Diocese Of Connor (Church Of Ireland) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Diocese of Connor is in the Province of Armagh of the
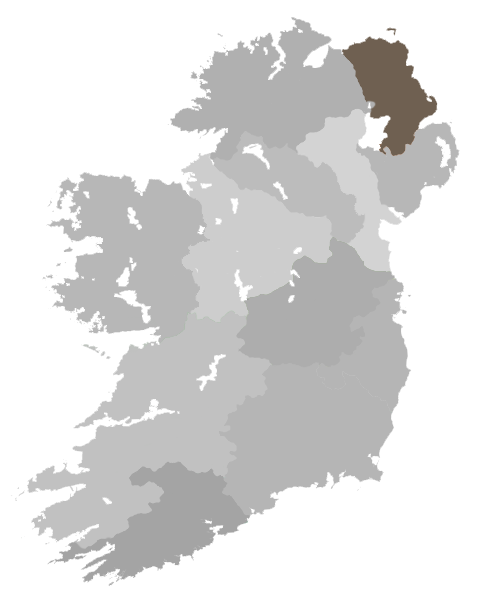 It is based on the traditional
It is based on the traditional
However, the Synod#Anglican usage, diocesan synod, unlike those in other Northern Dioceses with more strongly Evangelical traditions, failed to endorse a motion on Lambeth Conference Resolution I.10. Bishop George Davison, elected in February 2020, is seen as theologically conservative, having served previously in theEvangelical elected bishop of Connor, Anglican Ink, 17 February 2020
/ref>

Official website
{{authority control Connor Religion in County Antrim Religion in Belfast Christian organizations established in 1944 Diocese of Connor
Church of Ireland
The Church of Ireland ( ga, Eaglais na hÉireann, ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Kirk o Airlann, ) is a Christian church in Ireland and an autonomous province of the Anglican Communion. It is organised on an all-Ireland basis and is the second ...
.
Overview and history
Christianity has been present in Connor Diocese for over 1500 years. Tradition holds thatSt. Patrick
ST, St, or St. may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Stanza, in poetry
* Suicidal Tendencies, an American heavy metal/hardcore punk band
* Star Trek, a science-fiction media franchise
* Summa Theologica, a compendium of Catholic philosophy an ...
herded sheep on Slemish
Slemish, historically called Slieve Mish (), is a hill in County Antrim, Northern Ireland. It lies a few miles east of Ballymena, in the townland of Carnstroan. Tradition holds that Saint Patrick, enslaved as a youth, was brought to this area a ...
, in the heart of the Diocese, when first brought to Ireland as a slave. Saint Malachy, the great reformer of the Irish church, was consecrated Bishop of Connor
The Bishop of Connor is an episcopal title which takes its name after the village of Connor in County Antrim, Northern Ireland. The title is currently used by the Church of Ireland, but in the Roman Catholic Church it has been united with anoth ...
in 1124 and remained until his translation to the Archbishopric of Armagh in 1132. The see was originally at Connor. There is much evidence, from written sources and archaeological material, that Connor was a sizeable, complex settlement in the Early Christian period, probably with monastic and secular elements coexisting. There was no monastic establishment at Connor in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, though there was an Augustinian Augustinian may refer to:
*Augustinians, members of religious orders following the Rule of St Augustine
*Augustinianism, the teachings of Augustine of Hippo and his intellectual heirs
*Someone who follows Augustine of Hippo
* Canons Regular of Sain ...
community at Kells nearby.
When the Church in England broke communion with the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britain ...
was established by the state as the established church
A state religion (also called religious state or official religion) is a religion or creed officially endorsed by a sovereign state. A state with an official religion (also known as confessional state), while not secular, is not necessarily a t ...
. Later, by decree of the Irish Parliament, a similar new body became the State Church
A state religion (also called religious state or official religion) is a religion or creed officially endorsed by a sovereign state. A state with an official religion (also known as confessional state), while not secular, is not necessarily a t ...
in the Kingdom of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland ( ga, label=Classical Irish, an Ríoghacht Éireann; ga, label=Modern Irish, an Ríocht Éireann, ) was a monarchy on the island of Ireland that was a client state of England and then of Great Britain. It existed from ...
