hipparchus, and later found its way into the work of Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
. The diagram at the right shows how daily lunar parallax arises on the geocentric and geostatic planetary model in which the Earth is at the center of the planetary system and does not rotate. It also illustrates the important point that parallax need not be caused by any motion of the observer, contrary to some definitions of parallax that say it is, but may arise purely from motion of the observed.
Another method is to take two pictures of the Moon at the same time from two locations on Earth and compare the positions of the Moon relative to the stars. Using the orientation of the Earth, those two position measurements, and the distance between the two locations on the Earth, the distance to the Moon can be triangulated:
:
 This is the method referred to by Jules Verne in ''
This is the method referred to by Jules Verne in ''From the Earth to the Moon
''From the Earth to the Moon: A Direct Route in 97 Hours, 20 Minutes'' (french: De la Terre à la Lune, trajet direct en 97 heures 20 minutes) is an 1865 novel by Jules Verne. It tells the story of the Baltimore Gun Club, a post-American Civil W ...
'': Until then, many people had no idea how one could calculate the distance separating the Moon from the Earth. The circumstance was exploited to teach them that this distance was obtained by measuring the parallax of the Moon. If the word parallax appeared to amaze them, they were told that it was the angle subtended by two straight lines running from both ends of the Earth's radius to the Moon. If they had doubts about the perfection of this method, they were immediately shown that not only did this mean distance amount to a whole two hundred thirty-four thousand three hundred and forty-seven miles (94,330 leagues) but also that the astronomers were not in error by more than seventy miles (≈ 30 leagues).
Solar parallax
AfterCopernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (; pl, Mikołaj Kopernik; gml, Niklas Koppernigk, german: Nikolaus Kopernikus; 19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon, who formulated ...
proposed his heliocentric system, with the Earth in revolution around the Sun, it was possible to build a model of the whole Solar System without scale. To ascertain the scale, it is necessary only to measure one distance within the Solar System, e.g., the mean distance from the Earth to the Sun (now called an astronomical unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au, or or AU) is a unit of length, roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun and approximately equal to or 8.3 light-minutes. The actual distance from Earth to the Sun varies by about 3% as Earth orbits ...
, or AU). When found by triangulation, this is referred to as the ''solar parallax'', the difference in position of the Sun as seen from the Earth's center and a point one Earth radius away, i.e., the angle subtended at the Sun by the Earth's mean radius. Knowing the solar parallax and the mean Earth radius allows one to calculate the AU, the first, small step on the long road of establishing the size and expansion age of the visible Universe.
A primitive way to determine the distance to the Sun in terms of the distance to the Moon was already proposed by Aristarchus of Samos in his book '' On the Sizes and Distances of the Sun and Moon''. He noted that the Sun, Moon, and Earth form a right triangle (with the right angle at the Moon) at the moment of first or last quarter moon. He then estimated that the Moon–Earth–Sun angle was 87°. Using correct geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is ...
but inaccurate observational data, Aristarchus concluded that the Sun was slightly less than 20 times farther away than the Moon. The true value of this angle is close to 89° 50', and the Sun is about 390 times farther away. He pointed out that the Moon and Sun have nearly equal apparent angular sizes and therefore their diameters must be in proportion to their distances from Earth. He thus concluded that the Sun was around 20 times larger than the Moon; this conclusion, although incorrect, follows logically from his incorrect data. It does suggest that the Sun is larger than the Earth, which could be taken to support the heliocentric model.
transit of Venus
frameless, upright=0.5
A transit of Venus across the Sun takes place when the planet Venus passes directly between the Sun and a superior planet, becoming visible against (and hence obscuring a small portion of) the solar disk. During a tr ...
was correctly observed in 1761 and 1769. This method was proposed by Edmond Halley
Edmond (or Edmund) Halley (; – ) was an English astronomer, mathematician and physicist. He was the second Astronomer Royal in Britain, succeeding John Flamsteed in 1720.
From an observatory he constructed on Saint Helena in 1676–77, H ...
in 1716, although he did not live to see the results. The use of Venus transits was less successful than had been hoped due to the black drop effect, but the resulting estimate, 153 million kilometers, is just 2% above the currently accepted value, 149.6 million kilometers.
Much later, the Solar System was "scaled" using the parallax of asteroids, some of which, such as Eros
In Greek mythology, Eros (, ; grc, Ἔρως, Érōs, Love, Desire) is the Greek god of love and sex. His Roman counterpart was Cupid ("desire").''Larousse Desk Reference Encyclopedia'', The Book People, Haydock, 1995, p. 215. In the ear ...
