Destroyer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in 1885 by
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in 1885 by
 The emergence and development of the destroyer was related to the invention of the self-propelled torpedo in the 1860s. A navy now had the potential to destroy a superior enemy battle fleet using steam launches to fire torpedoes. Cheap, fast boats armed with torpedoes called torpedo boats were built and became a threat to large capital ships near enemy coasts. The first seagoing vessel designed to launch the self-propelled Whitehead torpedo was the 33-ton in 1876. She was armed with two drop collars to launch these weapons, these were replaced in 1879 by a single torpedo tube in the bow. By the 1880s, the type had evolved into small ships of 50–100 tons, fast enough to evade enemy picket boats.
At first, the threat of a torpedo boat attack to a battle fleet was considered to exist only when at anchor; but as faster and longer-range torpedo boats and torpedoes were developed, the threat extended to cruising at sea. In response to this new threat, more heavily gunned picket boats called "catchers" were built which were used to escort the battle fleet at sea. They needed significant seaworthiness and endurance to operate with the battle fleet, and as they inherently became larger, they became officially designated "torpedo boat destroyers", and by the First World War were largely known as "destroyers" in English. The anti-torpedo boat origin of this type of ship is retained in its name in other languages, including
The emergence and development of the destroyer was related to the invention of the self-propelled torpedo in the 1860s. A navy now had the potential to destroy a superior enemy battle fleet using steam launches to fire torpedoes. Cheap, fast boats armed with torpedoes called torpedo boats were built and became a threat to large capital ships near enemy coasts. The first seagoing vessel designed to launch the self-propelled Whitehead torpedo was the 33-ton in 1876. She was armed with two drop collars to launch these weapons, these were replaced in 1879 by a single torpedo tube in the bow. By the 1880s, the type had evolved into small ships of 50–100 tons, fast enough to evade enemy picket boats.
At first, the threat of a torpedo boat attack to a battle fleet was considered to exist only when at anchor; but as faster and longer-range torpedo boats and torpedoes were developed, the threat extended to cruising at sea. In response to this new threat, more heavily gunned picket boats called "catchers" were built which were used to escort the battle fleet at sea. They needed significant seaworthiness and endurance to operate with the battle fleet, and as they inherently became larger, they became officially designated "torpedo boat destroyers", and by the First World War were largely known as "destroyers" in English. The anti-torpedo boat origin of this type of ship is retained in its name in other languages, including
 An important development came with the construction of HMS ''Swift'' in 1884, later redesignated TB 81. This was a large (137 ton) torpedo boat with four 47 mm quick-firing guns and three torpedo tubes. At , while still not fast enough to engage enemy torpedo boats reliably, the ship at least had the armament to deal with them.
Another forerunner of the torpedo boat destroyer was the Japanese torpedo boat (''Falcon''), built in 1885. Designed to Japanese specifications and ordered from the Isle of Dogs, London Yarrow shipyard in 1885, she was transported in parts to Japan, where she was assembled and launched in 1887. The long vessel was armed with four 1-pounder (37 mm) quick-firing guns and six torpedo tubes, reached , and at 203 tons, was the largest torpedo boat built to date. In her trials in 1889, ''Kotaka'' demonstrated that she could exceed the role of coastal defense, and was capable of accompanying larger warships on the high seas. The Yarrow shipyards, builder of the parts for ''Kotaka'', "considered Japan to have effectively invented the destroyer".
The German aviso , launched in 1886, was designed as a "''torpedojäger''" (torpedo hunter), intended to screen the fleet against attacks by torpedo boats. The ship was significantly larger than torpedo boats of the period, displacing some , with an armament of guns and
An important development came with the construction of HMS ''Swift'' in 1884, later redesignated TB 81. This was a large (137 ton) torpedo boat with four 47 mm quick-firing guns and three torpedo tubes. At , while still not fast enough to engage enemy torpedo boats reliably, the ship at least had the armament to deal with them.
Another forerunner of the torpedo boat destroyer was the Japanese torpedo boat (''Falcon''), built in 1885. Designed to Japanese specifications and ordered from the Isle of Dogs, London Yarrow shipyard in 1885, she was transported in parts to Japan, where she was assembled and launched in 1887. The long vessel was armed with four 1-pounder (37 mm) quick-firing guns and six torpedo tubes, reached , and at 203 tons, was the largest torpedo boat built to date. In her trials in 1889, ''Kotaka'' demonstrated that she could exceed the role of coastal defense, and was capable of accompanying larger warships on the high seas. The Yarrow shipyards, builder of the parts for ''Kotaka'', "considered Japan to have effectively invented the destroyer".
The German aviso , launched in 1886, was designed as a "''torpedojäger''" (torpedo hunter), intended to screen the fleet against attacks by torpedo boats. The ship was significantly larger than torpedo boats of the period, displacing some , with an armament of guns and
 The first vessel designed for the explicit purpose of hunting and destroying torpedo boats was the
The first vessel designed for the explicit purpose of hunting and destroying torpedo boats was the  She displaced 348 tons, and was the first warship equipped with twin triple-expansion engines generating , for a maximum speed of , which made her one of the faster ships in the world in 1888. She was armed with one Spanish-designed Hontoria
She displaced 348 tons, and was the first warship equipped with twin triple-expansion engines generating , for a maximum speed of , which made her one of the faster ships in the world in 1888. She was armed with one Spanish-designed Hontoria
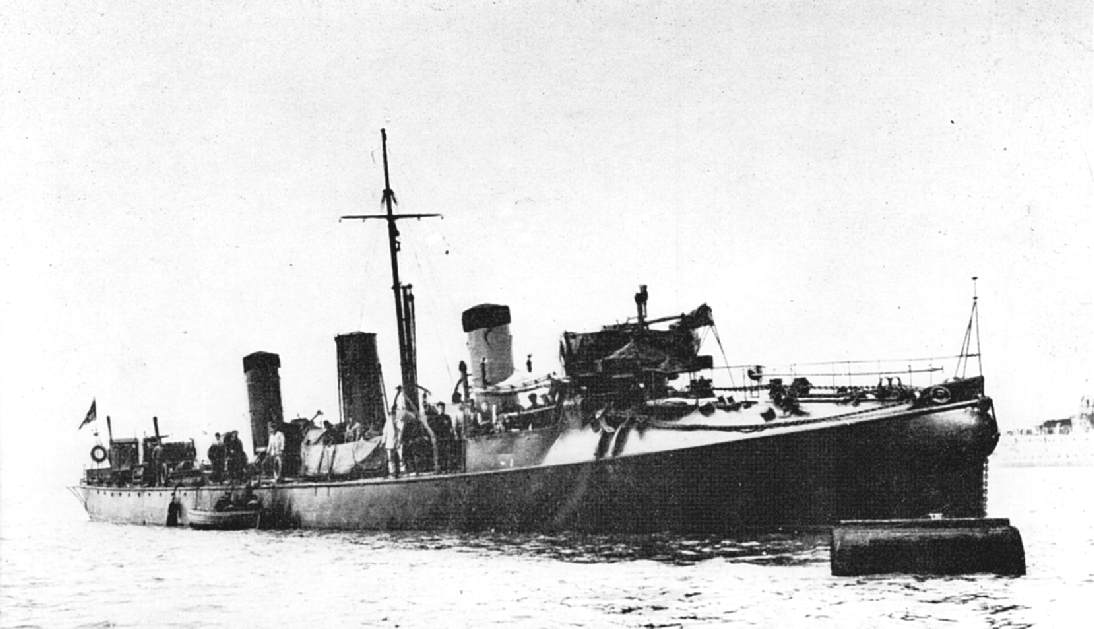 The first classes of ships to bear the formal designation "torpedo boat destroyer" (TBD) were the of two ships and of two ships of the
The first classes of ships to bear the formal designation "torpedo boat destroyer" (TBD) were the of two ships and of two ships of the
 Torpedo boat destroyer designs continued to evolve around the turn of the 20th century in several key ways. The first was the introduction of the steam turbine. The spectacular unauthorized demonstration of the turbine-powered at the 1897 Spithead Navy Review, which, significantly, was of torpedo boat size, prompted the Royal Navy to order a prototype turbine powered destroyer, of 1899. This was the first turbine warship of any kind and achieved a remarkable on sea trials. By 1910 the turbine had been widely adopted by all navies for their faster ships.
The second development was the replacement of the torpedo-boat-style turtleback foredeck by a raised
Torpedo boat destroyer designs continued to evolve around the turn of the 20th century in several key ways. The first was the introduction of the steam turbine. The spectacular unauthorized demonstration of the turbine-powered at the 1897 Spithead Navy Review, which, significantly, was of torpedo boat size, prompted the Royal Navy to order a prototype turbine powered destroyer, of 1899. This was the first turbine warship of any kind and achieved a remarkable on sea trials. By 1910 the turbine had been widely adopted by all navies for their faster ships.
The second development was the replacement of the torpedo-boat-style turtleback foredeck by a raised
 The torpedo boat destroyer's first major use in combat came during the Japanese surprise attack on the Russian fleet anchored in Port Arthur at the opening of the
The torpedo boat destroyer's first major use in combat came during the Japanese surprise attack on the Russian fleet anchored in Port Arthur at the opening of the  The threat evolved by
The threat evolved by  The desire to attack submarines underwater led to rapid destroyer evolution during the war. They were quickly equipped with strengthened bows for ramming, and depth charges and hydrophones for identifying submarine targets. The first submarine casualty credited to a destroyer was the German , rammed by on 29 October 1914. While ''U-19'' was only damaged, the next month successfully sank . The first depth-charge sinking was on 4 December 1916, when was sunk by HMS ''Llewellyn''.
The submarine threat meant that many destroyers spent their time on anti-submarine patrol. Once Germany adopted unrestricted submarine warfare in January 1917, destroyers were called on to escort merchant convoys. US Navy destroyers were among the first American units to be dispatched upon the American entry to the war, and a squadron of Japanese destroyers even joined Allied patrols in the Mediterranean. Patrol duty was far from safe; of the 67 British destroyers lost in the war, collisions accounted for 18, while 12 were wrecked.
