Dengue Fever on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne
 Dengue fever virus (DENV) is an
Dengue fever virus (DENV) is an
 Dengue virus is primarily transmitted by '' Aedes'' mosquitos, particularly '' A. aegypti''. WHO (2009), pp. 14–16. These mosquitos usually live between the
Dengue virus is primarily transmitted by '' Aedes'' mosquitos, particularly '' A. aegypti''. WHO (2009), pp. 14–16. These mosquitos usually live between the
 It is not entirely clear why secondary infection with a different strain of dengue virus places people at risk of dengue hemorrhagic fever and dengue shock syndrome. The most widely accepted hypothesis is that of
It is not entirely clear why secondary infection with a different strain of dengue virus places people at risk of dengue hemorrhagic fever and dengue shock syndrome. The most widely accepted hypothesis is that of
 The diagnosis of dengue fever may be confirmed by microbiological laboratory testing. This can be done by virus isolation in
The diagnosis of dengue fever may be confirmed by microbiological laboratory testing. This can be done by virus isolation in
 Prevention depends on control of and protection from the bites of the mosquito that transmits it. WHO (2009), pp. 59–64. The World Health Organization recommends an Integrated Vector Control program consisting of five elements:
# Advocacy, social mobilization and legislation to ensure that public health bodies and communities are strengthened;
# Collaboration between the health and other sectors (public and private);
# An integrated approach to disease control to maximize the use of resources;
# Evidence-based decision making to ensure any interventions are targeted appropriately; and
# Capacity-building to ensure an adequate response to the local situation.
The primary method of controlling ''A. aegypti'' is by eliminating its
Prevention depends on control of and protection from the bites of the mosquito that transmits it. WHO (2009), pp. 59–64. The World Health Organization recommends an Integrated Vector Control program consisting of five elements:
# Advocacy, social mobilization and legislation to ensure that public health bodies and communities are strengthened;
# Collaboration between the health and other sectors (public and private);
# An integrated approach to disease control to maximize the use of resources;
# Evidence-based decision making to ensure any interventions are targeted appropriately; and
# Capacity-building to ensure an adequate response to the local situation.
The primary method of controlling ''A. aegypti'' is by eliminating its
 International Anti-Dengue Day is observed every year on 15 June. The idea was first agreed upon in 2010 with the first event held in
International Anti-Dengue Day is observed every year on 15 June. The idea was first agreed upon in 2010 with the first event held in
 As of 2019, dengue was
As of 2019, dengue was
tropical disease
Tropical diseases are diseases that are prevalent in or unique to tropical and subtropical regions. The diseases are less prevalent in temperate climates, due in part to the occurrence of a cold season, which controls the insect population by f ...
caused by the dengue virus
''Dengue virus'' (DENV) is the cause of dengue fever. It is a mosquito-borne, single positive-stranded RNA virus of the family '' Flaviviridae''; genus '' Flavivirus''. Four serotypes of the virus have been found, a reported fifth has yet to ...
. Symptoms typically begin three to fourteen days after infection. These may include a high fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
, headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a result ...
, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenter ...
, muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of mus ...
and joint pains, and a characteristic skin itching and skin rash. Recovery generally takes two to seven days. In a small proportion of cases, the disease develops into a more severe dengue hemorrhagic fever, resulting in bleeding, low levels of blood platelets and blood plasma
Blood plasma is a light amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but contains proteins and other constituents of whole blood in suspension. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is the int ...
leakage, or into dengue shock syndrome, where dangerously low blood pressure occurs.
Dengue is spread by several species of female mosquitoes of the '' Aedes'' genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
, principally ''Aedes aegypti
''Aedes aegypti'', the yellow fever mosquito, is a mosquito that can spread dengue fever, chikungunya, Zika fever, Mayaro and yellow fever viruses, and other disease agents. The mosquito can be recognized by black and white markings on its l ...
''. The virus has five serotype
A serotype or serovar is a distinct variation within a species of bacteria or virus or among immune cells of different individuals. These microorganisms, viruses, or cells are classified together based on their surface antigens, allowing the ep ...
s; infection with one type usually gives lifelong immunity
Immunity may refer to:
Medicine
* Immunity (medical), resistance of an organism to infection or disease
* ''Immunity'' (journal), a scientific journal published by Cell Press
Biology
* Immune system
Engineering
* Radiofrequence immunity de ...
to that type, but only short-term immunity to the others. Subsequent infection with a different type increases the risk of severe complications. A number of tests are available to confirm the diagnosis including detecting antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of ...
to the virus or its RNA.
A vaccine for dengue fever has been approved and is commercially available in a number of countries. As of 2018, the vaccine is only recommended in individuals who have been previously infected, or in populations with a high rate of prior infection by age nine. Other methods of prevention include reducing mosquito habitat and limiting exposure to bites. This may be done by getting rid of or covering standing water and wearing clothing that covers much of the body. Treatment of acute dengue is supportive and includes giving fluid either by mouth or intravenously for mild or moderate disease. For more severe cases, blood transfusion
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood products into a person's circulation intravenously. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of the blood. Early transfusions used whole blood, but mo ...
may be required. Paracetamol
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol and Panadol.
At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature; it is inferio ...
(acetaminophen) is recommended instead of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration o ...
s (NSAIDs) for fever reduction and pain relief
Pain management is an aspect of medicine and health care involving relief of pain (pain relief, analgesia, pain control) in various dimensions, from acute and simple to chronic and challenging. Most physicians and other health professional ...
in dengue due to an increased risk of bleeding from NSAID use.
The earliest descriptions of an outbreak date from 1779. Its viral cause and spread were understood by the early 20th century. Dengue has become a global problem since the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
and is common
Common may refer to:
Places
* Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland
* Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts
* Cambridge Common, common land area in Cambridge, Massachusetts
* Clapham Common, originally ...
in more than 120 countries, mainly in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
, South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;; ...
and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
. About 390 million people are infected per year, about half a million require hospital admission, and approximately 40,000 die. In 2019, a significant increase in the number of cases was seen. Apart from eliminating the mosquitos, work is ongoing for medication targeted directly at the virus. It is classified as a neglected tropical disease
Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a diverse group of tropical infections that are common in low-income populations in developing regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. They are caused by a variety of pathogens, such as viruses, bac ...
.
Signs and symptoms
Typically, people infected with dengue virus areasymptomatic
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered a ...