, pass much closer to Earth than Venus. In a favorable opposition, Eros can approach the Earth to within 22 a millikilometersres. During the opposition of 1900–1901, a worldwide program was launched to make parallax measurements of Eros to determine the solar parallax (or distance to the Sun), with the results published in 1910 by Arthur Hinks of Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a College town, university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cam ...
and Charles D. Perrine of the Lick Observatory, University of California
The University of California (UC) is a public land-grant research university system in the U.S. state of California. The system is composed of the campuses at Berkeley, Davis, Irvine, Los Angeles, Merced, Riverside, San Diego, San Franci ...
. Perrine published progress reports in 1906 and 1908. He took 965 photographs with the Crossley Reflector
The Crossley telescope is a reflecting telescope located at Lick Observatory in the U.S. state of California. It was used between 1895 to 2010, and was donated to the observatory by Edward Crossley, its namesake.
It was the largest glass ref ...
and selected 525 for measurement. A similar program was then carried out, during a closer approach, in 1930–1931 by Harold Spencer Jones
Sir Harold Spencer Jones KBE FRS FRSE PRAS (29 March 1890 – 3 November 1960) was an English astronomer. He became renowned as an authority on positional astronomy and served as the tenth Astronomer Royal for 23 years. Although born " ...
. The value of the Astronomical Unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au, or or AU) is a unit of length, roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun and approximately equal to or 8.3 light-minutes. The actual distance from Earth to the Sun varies by about 3% as Earth orbits ...
(roughly the Earth-Sun distance) obtained by this program was considered definitive until 1968, when radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
and dynamical parallax
In astronomy, the distance to a visual binary star may be estimated from the masses of its two components, the size of their orbit, and the period of their orbit about one another. A dynamical parallax is an (annual) parallax which is computed fr ...
methods started producing more precise measurements.
Also radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
reflections, both off Venus (1958) and off asteroids, like Icarus, have been used for solar parallax determination. Today, use of spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, p ...
telemetry
Telemetry is the in situ collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek roots ''tele'', "remote", an ...
links has solved this old problem. The currently accepted value of solar parallax is 8".794 143.
Moving-cluster parallax
The open stellar cluster Hyades in Taurus extends over such a large part of the sky, 20 degrees, that the proper motions as derived from astrometry appear to converge with some precision to a perspective point north of Orion. Combining the observed apparent (angular) proper motion in seconds of arc with the also observed true (absolute) receding motion as witnessed by the Doppler redshift of the stellar spectral lines, allows estimation of the distance to the cluster (151 light-years) and its member stars in much the same way as using annual parallax.Dynamical parallax
Dynamical parallax has sometimes also been used to determine the distance to a supernova when the optical wavefront of the outburst is seen to propagate through the surrounding dust clouds at an apparent angular velocity, while its true propagation velocity is known to be thespeed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant that is important in many areas of physics. The speed of light is exactly equal to ). According to the special theory of relativity, is the upper limit ...
.
Derivation
For aright triangle
A right triangle (American English) or right-angled triangle ( British), or more formally an orthogonal triangle, formerly called a rectangled triangle ( grc, ὀρθόσγωνία, lit=upright angle), is a triangle in which one angle is a right a ...
,
:
where is the parallax, is approximately the average distance from the Sun to Earth, and is the distance to the star.
Using small-angle approximation
The small-angle approximations can be used to approximate the values of the main trigonometric functions, provided that the angle in question is small and is measured in radians:
:
\begin
\sin \theta &\approx \theta \\
\cos \theta &\approx 1 - \ ...
s (valid when the angle is small compared to 1 radian
The radian, denoted by the symbol rad, is the unit of angle in the International System of Units (SI) and is the standard unit of angular measure used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly an SI supplementary unit (before tha ...
),
:
so the parallax, measured in arcseconds, is
:
If the parallax is 1", then the distance is
:
This ''defines'' the parsec
The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System, approximately equal to or (au), i.e. . The parsec unit is obtained by the use of parallax and trigonometry, an ...
, a convenient unit for measuring distance using parallax. Therefore, the distance, measured in parsecs, is simply , when the parallax is given in arcseconds.
