Dunnotar Castle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dunnottar Castle ( gd, Dùn Fhoithear, "fort on the shelving slope") is a ruined
 A chapel at Dunnottar is said to have been founded by
A chapel at Dunnottar is said to have been founded by

 In 1639
In 1639
medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
fortress located upon a rocky headland on the north-eastern coast of Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a Anglo-Scottish border, border with England to the southeast ...
, about south of Stonehaven
Stonehaven ( , ) is a town in Scotland. It lies on Scotland's northeast coast and had a population of 11,602 at the 2011 Census.
After the demise of the town of Kincardine, which was gradually abandoned after the destruction of its royal cast ...
. The surviving buildings are largely of the 15th and 16th centuries, but the site is believed to have been fortified in the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
. Dunnottar has played a prominent role in the history of Scotland
The recorded begins with the arrival of the Roman Empire in the 1st century, when the province of Britannia reached as far north as the Antonine Wall. North of this was Caledonia, inhabited by the ''Picti'', whose uprisings forced Rome ...
through to the 18th-century Jacobite risings
, war =
, image = Prince James Francis Edward Stuart by Louis Gabriel Blanchet.jpg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = James Francis Edward Stuart, Jacobite claimant between 1701 and 1766
, active ...
because of its strategic location and defensive strength.
Dunnottar is best known as the place where the Honours of Scotland, the Scottish crown jewels, were hidden from Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three K ...
's invading army in the 17th century. The property of the Keiths from the 14th century, and the seat of the Earl Marischal
The title of Earl Marischal was created in the Peerage of Scotland for William Keith, the Great Marischal of Scotland.
History
The office of Marischal of Scotland (or ''Marascallus Scotie'' or ''Marscallus Scotiae'') had been hereditary, held b ...
, Dunnottar declined after the last Earl forfeited his titles by taking part in the Jacobite rebellion of 1715
The Jacobite rising of 1715 ( gd, Bliadhna Sheumais ;
or 'the Fifteen') was the attempt by James Edward Stuart (the Old Pretender) to regain the thrones of England, Ireland and Scotland for the exiled Stuarts.
At Braemar, Aberdeenshire ...
. The castle was restored in the 20th century and is now open to the public.
The ruins of the castle are spread over , surrounded by steep cliffs that drop to the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
, below. A narrow strip of land joins the headland to the mainland, along which a steep path leads up to the gatehouse. The various buildings within the castle include the 14th-century tower house as well as the 16th-century palace. Dunnottar Castle is a scheduled monument
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a nationally important archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorised change.
The various pieces of legislation that legally protect heritage assets from damage and d ...
, and twelve structures on the site were listed buildings
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
.
History
Early Middle Ages
 A chapel at Dunnottar is said to have been founded by
A chapel at Dunnottar is said to have been founded by St Ninian
Ninian is a Christian saint, first mentioned in the 8th century as being an early missionary among the Pictish peoples of what is now Scotland. For this reason he is known as the Apostle to the Southern Picts, and there are numerous dedication ...
in the 5th century, although it is not clear when the site was first fortified, but in any case the legend is late and highly implausible. Possibly the earliest written reference to the site is found in the '' Annals of Ulster'' which record two sieges of 'Dún Foither' in 681 and 694. The earlier event has been interpreted as an attack by Brude, the Pictish king of Fortriu
Fortriu ( la, Verturiones; sga, *Foirtrinn; ang, Wærteras; xpi, *Uerteru) was a Pictish kingdom that existed between the 4th and 10th centuries. It was traditionally believed to be located in and around Strathearn in central Scotland, but is ...
, to extend his power over the north-east coast of Scotland. The ''Chronicle of the Kings of Alba
The ''Chronicle of the Kings of Alba'', or ''Scottish Chronicle'', is a short written chronicle of the Kings of Alba, covering the period from the time of Kenneth MacAlpin (Cináed mac Ailpín) (d. 858) until the reign of Kenneth II (Cináed mac ...
'' records that King Donald II of Scotland, the first ruler to be called ''rí Alban'' (King of Alba
''Alba'' ( , ) is the Scottish Gaelic name for Scotland. It is also, in English language historiography, used to refer to the polity of Picts and Scots united in the ninth century as the Kingdom of Alba, until it developed into the Kingdom ...
), was killed at Dunnottar during an attack by Vikings in 900. The English king Æthelstan
Æthelstan or Athelstan (; ang, Æðelstān ; on, Aðalsteinn; ; – 27 October 939) was King of the Anglo-Saxons from 924 to 927 and King of the English from 927 to his death in 939. He was the son of King Edward the Elder and his fir ...
led a force into Scotland in 934, and raided as far north as Dunnottar according to the account of Symeon of Durham
__NOTOC__
Symeon (or Simeon) of Durham (died after 1129) was an English chronicler and a monk of Durham Priory.
Biography
Symeon entered the Benedictine monastery at Jarrow as a youth. It moved to Durham in 1074, and he was professed in 1085 or ...
.
W. D. Simpson
William Douglas Simpson CBE (2 August 1896 – 9 October 1968) was a Scottish academic and writer who focused on the study of medieval architecture and archaeology.
Career
Simpson was appointed Assistant in History at the University of A ...
speculated that a motte
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively easy to ...
might lie under the present castle, but excavations in the 1980s failed to uncover substantive evidence of early medieval fortification. The discovery of a group of Pictish stones
A Pictish stone is a type of monumental stele, generally carved or incised with symbols or designs. A few have ogham inscriptions. Located in Scotland, mostly north of the Clyde-Forth line and on the Eastern side of the country, these stones ar ...
at Dunnicaer
Dunnicaer, or Dun-na-caer, is a precipitous sea stack just off the coast of Aberdeenshire, Scotland, between Dunnottar Castle and Stonehaven. Despite the unusual difficulty of access, in 1832 Pictish symbol stones were found on the summit and ...
, a nearby sea stack
A stack or sea stack is a geology, geological landform consisting of a steep and often vertical column or columns of rock in the sea near a coast, formed by Coastal_erosion#Wave_action, wave erosion. Stacks are formed over time by wind and wate ...
, has prompted speculation that Dún Foither was actually located on the adjacent headland of Bowduns, to the north.
Later Middle Ages
During the reign of KingWilliam the Lion
William the Lion, sometimes styled William I and also known by the nickname Garbh, "the Rough"''Uilleam Garbh''; e.g. Annals of Ulster, s.a. 1214.6; Annals of Loch Cé, s.a. 1213.10. ( 1142 – 4 December 1214), reigned as King of Scots from 11 ...
(ruled 1165–1214) Dunnottar was a centre of local administration for The Mearns
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the m ...
. The castle is named in the ''Roman de Fergus
{{no footnotes, date=October 2015
The ''Roman de Fergus'' is an Arthurian romance written in Old French probably at the very beginning of the 13th century, by a very well educated author who named himself Guillaume le Clerc (William the Clerk). ...
'', an early 13th-century Arthurian
King Arthur ( cy, Brenin Arthur, kw, Arthur Gernow, br, Roue Arzhur) is a legendary king of Britain, and a central figure in the medieval literary tradition known as the Matter of Britain.
In the earliest traditions, Arthur appears as a ...
romance
Romance (from Vulgar Latin , "in the Roman language", i.e., "Latin") may refer to:
Common meanings
* Romance (love), emotional attraction towards another person and the courtship behaviors undertaken to express the feelings
* Romance languages, ...
, in which the hero Fergus must travel to Dunnottar to retrieve a magic shield.Simpson (1966), p. 4. In May 1276 a church on the site was consecrated by William Wishart
:''See also William Wishart (disambiguation)''
William Wishart (or Wischard) (died 28 May 1279) was a 13th-century Bishop of St. Andrews. He was postulated to the see of St. Andrews (''Cell Rígmonaid'' or ''Cill Rìmhinn'') while holding the ...
