Dzungarian Horse on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Przewalski's horse (, , (Пржевальский ), ) (''Equus ferus przewalskii'' or ''Equus przewalskii''), also called the takhi, Mongolian wild horse or Dzungarian horse, is a rare and endangered horse originally native to the
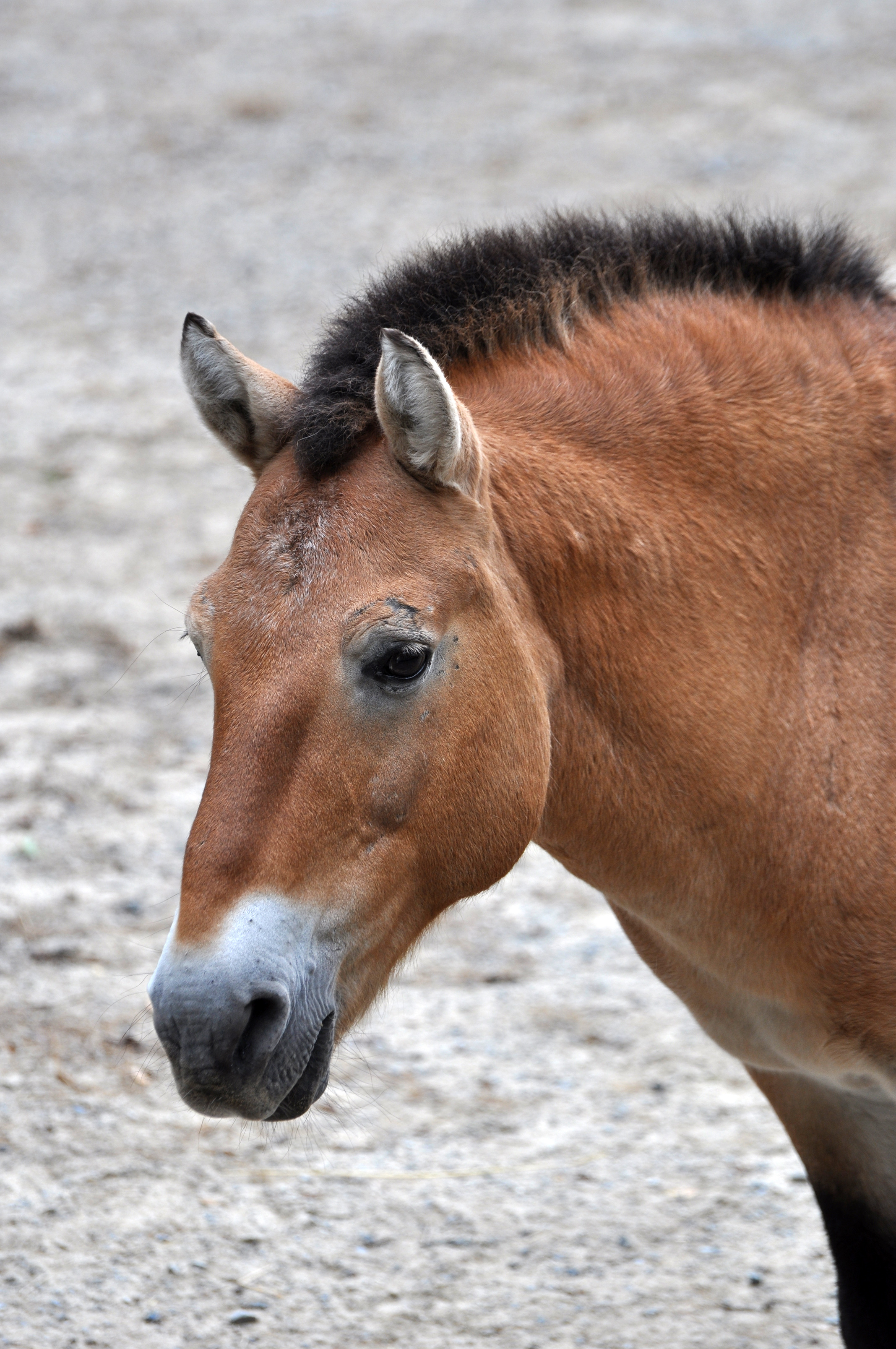

 Przewalski reported the horses forming troops of between five and fifteen members, consisting of an old stallion, his mares and foals. Modern reintroduced populations similarly form family groups of one adult stallion, one to three mares, and their common offspring that stay in the family group until they are no longer dependent, usually at two or three years old. Young females join other harems, while bachelor stallions as well as old stallions who have lost their harems join bachelor groups. Family groups can join to form a herd that moves together.
The patterns of their daily lives exhibit horse behavior similar to that of feral horse herds. Stallions herd, drive, and defend all members of their family, while the mares often display leadership in the family. Stallions and mares stay with their preferred partners for years. While behavioral synchronization is high among mares, stallions other than the main harem stallion are generally less stable in this respect.
Home range in the wild is little studied, but estimated as in the Hustai National Park and in the
Przewalski reported the horses forming troops of between five and fifteen members, consisting of an old stallion, his mares and foals. Modern reintroduced populations similarly form family groups of one adult stallion, one to three mares, and their common offspring that stay in the family group until they are no longer dependent, usually at two or three years old. Young females join other harems, while bachelor stallions as well as old stallions who have lost their harems join bachelor groups. Family groups can join to form a herd that moves together.
The patterns of their daily lives exhibit horse behavior similar to that of feral horse herds. Stallions herd, drive, and defend all members of their family, while the mares often display leadership in the family. Stallions and mares stay with their preferred partners for years. While behavioral synchronization is high among mares, stallions other than the main harem stallion are generally less stable in this respect.
