DNA-dependent RNA polymerase on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 Control of the process of
Control of the process of
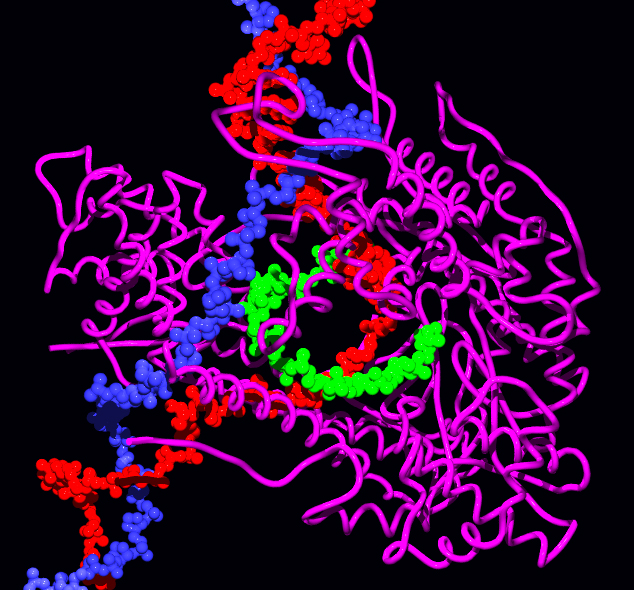
 The 17-bp transcriptional complex has an 8-bp DNA-RNA hybrid, that is, 8 base-pairs involve the RNA transcript bound to the DNA template strand. As transcription progresses, ribonucleotides are added to the 3′ end of the RNA transcript and the RNAP complex moves along the DNA. The characteristic elongation rates in prokaryotes and eukaryotes are about 10–100 nts/sec.
Aspartyl ( asp) residues in the RNAP will hold on to Mg2+ ions, which will, in turn, coordinate the phosphates of the ribonucleotides. The first Mg2+ will hold on to the α-phosphate of the NTP to be added. This allows the nucleophilic attack of the 3′-OH from the RNA transcript, adding another NTP to the chain. The second Mg2+ will hold on to the pyrophosphate of the NTP. The overall reaction equation is:
:(NMP)n + NTP → (NMP)n+1 + PPi
The 17-bp transcriptional complex has an 8-bp DNA-RNA hybrid, that is, 8 base-pairs involve the RNA transcript bound to the DNA template strand. As transcription progresses, ribonucleotides are added to the 3′ end of the RNA transcript and the RNAP complex moves along the DNA. The characteristic elongation rates in prokaryotes and eukaryotes are about 10–100 nts/sec.
Aspartyl ( asp) residues in the RNAP will hold on to Mg2+ ions, which will, in turn, coordinate the phosphates of the ribonucleotides. The first Mg2+ will hold on to the α-phosphate of the NTP to be added. This allows the nucleophilic attack of the 3′-OH from the RNA transcript, adding another NTP to the chain. The second Mg2+ will hold on to the pyrophosphate of the NTP. The overall reaction equation is:
:(NMP)n + NTP → (NMP)n+1 + PPi
DNAi
– DNA Interactive, including information and Flash clips on RNA Polymerase. * *
RNA Polymerase – Synthesis RNA from DNA Template
(
3D macromolecular structures of RNA Polymerase from the EM Data Bank(EMDB)
{{Authority control Gene expression RNA Enzymes EC 2.7.7
 In
In molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and physi ...
, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. ...
that synthesizes RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohyd ...
from a DNA template.
Using the enzyme helicase
Helicases are a class of enzymes thought to be vital to all organisms. Their main function is to unpack an organism's genetic material. Helicases are motor proteins that move directionally along a nucleic acid phosphodiester backbone, separating ...