(80%) or have only mild symptoms such as an uncomplicated fever. Others have more severe illness (5%), and in a small proportion it is life-threatening. The incubation period (time between exposure and onset of symptoms) ranges from 3 to 14 days, but most often it is 4 to 7 days. Therefore, travelers returning from endemic areas are unlikely to have dengue fever if symptoms start more than 14 days after arriving home. Children often experience symptoms similar to those of the common cold
The common cold or the cold is a viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract that primarily affects the respiratory mucosa of the nose, throat, sinuses, and larynx. Signs and symptoms may appear fewer than two days after expos ...
and gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea and gastro, is an inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of energy, and dehydr ...
(vomiting and diarrhea) and have a greater risk of severe complications, though initial symptoms are generally mild but include high fever.
Clinical course
The characteristic symptoms of dengue are sudden-onset fever, headache (typically located behind the eyes), muscle and joint pains, and a rash. An alternative name for dengue, "breakbone fever", comes from the associated muscle and joint pains. The course of infection is divided into three phases: febrile, critical, and recovery. WHO (2009), pp. 25–27. The febrile phase involves high fever, potentially over , and is associated with generalized pain and a headache; this usually lasts two to seven days. Nausea and vomiting may also occur. A rash occurs in 50–80% of those with symptoms in the first or second day of symptoms as flushed skin, or later in the course of illness (days 4–7), as a measles-like rash. A rash described as "islands of white in a sea of red" has also been observed. Some petechiae (small red spots that do not disappear when the skin is pressed, which are caused by broken capillaries) can appear at this point, as may some mild bleeding from the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose. The fever itself is classically biphasic or saddleback in nature, breaking and then returning for one or two days. In some people, the disease proceeds to a critical phase as fever resolves. During this period, there is leakage of plasma from the blood vessels, typically lasting one to two days. This may result in fluid accumulation in the chest andabdominal cavity
The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans and many other animals that contains many organs. It is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roof is th ...
as well as depletion of fluid from the circulation and decreased blood supply to vital organs. There may also be organ dysfunction and severe bleeding, typically from the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and ...
. Shock
Shock may refer to:
Common uses Collective noun
*Shock, a historic commercial term for a group of 60, see English numerals#Special names
* Stook, or shock of grain, stacked sheaves
Healthcare
* Shock (circulatory), circulatory medical emerge ...
(dengue shock syndrome) and hemorrhage (dengue hemorrhagic fever) occur in less than 5% of all cases of dengue; however, those who have previously been infected with other serotype
A serotype or serovar is a distinct variation within a species of bacteria or virus or among immune cells of different individuals. These microorganisms, viruses, or cells are classified together based on their surface antigens, allowing the ep ...
s of dengue virus ("secondary infection") are at an increased risk. This critical phase, while rare, occurs relatively more commonly in children and young adults.
The recovery phase occurs next, with resorption of the leaked fluid into the bloodstream. This usually lasts two to three days. The improvement is often striking, and can be accompanied with severe itching and a slow heart rate. Another rash may occur with either a maculopapular or a vasculitic appearance, which is followed by peeling of the skin. During this stage, a fluid overload
Hypervolemia, also known as fluid overload, is the medical condition where there is too much fluid in the blood. The opposite condition is hypovolemia, which is too little fluid volume in the blood. Fluid volume excess in the intravascular comp ...
state may occur; if it affects the brain, it may cause a reduced level of consciousness or seizures
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with lo ...
. A feeling of fatigue
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve ...
may last for weeks in adults.
Associated problems
Dengue can occasionally affect several otherbody systems
A biological system is a complex network which connects several biologically relevant entities. Biological organization spans several scales and are determined based different structures depending on what the system is. Examples of biological syst ...
, either in isolation or along with the classic dengue symptoms. A decreased level of consciousness occurs in 0.5–6% of severe cases, which is attributable either to inflammation of the brain by the virus or indirectly as a result of impairment of vital organs, for example, the liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it i ...
.
Other neurological disorders have been reported in the context of dengue, such as transverse myelitis and Guillain–Barré syndrome. Infection of the heart and acute liver failure are among the rarer complications.
A pregnant woman who develops dengue is at higher risk of miscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion and pregnancy loss, is the death of an embryo or fetus before it is able to survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks of gestation is defined by ESHRE as biochemica ...
, low birth weight
Low birth weight (LBW) is defined by the World Health Organization as a birth weight of an
infant of or less, regardless of gestational age. Infants born with LBW have added health risks which require close management, often in a neonatal int ...
birth, and premature birth
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is between ...
.
Cause
Virology
 Dengue fever virus (DENV) is an
Dengue fever virus (DENV) is an RNA virus
An RNA virus is a virusother than a retrovirusthat has ribonucleic acid ( RNA) as its genetic material. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA virus ...
of the family '' Flaviviridae''; genus '' Flavivirus''. Other members of the same genus include yellow fever virus, West Nile virus
West Nile virus (WNV) is a single-stranded RNA virus that causes West Nile fever. It is a member of the family '' Flaviviridae'', from the genus '' Flavivirus'', which also contains the Zika virus, dengue virus, and yellow fever virus. The v ...
, Zika virus
''Zika virus'' (ZIKV; pronounced or ) is a member of the virus family (biology), family ''Flaviviridae''. It is mosquito-borne disease, spread by daytime-active ''Aedes'' mosquitoes, such as ''Aedes aegypti, A. aegypti'' and ''Aedes albopict ...
, St. Louis encephalitis virus, Japanese encephalitis virus, tick-borne encephalitis virus, Kyasanur forest disease virus, and Omsk hemorrhagic fever virus
Omsk (; rus, Омск, p=omsk) is the administrative center and largest city of Omsk Oblast, Russia. It is situated in southwestern Siberia, and has a population of over 1.1 million. Omsk is the third largest city in Siberia after Novosibir ...
. Most are transmitted by arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
s (mosquitos or tick
Ticks (order Ixodida) are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living ...
s), and are therefore also referred to as arboviruses (''ar''thropod-''bo''rne viruses).
The dengue virus genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
(genetic material) contains about 11,000 nucleotide bases, which code
In communications and information processing, code is a system of rules to convert information—such as a letter, word, sound, image, or gesture—into another form, sometimes shortened or secret, for communication through a communicati ...
for the three different types of protein molecules (C, prM and E) that form the virus particle
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky' ...
and seven other non-structural protein molecules (NS1, NS2a, NS2b, NS3, NS4a, NS4b, NS5) that are found in infected host cells only and are required for replication of the virus. There are five strains of the virus, called serotype
A serotype or serovar is a distinct variation within a species of bacteria or virus or among immune cells of different individuals. These microorganisms, viruses, or cells are classified together based on their surface antigens, allowing the ep ...
s, of which the first four are referred to as DENV-1, DENV-2, DENV-3 and DENV-4. The fifth type was announced in 2013. The distinctions between the serotypes are based on their antigenicity.