Home range in the wild is little studied, but estimated as in the Hustai National Park and in the 
 The species is named after a Russian colonel of Polish descent,
The species is named after a Russian colonel of Polish descent,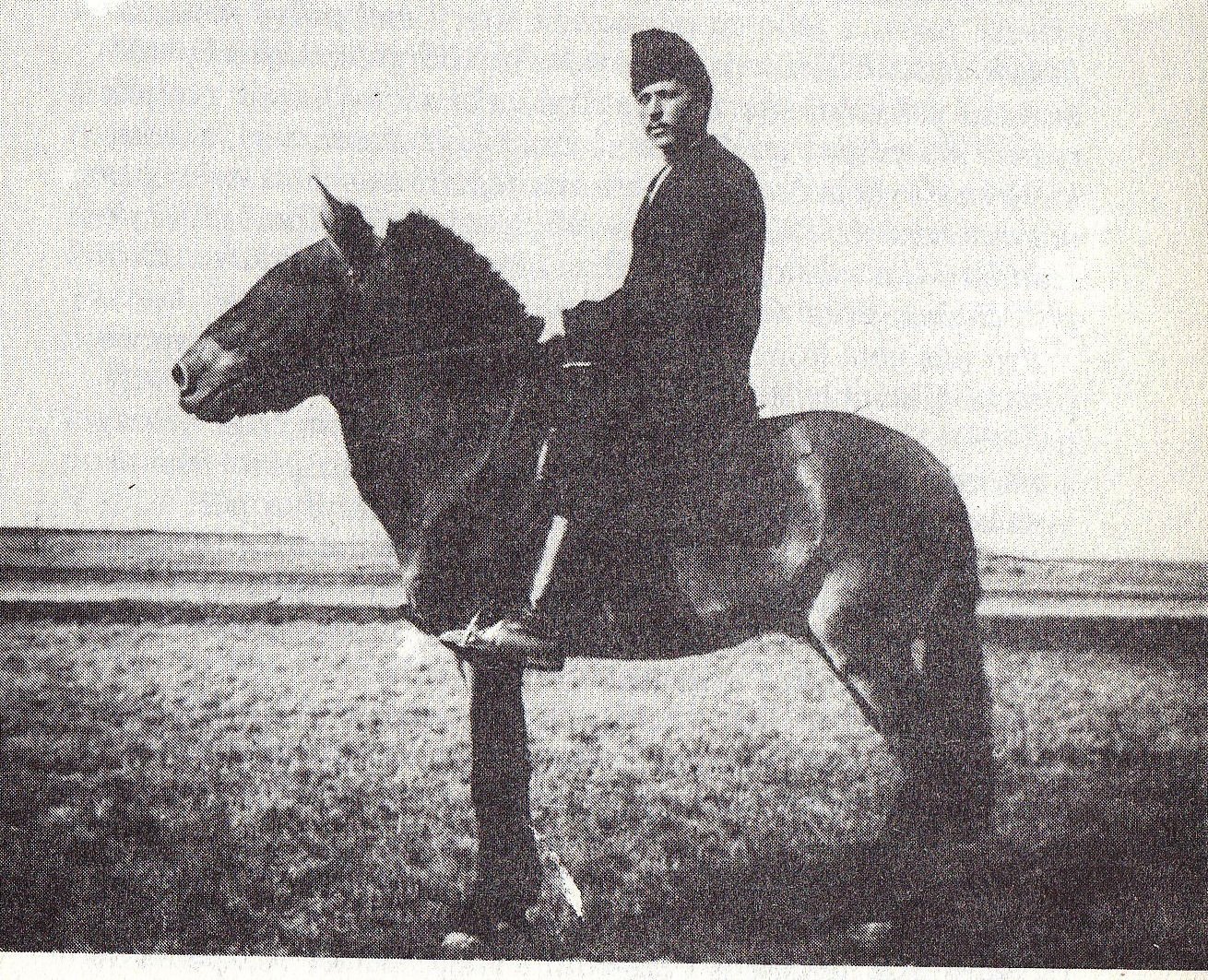 
 In 1977, the Foundation for the Preservation and Protection of the Przewalski Horse was founded in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, by Jan and Inge Bouman. The foundation started a program of exchange between captive populations in zoos throughout the world to reduce inbreeding, and later began a breeding program of its own. As a result of such efforts, the extant herd has retained a far greater genetic diversity than its genetic bottleneck made likely. By 1979, when this concerted program of population management to maximize
In 1977, the Foundation for the Preservation and Protection of the Przewalski Horse was founded in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, by Jan and Inge Bouman. The foundation started a program of exchange between captive populations in zoos throughout the world to reduce inbreeding, and later began a breeding program of its own. As a result of such efforts, the extant herd has retained a far greater genetic diversity than its genetic bottleneck made likely. By 1979, when this concerted program of population management to maximize 
 In the earlier decades of captivity, the insular breeding by individual zoos led to inbreeding and reduced fertility. In 1979, several American zoos began a collaborative breeding-exchange program to maximize genetic diversity. Recent advances in equine reproductive science have also been used to preserve and expand the gene pool. Scientists at the Smithsonian Institution's National Zoo successfully reversed a vasectomy on a Przewalski's horse in 2007—the first operation of its kind on this species, and possibly the first ever on any endangered species. While normally a vasectomy may be performed on an endangered animal under limited circumstances, particularly if an individual has already produced many offspring and its genes are overrepresented in the population, scientists realized the animal in question was one of the most genetically valuable Przewalski's horses in the North American breeding program. The first birth by artificial insemination occurred on 27 July 2013 at the
In the earlier decades of captivity, the insular breeding by individual zoos led to inbreeding and reduced fertility. In 1979, several American zoos began a collaborative breeding-exchange program to maximize genetic diversity. Recent advances in equine reproductive science have also been used to preserve and expand the gene pool. Scientists at the Smithsonian Institution's National Zoo successfully reversed a vasectomy on a Przewalski's horse in 2007—the first operation of its kind on this species, and possibly the first ever on any endangered species. While normally a vasectomy may be performed on an endangered animal under limited circumstances, particularly if an individual has already produced many offspring and its genes are overrepresented in the population, scientists realized the animal in question was one of the most genetically valuable Przewalski's horses in the North American breeding program. The first birth by artificial insemination occurred on 27 July 2013 at the
steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslands, ...
s of Central Asia. It is named after the Russian geographer and explorer Nikolay Przhevalsky
Nikolay Mikhaylovich Przhevalsky (or Prjevalsky;; pl, Nikołaj Przewalski, . – ) was a Russian geographer of Polish descent (he was born in a Polish noble family), and a renowned explorer of Central and East Asia.
