Dual X-ray Absorptiometry on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA, or DEXA) is a means of measuring bone mineral density (BMD) using

 The World Health Organization has defined the following categories based on bone density in white women:
Bone densities are often given to patients as a T score or a Z score. A T score tells the patient what their bone mineral density is in comparison to a young adult of the same gender with peak bone mineral density. A normal T score is -1.0 and above, low bone density is between -1.0 and -2.5, and osteoporosis is -2.5 and lower. A Z score is just a comparison of what a patient's bone mineral density is in comparison to the average bone mineral density of a male or female of their age and weight.
The WHO committee did not have enough data to create definitions for men or other ethnic groups.
Special considerations are involved in the use of DXA to assess bone mass in children. Specifically, comparing the bone mineral density of children to the reference data of adults (to calculate a T-score) will underestimate the BMD of children, because children have less bone mass than fully developed adults. This would lead to an over-diagnosis of
The World Health Organization has defined the following categories based on bone density in white women:
Bone densities are often given to patients as a T score or a Z score. A T score tells the patient what their bone mineral density is in comparison to a young adult of the same gender with peak bone mineral density. A normal T score is -1.0 and above, low bone density is between -1.0 and -2.5, and osteoporosis is -2.5 and lower. A Z score is just a comparison of what a patient's bone mineral density is in comparison to the average bone mineral density of a male or female of their age and weight.
The WHO committee did not have enough data to create definitions for men or other ethnic groups.
Special considerations are involved in the use of DXA to assess bone mass in children. Specifically, comparing the bone mineral density of children to the reference data of adults (to calculate a T-score) will underestimate the BMD of children, because children have less bone mass than fully developed adults. This would lead to an over-diagnosis of
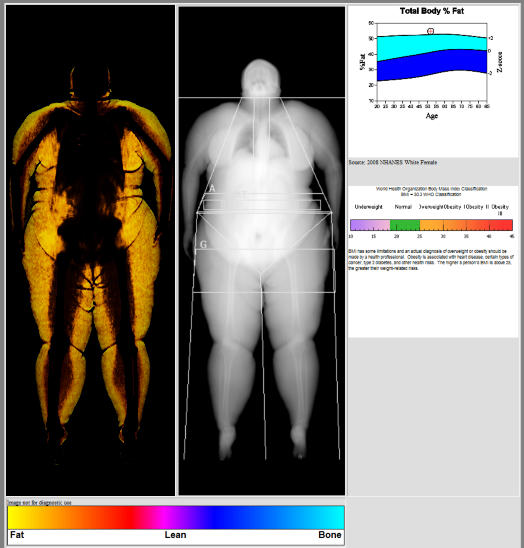 DXA scans can also be used to measure total
DXA scans can also be used to measure total 
Non-invasive testing of bone density explained
from RSNA
Bone Densitometry explained
{{DEFAULTSORT:Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Radiology Medical imaging es:Densitometría osea
spectral imaging
Spectral imaging is imaging that uses multiple bands across the electromagnetic spectrum. While an ordinary camera captures light across three wavelength bands in the visible spectrum, red, green, and blue (RGB), spectral imaging encompasses ...
. Two X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
beams, with different energy level
A quantum mechanical system or particle that is bound—that is, confined spatially—can only take on certain discrete values of energy, called energy levels. This contrasts with classical particles, which can have any amount of energy. The t ...
s, are aimed at the patient's bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
s. When soft tissue
Soft tissue is all the tissue in the body that is not hardened by the processes of ossification or calcification such as bones and teeth. Soft tissue connects, surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ...
absorption is subtracted out, the bone mineral density (BMD) can be determined from the absorption of each beam by bone. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry is the most widely used and most thoroughly studied bone density measurement technology.
The DXA scan is typically used to diagnose and follow osteoporosis, as contrasted to the nuclear bone scan
A bone scan or bone scintigraphy is a nuclear medicine imaging technique of the bone. It can help diagnose a number of bone conditions, including cancer of the bone or metastasis, location of bone inflammation and fractures (that may not be vi ...
, which is sensitive to certain metabolic diseases of bones in which bones are attempting to heal from infections, fractures, or tumors. It is also sometimes used to assess body composition
In physical fitness, body composition is used to describe the percentages of fat, bone, water, and muscle in human bodies. Because muscular tissue takes up less space in the body than fat tissue, body composition, as well as weight, determines ...
.
