Demographics Of The People's Republic Of China on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''
The


 During 1960–2015, the population grew to nearly 1.4 billion. Under
During 1960–2015, the population grew to nearly 1.4 billion. Under
File:China Sex by Age 1953 census.png, China population pyramid as of 1st National Census day on June 30, 1953
File:China Sex By Age 1964 census.png, China population pyramid as of 2nd National Census day on July 1, 1964
File:China Sex By Age 1982 census.png, China population pyramid as of 3rd National Census day on July 1, 1982
File:China Sex By Age 1990 census.png, China population pyramid as of 4th National Census day on July 1, 1990
File:China Sex By Age 2000 census.png, China population pyramid as of 5th National Census day on November 1, 2000
File:China Sex By Age 2010 census.png, China population pyramid as of 6th National Census day on November 1, 2010
File:China_population_sex_by_age_on_Nov,_1st,_2020.png, China population pyramid as of 7th National Census day on November 1, 2020
File:China_population_pyramid_projected_for_2030.png, China population pyramid as projected of 8th National Census day on November 1, 2030, in scenario of constant TFR at 2021 level and continued improvements in mortality
In 1982 China conducted its first population census since 1964. It was by far the most thorough and accurate census taken since 1949 and confirmed that China was a nation of more than 1 billion people, or about one-fifth of the world's population. The census provided demographers with a set of data on China's age-sex structure, fertility and mortality rates, and population density and distribution. Information was also gathered on minority ethnic groups, urban population, and marital status. For the first time since the People's Republic of China was founded, demographers had reliable information on the size and composition of the Chinese work force. The nation began preparing for the 1982 census in late 1976. Chinese census workers were sent to the United States and Japan to study modern census-taking techniques and automation. Computers were installed in every provincial-level unit except Tibet and were connected to a central processing system in the Beijing headquarters of the State Statistical Bureau. Pretests and small scale trial runs were conducted and checked for accuracy between 1980 and 1981 in twenty-four provincial-level units. Census stations were opened in rural production brigades and urban neighborhoods. Beginning on 1 July 1982, each household sent a representative to a census station to be enumerated. The census required about a month to complete and employed approximately 5 million census takers.
The 1982 census collected data in nineteen demographic categories relating to individuals and households. The thirteen areas concerning individuals were name, relationship to head of household, sex, age, nationality, registration status, educational level, profession, occupation, status of nonworking persons, marital status, number of children born and still living, and number of births in 1981. The six items pertaining to households were type (domestic or collective), serial number, number of persons, number of births in 1981, number of deaths in 1981, and number of registered persons absent for more than one year. Information was gathered in a number of important areas for which previous data were either extremely inaccurate or simply nonexistent, including fertility, marital status, urban population, minority ethnic groups, sex composition, age distribution, and employment and unemployment.
A fundamental anomaly in the 1982 statistics was noted by some Western analysts. They pointed out that although the birth and death rates recorded by the census and those recorded through the household registration system were different, the two systems arrived at similar population totals. The discrepancies in the vital rates were the result of the underreporting of both births and deaths to the authorities under the registration system; families would not report some births because of the one-child policy and would not report some deaths so as to hold on to the rations of the deceased.
Nevertheless, the 1982 census was a watershed for both Chinese and world demographics. After an eighteen-year gap, population specialists were given a wealth of reliable, up-to-date figures on which to reconstruct past demographic patterns, measure current population conditions, and predict future population trends. For example, Chinese and foreign demographers used the 1982 census age-sex structure as the base population for forecasting and making assumptions about future fertility trends. The data on age-specific
 Initially, China's post-1949 leaders were ideologically disposed to view a large population as an asset. But the liabilities of a large, rapidly growing population soon became apparent. For one year, starting in August 1956, vigorous support was given to the Ministry of Public Health's mass birth control efforts. These efforts, however, had little impact on fertility. After the interval of the Great Leap Forward, Chinese leaders again saw rapid population growth as an obstacle to development, and their interest in birth control revived. In the early 1960s, schemes somewhat more muted than during the first campaign, emphasized the virtues of late marriage. Birth control offices were set up in the central government and some provincial-level governments in 1964. The second campaign was particularly successful in the cities, where the birth rate was cut in half during the 1963–66 period. The upheaval of the
Initially, China's post-1949 leaders were ideologically disposed to view a large population as an asset. But the liabilities of a large, rapidly growing population soon became apparent. For one year, starting in August 1956, vigorous support was given to the Ministry of Public Health's mass birth control efforts. These efforts, however, had little impact on fertility. After the interval of the Great Leap Forward, Chinese leaders again saw rapid population growth as an obstacle to development, and their interest in birth control revived. In the early 1960s, schemes somewhat more muted than during the first campaign, emphasized the virtues of late marriage. Birth control offices were set up in the central government and some provincial-level governments in 1964. The second campaign was particularly successful in the cities, where the birth rate was cut in half during the 1963–66 period. The upheaval of the
 Source: ''UN World Population Prospects''
The latest data from the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) seems to contradict this, stating China's TFR for 2015 was 1.05. Although there is a natural margin of error since the NBS surveys only a thin cross-section of Chinese society, approximately 1% of the total population. Fertility according to National Bureau of Statistics (NBS):
Source: ''UN World Population Prospects''
The latest data from the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) seems to contradict this, stating China's TFR for 2015 was 1.05. Although there is a natural margin of error since the NBS surveys only a thin cross-section of Chinese society, approximately 1% of the total population. Fertility according to National Bureau of Statistics (NBS):
 In 1949 crude death rates were probably higher than 30 per 1,000, and the average life expectancy was only 35 years. Beginning in the early 1950s, mortality steadily declined; it continued to decline through 1978 and remained relatively constant through 1987. One major fluctuation was reported in a computer reconstruction of China's population trends from 1953 to 1987 produced by the
In 1949 crude death rates were probably higher than 30 per 1,000, and the average life expectancy was only 35 years. Beginning in the early 1950s, mortality steadily declined; it continued to decline through 1978 and remained relatively constant through 1987. One major fluctuation was reported in a computer reconstruction of China's population trends from 1953 to 1987 produced by the
 Urbanization increased in speed following the initiation of the reform and opening policy. By the end of 2014, 54.7% of the total population lived in urban areas, a rate that rose from 26% in 1990.
