Dental Alveolus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
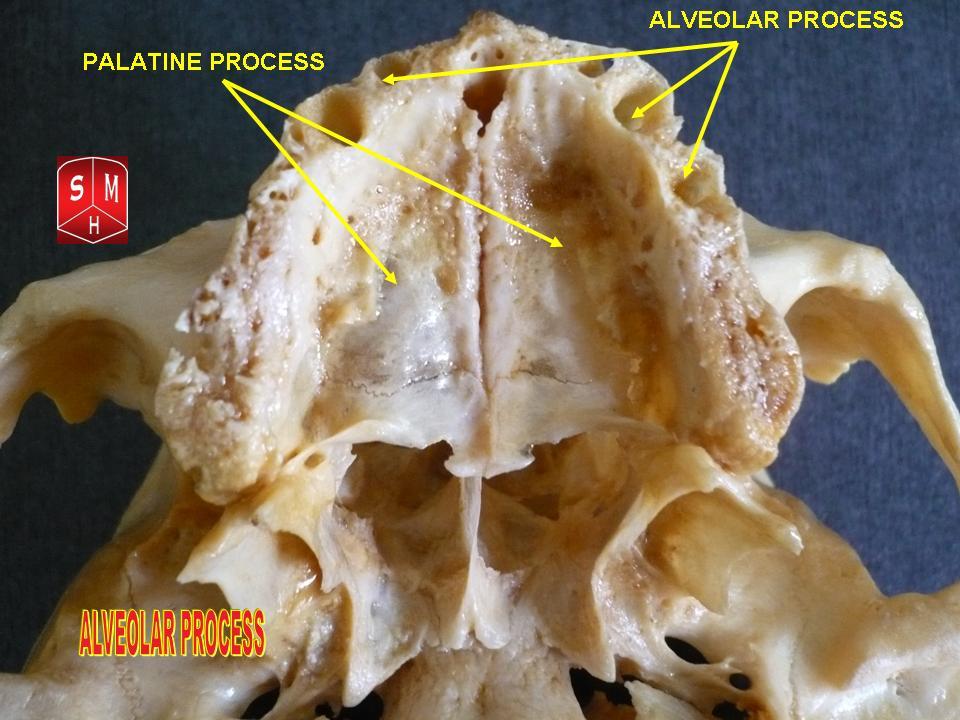 Dental alveoli (singular ''alveolus'') are sockets in the
Dental alveoli (singular ''alveolus'') are sockets in the
CRISP Database
{{Authority control Parts of tooth
 Dental alveoli (singular ''alveolus'') are sockets in the
Dental alveoli (singular ''alveolus'') are sockets in the jaw
The jaw is any opposable articulated structure at the entrance of the mouth, typically used for grasping and manipulating food. The term ''jaws'' is also broadly applied to the whole of the structures constituting the vault of the mouth and serv ...
s in which the roots of teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tear ...
are held in the alveolar process
The alveolar process () or alveolar bone is the thickened ridge of bone that contains the tooth sockets on the jaw bones (in humans, the maxilla and the mandible). The structures are covered by gums as part of the oral cavity.
The synonymous ter ...
with the periodontal ligament
The periodontal ligament, commonly abbreviated as the PDL, is a group of specialized connective tissue fibers that essentially attach a tooth to the alveolar bone within which it sits. It inserts into root cementum one side and onto alveolar b ...
. The lay term for dental alveoli is tooth sockets. A joint
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw ...
that connects the roots of the teeth and the alveolus is called ''gomphosis
In anatomy, fibrous joints are joints connected by fibrous tissue, consisting mainly of collagen. These are fixed joints where bones are united by a layer of white fibrous tissue of varying thickness. In the skull the joints between the bones are ...
'' (plural ''gomphoses''). Alveolar bone is the bone that surrounds the roots of the teeth forming bone sockets.
In mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s, tooth sockets are found in the maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The t ...
, the premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has b ...
, and the mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movabl ...
.Etymology
1706, "a hollow," especially "the socket of a tooth," from Latin alveolus "a tray, trough, basin; bed of a small river; small hollow or cavity," diminutive of alvus "belly, stomach, paunch, bowels; hold of a ship," from PIE root *aulo- "hole, cavity" (source also of Greek aulos "flute, tube, pipe;" Serbo-Croatian, Polish, Russian ulica "street," originally "narrow opening;" Old Church Slavonic uliji, Lithuanian aulys "beehive" (hollow trunk), Armenian yli "pregnant"). The word was extended in 19c. anatomy to other small pits, sockets, or cells.Socket preservation
Socket preservation
Socket preservation or alveolar ridge preservation is a procedure to reduce Dental alveolus, bone loss after tooth extraction. After tooth extraction, the jaw bone has a natural tendency to become bone remodeling, narrow, and lose its original sha ...
or alveolar ridge preservation (ARP) is a procedure to reduce bone loss after tooth extraction
A dental extraction (also referred to as tooth extraction, exodontia, exodontics, or informally, tooth pulling) is the removal of teeth from the dental alveolus (socket) in the alveolar bone. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reason ...
to preserve the dental alveolus (tooth socket) in the alveolar bone
The alveolar process () or alveolar bone is the thickened ridge of bone that contains the tooth sockets on the jaw bones (in humans, the maxilla and the mandible). The structures are covered by gums as part of the oral cavity.
The synonymous ter ...
. A platelet-rich fibrin Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) or leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF) is a second-generation PRP where autologous platelets and leukocytes are present in a complex fibrin matrix to accelerate the healing of soft and hard tissue and is used as ...
(PRF) membrane containing bone growth enhancing elements can be stitched over the wound or a graft material or scaffold is placed in the socket of an extracted tooth. The socket is then directly closed with stitches or covered with a non-resorbable or resorbable membrane and sutured.
Pathology
The swelling of the dental alveoli can result in alveolitis, causing pain and discomfort to the mouth.See also
*Alveolar ridge
The alveolar process () or alveolar bone is the thickened ridge of bone that contains the tooth sockets on the jaw bones (in humans, the maxilla and the mandible). The structures are covered by gums as part of the oral cavity.
The synonymous ter ...
* Polyphyodont
A polyphyodont is any animal whose teeth are continually replaced. In contrast, diphyodonts are characterized by having only two successive sets of teeth.
Polyphyodonts include most toothed fishes, many reptiles such as crocodiles and geckos, and ...
References
External links
* National Institute of HealthCRISP Database
{{Authority control Parts of tooth