Dynamic Speckle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In 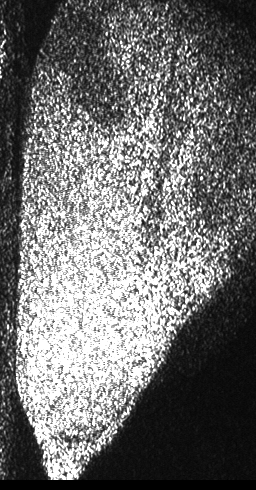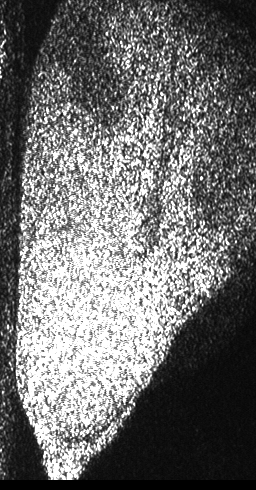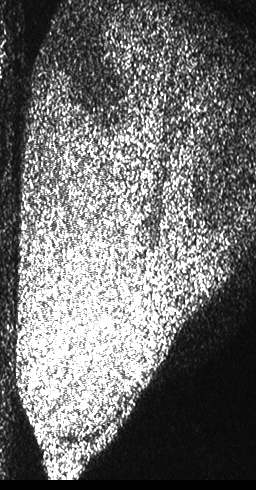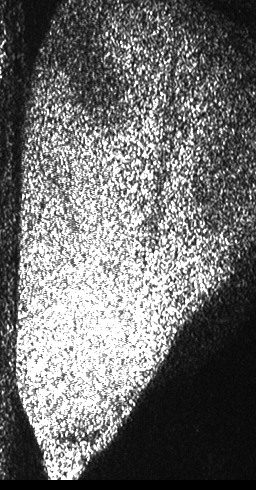
 Several mathematical and statistical tools have been proposed for the characterization of the activity of a dynamic speckle pattern.
Some of them are:
;Inertia Moment of the Co-Occurrence matrix (MOC)
;Fujii
;Generalized differences
;Temporal difference
These and other methods are gathered in
Several mathematical and statistical tools have been proposed for the characterization of the activity of a dynamic speckle pattern.
Some of them are:
;Inertia Moment of the Co-Occurrence matrix (MOC)
;Fujii
;Generalized differences
;Temporal difference
These and other methods are gathered in
physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which r ...
, dynamic speckle is a result of the temporal evolution of a speckle pattern
Speckle, speckle pattern, or speckle noise is a granular noise texture degrading the quality as a consequence of interference among wavefronts in coherent imaging systems, such as radar, synthetic aperture radar (SAR), medical ultrasound and o ...
where variations in the scattering elements responsible for the formation of the interference
Interference is the act of interfering, invading, or poaching. Interference may also refer to:
Communications
* Interference (communication), anything which alters, modifies, or disrupts a message
* Adjacent-channel interference, caused by extr ...
pattern in the static situation produce the changes that are seen in the speckle pattern
Speckle, speckle pattern, or speckle noise is a granular noise texture degrading the quality as a consequence of interference among wavefronts in coherent imaging systems, such as radar, synthetic aperture radar (SAR), medical ultrasound and o ...
, where its grains change their intensity (grey level) as well as their shape along time. One easy to observe example is milk: place some milk in a teaspoon and observe the surface in direct sunlight. There will be a visible "dancing" pattern of coloured points. Where the milk dries on the spoon at the edge, the speckle is seen to be static. This is direct evidence of the thermal motion of atoms, which cause the Brownian motion of the colloidal particles in the milk, which in turn results in the dynamic speckle visible to the naked eye.