, RNAP locally opens the double-stranded DNA so that one strand of the exposed nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules with ...
s can be used as a template for the synthesis of RNA, a process called transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
. A transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The fun ...
and its associated transcription mediator complex
Mediator is a multiprotein complex that functions as a transcriptional coactivator in all eukaryotes. It was discovered in 1990 in the lab of Roger D. Kornberg, recipient of the 2006 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Mediator complexes interact with tran ...
must be attached to a DNA binding site
DNA binding sites are a type of binding site found in DNA where other molecules may bind. DNA binding sites are distinct from other binding sites in that (1) they are part of a DNA sequence (e.g. a genome) and (2) they are bound by DNA-binding ...
called a promoter region
In genetics, a promoter is a sequence of DNA to which proteins bind to initiate transcription of a single RNA transcript from the DNA downstream of the promoter. The RNA transcript may encode a protein (mRNA), or can have a function in and of i ...
before RNAP can initiate the DNA unwinding at that position. RNAP not only initiates RNA transcription, it also guides the nucleotides into position, facilitates attachment and elongation, has intrinsic proofreading and replacement capabilities, and termination recognition capability. In eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bact ...
s, RNAP can build chains as long as 2.4 million nucleotides.
RNAP produces RNA that, functionally, is either for protein coding, i.e. messenger RNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the p ...
(mRNA); or non-coding (so-called "RNA genes"). At least four functional types of RNA genes exist:
; Transfer RNA
Transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA and formerly referred to as sRNA, for soluble RNA) is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes), that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino ac ...
(tRNA): Transfers specific amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
s to growing polypeptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A p ...
chains at the ribosomal site of protein synthesis
Protein biosynthesis (or protein synthesis) is a core biological process, occurring inside cells, balancing the loss of cellular proteins (via degradation or export) through the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of critical ...
during translation
Translation is the communication of the Meaning (linguistic), meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The ...
;
; Ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal ...
(rRNA): Incorporates into ribosomes;
; Micro RNA
MicroRNA (miRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21 to 23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals and some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. miRN ...
(miRNA): Regulates gene activity; and, RNA silencing
; Catalytic RNA
Ribozymes (ribonucleic acid enzymes) are RNA molecules that have the ability to catalyze specific biochemical reactions, including RNA splicing in gene expression, similar to the action of protein enzymes. The 1982 discovery of ribozymes demonst ...
(ribozyme
Ribozymes (ribonucleic acid enzymes) are RNA molecules that have the ability to catalyze specific biochemical reactions, including RNA splicing in gene expression, similar to the action of protein enzymes. The 1982 discovery of ribozymes demonst ...
): Functions as an enzymatically active RNA molecule.
RNA polymerase is essential to life, and is found in all living organism
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells ( cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and fung ...
s and many virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's ...
es. Depending on the organism, a RNA polymerase can be a protein complex
A protein complex or multiprotein complex is a group of two or more associated polypeptide chains. Protein complexes are distinct from multienzyme complexes, in which multiple catalytic domains are found in a single polypeptide chain.
Protein ...
(multi-subunit RNAP) or only consist of one subunit (single-subunit RNAP, ssRNAP), each representing an independent lineage. The former is found in bacteria, archaea, and eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bact ...
s alike, sharing a similar core structure and mechanism. The latter is found in phage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteri ...
s as well as eukaryotic chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in ...
s and mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is use ...
, and is related to modern DNA polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create ...
s. Eukaryotic and archaeal RNAPs have more subunits than bacterial ones do, and are controlled differently.
Bacteria and archaea only have one RNA polymerase. Eukaryotes have multiple types of nuclear RNAP, each responsible for synthesis of a distinct subset of RNA:
Structure
The 2006Nobel Prize in Chemistry
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "M ...
was awarded to Roger D. Kornberg
Roger David Kornberg (born April 24, 1947) is an American biochemist and professor of structural biology at Stanford University School of Medicine. Kornberg was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2006 for his studies of the process by which ...
for creating detailed molecular images of RNA polymerase during various stages of the transcription process.