Although he never reache ...
. Once extinct in the wild
A species that is extinct in the wild (EW) is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as known only by living members kept in captivity or as a naturalized population outside its historic range due ...
, it has been reintroduced
Species reintroduction is the deliberate release of a species into the wild, from captivity or other areas where the organism is capable of survival. The goal of species reintroduction is to establish a healthy, genetically diverse, self-sustainin ...
to its native habitat since the 1990s in Mongolia at the Khustain Nuruu National Park, Takhin Tal Nature Reserve, and Khomiin Tal, as well as several other locales in Central Asia and Eastern Europe.
Several genetic characteristics of Przewalski's horse differ from what is seen in modern domestic horses, indicating neither is an ancestor of the other. For example, the Przewalski has 33 chromosome pairs, compared to 32 for the domestic horse. Their ancestral lineages split from a common ancestor between 38,000 and 160,000 years ago, long before the domestication of the horse. Przewalski's horse was long considered the only remaining truly wild horse, in contrast with the American Mustang or the Australian brumby, which are instead feral horses descended from domesticated animals. This assumption was challenged in 2018 when DNA analysis of horse remains associated with the 5,000-year-old Botai culture
The Botai culture is an archaeological culture (c. 3700–3100 BC) of prehistoric northern Central Asia. It was named after the settlement of Botai in today's northern Kazakhstan. The Botai culture has two other large sites: Krasnyi ...
of Central Asia revealed the animals were of Przewalski lineage. However, the domestication status of these animals has been questioned. Its taxonomic
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.
A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ...
position is still debated, with some taxonomists treating Przewalski's horse as a species, ''E. przewalskii'', others as a subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
of wild horse (''E. ferus przewalskii'') or a variety of the domesticated horse (''E. caballus'').
The Przewalski's horse is stockily built, smaller, and shorter than its domesticated relatives. Typical height is about , and the average weight is around . They have a dun coat with '' pangaré'' features and often have dark primitive markings.
Taxonomy
Przewalski's horse was formally described as a novel species in 1881 by Ivan Semyonovich Polyakov. The taxonomic position of Przewalski's horse remains controversial, and no consensus exists whether it is a full species (as ''Equus przewalskii''); a subspecies of ''Equus ferus'' the wild horse, (as ''Equus ferus przewalskii'' in trinomial nomenclature, along with two other subspecies, the domestic horse ''E. f. caballus'', and the extinct tarpan ''E. f. ferus''), or even a subpopulation of the domestic horse. TheAmerican Society of Mammalogists
The American Society of Mammalogists (ASM) was founded in 1919. Its primary purpose is to encourage the study of mammals, and professions studying them. There are over 4,500 members of this society, and they are primarily professional scientists ...
considers the Przewalski's horse and the tarpan to both be subspecies of ''Equus ferus'', and classifies the domestic horse as separate species, ''Equus caballus''.
Lineage
Early sequencing studies of DNA revealed several genetic characteristics of Przewalski's horse that differ from what is seen in modern domestic horses, indicating neither is ancestor of the other, and supporting the status of Przewalski horses as a remnant wild population not derived from modern domestic horses. The evolutionary divergence of the two populations was estimated to have occurred about 45,000 YBP, while the archaeological record places the first horse domestication about 5,500 YBP by the ancient central-AsianBotai culture
The Botai culture is an archaeological culture (c. 3700–3100 BC) of prehistoric northern Central Asia. It was named after the settlement of Botai in today's northern Kazakhstan. The Botai culture has two other large sites: Krasnyi ...
. The two lineages thus split well before domestication, most likely due to climate, topography, or other environmental changes.
Several subsequent DNA studies produced partially contradictory results. A 2009 molecular analysis using ancient DNA recovered from archaeological sites placed Przewalski's horse in the middle of the domesticated horses. However, a 2011 mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial D ...
analysis suggested that Przewalski's and modern domestic horses diverged some 160,000 years ago. An analysis based on whole genome sequencing and calibration with DNA from old horse bones gave a divergence date of 38,000–72,000 years ago.
In 2018, a new analysis involved genomic sequencing of ancient DNA from horse remains associated with the mid-fourth-millennium BCE Botai culture and bearing marks considered characteristic of domestication, as well as domestic horses from more recent archaeological sites, for comparison with those of modern domestic and Przewalski's horses. The study revealed that the Botai horses were members of the Przewalski's horse lineage, rather than that of modern domestic horses as was previously believed. Further, all of the modern Przewalski's horses analyzed were found to nest within the phylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological spec ...
of the Botai horses, leading the authors to posit that modern Przewalski's horses are feral descendants of the ancient Botai domesticated animals, rather than representing a surviving population of never-domesticated horses. The researchers suggested that because Botai horse domestication was relatively short-lived before they again became feral, the Przewalski's horse retained more wild or primitive traits than did the domestic horse lineage. However, a 2021 reevaluation of the Botai horses reached a conclusion in favor of the traditional view of Przewalski's horses as a never-domesticated population. These authors viewed the tooth wear previously attributed to bridle mouthpieces as more likely to have been caused by natural processes, while the age structure of the Botai horses seemed inconsistent with domesticated herding. Furthermore, some specimens were found associated with arrowheads, suggesting they had been hunted. They concluded that the horses associated with the Botai culture were wild instead of domesticated animals, and that the Przewalski's horse lineage should indeed be viewed not as a feral lineage but as one that was always wild.
In any case, the Botai horses were found to have negligible genetic contribution to any of the ancient or modern domestic horses studied, indicating that the domestication of the latter was independent, involving a different wild population, from any possible domestication of Przewalski's horse by the Botai culture.