At the end of the war, the state-of-the-art was represented by the British W class.
The desire to attack submarines underwater led to rapid destroyer evolution during the war. They were quickly equipped with strengthened bows for ramming, and depth charges and hydrophones for identifying submarine targets. The first submarine casualty credited to a destroyer was the German , rammed by on 29 October 1914. While ''U-19'' was only damaged, the next month successfully sank . The first depth-charge sinking was on 4 December 1916, when was sunk by HMS ''Llewellyn''.
The submarine threat meant that many destroyers spent their time on anti-submarine patrol. Once Germany adopted unrestricted submarine warfare in January 1917, destroyers were called on to escort merchant convoys. US Navy destroyers were among the first American units to be dispatched upon the American entry to the war, and a squadron of Japanese destroyers even joined Allied patrols in the Mediterranean. Patrol duty was far from safe; of the 67 British destroyers lost in the war, collisions accounted for 18, while 12 were wrecked.
At the end of the war, the state-of-the-art was represented by the British W class.
 The trend during World War I had been towards larger destroyers with heavier armaments. A number of opportunities to fire at capital ships had been missed during the War, because destroyers had expended all their torpedoes in an initial salvo. The British V and W classes of the late war had sought to address this by mounting six torpedo tubes in two triple mounts, instead of the four or two on earlier models. The 'V' and 'W's set the standard of destroyer building well into the 1920s.
The two Romanian destroyers and , on the other hand, had the greatest firepower of all destroyers in the world throughout the first half of the 1920s. This was largely due to the fact that, between their commissioning in 1920 and 1926, they retained the armament that they had while serving in the Italian Navy as scout cruisers (''
The trend during World War I had been towards larger destroyers with heavier armaments. A number of opportunities to fire at capital ships had been missed during the War, because destroyers had expended all their torpedoes in an initial salvo. The British V and W classes of the late war had sought to address this by mounting six torpedo tubes in two triple mounts, instead of the four or two on earlier models. The 'V' and 'W's set the standard of destroyer building well into the 1920s.
The two Romanian destroyers and , on the other hand, had the greatest firepower of all destroyers in the world throughout the first half of the 1920s. This was largely due to the fact that, between their commissioning in 1920 and 1926, they retained the armament that they had while serving in the Italian Navy as scout cruisers ('' The next major innovation came with the Japanese or 'special type', designed in 1923 and delivered in 1928. The design was initially noted for its powerful armament of six five-inch (127 mm) guns and three triple torpedo mounts. The second batch of the class gave the guns high-angle turrets for anti-aircraft warfare, and the oxygen-fueled 'Long Lance' Type 93 torpedo. The later of 1931 further improved the torpedo armament by storing its reload torpedoes close at hand in the superstructure, allowing reloading within 15 minutes.
Most other nations replied with similar larger ships. The US adopted twin five-inch (127 mm) guns, and the subsequent and es (the latter of 1934) increased the number of torpedo tubes to 12 and 16 respectively.
The next major innovation came with the Japanese or 'special type', designed in 1923 and delivered in 1928. The design was initially noted for its powerful armament of six five-inch (127 mm) guns and three triple torpedo mounts. The second batch of the class gave the guns high-angle turrets for anti-aircraft warfare, and the oxygen-fueled 'Long Lance' Type 93 torpedo. The later of 1931 further improved the torpedo armament by storing its reload torpedoes close at hand in the superstructure, allowing reloading within 15 minutes.
Most other nations replied with similar larger ships. The US adopted twin five-inch (127 mm) guns, and the subsequent and es (the latter of 1934) increased the number of torpedo tubes to 12 and 16 respectively.
 In the Mediterranean, the Italian Navy's building of very fast light cruisers of the prompted the French to produce exceptional destroyer designs. The French had long been keen on large destroyers, with their of 1922 displacing over 2,000 tons and carrying 130 mm guns; a further three similar classes were produced around 1930. The of 1935 carried five guns and nine torpedo tubes, but could achieve speeds of , which remains the record speed for a steamship and for any destroyer. The Italians' own destroyers were almost as swift, most Italian designs of the 1930s being rated at over , while carrying torpedoes and either four or six 120 mm guns.
Germany started to build destroyers again during the 1930s as part of Hitler's rearmament program. The Germans were also fond of large destroyers, but while the initial Type 1934 displaced over 3,000 tons, their armament was equal to smaller vessels. This changed from the Type 1936 onwards, which mounted heavy guns. German destroyers also used innovative high-pressure steam machinery: while this should have helped their efficiency, it more often resulted in mechanical problems.
Once German and Japanese rearmament became clear, the British and American navies consciously focused on building destroyers that were smaller but more numerous than those used by other nations. The British built a series of destroyers (the to ) which were about 1,400 tons standard displacement, had four guns and eight torpedo tubes; the American of 1938 similar in size, but carried five guns and ten torpedo tubes. Realizing the need for heavier gun armament, the British built the of 1936 (sometimes called ''Afridi'' after one of two lead ships). These ships displaced 1,850 tons and were armed with eight guns in four twin turrets and four torpedo tubes. These were followed by the J-class and L-class destroyers, with six guns in twin turrets and eight torpedo tubes.
Anti-submarine sensors included
In the Mediterranean, the Italian Navy's building of very fast light cruisers of the prompted the French to produce exceptional destroyer designs. The French had long been keen on large destroyers, with their of 1922 displacing over 2,000 tons and carrying 130 mm guns; a further three similar classes were produced around 1930. The of 1935 carried five guns and nine torpedo tubes, but could achieve speeds of , which remains the record speed for a steamship and for any destroyer. The Italians' own destroyers were almost as swift, most Italian designs of the 1930s being rated at over , while carrying torpedoes and either four or six 120 mm guns.
Germany started to build destroyers again during the 1930s as part of Hitler's rearmament program. The Germans were also fond of large destroyers, but while the initial Type 1934 displaced over 3,000 tons, their armament was equal to smaller vessels. This changed from the Type 1936 onwards, which mounted heavy guns. German destroyers also used innovative high-pressure steam machinery: while this should have helped their efficiency, it more often resulted in mechanical problems.
Once German and Japanese rearmament became clear, the British and American navies consciously focused on building destroyers that were smaller but more numerous than those used by other nations. The British built a series of destroyers (the to ) which were about 1,400 tons standard displacement, had four guns and eight torpedo tubes; the American of 1938 similar in size, but carried five guns and ten torpedo tubes. Realizing the need for heavier gun armament, the British built the of 1936 (sometimes called ''Afridi'' after one of two lead ships). These ships displaced 1,850 tons and were armed with eight guns in four twin turrets and four torpedo tubes. These were followed by the J-class and L-class destroyers, with six guns in twin turrets and eight torpedo tubes.
Anti-submarine sensors included
 During the 1920s and 1930s, destroyers were often deployed to areas of diplomatic tension or humanitarian disaster. British and American destroyers were common on the Chinese coast and rivers, even supplying landing parties to protect colonial interests.
By
During the 1920s and 1930s, destroyers were often deployed to areas of diplomatic tension or humanitarian disaster. British and American destroyers were common on the Chinese coast and rivers, even supplying landing parties to protect colonial interests.
By
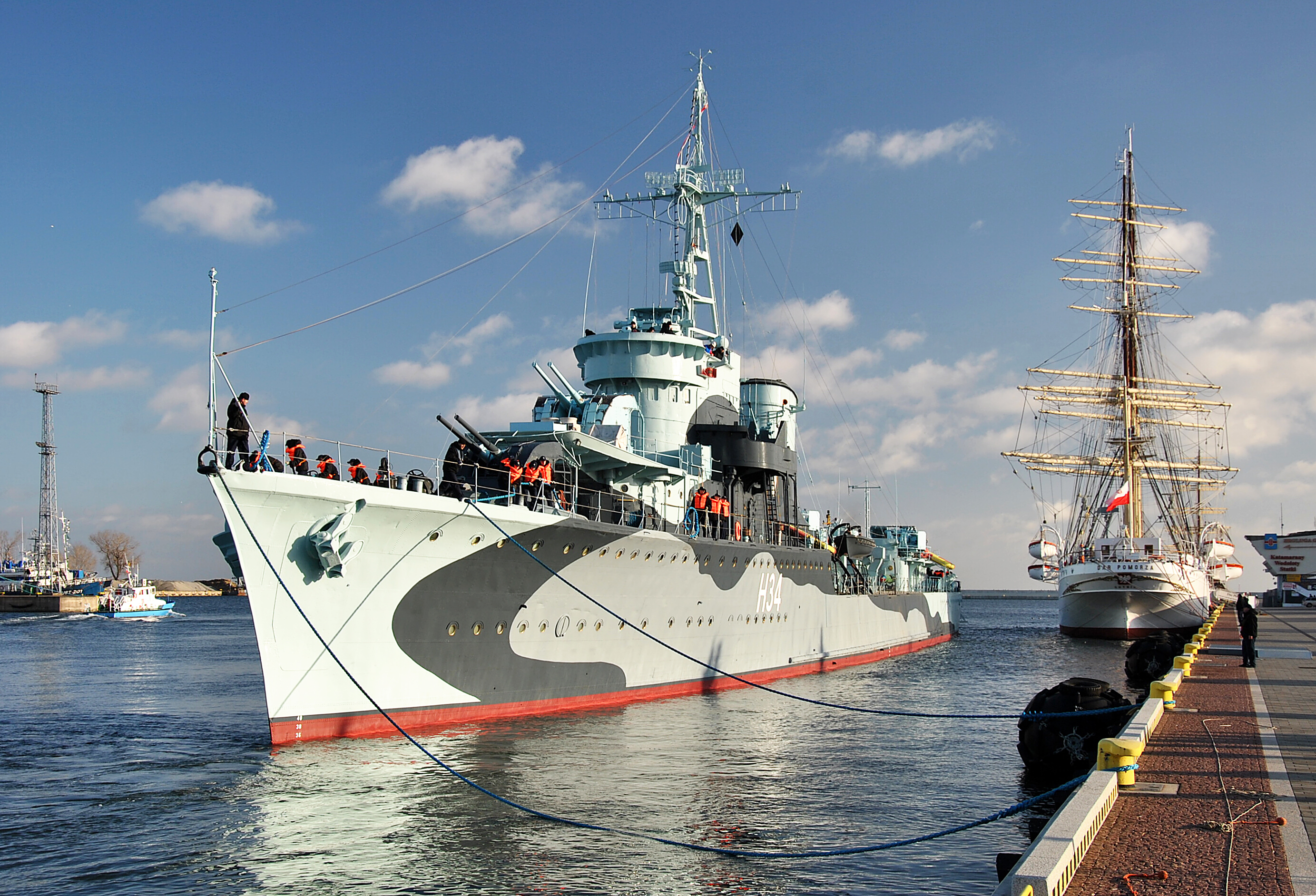 Some conventional destroyers were completed in the late 1940s and 1950s which built on wartime experience. These vessels were significantly larger than wartime ships and had fully automatic main guns, unit machinery, radar, sonar, and antisubmarine weapons such as the Squid mortar. Examples include the British , US , and the Soviet s.