Error
Precise parallax measurements of distance have an associated error. This error in the measured parallax angle does not translate directly into an error for the distance, except for relatively small errors. The reason for this is that an error toward a smaller angle results in a greater error in distance than an error toward a larger angle. However, an approximation of the distance error can be computed by : where ''d'' is the distance and ''p'' is the parallax. The approximation is far more accurate for parallax errors that are small relative to the parallax than for relatively large errors. For meaningful results in stellar astronomy, Dutch astronomer Floor van Leeuwen recommends that the parallax error be no more than 10% of the total parallax when computing this error estimate.Spatio-temporal parallax
From enhanced ''relativistic positioning systems'', Spatio-temporal parallax generalizing the usual notion of parallax in space only has been developed. Then, event fields in spacetime can be deduced directly without intermediate models of light bending by massive bodies such as the one used in the PPN formalism for instance.Metrology
multimeter
A multimeter is a measuring instrument that can measure multiple electrical properties. A typical multimeter can measure voltage, resistance, and current, in which case it is also known as a volt-ohm-milliammeter (VOM), as the unit is equipped w ...
. To help the user avoid this problem, the scale is sometimes printed above a narrow strip of mirror
A mirror or looking glass is an object that reflects an image. Light that bounces off a mirror will show an image of whatever is in front of it, when focused through the lens of the eye or a camera. Mirrors reverse the direction of the im ...
, and the user's eye is positioned so that the pointer obscures its reflection, guaranteeing that the user's line of sight is perpendicular to the mirror and therefore to the scale. The same effect alters the speed read on a car's speedometer by a driver in front of it and a passenger off to the side, values read from a graticule, not in actual contact with the display on an oscilloscope, etc.
Photogrammetry
When viewed through a stereo viewer, aerial picture pair offers a pronounced stereo effect of landscape and buildings. High buildings appear to "keel over" in the direction away from the center of the photograph. Measurements of this parallax are used to deduce the height of the buildings, provided that flying height and baseline distances are known. This is a key component of the process of photogrammetry.Photography
twin-lens reflex camera
A twin-lens reflex camera (TLR) is a type of camera with two objective lenses of the same focal length. One of the lenses is the photographic objective or "taking lens" (the lens that takes the picture), while the other is used for the viewfind ...
s and those including viewfinder
In photography, a viewfinder is what the photographer looks through to compose, and, in many cases, to focus the picture. Most viewfinders are separate, and suffer parallax, while the single-lens reflex camera lets the viewfinder use the main ...
s (such as rangefinder camera
A rangefinder camera is a camera fitted with a rangefinder, typically a split-image rangefinder: a range-finding focusing mechanism allowing the photographer to measure the subject distance and take photographs that are in sharp focus. Most va ...
s). In such cameras, the eye sees the subject through different optics (the viewfinder, or a second lens) than the one through which the photo is taken. As the viewfinder is often found above the lens of the camera, photos with parallax error are often slightly lower than intended, the classic example being the image of a person with their head cropped off. This problem is addressed in single-lens reflex cameras, in which the viewfinder sees through the same lens through which the photo is taken (with the aid of a movable mirror), thus avoiding parallax error.
Parallax is also an issue in image stitching, such as for panoramas.
Weapon sights
Parallax affects sighting devices of ranged weapons in many ways. On sights fitted on small arms and bows, etc., the perpendicular distance between the sight and the weapon's launch axis (e.g. thebore axis The bore axis of a firearm is the longitudinal axis through the geometric center of the gun barrel. In a rifled barrel, the projectile (bullet/ball, pellet or slug) will spin around the bore axis as it goes through the barrel.
Boresighting is a ...
of a gun)—generally referred to as "''sight height''"—can induce significant aiming errors when shooting at close range, particularly when shooting at small targets. This parallax error is compensated for (when needed) via calculations that also take in other variables such as bullet drop
External ballistics or exterior ballistics is the part of ballistics that deals with the behavior of a projectile in flight. The projectile may be powered or un-powered, guided or unguided, spin or fin stabilized, flying through an atmosphere or ...
, windage
Windage is a term used in aerodynamics, firearms ballistics, and automobiles.
Usage
Aerodynamics
Windage is a force created on an object by friction when there is relative movement between air and the object. Windage loss is the reduction in ...
, and the distance at which the target is expected to be. Sight height can be used to advantage when "sighting in" rifles for field use. A typical hunting rifle (.222 with telescopic sights) sighted in at 75m will still be useful from without needing further adjustment.