. It assumed possession of most Church property (and so retained a great repository of religious architecture and other items, though some were later destroyed). The substantial majority of the population remained faithful to the Latin Rite
Latin liturgical rites, or Western liturgical rites, are Catholic rites of public worship employed by the Latin Church, the largest particular church ''sui iuris'' of the Catholic Church, that originated in Europe where the Latin language once ...
of Roman Catholicism, despite the political and economic advantages of membership in the state church. They were obliged to find alternative premises and to conduct their services in secret. The English-speaking minority mostly adhered to the Church of Ireland or to Presbyterianism
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their nam ...
. On the death of Archbishop Trench of Tuam in 1839, the Province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''Roman province, provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire ...
of Tuam was united to the Armagh
Armagh ( ; ga, Ard Mhacha, , "Macha's height") is the county town of County Armagh and a city in Northern Ireland, as well as a civil parish. It is the ecclesiastical capital of Ireland – the seat of the Archbishops of Armagh, the Pri ...
. Over the centuries, numerous dioceses were merged, in view of declining membership.
The area remained a stronghold of Gaelic
Gaelic is an adjective that means "pertaining to the Gaels". As a noun it refers to the group of languages spoken by the Gaels, or to any one of the languages individually. Gaelic languages are spoken in Ireland, Scotland, the Isle of Man, and Ca ...
and Catholic culture until the Plantation of Ulster
The Plantation of Ulster ( gle, Plandáil Uladh; Ulster-Scots: ''Plantin o Ulstèr'') was the organised colonisation (''plantation'') of Ulstera province of Irelandby people from Great Britain during the reign of King James I. Most of the sett ...
. The majority of planters came from Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
and were not only Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their nam ...
but also covenanter
Covenanters ( gd, Cùmhnantaich) were members of a 17th-century Scottish religious and political movement, who supported a Presbyterian Church of Scotland, and the primacy of its leaders in religious affairs. The name is derived from ''Covenan ...
s and fiercely opposed to episcopacy
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
. Such was the anti-Anglican tenor of the Scottish settlers that the English divine, Jeremy Taylor
Jeremy Taylor (1613–1667) was a cleric in the Church of England who achieved fame as an author during the Protectorate of Oliver Cromwell. He is sometimes known as the "Shakespeare of Divines" for his poetic style of expression, and he is fr ...
, for a time Bishop of the United Dioceses of Down, Connor and Dromore, said of his new home, ''"I perceive myself thrown into a place of torment."'' County Antrim, corresponding closely with the Diocese of Connor soon became the most Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
county in Ireland, a situation which remains the case today.
Previous entities
The modern Anglican form of the diocese came into being when the Diocese of Connor was split from the hitherto United Dioceses of Down, Connor and Dromore in 1944. The Diocesan Cathedral is in Christ ChurchLisburn
Lisburn (; ) is a city in Northern Ireland. It is southwest of Belfast city centre, on the River Lagan, which forms the boundary between County Antrim and County Down. First laid out in the 17th century by English and Welsh settlers, with ...
, although this functions largely as a parish church for Lisburn City Centre. Because of its larger size, St Anne's Cathedral, Belfast, is shared with the Diocese of Down and Dromore
The Diocese of Down and Dromore (also known as the United Dioceses of Down and Dromore) is a diocese of the Church of Ireland in the south east of Northern Ireland. It is in the ecclesiastical province of Armagh. The geographical remit of the d ...
for major church events. With the translation of Alan Harper to Armagh
Armagh ( ; ga, Ard Mhacha, , "Macha's height") is the county town of County Armagh and a city in Northern Ireland, as well as a civil parish. It is the ecclesiastical capital of Ireland – the seat of the Archbishops of Armagh, the Pri ...
, the House of Bishops met in Dublin on 17 April 2007 to elect Archbishop Harper's successor.
Recent history
In the 19th century, Belfast became the epicentre of theIndustrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
in Ireland. Other towns in the diocese, such as Ballymena
Ballymena ( ; from ga, an Baile Meánach , meaning 'the middle townland') is a town in County Antrim, Northern Ireland. It is part of the Borough of Mid and East Antrim.
The town is built on land given to the Adair family by King Charles I i ...
, Larne
Larne (, , the name of a Gaelic Ireland, Gaelic territory) is a town on the east coast of County Antrim, Northern Ireland, with a population of 18,755 at the United Kingdom census, 2011, 2011 Census. It is a major passenger and freight Roll-on/ro ...
and Lisburn
Lisburn (; ) is a city in Northern Ireland. It is southwest of Belfast city centre, on the River Lagan, which forms the boundary between County Antrim and County Down. First laid out in the 17th century by English and Welsh settlers, with ...