Transmission
 Dengue virus is primarily transmitted by '' Aedes'' mosquitos, particularly '' A. aegypti''. WHO (2009), pp. 14–16. These mosquitos usually live between the
Dengue virus is primarily transmitted by '' Aedes'' mosquitos, particularly '' A. aegypti''. WHO (2009), pp. 14–16. These mosquitos usually live between the latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north ...
s of 35° North and 35° South below an elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § ...
of . They typically bite during the early morning and in the evening, but they may bite and thus spread infection at any time of day. Other ''Aedes'' species that transmit the disease include '' A. albopictus'', '' A. polynesiensis'' and '' A. scutellaris''. Humans are the primary host of the virus, but it also circulates in nonhuman primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter includin ...
s. An infection can be acquired via a single bite. A female mosquito that takes a blood meal from a person infected with dengue fever, during the initial 2- to 10-day febrile period, becomes itself infected with the virus in the cells lining its gut. About 8–10 days later, the virus spreads to other tissues including the mosquito's salivary glands and is subsequently released into its saliva. The virus seems to have no detrimental effect on the mosquito, which remains infected for life. ''Aedes aegypti'' is particularly involved, as it prefers to lay its eggs in artificial water containers, to live in close proximity to humans, and to feed on people rather than other vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with ...
s.
Dengue can also be transmitted via infected blood products and through organ donation. In countries such as Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
, where dengue is endemic, the risk is estimated to be between 1.6 and 6 per 10,000 transfusions. Vertical transmission Vertical transmission of symbionts is the transfer of a microbial symbiont from the parent directly to the offspring. Many metazoan species carry symbiotic bacteria which play a mutualistic, commensal, or parasitic role. A symbiont is acquir ...
(from mother to child) during pregnancy or at birth has been reported. Other person-to-person modes of transmission, including sexual transmission, have also been reported, but are very unusual. The genetic variation in dengue viruses is region specific, suggestive that establishment into new territories is relatively infrequent, despite dengue emerging in new regions in recent decades.
Predisposition
Severe disease is more common in babies and young children, and in contrast to many other infections, it is more common in children who are relatively well nourished. Otherrisk factor
In epidemiology, a risk factor or determinant is a variable associated with an increased risk of disease or infection.
Due to a lack of harmonization across disciplines, determinant, in its more widely accepted scientific meaning, is often u ...
s for severe disease include female sex, high body mass index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass ( weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is expressed in units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms and ...
, and viral load. While each serotype can cause the full spectrum of disease, virus strain is a risk factor. Infection with one serotype is thought to produce lifelong immunity to that type, but only short-term protection against the other three. The risk of severe disease from secondary infection increases if someone previously exposed to serotype DENV-1 contracts serotype DENV-2 or DENV-3, or if someone previously exposed to DENV-3 acquires DENV-2. Dengue can be life-threatening in people with chronic diseases such as diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
and asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, co ...
.
Polymorphisms (normal variations) in particular gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s have been linked with an increased risk of severe dengue complications. Examples include the genes coding for the proteins TNFα
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
, mannan-binding lectin, CTLA4
CTLA-4 or CTLA4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4), also known as CD152 (cluster of differentiation 152), is a protein receptor that functions as an immune checkpoint and downregulates immune responses. CTLA-4 is constitutively expre ...
, TGFβ, DC-SIGN, PLCE1
1-Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase epsilon-1 (PLCE1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PLCE1'' gene. This gene encodes a phospholipase enzyme (PLCE1) that catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bi ...
, and particular forms of human leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system or complex is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans which encode cell-surface proteins responsible for the regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of th ...
from gene variations of HLA-B
HLA-B (major histocompatibility complex, class I, B) is a human gene that provides instructions for making a protein that plays a critical role in the immune system. HLA-B is part of a family of genes called the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) c ...
. A common genetic abnormality, especially in Africans, known as glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, appears to increase the risk. Polymorphisms in the genes for the vitamin D receptor
The vitamin D receptor (VDR also known as the calcitriol receptor) is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors. Calcitriol (the active form of vitamin D, 1,25-(OH)2vitamin D3) binds to VDR, which then forms a heterod ...
and FcγR seem to offer protection against severe disease in secondary dengue infection.
Mechanism
When a mosquito carrying dengue virus bites a person, the virus enters the skin together with the mosquito's saliva. It binds to and enters white blood cells, and reproduces inside the cells while they move throughout the body. The white blood cells respond by producing several signaling proteins, such ascytokines
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
and interferons, which are responsible for many of the symptoms, such as the fever, the flu-like symptoms, and the severe pains. In severe infection, the virus production inside the body is greatly increased, and many more organs (such as the liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it i ...
and the bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
) can be affected. Fluid from the bloodstream leaks through the wall of small blood vessels into body cavities due to capillary permeability
Vascular permeability, often in the form of capillary permeability or microvascular permeability, characterizes the capacity of a blood vessel wall to allow for the flow of small molecules (drugs, nutrients, water, ions) or even whole cells (lymph ...
. As a result, less blood circulates in the blood vessels, and the blood pressure becomes so low that it cannot supply sufficient blood to vital organs. Furthermore, dysfunction of the bone marrow due to infection of the stromal cells leads to reduced numbers of platelets, which are necessary for effective blood clotting; this increases the risk of bleeding, the other major complication of dengue fever.
Viral replication
Once inside the skin, dengue virus binds to Langerhans cells (a population ofdendritic cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. Th ...
s in the skin that identifies pathogens). The virus enters the cells through binding between viral proteins and membrane proteins on the Langerhans cell, specifically, the C-type lectins called DC-SIGN, mannose receptor and CLEC5A
C-type lectin domain family 5 member A (CLEC5A), also known as C-type lectin superfamily member 5 (CLECSF5) and myeloid DAP12-associating lectin 1 (MDL-1) is a C-type lectin that in humans is encoded by the ''CLEC5A'' gene.
Structurally MDL-1 is ...
. DC-SIGN, a non-specific receptor for foreign material on dendritic cells, seems to be the main point of entry. The dendritic cell moves to the nearest lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
. Meanwhile, the virus genome is translated in membrane-bound vesicles on the cell's endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum ...
, where the cell's protein synthesis apparatus produces new viral proteins that replicate the viral RNA and begin to form viral particles. Immature virus particles are transported to the Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles i ...
, the part of the cell where some of the proteins receive necessary sugar chains (glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glyco ...
s). The now mature new viruses are released by exocytosis
Exocytosis () is a form of active transport and bulk transport in which a cell transports molecules (e.g., neurotransmitters and proteins) out of the cell ('' exo-'' + ''cytosis''). As an active transport mechanism, exocytosis requires the use ...