, Bishop of St Andrews. The poet Blind Harry
Blind Harry ( 1440 – 1492), also known as Harry, Hary or Henry the Minstrel, is renowned as the author of ''The Actes and Deidis of the Illustre and Vallyeant Campioun Schir William Wallace'', more commonly known as '' The Wallace''. This wa ...
relates that William Wallace
Sir William Wallace ( gd, Uilleam Uallas, ; Norman French: ; 23 August 1305) was a Scottish knight who became one of the main leaders during the First War of Scottish Independence.
Along with Andrew Moray, Wallace defeated an English army ...
captured Dunnottar from the English in 1297, during the Wars of Scottish Independence
The Wars of Scottish Independence were a series of military campaigns fought between the Kingdom of Scotland and the Kingdom of England in the late 13th and early 14th centuries.
The First War (1296–1328) began with the English invasion of ...
. He is said to have imprisoned 4,000 defeated English soldiers in the church and burned them alive.Coventry (2006), pp. 278–279.
In 1336 Edward III of England
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring ...
ordered William Sinclair, 8th Baron of Roslin, to sail eight ships to the partially ruined Dunnottar for the purpose of rebuilding and fortifying the site as a forward resupply base for his northern campaign. Sinclair took with him 160 soldiers, horses, and a corps of masons and carpenters.Sumption (1991). Edward himself visited in July, but the English efforts were undone before the end of the year when the Scottish Regent Sir Andrew Murray
Sir Andrew Murray (1298–1338), also known as Sir Andrew Moray, or Sir Andrew de Moray, was a Scottish military and political leader who supported King David II of Scotland against Edward Balliol and King Edward III of England during the Seco ...
led a force that captured and again destroyed the defences of Dunnottar.
In the 14th century, Dunnottar was granted to William de Moravia, 5th Earl of Sutherland
William de Moravia (also known as William Sutherland) (died 1370) was the 5th Earl of Sutherland and chief of the Clan Sutherland, a Scottish clan of the Scottish Highlands. William, 5th Earl of Sutherland was a loyal supporter of David II of Sco ...
(d.1370),McGladdery (2004). and in 1346 a licence to crenellate
In medieval England, Wales and the Channel Islands a licence to crenellate (or licence to fortify) granted the holder permission to fortify his property. Such licences were granted by the king, and by the rulers of the counties palatine within th ...
was issued by David II.Geddes (2001), pp. 25–27. Around 1359 William Keith, Marischal of Scotland, married Margaret Fraser, niece of Robert the Bruce
Robert I (11 July 1274 – 7 June 1329), popularly known as Robert the Bruce (Scottish Gaelic: ''Raibeart an Bruis''), was King of Scots from 1306 to his death in 1329. One of the most renowned warriors of his generation, Robert eventual ...
, and was granted the barony of Dunnottar at this time. Keith then gave the lands of Dunnottar to his daughter Christian and son-in-law William Lindsay of Byres, but in 1392 an excambion
In Scots law, excambion is the exchange of land. The deed whereby this is effected is termed "Contract of Excambion".
There is an implied real warranty in this contract, so that if one portion is evicted or taken away on a superior title, the party ...
(exchange) was agreed whereby Keith regained Dunnottar and Lindsay took lands in Fife. William Keith completed construction of the tower house at Dunnottar, but was excommunicated
Excommunication is an institutional act of religious censure used to end or at least regulate the communion of a member of a congregation with other members of the religious institution who are in normal communion with each other. The purpose ...
for building on the consecrated ground associated with the parish church. Keith had provided a new parish church closer to Stonehaven, but was forced to write to the Pope, Benedict XIII, who issued a bull in 1395 lifting the excommunication. William Keith's descendants were made Earls Marischal
The title of Earl Marischal was created in the Peerage of Scotland for William Keith, the Great Marischal of Scotland.
History
The office of Marischal of Scotland (or ''Marascallus Scotie'' or ''Marscallus Scotiae'') had been hereditary, held b ...
in the mid 15th century, and they held Dunottar until the 18th century.
16th century rebuilding

James IV
James IV (17 March 1473 – 9 September 1513) was King of Scotland from 11 June 1488 until his death at the Battle of Flodden in 1513. He inherited the throne at the age of fifteen on the death of his father, James III, at the Battle of Sauch ...
came to Dunnotar on 15 October 1504. A child played a musical instrument called a monochord
A monochord, also known as sonometer (see below), is an ancient musical and scientific laboratory instrument, involving one (mono-) string ( chord). The term ''monochord'' is sometimes used as the class-name for any musical stringed instrument h ...
for him, and he gave money to poor people. The king had brought his Italian minstrels and an African drummer, known as the "More taubronar The More Taubronar (died 1507) was a musician of African origin at the court of James IV of Scotland and his wife Margaret Tudor. His name is unknown. A "taubron" was a kind of drum, the word is related to the modern form "tabor". The word "More" or ...
".
Through the 16th century, the Keiths improved and expanded their principal seats: at Dunnottar and also at Keith Marischal
Keith Marischal is a Scottish Baronial Country house lying in the parish of Humbie, East Lothian, Scotland. The original building was an "L-shaped" Tower house, built long before 1589 when it was extended into a "U-shaped" courtyard house. The ...
in East Lothian. James IV
James IV (17 March 1473 – 9 September 1513) was King of Scotland from 11 June 1488 until his death at the Battle of Flodden in 1513. He inherited the throne at the age of fifteen on the death of his father, James III, at the Battle of Sauch ...
visited Dunnottar in 1504, and in 1531 James V exempted the Earl's men from military service on the grounds that Dunnottar was one of the "principall strenthis of our realme". Mary, Queen of Scots
Mary, Queen of Scots (8 December 1542 – 8 February 1587), also known as Mary Stuart or Mary I of Scotland, was Queen of Scotland from 14 December 1542 until her forced abdication in 1567.
The only surviving legitimate child of James V of S ...
, visited in 1562 after the Battle of Corrichie
The Battle of Corrichie, also known as the Battle of Corrichy was a battle fought near Meikle Tap, near Aberdeen, Scotland, on 28 October 1562. It was fought between the forces of George Gordon, 4th Earl of Huntly, chief of Clan Gordon, agains ...
, and returned in 1564. James VI
James is a common English language surname and given name:
*James (name), the typically masculine first name James
* James (surname), various people with the last name James
James or James City may also refer to:
People
* King James (disambiguat ...
stayed for 10 days in 1580, as part of his progress
Progress is the movement towards a refined, improved, or otherwise desired state. In the context of progressivism, it refers to the proposition that advancements in technology, science, and social organization have resulted, and by extension w ...
through Fife and Angus, during which a meeting of the Privy Council was convened at Dunnottar. King James came again on 17 April 1589 and spent the night at Cowie Cowie may refer to:
People
*Cowie (surname)
Places
*Cowie, Aberdeenshire, an historic fishing village located at the north side of Stonehaven, Scotland
**Cowie Castle, a ruined castle in Aberdeenshire, Scotland
** Chapel of St. Mary and St. Natha ...
watching for the Catholic rebel earls of Huntly and Erroll. During the rebellion of Catholic nobles in 1592, Dunnottar was captured by Captain Carr on behalf of the Earl of Huntly
Marquess of Huntly (traditionally spelled Marquis in Scotland; Scottish Gaelic: ''Coileach Strath Bhalgaidh'') is a title in the Peerage of Scotland that was created on 17 April 1599 for George Gordon, 6th Earl of Huntly. It is the oldest existin ...
, but was restored to Lord Marischal just a few weeks later.