Characteristics
Przewalski's horse is stockily built in comparison to domesticated horses, with shorter legs, though being much smaller and shorter than its domesticated relatives. Typical height is about , and length is about . It weighs around . The coat is generally dun in color with '' pangaré'' features, varying from dark brown around the mane, to pale brown on the flanks, and yellowish-white on the belly, as well as around the muzzle. The legs of Przewalski's horse are often faintly striped, also typical of primitive markings. The mane stands erect and does not extend as far forward, while the tail is about long, with a longerdock
A dock (from Dutch language, Dutch ''dok'') is the area of water between or next to one or a group of human-made structures that are involved in the handling of boats or ships (usually on or near a shore) or such structures themselves. The ex ...
and shorter hair than seen in domesticated horses. The hooves of Przewalski's horse are longer in the front and have significantly thicker sole horns than feral horses, an adaptation that improves hoof performance on terrain.
Genomics
Thekaryotype
A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of metaphase chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes. Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is disce ...
of Przewalski's horse differs from that of the domestic horse, having 33 chromosome pairs versus 32, apparently due to a fission
Fission, a splitting of something into two or more parts, may refer to:
* Fission (biology), the division of a single entity into two or more parts and the regeneration of those parts into separate entities resembling the original
* Nuclear fissio ...
of a large chromosome ancestral to domestic horse chromosome 5 to produce Przewalski's horse chromosomes 23 and 24, though conversely, a Robertsonian translocation
Robertsonian translocation (ROB) is a chromosomal abnormality wherein a certain type of a chromosome becomes attached to another. It is the most common form of chromosomal translocation in humans, affecting 1 out of every 1,000 babies born. It doe ...
that fused two chromosomes ancestral to those seen in Przewalski's horse to produce the single large domestic horse chromosome has also been proposed.
Many smaller inversions, insertions and other rearrangements were observed between the chromosomes of domestic and Przewalski's horses, while there was much lower hetero zygosity in Przewalski's horses, with extensive segments devoid of genetic diversity, a consequence of the recent severe bottleneck of the captive Przewalski's horse population. In comparison, the chromosomal differences between domestic horses and zebras include numerous large-scale translocations
In genetics, chromosome translocation is a phenomenon that results in unusual rearrangement of chromosomes. This includes balanced and unbalanced translocation, with two main types: reciprocal-, and Robertsonian translocation. Reciprocal translo ...
, fusions, inversions, and centromere repositioning. Przewalski's horse has the highest diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively ...
chromosome number among all equine species. They can interbreed with the domestic horse and produce fertile offspring, with 65 chromosomes.
Ecology and behavior
 Przewalski reported the horses forming troops of between five and fifteen members, consisting of an old stallion, his mares and foals. Modern reintroduced populations similarly form family groups of one adult stallion, one to three mares, and their common offspring that stay in the family group until they are no longer dependent, usually at two or three years old. Young females join other harems, while bachelor stallions as well as old stallions who have lost their harems join bachelor groups. Family groups can join to form a herd that moves together.
The patterns of their daily lives exhibit horse behavior similar to that of feral horse herds. Stallions herd, drive, and defend all members of their family, while the mares often display leadership in the family. Stallions and mares stay with their preferred partners for years. While behavioral synchronization is high among mares, stallions other than the main harem stallion are generally less stable in this respect.
Home range in the wild is little studied, but estimated as in the Hustai National Park and in the
Przewalski reported the horses forming troops of between five and fifteen members, consisting of an old stallion, his mares and foals. Modern reintroduced populations similarly form family groups of one adult stallion, one to three mares, and their common offspring that stay in the family group until they are no longer dependent, usually at two or three years old. Young females join other harems, while bachelor stallions as well as old stallions who have lost their harems join bachelor groups. Family groups can join to form a herd that moves together.
The patterns of their daily lives exhibit horse behavior similar to that of feral horse herds. Stallions herd, drive, and defend all members of their family, while the mares often display leadership in the family. Stallions and mares stay with their preferred partners for years. While behavioral synchronization is high among mares, stallions other than the main harem stallion are generally less stable in this respect.
Home range in the wild is little studied, but estimated as in the Hustai National Park and in the Great Gobi B Strictly Protected Area Great Gobi B Strictly Protected Area is a nature reserve in Gobi desert, situated in the south-western part of Mongolia at the border with China. A similar reserve in a drier part of the Gobi exists further to the east - the Great Gobi A Strictly ...
. The ranges of harems are separated, but slightly overlapping. They have few modern predators, but one of the few is the Himalayan wolf.
Horses maintain visual contact with their family and herd at all times, and have a host of ways to communicate with one another, including vocalizations, scent marking
In ethology, territory is the sociographical area that an animal consistently defends against conspecific competition (or, occasionally, against animals of other species) using agonistic behaviors or (less commonly) real physical aggression. ...
, and a wide range of visual and tactile signals. Each kick, groom, tilt of the ear, or other contact with another horse is a means of communicating. This constant communication leads to complex social behaviors among Przewalski's horses.
The historical population was said to have lived in the "wildest parts of the desert" with a preference for "especially saline districts". They were observed mostly during spring and summer at natural wells, migrating to them by crossing valleys rather than by way of higher mountains.

Diet
Przewalski horse's diet consists mostly of vegetation. Many plant species are in a typical Przewalski's horse environment, including: '' Elymus repens'', '' Carex ''spp., , and Asteraceae. Looking at the species' diet overall, Przewalski's horses most often eat ''E. repens'', '' Trifolium pratense'', '' Vicia cracca'', '' Poa trivialis'', '' Dactylis glomerata'', and ''Bromus inermis
''Bromus inermis'' is a species of the true grass family ( Poaceae). This rhizomatous grass is native to Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the ...
''.
While the horses eat a variety of different plant species, they tend to favor different species at different times of year. In the springtime, they favor ''Elymus repens'', ''Corynephorus canescens
''Corynephorus canescens,'' common name grey hair-grass or gray clubawn grass, is a species of plants in the grass family, native to Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa but widely naturalized in North America. In the United Kingdom it is r ...