. They are then able to enter other white blood cells, such as monocyte
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and conventional dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also ...
s and macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
s.
The initial reaction of infected cells is to produce interferon
Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten th ...
, a cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in au ...
that raises many defenses against viral infection through the innate immune system
The innate, or nonspecific, immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies (the other being the adaptive immune system) in vertebrates. The innate immune system is an older evolutionary defense strategy, relatively speaking, and is the ...
by augmenting the production of a large group of proteins mediated by the JAK-STAT pathway
The JAK-STAT signaling pathway is a chain of interactions between proteins in a cell, and is involved in processes such as immunity, cell division, cell death, and tumour formation. The pathway communicates information from chemical signals out ...
. Some serotypes of the dengue virus appear to have mechanisms to slow down this process. Interferon also activates the adaptive immune system
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system ...
, which leads to the generation of antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of ...
against the virus as well as T cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
s that directly attack any cell infected with the virus. Various antibodies are generated; some bind closely to the viral proteins and target them for phagocytosis (ingestion by specialized cells and destruction), but some bind the virus less well and appear instead to deliver the virus into a part of the phagocytes where it is not destroyed but can replicate further.
Severe disease
antibody-dependent enhancement
Antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE), sometimes less precisely called immune enhancement or disease enhancement, is a phenomenon in which binding of a virus to suboptimal antibodies enhances its entry into host cells, followed by its repl ...
(ADE). The exact mechanism behind ADE is unclear. It may be caused by poor binding of non-neutralizing antibodies and delivery into the wrong compartment of white blood cells that have ingested the virus for destruction. There is a suspicion that ADE is not the only mechanism underlying severe dengue-related complications, and various lines of research have implied a role for T cells and soluble factors such as cytokines and the complement system
The complement system, also known as complement cascade, is a part of the immune system that enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promote inflammation, and ...
.
Severe disease is marked by the problems of capillary permeability (an allowance of fluid and protein normally contained within the blood to pass) and disordered blood clotting
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechan ...
. These changes appear associated with a disordered state of the endothelial glycocalyx
The glycocalyx, also known as the pericellular matrix, is a glycoprotein and glycolipid covering that surrounds the cell membranes of bacteria, epithelial cells, and other cells. In 1970, Martinez-Palomo discovered the cell coating in animal c ...
, which acts as a molecular filter of blood components. Leaky capillaries (and the critical phase) are thought to be caused by an immune system response. Other processes of interest include infected cells that become necrotic—which affect both coagulation and fibrinolysis (the opposing systems of blood clotting and clot degradation)—and low platelets in the blood, also a factor in normal clotting.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of dengue is typically made clinically, on the basis of reported symptoms andphysical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the pati ...
; this applies especially in endemic areas. However, early disease can be difficult to differentiate from other viral infections. A probable diagnosis is based on the findings of fever plus two of the following: nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of th ...
and vomiting, rash, generalized pains, low white blood cell count, positive tourniquet test, or any warning sign (see table) in someone who lives in an endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
area. Warning signs typically occur before the onset of severe dengue. The tourniquet test, which is particularly useful in settings where no laboratory investigations are readily available, involves the application of a blood pressure cuff at between the diastolic and systolic pressure for five minutes, followed by the counting of any petechial
A petechia () is a small red or purple spot (≤4 mm in diameter) that can appear on the skin, conjunctiva, retina, and mucous membranes which is caused by haemorrhage of capillaries. The word is derived from Italian , 'freckle,' of obscure ori ...
hemorrhages; a higher number makes a diagnosis of dengue more likely with the cut off being more than 10 to 20 per 1 inch2 (6.25 cm2).
The diagnosis should be considered in anyone who develops a fever within two weeks of being in the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also refer ...
or subtropics
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° nort ...
. It can be difficult to distinguish dengue fever and chikungunya
Chikungunya is an infection caused by the ''Chikungunya virus'' (CHIKV). Symptoms include fever and joint pains. These typically occur two to twelve days after exposure. Other symptoms may include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, and a r ...
, a similar viral infection that shares many symptoms and occurs in similar parts of the world to dengue. Often, investigations are performed to exclude other conditions that cause similar symptoms, such as malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. ...
, leptospirosis
Leptospirosis is a blood infection caused by the bacteria '' Leptospira''. Signs and symptoms can range from none to mild (headaches, muscle pains, and fevers) to severe ( bleeding in the lungs or meningitis). Weil's disease, the acute, sever ...
, viral hemorrhagic fever
Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) are a diverse group of animal and human illnesses in which fever and hemorrhage are caused by a viral infection. VHFs may be caused by five distinct families of RNA viruses: the families ''Filoviridae'', ''Flavi ...
, typhoid fever
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by '' Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over severa ...
, meningococcal disease
Meningococcal disease describes infections caused by the bacterium ''Neisseria meningitidis'' (also termed meningococcus). It has a high mortality rate if untreated but is vaccine-preventable. While best known as a cause of meningitis, it can al ...
, measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
, and influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptom ...
. Zika fever
Zika fever, also known as Zika virus disease or simply Zika, is an infectious disease caused by the Zika virus. Most cases have no symptoms, but when present they are usually mild and can resemble dengue fever. Symptoms may include fever, red ...
also has similar symptoms as dengue.
The earliest change detectable on laboratory investigations is a low white blood cell count, which may then be followed by low platelets and metabolic acidosis
Metabolic acidosis is a serious electrolyte disorder characterized by an imbalance in the body's acid-base balance. Metabolic acidosis has three main root causes: increased acid production, loss of bicarbonate, and a reduced ability of the kidneys ...
. A moderately elevated level of aminotransferase
Transaminases or aminotransferases are enzymes that catalyze a transamination reaction between an amino acid and an α-keto acid. They are important in the synthesis of amino acids, which form proteins.
Function and mechanism
An amino acid c ...
( AST and ALT
Alt or ALT may refer to:
Abbreviations for words
* Alt account, an alternative online identity also known as a sock puppet account
* Alternate character, in online gaming
* Alternate route, type of highway designation
* Alternating group, mathema ...
) from the liver is commonly associated with low platelets and white blood cells. In severe disease, plasma leakage results in hemoconcentration (as indicated by a rising hematocrit) and hypoalbuminemia. Pleural effusions or ascites can be detected by physical examination when large, but the demonstration of fluid on ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
may assist in the early identification of dengue shock syndrome. The use of ultrasound is limited by lack of availability in many settings. Dengue shock syndrome is present if pulse pressure drops to ≤ 20 mm Hg along with peripheral vascular collapse. Peripheral vascular collapse is determined in children via delayed capillary refill
Capillary refill time (CRT) is defined as the time taken for color to return to an external capillary bed after pressure is applied to cause blanching. It can be measured by holding a hand higher than heart-level and pressing the soft pad of a f ...