In 1581 George Keith succeeded as 5th Earl Marischal, and began a large-scale reconstruction that saw the medieval fortress converted into a more comfortable home. As the founder of Marischal College
Marischal College ( ) is a large granite building on Broad Street in the centre of Aberdeen in north-east Scotland, and since 2011 has acted as the headquarters of Aberdeen City Council. However, the building was constructed for and is on long- ...
in Aberdeen, the 5th Earl valued Dunnottar as much for its dramatic situation as for its security. A "palace" comprising a series of ranges around a quadrangle was built on the north-eastern cliffs, creating luxurious living quarters with sea views. The 13th-century chapel was restored and incorporated into the quadrangle. An impressive stone gatehouse was constructed, now known as Benholm's Lodging, featuring numerous gun ports facing the approach. Although impressive, these are likely to have been fashionable embellishments rather than genuine defensive features. The earl had a suite of 'Samson
Samson (; , '' he, Šīmšōn, label= none'', "man of the sun") was the last of the judges of the ancient Israelites mentioned in the Book of Judges (chapters 13 to 16) and one of the last leaders who "judged" Israel before the institution o ...
' tapestries which may have represented his religious outlook.
Civil wars
 In 1639
In 1639 William Keith, 7th Earl Marischal
William Keith, 7th Earl Marischal (16101670 or 1671) was a Scottish nobleman and Covenanter. He was the eldest son of William Keith, 6th Earl Marischal.
Life
During the English Civil War, the 7th Earl Marischal joined James Graham, 1st Marques ...
, came out in support of the Covenanters, a Presbyterian movement who opposed the established Episcopal Church and the changes which Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
was attempting to impose. With James Graham, 1st Marquess of Montrose, he marched against the Catholic James Gordon, 2nd Viscount Aboyne
James Gordon, 2nd Viscount Aboyne (c. 1620 – February 1649) was the second son of George Gordon, 2nd Marquess of Huntly, a Scottish royalist commander in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms.
Early life
Aboyne was a member of the powerful Gordon ...
, Earl of Huntly
Marquess of Huntly (traditionally spelled Marquis in Scotland; Scottish Gaelic: ''Coileach Strath Bhalgaidh'') is a title in the Peerage of Scotland that was created on 17 April 1599 for George Gordon, 6th Earl of Huntly. It is the oldest existin ...
, and defeated an attempt by the Royalists to seize Stonehaven
Stonehaven ( , ) is a town in Scotland. It lies on Scotland's northeast coast and had a population of 11,602 at the 2011 Census.
After the demise of the town of Kincardine, which was gradually abandoned after the destruction of its royal cast ...
. However, when Montrose changed sides to the Royalists and marched north, Marischal remained in Dunnottar, even when given command of the area by Parliament, and even when Montrose burned Stonehaven.Stevenson (2004).
Marischal then joined with the Engager
The Engagers were a faction of the Scottish Covenanters, who made "The Engagement" with King Charles I in December 1647 while he was imprisoned in Carisbrooke Castle by the English Parliamentarians after his defeat in the First Civil War.
Back ...
faction, who had made a deal with the king, and led a troop of horse to the Battle of Preston (1648)
The Battle of Preston (17–19 August 1648), fought largely at Walton-le-Dale near Preston in Lancashire, resulted in a victory for the New Model Army under the command of Oliver Cromwell over the Royalists and Scots commanded by the Duke of ...
in support of the royalists. Following the execution of Charles I in 1649, the Engagers gave their allegiance to his son and heir. Charles II was proclaimed king, arriving in Scotland in June 1650. He visited Dunnottar in July 1650, but his presence in Scotland prompted Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three K ...
to lead a force into Scotland, defeating the Scots at Dunbar
Dunbar () is a town on the North Sea coast in East Lothian in the south-east of Scotland, approximately east of Edinburgh and from the English border north of Berwick-upon-Tweed.
Dunbar is a former royal burgh, and gave its name to an ecc ...
in September 1650.
Honours of Scotland
Charles II was crowned atScone Palace
Scone Palace is a Category A-listed historic house near the village of Scone and the city of Perth, Scotland. Built in red sandstone with a castellated roof, it is an example of the Gothic Revival style in Scotland.
Scone was originally the s ...
on 1 January 1651, at which the Honours of Scotland (the regalia of crown, sword and sceptre) were used. However, with Cromwell's troops in Lothian, the honours could not be returned to Edinburgh. The Earl Marischal, as Marischal of Scotland, had formal responsibility for the honours, and in June the Privy Council duly decided to place them at Dunnottar.Groome (1885), pp. 442–443. They were brought to the castle by Katherine Drummond, hidden in sacks of wool.Baigent (2004). Sir George Ogilvie (or Ogilvy) of Barras was appointed lieutenant-governor of the castle, and given responsibility for its defence.Henderson & Furgol (2004).
In November 1651, Cromwell's troops called on Ogilvie to surrender, but he refused. During the subsequent blockade of the castle, the removal of the Honours of Scotland was planned by Elizabeth Douglas, wife of Sir George Ogilvie, and Christian Fletcher
Christian Fletcher, Lady Abercrombie (1619 or 1620 – February 1691), was a Scottish minister's wife who helped save the Honours of Scotland from Cromwell's troops during the English invasion of Scotland. She was married from 1642 to James ...
, wife of James Granger, minister of Kinneff Parish Church. The king's papers were first removed from the castle by Anne Lindsay, a kinswoman of Elizabeth Douglas, who walked through the besieging force with the papers sewn into her clothes. Two stories exist regarding the removal of the honours themselves. Fletcher stated in 1664 that over the course of three visits to the castle in February and March 1652, she carried away the crown, sceptre, sword and sword case hidden amongst sacks of goods. Another account, given in the 18th century by a tutor to the Earl Marischal, records that the honours were lowered from the castle onto the beach, where they were collected by Fletcher's servant and carried off in a creel (basket) of seaweed. Having smuggled the honours from the castle, Fletcher and her husband buried them under the floor of the Old Kirk at Kinneff
Kinneff is a roadside hamlet in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, just north of Inverbervie.Kinneff.