In most prokaryote
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Connec ...
s, a single RNA polymerase species transcribes all types of RNA. RNA polymerase "core" from E. coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Esche ...
consists of five subunits: two alpha (α) subunits of 36 kDa
The dalton or unified atomic mass unit (symbols: Da or u) is a non-SI unit of mass widely used in physics and chemistry. It is defined as of the mass of an unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state and at r ...
, a beta (β) subunit of 150 kDa, a beta prime subunit (β′) of 155 kDa, and a small omega (ω) subunit. A sigma (σ) factor binds to the core, forming the holoenzyme. After transcription starts, the factor can unbind and let the core enzyme proceed with its work. The core RNA polymerase complex forms a "crab claw" or "clamp-jaw" structure with an internal channel running along the full length. Eukaryotic and archaeal RNA polymerases have a similar core structure and work in a similar manner, although they have many extra subunits.
All RNAPs contain metal cofactors
Cofactor may also refer to:
* Cofactor (biochemistry), a substance that needs to be present in addition to an enzyme for a certain reaction to be catalysed
* A domain parameter in elliptic curve cryptography, defined as the ratio between the order ...
, in particular zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic ta ...
and magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
cations which aid in the transcription process.
Function
 Control of the process of
Control of the process of gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
transcription affects patterns of gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. The ...
and, thereby, allows a cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
to adapt to a changing environment, perform specialized roles within an organism, and maintain basic metabolic processes necessary for survival. Therefore, it is hardly surprising that the activity of RNAP is long, complex, and highly regulated. In ''Escherichia coli'' bacteria, more than 100 transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The fun ...
s have been identified, which modify the activity of RNAP.
RNAP can initiate transcription at specific DNA sequences known as promoters. It then produces an RNA chain, which is complementary
A complement is something that completes something else.
Complement may refer specifically to:
The arts
* Complement (music), an interval that, when added to another, spans an octave
** Aggregate complementation, the separation of pitch-class ...
to the template DNA strand. The process of adding nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules with ...
s to the RNA strand is known as elongation; in eukaryotes, RNAP can build chains as long as 2.4 million nucleotides
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules with ...
(the full length of the dystrophin
Dystrophin is a rod-shaped cytoplasmic protein, and a vital part of a protein complex that connects the cytoskeleton of a muscle fiber to the surrounding extracellular matrix through the cell membrane. This complex is variously known as the c ...
gene). RNAP will preferentially release its RNA transcript at specific DNA sequences encoded at the end of genes, which are known as terminators.
Products of RNAP include:
*Messenger RNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the p ...
(mRNA)—template for the synthesis of proteins by ribosome
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to f ...
s.
*Non-coding RNA
A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is a functional RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene. Abundant and functionally important types of non- ...
or "RNA genes"—a broad class of genes that encode RNA that is not translated into protein. The most prominent examples of RNA genes are transfer RNA
Transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA and formerly referred to as sRNA, for soluble RNA) is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes), that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino ac ...
(tRNA) and ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal ...
(rRNA), both of which are involved in the process of translation
Translation is the communication of the Meaning (linguistic), meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The ...
. However, since the late 1990s, many new RNA genes have been found, and thus RNA genes may play a much more significant role than previously thought.
**Transfer RNA
Transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA and formerly referred to as sRNA, for soluble RNA) is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes), that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino ac ...
(tRNA)—transfers specific amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
s to growing polypeptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A p ...
chains at the ribosomal site of protein synthesis during translation
Translation is the communication of the Meaning (linguistic), meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The ...
**Ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal ...
(rRNA)—a component of ribosomes
**Micro RNA
MicroRNA (miRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21 to 23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals and some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. miRN ...
—regulates gene activity
**Catalytic RNA (Ribozyme
Ribozymes (ribonucleic acid enzymes) are RNA molecules that have the ability to catalyze specific biochemical reactions, including RNA splicing in gene expression, similar to the action of protein enzymes. The 1982 discovery of ribozymes demonst ...