, rapid heart rate, or cold extremities. While warning signs are an important aspect for early detection of potential serious disease, the evidence for any specific clinical or laboratory marker is weak.
Classification
TheWorld Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
's 2009 classification divides dengue fever into two groups: uncomplicated and severe. WHO (2009), pp. 10–11. This replaces the 1997 WHO classification, which needed to be simplified as it had been found to be too restrictive, though the older classification is still widely used including by the World Health Organization's Regional Office for Southeast Asia . Severe dengue is defined as that associated with severe bleeding, severe organ dysfunction, or severe plasma leakage while all other cases are uncomplicated. The 1997 classification divided dengue into an undifferentiated fever, dengue fever, and dengue hemorrhagic fever. Dengue hemorrhagic fever was subdivided further into grades I–IV. Grade I is the presence only of easy bruising or a positive tourniquet test in someone with fever, grade II is the presence of spontaneous bleeding into the skin and elsewhere, grade III is the clinical evidence of shock, and grade IV is shock so severe that blood pressure and pulse cannot be detected. Grades III and IV are referred to as "dengue shock syndrome".
Laboratory tests
 The diagnosis of dengue fever may be confirmed by microbiological laboratory testing. This can be done by virus isolation in
The diagnosis of dengue fever may be confirmed by microbiological laboratory testing. This can be done by virus isolation in cell culture
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. The term "tissue culture" was coined by American pathologist Montrose Thomas Burrows. This tec ...
s, nucleic acid detection by PCR, viral antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respon ...
detection (such as for NS1) or specific antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of ...
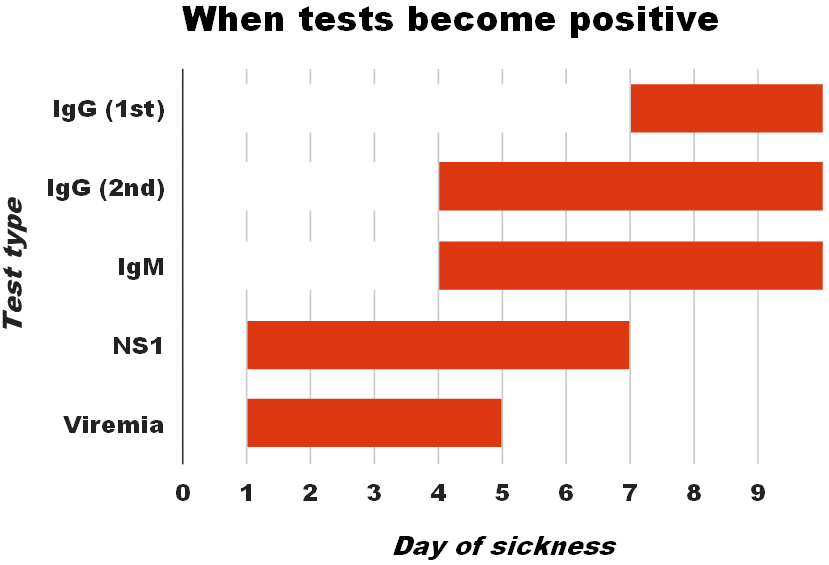
(serology). WHO (2009), pp. 90–95. Virus isolation and nucleic acid detection are more accurate than antigen detection, but these tests are not widely available due to their greater cost. Detection of NS1 during the febrile phase of a primary infection may be greater than 90% sensitive however is only 60–80% in subsequent infections. All tests may be negative in the early stages of the disease. PCR and viral antigen detection are more accurate in the first seven days. In 2012 a PCR test was introduced that can run on equipment used to diagnose influenza; this is likely to improve access to PCR-based diagnosis.
These laboratory tests are only of diagnostic value during the acute phase of the illness with the exception of serology. Tests for dengue virus-specific antibodies, types IgG
Immunoglobulin G (Ig G) is a type of antibody. Representing approximately 75% of serum antibodies in humans, IgG is the most common type of antibody found in blood circulation. IgG molecules are created and released by plasma B cells. Each IgG an ...
and IgM, can be useful in confirming a diagnosis in the later stages of the infection. Both IgG and IgM are produced after 5–7 days. The highest levels ( titres) of IgM are detected following a primary infection, but IgM is also produced in reinfection. IgM becomes undetectable 30–90 days after a primary infection, but earlier following re-infections. IgG, by contrast, remains detectable for over 60 years and, in the absence of symptoms, is a useful indicator of past infection. After a primary infection, IgG reaches peak levels in the blood after 14–21 days. In subsequent re-infections, levels peak earlier and the titres are usually higher. Both IgG and IgM provide protective immunity to the infecting serotype of the virus. In testing for IgG and IgM antibodies there may be cross-reactivity with other flaviviruses which may result in a false positive after recent infections or vaccinations with yellow fever virus or Japanese encephalitis. The detection of IgG alone is not considered diagnostic unless blood samples are collected 14 days apart and a greater than fourfold increase in levels of specific IgG is detected. In a person with symptoms, the detection of IgM is considered diagnostic.
Prevention
 Prevention depends on control of and protection from the bites of the mosquito that transmits it. WHO (2009), pp. 59–64. The World Health Organization recommends an Integrated Vector Control program consisting of five elements:
# Advocacy, social mobilization and legislation to ensure that public health bodies and communities are strengthened;
# Collaboration between the health and other sectors (public and private);
# An integrated approach to disease control to maximize the use of resources;
# Evidence-based decision making to ensure any interventions are targeted appropriately; and
# Capacity-building to ensure an adequate response to the local situation.
The primary method of controlling ''A. aegypti'' is by eliminating its
Prevention depends on control of and protection from the bites of the mosquito that transmits it. WHO (2009), pp. 59–64. The World Health Organization recommends an Integrated Vector Control program consisting of five elements:
# Advocacy, social mobilization and legislation to ensure that public health bodies and communities are strengthened;
# Collaboration between the health and other sectors (public and private);
# An integrated approach to disease control to maximize the use of resources;
# Evidence-based decision making to ensure any interventions are targeted appropriately; and
# Capacity-building to ensure an adequate response to the local situation.
The primary method of controlling ''A. aegypti'' is by eliminating its habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
s. This is done by getting rid of open sources of water, or if this is not possible, by adding insecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed t ...
s or biological control agents to these areas. Generalized spraying with organophosphate
In organic chemistry, organophosphates (also known as phosphate esters, or OPEs) are a class of organophosphorus compounds with the general structure , a central phosphate molecule with alkyl or aromatic substituents. They can be considered ...