Thomas Morgan, had taken delivery of the
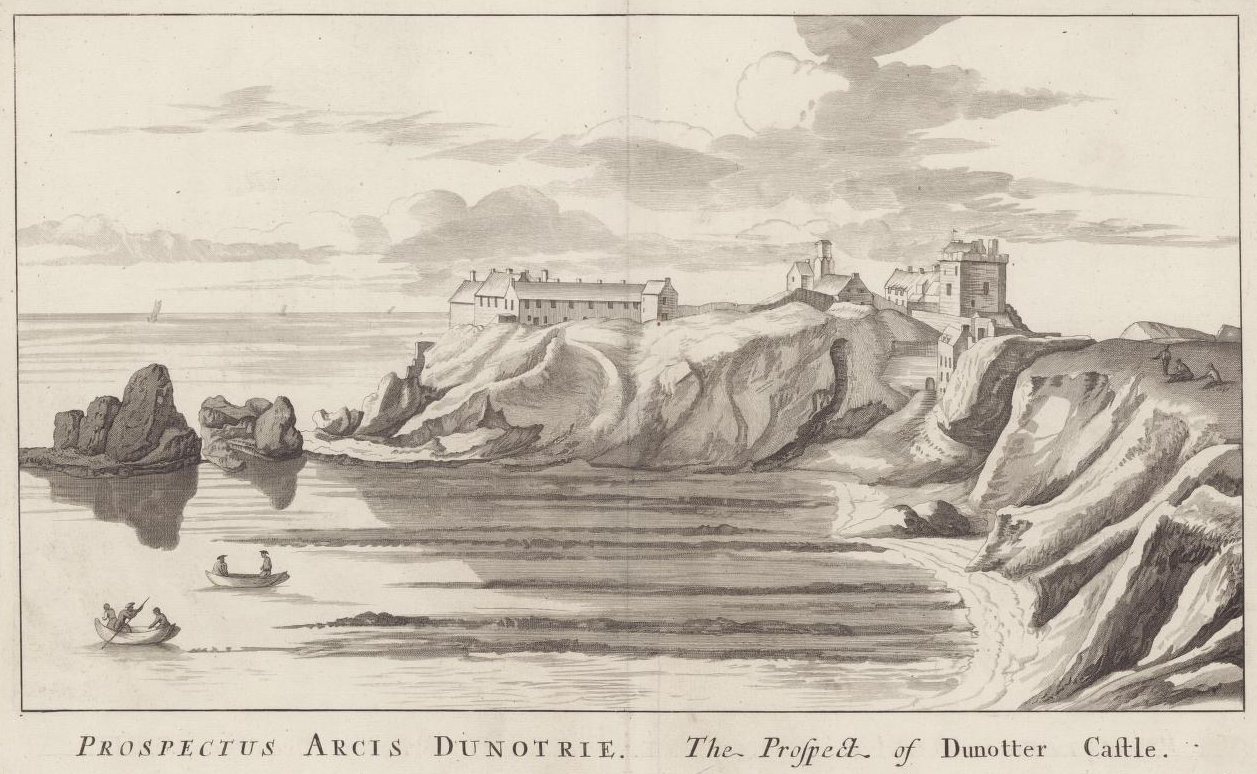 Religious and political conflicts continued to be played out at Dunnottar through the 17th and early 18th centuries. In 1685, during the rebellion of the Earl of Argyll against the new king
Religious and political conflicts continued to be played out at Dunnottar through the 17th and early 18th centuries. In 1685, during the rebellion of the Earl of Argyll against the new king

 The seized estates of the Earl Marischal were purchased in 1720 for £41,172, by the
The seized estates of the Earl Marischal were purchased in 1720 for £41,172, by the
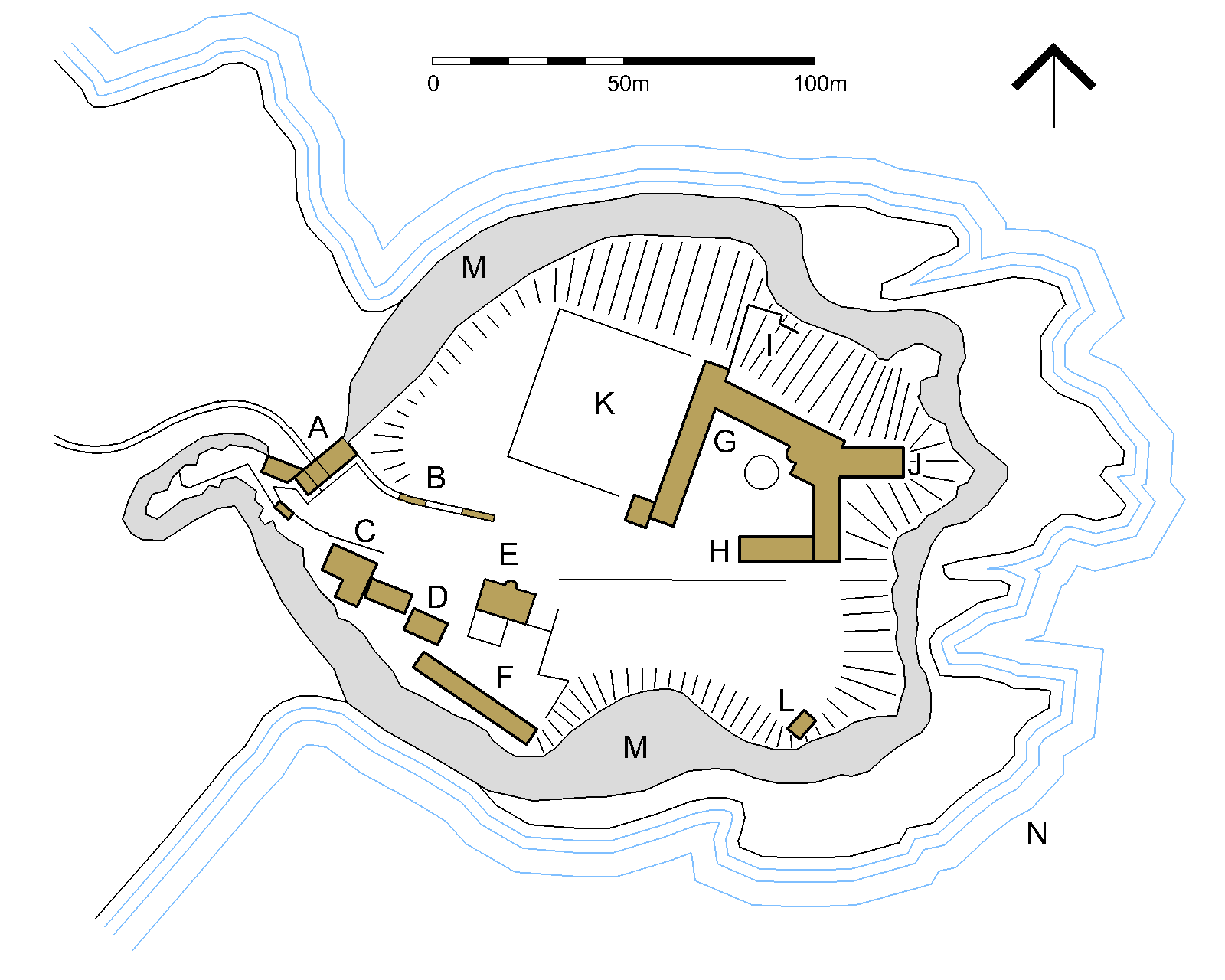 Dunnottar's strategic location allowed its owners to control the coastal terrace between the North Sea cliffs and the hills of the
Dunnottar's strategic location allowed its owners to control the coastal terrace between the North Sea cliffs and the hills of the
 The approach to the castle is overlooked by outworks on the "Fiddle Head", a promontory on the western side of the headland. The entrance is through the well-defended main gate, set in a curtain wall which entirely blocks a cleft in the rocky cliffs. The gate has a portcullis and has been partly blocked up. Alongside the main gate is the 16th-century Benholm's Lodging, a five-storey building cut into the rock, which incorporated a prison with apartments above. Three tiers of gun ports face outwards from the lower floors of Benholm's Lodging, while inside the main gate, a group of four gun ports face the entrance. The entrance passage then turns sharply to the left, running underground through two tunnels to emerge near the tower house.
Simpson contends that these defences are "without exception the strongest in Scotland", although later writers have doubted the effectiveness of the gun ports. Cruden notes that the alignment of the gun ports in Benholm's Lodging, facing across the approach rather than along, means that they are of limited efficiency. The practicality of the gun ports facing the entrance has also been questioned, though an inventory of 1612 records that four brass cannons were placed here.
A second access to the castle leads up from a rocky cove, the aperture to a marine cave on the northern side of the Dunnottar cliffs into which a small boat could be brought. From here a steep path leads to the well-fortified
The approach to the castle is overlooked by outworks on the "Fiddle Head", a promontory on the western side of the headland. The entrance is through the well-defended main gate, set in a curtain wall which entirely blocks a cleft in the rocky cliffs. The gate has a portcullis and has been partly blocked up. Alongside the main gate is the 16th-century Benholm's Lodging, a five-storey building cut into the rock, which incorporated a prison with apartments above. Three tiers of gun ports face outwards from the lower floors of Benholm's Lodging, while inside the main gate, a group of four gun ports face the entrance. The entrance passage then turns sharply to the left, running underground through two tunnels to emerge near the tower house.
Simpson contends that these defences are "without exception the strongest in Scotland", although later writers have doubted the effectiveness of the gun ports. Cruden notes that the alignment of the gun ports in Benholm's Lodging, facing across the approach rather than along, means that they are of limited efficiency. The practicality of the gun ports facing the entrance has also been questioned, though an inventory of 1612 records that four brass cannons were placed here.