)—enzymatically active RNA molecules
RNAP accomplishes ''de novo'' synthesis. It is able to do this because specific interactions with the initiating nucleotide hold RNAP rigidly in place, facilitating chemical attack on the incoming nucleotide. Such specific interactions explain why RNAP prefers to start transcripts with ATP (followed by GTP, UTP, and then CTP). In contrast to DNA polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create ...
, RNAP includes helicase
Helicases are a class of enzymes thought to be vital to all organisms. Their main function is to unpack an organism's genetic material. Helicases are motor proteins that move directionally along a nucleic acid phosphodiester backbone, separating ...
activity, therefore no separate enzyme is needed to unwind DNA.
Action
Initiation
RNA polymerase binding in bacteria involves thesigma factor
A sigma factor (σ factor or specificity factor) is a protein needed for initiation of transcription in bacteria. It is a bacterial transcription initiation factor that enables specific binding of RNA polymerase (RNAP) to gene promoters. It is ho ...
recognizing the core promoter region containing the −35 and −10 elements (located ''before'' the beginning of sequence to be transcribed) and also, at some promoters, the α subunit C-terminal domain recognizing promoter upstream elements. There are multiple interchangeable sigma factors, each of which recognizes a distinct set of promoters. For example, in ''E. coli'', σ70 is expressed under normal conditions and recognizes promoters for genes required under normal conditions ("housekeeping gene
In molecular biology, housekeeping genes are typically constitutive genes that are required for the maintenance of basic cellular function, and are expressed in all cells of an organism under normal and patho-physiological conditions. Although ...
s"), while σ32 recognizes promoters for genes required at high temperatures (" heat-shock genes"). In archaea and eukaryotes, the functions of the bacterial general transcription factor sigma are performed by multiple general transcription factor
General transcription factors (GTFs), also known as basal transcriptional factors, are a class of protein transcription factors that bind to specific sites ( promoter) on DNA to activate transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger ...
s that work together. The RNA polymerase-promoter closed complex is usually referred to as the "transcription preinitiation complex
The preinitiation complex (abbreviated PIC) is a complex of approximately 100 proteins that is necessary for the transcription of protein-coding genes in eukaryotes and archaea. The preinitiation complex positions RNA polymerase II at gene tran ...
."
After binding to the DNA, the RNA polymerase switches from a closed complex to an open complex. This change involves the separation of the DNA strands to form an unwound section of DNA of approximately 13 bp, referred to as the "transcription bubble
A transcription bubble is a molecular structure formed during DNA transcription when a limited portion of the DNA double helix is unwound. The size of a transcription bubble ranges from 12-14 base pairs. A transcription bubble is formed when the ...
". Supercoiling plays an important part in polymerase activity because of the unwinding and rewinding of DNA. Because regions of DNA in front of RNAP are unwound, there are compensatory positive supercoils. Regions behind RNAP are rewound and negative supercoils are present.
Promoter escape
RNA polymerase then starts to synthesize the initial DNA-RNA heteroduplex, with ribonucleotides base-paired to the template DNA strand according to Watson-Crick base-pairing interactions. As noted above, RNA polymerase makes contacts with the promoter region. However these stabilizing contacts inhibit the enzyme's ability to access DNA further downstream and thus the synthesis of the full-length product. In order to continue RNA synthesis, RNA polymerase must escape the promoter. It must maintain promoter contacts while unwinding more downstream DNA for synthesis, "scrunching" more downstream DNA into the initiation complex. During the promoter escape transition, RNA polymerase is considered a "stressed intermediate." Thermodynamically the stress accumulates from the DNA-unwinding and DNA-compaction activities. Once the DNA-RNA heteroduplex is long enough (~10 bp), RNA polymerase releases its upstream contacts and effectively achieves the promoter escape transition into the elongation phase. The heteroduplex at the active center stabilizes the elongation complex. However, promoter escape is not the only outcome. RNA polymerase can also relieve the stress by releasing its downstream contacts, arresting transcription. The paused transcribing complex has two options: (1) release the nascent transcript and begin anew at the promoter or (2) reestablish a new 3′-OH on the nascent transcript at the active site via RNA polymerase's catalytic activity and recommence DNA scrunching to achieve promoter escape.Abortive initiation Abortive initiation, also known as abortive transcription, is an early process of genetic transcription in which RNA polymerase binds to a DNA promoter and enters into cycles of synthesis of short mRNA transcripts which are released before the tra ...