Urbanization increased in speed following the initiation of the reform and opening policy. By the end of 2014, 54.7% of the total population lived in urban areas, a rate that rose from 26% in 1990.
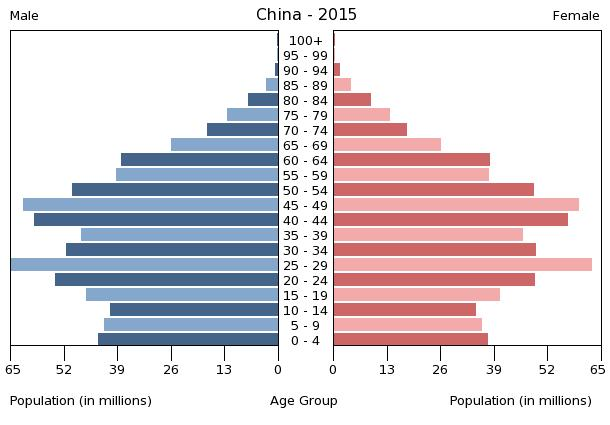 *0–14 years: 17.29% (male 129,296,339/female 111,782,427)
*15–24 years: 11.48% (male 86,129,841/female 73,876,148)
*25–54 years: 46.81% (male 333,789,731/female 318,711,557)
*55–64 years: 12.08% (male 84,827,645/female 83,557,507)
*65 years and over: 12.34% (male 81,586,490/female 90,458,292) (2020 est.)
*0–14 years: 17.2% (2015)
*15–64 years: 72.0% (2015)
*65 years and: 10.8% (2015)
;Median age
*total: 38.4 years Country comparison to the world: 62nd
*male: 37.5 years
*female: 38.4 years (2021 est.)
;Population growth rate:
*0.19% (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 175th
;Birth rate:
*11.3 births/1,000 population (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 169th
;Death rate:
*8.26 deaths/1,000 population (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 77th
;Net migration rate:
*-0.43 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 122nd
;Population growth rate
*Population growth rate: 0.19% (2022)
;Sex distribution
*Sex distribution: 1.06 males/females (2020)
;Sex ratio
*At birth: 1.11 male(s)/female (2020)
*Under 15 years: 1.16 male(s)/female (2020)
*15–24 years: 1.17 male(s)/female (2020)
*25–54 years: 1.02 male(s)/female (2020)
*65 years and over: 0.9 male(s)/female (2020)
*Total population: 1.06 male(s)/female (2020)
;Infant mortality rate
*Total: 11.5 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est)
*Male: 11.6 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est)
*Female: 10.64 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est)
See Infant mortality in China
;Urbanization:
*urban population: 59.2% of total population (2018)
*rate of urbanization: 2.4% annual rate of change (2015–20 est.)
note: data do not include Hong Kong and Macau
;Life expectancy at birth
*Total population: 76.31 years (2021)
*Male: 74.23 years (2021)
*Female: 78.62 years (2021)
;Religious affiliation
* ''Predominantly:'' Mahayana Buddhism,
*0–14 years: 17.29% (male 129,296,339/female 111,782,427)
*15–24 years: 11.48% (male 86,129,841/female 73,876,148)
*25–54 years: 46.81% (male 333,789,731/female 318,711,557)
*55–64 years: 12.08% (male 84,827,645/female 83,557,507)
*65 years and over: 12.34% (male 81,586,490/female 90,458,292) (2020 est.)
*0–14 years: 17.2% (2015)
*15–64 years: 72.0% (2015)
*65 years and: 10.8% (2015)
;Median age
*total: 38.4 years Country comparison to the world: 62nd
*male: 37.5 years
*female: 38.4 years (2021 est.)
;Population growth rate:
*0.19% (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 175th
;Birth rate:
*11.3 births/1,000 population (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 169th
;Death rate:
*8.26 deaths/1,000 population (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 77th
;Net migration rate:
*-0.43 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 122nd
;Population growth rate
*Population growth rate: 0.19% (2022)
;Sex distribution
*Sex distribution: 1.06 males/females (2020)
;Sex ratio
*At birth: 1.11 male(s)/female (2020)
*Under 15 years: 1.16 male(s)/female (2020)
*15–24 years: 1.17 male(s)/female (2020)
*25–54 years: 1.02 male(s)/female (2020)
*65 years and over: 0.9 male(s)/female (2020)
*Total population: 1.06 male(s)/female (2020)
;Infant mortality rate
*Total: 11.5 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est)
*Male: 11.6 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est)
*Female: 10.64 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est)
See Infant mortality in China
;Urbanization:
*urban population: 59.2% of total population (2018)
*rate of urbanization: 2.4% annual rate of change (2015–20 est.)
note: data do not include Hong Kong and Macau
;Life expectancy at birth
*Total population: 76.31 years (2021)
*Male: 74.23 years (2021)
*Female: 78.62 years (2021)
;Religious affiliation
* ''Predominantly:'' Mahayana Buddhism,
demographics
Demography () is the statistical study of populations, especially human beings.
Demographic analysis examines and measures the dimensions and dynamics of populations; it can cover whole societies or groups defined by criteria such as ed ...
of China demonstrate a huge population with a relatively small youth component, partially a result of China's one-child policy
The term one-child policy () refers to a population planning initiative in China implemented between 1980 and 2015 to curb the country's population growth by restricting many families to a single child. That initiative was part of a much br ...
. China's population reached 1 billion in late 1981.
As of December 2021, China's population stood at 1.413 billion. According to the 2020 census, 91.11% of the population was Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctiv ...
, and 8.89% were minorities. China's population growth rate is only 0.03%, ranking 159th in the world. China conducted its sixth national population census in 2010, and its seventh census was completed in late 2020, with data released in May 2021. Unless otherwise indicated, the statistics on this page pertain to mainland China
"Mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the People's Republic of China (including islands like Hainan or Chongming), excluding dependent territories of the PRC, and other territories within Greater China. ...
only; see also Demographics of Hong Kong
This article is about the demographic features of the population of Hong Kong, including population density, ethnicity, education level, the health of the populace, religious affiliations, and other aspects of the population.