A second access to the castle leads up from a rocky cove, the aperture to a marine cave on the northern side of the Dunnottar cliffs into which a small boat could be brought. From here a steep path leads to the well-fortified
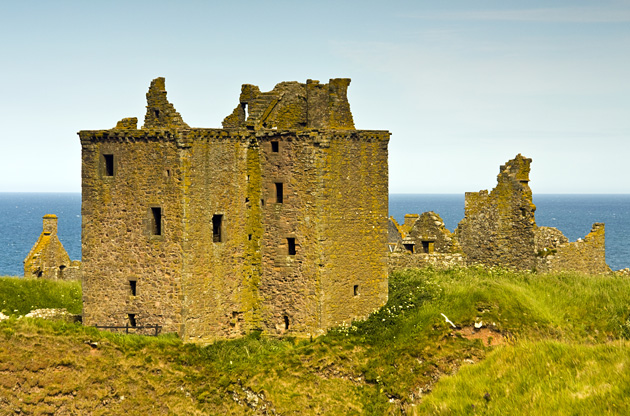 The late 14th-century tower house has a stone-vaulted basement, and originally had three further storeys and a garret above. Measuring , the tower house stood high to its gable. The principal rooms included a great hall and a private chamber for the lord, with bedrooms upstairs. Beside the tower house is a storehouse, and a blacksmith's forge with a large chimney. A stable block is ranged along the southern edge of the headland. Nearby is Waterton's Lodging, also known as the Priest's House, built around 1574,Howard (1995), p. 83. possibly for the use of William Keith (died 1580), son of the 4th Earl Marischal. This small self-contained house includes a hall and kitchen at ground level, with private chambers above, and has a projecting spiral stair on the north side. It is named for Thomas Forbes of Waterton, an attendant of the 7th Earl.
The late 14th-century tower house has a stone-vaulted basement, and originally had three further storeys and a garret above. Measuring , the tower house stood high to its gable. The principal rooms included a great hall and a private chamber for the lord, with bedrooms upstairs. Beside the tower house is a storehouse, and a blacksmith's forge with a large chimney. A stable block is ranged along the southern edge of the headland. Nearby is Waterton's Lodging, also known as the Priest's House, built around 1574,Howard (1995), p. 83. possibly for the use of William Keith (died 1580), son of the 4th Earl Marischal. This small self-contained house includes a hall and kitchen at ground level, with private chambers above, and has a projecting spiral stair on the north side. It is named for Thomas Forbes of Waterton, an attendant of the 7th Earl.
 The palace, to the north-east of the headland, was built in the late 16th century and early to mid-17th century. It comprises three main wings set out around a quadrangle, and for the most part is probably the work of the 5th Earl Marischal who succeeded in 1581.The order of construction of the palace is debated: Simpson (1966, pp.43–49) interprets the west range as the earliest (possibly before 1580), followed by the north and east ranges together, with the north-east wing added last, in 1645. Cruden follows Simpson, though McKean (2004, pp.173–174) states that the north-east wing is contemporary with the east range, and that the north range is later. Geddes (2001, pp.25–27) suggests that the palace was built from east to west. It provided extensive and comfortable accommodation to replace the rooms in the tower house. In its long, low design it has been compared to contemporary English buildings, in contrast to the Scottish tradition of taller towers still prevalent in the 16th century.
Seven identical lodgings are arranged along the west range, each opening onto the quadrangle and including windows and fireplaces. Above the lodgings of the west range comprised a
The palace, to the north-east of the headland, was built in the late 16th century and early to mid-17th century. It comprises three main wings set out around a quadrangle, and for the most part is probably the work of the 5th Earl Marischal who succeeded in 1581.The order of construction of the palace is debated: Simpson (1966, pp.43–49) interprets the west range as the earliest (possibly before 1580), followed by the north and east ranges together, with the north-east wing added last, in 1645. Cruden follows Simpson, though McKean (2004, pp.173–174) states that the north-east wing is contemporary with the east range, and that the north range is later. Geddes (2001, pp.25–27) suggests that the palace was built from east to west. It provided extensive and comfortable accommodation to replace the rooms in the tower house. In its long, low design it has been compared to contemporary English buildings, in contrast to the Scottish tradition of taller towers still prevalent in the 16th century.
Seven identical lodgings are arranged along the west range, each opening onto the quadrangle and including windows and fireplaces. Above the lodgings of the west range comprised a  The basement of the north range incorporates kitchens and stores, with a dining room and great chamber above. At ground floor level is the Water Gate, between the north and west ranges, which gives access to the postern on the northern cliffs. The east and north ranges are linked via a rectangular stair. The east range has a larder, brewhouse and bakery at ground level, with a suite of apartments for the countess above. A north-east wing contains the Earl's apartments, and includes the "King's Bedroom" in which Charles II stayed. In this room is a carved stone inscribed with the arms of the 7th Earl and his wife, and the date 1645. Below these rooms is the Whigs' Vault, a cellar measuring . This cellar, in which the Covenanters were held in 1685, has a large eastern window, as well as a lower vault accessed via a trapdoor in the floor. Of the chambers in the palace, only the dining room and the Silver House remain roofed, having been restored in the 1920s.
The central area contains a circular cistern or fish pond, across and deep,Simpson (1966), pp. 52–53. and a bowling green is located to the west. At the south-east corner of the quadrangle is the chapel, consecrated in 1276 and largely rebuilt in the 16th century. Medieval walling and two 13th-century windows remain, and there is a graveyard to the south.
The basement of the north range incorporates kitchens and stores, with a dining room and great chamber above. At ground floor level is the Water Gate, between the north and west ranges, which gives access to the postern on the northern cliffs. The east and north ranges are linked via a rectangular stair. The east range has a larder, brewhouse and bakery at ground level, with a suite of apartments for the countess above. A north-east wing contains the Earl's apartments, and includes the "King's Bedroom" in which Charles II stayed. In this room is a carved stone inscribed with the arms of the 7th Earl and his wife, and the date 1645. Below these rooms is the Whigs' Vault, a cellar measuring . This cellar, in which the Covenanters were held in 1685, has a large eastern window, as well as a lower vault accessed via a trapdoor in the floor. Of the chambers in the palace, only the dining room and the Silver House remain roofed, having been restored in the 1920s.
The central area contains a circular cistern or fish pond, across and deep,Simpson (1966), pp. 52–53. and a bowling green is located to the west. At the south-east corner of the quadrangle is the chapel, consecrated in 1276 and largely rebuilt in the 16th century. Medieval walling and two 13th-century windows remain, and there is a graveyard to the south.