, were also among Ireland's foremost industrial centres. The Church of Ireland population of the Diocese increased dramatically as people moved to the area to work in the factories in the major towns, both from rural areas of Ulster
Ulster (; ga, Ulaidh or ''Cúige Uladh'' ; sco, label= Ulster Scots, Ulstèr or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional Irish provinces. It is made up of nine counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United King ...
with large Anglican populations like County Armagh
County Armagh (, named after its county town, Armagh) is one of the six counties of Northern Ireland and one of the traditional thirty-two counties of Ireland. Adjoined to the southern shore of Lough Neagh, the county covers an area of and ha ...
and County Fermanagh
County Fermanagh ( ; ) is one of the thirty-two counties of Ireland, one of the nine counties of Ulster and one of the six counties of Northern Ireland.
The county covers an area of 1,691 km2 (653 sq mi) and has a population of 61,805 a ...
and from England.
The rapid growth in the population of the Greater Belfast area as well as the rapid drop in the Protestant population of the Republic after Partition of Ireland
The partition of Ireland ( ga, críochdheighilt na hÉireann) was the process by which the Government of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland divided Ireland into two self-governing polities: Northern Ireland and Southern Ireland. I ...
in 1922 led to the bizarre situation where the United Dioceses of Down, Connor and Dromore, just one of fourteen Church of Ireland Dioceses had over half the Anglican population of the whole island. In 1944, therefore Connor Diocese was split off from the other two. St. Anne's Cathedral, Belfast built in 1905 to serve as a single cathedral for the Diocese, theoretically running alongside, but in practice replacing the existing cathedrals in Lisburn, Downpatrick
Downpatrick () is a town in County Down, Northern Ireland. It is on the Lecale peninsula, about south of Belfast. In the Middle Ages, it was the capital of the Dál Fiatach, the main ruling dynasty of Ulaid. Its cathedral is said to be the bu ...
and Dromore, saw two bishops of two distinct dioceses have stalls in the cathedral within forty years.
In the 1950s and 1960s rapid slum clearance
Slum clearance, slum eviction or slum removal is an urban renewal strategy used to transform low income settlements with poor reputation into another type of development or housing. This has long been a strategy for redeveloping urban communities; ...
and suburbanisation saw a number of new parishes created, however demographic changes, movement of people to suburban areas in the Diocese of Down and Dromore
The Diocese of Down and Dromore (also known as the United Dioceses of Down and Dromore) is a diocese of the Church of Ireland in the south east of Northern Ireland. It is in the ecclesiastical province of Armagh. The geographical remit of the d ...
and the growth of both secularism
Secularism is the principle of seeking to conduct human affairs based on Secularity, secular, Naturalism (philosophy), naturalistic considerations.
Secularism is most commonly defined as the Separation of church and state, separation of relig ...
and small Evangelical
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide Interdenominationalism, interdenominational movement within Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being "bor ...
churches saw a decline in membership. Between the end of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
and 2001, the number of Anglicans in the Diocese decreased by 30%, the largest drop in Ireland, although it remains the largest Diocese in the Church.
The Troubles
The Troubles ( ga, Na Trioblóidí) were an ethno-nationalist conflict in Northern Ireland that lasted about 30 years from the late 1960s to 1998. Also known internationally as the Northern Ireland conflict, it is sometimes described as an "i ...
presented the Diocese with major challenges – in common with every other community in Northern Ireland, many Anglicans in the Diocese were killed or injured in terrorist related incidents. Ecumenism
Ecumenism (), also spelled oecumenism, is the concept and principle that Christians who belong to different Christian denominations should work together to develop closer relationships among their churches and promote Christian unity. The adjec ...
, which since the 1960s has become a steadily more important part of Anglican life in the Diocese, had to be carried out against the background of civil strife in which religion played a major factor. Demographic change, exacerbated by sectarian tensions, meant that North and West Belfast, within the Diocese, became more and more Catholic, while many Church of Ireland members who had previously lived there moved to suburban areas in County Down
County Down () is one of the six counties of Northern Ireland, one of the nine counties of Ulster and one of the traditional thirty-two counties of Ireland. It covers an area of and has a population of 531,665. It borders County Antrim to the ...