Hong Kong i ...
and Demographics of Macau
This article is about the demographic features of the population of Macau, including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
Macau's ...
.
History
Population
Historical population
 During 1960–2015, the population grew to nearly 1.4 billion. Under
During 1960–2015, the population grew to nearly 1.4 billion. Under Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC) ...
, China nearly doubled in population from 540 million in 1949 to 969 million in 1979. This growth slowed because of the one-child policy instituted in 1979.
Census data
Censuses in China
The People's Republic of China conducted censuses in1953
Events
January
* January 6 – The Asian Socialist Conference opens in Rangoon, Burma.
* January 12 – Estonian émigrés found a government-in-exile in Oslo.
* January 14
** Marshal Josip Broz Tito is chosen President of Yug ...
, 1964
Events January
* January 1 – The Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland is dissolved.
* January 5 - In the first meeting between leaders of the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches since the fifteenth century, Pope Paul VI and Patriarc ...
, 1982, 1990
File:1990 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 1990 FIFA World Cup is played in Italy; The Human Genome Project is launched; Voyager I takes the famous Pale Blue Dot image- speaking on the fragility of humanity on Earth, astrophysicist ...
, 2000
File:2000 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: Protests against Bush v. Gore after the 2000 United States presidential election; Heads of state meet for the Millennium Summit; The International Space Station in its infant form as seen from S ...
, and 2010. In 1987, the government announced that the fourth national census would take place in 1990 and that there would be one every ten years thereafter. The 1982 census (which reported a total population of 1,008,180,738) is generally accepted as significantly more reliable, accurate, and thorough than the previous two. Various international organizations eagerly assisted the Chinese in conducting the 1982 census, including the United Nations Fund for Population Activities, which donated US$100.0 million between 1980-1989 for a variety of projects, one of which being the 1982 census.
China has been the world's most populous nation for many centuries. When China took its first post-1949 census in 1953, the population stood at 583 million; by the fifth census in 2000, the population had more than doubled, reaching 1.2 billion.
By the sixth census in 2020, the total population had reached to 1,419,933,142, with the mainland having 1,411,778,724, Hong Kong having 7,474,200, and Macau having 683,218. However, this number is disputed by some scholars, such as obstetrics researcher Yi Fuxian, who argues that data related to population growth is inflated by local governments to obtain financial subsidies from the central government.
Population of China by age and sex (demographic pyramid)
fertility
Fertility is the capability to produce offspring through reproduction following the onset of sexual maturity. The fertility rate is the average number of children born by a female during her lifetime and is quantified demographically. Fertili ...
and mortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of d ...
s provided the necessary base-line information for making population projections. The census data also were useful for estimating future manpower
Human resources (HR) is the set of people who make up the workforce of an organization, business sector, industry, or economy. A narrower concept is human capital, the knowledge and skills which the individuals command. Similar terms include ...
potential, consumer needs
The theory of consumer choice is the branch of microeconomics that relates preferences to consumption expenditures and to consumer demand curves. It analyzes how consumers maximize the desirability of their consumption as measured by their pre ...
, and utility
As a topic of economics, utility is used to model worth or value. Its usage has evolved significantly over time. The term was introduced initially as a measure of pleasure or happiness as part of the theory of utilitarianism by moral philosoph ...
, energy, and health-service requirements. The sudden abundance of demographic data helped population specialists immeasurably in their efforts to estimate world population. Previously, there had been no accurate information on these 21% of the Earth's inhabitants. Demographers who had been conducting research on global population without accurate data on the Chinese fifth of the world's population were particularly thankful for the 1982 breakthrough census.
Population control
Cultural Revolution
The Cultural Revolution, formally known as the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, was a sociopolitical movement in the People's Republic of China (PRC) launched by Mao Zedong in 1966, and lasting until his death in 1976. Its stated goa ...
brought the program to a halt, however.
In 1972 and 1973 the party mobilized its resources for a nationwide birth control campaign administered by a group in the State Council State Council may refer to:
Government
* State Council of the Republic of Korea, the national cabinet of South Korea, headed by the President
* State Council of the People's Republic of China, the national cabinet and chief administrative auth ...
. Committees to oversee birth control activities were established at all administrative levels and in various collective enterprises. This extensive and seemingly effective network covered both the rural and the urban population. In urban areas public security headquarters included population control sections. In rural areas the country's "barefoot doctor
Barefoot doctors () were healthcare providers who underwent basic medical training and worked in rural villages in China. They included farmers, folk healers, rural healthcare providers, and recent middle or secondary school graduates who receiv ...
s" distributed information and contraceptives to people's commune members. By 1973 Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC) ...
was personally identified with the family planning movement, signifying a greater leadership commitment to controlled population growth than ever before. Yet until several years after Mao's death in 1976, the leadership was reluctant to put forth directly the rationale that population control was necessary for economic growth and improved living standards.
Population growth targets were set for both administrative units and individual families. In the mid-1970s the maximum recommended family size was two children in cities and three or four in the country. Since 1979 the government has advocated a one-child limit for both rural and urban areas and has generally set a maximum of two children in special circumstances. As of 1986 the policy for minority nationalities was two children per couple, three in special circumstances, and no limit for ethnic groups with very small populations. The overall goal of the one-child policy was to keep the total population within 1.2 billion through the year 2000, on the premise that the Four Modernizations program would be of little value if population growth was not brought under control.
The one-child policy was a highly ambitious population control program. Like previous programs of the 1960s and 1970s, the one-child policy employed a combination of public education, social pressure, and in some cases coercion. The one-child policy was unique, however, in that it linked reproduction with economic cost or benefit.
Under the one-child program, a sophisticated system rewarded those who observed the policy and penalized those who did not. Through this policy, the rate of increasing population was tempered after the penalties were made. Couples with only one child were given a "one-child certificate" entitling them to such benefits as cash bonuses, longer maternity leave
Parental leave, or family leave, is an employee benefit available in almost all countries. The term "parental leave" may include maternity, Paternity (law), paternity, and adoption leave; or may be used distinctively from "maternity leave" an ...