Dunnottar Castle homepageDunecht Estates homepageGhosts, History, Photographs and Paintings of Dunnottar Castle from Aboutaberdeen.com
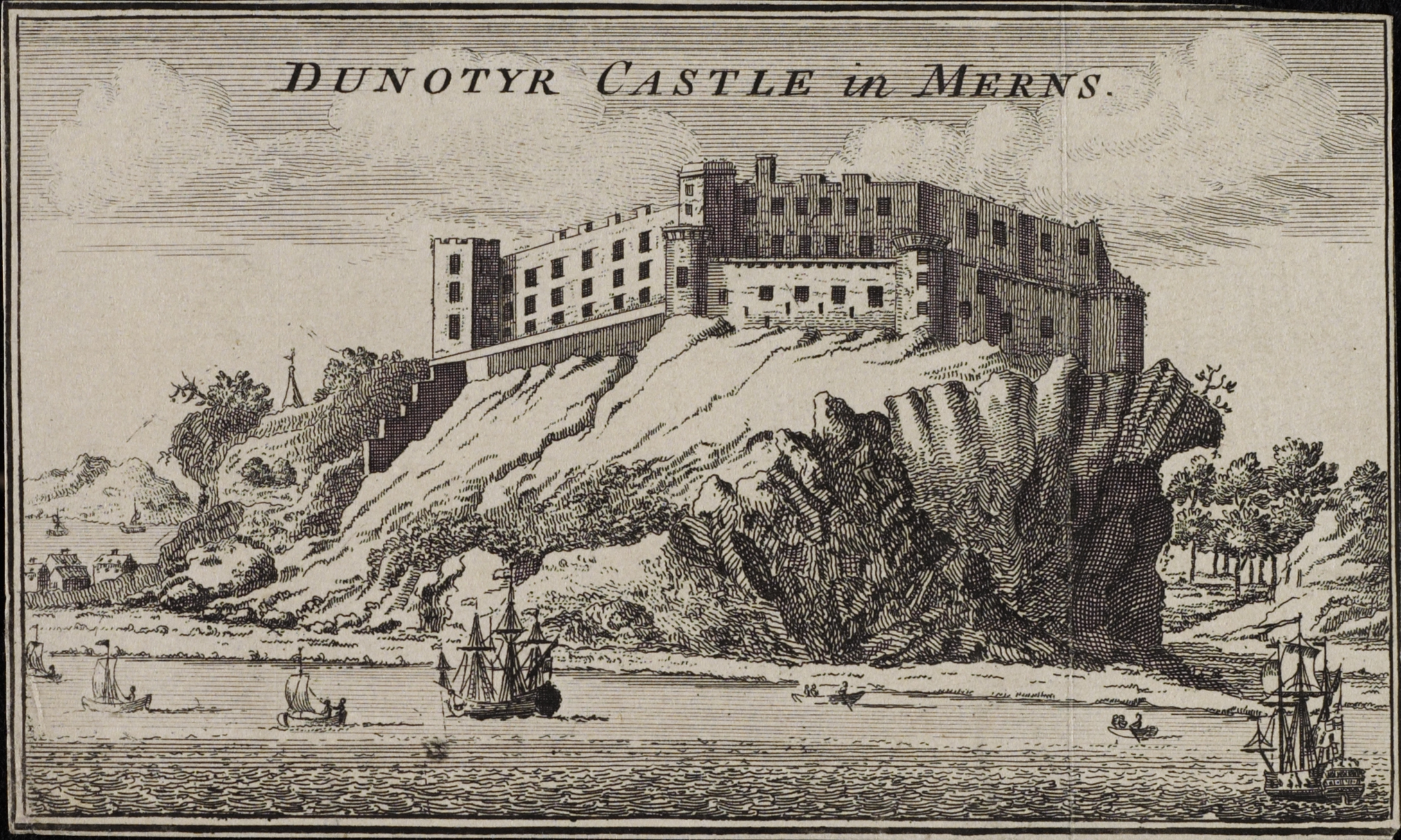
Engraving of Dunottar in 1693
by
Dunnotter Castle Virtual Tour
{{Kincardine and Mearns, Aberdeenshire places, state = collapsed Headlands of Scotland Listed castles in Scotland Promontory forts in Scotland Ruined castles in Aberdeenshire Scheduled Ancient Monuments in Aberdeenshire Romanesque architecture in Scotland 13th-century establishments in Scotland Stonehaven Landforms of Aberdeenshire Castles in Aberdeenshire African presence at the Scottish royal court
Thomas Morgan, had taken delivery of the
artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during siege ...
necessary for the reduction of Dunnottar. Ogilvie surrendered on 24 May, on condition that the garrison could go free. Finding the honours gone, the Cromwellians imprisoned Ogilvie and his wife in the castle until the following year, when a false story was put about suggesting that the honours had been taken overseas. Much of the castle property was removed, including twenty-one brass cannons, and Marischal was required to sell further lands and possessions to pay fines imposed by Cromwell's government.
At the Restoration
Restoration is the act of restoring something to its original state and may refer to:
* Conservation and restoration of cultural heritage
** Audio restoration
** Film restoration
** Image restoration
** Textile restoration
* Restoration ecology
...
of Charles II in 1660, the honours were removed from Kinneff Church and returned to the king. Ogilvie quarrelled with Marischal's mother over who would take credit for saving the honours, though he was eventually rewarded with a baronet
A baronet ( or ; abbreviated Bart or Bt) or the female equivalent, a baronetess (, , or ; abbreviation Btss), is the holder of a baronetcy, a hereditary title awarded by the British Crown. The title of baronet is mentioned as early as the 14t ...
cy. Fletcher was awarded 2,000 merks by Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
but the sum was never paid.
Whigs and Jacobites
James VII
James VII and II (14 October 1633 16 September 1701) was King of England and King of Ireland as James II, and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II, on 6 February 1685. He was deposed in the Glorious Re ...
, 167 Covenanters were seized and held in a cellar at Dunnottar. The prisoners included 122 men and 45 women associated with the Whigs, an anti-Royalist group within the Covenanter movement, and had refused to take an oath of allegiance to the new king. The Whigs were imprisoned from May 24 until late July. A group of 25 escaped, although two of these were killed in a fall from the cliffs, and another 15 were recaptured. Five prisoners died in the vault, and 37 of the Whigs were released after taking the oath of allegiance. The remaining prisoners were transported
''Transported'' is an Australian convict melodrama film directed by W. J. Lincoln. It is considered a lost film.
Plot
In England, Jessie Grey is about to marry Leonard Lincoln but the evil Harold Hawk tries to force her to marry him and she w ...
to Perth Amboy, New Jersey
Perth Amboy is a city in Middlesex County, New Jersey. Perth Amboy is part of the New York metropolitan area. As of the 2020 U.S. census, the city's population was 55,436. Perth Amboy has a Hispanic majority population. In the 2010 census, th ...
, as part of a colonisation scheme devised by George Scot of Pitlochie
George Scot or Scott ( – 1685) of Pitlochie, Fife was a Scottish writer on colonisation in North America.
Early life
Scot, who was born around 1640, was the only son of John Scot of Scotstarvet by his second wife, Elizabeth Melville, daugh ...
. Many, like Scot himself, died on the voyage. The cellar, located beneath the "King's Bedroom" in the 16th-century castle buildings, has since become known as the "Whigs' Vault".
Both the Jacobites
Jacobite means follower of Jacob or James. Jacobite may refer to:
Religion
* Jacobites, followers of Saint Jacob Baradaeus (died 578). Churches in the Jacobite tradition and sometimes called Jacobite include:
** Syriac Orthodox Church, sometime ...
(supporters of the exiled Stuarts) and the Hanoverians
The House of Hanover (german: Haus Hannover), whose members are known as Hanoverians, is a European royal house of German origin that ruled Hanover, Great Britain, and Ireland at various times during the 17th to 20th centuries. The house orig ...
(supporters of George I George I or 1 may refer to:
People
* Patriarch George I of Alexandria (fl. 621–631)
* George I of Constantinople (d. 686)
* George I of Antioch (d. 790)
* George I of Abkhazia (ruled 872/3–878/9)
* George I of Georgia (d. 1027)
* Yuri Dolgor ...
and his descendants) used Dunnottar Castle. In 1689 during Viscount Dundee
Viscount of Dundee was a title in the Peerage of Scotland. It was created on 12 November 1688 for John Graham with remainder to him and his heirs male of his body, which failing, to his other heirs male. He was made Lord Graham of Claverhouse at ...
's campaign in support of the deposed James VII
James VII and II (14 October 1633 16 September 1701) was King of England and King of Ireland as James II, and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II, on 6 February 1685. He was deposed in the Glorious Re ...
, the castle was garrisoned for William III and Mary II with Lord Marischal appointed captain. Seventeen suspected Jacobites from Aberdeen were seized and held in the fortress for around three weeks, including George Liddell, professor of mathematics at Marischal College. In the Jacobite Rising of 1715
The Jacobite rising of 1715 ( gd, Bliadhna Sheumais ;
or 'the Fifteen') was the attempt by James Edward Stuart (the Old Pretender) to regain the thrones of England, Ireland and Scotland for the exiled Stuarts.
At Braemar, Aberdeenshire ...
George Keith, 10th Earl Marischal
{{Infobox noble
, name = George Keith, 10th Earl Marischal
, title = Earl Marischal
, image = George Keith, 10th Earl Marischal by Placido Costanzi.jpg
, caption = George Keith, 10th Earl Marischal ...
