Diffuse alopecia areata on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Alopecia areata, also known as spot baldness, is a condition in which hair is lost from some or all areas of the body. Often, it results in a few bald spots on the scalp, each about the size of a coin. Psychological stress and illness are possible factors in bringing on alopecia areata in individuals at risk, but in most cases there is no obvious trigger. People are generally otherwise healthy. In a few cases, all the hair on the scalp is lost ('' alopecia totalis''), or all body hair is lost (''
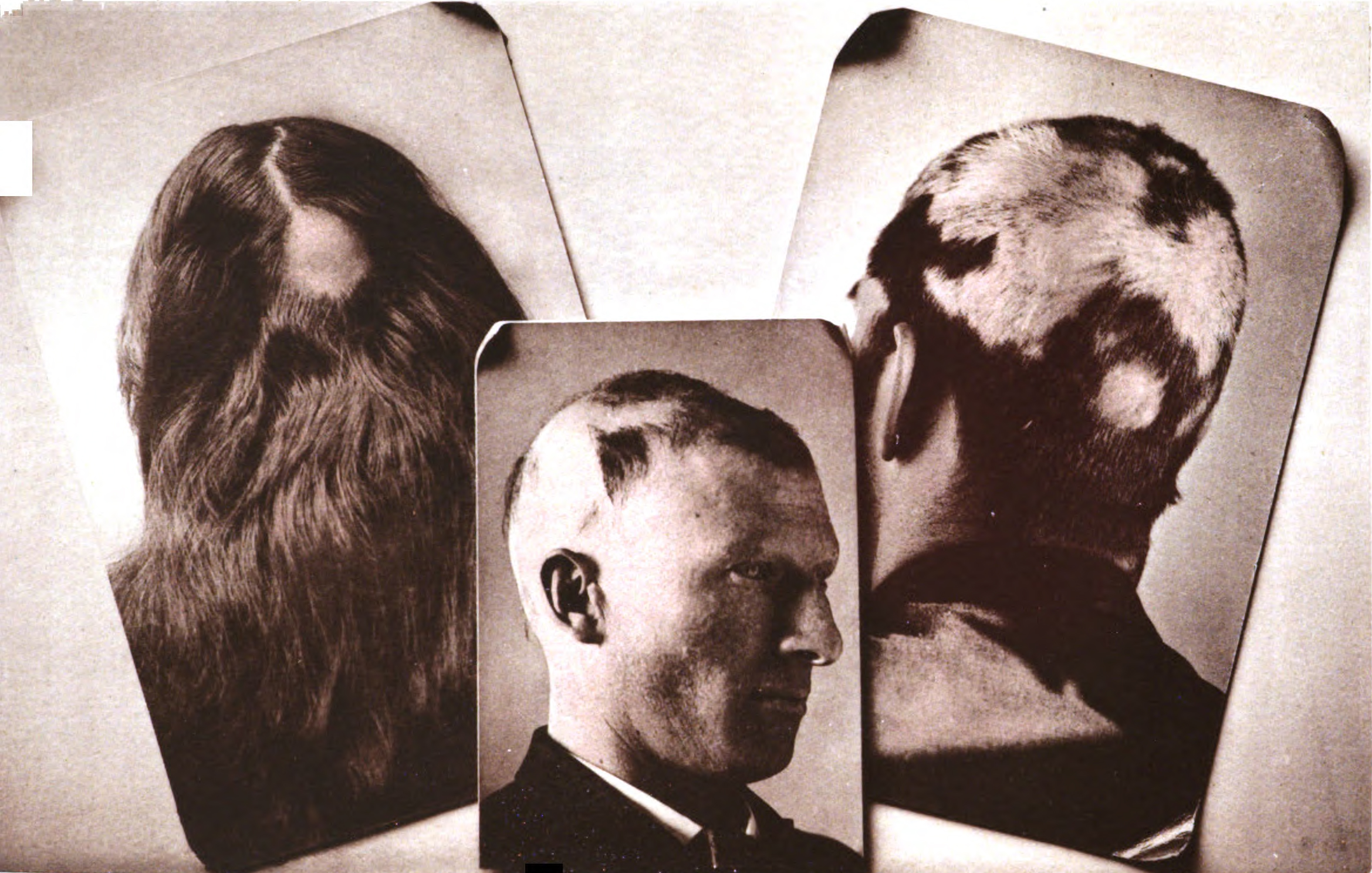 Typical first symptoms of alopecia areata are small bald patches. The underlying skin is unscarred and looks superficially normal. Although these patches can take many shapes, they are usually round or oval. Alopecia areata most often affects the scalp and beard, but may occur on any part of the body with hair. Different areas of the skin may exhibit hair loss and regrowth at the same time. The disease may also go into remission for a time, or may be permanent. It is common in children.