Optical sights
 In some
In some reticle
A reticle, or reticule also known as a graticule, is a pattern of fine lines or markings built into the eyepiece of an optical device such as a telescopic sight, spotting scope, theodolite, optical microscope or the screen of an oscilloscop ...
d optical instrument
An optical instrument (or "optic" for short) is a device that processes light waves (or photons), either to enhance an image for viewing or to analyze and determine their characteristic properties. Common examples include periscopes, microscopes, ...
s such as telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally meaning only an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observ ...
s, microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisi ...
s or in telescopic sight
A telescopic sight, commonly called a scope informally, is an optical sighting device based on a refracting telescope. It is equipped with some form of a referencing pattern – known as a '' reticle'' – mounted in a focally appropriate ...
s ("scopes") used on small arm
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions).
The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes ...
s and theodolite
A theodolite () is a precision optical instrument for measuring angles between designated visible points in the horizontal and vertical planes. The traditional use has been for land surveying, but it is also used extensively for building an ...
s, parallax can create problems when the reticle is not coincident with the focal plane of the target image. This is because when the reticle and the target are not at the same focus, the optically corresponded distances being projected through the eyepiece
An eyepiece, or ocular lens, is a type of lens that is attached to a variety of optical devices such as telescopes and microscopes. It is named because it is usually the lens that is closest to the eye when someone looks through the device. The ...
are also different, and the user's eye will register the difference in parallaxes between the reticle and the target (whenever eye position changes) as a relative displacement on top of each other. The term ''parallax shift'' refers to the resultant apparent "floating" movements of the reticle over the target image when the user moves his/her head/eye laterally (up/down or left/right) behind the sight, i.e. an error where the reticle does not stay aligned with the user's optical axis.
Some firearm scopes are equipped with a parallax compensation mechanism, which consists of a movable optical element that enables the optical system to shift the focus of the target image at varying distances into the same optical plane of the reticle (or vice versa). Many low-tier telescopic sights may have no parallax compensation because in practice they can still perform very acceptably without eliminating parallax shift. In this case, the scope is often set fixed at a designated parallax-free distance that best suits their intended usage. Typical standard factory parallax-free distances for hunting scopes are 100 yd (or 90 m) to make them suited for hunting shots that rarely exceed 300 yd/m. Some competition and military-style scopes without parallax compensation may be adjusted to be parallax free at ranges up to 300 yd/m to make them better suited for aiming at longer ranges. Scopes for guns with shorter practical ranges, such as airguns, rimfire rifles, shotguns, and muzzleloaders, will have parallax settings for shorter distances, commonly for rimfire scopes and for shotguns and muzzleloaders. Airgun scopes are very often found with adjustable parallax, usually in the form of an adjustable objective (or "AO" for short) design, and may adjust down to as near as .
Non-magnifying reflector or "reflex" sights can be theoretically "parallax free." But since these sights use parallel collimated light
A collimated beam of light or other electromagnetic radiation has parallel rays, and therefore will spread minimally as it propagates. A perfectly collimated light beam, with no divergence, would not disperse with distance. However, diffraction ...
this is only true when the target is at infinity. At finite distances, eye movement perpendicular to the device will cause parallax movement in the reticle image in exact relationship to the eye position in the cylindrical column of light created by the collimating optics. Firearm sights, such as some red dot sights, try to correct for this via not focusing the reticle at infinity, but instead at some finite distance, a designed target range where the reticle will show very little movement due to parallax. Some manufacturers market reflector sight models they call "parallax free," but this refers to an optical system that compensates for off axis spherical aberration, an optical error induced by the spherical mirror used in the sight that can cause the reticle position to diverge off the sight's optical axis with change in eye position.
Artillery gunfire
Because of the positioning of field ornaval artillery
Naval artillery is artillery mounted on a warship, originally used only for naval warfare and then subsequently used for shore bombardment and anti-aircraft roles. The term generally refers to tube-launched projectile-firing weapons and exclude ...
guns, each one has a slightly different perspective of the target relative to the location of the fire-control system itself. Therefore, when aiming its guns at the target, the fire control system must compensate for parallax in order to assure that fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material (the fuel) in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction products.
At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition point, flames a ...
from each gun converges on the target.
Rangefinders
coincidence rangefinder
A coincidence rangefinder or coincidence telemeter is a type of rangefinder that uses mechanical and optical principles to allow an operator to determine the distance to a visible object. There are subtypes split-image telemeter, inverted image, ...
or parallax rangefinder can be used to find distance to a target.