, took an active role with the rebels, leading cavalry at the Battle of Sheriffmuir. After the subsequent abandonment of the rising Lord Marischal fled to the Continent, eventually becoming French ambassador for Frederick the Great
Frederick II (german: Friedrich II.; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was King in Prussia from 1740 until 1772, and King of Prussia from 1772 until his death in 1786. His most significant accomplishments include his military successes in the S ...
of Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
. Meanwhile, in 1716, his titles and estates including Dunnottar were declared forfeit
Forfeit or forfeiture may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Forfeit'', a 2007 thriller film starring Billy Burke
* "Forfeit", a song by Chevelle from ''Wonder What's Next''
* ''Forfeit/Fortune'', a 2008 album by Crooked Fingers
L ...
to the crown.
Later history

York Buildings Company
The York Buildings Company was an English company in the late 17th and early 18th centuries.
Waterworks
The full name of the company was The Governor and Company for raising the Thames Water at York Buildings. The undertaking was established in ...
who dismantled much of the castle. In 1761 the Earl briefly returned to Scotland and bought back Dunnottar only to sell it five years later to Alexander Keith (1736–1819), an Edinburgh lawyer who served as Knight Marischal
The office of Knight Marischal was first created for the Scottish coronation of Charles I in 1633, at Scone. Unlike the separate office of Marischal, the office of Knight Marischal is not heritable, and has continued to be filled up to the deat ...
of Scotland. Dunnottar was held by Alexander Keith then his son, Sir Alexander Keith (1768–1832) before being inherited in 1852 by Sir Patrick Keith-Murray of Ochtertyre, who in turn sold it in July 1873 to Major Alexander Innes of Cowie and Raemoir for about £80,000. It was purchased by Weetman Pearson, 1st Viscount Cowdray
Weetman Dickinson Pearson, 1st Viscount Cowdray, (15 July 1856 – 1 May 1927), known as Sir Weetman Pearson, Bt between 1894 and 1910, and as Lord Cowdray between 1910 and 1917, was a British engineer, oil industrialist, benefactor and Lib ...
, in 1925, after which his wife embarked on a programme of repairs. Since that time the castle has remained in the family, and has been open to the public, attracting 52,500 visitors in 2009.
Dunnottar Castle, and the headland on which is stands, was designated as a Scheduled monument
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a nationally important archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorised change.
The various pieces of legislation that legally protect heritage assets from damage and d ...
in 1970.
In 1972 twelve of the structures at Dunnottar were listed
Listed may refer to:
* Listed, Bornholm, a fishing village on the Danish island of Bornholm
* Listed (MMM program), a television show on MuchMoreMusic
* Endangered species in biology
* Listed building, in architecture, designation of a historicall ...
. Three buildings were listed at category A as being of "national importance": the keep; the entrance gateway; and Benholm's Lodging. The remaining listings were at category B as being of "regional importance". However, in 2018 the listed status for these buildings was removed as part of Historic Environment Scotland
Historic Environment Scotland (HES) ( gd, Àrainneachd Eachdraidheil Alba) is an executive non-departmental public body responsible for investigating, caring for and promoting Scotland's historic environment. HES was formed in 2015 from the mer ...
s "Dual Designation 2A Project".
The Hon. Charles Anthony Pearson, the younger son of the 3rd Viscount Cowdray
Viscount Cowdray, of Cowdray in the County of Sussex, is a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. It was created in 1917 for the industrialist Weetman Pearson, 1st Baron Cowdray, head of the Pearson conglomerate. He had already been creat ...
, currently owns and runs Dunnottar Castle which is part of the Dunecht Estates
The Dunecht Estate is one of the largest private estates in Aberdeenshire, Scotland at . It is owned by The Hon Charles Anthony Pearson, the younger son of the 3rd Viscount Cowdray. Dunecht’s business interests include farming (in hand and let ...
. Portions of the 1990 film ''Hamlet'', starring Mel Gibson
Mel Columcille Gerard Gibson (born January 3, 1956) is an American actor, film director, and producer. He is best known for his action hero roles, particularly his breakout role as Max Rockatansky in the first three films of the post-apoca ...
and Glenn Close
Glenn Close (born March 19, 1947) is an American actress. Throughout her career spanning over four decades, Close has garnered numerous accolades, including two Screen Actors Guild Awards, three Golden Globe Awards, three Primetime Emmy Awards ...
, were shot there.
Description
 Dunnottar's strategic location allowed its owners to control the coastal terrace between the North Sea cliffs and the hills of the
Dunnottar's strategic location allowed its owners to control the coastal terrace between the North Sea cliffs and the hills of the Mounth
The Mounth ( ) is the broad upland in northeast Scotland between the Highland Boundary and the River Dee, at the eastern end of the Grampians.
Name and etymology
The name ''Mounth'' is ultimately of Pictish origin. The name is derived from ...
, inland, which enabled access to and from the north-east of Scotland. The site is accessed via a steep, footpath (with modern staircases) from a car park on the coastal road, or via a cliff-top path from Stonehaven.
Dunnottar's several buildings, put up between the 13th and 17th centuries, are arranged across a headland covering around . The dominant building, viewed from the land approach, is the 14th-century keep or tower house. The other principal buildings are the gatehouse; the chapel; and the 16th-century "palace" which incorporates the "Whigs' Vault".
Defences
 The approach to the castle is overlooked by outworks on the "Fiddle Head", a promontory on the western side of the headland. The entrance is through the well-defended main gate, set in a curtain wall which entirely blocks a cleft in the rocky cliffs. The gate has a portcullis and has been partly blocked up. Alongside the main gate is the 16th-century Benholm's Lodging, a five-storey building cut into the rock, which incorporated a prison with apartments above. Three tiers of gun ports face outwards from the lower floors of Benholm's Lodging, while inside the main gate, a group of four gun ports face the entrance. The entrance passage then turns sharply to the left, running underground through two tunnels to emerge near the tower house.
Simpson contends that these defences are "without exception the strongest in Scotland", although later writers have doubted the effectiveness of the gun ports. Cruden notes that the alignment of the gun ports in Benholm's Lodging, facing across the approach rather than along, means that they are of limited efficiency. The practicality of the gun ports facing the entrance has also been questioned, though an inventory of 1612 records that four brass cannons were placed here.
A second access to the castle leads up from a rocky cove, the aperture to a marine cave on the northern side of the Dunnottar cliffs into which a small boat could be brought. From here a steep path leads to the well-fortified
The approach to the castle is overlooked by outworks on the "Fiddle Head", a promontory on the western side of the headland. The entrance is through the well-defended main gate, set in a curtain wall which entirely blocks a cleft in the rocky cliffs. The gate has a portcullis and has been partly blocked up. Alongside the main gate is the 16th-century Benholm's Lodging, a five-storey building cut into the rock, which incorporated a prison with apartments above. Three tiers of gun ports face outwards from the lower floors of Benholm's Lodging, while inside the main gate, a group of four gun ports face the entrance. The entrance passage then turns sharply to the left, running underground through two tunnels to emerge near the tower house.
Simpson contends that these defences are "without exception the strongest in Scotland", although later writers have doubted the effectiveness of the gun ports. Cruden notes that the alignment of the gun ports in Benholm's Lodging, facing across the approach rather than along, means that they are of limited efficiency. The practicality of the gun ports facing the entrance has also been questioned, though an inventory of 1612 records that four brass cannons were placed here.
A second access to the castle leads up from a rocky cove, the aperture to a marine cave on the northern side of the Dunnottar cliffs into which a small boat could be brought. From here a steep path leads to the well-fortified postern gate
A postern is a secondary door or gate in a fortification such as a city wall or castle curtain wall. Posterns were often located in a concealed location which allowed the occupants to come and go inconspicuously. In the event of a siege, a postern ...
on the cliff-top, which in turn offers access to the castle via the Water Gate in the palace. Artillery defences, taking the form of earthworks, surround the north-west corner of the castle, facing inland, and the south-east, facing seaward.MacGibbon & Ross (1887), p. 573. A small sentry box or guard house stands by the eastern battery, overlooking the coast.