The area of hair loss may tingle or be mildly painful.American Osteopathic College of Dermatology
Typical first symptoms of alopecia areata are small bald patches. The underlying skin is unscarred and looks superficially normal. Although these patches can take many shapes, they are usually round or oval. Alopecia areata most often affects the scalp and beard, but may occur on any part of the body with hair. Different areas of the skin may exhibit hair loss and regrowth at the same time. The disease may also go into remission for a time, or may be permanent. It is common in children.
The area of hair loss may tingle or be mildly painful.American Osteopathic College of Dermatology
Alopecia Areata.
Dermatologic Disease Database. Aocd.org. Retrieved on 3 December 2007. The hair tends to fall out over a short period of time, with the loss commonly occurring more on one side of the scalp than the other. Exclamation point hairs, narrower along the length of the strand closer to the base, producing a characteristic "exclamation point" appearance, are often present.Zoe Diana Draelos (30 August 2007)
. MedicineNet.com. Retrieved on 2 December 2007 These hairs are very short (3–4 mm), and can be seen surrounding the bald patches. When healthy hair is pulled out, at most a few should come out, and ripped hair should not be distributed evenly across the tugged portion of the scalp. In cases of alopecia areata, hair tends to pull out more easily along the edge of the patch where the follicles are already being attacked by the body's immune system than away from the patch where they are still healthy. Nails may have pitting or trachyonychia.
 Alopecia areata is thought to be a systemic autoimmune disorder in which the body attacks its own anagen hair follicles and suppresses or stops hair growth. For example,
Alopecia areata is thought to be a systemic autoimmune disorder in which the body attacks its own anagen hair follicles and suppresses or stops hair growth. For example,
. WebMD. Retrieved on 2 December 2007.
National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases
at
alopecia universalis
__NOTOC__
Alopecia universalis (AU), also known as alopecia areata universalis, is a medical condition involving the loss of all body hair, including eyebrows, eyelashes, chest hair, armpit hair, and pubic hair. It is the most severe form of alop ...
''). Hair loss can be permanent, or temporary. It is distinct from pattern hair loss
Pattern hair loss (also known as androgenetic alopecia (AGA)) is a hair loss condition that primarily affects the top and front of the scalp. In male-pattern hair loss (MPHL), the hair loss typically presents itself as either a receding front ...
, which is common among males.
Alopecia areata is believed to be an autoimmune disease resulting from a breach in the immune privilege
Certain sites of the mammalian body have immune privilege, meaning they are able to tolerate the introduction of antigens without eliciting an inflammatory immune response. Tissue grafts are normally recognised as foreign antigen by the body and ...
of the hair follicles. Risk factors include a family history of the condition. Among identical twins
Twins are two offspring produced by the same pregnancy.MedicineNet > Definition of TwinLast Editorial Review: 19 June 2000 Twins can be either ''monozygotic'' ('identical'), meaning that they develop from one zygote, which splits and forms two em ...
, if one is affected, the other has about a 50% chance of also being affected. The underlying mechanism involves failure by the body to recognize its own cells, with subsequent immune-mediated destruction of the hair follicle.
No cure for the condition is known. Some treatments, particularly triamcinolone
Triamcinolone is a glucocorticoid used to treat certain skin diseases, allergies, and rheumatic disorders among others. It is also used to prevent worsening of asthma and COPD. It can be taken in various ways including by mouth, injection i ...
injections and 5% minoxidil
Minoxidil, sold under the brand name Rogaine among others, is a medication used for the treatment of high blood pressure and pattern hair loss. It is an antihypertensive vasodilator. It is available as a generic medication by prescription in or ...
topical creams, are effective in speeding hair regrowth. Sunscreen, head coverings to protect from cold and sun, and glasses
Glasses, also known as eyeglasses or spectacles, are vision eyewear, with lenses (clear or tinted) mounted in a frame that holds them in front of a person's eyes, typically utilizing a bridge over the nose and hinged arms (known as temples ...
