Daniel Vrooman on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Daniel Vrooman (1818–1895) was an American
Daniel Vrooman (1818–1895) was an American
 Daniel Vrooman (1818–1895) was an American
Daniel Vrooman (1818–1895) was an American missionary
A missionary is a member of a religious group which is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Thomas Hale 'On Being a Mi ...
, diplomat, and cartographer.
Early life and China
Vrooman was born in Allegany County, New York, on 15 August 1818.. He and his wife Elizabeth Clemens (1826–1854) went toGuangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kon ...
(then known as "Canton") in March 1852, having been posted there by the American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions
The American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions (ABCFM) was among the first American Christian missionary organizations. It was created in 1810 by recent graduates of Williams College. In the 19th century it was the largest and most imp ...
.. Soon after their arrival, he wrote to ''Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many famous scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it. In print since 1845, it ...
'', with questions regarding the use of photographs
A photograph (also known as a photo, image, or picture) is an image created by light falling on a photosensitive surface, usually photographic film or an electronic image sensor, such as a CCD or a CMOS chip. Most photographs are now created ...
in magic lantern
The magic lantern, also known by its Latin name , is an early type of image projector that used pictures—paintings, prints, or photographs—on transparent plates (usually made of glass), one or more lenses, and a light source. Because a si ...
s, the standard American methods of rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
cleaning, and the use of india rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, and ...
in printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in which the ...
es.
Although Guangzhou had been opened to foreign trade by the 1842 Treaty of Nanjing
The Treaty of Nanjing was the peace treaty which ended the First Opium War (1839–1842) between Great Britain and the Qing dynasty of China on 29 August 1842. It was the first of what the Chinese later termed the Unequal Treaties.
In the ...
ending the First Opium War, access to the walled cities of the Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
and Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
continued to be denied to foreigners, who were mostly kept to the mercantile ghetto of the Thirteen Factories
The Thirteen Factories, also known as the , was a neighbourhood along the Pearl River in southwestern Guangzhou (Canton) in the Qing Empire from to 1856 around modern day Xiguan, in Guangzhou's Liwan District. These warehouses and stores were ...