, the unproductive cycling of RNA polymerase before the promoter escape transition, results in short RNA fragments of around 9 bp in a process known as abortive transcription. The extent of abortive initiation depends on the presence of transcription factors and the strength of the promoter contacts.
Elongation
 The 17-bp transcriptional complex has an 8-bp DNA-RNA hybrid, that is, 8 base-pairs involve the RNA transcript bound to the DNA template strand. As transcription progresses, ribonucleotides are added to the 3′ end of the RNA transcript and the RNAP complex moves along the DNA. The characteristic elongation rates in prokaryotes and eukaryotes are about 10–100 nts/sec.
Aspartyl ( asp) residues in the RNAP will hold on to Mg2+ ions, which will, in turn, coordinate the phosphates of the ribonucleotides. The first Mg2+ will hold on to the α-phosphate of the NTP to be added. This allows the nucleophilic attack of the 3′-OH from the RNA transcript, adding another NTP to the chain. The second Mg2+ will hold on to the pyrophosphate of the NTP. The overall reaction equation is:
:(NMP)n + NTP → (NMP)n+1 + PPi
The 17-bp transcriptional complex has an 8-bp DNA-RNA hybrid, that is, 8 base-pairs involve the RNA transcript bound to the DNA template strand. As transcription progresses, ribonucleotides are added to the 3′ end of the RNA transcript and the RNAP complex moves along the DNA. The characteristic elongation rates in prokaryotes and eukaryotes are about 10–100 nts/sec.
Aspartyl ( asp) residues in the RNAP will hold on to Mg2+ ions, which will, in turn, coordinate the phosphates of the ribonucleotides. The first Mg2+ will hold on to the α-phosphate of the NTP to be added. This allows the nucleophilic attack of the 3′-OH from the RNA transcript, adding another NTP to the chain. The second Mg2+ will hold on to the pyrophosphate of the NTP. The overall reaction equation is:
:(NMP)n + NTP → (NMP)n+1 + PPi
Fidelity
Unlike the proofreading mechanisms ofDNA polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create ...
those of RNAP have only recently been investigated. Proofreading begins with separation of the mis-incorporated nucleotide from the DNA template. This pauses transcription. The polymerase then backtracks by one position and cleaves the dinucleotide that contains the mismatched nucleotide. In the RNA polymerase this occurs at the same active site used for polymerization and is therefore markedly different from the DNA polymerase where proofreading occurs at a distinct nuclease active site.
The overall error rate is around 10−4 to 10−6.
Termination
In bacteria, termination of RNA transcription can be rho-dependent or rho-independent. The former relies on therho factor
A ρ factor (Rho factor) is a bacterial protein involved in the termination of transcription.
* Rho factor binds to the transcription terminator pause site, an exposed region of single stranded RNA (a stretch of 72 nucleotides) after the open r ...
, which destabilizes the DNA-RNA heteroduplex and causes RNA release. The latter, also known as intrinsic termination
Intrinsic, or rho-independent termination, is a process in prokaryotes to signal the end of transcription and release the newly constructed RNA molecule. In prokaryotes such as E. coli, transcription is terminated either by a rho-dependent process ...
, relies on a palindromic region of DNA. Transcribing the region causes the formation of a "hairpin" structure from the RNA transcription looping and binding upon itself. This hairpin structure is often rich in G-C base-pairs, making it more stable than the DNA-RNA hybrid itself. As a result, the 8 bp DNA-RNA hybrid in the transcription complex shifts to a 4 bp hybrid. These last 4 base pairs are weak A-U base pairs, and the entire RNA transcript will fall off the DNA.