Some World War II–vintage ships were modernized for anti-submarine warfare, and to extend their service lives, to avoid having to build (expensive) brand-new ships. Examples include the US FRAM I programme and the British
Some conventional destroyers were completed in the late 1940s and 1950s which built on wartime experience. These vessels were significantly larger than wartime ships and had fully automatic main guns, unit machinery, radar, sonar, and antisubmarine weapons such as the Squid mortar. Examples include the British , US , and the Soviet s.
Some World War II–vintage ships were modernized for anti-submarine warfare, and to extend their service lives, to avoid having to build (expensive) brand-new ships. Examples include the US FRAM I programme and the British
 * operates four Renhai-class destroyers, two Luyang I-class destroyers, six Luyang II-class destroyers, more than 18 Luyang III-class destroyers and two Luzhou-class destroyers. China also operates two Luhu-class destroyers, one Luhai-class destroyer and four -class destroyers that are of older models. It is notable that the Renhai class (Type 055) is considered to be a cruiser by
* operates four Renhai-class destroyers, two Luyang I-class destroyers, six Luyang II-class destroyers, more than 18 Luyang III-class destroyers and two Luzhou-class destroyers. China also operates two Luhu-class destroyers, one Luhai-class destroyer and four -class destroyers that are of older models. It is notable that the Renhai class (Type 055) is considered to be a cruiser by
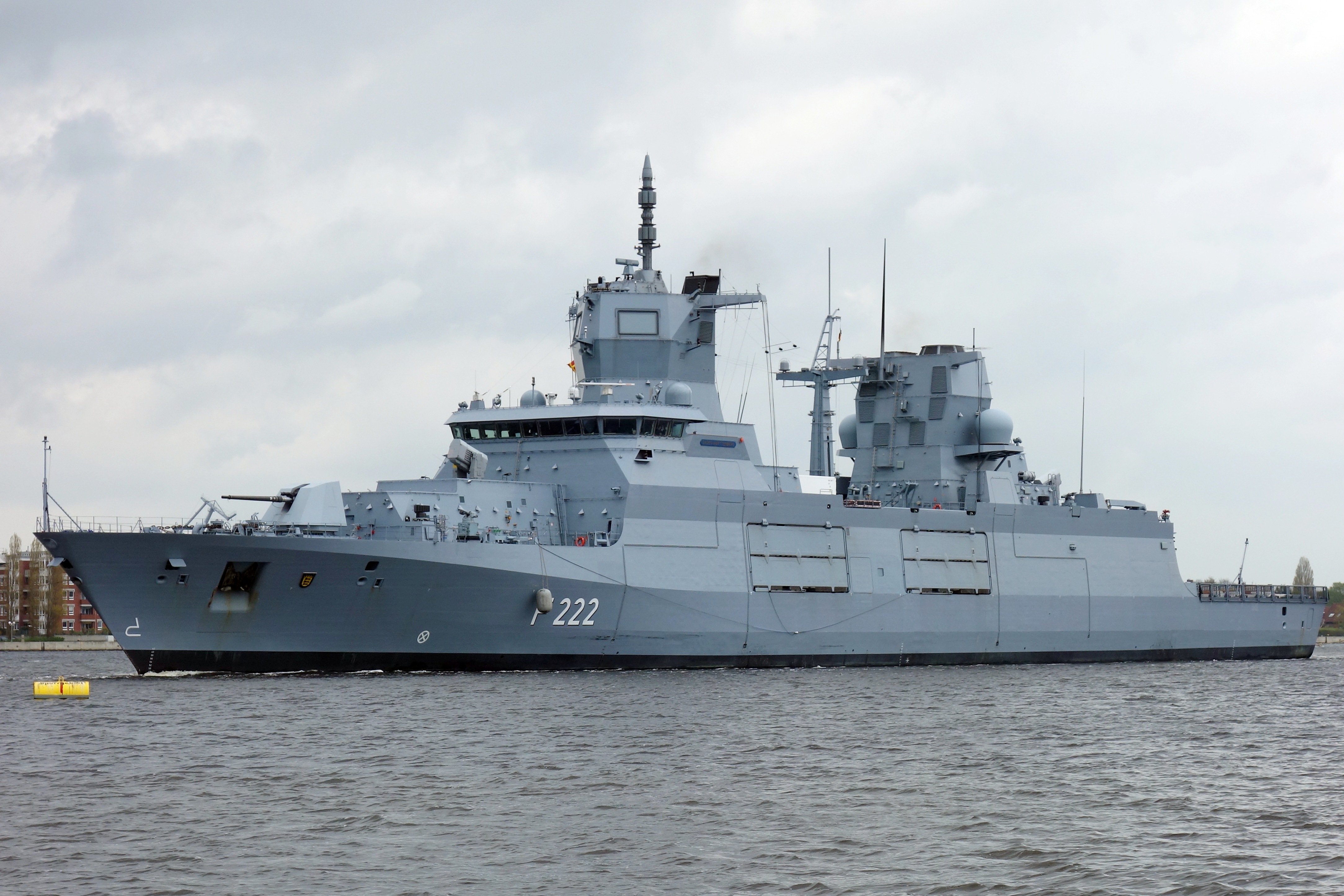 * plans to build 7,000-ton destroyers after the delivery of the new frigates, and TKMS presented to the Navy its most modern 7,200-ton MEKO A-400 air defense destroyer, an updated version of the German F-125-class frigates. The similarities between the projects and the high rate of commonality between requirements were also crucial for the consortium's victory.
* is adding six more Type 052D destroyer and sixteen more Type 055 destroyer class ships to its navy.
* is building five new ''Amiral Ronarc'h''-class destroyers (classed as "first rank frigates" in the French Navy).
* Six multi-mission surface combat ships are planned under the name 'Mehrzweckkampfschiff 180' (MKS 180), which will have destroyer-size and corresponding capabilities (Length: 163 m, displacement: 10,400 tons)
* has ordered three Frégate de défense et d'intervention (with an option on a fourth) from France.
* is building four s, of which two have been commissioned. The nation has also begun development of its
* plans to build 7,000-ton destroyers after the delivery of the new frigates, and TKMS presented to the Navy its most modern 7,200-ton MEKO A-400 air defense destroyer, an updated version of the German F-125-class frigates. The similarities between the projects and the high rate of commonality between requirements were also crucial for the consortium's victory.
* is adding six more Type 052D destroyer and sixteen more Type 055 destroyer class ships to its navy.
* is building five new ''Amiral Ronarc'h''-class destroyers (classed as "first rank frigates" in the French Navy).
* Six multi-mission surface combat ships are planned under the name 'Mehrzweckkampfschiff 180' (MKS 180), which will have destroyer-size and corresponding capabilities (Length: 163 m, displacement: 10,400 tons)
* has ordered three Frégate de défense et d'intervention (with an option on a fourth) from France.
* is building four s, of which two have been commissioned. The nation has also begun development of its
The Yard: Building a Destroyer at the Bath Iron Works
', HarperCollins, * Simpson, Richard V. ''Building The Mosquito Fleet, The US Navy's First Torpedo Boats.'' Arcadia Publishing, (2001); Charleston, South Carolina, USA. . * Preston, Anthony. ''Destroyers'', Bison Books (London) 1977. * Van der Vat, Dan. ''The Atlantic Campaign''.
 In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in 1885 by
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in 1885 by Fernando Villaamil
Fernando Villaamil Fernández-Cueto (November 23, 1845 – July 3, 1898) was a Spanish naval officer, remembered for his internationally recognized professionalism, for being the inventor of the destroyer warship and for his death in action during ...
for the Spanish NavySmith, Charles Edgar: ''A short history of naval and marine engineering.'' Babcock & Wilcox, ltd. at the University Press, 1937, page 263 as a defense against torpedo boats, and by the time of the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
in 1904, these "torpedo boat destroyers" (TBDs) were "large, swift, and powerfully armed torpedo boats designed to destroy other torpedo boats". Although the term "destroyer" had been used interchangeably with "TBD" and "torpedo boat destroyer" by navies since 1892, the term "torpedo boat destroyer" had been generally shortened to simply "destroyer" by nearly all navies by the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
.
Before World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, destroyers were light vessels with little endurance for unattended ocean operations; typically a number of destroyers and a single destroyer tender operated together. After the war, the advent of the guided missile allowed destroyers to take on the surface combatant roles previously filled by battleships and cruisers. This resulted in larger and more powerful guided missile destroyers more capable of independent operation.