, better child care
Child care, otherwise known as day care, is the care and supervision of a child or multiple children at a time, whose ages range from two weeks of age to 18 years. Although most parents spend a significant amount of time caring for their child(r ...
, and preferential housing assignments. In return, they were required to pledge that they would not have more children. In the countryside, there was great pressure to adhere to the one-child limit. Because the rural population accounted for approximately 60% of the total, the effectiveness of the one-child policy in rural areas was considered the key to the success or failure of the program as a whole.
In rural areas the day-to-day work of family planning was done by cadres at the team and brigade levels who were responsible for women's affairs and by health workers. The women's team leader made regular household visits to keep track of the status of each family under her jurisdiction and collected information on which women were using contraceptives, the methods used, and which had become pregnant. She then reported to the brigade women's leader, who documented the information and took it to a monthly meeting of the commune birth-planning committee. According to reports, ceilings or quotas had to be adhered to; to satisfy these cutoffs, unmarried young people were persuaded to postpone marriage, couples without children were advised to "wait their turn," women with unauthorized pregnancies were pressured to have abortions, and those who already had children were urged to use contraception
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent unwanted pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth contr ...
or undergo sterilization. Couples with more than one child were exhorted to be sterilized.
The one-child policy enjoyed much greater success in urban than in rural areas. Even without state intervention, there were compelling reasons for urban couples to limit the family to a single child. Raising a child required a significant portion of family income, and in the cities a child did not become an economic asset until he or she entered the work force at age sixteen. Couples with only one child were given preferential treatment in housing allocation. In addition, because city dwellers who were employed in state enterprises received pensions after retirement, the sex of their first child was less important to them than it was to those in rural areas.
Numerous reports surfaced of coercive measures used to achieve the desired results of the one-child policy. The alleged methods ranged from intense psychological pressure to the use of physical force, including some grisly accounts of forced abortions and infanticide. Chinese officials admitted that isolated, uncondoned abuses of the program occurred and that they condemned such acts, but they insisted that the family planning program was administered on a voluntary basis using persuasion and economic measures only. International reaction to the allegations were mixed. The UN Fund for Population Activities and the International Planned Parenthood Federation
The International Planned Parenthood Federation (IPPF) is a global non-governmental organisation with the broad aims of promoting sexual and reproductive health, and advocating the right of individuals to make their own choices in family ...
were generally supportive of China's family planning program. The United States Agency for International Development
The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) is an independent agency of the U.S. federal government that is primarily responsible for administering civilian foreign aid and development assistance. With a budget of over $27 b ...
, however, withdrew US$10 million from the Fund in March 1985 based on allegations that coercion had been used.
Observers suggested that an accurate assessment of the one-child program would not be possible until all women who came of childbearing age in the early 1980s passed their fertile years. As of 1987 the one-child program had achieved mixed results. In general, it was very successful in almost all urban areas but less successful in rural areas.
Rapid fertility reduction associated with the one-child policy has potentially negative results. For instance, in the future the elderly might not be able to rely on their children to care for them as they have in the past, leaving the state to assume the expense, which could be considerable. Based on United Nations and Chinese government statistics, it was estimated in 1987 that by 2000 the population 60 years and older (the retirement age is 60 in urban areas) would number 127 million, or 10.1% of the total population; the projection for 2025 was 234 million elderly, or 16.4%. According to projections based on the 1982 census, if the one-child policy were maintained to the year 2000, 25% of China's population would be age 65 or older by 2040. In 2050, the number of people over 60 is expected to increase to 430 million. Even though China has already opened two-child policy since 2016, data shows that the second-child policy cannot stop the problem of an aging population. China needs to find an appropriate birth policy to optimize the demographic dividend, which refers to the proportion of labor-age population. On the other hand, the higher house prices squeeze the marriage in China. The house price plays an important role on the influence of marriage and fertility. The increasing house price leads to the lower marriage rate and cause the other serious social problems in China. For the rapid reduction of marriage and fertility, the central government should establish the policy to deal with the high house price.
Population density and distribution
China is the most populated country in the world and its national population density (137/km2) is very similar to those of countries likeDenmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
(excluding Greenland) or the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
. However, the overall population density of China conceals major regional variations. In 2002, about 94% of the population lived east of the Heihe–Tengchong Line
The Heihe–Tengchong Line (), also called the Aihui-Tengchong Line (and internationally as the Hu line), is an imaginary line that divides the area of China into two parts with contrasting population densities. It stretches from the city of H ...
, which makes up only 43% of the total land area, which leads to much higher average density (about 280/km2, little less than Japan).
Broadly speaking, the population was concentrated east of the mountains and south of the northern steppe. The most densely populated areas included the Yangtze River Valley
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flow ...
(of which the delta region was the most populous), Sichuan Basin
The Sichuan Basin (), formerly transliterated as the Szechwan Basin, sometimes called the Red Basin, is a lowland region in southwestern China. It is surrounded by mountains on all sides and is drained by the upper Yangtze River and its tributar ...
, North China Plain, Pearl River Delta, and the industrial area around the city of Shenyang in the northeast.
Population is most sparse in the mountainous, desert, and grassland regions of the northwest and southwest. In Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a ...
Autonomous Region, portions are completely uninhabited, and only a few sections have populations denser than ten people per km2. The Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a ...
, Xinjiang, and Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa, Taman ...
autonomous regions and Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest po ...
and Gansu comprise 55% of the country's land area but in 1985 contained only 5.7% of its population.
Vital statistics
Table of births and deaths 1949–2021
China's fertility statistics differ depending on the source. According to the Ministry of Health and Family Planning November 2015 announcement, China's 2015 Total Fertility Rate or TFR was somewhere between 1.5 and 1.6.
Total fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if:
# she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through her lifetime
# she were t ...
from 1930 to 1949
Children born per woman from 1930 to 1949. It is based on fairly good data for the entire period. Sources: Our World In Data
Our World in Data (OWID) is a scientific online publication that focuses on large global problems such as poverty, disease, hunger, climate change, war, existential risks, and inequality.