'', ''Festuca valesiaca
''Festuca valesiaca'', the Volga fescue, is a species of flowering plant in the family Poaceae. It is native to Europe and Asia. It was introduced to North America when it was deliberately planted.Darbyshire, S. J. and L. E. Pavlick. (2007)''Fes ...
,'' and '' Chenopodium album''. In early summer, they favor ''Dactylis glomerata'' and ''Trifolium
Clover or trefoil are common names for plants of the genus ''Trifolium'' (from Latin ''tres'' 'three' + ''folium'' 'leaf'), consisting of about 300 species of flowering plants in the legume or pea family Fabaceae originating in Europe. The genus h ...
'', and in late summer, they gravitate towards ''E. repens'' and ''Vicia cracca''.
In winter the horses eat '' Salix ''spp., '' Pyrus communis'', '' Malus sylvatica'', '' Pinus sylvestris'', '' Rosa'' spp., and '' Alnus'' spp. Additionally, Przewalski's horses may dig for '' Festuca'' spp., ''Bromus inermis'', and ''E. repens'' that grow beneath the ice and snow. Their winter diet is very similar to the winter diet of domestic horses, but differs from that revealed by isotope analysis of the historical (pre-captivity) population, which switched in winter to browsing shrubs, though the difference may be due to the extreme habitat pressure the historical population was under. In the wintertime, they eat their food more slowly than they do during other times of the year. Przewalski's horses seasonally display a set of changes collectively characteristic of physiologic adaptation to starvation, with their basal metabolic rate in winter being half what it is during springtime. This is not a direct consequence of decreased nutrient intake, but rather a programmed response to predictable seasonal dietary fluctuation.
Reproduction
Mating occurs in late spring or early summer. Mating stallions do not start looking for mating partners until the age of five. Stallions assemble groups of mares or challenge the leader of another group for dominance. Females are able to give birth at the age of three and have a gestation period of 11–12 months. Foals are able to stand about an hour after birth. The rate of infant mortality among foals is 25%, with 83.3% of these deaths resulting from leading stallion infanticide. Foals begin grazing within a few weeks but are not weaned for 8–13 months after birth. They reach sexual maturity at two years of age.Population
History
Przewalski's-type wild horses appear in European cave art dating as far back as 20,000 years ago, but genetic investigation of a 35,870-year-old specimen from one such cave instead showed affinity with extinct Iberian horse lineage and the modern domestic horse, suggesting that it was not Przewalski's horse being depicted in this art. Horse skeletons dating to the fifth to the third millennia BCE, found in Central Asia, with a range extending to the southern Urals and the Altai, belong to the genetic lineage of Przewalski's horse. of particular note are the horses of this lineage found in the archaeological sites of the Chalcolithic Botai culture. Sites dating from the mid-fourth-millennium BCE show evidence of horse domestication, though their status as domesticated horses has been recently challenged. Analysis of ancient DNA from Botai horse specimens from about 3000 BCE reveal them to have DNA markers consistent with the lineage of modern Przewalski's horses. There are sporadic reports of Przewalski's horse in the historical record prior to its formal characterization. The Buddhist monk Bodowa wrote a description of what is thought to have been Przewalski's horse about AD 900, and an account from 1226 reports an incident involving wild horses duringGenghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
's campaign against the Tangut empire
The Western Xia or the Xi Xia (), officially the Great Xia (), also known as the Tangut Empire, and known as ''Mi-nyak''Stein (1972), pp. 70–71. to the Tanguts and Tibetans, was a Tangut-led Buddhist imperial dynasty of China tha ...
. In the fifteenth century, Johann Schiltberger
Johann (Hans) Schiltberger (1380) was a German traveller and writer. He was born of a noble family, probably at Hollern near Lohhof halfway between Munich and Freising.
Travels
Schiltberger joined the suite of Lienhart Richartinger in 1394, a ...
recorded one of the first European sightings of the horses in the journal recounting his trip to Mongolia as a prisoner of the Mongol Khan
Khan may refer to:
*Khan (inn), from Persian, a caravanserai or resting-place for a travelling caravan
*Khan (surname), including a list of people with the name
*Khan (title), a royal title for a ruler in Mongol and Turkic languages and used by ...
. Another was recorded as a gift to the Manchurian emperor around 1630, its value as a gift suggesting a difficulty in obtaining them. John Bell, a Scottish doctor in service to Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
from 1719 to 1722, observed a horse in Russia's Tomsk Oblast that was apparently this species, and a few decades later in 1750, a large hunt with thousands of beaters organized by the Manchurian emperor killed between two and three hundred of these horses.
Nikolai Przhevalsky
Nikolay Mikhaylovich Przhevalsky (or Prjevalsky;; pl, Nikołaj Przewalski, . – ) was a Russian geographer of Polish descent (he was born in a Polish noble family), and a renowned explorer of Central and East Asia.
Although he never reache ...
(1839–1888) (Nikołaj Przewalski in Polish). An explorer and naturalist, he obtained a skull and hide of an animal shot in 1878 in the Gobi near what is today's China–Mongolia border, and he would make an expedition into the Dzungarian Basin to observe it in the wild. In 1881, the horse received a formal scientific description and was named ''Equus przevalskii'' by Ivan Semyonovich Polyakov, based on Przewalski's collection and description, while in 1884, the sole exemplar of the horse in Europe was a preserved specimen in the Museum of the Russian Academy of Sciences in St. Petersburg. This was supplemented in 1894 when the brothers Grum-Grzhimailo returned several hides and skulls to St. Petersburg and provided a description of the horse's behavior in the wild. A number of these horses were captured around 1900 by Carl Hagenbeck
Carl Hagenbeck (10 June 1844 – 14 April 1913) was a Germans, German merchant of wild animals who supplied many European zoos, as well as P. T. Barnum. He created the modern zoo with animal enclosures without bars that were closer to their natu ...
and placed in zoos, and these, along with one later captive, reproduced to give rise to today's population.