or pyrethroid
A pyrethroid is an organic compound similar to the natural pyrethrins, which are produced by the flowers of pyrethrums ('' Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium'' and '' C. coccineum''). Pyrethroids are used as commercial and household insecticides. ...
insecticides, while sometimes done, is not thought to be effective. Reducing open collections of water through environmental modification is the preferred method of control, given the concerns of negative health effects from insecticides and greater logistical difficulties with control agents. People can prevent mosquito bites by wearing clothing that fully covers the skin, using mosquito net
A mosquito net is a type of meshed curtain that is circumferentially draped over a bed or a sleeping area, to offer the sleeper barrier protection against bites and stings from mosquitos, flies, and other pest insects, and thus against the ...
ting while resting, and/or the application of insect repellent (DEET
''N'',''N''-Diethyl-''meta''-toluamide, also called DEET () or diethyltoluamide, is the most common active ingredient in insect repellents. It is a slightly yellow oil intended to be applied to the skin or to clothing and provides protection a ...
being the most effective). While these measures can be an effective means of reducing an individual's risk of exposure, they do little in terms of mitigating the frequency of outbreaks, which appear to be on the rise in some areas, probably due to urbanization increasing the habitat of ''A. aegypti''. The range of the disease also appears to be expanding possibly due to climate change.
Vaccine
In 2016 a partially effective vaccine for dengue fever became commercially available in the Philippines and Indonesia. It has been approved for use by Mexico, Brazil, El Salvador, Costa Rica, Singapore, Paraguay, much of Europe, and the United States. The vaccine is only recommended in individuals who have had a prior dengue infection or in populations where most (>80%) of people have been infected by age 9. In those who have not had a prior infection there is evidence it may worsen subsequent infections. For this reasonPrescrire
''Prescrire'' also known as ''La Revue Prescrire'' is a monthly medical journal in French which addresses developments in diseases, medications, and in medical techniques and technologies. ''Prescrire'' contains no advertising, and is internally fi ...
does not see it as suitable for wide scale immunization, even in areas where the disease is common.
The vaccine is produced by Sanofi and goes by the brand name Dengvaxia
Dengue vaccine is a vaccine used to prevent dengue fever in humans. Development of dengue vaccines began in the 1920s, but was hindered by the need to create immunity against all four dengue serotypes.
As of 2022, there are two commercially ava ...
. It is based on a weakened combination of the yellow fever virus and each of the four dengue serotypes. Studies of the vaccine found it was 66% effective and prevented more than 80 to 90% of severe cases. This is less than wished for by some. In Indonesia it costs about US$207 for the recommended three doses.
Given the limitations of the current vaccine, research on vaccines continues, and the fifth serotype may be factored in. One of the concerns is that a vaccine could increase the risk of severe disease through antibody-dependent enhancement
Antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE), sometimes less precisely called immune enhancement or disease enhancement, is a phenomenon in which binding of a virus to suboptimal antibodies enhances its entry into host cells, followed by its repl ...
(ADE). The ideal vaccine is safe, effective after one or two injections, covers all serotypes, does not contribute to ADE, is easily transported and stored, and is both affordable and cost-effective.
Anti-dengue day
 International Anti-Dengue Day is observed every year on 15 June. The idea was first agreed upon in 2010 with the first event held in
International Anti-Dengue Day is observed every year on 15 June. The idea was first agreed upon in 2010 with the first event held in Jakarta
Jakarta (; , bew, Jakarte), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta ( id, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta) is the capital city, capital and list of Indonesian cities by population, largest city of Indonesia. Lying on the northwest coa ...
, Indonesia, in 2011. Further events were held in 2012 in Yangon
Yangon ( my, ရန်ကုန်; ; ), formerly spelled as Rangoon, is the capital of the Yangon Region and the largest city of Myanmar (also known as Burma). Yangon served as the capital of Myanmar until 2006, when the military government ...
, Myanmar, and in 2013 in Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
. Goals are to increase public awareness about dengue, mobilize resources for its prevention and control and, to demonstrate the Southeast Asian region's commitment in tackling the disease.
Management
There are no specificantiviral drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Unlike most antibiotics, antiviral drugs do n ...
s for dengue; however, maintaining proper fluid balance is important. Treatment depends on the symptoms. Those who can drink, are passing urine, have no "warning signs" and are otherwise healthy can be managed at home with daily follow-up and oral rehydration therapy. WHO (2009), pp. 32–37. Those who have other health problems, have "warning signs", or cannot manage regular follow-up should be cared for in hospital. In those with severe dengue care should be provided in an area where there is access to an intensive care unit
220px, Intensive care unit
An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensi ...
.
Intravenous hydration, if required, is typically only needed for one or two days. In children with shock
Shock may refer to:
Common uses Collective noun
*Shock, a historic commercial term for a group of 60, see English numerals#Special names
* Stook, or shock of grain, stacked sheaves
Healthcare
* Shock (circulatory), circulatory medical emerge ...
due to dengue a rapid dose of 20 mL/kg is reasonable. The rate of fluid administration is then titrated to a urinary output
Urination, also known as micturition, is the release of urine from the urinary bladder through the urethra to the outside of the body. It is the urinary system's form of excretion. It is also known medically as micturition, voiding, uresis, ...
of 0.5–1 mL/kg/h, stable vital signs
Vital signs (also known as vitals) are a group of the four to six most crucial medical signs that indicate the status of the body's vital (life-sustaining) functions. These measurements are taken to help assess the general physical health of a ...
and normalization of hematocrit. The smallest amount of fluid required to achieve this is recommended.
Invasive medical procedures such as nasogastric intubation, intramuscular injection
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles hav ...
s and arterial punctures are avoided, in view of the bleeding risk. Paracetamol
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol and Panadol.
At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature; it is inferio ...
(acetaminophen) is used for fever and discomfort while NSAIDs such as ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used for treating pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It may also be used to close a patent ductus ar ...
and aspirin
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and/or inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat inc ...
are avoided as they might aggravate the risk of bleeding. Blood transfusion
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood products into a person's circulation intravenously. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of the blood. Early transfusions used whole blood, but mo ...
is initiated early in people presenting with unstable vital signs in the face of a ''decreasing hematocrit'', rather than waiting for the hemoglobin concentration to decrease to some predetermined "transfusion trigger" level. WHO (2009), pp. 40–43. Packed red blood cells or whole blood are recommended, while platelets and fresh frozen plasma are usually not. There is not enough evidence to determine if corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are inv ...
s have a positive or negative effect in dengue fever.
During the recovery phase intravenous fluids are discontinued to prevent a state of fluid overload
Hypervolemia, also known as fluid overload, is the medical condition where there is too much fluid in the blood. The opposite condition is hypovolemia, which is too little fluid volume in the blood. Fluid volume excess in the intravascular comp ...