At the start of the 21st century, destroyers are the global standard for surface combatant ships, with only two nations (United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
and Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
) officially operating the heavier class cruisers, with no battleships or true battlecruisers remaining. Modern guided missile destroyers are equivalent in tonnage but vastly superior in firepower to cruisers of the World War II era, and are capable of carrying nuclear-tipped cruise missile
A cruise missile is a guided missile used against terrestrial or naval targets that remains in the atmosphere and flies the major portion of its flight path at approximately constant speed. Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large warh ...
s. At long, a displacement of 9,200 tons, and with an armament of more than 90 missiles, guided missile destroyers such as the are actually larger and more heavily armed than most previous ships classified as guided missile cruisers. The Chinese Type 055 destroyer has been described as a cruiser in some US Navy reports due to its size and armament.
Some NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
navies, such as the Canadian
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
, French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, Spanish, Dutch and German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, use the term " frigate" for their destroyers, which leads to some confusion.
After the Second World War, destroyers grew in size. The American s had a displacement of 2,200 tons, while the ''Arleigh Burke'' class has a displacement of up to 9,600 tons, thus growing in size almost 340%.
Origins
 The emergence and development of the destroyer was related to the invention of the self-propelled torpedo in the 1860s. A navy now had the potential to destroy a superior enemy battle fleet using steam launches to fire torpedoes. Cheap, fast boats armed with torpedoes called torpedo boats were built and became a threat to large capital ships near enemy coasts. The first seagoing vessel designed to launch the self-propelled Whitehead torpedo was the 33-ton in 1876. She was armed with two drop collars to launch these weapons, these were replaced in 1879 by a single torpedo tube in the bow. By the 1880s, the type had evolved into small ships of 50–100 tons, fast enough to evade enemy picket boats.
At first, the threat of a torpedo boat attack to a battle fleet was considered to exist only when at anchor; but as faster and longer-range torpedo boats and torpedoes were developed, the threat extended to cruising at sea. In response to this new threat, more heavily gunned picket boats called "catchers" were built which were used to escort the battle fleet at sea. They needed significant seaworthiness and endurance to operate with the battle fleet, and as they inherently became larger, they became officially designated "torpedo boat destroyers", and by the First World War were largely known as "destroyers" in English. The anti-torpedo boat origin of this type of ship is retained in its name in other languages, including
The emergence and development of the destroyer was related to the invention of the self-propelled torpedo in the 1860s. A navy now had the potential to destroy a superior enemy battle fleet using steam launches to fire torpedoes. Cheap, fast boats armed with torpedoes called torpedo boats were built and became a threat to large capital ships near enemy coasts. The first seagoing vessel designed to launch the self-propelled Whitehead torpedo was the 33-ton in 1876. She was armed with two drop collars to launch these weapons, these were replaced in 1879 by a single torpedo tube in the bow. By the 1880s, the type had evolved into small ships of 50–100 tons, fast enough to evade enemy picket boats.
At first, the threat of a torpedo boat attack to a battle fleet was considered to exist only when at anchor; but as faster and longer-range torpedo boats and torpedoes were developed, the threat extended to cruising at sea. In response to this new threat, more heavily gunned picket boats called "catchers" were built which were used to escort the battle fleet at sea. They needed significant seaworthiness and endurance to operate with the battle fleet, and as they inherently became larger, they became officially designated "torpedo boat destroyers", and by the First World War were largely known as "destroyers" in English. The anti-torpedo boat origin of this type of ship is retained in its name in other languages, including French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
(), Italian (), Portuguese (), Czech (), Greek (, ''αντιτορπιλικό''), Dutch () and, up until the Second World War, Polish (, now obsolete).
Once destroyers became more than just catchers guarding an anchorage, it was realized that they were also ideal to take over the offensive role of torpedo boats themselves, so they were also fitted with torpedo tubes in addition to their anti torpedo-boat guns. At that time, and even into World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, the only function of destroyers was to protect their own battle fleet from enemy torpedo attacks and to make such attacks on the battleships of the enemy. The task of escorting merchant convoys was still in the future.
Early designs
 An important development came with the construction of HMS ''Swift'' in 1884, later redesignated TB 81. This was a large (137 ton) torpedo boat with four 47 mm quick-firing guns and three torpedo tubes. At , while still not fast enough to engage enemy torpedo boats reliably, the ship at least had the armament to deal with them.
Another forerunner of the torpedo boat destroyer was the Japanese torpedo boat (''Falcon''), built in 1885. Designed to Japanese specifications and ordered from the Isle of Dogs, London Yarrow shipyard in 1885, she was transported in parts to Japan, where she was assembled and launched in 1887. The long vessel was armed with four 1-pounder (37 mm) quick-firing guns and six torpedo tubes, reached , and at 203 tons, was the largest torpedo boat built to date. In her trials in 1889, ''Kotaka'' demonstrated that she could exceed the role of coastal defense, and was capable of accompanying larger warships on the high seas. The Yarrow shipyards, builder of the parts for ''Kotaka'', "considered Japan to have effectively invented the destroyer".
The German aviso , launched in 1886, was designed as a "''torpedojäger''" (torpedo hunter), intended to screen the fleet against attacks by torpedo boats. The ship was significantly larger than torpedo boats of the period, displacing some , with an armament of guns and
An important development came with the construction of HMS ''Swift'' in 1884, later redesignated TB 81. This was a large (137 ton) torpedo boat with four 47 mm quick-firing guns and three torpedo tubes. At , while still not fast enough to engage enemy torpedo boats reliably, the ship at least had the armament to deal with them.
Another forerunner of the torpedo boat destroyer was the Japanese torpedo boat (''Falcon''), built in 1885. Designed to Japanese specifications and ordered from the Isle of Dogs, London Yarrow shipyard in 1885, she was transported in parts to Japan, where she was assembled and launched in 1887. The long vessel was armed with four 1-pounder (37 mm) quick-firing guns and six torpedo tubes, reached , and at 203 tons, was the largest torpedo boat built to date. In her trials in 1889, ''Kotaka'' demonstrated that she could exceed the role of coastal defense, and was capable of accompanying larger warships on the high seas. The Yarrow shipyards, builder of the parts for ''Kotaka'', "considered Japan to have effectively invented the destroyer".
The German aviso , launched in 1886, was designed as a "''torpedojäger''" (torpedo hunter), intended to screen the fleet against attacks by torpedo boats. The ship was significantly larger than torpedo boats of the period, displacing some , with an armament of guns and Hotchkiss revolver cannon
The Hotchkiss gun can refer to different products of the Hotchkiss arms company starting in the late 19th century. It usually refers to the 1.65-inch (42 mm) light mountain gun; there were also a navy (47 mm) and a 3-inch (76&nbs ...
.
Torpedo gunboat
 The first vessel designed for the explicit purpose of hunting and destroying torpedo boats was the
The first vessel designed for the explicit purpose of hunting and destroying torpedo boats was the torpedo gunboat
In late 19th-century naval terminology, torpedo gunboats were a form of gunboat armed with torpedoes and designed for hunting and destroying smaller torpedo boats. By the end of the 1890s torpedo gunboats were superseded by their more successful ...
. Essentially very small cruisers, torpedo gunboats were equipped with torpedo tubes and an adequate gun armament, intended for hunting down smaller enemy boats. By the end of the 1890s torpedo gunboats were made obsolete by their more successful contemporaries, the torpedo boat destroyers, which were much faster.
The first example of this was , designed by Nathaniel Barnaby in 1885, and commissioned in response to the Russian War scare. The gunboat was armed with torpedoes and designed for hunting and destroying smaller torpedo boats. Exactly long and in beam, she displaced 550 tons. Built of steel, ''Rattlesnake'' was un-armoured with the exception of a -inch protective deck. She was armed with a single 4-inch/25-pounder breech-loading gun, six 3-pounder QF guns and four torpedo tubes, arranged with two fixed tubes at the bow and a set of torpedo dropping carriages on either side. Four torpedo reloads were carried.
A number of torpedo gunboat classes followed, including the ''Grasshopper'' class, the , the and the – all built for the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
during the 1880s and the 1890s. In the 1880s, the Chilean Navy ordered the construction of two torpedo gunboats from the British shipyard Laird Brothers, which specialized in the construction of this type of vessel. The novelty is that one of these ''Almirante Lynch'' class torpedo boats managed to sink the ironclad with a self-propelled torpedoes in the Battle of Caldera Bay in 1891, thus surpassing its main function of hunting torpedo boats.
Fernando Villaamil
Fernando Villaamil Fernández-Cueto (November 23, 1845 – July 3, 1898) was a Spanish naval officer, remembered for his internationally recognized professionalism, for being the inventor of the destroyer warship and for his death in action during ...
, second officer of the Ministry of the Navy of Spain, designed his own torpedo gunboat to combat the threat from the torpedo boat. He asked several British shipyards to submit proposals capable of fulfilling these specifications. In 1885 the Spanish Navy chose the design submitted by the shipyard of James and George Thomson of Clydebank. (''Destroyer'' in Spanish) was laid down at the end of the year, launched in 1886, and commissioned in 1887. Some authors considered her as the first destroyer ever built.
breech-loading
A breechloader is a firearm in which the user loads the ammunition ( cartridge or shell) via the rear (breech) end of its barrel, as opposed to a muzzleloader, which loads ammunition via the front ( muzzle).
Modern firearms are generally breec ...
gun,Fitzsimmons, Bernard: ''The Illustrated encyclopedia of 20th century weapons and warfare.'' Columbia House, 1978, v. 8, page 835 four (6-pounder 6-pounder gun or 6-pdr, usually denotes a gun firing a projectile weighing approximately .
Guns of this type include:
*QF 6 pounder Hotchkiss, a 57 mm naval gun of the 1880s; a similar weapon was designed by Driggs-Schroeder for the US Navy
...