It is a project of the Global Change Data Lab, a re ...
and Gapminder Foundation
Gapminder Foundation is a non-profit venture registered in Stockholm, Sweden, that promotes sustainable global development and achievement of the United Nations Millennium Development Goals by increased use and understanding of statistics and ...
.
Structure of the population
Population by Sex and Age Group (Census 01.XI.2010):Life expectancy
Fertility and mortality
 In 1949 crude death rates were probably higher than 30 per 1,000, and the average life expectancy was only 35 years. Beginning in the early 1950s, mortality steadily declined; it continued to decline through 1978 and remained relatively constant through 1987. One major fluctuation was reported in a computer reconstruction of China's population trends from 1953 to 1987 produced by the
In 1949 crude death rates were probably higher than 30 per 1,000, and the average life expectancy was only 35 years. Beginning in the early 1950s, mortality steadily declined; it continued to decline through 1978 and remained relatively constant through 1987. One major fluctuation was reported in a computer reconstruction of China's population trends from 1953 to 1987 produced by the United States Bureau of the Census
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
. The computer model showed that the crude death rate increased dramatically during the famine years associated with the Great Leap Forward (1958–60).
According to Chinese government statistics, the crude birth rate followed five distinct patterns from 1949 to 1982. It remained stable from 1949 to 1954, varied widely from 1955 to 1965, experienced fluctuations between 1966 and 1969, dropped sharply in the late 1970s, and increased from 1980 to 1981. Between 1970 and 1980, the crude birth rate dropped from 33.4 per 1,000 to 18.2 per 1,000. The government attributed this dramatic decline in fertility to the ''wǎn xī shǎo'' ("晚、稀、少", or "late, long, few": later marriages, longer intervals between births, and fewer children) birth control campaign. However, elements of socioeconomic change, such as increased employment of women in both urban and rural areas and reduced infant mortality (a greater percentage of surviving children would tend to reduce demand for additional children), may have played some role. The birth rate increased in the 1980s to a level over 20 per 1,000, primarily as a result of a marked rise in marriages and first births. The rise was an indication of problems with the one-child policy of 1979. Chinese sources, however, indicate that the birth rate started to decrease again in the 1990s and reached a level of around 12 per 1,000 in recent years.
In urban areas, the housing shortage may have been at least partly responsible for the decreased birth rate. Also, the policy in force during most of the 1960s and the early 1970s of sending large numbers of high school graduates to the countryside deprived cities of a significant proportion of persons of childbearing age and undoubtedly had some effect on birth rates (see Cultural Revolution
The Cultural Revolution, formally known as the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, was a sociopolitical movement in the People's Republic of China (PRC) launched by Mao Zedong in 1966, and lasting until his death in 1976. Its stated goa ...
(1966–76)). Primarily for economic reasons, rural birth rates tended to decline less than urban rates. The right to grow and sell agricultural products for personal profit and the lack of an old-age Welfare system were incentives for rural people to produce many children, especially sons, for help in the fields and for support in old age. Because of these conditions, it is unclear to what degree education had been able to erode traditional values favoring large families.
Today, the population continues to grow. There is also a serious gender imbalance. Census data obtained in 2000 revealed that 119 boys were born for every 100 girls, and among China's "floating population" the ratio was as high as 128:100. These situations led the government in July 2004 to ban selective abortions of female fetuses. It is estimated that this imbalance will rise until 2025–2030 to reach 20% then slowly decrease.
China now has an increasingly aging population
Population ageing is an increasing median age in a population because of declining fertility rates and rising life expectancy. Most countries have rising life expectancy and an ageing population, trends that emerged first in developed countries ...
; it is projected that 11.8% of the population in 2020 will be 65 years of age and older. Health care has improved dramatically in China since 1949. Major diseases such as cholera, typhoid
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by ''Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several d ...
, and scarlet fever have been brought under control. Life expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
has more than doubled, and infant mortality has dropped significantly. On the negative side, the incidence of cancer, cerebrovascular disease
Cerebrovascular disease includes a variety of medical conditions that affect the blood vessels of the brain and the cerebral circulation. Arteries supplying oxygen and nutrients to the brain are often damaged or deformed in these disorders. Th ...
, and heart disease has increased to the extent that these have become the leading causes of death. Economic reforms initiated in the late 1970s fundamentally altered methods of providing health care; the collective medical care system has been gradually replaced by a more individual-oriented approach.
In 2018
File:2018 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: The 2018 Winter Olympics opening ceremony in PyeongChang, South Korea; Protests erupt following the Assassination of Jamal Khashoggi; March for Our Lives protests take place across the Unit ...
, China had the lowest birth rate since 1961
Events January
* January 3
** United States President Dwight D. Eisenhower announces that the United States has severed diplomatic and consular relations with Cuba (Cuba–United States relations are restored in 2015).
** Aero Flight 311 (K ...
, with an estimated of 15.23 million babies being born. The birth figure was 11.6 percent lower compared with 17,23 million in 2017. Officials had expected 21-23 million births in 2018, much more than the 15.23 that occurred. James Liang
James Jianzhang Liang (; born December 1969) is a Chinese businessman, and the executive chairman, former CEO, and co-founder of Trip.com Group (formerly Ctrip), a provider of travel services including accommodation reservation, transportation ...
, an economics professor at Peking University, stated that the apparent birth peak was in 2016, and predicted that birth rates will continue to fall dramatically and that the birthrate will not be higher than 2018 for at least 100 years.
In Hong Kong, the birth rate of 0.9% is lower than its death rate. Hong Kong's population increases because of immigration from the mainland and a large expatriate
An expatriate (often shortened to expat) is a person who resides outside their native country. In common usage, the term often refers to educated professionals, skilled workers, or artists taking positions outside their home country, either ...
population comprising about 4%. Like Hong Kong, Macau
Macau or Macao (; ; ; ), officially the Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (MSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China in the western Pearl River Delta by the South China Sea. With a p ...
also has a low birth rate relying on immigration to maintain its population.
