Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
centered at Wittenberg, which emerged after the dissolution of the stem duchy of Saxony. The Ascanian dukes prevailed in obtaining the Saxon electoral dignity until their duchy was finally elevated to the Electorate of Saxony by the Golden Bull of 1356.
History
Ascanian struggle for Saxony
TheEastphalia
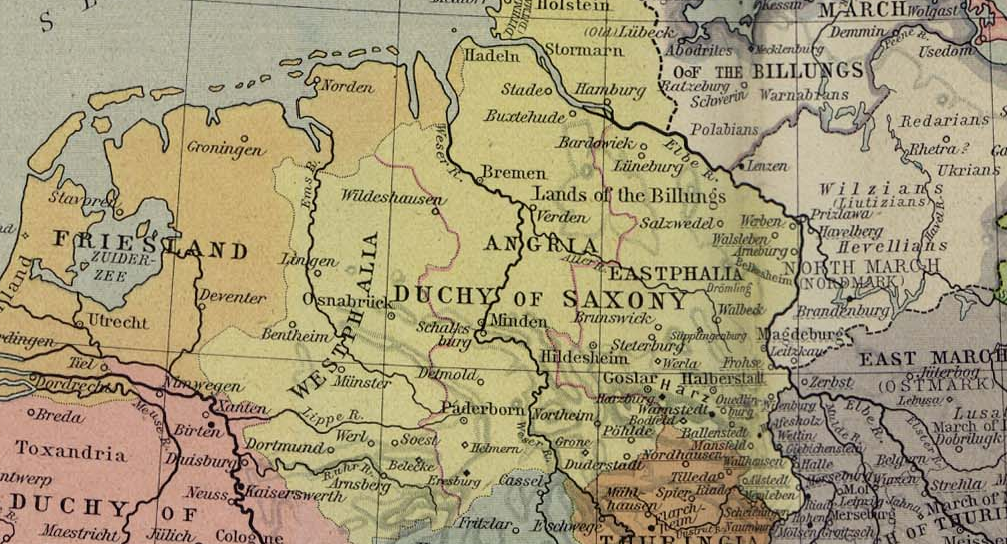
Eastphalia (german: Ostfalen; Eastphalian: ''Oostfalen'') is a historical region in northern Germany, encompassing the eastern '' Gaue'' (shires) of the historic stem duchy of Saxony, roughly confined by the River Leine in the west and the El ...
n count Otto of Ballenstedt (d. 1123), ancestor of the House of Ascania, had married Eilika, a daughter of Duke Magnus of Saxony from the House of Billung. As the Billung male line became extinct upon Magnus's death in 1106, Otto hoped to succeed him, however King Henry V of Germany enfeoffed Count Lothair of Supplinburg. During the following long-term dispute between Henry and Lothair, Otto was able to gain the title of a Saxon (anti-)duke, though only for a short time in 1122.
 Lothair was elected King of the Romans in 1125 and in 1134 he vested Otto's son Albert the Bear with the Saxon Northern March. Upon his death in 1137, Albert once again strived for the Saxon duchy, which however fell to Lothair's son-in-law Henry the Proud from the Bavarian
Lothair was elected King of the Romans in 1125 and in 1134 he vested Otto's son Albert the Bear with the Saxon Northern March. Upon his death in 1137, Albert once again strived for the Saxon duchy, which however fell to Lothair's son-in-law Henry the Proud from the Bavarian House of Welf
The House of Welf (also Guelf or Guelph) is a European dynasty that has included many German and British monarchs from the 11th to 20th century and Emperor Ivan VI of Russia in the 18th century. The originally Franconia, Franconian family from ...
. Albert concluded a deal with the rising House of Hohenstaufen: He backed the succession of Conrad of Hohenstaufen as German king, who in turn deprived his Welf rival Henry the Proud of the Saxonian Duchy in 1138 and gave it to Albert. However, his rule was strongly contested by the local nobility and in 1142 Albert finally had to resign as duke in favour of Henry the Proud's son Henry the Lion. Albert later took part in the Wendish Crusade of 1147 and in 1157 established the Margraviate of Brandenburg. He died in 1170.
The third chance for the Ascanians came, when in 1180 ambitious Henry the Lion was deposed as Saxon Duke by Emperor Frederick Barbarossa. Frederick partitioned Saxony among his allies into more than a dozen immediate territories. Among the supporters, Archbishop Philip of Cologne received the largest share as the newly created Duchy of Westphalia. The Saxon ducal title at least passed to late Albert's youngest son, Count Bernhard of Ballenstedt, who nevertheless only ruled over small, mostly Eastphalian fringes of the old duchy.