) Nordenfelt
The Nordenfelt gun was a multiple-barrel organ gun that had a row of up to twelve barrels. It was fired by pulling a lever back and forth and ammunition was gravity fed through chutes for each barrel. It was produced in a number of different c ...
guns, two (3-pdr) Hotchkiss
Hotchkiss may refer to:
Places Canada
* Hotchkiss, Alberta
* Hotchkiss, Calgary
United States
* Hotchkiss, Colorado
* Hotchkiss, Virginia
* Hotchkiss, West Virginia
Business and industry
* Hotchkiss (car), a French automobile manufacturer ...
cannons and two Schwartzkopff torpedo
The Schwartzkopff torpedo was a torpedo manufactured in the late 19th century by the German firm ''Eisengießerei und Maschinen-Fabrik von L. Schwartzkopff'', later known as Berliner Maschinenbau, based on the Whitehead design. Unlike the Whit ...
tubes. The ship carried three torpedoes per tube. She carried a crew of 60.
In terms of gunnery, speed and dimensions, the specialised design to chase torpedo boats and her high seas capabilities, ''Destructor'' was an important precursor to the torpedo boat destroyer.
Development of modern destroyers
 The first classes of ships to bear the formal designation "torpedo boat destroyer" (TBD) were the of two ships and of two ships of the
The first classes of ships to bear the formal designation "torpedo boat destroyer" (TBD) were the of two ships and of two ships of the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
.
Early torpedo gunboat
In late 19th-century naval terminology, torpedo gunboats were a form of gunboat armed with torpedoes and designed for hunting and destroying smaller torpedo boats. By the end of the 1890s torpedo gunboats were superseded by their more successful ...
designs lacked the range and speed to keep up with the fleet they were supposed to protect. In 1892, the Third Sea Lord, Rear Admiral John "Jacky" Fisher ordered the development of a new type of ships equipped with the then novel water-tube boilers and quick-firing small calibre guns. Six ships to the specifications circulated by the Admiralty were ordered initially, comprising three different designs each produced by a different shipbuilder: and from John I. Thornycroft & Company, and from Yarrows, and and from Laird, Son & Company.
These torpedo boat destroyers all featured a turtleback (i.e. rounded) forecastle
The forecastle ( ; contracted as fo'c'sle or fo'c's'le) is the upper deck of a sailing ship forward of the foremast, or, historically, the forward part of a ship with the sailors' living quarters. Related to the latter meaning is the phrase " ...
that was characteristic of early British TBDs. and were both built by Thornycroft, displaced 260 tons (287.8 tons full load) and were 185 feet in length. They were armed with one 12-pounder gun and three 6-pounder guns, with one fixed 18-in torpedo tube in the bow plus two more torpedo tubes on a revolving mount abaft the two funnels. Later the bow torpedo tube was removed and two more 6-pounder guns added instead. They produced 4,200 hp from a pair of Thornycroft water-tube boilers, giving them a top speed of 27 knots, giving the range and speed to travel effectively with a battle fleet. In common with subsequent early Thornycroft boats, they had sloping sterns and double rudders.
The French navy, an extensive user of torpedo boats, built its first torpedo boat destroyer in 1899, with the 'torpilleur d'escadre'. The United States commissioned its first torpedo boat destroyer, , Destroyer No. 1, in 1902 and by 1906 there were 16 destroyers in service with the US Navy.
Subsequent improvements
 Torpedo boat destroyer designs continued to evolve around the turn of the 20th century in several key ways. The first was the introduction of the steam turbine. The spectacular unauthorized demonstration of the turbine-powered at the 1897 Spithead Navy Review, which, significantly, was of torpedo boat size, prompted the Royal Navy to order a prototype turbine powered destroyer, of 1899. This was the first turbine warship of any kind and achieved a remarkable on sea trials. By 1910 the turbine had been widely adopted by all navies for their faster ships.
The second development was the replacement of the torpedo-boat-style turtleback foredeck by a raised
Torpedo boat destroyer designs continued to evolve around the turn of the 20th century in several key ways. The first was the introduction of the steam turbine. The spectacular unauthorized demonstration of the turbine-powered at the 1897 Spithead Navy Review, which, significantly, was of torpedo boat size, prompted the Royal Navy to order a prototype turbine powered destroyer, of 1899. This was the first turbine warship of any kind and achieved a remarkable on sea trials. By 1910 the turbine had been widely adopted by all navies for their faster ships.
The second development was the replacement of the torpedo-boat-style turtleback foredeck by a raised forecastle
The forecastle ( ; contracted as fo'c'sle or fo'c's'le) is the upper deck of a sailing ship forward of the foremast, or, historically, the forward part of a ship with the sailors' living quarters. Related to the latter meaning is the phrase " ...
for the new s built in 1903, which provided better sea-keeping as well as more space below deck.
The first warship to use only fuel oil propulsion was the Royal Navy's torpedo boat destroyer , after experiments in 1904, although the obsolescence of coal as a fuel in British warships was delayed by its availability. Other navies also adopted oil, for instance the USN with the of 1909.
In spite of all this variety, destroyers adopted a largely similar pattern. The hull was long and narrow, with a relatively shallow draft. The bow was either raised in a forecastle or covered under a turtleback; underneath this were the crew spaces, extending to the way along the hull. Aft of the crew spaces was as much engine space as the technology of the time would allow: several boilers and engines or turbines. Above deck, one or more quick-firing guns were mounted in the bows, in front of the bridge; several more were mounted amidships and astern. Two tube mountings (later on, multiple mountings) were generally found amidships.
Between 1892 and 1914 destroyers became markedly larger: initially 275 tons with a length of for the Royal Navy's first of torpedo boat destroyers, up to the First World War with long destroyers displacing 1,000 tons was not unusual. However, construction remained focused on putting the biggest possible engines into a small hull, resulting in a somewhat flimsy construction. Often hulls were built of high-tensile steel only thick.
By 1910 the steam-driven displacement (that is, not hydroplaning) torpedo boat had become redundant as a separate type. Germany nevertheless continued to build such boats until the end of World War I, although these were effectively small coastal destroyers. In fact Germany never distinguished between the two types, giving them pennant numbers in the same series and never giving names to destroyers. Ultimately the term ''torpedo boat'' came to be attached to a quite different vessel – the very fast hydroplaning motor driven MTB.
Early use and World War I
Navies originally built torpedo boat destroyers to protect against torpedo boats, but admirals soon appreciated the flexibility of the fast, multi-purpose vessels that resulted. Vice-Admiral SirBaldwin Walker
Admiral Sir Baldwin Wake Walker, 1st Baronet, (6 January 1802 – 12 February 1876) was Surveyor of the Navy from 1848 to 1861. and was responsible for the Royal Navy's warship construction programme during the 1850s naval arms race and at th ...
laid down destroyer duties for the Royal Navy:
* screening the advance of a fleet when hostile torpedo craft are about
* searching a hostile coast along which a fleet might pass
* watching an enemy's port for the purpose of harassing his torpedo craft and preventing their return
* attacking an enemy fleet
Early destroyers were extremely cramped places to live, being "without a doubt magnificent fighting vessels... but unable to stand bad weather". During the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
in 1904, the commander of the Imperial Japanese Navy torpedo boat destroyer ''Akatsuki'' described "being in command of a destroyer for a long period, especially in wartime... is not very good for the health". Stating that he had originally been strong and healthy, he continued, "life on a destroyer in winter, with bad food, no comforts, would sap the powers of the strongest men in the long run. A ''destroyer'' is always more uncomfortable than the others, and rain, snow, and ''sea-water'' combine to make them damp; in fact, in bad weather there is not a dry spot where one can rest for a moment."Grant p. 102, 103
The Japanese destroyer-commander finished with, "Yesterday I looked at myself in a mirror for a long time; I was disagreeably surprised to see my face thin, full of wrinkles, and as old as though I were fifty. My clothes (uniform) cover nothing but a skeleton, and my bones are full of rheumatism."
In 1898, the US Navy officially classified , a long all steel vessel displacing 165 tons, as a ''torpedo boat.'' However, her commander, LT. John C. Fremont, described her as "...a compact mass of machinery not meant to keep the sea nor to live in... as five sevenths of the ship are taken up by machinery and fuel, whilst the remaining two sevenths, fore and aft, are the crew's quarters; officers forward and the men placed aft. And even in those spaces are placed anchor engines, steering engines, steam pipes, etc. rendering them unbearably hot in tropical regions."
Early combat
 The torpedo boat destroyer's first major use in combat came during the Japanese surprise attack on the Russian fleet anchored in Port Arthur at the opening of the
The torpedo boat destroyer's first major use in combat came during the Japanese surprise attack on the Russian fleet anchored in Port Arthur at the opening of the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
on 8 February 1904.
Three destroyer divisions attacked the Russian fleet in port, firing a total of 18 torpedoes. However, only two Russian battleships, and , and a protected cruiser, , were seriously damaged due to the proper deployment of torpedo nets. ''Tsesarevich'', the Russian flagship, had her nets deployed, with at least four enemy torpedoes "hung up" in them, and other warships were similarly saved from further damage by their nets.
While capital ship engagements were scarce in World War I, destroyer units engaged almost continually in raiding and patrol actions. The first shot of the war at sea was fired on 5 August 1914 by , one of the 3rd Destroyer Flotilla
The British 3rd Destroyer Flotilla, also styled as Third Destroyer Flotilla, was a naval formation of the Royal Navy from 1909 to 1939 and again from 1945 to 1951.
History
In 1907 the Channel Fleet had a large Channel Flotilla of destroyers in Fe ...
, in an engagement with the German auxiliary minelayer .
Destroyers were involved in the skirmishes that prompted the Battle of Heligoland Bight, and filled a range of roles in the Battle of Gallipoli, acting as troop transports and as fire-support vessels, as well as their fleet-screening role. Over 80 British destroyers and 60 German torpedo-boats took part in the Battle of Jutland, which involved pitched small-boat actions between the main fleets, and several foolhardy attacks by unsupported destroyers on capital ships. Jutland also concluded with a messy night action between the German High Seas Fleet and part of the British destroyer screen.