, if the eyelashes
An eyelash (also called lash) (Latin: ''Cilia'') is one of the hairs that grows at the edge of the eyelids. It grows in one layer on the edge of the upper and lower eyelids. Eyelashes protect the eye from debris, dust, and small particles and p ...
are missing, are also recommended. In more than 50% of cases of sudden-onset localized "patchy" disease, hair regrows within a year. In patients with only one or two patches, this 1-year recovery will occur in up to 80%. However, most patients will have more than one episode over the course of a lifetime. In many patients, hair loss and regrowth occurs simultaneously over the course of several years. Among those in whom all body hair is lost, fewer than 10% recover.
About 0.15% of people are affected at any one time, and 2% of people are affected at some point in time. Onset is usually in childhood. Females are affected at higher rates than males.
Signs and symptoms
 Typical first symptoms of alopecia areata are small bald patches. The underlying skin is unscarred and looks superficially normal. Although these patches can take many shapes, they are usually round or oval. Alopecia areata most often affects the scalp and beard, but may occur on any part of the body with hair. Different areas of the skin may exhibit hair loss and regrowth at the same time. The disease may also go into remission for a time, or may be permanent. It is common in children.
The area of hair loss may tingle or be mildly painful.American Osteopathic College of Dermatology
Typical first symptoms of alopecia areata are small bald patches. The underlying skin is unscarred and looks superficially normal. Although these patches can take many shapes, they are usually round or oval. Alopecia areata most often affects the scalp and beard, but may occur on any part of the body with hair. Different areas of the skin may exhibit hair loss and regrowth at the same time. The disease may also go into remission for a time, or may be permanent. It is common in children.
The area of hair loss may tingle or be mildly painful.American Osteopathic College of DermatologyAlopecia Areata.
Dermatologic Disease Database. Aocd.org. Retrieved on 3 December 2007. The hair tends to fall out over a short period of time, with the loss commonly occurring more on one side of the scalp than the other. Exclamation point hairs, narrower along the length of the strand closer to the base, producing a characteristic "exclamation point" appearance, are often present.Zoe Diana Draelos (30 August 2007)
. MedicineNet.com. Retrieved on 2 December 2007 These hairs are very short (3–4 mm), and can be seen surrounding the bald patches. When healthy hair is pulled out, at most a few should come out, and ripped hair should not be distributed evenly across the tugged portion of the scalp. In cases of alopecia areata, hair tends to pull out more easily along the edge of the patch where the follicles are already being attacked by the body's immune system than away from the patch where they are still healthy. Nails may have pitting or trachyonychia.
Causes
T cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
lymphocytes cluster around affected follicles, causing inflammation and subsequent hair loss. Hair follicles in a normal state are thought to be kept secure from the immune system, a phenomenon called immune privilege. A breach in this immune privilege state is considered as the cause of alopecia areata. A few cases of babies being born with congenital alopecia areata have been reported.
Alopecia areata is not contagious. It occurs more frequently in people who have affected family members, suggesting heredity may be a factor. Strong evidence of genetic association with increased risk for alopecia areata was found by studying families with two or more affected members. This study identified at least four regions in the genome that are likely to contain these genes. In addition, alopecia areata shares genetic risk factors with other autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are invol ...
, type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that originates when cells that make insulin (beta cells) are destroyed by the immune system. Insulin is a hormone required for the cells to use blood sugar ...
, and celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barle ...
. It may be the only manifestation of celiac disease.
Endogenous retinoids metabolic defect is a key part of the pathogenesis of the alopecia areata.
In 2010, a genome-wide association study was completed that identified 129 single nucleotide polymorphisms that were associated with alopecia areata. The genes that were identified include those involved in
controlling the activation and proliferation of regulatory T cells, cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4, interleukin-2, interleukin-2 receptor A, and Eos (also known as Ikaros family zinc finger 4), as well as the human leukocyte antigen. The study also identified two genes, ''PRDX5'' and ''STX17'', that are expressed in the hair follicle.