Information content
The dynamic pattern shows then the changes that, if they are analyzed along time, represent the activity of the illuminated material. The visual effect is that of a boiling liquid or the image in a TV set far from tuning. It can be analyzed by means of several mathematical and statistical tools and provide numeric or visual information on its magnitude, the not well defined idea of activity. Because the number of scattering centers is very high the collective phenomenon is hard to interpret and their individual contributions to the final result can not be inferred. The measurements that are obtained by means of the analysis tools present the activity level as a sum of the contributions of phenomena due to Doppler effect of the scattered light as well as other phenomena eventually present (time variations of the refractive index of the sample, etc.) Light scattered with small Doppler shifts in its frequency beats on the detector (eventually the eye) giving rise to the slow intensity variations that constitute the dynamic of the speckle pattern. A biological sample, for example, that is a material that contains a huge number of mobile scattering centers, presents refractive index variations in the materials that compose it with power changes as well as many other effects increasing the complexity in the identification and isolation of these phenomena. Then, the complete interpretation of the activity of a sample, by means of dynamic speckle, presents itself big challenges. Figure 1 shows a sequence of speckle patterns in a corn seed in the start of its germination process where the dynamic effect is higher in the areas where the scattering centers are expected to be more active as is the case of the embryo and in a break in the endosperm region of the seed. The embryo is in the lower left side and the break is a river-like region in the center. In the crack, the activity is due to intensive inner water evaporation while in the embryo activity is higher due to metabolism of the alive tissue together with the activity caused by water evaporation. In the endosperm, the high right region of the image represents that the relatively low activity is due only to water evaporation.Applications
Biological tissue is one of the most complex that can be found in nature. Besides it is worsened by the intrinsic variability present between one sample and another. These facts make even more difficult the comparison of results between different samples even in presence of the same stimulus. In this context, speckle patterns have been applied to study bacteria, parasites, seeds and plants. Other fields of application are the analysis of drying paint, control in gels,foam
Foams are materials formed by trapping pockets of gas in a liquid or solid.
A bath sponge and the head on a glass of beer are examples of foams. In most foams, the volume of gas is large, with thin films of liquid or solid separating the ...
s, corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engi ...
, efflorescence
In chemistry, efflorescence (which means "to flower out" in French) is the migration of a salt to the surface of a porous material, where it forms a coating. The essential process involves the dissolving of an internally held salt in water, or ...
, etc.
Dynamic Speckle analysis
 Several mathematical and statistical tools have been proposed for the characterization of the activity of a dynamic speckle pattern.
Some of them are:
;Inertia Moment of the Co-Occurrence matrix (MOC)
;Fujii
;Generalized differences
;Temporal difference
These and other methods are gathered in
Several mathematical and statistical tools have been proposed for the characterization of the activity of a dynamic speckle pattern.
Some of them are:
;Inertia Moment of the Co-Occurrence matrix (MOC)
;Fujii
;Generalized differences
;Temporal difference
These and other methods are gathered in Biospeckle laser tool library
The biospeckle laser tool library, or BSLTL, is a free project to help researchers to work with dynamic speckle. The library is based on Mcode to GNU Octave and Matlab and in the free ''ebook'' A Practical Guide to Biospeckle Laser Analysis: Theory ...
.
See also
*Speckle pattern
Speckle, speckle pattern, or speckle noise is a granular noise texture degrading the quality as a consequence of interference among wavefronts in coherent imaging systems, such as radar, synthetic aperture radar (SAR), medical ultrasound and o ...
*Speckle noise
Speckle, speckle pattern, or speckle noise is a granular noise texture degrading the quality as a consequence of interference among wavefronts in coherent imaging systems, such as radar, synthetic aperture radar (SAR), medical ultrasound and op ...
*Speckle imaging
Speckle imaging describes a range of high-resolution astronomical imaging techniques based on the analysis of large numbers of short exposures that freeze the variation of atmospheric turbulence. They can be divided into the shift-and-add ("'' ...
References
Patent http://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=AR5324365&recNum=1&docAn=P060104012&queryString=055432&maxRec=1, http://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=AR5324365 {{DEFAULTSORT:Dynamic Speckle Interference