, causing many Belfast parishes to close or severely cut back their activities.
Geographic remit
 It is based on the traditional
It is based on the traditional County Antrim
County Antrim (named after the town of Antrim, ) is one of six counties of Northern Ireland and one of the thirty-two counties of Ireland. Adjoined to the north-east shore of Lough Neagh, the county covers an area of and has a population o ...
, including those parts of Belfast
Belfast ( , ; from ga, Béal Feirste , meaning 'mouth of the sand-bank ford') is the capital and largest city of Northern Ireland, standing on the banks of the River Lagan on the east coast. It is the 12th-largest city in the United Kingdo ...
west of the River Lagan
The River Lagan (; Ulster Scots: ''Lagan Wattèr'') is a major river in Northern Ireland which runs 53.5 miles (86 km) from the Slieve Croob mountain in County Down to Belfast where it enters Belfast Lough, an inlet of the Irish Sea. The ...
, and a small part of County Londonderry
County Londonderry ( Ulster-Scots: ''Coontie Lunnonderrie''), also known as County Derry ( ga, Contae Dhoire), is one of the six counties of Northern Ireland, one of the thirty two counties of Ireland and one of the nine counties of Ulster. B ...
including Portstewart
Portstewart () is a small town in County Londonderry, Northern Ireland. It had a population of 8,003 people in the 2011 Census. It is a seaside resort neighbouring Portrush. Its harbour and scenic coastal paths form an Atlantic promenade leadin ...
and those parts of Coleraine
Coleraine ( ; from ga, Cúil Rathain , 'nook of the ferns'Flanaghan, Deirdre & Laurence; ''Irish Place Names'', page 194. Gill & Macmillan, 2002. ) is a town and civil parish near the mouth of the River Bann in County Londonderry, Northern I ...
east of the River Bann
The River Bann (from ga, An Bhanna, meaning "the goddess"; Ulster-Scots: ''Bann Wattèr'') is one of the longest rivers in Northern Ireland, its length, Upper and Lower Bann combined, being 129 km (80 mi). However, the total lengt ...
.
Based on Census figures, more than 100,000 self-described adherents of the Church of Ireland live in the Diocese, making it home to the largest Anglican population of any Irish diocese and more than one in four members of the Church of Ireland. It is unusual in being the only Church of Ireland diocese where Presbyteriansm, rather than Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
is the religious denomination of a plurality of the population.
Style and ethos
In common with much of the Church of Ireland, most parishes in the Diocese are very moderately Low Church in ethos or part of the central liturgical tradition. However, there are a growing number of distinctlyEvangelical
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide Interdenominationalism, interdenominational movement within Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being "bor ...
Anglican parishes in the Diocese, while a small number of parishes in Belfast could be described as High Church
The term ''high church'' refers to beliefs and practices of Christian ecclesiology, liturgy, and theology that emphasize formality and resistance to modernisation. Although used in connection with various Christian traditions, the term originate ...
, in the case of St. George's in Belfast City Centre even Anglo-Catholic
Anglo-Catholicism comprises beliefs and practices that emphasise the Catholic heritage and identity of the various Anglican churches.
The term was coined in the early 19th century, although movements emphasising the Catholic nature of Anglican ...
.
In consonance with this moderate tradition, the Diocese has retained a cautious line in the Anglican debate on homosexuality. Bishop Harper, although perceived as one of the more liberal bishops in the Church of Ireland, stated that "it is not appropriate to proceed to any form of Blessing of a Registered Civil Partnership
A civil union (also known as a civil partnership) is a legally recognized arrangement similar to marriage, created primarily as a means to provide recognition in law for same-sex couples. Civil unions grant some or all of the rights of marriage ...
.However, the Synod#Anglican usage, diocesan synod, unlike those in other Northern Dioceses with more strongly Evangelical traditions, failed to endorse a motion on Lambeth Conference Resolution I.10. Bishop George Davison, elected in February 2020, is seen as theologically conservative, having served previously in the
Diocese of Kilmore, Elphin and Ardagh
The United Dioceses of Kilmore, Elphin and Ardagh is a diocese of the Church of Ireland located in central Ireland. It is in the ecclesiastical province of Armagh.
It is one of twelve Anglican dioceses in the island of Ireland. The geograph ...