Anhalt, Wittenberg and Lauenburg
Duke Bernard died in 1212 and his two surviving sons divided the Saxon heritage: the elder Henry took the old Ascanianallodial
Allodial title constitutes ownership of real property (land, buildings, and fixtures) that is independent of any superior landlord. Allodial title is related to the concept of land held "in allodium", or land ownership by occupancy and defense ...
possessions around Ballenstedt where he established the Ascanian County of Anhalt, while his younger brother Albert I Albert I may refer to:
People Born before 1300
* Albert I, Count of Vermandois (917–987)
*Albert I, Count of Namur ()
*Albert I of Moha
*Albert I of Brandenburg (), first margrave of Brandenburg
*Albert I, Margrave of Meissen (1158–1195)
*Alber ...
inherited the title of a Duke of Saxony and retained three territorially unconnected Eastphalian estates on the Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Rep ...
river around the towns of Wittenberg and Belzig as well as the northern lordship of Lauenburg with Amt Neuhaus and Land Hadeln at the Elbe estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
.
After Albert I's death in 1260 his two heirs, John I and his younger brother Albert II ruled jointly. In 1269, 1272 and 1282 they gradually divided their governing competences within the then three territorially unconnected Saxon areas (Hadeln, Lauenburg and Wittenberg), thus preparing a partition, whereby Albert II, Burgrave of Magdeburg
Magdeburg (; nds, label= Low Saxon, Meideborg ) is the capital and second-largest city of the German state Saxony-Anhalt. The city is situated at the Elbe river.
Otto I, the first Holy Roman Emperor and founder of the Archdiocese of Mag ...
since 1269, concentrated on the Wittenberg territory. He consolidated his position by marrying Agnes, daughter of Rudolph of Habsburg, whom he elected King of the Romans in 1273. After Duke John I had resigned in 1282 in favour of his three minor sons Eric I, John II and Albert III, followed by his death three years later, the three brothers and their uncle Albert II continued the joint rule as Saxon dukes.
Upon the death of Margrave Henry III of Meissen in 1288, Duke Albert II applied at his father-in-law King Rudolph I for the enfeoffment of his son and heir Rudolph with the Saxon County palatine on the Unstrut river, which ensued a long lasting dispute with the eager clan of the House of Wettin
The House of Wettin () is a dynasty of Germany, German monarch, kings, Prince Elector, prince-electors, dukes, and counts that once ruled territories in the present-day German states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynasty is one of ...
. Albert's attempts to secure the succession in the lands of the extinct Counts of Brehna
Brehna is a town and a former municipality in the district of Anhalt-Bitterfeld, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Since 1 July 2009, it is part of the town Sandersdorf-Brehna.
It is situated southwest of Bitterfeld. Important in this city is the chur ...
were more successful: when their fiefs were reverted to the Empire in 1290, the king enfeoffed his son Rudolph. After King Rudolph had died, Albert II with his nephews still minor on 27 April 1292 wielded the Saxon electoral vote, electing Adolph of Nassau, the brother-in-law of Archbishop Siegfried II of Cologne. The bishop together with King Wenceslaus II of Bohemia had succeeded in bringing Albert II in favour of electing Adolph: he had signed an elector pact on 29 November 1291 that he would vote the same as Wenceslaus. In 1295 Albert II could again enlarge his Saxon territory, when he acquired the County of Gommern
Gommern () is a town in the Jerichower Land district, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is situated approximately southeast of Magdeburg. On January 1, 2005, the municipalities Dannigkow, Dornburg, Karith, Ladeburg, Leitzkau, Menz, Nedlitz, Vehli ...
.
Duchy of Wittenberg
The last document, mentioning the joint government of Albert II with his nephews as Saxon fellow dukes dates back to 1295.Cordula Bornefeld, "Die Herzöge von Sachsen-Lauenburg", in: ''Die Fürsten des Landes: Herzöge und Grafen von Schleswig, Holstein und Lauenburg''e slevigske hertuger; German
E, or e, is the fifth Letter (alphabet), letter and the second vowel#Written vowels, vowel letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worl ...
Carsten Porskrog Rasmussen (ed.) on behalf of the Gesellschaft für Schleswig-Holsteinische Geschichte, Neumünster: Wachholtz, 2008, pp. 373-389, here p. 375. The definite partitioning of the Duchy of Saxony into Saxe-Lauenburg (german: Herzogtum Sachsen-Lauenburg), jointly ruled by the brothers Albert III, Eric I and John II and Saxe-Wittenberg (german: Herzogtum Sachsen-Wittenberg), ruled by Albert II took place before 20 September 1296. The Vierlande, Sadelbande (Land of Lauenburg), the Land of Ratzeburg, the Land of Darzing (today's Amt Neuhaus), and the Land of Hadeln are mentioned as the separate territory of the brothers. Duke Albert II received the Wittenberg lands around the eponymous city, Brehna and Gommern. He thus became the founder of the Ascanian line of Saxe-Wittenberg.