. If fluid overload occurs and vital signs are stable, stopping further fluid may be all that is needed. If a person is outside of the critical phase, a loop diuretic
Loop diuretics are diuretics that act on the Na-K-Cl cotransporter along the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle in the kidney. They are primarily used in medicine to treat hypertension and edema often due to congestive heart failure o ...
such as furosemide
Furosemide is a loop diuretic medication used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It may also be used for the treatment of high blood pressure. It can be taken by injection into a vein or by mo ...
may be used to eliminate excess fluid from the circulation.
Prognosis
Most people with dengue recover without any ongoing problems. The risk of death among those with severe dengue is 0.8% to 2.5%, and with adequate treatment this is less than 1%. However, those who develop significantly low blood pressure may have a fatality rate of up to 26%. The risk of death among children less than five years old is four times greater than among those over the age of 10. Elderly people are also at higher risk of a poor outcome.Epidemiology
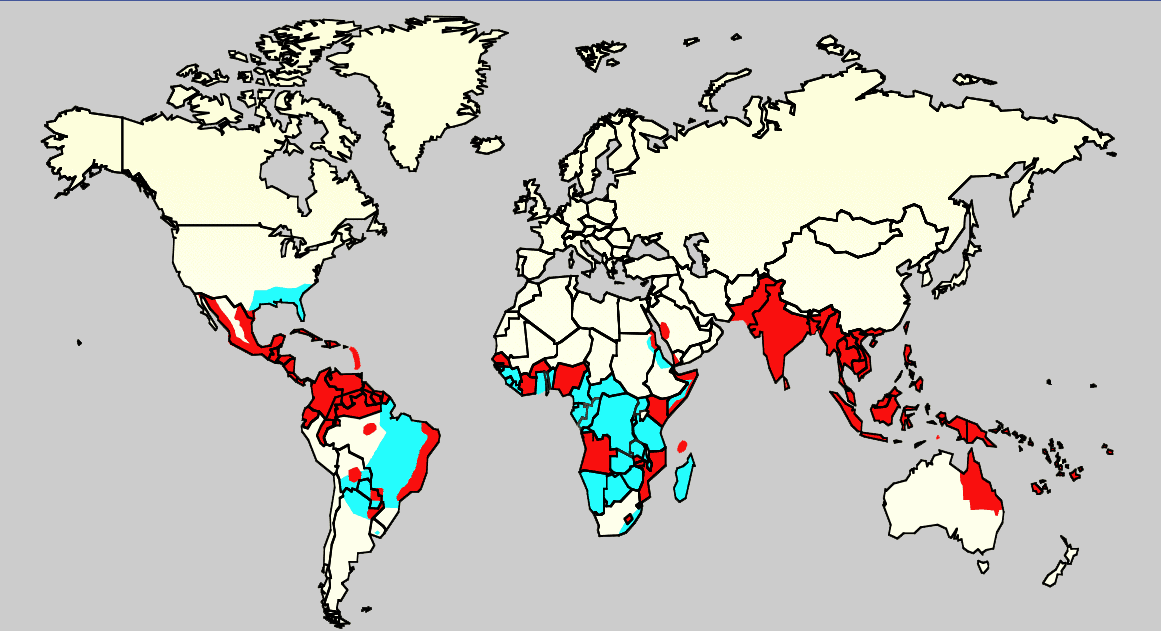
 As of 2019, dengue was
As of 2019, dengue was common
Common may refer to:
Places
* Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland
* Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts
* Cambridge Common, common land area in Cambridge, Massachusetts
* Clapham Common, originally ...
in more than 120 countries. In 2013 it caused about 60 million symptomatic infections worldwide, with 18% admitted to hospital and about 13,600 deaths. The worldwide cost of dengue case is estimated US$9 billion. For the decade of the 2000s, 12 countries in Southeast Asia were estimated to have about 3 million infections and 6,000 deaths annually. In 2019 the Philippines declared a national dengue epidemic due to the deaths reaching 622 people that year. It is reported in at least 22 countries in Africa; but is likely present in all of them with 20% of the population at risk. This makes it one of the most common vector-borne diseases worldwide.
Infections are most commonly acquired in urban environments. In recent decades, the expansion of villages, towns and cities in the areas in which it is common, and the increased mobility of people has increased the number of epidemics and circulating viruses. Dengue fever, which was once confined to Southeast Asia, has now spread to southern China in East Asia, countries in the Pacific Ocean and the Americas, and might pose a threat to Europe. In November 2022, the first locally transmitted case of dengue was reported in Maricopa County, Arizona and Arizona state as a whole.
Rates of dengue increased 30 fold between 1960 and 2010. WHO (2009), p. 3. This increase is believed to be due to a combination of urbanization, population growth, increased international travel, and global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
. The geographical distribution is around the equator. Of the 2.5 billion people living in areas where it is common 70% are from the WHO Southeast Asia Region and Western Pacific Region. An infection with dengue is second only to malaria as a diagnosed cause of fever among travelers returning from the developing world. It is the most common viral disease transmitted by arthropods, and has a disease burden
Disease burden is the impact of a health problem as measured by financial cost, mortality, morbidity, or other indicators. It is often quantified in terms of quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) or disability-adjusted life years (DALYs). Both ...
estimated at 1,600 disability-adjusted life year
The disability-adjusted life year (DALY) is a measure of overall disease burden, expressed as the number of years lost due to ill-health, disability or early death. It was developed in the 1990s as a way of comparing the overall health and life ex ...
s per million population. The World Health Organization counts dengue as one of seventeen neglected tropical diseases
Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a diverse group of tropical infections that are common in low-income populations in developing regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. They are caused by a variety of pathogens, such as viruses, bact ...
.
Like most arboviruses, dengue virus is maintained in nature in cycles that involve preferred blood-sucking vectors and vertebrate hosts. The viruses are maintained in the forests of Southeast Asia and Africa by transmission from female ''Aedes'' mosquitos—of species other than ''A. aegypti''—to their offspring and to lower primates. In towns and cities, the virus is primarily transmitted by the highly domesticated ''A. aegypti''. In rural settings the virus is transmitted to humans by ''A. aegypti'' and other species of ''Aedes'' such as '' A. albopictus''. Both these species had expanding ranges in the second half of the 20th century. In all settings the infected lower primates or humans greatly increase the number of circulating dengue viruses, in a process called amplification. One projection estimates that climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
, urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly th ...
, and other factors could result in more than 6 billion people at risk of dengue infection by 2080.