Total fertility rate
According to the 2000 census, the TFR was 1.22 (0.86 for cities, 1.08 for towns and 1.43 for villages/outposts). Beijing had the lowest TFR at 0.67, whileGuizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to the ...
had the highest at 2.19. The Xiangyang district of Jiamusi
Jiamusi (Manchu: ; formerly Kiamusze) is a prefecture-level city in eastern Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China. Located along the middle and lower reaches of the Songhua River, it faces Russia's Khabarovsk Krai across the Ussuri R ...
city (Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang () formerly romanized as Heilungkiang, is a province in northeast China. The standard one-character abbreviation for the province is (). It was formerly romanized as "Heilungkiang". It is the northernmost and easternmost province ...
) has a TFR of 0.41, which is the lowest TFR recorded anywhere in the world in recorded history. Other extremely low TFR counties are: 0.43 in the Heping district of Tianjin city
Tianjin (; ; Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Tientsin (), is a municipality and a coastal metropolis in Northern China on the shore of the Bohai Sea. It is one of the nine national central cities in Mainland China, with a total popula ...
(Tianjin
Tianjin (; ; Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Tientsin (), is a municipality and a coastal metropolis in Northern China on the shore of the Bohai Sea. It is one of the nine national central cities in Mainland China, with a total popu ...
), and 0.46 in the Mawei district
Mawei (; Foochow Romanized: Mā-muōi) is one of 6 urban districts of the prefecture-level city of Fuzhou, the capital of Fujian Province, China. The district spans an area of 319.66 square kilometers, of which, 275.66 square kilometers is land. ...
of Fuzhou city (Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
). At the other end TFR was 3.96 in Geji County (Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa, Taman ...
), 4.07 in Jiali County (Tibet), and 5.47 in Baqing County (Tibet).
The 2010 census reported a TFR of 1.18 (0.88 in cities, 1.15 in townships, and
1.44 in rural areas).
The five regions with the lowest fertility rates were Beijing (0.71), Shanghai
(0.74), Liaoning (0.74), Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang () formerly romanized as Heilungkiang, is a province in northeast China. The standard one-character abbreviation for the province is (). It was formerly romanized as "Heilungkiang". It is the northernmost and easternmost province ...
(0.75), and Jilin
Jilin (; alternately romanized as Kirin or Chilin) is one of the three provinces of Northeast China. Its capital and largest city is Changchun. Jilin borders North Korea ( Rasŏn, North Hamgyong, Ryanggang and Chagang) and Russia (Prim ...
(0.76). The five regions with the highest
fertility rates were Guangxi (1.79), Guizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to the ...
(1.75), Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
(1.53), Hainan
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slightly l ...
(1.51), and Anhui
Anhui , (; formerly romanized as Anhwei) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the East China region. Its provincial capital and largest city is Hefei. The province is located across the basins of the Yangtze River ...
(1.48).
Total fertility rate by ethnic group (2010 census): Han
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
(1.14), Zhuang (1.59), Hui
The Hui people ( zh, c=, p=Huízú, w=Hui2-tsu2, Xiao'erjing: , dng, Хуэйзў, ) are an East Asian ethnoreligious group predominantly composed of Chinese-speaking adherents of Islam. They are distributed throughout China, mainly in the n ...
(1.48), Manchu (1.18), Uyghur (2.04), Miao Miao may refer to:
* Miao people, linguistically and culturally related group of people, recognized as such by the government of the People's Republic of China
* Miao script or Pollard script, writing system used for Miao languages
* Miao (Unicode ...
(1.82), Yi (1.82), Tujia (1.74), Tibetan (1.60), Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
(1.26).
The 2020 census reported a TFR of 1.3, but some experts believe that after adjusting for the transient effects of the relaxation of restrictions, China’s actual TFR is as low as 1.1.
Labor force
In 2012, for the first time, according to the National Bureau of Statistics in January 2013, the number of people theoretically able to enter the Chinese labor force (individuals aged 15 to 59), shrank slightly to 937.27 million, a decrease of 3.45 million from 2011. This trend, resulting from ademographic transition
In demography, demographic transition is a phenomenon and theory which refers to the historical shift from high birth rates and high death rates in societies with minimal technology, education (especially of women) and economic development, to l ...
, is anticipated to continue until at least 2030.
The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is available ...
estimated the 2019 active labor force was 774.71 million.
Height and weight
As of 2020, the average Chinese man was 169.7 centimeters tall (5 ft 7 in) in 2019, the figures showed, and women's average height was 158 centimeters (5 ft 2.2 in). The same study showed an average Chinese man weighed 69.6 kilograms (153.4 lbs, or 11 stone 0 lbs), up 3.4 kilograms (7.5 lbs) over 10 years, while women were 1.7 kilograms (3.8 pounds) heavier on average at 59 kilograms (130.1 pounds, or 9 stone 4.1 lbs). They were up 1.2 centimeters (0.47 in) and 0.8 centimeters (0.31 in) respectively from 5 years earlier.Gender balance
Future challenges for China will be the gender disparity. According to the 2020 census, males account for 51.24% of China's 1.41 billion people, while females made up 48.76% of the total. The sex ratio (the number of males for each female in a population) at birth was 118.06 boys to every 100 girls (54.14%) in 2010, higher than the 116.86 (53.89%) of 2000, but 0.53 points lower than the ratio of 118.59 (54.25%) in 2005. In most Western countries the sex ratio at birth is around 105 boys to 100 girls (51.22%).Ethnic groups
The People's Republic of China (PRC) officially recognizes 56 distinct ethnic groups, the largest of which areHan
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
, who constitute 91.51% of the total population in 2010. Ethnic minorities constitute 8.49% or 113.8 million of China's population in 2010. During the past decades ethnic minorities have experienced higher growth rates than the majority Han
Han may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group.
** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese p ...
population, because they are not under the one-child policy. Their proportion of the population in China has grown from 6.1% in 1953, to 8.04% in 1990, 8.41% in 2000, and 8.49% in 2010. Large ethnic minorities (data according to the 2000 census) include the Zhuang (16 million, 1.28%), Manchu (10 million, 0.84%), Uyghur (9 million, 0.78%), Hui
The Hui people ( zh, c=, p=Huízú, w=Hui2-tsu2, Xiao'erjing: , dng, Хуэйзў, ) are an East Asian ethnoreligious group predominantly composed of Chinese-speaking adherents of Islam. They are distributed throughout China, mainly in the n ...