Tower house and surrounding buildings
 The late 14th-century tower house has a stone-vaulted basement, and originally had three further storeys and a garret above. Measuring , the tower house stood high to its gable. The principal rooms included a great hall and a private chamber for the lord, with bedrooms upstairs. Beside the tower house is a storehouse, and a blacksmith's forge with a large chimney. A stable block is ranged along the southern edge of the headland. Nearby is Waterton's Lodging, also known as the Priest's House, built around 1574,Howard (1995), p. 83. possibly for the use of William Keith (died 1580), son of the 4th Earl Marischal. This small self-contained house includes a hall and kitchen at ground level, with private chambers above, and has a projecting spiral stair on the north side. It is named for Thomas Forbes of Waterton, an attendant of the 7th Earl.
The late 14th-century tower house has a stone-vaulted basement, and originally had three further storeys and a garret above. Measuring , the tower house stood high to its gable. The principal rooms included a great hall and a private chamber for the lord, with bedrooms upstairs. Beside the tower house is a storehouse, and a blacksmith's forge with a large chimney. A stable block is ranged along the southern edge of the headland. Nearby is Waterton's Lodging, also known as the Priest's House, built around 1574,Howard (1995), p. 83. possibly for the use of William Keith (died 1580), son of the 4th Earl Marischal. This small self-contained house includes a hall and kitchen at ground level, with private chambers above, and has a projecting spiral stair on the north side. It is named for Thomas Forbes of Waterton, an attendant of the 7th Earl.
Palace
 The palace, to the north-east of the headland, was built in the late 16th century and early to mid-17th century. It comprises three main wings set out around a quadrangle, and for the most part is probably the work of the 5th Earl Marischal who succeeded in 1581.The order of construction of the palace is debated: Simpson (1966, pp.43–49) interprets the west range as the earliest (possibly before 1580), followed by the north and east ranges together, with the north-east wing added last, in 1645. Cruden follows Simpson, though McKean (2004, pp.173–174) states that the north-east wing is contemporary with the east range, and that the north range is later. Geddes (2001, pp.25–27) suggests that the palace was built from east to west. It provided extensive and comfortable accommodation to replace the rooms in the tower house. In its long, low design it has been compared to contemporary English buildings, in contrast to the Scottish tradition of taller towers still prevalent in the 16th century.
Seven identical lodgings are arranged along the west range, each opening onto the quadrangle and including windows and fireplaces. Above the lodgings of the west range comprised a
The palace, to the north-east of the headland, was built in the late 16th century and early to mid-17th century. It comprises three main wings set out around a quadrangle, and for the most part is probably the work of the 5th Earl Marischal who succeeded in 1581.The order of construction of the palace is debated: Simpson (1966, pp.43–49) interprets the west range as the earliest (possibly before 1580), followed by the north and east ranges together, with the north-east wing added last, in 1645. Cruden follows Simpson, though McKean (2004, pp.173–174) states that the north-east wing is contemporary with the east range, and that the north range is later. Geddes (2001, pp.25–27) suggests that the palace was built from east to west. It provided extensive and comfortable accommodation to replace the rooms in the tower house. In its long, low design it has been compared to contemporary English buildings, in contrast to the Scottish tradition of taller towers still prevalent in the 16th century.
Seven identical lodgings are arranged along the west range, each opening onto the quadrangle and including windows and fireplaces. Above the lodgings of the west range comprised a gallery
Gallery or The Gallery may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Art gallery
** Contemporary art gallery
Music
* Gallery (band), an American soft rock band of the 1970s
Albums
* ''Gallery'' (Elaiza album), 2014 album
* ''Gallery'' (Gr ...
. Now roofless, the gallery originally had an elaborate oak ceiling, and on display was a Roman tablet taken from the Antonine Wall.The tablet is now in the Hunterian Museum
The Hunterian is a complex of museums located in and operated by the University of Glasgow in Glasgow, Scotland. It is the oldest museum in Scotland. It covers the Hunterian Museum, the Hunterian Art Gallery, the Mackintosh House, the Zoology M ...
, Glasgow. Simpson (1966), p. 43. At the north end of the gallery was a drawing room
A drawing room is a room in a house where visitors may be entertained, and an alternative name for a living room. The name is derived from the 16th-century terms withdrawing room and withdrawing chamber, which remained in use through the 17th cent ...
linked to the north range. The gallery could also be accessed from the Silver House to the south, which incorporated a broad stairway with a treasury above.
 The basement of the north range incorporates kitchens and stores, with a dining room and great chamber above. At ground floor level is the Water Gate, between the north and west ranges, which gives access to the postern on the northern cliffs. The east and north ranges are linked via a rectangular stair. The east range has a larder, brewhouse and bakery at ground level, with a suite of apartments for the countess above. A north-east wing contains the Earl's apartments, and includes the "King's Bedroom" in which Charles II stayed. In this room is a carved stone inscribed with the arms of the 7th Earl and his wife, and the date 1645. Below these rooms is the Whigs' Vault, a cellar measuring . This cellar, in which the Covenanters were held in 1685, has a large eastern window, as well as a lower vault accessed via a trapdoor in the floor. Of the chambers in the palace, only the dining room and the Silver House remain roofed, having been restored in the 1920s.
The central area contains a circular cistern or fish pond, across and deep,Simpson (1966), pp. 52–53. and a bowling green is located to the west. At the south-east corner of the quadrangle is the chapel, consecrated in 1276 and largely rebuilt in the 16th century. Medieval walling and two 13th-century windows remain, and there is a graveyard to the south.
The basement of the north range incorporates kitchens and stores, with a dining room and great chamber above. At ground floor level is the Water Gate, between the north and west ranges, which gives access to the postern on the northern cliffs. The east and north ranges are linked via a rectangular stair. The east range has a larder, brewhouse and bakery at ground level, with a suite of apartments for the countess above. A north-east wing contains the Earl's apartments, and includes the "King's Bedroom" in which Charles II stayed. In this room is a carved stone inscribed with the arms of the 7th Earl and his wife, and the date 1645. Below these rooms is the Whigs' Vault, a cellar measuring . This cellar, in which the Covenanters were held in 1685, has a large eastern window, as well as a lower vault accessed via a trapdoor in the floor. Of the chambers in the palace, only the dining room and the Silver House remain roofed, having been restored in the 1920s.
The central area contains a circular cistern or fish pond, across and deep,Simpson (1966), pp. 52–53. and a bowling green is located to the west. At the south-east corner of the quadrangle is the chapel, consecrated in 1276 and largely rebuilt in the 16th century. Medieval walling and two 13th-century windows remain, and there is a graveyard to the south.
See also
*Dunnottar Parish Church
Dunnottar Parish Church is a parish church of the Church of Scotland, serving Stonehaven in the south of Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It is within the Church of Scotland's Presbytery of Kincardine and Deeside. During 2020, the congregation united to ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Dunnottar Castle homepage
Engraving of Dunottar in 1693
by
John Slezer
John Abraham Slezer (before 1650 – 1717) was a Dutch-born military engineer and artist.
Life
He was born in Holland and began a military career in service to the House of Orange.
He arrived in the Kingdom of Scotland in 1669, and was app ...
at National Library of ScotlandDunnotter Castle Virtual Tour
{{Kincardine and Mearns, Aberdeenshire places, state = collapsed Headlands of Scotland Listed castles in Scotland Promontory forts in Scotland Ruined castles in Aberdeenshire Scheduled Ancient Monuments in Aberdeenshire Romanesque architecture in Scotland 13th-century establishments in Scotland Stonehaven Landforms of Aberdeenshire Castles in Aberdeenshire African presence at the Scottish royal court