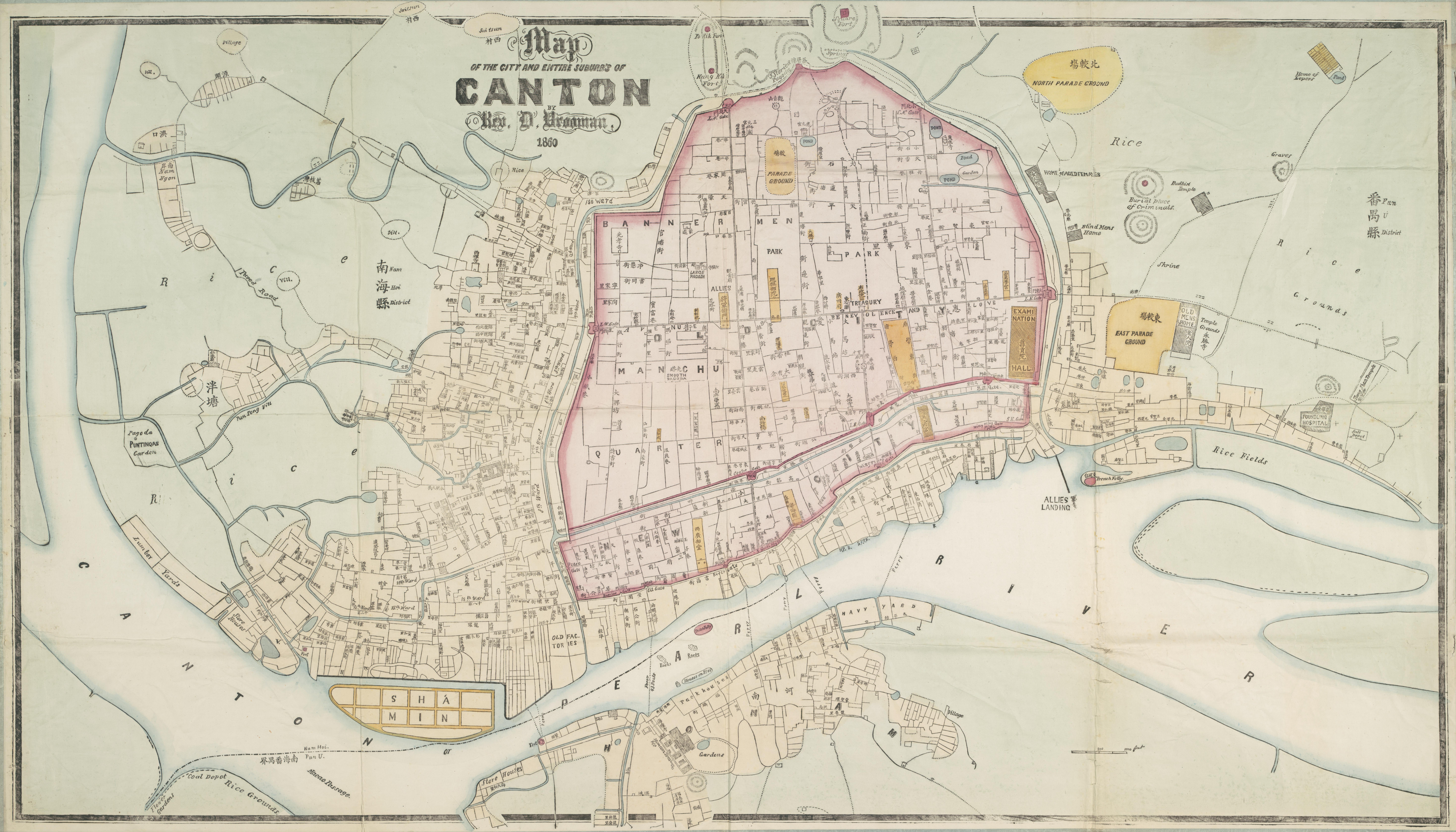
on the southern shore of the western suburbs. Vrooman successfully made a highly accurate . map of the forbidden cities in 1855 by training one of his converts to pace the streets between major landmarks, marking a course by means of a compass and reference to the wall's major gates.. These measurements were then compared against Vrooman's own, based on the angles of the visible landmarks with the high points of the city's suburbs. The map was so well done that, upon the opening of the city by the treaties of Tianjin
Tianjin (; ; Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Tientsin (), is a municipality and a coastal metropolis in Northern China on the shore of the Bohai Sea. It is one of the nine national central cities in Mainland China, with a total popu ...
(1858) and Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
(1860), they were found to need no major changes, although the Second Opium War had seen the destruction of the Thirteen Factories and the creation of a new enclave at Shamian
Shamian (also romanized as Shameen or Shamin, both from its Cantonese pronunciation) is a sandbank island in the Liwan District of Guangzhou, Guangdong, China. The island's name literally means "sandy surface" in Chinese.
The territory ...
.
Elizabeth died in Macao
Macau or Macao (; ; ; ), officially the Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (MSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China in the western Pearl River Delta by the South China Sea. With a po ...
in 1854 and he remarried three years later to Maria Wilberforce (1836–1866). He served as the American vice-consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states throu ...
and was said to have introduced mechanized cotton spinning to the city. In 1863, he published a Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding ar ...
phonetic alphabet of his own devising.
Later life
Vrooman retired from the ABCFM's Guangzhou mission in 1866 or '67, but continued to work as an independent missionary in Guangzhou until 1878. In 1878, he was made superintendent over a mission to theChinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
in Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
, Australia. He retired from this post in 1881.
He died in Oakland, California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
, on 3 March 1895.
Works
* "Map of the City and Entire Suburbs of Canton", 1855, rev. 1860 * "Vrooman Phonetic Alphabet for the Canton Dialect of the Chinese Language", 1863References
Citations
Bibliography
* . * . * . * . {{DEFAULTSORT:Vrooman, Daniel 1818 births People from Allegany County, New York American Protestant missionaries Protestant missionaries in China 19th-century cartographers American consuls American expatriates in China Protestant missionaries in Australia American expatriates in Australia 1895 deaths