./ref>
Ordinaries
The current Bishop of Connor is George Davison, who was elected on 17 February 2020 and consecrated a bishop on 3 September 2020. The previous bishop, Alan Francis Abernethy, retired on 31 December 2019. He was consecrated on Friday 29 June 2007 by the Archbishop of Armagh. The consecration took place on the feast day of St Peter and St Paul, coinciding with the Bishop's ordination as priest twenty five years earlier. *Charles King Irwin
Charles King Irwin (also Irvine; 30 March 1874 – 15 January 1960) was an eminent Irish clergyman in the middle third of the 20th century.
Born on 30 March 1874 into an eminent ecclesiastical family, he was ordained in 1898 and began his car ...
(1945–1956)
* Robert Cyril Hamilton Glover Elliott (1956–1969)
* Arthur Hamilton Butler (1969–1981)
* William John McCappin (1981–1987)
* Samuel Greenfield Poyntz
Samuel Greenfield Poyntz (4 March 1926 – 18 February 2017) was an Irish bishop and author in the last third of the 20th century.
He was born in Manitoba in Canada to the Revd James Poyntz and Catherine Greenfield. Poyntz was educated at Por ...
(1987–1995)
* James Edward Moore (1995–2001)
* Alan Edwin Thomas Harper (2002–2007)
* Alan Abernethy
Alan Francis Abernethy (born 12 April 1957) is an Irish Anglican bishop, and former Bishop of Connor.
Educated at Grosvenor Grammar School, Grosvenor High School, Belfast, Queen's University Belfast and Trinity College Dublin, and ordained in 1 ...
(2007–2019)
* George Davison (2020–present)
Cathedrals
*
Christ Church Cathedral, Lisburn
Christ Church Cathedral, Lisburn (also known as Lisburn Cathedral), is the cathedral church of the Diocese of Connor in the Church of Ireland. It is situated in Lisburn, Northern Ireland, in the ecclesiastical province of Armagh. Previously S ...
* St Anne's Cathedral, Belfast
Administration
Since early 2007 the Diocese has comprised three archdeaconries: # Belfast # Connor # Dalriada and ten rural deaneries (some of them far from rural): # North Belfast # Mid Belfast # South Belfast # Antrim #Ballymena
Ballymena ( ; from ga, an Baile Meánach , meaning 'the middle townland') is a town in County Antrim, Northern Ireland. It is part of the Borough of Mid and East Antrim.
The town is built on land given to the Adair family by King Charles I i ...
# Carey (centred on Ballycastle)
# Carrickfergus
Carrickfergus ( , meaning " Fergus' rock") is a large town in County Antrim, Northern Ireland. It sits on the north shore of Belfast Lough, from Belfast. The town had a population of 27,998 at the 2011 Census. It is County Antrim's oldest t ...
# Coleraine
Coleraine ( ; from ga, Cúil Rathain , 'nook of the ferns'Flanaghan, Deirdre & Laurence; ''Irish Place Names'', page 194. Gill & Macmillan, 2002. ) is a town and civil parish near the mouth of the River Bann in County Londonderry, Northern I ...
# Derryaghy
# Lisburn
Lisburn (; ) is a city in Northern Ireland. It is southwest of Belfast city centre, on the River Lagan, which forms the boundary between County Antrim and County Down. First laid out in the 17th century by English and Welsh settlers, with ...
Belfast Archdeaconry has been created from Connor Archdeaconry, and a more general re-organisation of the rural deaneries is expected.
The following are the current Archdeacons:
* Belfast: The Venerable George Davison
* Connor: The Venerable Stephen McBride
* Dalriada: The Venerable Paul Dundas
See also
*Dean of Connor
The Dean of Connor is based at Christ Church Cathedral, Lisburn in the Diocese of Connor (Church of Ireland) within the Church of Ireland. The chapter is however known as the Chapter of St Saviours, Connor after the previous (prior to 1662) cathed ...
*List of Anglican dioceses in the United Kingdom and Ireland
The following lists the Anglican dioceses in the Church of England, the Church in Wales, the Scottish Episcopal Church and the Church of Ireland. For a list of all dioceses worldwide see List of Anglican dioceses.
Church of England
Church in ...
References
External links
Official website
{{authority control Connor Religion in County Antrim Religion in Belfast Christian organizations established in 1944 Diocese of Connor