(9 million, 0.71%), Miao Miao may refer to:
* Miao people, linguistically and culturally related group of people, recognized as such by the government of the People's Republic of China
* Miao script or Pollard script, writing system used for Miao languages
* Miao (Unicode ...
(8 million, 0.71%), Yi (7 million, 0.61%), Tujia (5.75 million, 0.63%), Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
(5 million, 0.46%), Tibetan (5 million, 0.43%), Buyei
The Bouyei (also spelled ''Puyi'', ''Buyei'' and ''Buyi''; self called: Buxqyaix, or "Puzhong", "Burao", "Puman"; ; vi, người Bố Y), otherwise known as the Zhongjia, are an ethnic group living in Southern Mainland China. Numbering 2.5 mil ...
(3 million, 0.23%), and Korean
Korean may refer to:
People and culture
* Koreans, ethnic group originating in the Korean Peninsula
* Korean cuisine
* Korean culture
* Korean language
**Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Chosŏn'gŭl
**Korean dialects and the Jeju language
** ...
(2 million, 0.15%). Over 126,000 Westerners from Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, the US and Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
are living in Mainland China. Almost 1% of people living in Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta i ...
are Westerners
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania.
.
Neither Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta i ...
nor Macau
Macau or Macao (; ; ; ), officially the Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (MSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China in the western Pearl River Delta by the South China Sea. With a p ...
recognizes the official ethnic classifications maintained by the central government. In Macau, the largest substantial ethnic groups of non-Chinese descent are the Macanese, of mixed Chinese and Portuguese descent (Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
ns), as well as migrants from the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
and Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
. Overseas Filipinos (overwhelmingly female) working as domestic workers comprise the largest non-Han Chinese ethnic group in Hong Kong.
People from other immigration jurisdictions
The 2010 Census counted 234,829 residents from Hong Kong, 21,201 residents fromMacao
Macau or Macao (; ; ; ), officially the Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (MSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China in the western Pearl River Delta by the South China Sea. With a po ...
, 170,283 residents from Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
, and 593,832 residents from other locations, totaling 1,020,145 residents.
Religions
Migration
Internal migration Internal migration or domestic migration is human migration within a country. Internal migration tends to be travel for education and for economic improvement or because of a natural disaster or civil disturbance, though a study based on the full ...
in the People's Republic of China is one of the most extensive in the world according to the International Labour Organization
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is the first and o ...
. In fact, research done by Kam Wing Chan of the University of Washington
The University of Washington (UW, simply Washington, or informally U-Dub) is a public research university in Seattle, Washington.
Founded in 1861, Washington is one of the oldest universities on the West Coast; it was established in Seattl ...
suggests that "In the 30 years since 1979, China's urban population has grown by about 440 million to 622 million in 2009. Of the 440 million increase, about 340 million was attributable to net migration and urban reclassification. Even if only half of that increase was migration, the volume of rural-urban migration in such a short period is likely the largest in human history." Migrants in China are commonly members of a floating population Floating population is a terminology used to describe a group of people who reside in a given population for a certain amount of time and for various reasons, but are not generally considered part of the official census count.
A population is usual ...
, which refers primarily to migrants in China without local household registration status through the Chinese Hukou system
''Hukou'' () is a system of household registration used in mainland China. The system itself is more properly called "''huji''" (), and has origins in ancient China; ''hukou'' is the registration of an individual in the system (''kou'' lit ...
. In general, rural-urban migrant workers are most excluded from local educational resources, citywide social welfare programs and many jobs because of their lack of hukou status.
In 2011 a total of 252.78 million migrant worker
A migrant worker is a person who migrates within a home country or outside it to pursue work. Migrant workers usually do not have the intention to stay permanently in the country or region in which they work.
Migrant workers who work outsi ...
s (an increase of 4.4% compared to 2010) existed in China. Out of these, migrant workers who left their hometown and worked in other provinces accounted for 158.63 million (an increase of 3.4% compared to 2010) and migrant workers who worked within their home provinces reached 94.15 million (an increase of 5.9% compared to 2010). Estimations are that Chinese cities will face an influx of another 243 million migrants by 2025, taking the urban population up to nearly 1 billion people. This population of migrants would represent "almost 40 percent of the total urban population," a number which is almost three times the current level. While it is often difficult to collect accurate statistical data on migrant floating populations, the number of migrants is undoubtedly quite large. "In China's largest cities, for instance, it is often quoted that at least one out of every five persons is a migrant." China's government influences the pattern of urbanization through the Hukou
''Hukou'' () is a system of household registration used in mainland China. The system itself is more properly called "''huji''" (), and has origins in ancient China; ''hukou'' is the registration of an individual in the system (''kou'' li ...
permanent residence registration system, land-sale policies, infrastructure investment and the incentives offered to local government officials. The other factors influencing migration of people from rural provincial areas to large cities are employment, education, business opportunities and higher standard of living.
The mass emigration known as the Chinese diaspora, which occurred from the 19th century to 1949, was mainly caused by wars and starvation in mainland China
"Mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the People's Republic of China (including islands like Hainan or Chongming), excluding dependent territories of the PRC, and other territories within Greater China. ...
, invasion from various foreign countries, as well as the problems resulting from political corruption. Most immigrants were illiterate peasants and manual labourers, called "coolies
A coolie (also spelled koelie, kuli, khuli, khulie, cooli, cooly, or quli) is a term for a low-wage labourer, typically of South Asian or East Asian descent.
The word ''coolie'' was first popularized in the 16th century by European traders acros ...
" by analogy to the same pattern of immigration from India, who emigrated to work in countries such as the Americas, Australia, South Africa and Southeast Asia.
Urbanization
 Urbanization increased in speed following the initiation of the reform and opening policy. By the end of 2014, 54.7% of the total population lived in urban areas, a rate that rose from 26% in 1990.
Urbanization increased in speed following the initiation of the reform and opening policy. By the end of 2014, 54.7% of the total population lived in urban areas, a rate that rose from 26% in 1990.