Physics
Soft tissue and bone have different attenuation coefficients to X-rays. A single X-ray beam passing through the body will be attenuated by both soft tissue and bone, and it is not possible to determine, from a single beam, how much attenuation was attributable to the bone. However, the attenuation coefficients vary with the energy of the X-rays, and, crucially, the ratio of the attenuation coefficients also varies. DXA uses two energies of X-ray. The difference in total absorption between the two can be used, by suitable weighting, to subtract out the absorption by soft tissue, leaving just the absorption by bone, which is related to bone density. One type of DXA scanner uses acerium
Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. Cerium is a soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it often shows the +3 ...
filter with a tube voltage of 80 kV, resulting in effective photon energies of about 40 and 70 keV Kev can refer to:
Given name
* Kev Adams, French comedian, actor, screenwriter and film producer born Kevin Smadja in 1991
* Kevin Kev Carmody (born 1946), Indigenous Australian singer-songwriter
* Kev Coghlan (born 1988), Scottish Grand Prix moto ...
. There is also a DXA scanner type using a samarium
Samarium is a chemical element with symbol Sm and atomic number 62. It is a moderately hard silvery metal that slowly oxidizes in air. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, samarium usually has the oxidation state +3. Compounds of samar ...
filter with a tube voltage of 100 kV, resulting in effective energies of 47 and 80 keV. Also, the tube voltage can be continuously switched between a low (for example 70 kV) and high (for example 140 kV) value in synchronism with the
frequency of the electrical mains, resulting in effective energies alternating between 45 and 100 keV.
The combination of dual X-ray absorptiometry and laser
Dual X-ray absorptiometry and laser technique (DXL) in the area of bone density studies for osteoporosis assessment is an improvement to the DXA Technique, adding an exact laser measurement of the thickness of the region scanned. The addition of ...
uses the laser to measure the thickness of the region scanned, allowing for varying proportions of lean soft tissue and adipose tissue
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular ...
within the soft tissue to be controlled for and improving the accuracy.
Bone density measurement

Indications
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that women over the age of 65 should get a DXA scan. The date at which men should be tested is uncertain but some sources recommend age 70. At risk women should consider getting a scan when their risk is equal to that of a normal 65-year-old woman. A person's risk can be measured using the University of Sheffield'sFRAX
FRAX (Fracture Risk Assessment Tool) is a diagnostic tool used to evaluate the 10-year probability of bone fracture risk. It was developed by the University of Sheffield. FRAX integrates clinical risk factors and bone mineral density at the femora ...
calculator, which includes many different clinical risk factors including prior fragility fracture, use of glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebr ...
, heavy smoking, excess alcohol intake, rheumatoid arthritis, history of parental hip fracture, chronic renal and liver disease, chronic respiratory disease, long-term use of phenobarbital or phenytoin, celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and other risks.
Scoring
 The World Health Organization has defined the following categories based on bone density in white women:
Bone densities are often given to patients as a T score or a Z score. A T score tells the patient what their bone mineral density is in comparison to a young adult of the same gender with peak bone mineral density. A normal T score is -1.0 and above, low bone density is between -1.0 and -2.5, and osteoporosis is -2.5 and lower. A Z score is just a comparison of what a patient's bone mineral density is in comparison to the average bone mineral density of a male or female of their age and weight.
The WHO committee did not have enough data to create definitions for men or other ethnic groups.
Special considerations are involved in the use of DXA to assess bone mass in children. Specifically, comparing the bone mineral density of children to the reference data of adults (to calculate a T-score) will underestimate the BMD of children, because children have less bone mass than fully developed adults. This would lead to an over-diagnosis of
The World Health Organization has defined the following categories based on bone density in white women:
Bone densities are often given to patients as a T score or a Z score. A T score tells the patient what their bone mineral density is in comparison to a young adult of the same gender with peak bone mineral density. A normal T score is -1.0 and above, low bone density is between -1.0 and -2.5, and osteoporosis is -2.5 and lower. A Z score is just a comparison of what a patient's bone mineral density is in comparison to the average bone mineral density of a male or female of their age and weight.
The WHO committee did not have enough data to create definitions for men or other ethnic groups.
Special considerations are involved in the use of DXA to assess bone mass in children. Specifically, comparing the bone mineral density of children to the reference data of adults (to calculate a T-score) will underestimate the BMD of children, because children have less bone mass than fully developed adults. This would lead to an over-diagnosis of osteopenia
Osteopenia, known as "low bone mass" or "low bone density", is a condition in which bone mineral density is low. Because their bones are weaker, people with osteopenia may have a higher risk of fractures, and some people may go on to develop osteop ...
for children. To avoid an overestimation of bone mineral deficits, BMD scores are commonly compared to reference data for the same gender and age (by calculating a Z-score
In statistics, the standard score is the number of standard deviations by which the value of a raw score (i.e., an observed value or data point) is above or below the mean value of what is being observed or measured. Raw scores above the mean ...