Diagnosis
Alopecia areata is usually diagnosed based on clinical features.Trichoscopy
Trichoscopy is a method of hair and scalp evaluation and is used for diagnosing hair and scalp diseases. The method is based on dermoscopy. In trichoscopy hair and scalp structures may be visualized at many-fold magnification. Currently magnificat ...
may aid in establishing the diagnosis. In alopecia areata, trichoscopy shows regularly distributed "yellow dots" (hyperkeratotic
Hyperkeratosis is thickening of the stratum corneum (the outermost layer of the epidermis, or skin), often associated with the presence of an abnormal quantity of keratin,Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelso; Abbas, Abul (2004) ''Robbins & Cotran Pathologi ...
plugs), small exclamation-mark hairs, and "black dots" (destroyed hairs in the hair follicle opening).
Oftentimes, however, discrete areas of hair loss surrounded by exclamation mark hairs is sufficient for clinical diagnosis of alopecia areata. Sometimes, reddening of the skin, erythema
Erythema (from the Greek , meaning red) is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not asso ...
, may also be present in the balding area.
A biopsy is rarely needed to make the diagnosis or aid in the management of alopecia areata. Histologic
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures vis ...
findings may include peribulbar lymphocytic
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of gnathostomata, most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated immunity, cell-mediated, cytotoxicity, cytotoxic innate imm ...
infiltration resembling a "swarm of bees", a shift in the anagen-to-telogen ratio towards telogen, and dilated follicular infundibulae. Other helpful findings can include pigment incontinence in the hair bulb
Hair is a protein filament that grows from hair follicle, follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals.
The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick ter ...
and follicular stelae. Occasionally, in inactive alopecia areata, no inflammatory infiltrates are found.
Classification
Commonly, alopecia areata involves hair loss in one or more round spots on the scalp.. * Hair may also be lost more diffusely over the whole scalp, in which case the condition is called diffuse alopecia areata. * Alopecia areata monolocularis describes baldness in only one spot. It may occur anywhere on the head. * Alopecia areata multilocularis refers to multiple areas of hair loss. * Ophiasis refers to hair loss in the shape of a wave at the circumference of the head. * The disease may be limited only to the beard, in which case it is called alopecia areata barbae. * If the person loses all the hair on the scalp, the disease is then called alopecia areata totalis. * If all body hair, including pubic hair, is lost, the diagnosis then becomes alopecia areata universalis. Alopecia areata totalis and universalis are rare.Skin Conditions: Alopecia Areata. WebMD. Retrieved on 2 December 2007.
Treatment
The objective assessment of treatment efficacy is very difficult and spontaneous remission is unpredictable, but if the affected area is patchy, the hair may regrow spontaneously in many cases. None of the existing therapeutic options are curative or preventive. A 2020 systematic review showed greater than 50% hair regrowth in 80.9% of patients treated with 5 mg/mLtriamcinolone
Triamcinolone is a glucocorticoid used to treat certain skin diseases, allergies, and rheumatic disorders among others. It is also used to prevent worsening of asthma and COPD. It can be taken in various ways including by mouth, injection i ...
injections. A Cochrane-style systematic review published in 2019 showed 5% topical minoxidil
Minoxidil, sold under the brand name Rogaine among others, is a medication used for the treatment of high blood pressure and pattern hair loss. It is an antihypertensive vasodilator. It is available as a generic medication by prescription in or ...
was more than 8x more associated with >50% hair regrowth at 6 months compared to placebo. In cases of severe hair loss, limited success has been achieved by using the corticosteroid medications clobetasol or fluocinonide
Fluocinonide (sold under various brand names) is a potent glucocorticoid used topically as an anti-inflammatory agent for the treatment of skin disorders such as eczema and seborrhoeic dermatitis. It relieves itching, redness, dryness, crusti ...
as an injection or cream. Application of corticosteroid creams to the affected skin is less effective and takes longer to produce results. Steroid injections are commonly used in sites where the areas of hair loss on the head are small or especially where eyebrow hair has been lost. Whether they are effective is uncertain. Some other medications that have been used are minoxidil
Minoxidil, sold under the brand name Rogaine among others, is a medication used for the treatment of high blood pressure and pattern hair loss. It is an antihypertensive vasodilator. It is available as a generic medication by prescription in or ...