 The threat evolved by
The threat evolved by World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
with the development of the submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
, or U-boat. The submarine had the potential to hide from gunfire and close underwater to fire torpedoes. Early-war destroyers had the speed and armament to intercept submarines before they submerged, either by gunfire or by ramming. Destroyers also had a shallow enough draft that torpedoes would find it difficult to hit them.
 The desire to attack submarines underwater led to rapid destroyer evolution during the war. They were quickly equipped with strengthened bows for ramming, and depth charges and hydrophones for identifying submarine targets. The first submarine casualty credited to a destroyer was the German , rammed by on 29 October 1914. While ''U-19'' was only damaged, the next month successfully sank . The first depth-charge sinking was on 4 December 1916, when was sunk by HMS ''Llewellyn''.
The submarine threat meant that many destroyers spent their time on anti-submarine patrol. Once Germany adopted unrestricted submarine warfare in January 1917, destroyers were called on to escort merchant convoys. US Navy destroyers were among the first American units to be dispatched upon the American entry to the war, and a squadron of Japanese destroyers even joined Allied patrols in the Mediterranean. Patrol duty was far from safe; of the 67 British destroyers lost in the war, collisions accounted for 18, while 12 were wrecked.
At the end of the war, the state-of-the-art was represented by the British W class.
The desire to attack submarines underwater led to rapid destroyer evolution during the war. They were quickly equipped with strengthened bows for ramming, and depth charges and hydrophones for identifying submarine targets. The first submarine casualty credited to a destroyer was the German , rammed by on 29 October 1914. While ''U-19'' was only damaged, the next month successfully sank . The first depth-charge sinking was on 4 December 1916, when was sunk by HMS ''Llewellyn''.
The submarine threat meant that many destroyers spent their time on anti-submarine patrol. Once Germany adopted unrestricted submarine warfare in January 1917, destroyers were called on to escort merchant convoys. US Navy destroyers were among the first American units to be dispatched upon the American entry to the war, and a squadron of Japanese destroyers even joined Allied patrols in the Mediterranean. Patrol duty was far from safe; of the 67 British destroyers lost in the war, collisions accounted for 18, while 12 were wrecked.
At the end of the war, the state-of-the-art was represented by the British W class.
1918–1945
 The trend during World War I had been towards larger destroyers with heavier armaments. A number of opportunities to fire at capital ships had been missed during the War, because destroyers had expended all their torpedoes in an initial salvo. The British V and W classes of the late war had sought to address this by mounting six torpedo tubes in two triple mounts, instead of the four or two on earlier models. The 'V' and 'W's set the standard of destroyer building well into the 1920s.
The two Romanian destroyers and , on the other hand, had the greatest firepower of all destroyers in the world throughout the first half of the 1920s. This was largely due to the fact that, between their commissioning in 1920 and 1926, they retained the armament that they had while serving in the Italian Navy as scout cruisers (''
The trend during World War I had been towards larger destroyers with heavier armaments. A number of opportunities to fire at capital ships had been missed during the War, because destroyers had expended all their torpedoes in an initial salvo. The British V and W classes of the late war had sought to address this by mounting six torpedo tubes in two triple mounts, instead of the four or two on earlier models. The 'V' and 'W's set the standard of destroyer building well into the 1920s.
The two Romanian destroyers and , on the other hand, had the greatest firepower of all destroyers in the world throughout the first half of the 1920s. This was largely due to the fact that, between their commissioning in 1920 and 1926, they retained the armament that they had while serving in the Italian Navy as scout cruisers (''esploratori
An esploratore (meaning "scout") was a type of Italian warship intermediate between destroyers and light cruisers. Before World War II, existing ''esploratori'' were reclassified as destroyers (Italian: ''cacciatorpediniere'').
There was a furth ...
''). When initially ordered by Romania in 1913, the Romanian specifications envisioned three 120 mm guns, a caliber which would eventually be adopted as the standard for future Italian destroyers. Armed with three 152 mm and four 76 mm guns after being completed as scout cruisers, the two warships were officially re-rated as destroyers by the Romanian Navy. The two Romanian warships were thus the destroyers with the greatest firepower in the world throughout much of the interwar period. As of 1939, when the Second World War started, their artillery, although changed, was still close to cruiser standards, amounting to nine heavy naval guns (five of 120 mm and four of 76 mm). In addition, they retained their two twin 457 mm torpedo tubes as well as two machine guns, plus the capacity to carry up to 50 mines.
 The next major innovation came with the Japanese or 'special type', designed in 1923 and delivered in 1928. The design was initially noted for its powerful armament of six five-inch (127 mm) guns and three triple torpedo mounts. The second batch of the class gave the guns high-angle turrets for anti-aircraft warfare, and the oxygen-fueled 'Long Lance' Type 93 torpedo. The later of 1931 further improved the torpedo armament by storing its reload torpedoes close at hand in the superstructure, allowing reloading within 15 minutes.
Most other nations replied with similar larger ships. The US adopted twin five-inch (127 mm) guns, and the subsequent and es (the latter of 1934) increased the number of torpedo tubes to 12 and 16 respectively.
The next major innovation came with the Japanese or 'special type', designed in 1923 and delivered in 1928. The design was initially noted for its powerful armament of six five-inch (127 mm) guns and three triple torpedo mounts. The second batch of the class gave the guns high-angle turrets for anti-aircraft warfare, and the oxygen-fueled 'Long Lance' Type 93 torpedo. The later of 1931 further improved the torpedo armament by storing its reload torpedoes close at hand in the superstructure, allowing reloading within 15 minutes.
Most other nations replied with similar larger ships. The US adopted twin five-inch (127 mm) guns, and the subsequent and es (the latter of 1934) increased the number of torpedo tubes to 12 and 16 respectively.
 In the Mediterranean, the Italian Navy's building of very fast light cruisers of the prompted the French to produce exceptional destroyer designs. The French had long been keen on large destroyers, with their of 1922 displacing over 2,000 tons and carrying 130 mm guns; a further three similar classes were produced around 1930. The of 1935 carried five guns and nine torpedo tubes, but could achieve speeds of , which remains the record speed for a steamship and for any destroyer. The Italians' own destroyers were almost as swift, most Italian designs of the 1930s being rated at over , while carrying torpedoes and either four or six 120 mm guns.
Germany started to build destroyers again during the 1930s as part of Hitler's rearmament program. The Germans were also fond of large destroyers, but while the initial Type 1934 displaced over 3,000 tons, their armament was equal to smaller vessels. This changed from the Type 1936 onwards, which mounted heavy guns. German destroyers also used innovative high-pressure steam machinery: while this should have helped their efficiency, it more often resulted in mechanical problems.
Once German and Japanese rearmament became clear, the British and American navies consciously focused on building destroyers that were smaller but more numerous than those used by other nations. The British built a series of destroyers (the to ) which were about 1,400 tons standard displacement, had four guns and eight torpedo tubes; the American of 1938 similar in size, but carried five guns and ten torpedo tubes. Realizing the need for heavier gun armament, the British built the of 1936 (sometimes called ''Afridi'' after one of two lead ships). These ships displaced 1,850 tons and were armed with eight guns in four twin turrets and four torpedo tubes. These were followed by the J-class and L-class destroyers, with six guns in twin turrets and eight torpedo tubes.
Anti-submarine sensors included
In the Mediterranean, the Italian Navy's building of very fast light cruisers of the prompted the French to produce exceptional destroyer designs. The French had long been keen on large destroyers, with their of 1922 displacing over 2,000 tons and carrying 130 mm guns; a further three similar classes were produced around 1930. The of 1935 carried five guns and nine torpedo tubes, but could achieve speeds of , which remains the record speed for a steamship and for any destroyer. The Italians' own destroyers were almost as swift, most Italian designs of the 1930s being rated at over , while carrying torpedoes and either four or six 120 mm guns.
Germany started to build destroyers again during the 1930s as part of Hitler's rearmament program. The Germans were also fond of large destroyers, but while the initial Type 1934 displaced over 3,000 tons, their armament was equal to smaller vessels. This changed from the Type 1936 onwards, which mounted heavy guns. German destroyers also used innovative high-pressure steam machinery: while this should have helped their efficiency, it more often resulted in mechanical problems.
Once German and Japanese rearmament became clear, the British and American navies consciously focused on building destroyers that were smaller but more numerous than those used by other nations. The British built a series of destroyers (the to ) which were about 1,400 tons standard displacement, had four guns and eight torpedo tubes; the American of 1938 similar in size, but carried five guns and ten torpedo tubes. Realizing the need for heavier gun armament, the British built the of 1936 (sometimes called ''Afridi'' after one of two lead ships). These ships displaced 1,850 tons and were armed with eight guns in four twin turrets and four torpedo tubes. These were followed by the J-class and L-class destroyers, with six guns in twin turrets and eight torpedo tubes.
Anti-submarine sensors included sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on o ...
(or ASDIC), although training in their use was indifferent. Anti-submarine weapons changed little, and ahead-throwing weapons, a need recognized in World War I, had made no progress.
Later combat
 During the 1920s and 1930s, destroyers were often deployed to areas of diplomatic tension or humanitarian disaster. British and American destroyers were common on the Chinese coast and rivers, even supplying landing parties to protect colonial interests.
By
During the 1920s and 1930s, destroyers were often deployed to areas of diplomatic tension or humanitarian disaster. British and American destroyers were common on the Chinese coast and rivers, even supplying landing parties to protect colonial interests.
By World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
the threat had evolved once again. Submarines were more effective, and aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining support from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. It counters the force of gravity by using either Buoyancy, static lift or by using the Lift (force), dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in ...
had become important weapons of naval warfare; once again the early-war fleet destroyers were ill-equipped for combating these new targets. They were fitted with new light anti-aircraft guns, radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, Marine radar, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor v ...
, and forward-launched ASW weapons, in addition to their existing dual-purpose gun
A dual-purpose gun is a naval artillery mounting designed to engage both surface and air targets.