After 1903, there were no reports of the wild population until 1947, when several isolated groups were observed and a lone filly
A filly is a female horse that is too young to be called a mare. There are two specific definitions in use:
*In most cases, a ''filly'' is a female horse under four years old.
*In some nations, such as the United Kingdom and the United States, t ...
captured. Although local herdsmen reported seeing as many as 50 to 100 takhis grazing in small groups at that time, there were only sporadic sightings of single groups of two or three animals thereafter, mostly near natural wells. Two scientific expeditions in 1955 and 1962 failed to find any, and after herders and naturalists reported single harem groups in 1966 and 1967, the last observation of the wild horse in its native habitat was of a single stallion in 1969. Expeditions after this failed to locate any horses, and the species would be designated "extinct in the wild" for over 30 years. Competition with livestock, hunting, capture of foals for zoological collections, military activities, and harsh winters recorded in 1945, 1948, and 1956 are considered to be main causes of the decline in Przewalski's horse population.
The wild population was already rare at the time of its first scientific characterization. Przewalski reported seeing them only from a distance and may actually have instead sighted herds of local onager, Mongolian wild asses, and he was only able to obtain the type specimen from Kirghiz hunters. The range of Przewalski's horse was limited to the arid Dzungarian Basin in the Gobi Desert
The Gobi Desert (Chinese: 戈壁 (沙漠), Mongolian: Говь (ᠭᠣᠪᠢ)) () is a large desert or brushland region in East Asia, and is the sixth largest desert in the world.
Geography
The Gobi measures from southwest to northeast an ...
."Przevalsky's Wild Horse", ''Nature'', 30:391-392 (1884). It has been suggested that this was not their natural habitat, but, like the onager, they were a steppe animal driven to this inhospitable last refuge by the dual pressures of hunting and habitat loss to agricultural grazing. There were two distinct populations recognized by local Mongolians, a lighter steppe variety and a darker mountain one, and this distinction is seen in early twentieth-century descriptions. Their mountainous habitat included the ''Takhiin Shar Nuruu'' (The Yellow Wild-Horse Mountain Range). In their last decades in the wild, the remnant population was limited to the small region between the Takhiin Shar Nuruu and Bajtag-Bogdo mountain ridges.

Captivity
Attempts to obtain specimens for exhibit andcaptive breeding
Captive breeding, also known as captive propagation, is the process of plants or animals in controlled environments, such as wildlife reserves, zoos, botanic gardens, and other conservation facilities. It is sometimes employed to help species that ...
were largely unsuccessful until 1902, when 28 captured foals were brought to Europe. These, along with a small number of additional captives, would be distributed among zoos and breeding centers in Europe and the United States. Many facilities failed in their attempts at captive breeding, but a few programs were established. However, by the mid-1930s, inbreeding had caused reduced fertility and the captive population experienced a genetic bottleneck, with the surviving captive breeding stock descended from only 11 of the founder captives. In addition, in at least one instance the progeny of interbreeding with a domestic horse was bred back into the captive Przewalski's horse population, though recent studies have shown only minimal genetic contribution of this domestic horse to the captive population.
The situation was improved when the exchange of breeding animals among facilities increased genetic diversity and there was a consequent improvement in fertility, but the population experienced another genetic bottleneck when many of the horses failed to survive World War II. The most valuable group, in Askania Nova
Askania-Nova ( uk, Асканія-Нова) is a Ukrainian nature reserve located in Kherson Oblast, Ukraine, within the dry Taurida steppe near Oleshky Sands and active member of the UNESCO Man and the Biosphere Programme. It is also a resea ...
, Ukraine, was shot by German soldiers during World War II occupation, and the group in the United States had died out. Only two captive populations in zoos remained, in Munich and in Prague, and of the 31 remaining horses at war's end, only 9 became ancestors of the subsequent captive population. By the end of the 1950s, only 12 individual horses were left in the world's zoos.
In 1957, a wild-caught mare captured as a foal a decade earlier was introduced into the Ukrainian captive population. This would prove the last wild-caught horse, and with the presumed extinction of wild population, last sighted in Mongolia in the late 1960s, the captive population became the sole representatives of Przewalski's horse. Genetic diversity received a much needed boost from this new source, with the spread of her bloodline through the inbred captive groups leading to their increased reproductive success, and by 1965 there were more than 130 animals spread among thirty-two zoos and parks.
Conservation efforts
 In 1977, the Foundation for the Preservation and Protection of the Przewalski Horse was founded in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, by Jan and Inge Bouman. The foundation started a program of exchange between captive populations in zoos throughout the world to reduce inbreeding, and later began a breeding program of its own. As a result of such efforts, the extant herd has retained a far greater genetic diversity than its genetic bottleneck made likely. By 1979, when this concerted program of population management to maximize
In 1977, the Foundation for the Preservation and Protection of the Przewalski Horse was founded in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, by Jan and Inge Bouman. The foundation started a program of exchange between captive populations in zoos throughout the world to reduce inbreeding, and later began a breeding program of its own. As a result of such efforts, the extant herd has retained a far greater genetic diversity than its genetic bottleneck made likely. By 1979, when this concerted program of population management to maximize genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species, it ranges widely from the number of species to differences within species and can be attributed to the span of survival for a species. It is dis ...
was begun, there were almost four hundred horses in sixteen facilities, a number that had grown by the early 1990s to over 1,500.
While dozens of zoos worldwide have Przewalski's horses in small numbers, specialized reserves are also dedicated primarily to the species. The world's largest captive-breeding program for Przewalski's horses is at the Askania Nova
Askania-Nova ( uk, Асканія-Нова) is a Ukrainian nature reserve located in Kherson Oblast, Ukraine, within the dry Taurida steppe near Oleshky Sands and active member of the UNESCO Man and the Biosphere Programme. It is also a resea ...
preserve in Ukraine. From 1998, thirty one horses were also released in the unenclosed Chernobyl Exclusion Zone in Ukraine and Belarus, evacuated after the Chernobyl accident
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the No. 4 reactor in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, near the city of Pripyat in the north of the Ukrainian SSR in the Soviet Union. It is one of only two nu ...