, Elocon (mometasone) ointment (steroid cream), irritants (anthralin
Dithranol (INN) or anthralin (USAN and former BAN) is a hydroxy anthrone, anthracene derivative, medicine applied to the skin of people with psoriasis.
It is available as creams, ointment or pastes in 0.1 to 2% strengths (Drithocreme, Dithrocream, ...
or topical coal tar
Coal tar is a thick dark liquid which is a by-product of the production of coke and coal gas from coal. It is a type of creosote. It has both medical and industrial uses. Medicinally it is a topical medication applied to skin to treat psorias ...
), and topical immunotherapy ciclosporin
Ciclosporin, also spelled cyclosporine and cyclosporin, is a calcineurin inhibitor, used as an immunosuppressant medication. It is a natural product. It is taken orally or intravenously for rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, Crohn's disease ...
, sometimes in different combinations. Topical corticosteroids frequently fail to enter the skin deeply enough to affect the hair bulbs, which are the treatment target, and small lesions typically also regrow spontaneously. Oral corticosteroids may decrease the hair loss, but only for the period during which they are taken, and these medications can cause serious side effects
In medicine, a side effect is an effect, whether therapeutic or adverse, that is secondary to the one intended; although the term is predominantly employed to describe adverse effects, it can also apply to beneficial, but unintended, consequence ...
. No one treatment is effective in all cases, and some individuals may show no response to any treatment.
For more severe cases, recent studies have shown promising results with the individual use of the immunosuppressant Methotrexate or adjunct use with corticosteroids. However, as relapse of the condition may occur long-term treatment is recommended.
When alopecia areata is associated with celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barle ...
, treatment with a gluten-free diet
A gluten-free diet (GFD) is a nutritional plan that strictly excludes gluten, which is a mixture of proteins found in wheat (and all of its species and hybrids, such as spelt, kamut, and triticale), as well as barley, rye, and oats. The incl ...
allows for complete and permanent regrowth of scalp and other body hair in many people, but in others, remissions and recurrences are seen. This improvement is probably due to the normalization of the immune response
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders. These invaders include a wide variety of different microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi which could ...
as a result of gluten
Gluten is a structural protein naturally found in certain cereal grains. Although "gluten" often only refers to wheat proteins, in medical literature it refers to the combination of prolamin and glutelin proteins naturally occurring in all grai ...
withdrawal from the diet.
In June 2022, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ...
(FDA) authorized baricitinib
Baricitinib, sold under the brand name Olumiant among others, is a medication used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, alopecia areata, and COVID-19. It acts as an inhibitor of janus kinase (JAK), blocking the subtypes JAK1 and JAK2. ...
for the treatment of severe alopecia areata.
Fecal matter transplants (FMT) have been shown to reverse AA and support hair growth, with long lasting results, even going as far as growing additional hair on arms and face while grey hairs even regained colour. This supports the idea of a connection between gut microbiota having a part in hair loss.
Prognosis
In most cases that begin with a small number of patches of hair loss, hair grows back after a few months to a year. In cases with a greater number of patches, hair can either grow back or progress to alopecia areata totalis or, in rare cases, alopecia areata universalis. No loss of body function occurs, and the effects of alopecia areata are psychological (loss of self-image due to hair loss), although these can be severe. Loss of hair also means the scalp burns more easily in the sun. Patients may also have aberrant nail formation becausekeratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ...
forms both hair and nails.
Hair may grow back and then fall out again later. This may not indicate a recurrence of the condition, but rather a natural cycle of growth-and-shedding from a relatively synchronised start; such a pattern will fade over time. Episodes of alopecia areata before puberty predispose to chronic recurrence of the condition.
Alopecia can be the cause of psychological stress
Stress may refer to:
Science and medicine
* Stress (biology), an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition
* Stress (linguistics), relative emphasis or prominence given to a syllable in a word, or to a word in a phrase ...
. Because hair loss can lead to significant changes in appearance, individuals with it may experience social phobia
Social anxiety disorder (SAD), also known as social phobia, is an anxiety disorder characterized by sentiments of fear and anxiety in social situations, causing considerable distress and impaired ability to function in at least some aspects o ...
, anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
, and depression.