Transcription termination in eukaryotes is less well understood than in bacteria, but involves cleavage of the new transcript followed by template-independent addition of adenines at its new 3′ end, in a process called polyadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to an RNA transcript, typically a messenger RNA (mRNA). The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In euk ...
.
Other organisms
Given that DNA and RNA polymerases both carry out template-dependent nucleotide polymerization, it might be expected that the two types of enzymes would be structurally related. However, x-ray crystallographic studies of both types of enzymes reveal that, other than containing a critical Mg2+ ion at the catalytic site, they are virtually unrelated to each other; indeed template-dependent nucleotide polymerizing enzymes seem to have arisen independently twice during the early evolution of cells. One lineage led to the modern DNA polymerases and reverse transcriptases, as well as to a few single-subunit RNA polymerases (ssRNAP) from phages and organelles. The other multi-subunit RNAP lineage formed all of the modern cellular RNA polymerases.Bacteria
In bacteria, the same enzyme catalyzes the synthesis ofmRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the p ...
and non-coding RNA (ncRNA).
RNAP is a large molecule. The core enzyme has five subunits (~400 kDa
The dalton or unified atomic mass unit (symbols: Da or u) is a non-SI unit of mass widely used in physics and chemistry. It is defined as of the mass of an unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state and at r ...
):
; β′: The β′ subunit is the largest subunit, and is encoded by the rpoC gene. The β′ subunit contains part of the active center responsible for RNA synthesis and contains some of the determinants for non-sequence-specific interactions with DNA and nascent RNA. It is split into two subunits in Cyanobacteria and chloroplasts.
; β: The β subunit is the second-largest subunit, and is encoded by the rpoB
The ''rpoB'' gene encodes the β subunit of bacterial RNA polymerase and the homologous plastid-encoded RNA polymerase (PEP). It codes for 1342 amino acids in ''E. coli'', making it the second-largest polypeptide in the bacterial cell. It is targe ...
gene. The β subunit contains the rest of the active center responsible for RNA synthesis and contains the rest of the determinants for non-sequence-specific interactions with DNA and nascent RNA.
; α (αI and αII): Two copies of the α subunit, being the third-largest subunit, are present in a molecule of RNAP: αI and αII (one and two). Each α subunit contains two domains: αNTD (N-terminal domain) and αCTD (C-terminal domain). αNTD contains determinants for assembly of RNAP. αCTD (C-terminal domain) contains determinants for interaction with promoter DNA, making non-sequence-non-specific interactions at most promoters and sequence-specific interactions at upstream-element-containing promoters, and contains determinants for interactions with regulatory factors.
; ω: The ω subunit is the smallest subunit. The ω subunit facilitates assembly of RNAP and stabilizes assembled RNAP.
In order to bind promoters, RNAP core associates with the transcription initiation factor sigma
Sigma (; uppercase Σ, lowercase σ, lowercase in word-final position ς; grc-gre, σίγμα) is the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 200. In general mathematics, uppercase Σ is used a ...
(σ) to form RNA polymerase holoenzyme. Sigma reduces the affinity of RNAP for nonspecific DNA while increasing specificity for promoters, allowing transcription to initiate at correct sites. The complete holoenzyme therefore has 6 subunits: β′βαI and αIIωσ (~450 kDa).
Eukaryotes
Eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bact ...
s have multiple types of nuclear RNAP, each responsible for synthesis of a distinct subset of RNA. All are structurally and mechanistically related to each other and to bacterial RNAP:
Eukaryotic chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in ...
s contain an RNAP very highly similar to bacterial RNAP ("plastid-encoded polymerase, PEP"). They use sigma factors encoded in the nuclear genome.