Description
Second World War-era capital ships had four classes of artillery: the heavy main battery, intended to engage opposing battleships and ...
s, depth charges, and torpedoes. Increasing size allowed improved internal arrangement of propulsion machinery with compartmentation so ships were less likely to be sunk by a single hit. In most cases torpedo and/or dual-purpose gun armament was reduced to accommodate new anti-air and anti-submarine
An anti-submarine weapon (ASW) is any one of a number of devices that are intended to act against a submarine and its crew, to destroy (sink) the vessel or reduce its capability as a weapon of war. In its simplest sense, an anti-submarine weapo ...
weapons. By this time the destroyers had become large, multi-purpose vessels, expensive targets in their own right. As a result, casualties on destroyers were among the highest. In the US Navy, particularly in World War II, destroyers became known as tin cans due to their light armor compared to battleships and cruisers.
The need for large numbers of anti-submarine ships led to the introduction of smaller and cheaper specialized anti-submarine warships called corvettes and frigates by the Royal Navy and destroyer escorts by the USN. A similar programme was belatedly started by the Japanese (see ). These ships had the size and displacement of the original torpedo boat destroyers that the contemporary destroyer had evolved from.
Post-World War II
 Some conventional destroyers were completed in the late 1940s and 1950s which built on wartime experience. These vessels were significantly larger than wartime ships and had fully automatic main guns, unit machinery, radar, sonar, and antisubmarine weapons such as the Squid mortar. Examples include the British , US , and the Soviet s.
Some World War II–vintage ships were modernized for anti-submarine warfare, and to extend their service lives, to avoid having to build (expensive) brand-new ships. Examples include the US FRAM I programme and the British
Some conventional destroyers were completed in the late 1940s and 1950s which built on wartime experience. These vessels were significantly larger than wartime ships and had fully automatic main guns, unit machinery, radar, sonar, and antisubmarine weapons such as the Squid mortar. Examples include the British , US , and the Soviet s.
Some World War II–vintage ships were modernized for anti-submarine warfare, and to extend their service lives, to avoid having to build (expensive) brand-new ships. Examples include the US FRAM I programme and the British Type 15 frigate
The Type 15 frigate was a class of British anti-submarine frigates of the Royal Navy. They were conversions based on the hulls of World War II-era destroyers built to the standard War Emergency Programme "utility" design.
History
By 1945 the ...
s converted from fleet destroyers.
The advent of surface-to-air missiles and surface-to-surface missiles, such as the Exocet, in the early 1960s changed naval warfare. Guided missile destroyers (DDG in the US Navy) were developed to carry these weapons and protect the fleet from air, submarine and surface threats. Examples include the Soviet , the British , and the US .
21st century destroyers tend to display features such as large, slab sides without complicated corners and crevices to keep the radar cross-section small, vertical launch systems to carry a large number of missiles at high readiness to fire and helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attribu ...
flight decks and hangars
A hangar is a building or structure designed to hold aircraft or spacecraft. Hangars are built of metal, wood, or concrete. The word ''hangar'' comes from Middle French ''hanghart'' ("enclosure near a house"), of Germanic origin, from Frankish ...
.
Operators
* operates four s. * operates three s. They are the first Australian warships to use theAegis Combat System
The Aegis Combat System is an American integrated naval weapons system developed by the Missile and Surface Radar Division of RCA, and it is now produced by Lockheed Martin.
Initially used by the United States Navy, Aegis is now used also by ...
and are based on Spain's s.
 * operates four Renhai-class destroyers, two Luyang I-class destroyers, six Luyang II-class destroyers, more than 18 Luyang III-class destroyers and two Luzhou-class destroyers. China also operates two Luhu-class destroyers, one Luhai-class destroyer and four -class destroyers that are of older models. It is notable that the Renhai class (Type 055) is considered to be a cruiser by
* operates four Renhai-class destroyers, two Luyang I-class destroyers, six Luyang II-class destroyers, more than 18 Luyang III-class destroyers and two Luzhou-class destroyers. China also operates two Luhu-class destroyers, one Luhai-class destroyer and four -class destroyers that are of older models. It is notable that the Renhai class (Type 055) is considered to be a cruiser by NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
and the U.S. Department of Defense for its tonnage and capability matching that of the .
* (Taiwan) operates four s, purchased from the United States.
* Operates a single FREMM multipurpose frigate purchased from France, and a single Z-class destroyer for training use.
* operates eight FREMM multipurpose frigates and two s. The French Navy does not use the term "destroyer" but rather "first-rate frigate" to these ship types, but they are marked with the NATO "D" hull code which places them in the destroyer type, as opposed to "F" for frigate.
* operates three s and four s. These ships are officially classified as frigates by Germany, but regarded as destroyers internationally due to size and capability.
* HS ''Velos'', a , remains ceremonially in commission due to her historical significance.
* operates two s, three s, three , and three destroyers.
* operates three s. These ships are classified as destroyers by Iran, but internationally regarded as light frigates.
* operates two s and two Orizzonte-class destroyers.
* operates the two , two , and four destroyers which all employ the Aegis combat system
The Aegis Combat System is an American integrated naval weapons system developed by the Missile and Surface Radar Division of RCA, and it is now produced by Lockheed Martin.
Initially used by the United States Navy, Aegis is now used also by ...
. Japan also operates two , two , four , five , nine , eight , and six destroyers.
* Operates several classes of destroyers including the (KDX-III), the (KDX-II) and (KDX-I) destroyers. The KDX-III is equipped with the Aegis combat system
The Aegis Combat System is an American integrated naval weapons system developed by the Missile and Surface Radar Division of RCA, and it is now produced by Lockheed Martin.
Initially used by the United States Navy, Aegis is now used also by ...
, Goalkeeper CIWS, Hyunmoo cruise missile
A cruise missile is a guided missile used against terrestrial or naval targets that remains in the atmosphere and flies the major portion of its flight path at approximately constant speed. Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large warh ...
and the Hae Sung anti-ship missile
An anti-ship missile (AShM) is a guided missile that is designed for use against ships and large boats. Most anti-ship missiles are of the sea skimming variety, and many use a combination of inertial guidance and active radar homing. A goo ...
.
* operates a single FREMM multipurpose frigate ordered from France.
* operates four s. These ships are classified as frigates by The Netherlands, but regarded as destroyers internationally due to size and capability.
* operates four s. These ships are officially classified as frigates by Norway, but are regarded both internationally and by their officers as destroyers. They carry the Aegis combat system
The Aegis Combat System is an American integrated naval weapons system developed by the Missile and Surface Radar Division of RCA, and it is now produced by Lockheed Martin.
Initially used by the United States Navy, Aegis is now used also by ...
. They are a subclass of Spain's ''Álvaro de Bazán''-class destroyers.
* operates two s purchased from the United Kingdom.
* The , remains ceremonially in commission due to her historical significance.
* operates . This ship was classified as a destroyer from 1990 to 2001, when she was reclassified as a frigate. No official reason was given for this and there was no change in armament or capability, thus remaining in the destroyer type.
* The Russian Navy operates two (plus one in prolonged refit/reserve) and eight destroyers.
* operates five s. These ships are officially classified as a frigates by Spain, but due to their size and capabilities are regarded internationally as destroyers. the design draws elements from the American ''Arleigh Burke''-class destroyers and carry the Aegis combat system
The Aegis Combat System is an American integrated naval weapons system developed by the Missile and Surface Radar Division of RCA, and it is now produced by Lockheed Martin.
Initially used by the United States Navy, Aegis is now used also by ...
and inspired the design of the ''Hobart'' and ''Fridtjof Nansen''-class destroyers.
* operates a single purchased from the United States for training use.
* operates the Type 45, or ''Daring''-class, stealth destroyer which displaces roughly 8,000 tonnes. Six ships of the class are operational. They are equipped with the UK variant of the Principal Anti-Air Missile System (PAAMS) and BAE Systems SAMPSON radar.
* operates 70 active guided missile destroyers (DDGs) of a planned class of 89, and also has two active destroyer of a planned class of three, all .
Former operators
* lost its entire navy upon the Empire's collapse following World War I. * lost its entire navy upon its forced integration into the Soviet Union in 1921. * sold its two and s to Peru in 1933, to prevent their capture by the Soviet Union. * transferred its only back to Japan in 1942. * decommissioned its only in 1963. * decommissioned its last in 1965. * decommissioned its last in 1967. * decommissioned its last Z-class destroyer in 1972. * decommissioned itsH-class destroyer
The G- and H-class destroyers were a group of 18 destroyers built for the Royal Navy during the 1930s. Six additional ships being built for the Brazilian Navy when World War II began in 1939 were purchased by the British and named the ''Havant ...
in 1972.
* transferred its remaining to The Philippines in 1975 following the Fall of Saigon.
* decommissioned its last W-class destroyer in 1976.
* decommissioned its only destroyer, in 1980.
* decommissioned both its and four s in 1982 following defense reviews.
* decommissioned both its s and its lone in 1986.
* decommissioned its last in 1991.
* lone was destroyed by a fire in 1992.
* decommissioned its lone in 1994.
* decommissioned its lone in 1997.
* decommissioned its last in 2000.
* decommissioned its lone in 2003.
* decommissioned all four s in 2003.
* decommissioned its last in 2004.
* decommissioned its last in 2006.
* decommissioned its last in 2007.
* decommissioned its last ''Garcia''-class destroyer escort in 2008.
* decommissioned its last in 2011.
* decommissioned its last in 2015.
* decommissioned its last in 2017.
* decommissioned its last in 2018.
Future development
 * plans to build 7,000-ton destroyers after the delivery of the new frigates, and TKMS presented to the Navy its most modern 7,200-ton MEKO A-400 air defense destroyer, an updated version of the German F-125-class frigates. The similarities between the projects and the high rate of commonality between requirements were also crucial for the consortium's victory.