History
The first record of a case of probable dengue fever is in a Chinese medical encyclopedia from theJin Dynasty (266–420)
The Jin dynasty (; ) or the Jin Empire, sometimes distinguished as the (司馬晉) or the (兩晉), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed from 266 to 420. It was founded by Sima Yan (Emperor Wu), eldest son of Sima Zhao, who had p ...
which referred to a "water poison" associated with flying insects. The primary vector, ''A. aegypti'', spread out of Africa in the 15th to 19th centuries due in part to increased globalization secondary to the slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
. There have been descriptions of epidemics in the 17th century, but the most plausible early reports of dengue epidemics are from 1779 and 1780, when an epidemic swept across Southeast Asia, Africa and North America. From that time until 1940, epidemics were infrequent.
In 1906, transmission by the ''Aedes'' mosquitos was confirmed, and in 1907 dengue was the second disease (after yellow fever) that was shown to be caused by a virus. Further investigations by John Burton Cleland
Sir John Burton Cleland CBE (22 June 1878 – 11 August 1971) was a renowned Australian naturalist, microbiologist, mycologist and ornithologist. He was Professor of Pathology at the University of Adelaide and was consulted on high-level poli ...
and Joseph Franklin Siler
Colonel Joseph Franklin Siler, MD (1875–1960) was a U.S. Army physician noted for investigations of mosquito transmission of dengue fever in the Philippines and for '' Marijuana Smoking in Panama'', one of the first experimental reports on c ...
completed the basic understanding of dengue transmission.
The marked spread of dengue during and after the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
has been attributed to ecologic disruption. The same trends also led to the spread of different serotypes of the disease to new areas and the emergence of dengue hemorrhagic fever. This severe form of the disease was first reported in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
in 1953; by the 1970s, it had become a major cause of child mortality
Child mortality is the mortality of children under the age of five. The child mortality rate, also under-five mortality rate, refers to the probability of dying between birth and exactly five years of age expressed per 1,000 live births.
It e ...
and had emerged in the Pacific and the Americas. Dengue hemorrhagic fever and dengue shock syndrome were first noted in Central and South America in 1981, as DENV-2 was contracted by people who had previously been infected with DENV-1 several years earlier.
Etymology
The name came into English in the early 19th century from West Indian Spanish, which borrowed it from the Kiswahili term ''dinga'' (in full ''kidingapopo'', "disease caused by an evil spirit"). The borrowed term changed to ''dengue'' in Spanish due to this word existing in Spanish with the meaning "fastidiousness" and thisfolk etymology
Folk etymology (also known as popular etymology, analogical reformation, reanalysis, morphological reanalysis or etymological reinterpretation) is a change in a word or phrase resulting from the replacement of an unfamiliar form by a more famili ...
referring to the dislike of movement by affected patients. Slaves in the West Indies having contracted dengue were said to have the posture and gait of a dandy, and the disease was known as "dandy fever".
The term ''break-bone fever'' was applied by physician and United States Founding Father Benjamin Rush, in a 1789 report of the 1780 epidemic in Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since ...
. In the report title he uses the more formal term "bilious remitting fever". The term dengue fever came into general use only after 1828. Other historical terms include "breakheart fever" and "la dengue". Terms for severe disease include "infectious thrombocytopenic purpura" and "Philippine", "Thai", or "Singapore hemorrhagic fever".
Society and culture
Blood donation
Outbreaks of dengue fever increase the need for blood products while decreasing the number of potential blood donors due to potential infection with the virus. Someone who has a dengue infection is typically not allowed to donate blood for at least the next six months.Awareness efforts
A National Dengue Day is held in India on 16 May in an effort to raise awareness in affected countries. Efforts are ongoing as of 2019 to make it a global event. The Philippines has an awareness month in June since 1998.Research
Research efforts to prevent and treat dengue include various means of vector control, WHO (2009), p. 71. vaccine development, and antiviral drugs. WHO (2009) pp. 137–46. A vaccine candidate, TAK-003, has shown 73% efficacy in a clinical trial of more than 20,000 children in endemic regions and 90% efficacy for hospitalized patients.Vector
With regards to vector control, a number of novel methods have been used to reduce mosquito numbers with some success including the placement of the guppy ('' Poecilia reticulata'') orcopepods
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthic (living on the ocean floor), a number of species have p ...
in standing water to eat the mosquito larvae. There are also trials with genetically modified male ''A. aegypti'' that after release into the wild mate with females, and render their offspring unable to fly.
Wolbachia
In 2021 research inYogyakarta
Yogyakarta (; jv, ꦔꦪꦺꦴꦒꦾꦏꦂꦠ ; pey, Jogjakarta) is the capital city of Special Region of Yogyakarta in Indonesia, in the south-central part of the island of Java. As the only Indonesian royal city still ruled by a monarchy, ...
, Indonesia, infected ''A. aegypti'' with the ''w''Mel strain of '' Wolbachia pipientis.'' Infected mosquitos were less susceptible to dengue virus infection. Odds ratio of intervention clusters versus control clusters was .23 (95% confidence interval I 0.15 to 0.35; P=0.004).
Treatment
Apart from the attempts to control the spread of the ''Aedes'' mosquito there are ongoing efforts to developantiviral drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Unlike most antibiotics, antiviral drugs do n ...
s that would be used to treat attacks of dengue fever and prevent severe complications. Discovery of the structure of the viral proteins may aid the development of effective drugs. There are several plausible targets. The first approach is inhibition of the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) or RNA replicase is an enzyme that catalyzes the replication of RNA from an RNA template. Specifically, it catalyzes synthesis of the RNA strand complementary to a given RNA template. This is in contrast to ...
(coded by NS5), which copies the viral genetic material, with nucleoside analogs. Secondly, it may be possible to develop specific inhibitors of the viral protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the ...
(coded by NS3), which splices viral proteins. Finally, it may be possible to develop entry inhibitor
Entry inhibitors, also known as fusion inhibitors, are a class of antiviral drugs that prevent a virus from entering a cell, for example, by blocking a receptor. Entry inhibitors are used to treat conditions such as HIV and hepatitis D.
HIV entr ...
s, which stop the virus entering cells, or inhibitors of the 5′ capping process, which is required for viral replication.
''Carica papaya'' leaf extract has been studied and has been used for treatment and in hospitals. As of 2020, studies have shown positive benefits on clinical blood parameters, but a beneficial effect on disease outcome has yet to be studied, and papaya leaf extract is not considered a standard of practice therapy.
In october 2021, the Catholic University of Leuven in Belgium announced it has developed an antiviral in cooperation with Janssen Pharmaceutica, which can also be used to prevent the disease.
References
*External links
* {{Authority control Tropical diseases Vaccine-preventable diseases Zoonoses Insect-borne diseases