Chloroplast also contain a second, structurally and mechanistically unrelated, single-subunit RNAP ("nucleus-encoded polymerase, NEP"). Eukaryotic mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is use ...
use POLRMT
POLRMT is a symbol of RNA polymerase mitochondrial
It is a DNA-directed RNA polymerase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''POLRMT'' gene.
Function
This gene encodes a mitochondrial DNA-directed RNA polymerase. The gen ...
(human), a nucleus-encoded single-subunit RNAP. Such phage-like polymerases are referred to as RpoT in plants.
Archaea
Archaea have a single type of RNAP, responsible for the synthesis of all RNA. Archaeal RNAP is structurally and mechanistically similar to bacterial RNAP and eukaryotic nuclear RNAP I-V, and is especially closely structurally and mechanistically related to eukaryotic nuclear RNAP II. The history of the discovery of the archaeal RNA polymerase is quite recent. The first analysis of the RNAP of an archaeon was performed in 1971, when the RNAP from the extremehalophile
The halophiles, named after the Greek word for "salt-loving", are extremophiles that thrive in high salt concentrations. While most halophiles are classified into the domain Archaea, there are also bacterial halophiles and some eukaryotic species, ...
'' Halobacterium cutirubrum'' was isolated and purified. Crystal structures of RNAPs from ''Sulfolobus solfataricus
''Saccharolobus solfataricus'' is a species of thermophilic archaeon. It was transferred from the genus ''Sulfolobus'' to the new genus ''Saccharolobus'' with the description of Saccharolobus caldissimus in 2018.
It was first isolated and disc ...
'' and '' Sulfolobus shibatae'' set the total number of identified archaeal subunits at thirteen.
Archaea has the subunit corresponding to Eukaryotic Rpb1 split into two. There is no homolog to eukaryotic Rpb9 ( POLR2I) in the ''S. shibatae'' complex, although TFS (TFIIS homolog) has been proposed as one based on similarity. There is an additional subunit dubbed Rpo13; together with Rpo5 it occupies a space filled by an insertion found in bacterial β′ subunits (1,377–1,420 in ''Taq''). An earlier, lower-resolution study on ''S. solfataricus'' structure did not find Rpo13 and only assigned the space to Rpo5/Rpb5. Rpo3 is notable in that it's an iron–sulfur protein
Iron–sulfur proteins (or iron–sulphur proteins in British spelling) are proteins characterized by the presence of iron–sulfur clusters containing sulfide-linked di-, tri-, and tetrairon centers in variable oxidation states. Iron–sulfur cl ...
. RNAP I/III subunit AC40 found in some eukaryotes share similar sequences, but does not bind iron. This domain, in either case, serves a structural function.
Archaeal RNAP subunit previously used an "RpoX" nomenclature where each subunit is assigned a letter in a way unrelated to any other systems. In 2009, a new nomenclature based on Eukaryotic Pol II subunit "Rpb" numbering was proposed.
Viruses

Orthopoxvirus
''Orthopoxvirus'' is a genus of viruses in the family ''Poxviridae'' and subfamily ''Chordopoxvirinae''. Vertebrates, including mammals and humans, and arthropods serve as natural hosts. There are 12 species in this genus. Diseases associated wi ...
es and some other nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses
''Nucleocytoviricota'' is a phylum of viruses. Members of the phylum are also known as the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses (NCLDV), which serves as the basis of the name of the phylum with the suffix - for virus phylum. These viruses are refe ...
synthesize RNA using a virally encoded multi-subunit RNAP. They are most similar to eukaryotic RNAPs, with some subunits minified or removed. Exactly which RNAP they are most similar to is a topic of debate. Most other viruses that synthesize RNA use unrelated mechanics.
Many viruses use a single-subunit DNA-dependent RNAP (ssRNAP) that is structurally and mechanistically related to the single-subunit RNAP of eukaryotic chloroplasts (RpoT) and mitochondria (POLRMT
POLRMT is a symbol of RNA polymerase mitochondrial
It is a DNA-directed RNA polymerase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''POLRMT'' gene.