Demographic statistics
Demographic statistics according to the World Population Review. The following demographic statistics are from the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated. No statistics have been included for areas currently governed by the Republic of China (Taiwan). Unless stated otherwise, statistics refer only tomainland China
"Mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the People's Republic of China (including islands like Hainan or Chongming), excluding dependent territories of the PRC, and other territories within Greater China. ...
. (See Demographics of Hong Kong
This article is about the demographic features of the population of Hong Kong, including population density, ethnicity, education level, the health of the populace, religious affiliations, and other aspects of the population.
Hong Kong i ...
and Demographics of Macau
This article is about the demographic features of the population of Macau, including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
Macau's ...
.)
;Population
*Mainland only: 1,410,539,758 (2022)
*Hong Kong: 7,276,588 (2015)
*Macau: 635,293 (2015)
*Total: 1,387,096,243 (2015).
*Population rank: 1 (See List of countries by population.)
;Urban-rural ratio
*Urban: 61.4% (2020)
*Rural: 38.6% (2020)
;Age structure
 *0–14 years: 17.29% (male 129,296,339/female 111,782,427)
*15–24 years: 11.48% (male 86,129,841/female 73,876,148)
*25–54 years: 46.81% (male 333,789,731/female 318,711,557)
*55–64 years: 12.08% (male 84,827,645/female 83,557,507)
*65 years and over: 12.34% (male 81,586,490/female 90,458,292) (2020 est.)
*0–14 years: 17.2% (2015)
*15–64 years: 72.0% (2015)
*65 years and: 10.8% (2015)
;Median age
*total: 38.4 years Country comparison to the world: 62nd
*male: 37.5 years
*female: 38.4 years (2021 est.)
;Population growth rate:
*0.19% (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 175th
;Birth rate:
*11.3 births/1,000 population (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 169th
;Death rate:
*8.26 deaths/1,000 population (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 77th
;Net migration rate:
*-0.43 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 122nd
;Population growth rate
*Population growth rate: 0.19% (2022)
;Sex distribution
*Sex distribution: 1.06 males/females (2020)
;Sex ratio
*At birth: 1.11 male(s)/female (2020)
*Under 15 years: 1.16 male(s)/female (2020)
*15–24 years: 1.17 male(s)/female (2020)
*25–54 years: 1.02 male(s)/female (2020)
*65 years and over: 0.9 male(s)/female (2020)
*Total population: 1.06 male(s)/female (2020)
;Infant mortality rate
*Total: 11.5 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est)
*Male: 11.6 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est)
*Female: 10.64 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est)
See Infant mortality in China
;Urbanization:
*urban population: 59.2% of total population (2018)
*rate of urbanization: 2.4% annual rate of change (2015–20 est.)
note: data do not include Hong Kong and Macau
;Life expectancy at birth
*Total population: 76.31 years (2021)
*Male: 74.23 years (2021)
*Female: 78.62 years (2021)
;Religious affiliation
* ''Predominantly:'' Mahayana Buddhism,
*0–14 years: 17.29% (male 129,296,339/female 111,782,427)
*15–24 years: 11.48% (male 86,129,841/female 73,876,148)
*25–54 years: 46.81% (male 333,789,731/female 318,711,557)
*55–64 years: 12.08% (male 84,827,645/female 83,557,507)
*65 years and over: 12.34% (male 81,586,490/female 90,458,292) (2020 est.)
*0–14 years: 17.2% (2015)
*15–64 years: 72.0% (2015)
*65 years and: 10.8% (2015)
;Median age
*total: 38.4 years Country comparison to the world: 62nd
*male: 37.5 years
*female: 38.4 years (2021 est.)
;Population growth rate:
*0.19% (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 175th
;Birth rate:
*11.3 births/1,000 population (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 169th
;Death rate:
*8.26 deaths/1,000 population (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 77th
;Net migration rate:
*-0.43 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 122nd
;Population growth rate
*Population growth rate: 0.19% (2022)
;Sex distribution
*Sex distribution: 1.06 males/females (2020)
;Sex ratio
*At birth: 1.11 male(s)/female (2020)
*Under 15 years: 1.16 male(s)/female (2020)
*15–24 years: 1.17 male(s)/female (2020)
*25–54 years: 1.02 male(s)/female (2020)
*65 years and over: 0.9 male(s)/female (2020)
*Total population: 1.06 male(s)/female (2020)
;Infant mortality rate
*Total: 11.5 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est)
*Male: 11.6 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est)
*Female: 10.64 deaths/1,000 live births (2020 est)
See Infant mortality in China
;Urbanization:
*urban population: 59.2% of total population (2018)
*rate of urbanization: 2.4% annual rate of change (2015–20 est.)
note: data do not include Hong Kong and Macau
;Life expectancy at birth
*Total population: 76.31 years (2021)
*Male: 74.23 years (2021)
*Female: 78.62 years (2021)
;Religious affiliation
* ''Predominantly:'' Mahayana Buddhism, Taoism
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Ta ...
, Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or a ...
(via ancestral worship
The veneration of the dead, including one's ancestors, is based on love and respect for the deceased. In some cultures, it is related to beliefs that the dead have a continued existence, and may possess the ability to influence the fortune of t ...
).
* ''Others:'' Christianity (3–4%), Islam (1.5%), ethnic minority religions, others.
* ''Note:'' State atheism
State atheism is the incorporation of positive atheism or non-theism into political regimes. It may also refer to large-scale secularization attempts by governments. It is a form of religion-state relationship that is usually ideologically l ...
, but traditionally pragmatic and eclectic.
Sources:
See also
* Megalopolises in China * Metropolitan cities of China * Demographics of Central Asia * Demographics of Beijing *Population history of China
The population history of China covers the long-term pattern of population growth in China and its impact on the history of China.
The population went through many cycles that generally reached peaks along each imperial power and was decimated d ...
*Secession in China
Secession in China refers to several secessionist movements in the People's Republic of China. Many current separatist movements in China arise from the country's ethnic issues. Some of the factors that have created these ethnic issues include ...
*Language Atlas of China
The ''Language Atlas of China'' (), published in two parts in 1987 and 1989, maps the distribution of both the varieties of Chinese and minority languages of China.
It was a collaborative effort by the Australian Academy of the Humanities and the ...
* Yi Fuxian
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Demographics Of China