When Rudolph succeeded his father Albert II as Duke of Saxe-Wittenberg in 1298, he and the Dukes of Saxe-Lauenburg rivallingly claimed the Saxon electoral privilege. Upon the assassination of his brother-in-law King Albert I Albert I may refer to:
People Born before 1300
* Albert I, Count of Vermandois (917–987)
*Albert I, Count of Namur ()
*Albert I of Moha
*Albert I of Brandenburg (), first margrave of Brandenburg
*Albert I, Margrave of Meissen (1158–1195)
*Alber ...
in 1308, he voted for Count Henry of Luxembourg. In 1314 both duchies participated in the double election of the German kings, Frederick III, ''the Fair'' from the House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
and his Wittelsbach cousin Louis IV, ''the Bavarian''. Louis received five of the seven votes, to wit Archbishop-Elector Baldwin
Baldwin is a Germanic name, composed of the elements ''bald'' "bold" and ''win'' "friend".
People
* Baldwin (name)
Places Canada
* Baldwin, York Regional Municipality, Ontario
* Baldwin, Ontario, in Sudbury District
* Baldwin's Mills, Qu ...
of Trier
Trier ( , ; lb, Tréier ), formerly known in English as Trèves ( ;) and Triers (see also names in other languages), is a city on the banks of the Moselle in Germany. It lies in a valley between low vine-covered hills of red sandstone in the ...
, the legitimate King John of Bohemia
John the Blind or John of Luxembourg ( lb, Jang de Blannen; german: link=no, Johann der Blinde; cz, Jan Lucemburský; 10 August 1296 – 26 August 1346), was the Count of Luxembourg from 1313 and King of Bohemia from 1310 and titular King ...
, Duke John II of Saxe-Lauenburg, claiming the Saxon prince-electoral power, Archbishop Peter of Mainz, and Albert's Ascanian cousin Margrave Waldemar of Brandenburg. Frederick the Fair received in the same election four of the seven votes, with the deposed King Henry of Bohemia, illegitimately assuming electoral power, Archbishop Henry II of Cologne, Louis' brother Count Rudolph I of the Palatinate, and Duke Rudolph I of Saxe-Wittenberg, equally exercising the Saxon electoral dignity.
However, only Louis the Bavarian, co-elected with Saxe-Lauenburg's vote, finally asserted himself as emperor after the 1322 Battle of Mühldorf by the Treaty of Trausnitz on March 13, 1325. As an obvious opponent, Duke Rudolph I failed with his claims to Brandenburg after the line of his Ascanian cousins became extinct in 1319: King Louis IV seized the margraviate and enfeoffed his son Louis V instead. Rudolph I in turn allied with the rivaling House of Luxembourg. He supported Count Charles IV of Luxembourg
Charles IV ( cs, Karel IV.; german: Karl IV.; la, Carolus IV; 14 May 1316 – 29 November 1378''Karl IV''. In: (1960): ''Geschichte in Gestalten'' (''History in figures''), vol. 2: ''F–K''. 38, Frankfurt 1963, p. 294), also known as Charle ...
as anti-king to Louis IV and on that account exclusively received the Saxon electoral dignity with the Golden Bull of 1356, thus slighting Saxe-Lauenburg. Saxe-Wittenberg thereupon came to be known as the Electorate of Saxony (''Kursachsen'').
House of Wettin
The House of Wettin () is a dynasty of Germany, German monarch, kings, Prince Elector, prince-electors, dukes, and counts that once ruled territories in the present-day German states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynasty is one of ...
, who united the Meissen and the Saxon lands of Wittenberg under his rule. He assumed the electoral title and thereby transferred the state of Saxony up the Elbe river to his Meissen residence. His lands were also called "Upper Saxony" (see: Upper Saxon Circle) to distinguish them from the territory of the medieval stem duchy, the later Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
. The territory of former Saxe-Wittenberg became known as the ''Kurkreis'' ("Electoral District"). By the division of the Saxon Electorate according to the 1485 Treaty of Leipzig, the Wittenberg lands including the electoral dignity fell to Ernest of Wettin.
Notes
{{Coord missing, Germany Duchy of Saxony Saxe-Wittenberg 1290s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire 1296 establishments in Europe 1350s disestablishments in the Holy Roman Empire 1356 disestablishments in Europe Duchies of the Holy Roman Empire