, which now serves as a deserted '' de facto'' nature reserve. Though poaching took a toll on numbers, as of 2019 the estimated population in the Chernobyl zone was over 100 individuals.
Le Villaret, located in the Cevennes National Park in southern France and run by the Association Takh, is a breeding site for Przewalski's horses that was created to allow the free expression of natural Przewalski's horse behaviors. In 1993, eleven zoo-born horses were brought to Le Villaret. Horses born there are adapted to life in the wild, being free to choose their own mates and required to forage on their own. This was intended to produce individuals capable of being reintroduced into Mongolia. In 2012, 39 individuals were at Le Villaret. An intensely researched population of free-ranging animals was also introduced to the Hortobágy National Park ''puszta
The Hungarian Puszta () is a temperate grassland biome of the Alföld or Great Hungarian Plain. It is an exclave of the Eurasian Steppe, and lies mainly around the River Tisza in the eastern part of Hungary, as well as in the western part of t ...
'' in Hungary; data on social structure, behavior, and diseases gathered from these animals are used to improve the Mongolian conservation effort. An additional breeding population of Przewalski's horses roams the former Döberitzer Heide military proving ground, now a nature reserve in Dallgow-Döberitz, Germany. Established in 2008, this population comprised 24 horses in 2019.

Reintroduction
Reintroductions organized by Western European countries started in the 1990s. These were later stopped, mostly for financial reasons. In 2011,Prague Zoo
Prague Zoological Garden (Czech: ''Zoologická zahrada hl. m. Prahy'') is a zoo in Prague, Czech Republic. It was opened in 1931 with the goal to "advance the study of zoology, protect wildlife, and educate the public" in the district of Troja in ...
started a new project, Return of the Wild Horses. With the support of public and many strategic partners, these yearly transports of captive-bred horses into the Great Gobi B Strictly Protected Area Great Gobi B Strictly Protected Area is a nature reserve in Gobi desert, situated in the south-western part of Mongolia at the border with China. A similar reserve in a drier part of the Gobi exists further to the east - the Great Gobi A Strictly ...
continue today. Since 2004, there is also a program to reintroduce Przewalski's horses that were bred in France into Mongolia.
Several populations have now been released into the wild. A cooperative venture between the Zoological Society of London and Mongolian scientists has resulted in successful reintroduction
Species reintroduction is the deliberate release of a species into the wild, from captivity or other areas where the organism is capable of survival. The goal of species reintroduction is to establish a healthy, genetically diverse, self-sustainin ...
of these horses from zoos into their natural habitat in Mongolia. In 1992, 16 horses were released into the wild in Mongolia, followed by additional animals later on. One of the areas to which they were reintroduced became Khustain Nuruu National Park in 1998. Another reintroduction site is Great Gobi B Strictly Protected Area, located at the fringes of the Gobi desert
The Gobi Desert (Chinese: 戈壁 (沙漠), Mongolian: Говь (ᠭᠣᠪᠢ)) () is a large desert or brushland region in East Asia, and is the sixth largest desert in the world.
Geography
The Gobi measures from southwest to northeast an ...
. Lastly, in 2004 and 2005, 22 horses were released by the Association Takh to a third reintroduction site in the buffer zone of the Khar Us Nuur National Park
Har Us Nuur National Park ( mn, Хар Ус Нуур) covers a chain of three large lakes in the Great Lakes Basin of western Mongolia. The lakes, Khar-Us Nuur, Khar Lake and Dörgön Lake are bordered by marshes and reed-beds that are an importa ...
, in the northern edge of the Gobi ecoregion. In the winter of 2009–2010, one of the worst ''dzud
A zud, dzud ( mn, зуд) of dzhut, zhut, djut, jut ( kz, жұт, ky, жут, russian: джут) is a disaster in steppe, semi-desert and desert regions in Mongolia and Central Asia in which large numbers of livestock die, primarily due to starva ...
'' or snowy winter conditions ever hit Mongolia. The population of Przewalski's horse in the Great Gobi B SPA was drastically affected, providing clear evidence of the risks associated with reintroducing small and sequestered species in unpredictable and unfamiliar environments. , an estimated total of almost 400 horses existed in three free-ranging populations in the wild. Since 2011, Prague Zoo
Prague Zoological Garden (Czech: ''Zoologická zahrada hl. m. Prahy'') is a zoo in Prague, Czech Republic. It was opened in 1931 with the goal to "advance the study of zoology, protect wildlife, and educate the public" in the district of Troja in ...
has transported 35 horses to Mongolia in eight rounds, in cooperation with partners (Czech Air Force, European Breeding Programme for Przewalski's Horses, Association pour de cheval du Przewalski: Takh, Czech Development Agency, Czech Embassy in Mongolia, and others) and it plans to continue to return horses to the wild in the future. In the framework of the project Return of the Wild Horses, it sustains its activities by supporting local inhabitants. The zoo has the longest uninterrupted history of breeding Przewalski's horses in the world and keeps the studbook of this species.
In 2001, Przewalski's horses were reintroduced into the Kalamaili Nature Reserve in Xinjiang, China. The Przewalski's Horse Reintroduction Project of China was initiated in 1985 when 11 wild horses were imported from overseas. After more than two decades of effort, the Xinjiang Wild Horse Breeding Centre has bred a large number of the horses, 55 of which were released into the Kalamely Mountain area. The animals quickly adapted to their new environment. In 1988, six foals were born and survived, and by 2001, over 100 horses were at the centre. , the center hosted 127 horses divided into 13 breeding herds and three bachelor herds.