* is adding six more Type 052D destroyer and sixteen more Type 055 destroyer class ships to its navy.
* is building five new ''Amiral Ronarc'h''-class destroyers (classed as "first rank frigates" in the French Navy).
* Six multi-mission surface combat ships are planned under the name 'Mehrzweckkampfschiff 180' (MKS 180), which will have destroyer-size and corresponding capabilities (Length: 163 m, displacement: 10,400 tons)
* has ordered three Frégate de défense et d'intervention (with an option on a fourth) from France.
* is building four s, of which two have been commissioned. The nation has also begun development of its
* plans to build 7,000-ton destroyers after the delivery of the new frigates, and TKMS presented to the Navy its most modern 7,200-ton MEKO A-400 air defense destroyer, an updated version of the German F-125-class frigates. The similarities between the projects and the high rate of commonality between requirements were also crucial for the consortium's victory.
* is adding six more Type 052D destroyer and sixteen more Type 055 destroyer class ships to its navy.
* is building five new ''Amiral Ronarc'h''-class destroyers (classed as "first rank frigates" in the French Navy).
* Six multi-mission surface combat ships are planned under the name 'Mehrzweckkampfschiff 180' (MKS 180), which will have destroyer-size and corresponding capabilities (Length: 163 m, displacement: 10,400 tons)
* has ordered three Frégate de défense et d'intervention (with an option on a fourth) from France.
* is building four s, of which two have been commissioned. The nation has also begun development of its Next Generation Destroyer (NGD)
The Project 18 is a class of Next Generation Stealth Guided Missile Destroyers (NGD) designed for the Indian Navy. They are projected to be the replacement of the Rajput-class guided-missile destroyers. Recently, the Indian Navy has showcased ...
, also referred to as ''Project 18''-class destroyers.
* is currently building 1-2 s.
* is currently researching development into their new DDX project to replace their ''Durand da le Penne''-class destroyers.
* Is developing plans for its DDR Destroyer Revolution Project.
* has begun development of its KDX-IIA destroyers. These ships are to be a subclass of South Korea's s. The first unit is expected to enter service in 2019. Additionally, s are being built.
* has begun development of its . Design work was ongoing as of 2020.
* is currently developing its TF2000-class destroyer as the largest part of the MILGEM project. A total of seven ships will be constructed and will specialise in anti-air warfare.
* is in the early stages of developing a Type 83 destroyer
The Type 83 destroyer is a class of guided missile destroyers which is planned to enter service with the United Kingdom's Royal Navy in the late 2030s as a replacement for the current Type 45 destroyer.
Background
The Royal Navy currently opera ...
design after the unveiling of these plans in the 2021 defence white paper. The class is projected to replace the current Type 45 destroyer fleet beginning in the latter 2030s.
*, currently has 19 additional ''Arleigh Burke'' destroyers planned or under construction. The new ships will be the upgraded "flight III" version. The United States has also started development of its DDG(X)
The DDG(X) program, also known as the Next-Generation Guided-Missile Destroyer program, is a United States Navy program to develop a class of surface combatant vessels to succeed its 22 Flight II s and 27 Flight I/II s. The program is the culmin ...
next-generation destroyer project. Construction of the first ship is expected to start in 2028.
Preserved destroyers
A number of countries have destroyers preserved as museum ships. These include: * inSydney
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mounta ...
, New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
.
* BNS ''Bauru'', formerly in Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a b ...
, Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
.
* in Hamilton Hamilton may refer to:
People
* Hamilton (name), a common British surname and occasional given name, usually of Scottish origin, including a list of persons with the surname
** The Duke of Hamilton, the premier peer of Scotland
** Lord Hamilto ...
, Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
.
* in Qingdao, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
.
* in Rushan, China
* in Dalian, China
* in Wuhan, China
* in Yinchuan
Yinchuan (, ; ) is the capital of the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China, and was the capital of the Tangut-led Western Xia dynasty. It has an area of and a total population of 2,859,074 according to the 2020 Chinese census, and its built ...
, China
* in Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Chinese, Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four Direct-administered municipalities of China, direct-administered municipalities of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the ...
, China
* in Qingdao, China
* in Taizhou, China
* in Nanchang, China
* in Tianjin, China
* , in Guizhou
Guizhou (; Postal romanization, formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked Provinces of China, province in the Southwest China, southwest region of the China, People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the pr ...
, China
* in Shandong, China
* in Shandong, China
* has been slated for preservation in China
* has been slated for preservation in China
* ARC ''Boyaca'' (DE-16), formerly in Guatape, Colombia.
* in Nantes, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
.
* in Wilhelmshaven, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
.
* HS ''Velos'' (D-16), formerly in Palaio Faliro, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
.
* in Sangley Point, Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
* in Gdynia, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
. The oldest preserved destroyer in the world.
* Russian destroyer ''Bespokoynyy'' in Kronstadt, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
* Russian destroyer ''Smetlivy'' in Sevastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
, Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
* ROKS ''Jeong Ju'' (DD-925), formerly in Dangjin, South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
.
* in Gothenburg, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
.
* ROCS ''Te Yang'' (DDG-925), formerly in Tainan City
Tainan (), officially Tainan City, is a special municipality in southern Taiwan facing the Taiwan Strait on its western coast. Tainan is the oldest city on the island and also commonly known as the "Capital City" for its over 200 years of h ...
, Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the no ...
* TCG ''Gayret'' (D352), formerly in Izmit, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
.
* in Chatham, Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
.
* in Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut Massachusett_writing_systems.html" ;"title="nowiki/> məhswatʃəwiːsət.html" ;"title="Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət">Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət'' En ...
.
* in Buffalo, New York.
* in Baton Rouge, Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is bord ...
.
* in Albany, New York.
* in Galveston, Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
.
* in Jacksonville, Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and ...
.
* in Bremerton, Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
.
* in Mount Pleasant, South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
.
* in Bay City, Michigan
Michigan () is a state in the Great Lakes region of the upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the 10th-largest state by population, the 11th-largest by area, and t ...
.
* in Fall River
Fall River is a city in Bristol County, Massachusetts, Bristol County, Massachusetts, United States. The City of Fall River's population was 94,000 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 United States Census, making it the List of municipaliti ...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut Massachusett_writing_systems.html" ;"title="nowiki/> məhswatʃəwiːsət.html" ;"title="Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət">Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət'' En ...
.
Former museums
* was on display in Bridgewater, Nova Scotia from 1994 to 2011. Later scrapped due to her deteriorating condition. * IJN ''Shiga'' was on display in Chiba City, Japan from 1964 to 1998 when she was scrapped due to her deteriorating condition. * ROKS ''Kang Won'' (DD-922) was on display from 2000 to 2016, when she was closed due to her deteriorating condition, and later scrapped. * ROKS ''Jeong Buk'' (DD-916) was on display inGangneung
Gangneung () is a municipal city in the province of Gangwon-do, on the east coast of South Korea. It has a population of 213,658 (as of 2017).Gangneung City (2003)Population & Households. Retrieved January 14, 2006. Gangneung is the economic ...
, South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
from 1999 to 2021, when she was scrapped.
* ORP ''Burza'' was on display in Gdynia, Poland from 1951 to 1977, until she was replaced in the role by ''Blyskawica'' due to her deteriorating condition, and later scrapped.
* was on display in Washington, D. C. from 1984 to 2015, until she was closed to make room for a bridge expansion. She is currently in lay up in Philadelphia awaiting scrapping.
See also
* List of destroyer classes *United States Navy 1975 ship reclassification
The United States Navy reclassified many of its surface vessels in 1975, changing terminology and hull classification symbols for cruisers, frigates, and ocean escorts.
Classification prior to 1975
From the 1950s to 1975, the US Navy had three ...
* Bombardment of Cherbourg
The bombardment of Cherbourg took place on June 25, 1944, during World War II, when ships from the United States Navy and the British Royal Navy attacked German fortifications in and near the city, firing in support of U.S. Army units that were ...
* List of destroyers of the Second World War
This is a list of destroyers of the Second World War.
The List of ships of the Second World War contains major military vessels of the war, arranged alphabetically and by type. The list includes armed vessels that served during the war and in the ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* Evans, David C. ''Kaigun'': Strategy, Tactics, and Technology in the Imperial Japanese Navy'', 1887–1941,Mark R. Peattie
Mark R. Peattie (May 3, 1930 in Nice, France – January 22, 2014 in San Rafael, California) was an American academic and Japanologist. Peattie was a specialist in modern Japanese military, naval, and imperial history.Hoover Institution, Stanfo ...
. Naval Institute Press, Annapolis, Maryland
* Gardiner, Robert (Editor). ''Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships (1860–1905)'': Naval Institute Press, 1985.
* Gove, Philip Babock (Editor in Chief). ''Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language Unabridged.'' (2002) Merriam-Webster Inc., Publishers, Massachusetts, USA.
* Grant, R. Captain. ''Before Port Arthur in a Destroyer; The Personal Diary of a Japanese Naval Officer.'' London, John Murray; first and second editions published in 1907.
* Howe, Christopher. ''Origins of Japanese Trade Supremacy: Development and Technology in Asia from 1540 to the Pacific War,'' The University of Chicago Press,
* Jentschura, Hansgeorg. ''Warships of the Imperial Japanese Navy, 1869–1945.'' United States Naval Institute, Annapolis, Maryland, 1977. .
* Lyon, David, ''The First Destroyers.'' Chatham Publishing, 1 & 2 Faulkner's Alley, Cowcross St. London, Great Britain; 1996. .
* Sanders, Michael S. (2001) The Yard: Building a Destroyer at the Bath Iron Works
', HarperCollins, * Simpson, Richard V. ''Building The Mosquito Fleet, The US Navy's First Torpedo Boats.'' Arcadia Publishing, (2001); Charleston, South Carolina, USA. . * Preston, Anthony. ''Destroyers'', Bison Books (London) 1977. * Van der Vat, Dan. ''The Atlantic Campaign''.
External links
{{Authority control Ship types