Art
Several of Mark Renn's sculptural works play with parallax, appearing abstract until viewed from a specific angle. One such sculpture is ''The Darwin Gate'' (pictured) in Shrewsbury, England, which from a certain angle appears to form a dome, according toHistoric England
Historic England (officially the Historic Buildings and Monuments Commission for England) is an executive non-departmental public body of the British Government sponsored by the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport. It is tasked w ...
, in "the form of a Saxon helmet with a Norman window... inspired by features of St Mary's Church which was attended by Charles Darwin as a boy".
As a metaphor
In a philosophic/geometric sense: an apparent change in the direction of an object, caused by a change in observational position that provides a new line of sight. The apparent displacement, or difference of position, of an object, as seen from two different stations, or points of view. In contemporary writing, parallax can also be the same story, or a similar story from approximately the same timeline, from one book, told from a different perspective in another book. The word and concept feature prominently inJames Joyce
James Augustine Aloysius Joyce (2 February 1882 – 13 January 1941) was an Irish novelist, poet, and literary critic. He contributed to the modernist avant-garde movement and is regarded as one of the most influential and important writers of ...
's 1922 novel, '' Ulysses''. Orson Scott Card
Orson Scott Card (born August 24, 1951) is an American writer known best for his science fiction works. He is the first and (as of 2022) only person to win both a Hugo Award and a Nebula Award in consecutive years, winning both awards for both ...
also used the term when referring to Ender's Shadow as compared to Ender's Game.
The metaphor is invoked by Slovenian philosopher Slavoj Žižek in his 2006 book ''The Parallax View
''The Parallax View'' is a 1974 American political thriller film produced and directed by Alan J. Pakula, and starring Warren Beatty, Hume Cronyn, William Daniels and Paula Prentiss. The screenplay by David Giler and Lorenzo Semple Jr. was base ...
'', borrowing the concept of "parallax view" from the Japanese philosopher and literary critic Kojin Karatani
is a Japanese philosopher and literary critic.
Biography
Karatani entered the University of Tokyo in 1960, where he joined the radical Marxist Communist League, better known as "The Bund," and participated in the massive 1960 Anpo protests aga ...
. Žižek notes,
See also
* Binocular disparity *Lutz–Kelker bias The Lutz–Kelker bias is a supposed systematic bias that results from the assumption that the probability of a star being at distance s
increases with the square of the distance which is equivalent to the assumption that the distribution of stars ...
* Parallax mapping
Parallax mapping (also called offset mapping or virtual displacement mapping) is an enhancement of the bump mapping or normal mapping techniques applied to textures in 3D rendering applications such as video games. To the end user, this means t ...
, in computer graphics
* Parallax scrolling
Parallax scrolling is a technique in computer graphics where background images move past the camera more slowly than foreground images, creating an illusion of depth in a 2D scene of distance. The technique grew out of the multiplane camera tec ...
, in computer graphics
* Refraction
In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commonly observed phenome ...
, a visually similar principle caused by water, etc.
* Spectroscopic parallax Spectroscopic parallax or main sequence fitting is an astronomical method for measuring the distances to stars.
Despite its name, it does not rely on the geometric parallax effect. The spectroscopic parallax technique can be applied to any main se ...
* Triangulation, wherein a point is calculated given its angles from other known points
* Trigonometry
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships between side lengths and angles of triangles. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical studies ...
* True range multilateration
True most commonly refers to truth, the state of being in congruence with fact or reality.
True may also refer to:
Places
* True, West Virginia, an unincorporated community in the United States
* True, Wisconsin, a town in the United States
* ...
, wherein a point is calculated given its distances from other known points
* Xallarap Xallarap is a variation in a gravitational lensing observation caused by the orbital motion of the source. A more traditional and similar effect, parallax, is the variation caused by motion of the earth around the sun. Since the two effects are c ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * . * .External links
Instructions for having background images on a web page use parallax effects
* BBC's ttp://www.bbc.co.uk/science/space/universe/questions_and_ideas/astronomical_distances/#p00bf0l7 Sky at Nightprogram: Patrick Moore demonstrates Parallax using Cricket. (Requires RealPlayer) * Berkeley Center for Cosmological Physic
Parallax
on an educational website, including a quick estimate of distance based on parallax using eyes and a thumb only * {{Portal bar, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System Optics Vision Angle Astrometry Geometry in computer vision Trigonometry