Function
This gene encodes a mitochondrial DNA-directed RNA polymerase. The gen ...
) and, more distantly, to DNA polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create ...
s and reverse transcriptases. Perhaps the most widely studied such single-subunit RNAP is bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteri ...
T7 RNA polymerase
T7 RNA Polymerase is an RNA polymerase from the T7 bacteriophage that catalyzes the formation of RNA from DNA in the 5'→ 3' direction.
Activity
T7 polymerase is extremely promoter-specific and transcribes only DNA downstream of a T7 promot ...
. ssRNAPs cannot proofread.
B. subtilis prophage A prophage is a bacteriophage (often shortened to "phage") genome that is integrated into the circular bacterial chromosome or exists as an extrachromosomal plasmid within the bacterial cell. Integration of prophages into the bacterial host is the c ...
SPβ uses YonO, a homolog of the β+β′ subunits of msRNAPs to form a monomeric (both barrels on the same chain) RNAP distinct from the usual "right hand" ssRNAP. It probably diverged very long ago from the canonical five-unit msRNAP, before the time of the last universal common ancestor
The last universal common ancestor (LUCA) is the most recent population from which all organisms now living on Earth share common descent—the most recent common ancestor of all current life on Earth. This includes all cellular organisms; th ...
.
Other viruses use a RNA-dependent RNAP (an RNAP that employs RNA as a template instead of DNA). This occurs in negative strand RNA viruses and dsRNA viruses, both of which exist for a portion of their life cycle as double-stranded RNA. However, some positive strand RNA viruses, such as polio
Poliomyelitis, commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 70% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe sy ...
virus, also contain RNA-dependent RNAP.
History
RNAP was discovered independently by Charles Loe, Audrey Stevens, andJerard Hurwitz
Jerard Hurwitz (November 20, 1928 – January 24, 2019) was an American biochemist who co-discovered RNA polymerase in 1960 along with Sam Weiss, Audrey Stevens, and James Bonner. He most recently worked at the Sloan-Kettering Institute in New Yo ...
in 1960. By this time, one half of the 1959 Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
in Medicine had been awarded to Severo Ochoa
Severo Ochoa de Albornoz (; 24 September 1905 – 1 November 1993) was a Spanish physician and biochemist, and winner of the 1959 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine together with Arthur Kornberg for their discovery of "the mechanisms in th ...
for the discovery of what was believed to be RNAP, but instead turned out to be polynucleotide phosphorylase
Polynucleotide Phosphorylase (PNPase) is a bifunctional enzyme with a phosphorolytic 3' to 5' exoribonuclease activity and a 3'-terminal oligonucleotide polymerase activity. That is, it dismantles the RNA chain starting at the 3' end and working ...
.
Purification
RNA polymerase can be isolated in the following ways: *By a phosphocellulose column. *By glycerol gradient centrifugation. *By a DNA column. *By anion chromatography
Ion chromatography (or ion-exchange chromatography) separates ions and polar molecules based on their affinity to the ion exchanger. It works on almost any kind of charged molecule—including large proteins, small nucleotides, and amino aci ...
column.
And also combinations of the above techniques.
See also
* Alpha-amanitin *Primase
DNA primase is an enzyme involved in the replication of DNA and is a type of RNA polymerase. Primase catalyzes the synthesis of a short RNA (or DNA in some
living organisms) segment called a primer complementary to a ssDNA (single-stranded ...
References
External links
DNAi
– DNA Interactive, including information and Flash clips on RNA Polymerase. * *
RNA Polymerase – Synthesis RNA from DNA Template
(
Wayback Machine
The Wayback Machine is a digital archive of the World Wide Web founded by the Internet Archive, a nonprofit based in San Francisco, California. Created in 1996 and launched to the public in 2001, it allows the user to go "back in time" and se ...
copy)3D macromolecular structures of RNA Polymerase from the EM Data Bank(EMDB)
{{Authority control Gene expression RNA Enzymes EC 2.7.7