The first reintroduction into the Orenburg
Orenburg (russian: Оренбу́рг, ), formerly known as Chkalov (1938–1957), is the administrative center of Orenburg Oblast, Russia. It lies on the Ural River, southeast of Moscow. Orenburg is also very close to the Kazakhstan-Russia bor ...
region, on the Russian steppe, occurred in 2016. Plans were also announced in 2014 to reintroduce them in central Kazakhstan.
The reintroduced horses successfully reproduced, and the status of the animal was changed from "extinct in the wild" to "endangered" in 2005, while on the IUCN Red List they were reclassified from "extinct in the wild" to "critically endangered" after a reassessment in 2008, and from "critically endangered" to "endangered" after a 2011 reassessment.
Assisted reproduction and cloning
 In the earlier decades of captivity, the insular breeding by individual zoos led to inbreeding and reduced fertility. In 1979, several American zoos began a collaborative breeding-exchange program to maximize genetic diversity. Recent advances in equine reproductive science have also been used to preserve and expand the gene pool. Scientists at the Smithsonian Institution's National Zoo successfully reversed a vasectomy on a Przewalski's horse in 2007—the first operation of its kind on this species, and possibly the first ever on any endangered species. While normally a vasectomy may be performed on an endangered animal under limited circumstances, particularly if an individual has already produced many offspring and its genes are overrepresented in the population, scientists realized the animal in question was one of the most genetically valuable Przewalski's horses in the North American breeding program. The first birth by artificial insemination occurred on 27 July 2013 at the
In the earlier decades of captivity, the insular breeding by individual zoos led to inbreeding and reduced fertility. In 1979, several American zoos began a collaborative breeding-exchange program to maximize genetic diversity. Recent advances in equine reproductive science have also been used to preserve and expand the gene pool. Scientists at the Smithsonian Institution's National Zoo successfully reversed a vasectomy on a Przewalski's horse in 2007—the first operation of its kind on this species, and possibly the first ever on any endangered species. While normally a vasectomy may be performed on an endangered animal under limited circumstances, particularly if an individual has already produced many offspring and its genes are overrepresented in the population, scientists realized the animal in question was one of the most genetically valuable Przewalski's horses in the North American breeding program. The first birth by artificial insemination occurred on 27 July 2013 at the Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute
The Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute (SCBI) is a unit of the Smithsonian Institution located on a campus located just outside the town of Front Royal, Virginia. An extension of the National Zoo in Washington, D.C., the SCBI has played ...
.
In 2020, the first cloned Przewalski's horse was born, the result of a collaboration between San Diego Zoo Global, ViaGen Equine and Revive & Restore
Revive & Restore is a nonprofit wildlife conservation organization bringing biotechnology to conservation. Biotechnology can be used to increase genetic diversity, build disease resistance, and facilitate adaptation. Headquartered in Sausalito, C ...
. The cloning was carried out by somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT), whereby a viable embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
is created by transplanting the DNA-containing nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
of a somatic cell
A somatic cell (from Ancient Greek σῶμα ''sôma'', meaning "body"), or vegetal cell, is any biological cell forming the body of a multicellular organism other than a gamete, germ cell, gametocyte or undifferentiated stem cell. Such cells compo ...
into an immature egg cell ( oocyte) that has had its own nucleus removed, producing offspring genetically identical to the somatic cell donor. Since the oocyte used was from a domestic horse, this was an example of interspecies SCNT.
The somatic cell donor was a Przewalski's horse stallion named Kuporovic, born in the UK in 1975, and relocated three years later to the US, where he died in 1998. Due to concerns over the loss of genetic variation
Genetic variation is the difference in DNA among individuals or the differences between populations. The multiple sources of genetic variation include mutation and genetic recombination. Mutations are the ultimate sources of genetic variation, ...
in the captive Przewalski's horse population, and in anticipation of the development of new cloning techniques, tissue from the stallion was cryopreserved at the San Diego Zoo's Frozen Zoo. Breeding of this individual in the 1980s had already substantially increased the genetic diversity of the captive population, after he was discovered to have more unique alleles than any other horse living at the time, including otherwise-lost genetic material from two of the original captive founders. To produce the clone, frozen skin fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of cell (biology), biological cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework (Stroma (tissue), stroma) for animal Tissue (biology), tissues, and plays a critical role in wound ...
s were thawed, and grown in cell culture
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. The term "tissue culture" was coined by American pathologist Montrose Thomas Burrows. This te ...
. An oocyte was collected from a domestic horse, and its nucleus replaced by a nucleus collected from a cultured Przewalski's horse fibroblast. The resulting embryo was induced to begin division, and was cultured until it reached the blastocyst
The blastocyst is a structure formed in the early embryonic development of mammals. It possesses an inner cell mass (ICM) also known as the ''embryoblast'' which subsequently forms the embryo, and an outer layer of trophoblast cells called the t ...
stage, then implanted into a domestic horse surrogate
A surrogate is a substitute or deputy for another person in a specific role and may refer to:
Relationships
* Surrogacy, an arrangement where a woman agrees to carry and give birth to a child for another person who will become its parent at bi ...
mare, which carried the embryo to term and delivered a foal with the Przewalski's horse DNA of the long-deceased stallion.
The cloned horse was named Kurt, after Dr. Kurt Benirschke
Kurt Benirschke (May 26, 1924 – September 10, 2018) was a German-American pathologist, geneticist and expert on the placenta and reproduction in humans and myriad mammalian species. At the San Diego Zoo, he created the world's first frozen zoo ...
, a geneticist who developed the idea of cryopreserving genetic material from species considered to be endangered. His ideas led to the creation of the Frozen Zoo as a genetic library. Once the foal matures, he will be relocated to the breeding herd at the San Diego Zoo Safari Park, so as to pass Kuporovic's genes into the larger captive Przewalski's horse population and thereby increase the genetic variation of the species.
See also
* Mongolian horse (domestic)References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * ** * * * * * * * * *External links
* * * * {{Authority control Horse subspecies Mammals of Mongolia Mammals of Central Asia Mammals of Russia Natural history of China Endangered fauna of Asia Mammals of Europe Mammals described in 1881