Epidemiology
The condition affects 0.1%–0.2% of the population, with a lifetime risk of 1%-2%. and is more common in females. Alopecia areata occurs in people who are otherwise healthy and have no other skin disorders. Initial presentation most commonly occurs in the early childhood, lateteenage
Adolescence () is a transitional stage of physical and psychological development that generally occurs during the period from puberty to adulthood (typically corresponding to the age of majority). Adolescence is usually associated with the te ...
years, or young adulthood, but can happen at any ages. Patients also tend to have a slightly higher incidence of conditions related to the immune system, such as asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, co ...
, allergies, atopic
Atopy is the tendency to produce an exaggerated immunoglobulin E (IgE) immune response to otherwise harmless substances in the environment. Allergic diseases are clinical manifestations of such inappropriate, atopic responses.
Atopy may have a ...
dermatitis, and hypothyroidism.
Research
Many medications are being studied. Some of these medications are approved for other diseases, others are not available outside of studies. In 2014, preliminary findings showing that oralruxolitinib
Ruxolitinib, sold under the brand names Jakafi and Jakavi, is a medication used for the treatment of intermediate or high-risk myelofibrosis, a type of myeloproliferative disorder that affects the bone marrow; polycythemia vera (PCV), when ther ...
, a drug approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
) for bone marrow disorder myelofibrosis
Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) is a rare bone marrow blood cancer. It is classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a type of myeloproliferative neoplasm, a group of cancers in which there is growth of abnormal cells in the bone marrow. ...
, restored hair growth in three individuals with long-standing and severe disease. The medicine costs almost US$10,000 a month.
History
Alopecia areata and alopecia barbae have been identified by some as the biblical condition that is part of the greater family of skin disorders; the said disorders are purported to being discussed in theBook of Leviticus
The book of Leviticus (, from grc, Λευιτικόν, ; he, וַיִּקְרָא, , "And He called") is the third book of the Torah (the Pentateuch) and of the Old Testament, also known as the Third Book of Moses. Scholars generally agree ...
, chapter 13.
Notable people
Actor Anthony Carrigan, athlete ofAmerican Ninja Warrior
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, p ...
fame Kevin Bull, Australian politician Peter Dutton
Peter Craig Dutton (born 18 November 1970) is an Australian politician who has been leader of the opposition and leader of the Liberal Party since May 2022. He has represented the Queensland seat of Dickson in the House of Representatives sinc ...
, Australian actor Alan Fletcher, Congresswoman Ayanna Pressley
Ayanna Soyini Pressley (born February 3, 1974) is an American politician who has served as the U.S. representative for Massachusetts's 7th congressional district since 2019. This district includes the northern three quarters of Boston, most of C ...
, K-pop singer Peniel Shin
Peniel Shin (; born March 10, 1993), better known mononymously as Peniel (), is an American rapper, singer, songwriter and host based in South Korea. He debuted as a member of the South Korean boy group BtoB in 2012.
Biography
Shin was born i ...
of BtoB
}
BtoB ( ; ; acronym for Born to Beat; often stylized as BTOB) is a South Korean boy band formed in 2012 by Cube Entertainment. The group consists of Seo Eun-kwang, Lee Min-hyuk, Lee Chang-sub, Im Hyun-sik, Peniel Shin and Yook Sung-jae. Or ...
, and actresses Jada Pinkett Smith
Jada Koren Pinkett Smith (; née Pinkett; born September 18, 1971) is an American actress and talk show host. She is co-host of the Facebook Watch talk show '' Red Table Talk'', for which she has received a Daytime Emmy Award. ''Time'' name ...
, and May Calamawy
May El Calamawy ( ar, مي القلماوي, , born October 28, 1986) is an Egyptian-Palestinian actress who has worked and resided in the United States since 2015. She is known for her roles in the American television series '' Ramy'' as Dena H ...
all have some form of alopecia areata.
See also
*Noncicatricial alopecia
Non scarring hair loss, also known as noncicatricial alopecia is the loss of hair without any scarring being present.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders ...
* Trichotillomania
Trichotillomania (TTM), also known as hair-pulling disorder or compulsive hair pulling, is a mental disorder characterized by a long-term urge that results in the pulling out of one's own hair. A brief positive feeling may occur as hair is remov ...
References
External links
National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases
at
NIH
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late ...
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Alopecia Areata
Autoimmune diseases
Conditions of the skin appendages
Human hair
Hair diseases
Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate
de:Haarausfall#Alopecia areata