).
Also, there are other variables in addition to age that are suggested to confound the interpretation of BMD as measured by DXA. One important confounding variable is bone size. DXA has been shown to overestimate the bone mineral density of taller subjects and underestimate the bone mineral density of smaller subjects. This error is due to the way by which DXA calculates BMD. In DXA, bone mineral content (measured as the attenuation of the X-ray by the bones being scanned) is divided by the area (also measured by the machine) of the site being scanned.
Because DXA calculates BMD using area (aBMD: areal Bone Mineral Density), it is not an accurate measurement of true bone mineral density, which is mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different eleme ...
divided by a volume
Volume is a measure of occupied three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). Th ...
. In order to distinguish DXA BMD from volumetric
Volume is a measure of occupied three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). Th ...
bone-mineral density, researchers sometimes refer to DXA BMD as an areal bone mineral density (aBMD). The confounding effect of differences in bone size is due to the missing depth value in the calculation of bone mineral density. Despite DXA technology's problems with estimating volume, it is still a fairly accurate measure of bone mineral content. Methods to correct for this shortcoming include the calculation of a volume that is approximated from the projected area measure by DXA. DXA BMD results adjusted in this manner are referred to as the bone mineral apparent density (BMAD) and are a ratio
In mathematics, a ratio shows how many times one number contains another. For example, if there are eight oranges and six lemons in a bowl of fruit, then the ratio of oranges to lemons is eight to six (that is, 8:6, which is equivalent to the ...
of the bone mineral content versus a cuboidal estimation of the volume of bone. Like the results for aBMD, BMAD results do not accurately represent true bone mineral density, since they use approximations of the bone's volume. BMAD is used primarily for research purposes and is not yet used in clinical settings.
Other imaging technologies such as quantitative computed tomography (QCT) are capable of measuring the bone's volume, and are, therefore, not susceptible to the confounding effect of bone-size in the way that DXA results are susceptible.
It is important for patients to get repeat BMD measurements done on the same machine each time, or at least a machine from the same manufacturer. Error between machines, or trying to convert measurements from one manufacturer's standard to another can introduce errors large enough to wipe out the sensitivity of the measurements.
DXA results need to be adjusted if the patient is taking strontium supplements.
DXA can also used to measure trabecular bone score.
Current clinical practice in pediatrics
DXA is, by far, the most widely used technique for bone mineral density measurements, since it is considered to be cheap, accessible, easy to use, and able to provide an accurate estimation of bone mineral density in adults. The official position of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry (ISCD) is that a patient may be tested for BMD if they have a condition that could precipitate bone loss, is going to be prescribed pharmaceuticals known to cause bone loss, or is being treated and needs to be monitored. The ISCD states that there is no clearly understood correlation between BMD and the risk of a child's sustaining a fracture; the diagnosis of osteoporosis in children cannot be made using the basis of a densitometry criteria. T-scores are prohibited with children and should not even appear on DXA reports. Thus, the WHO classification of osteoporosis and osteopenia in adults cannot be applied to children, but Z-scores can be used to assist diagnosis. Some clinics may routinely carry out DXA scans on pediatric patients with conditions such as nutritionalrickets
Rickets is a condition that results in weak or soft bones in children, and is caused by either dietary deficiency or genetic causes. Symptoms include bowed legs, stunted growth, bone pain, large forehead, and trouble sleeping. Complications ma ...
, lupus, and Turner syndrome
Turner syndrome (TS), also known as 45,X, or 45,X0, is a genetic condition in which a female is partially or completely missing an X chromosome. Signs and symptoms vary among those affected. Often, a short and webbed neck, low-set ears, low hair ...
. DXA has been demonstrated to measure skeletal maturity and body fat composition and has been used to evaluate the effects of pharmaceutical therapy. It may also aid pediatricians in diagnosing and monitoring treatment of disorders of bone mass acquisition in childhood.
However, it seems that DXA is still in its early days in pediatrics, and there are widely acknowledged limitations and disadvantages with DXA. A view exists that DXA scans for diagnostic purposes should not even be performed outside specialist centers, and, if a scan is done outside one of these centers, it should not be interpreted without consultation with an expert in the field. Furthermore, most of the pharmaceuticals given to adults with low bone mass can be given to children only in strictly monitored clinical trials.
Whole-body calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
measured by DXA has been validated in adults using in-vivo neutron activation
Neutron activation is the process in which neutron radiation induces radioactivity in materials, and occurs when atomic nuclei capture free neutrons, becoming heavier and entering excited states. The excited nucleus decays immediately by emit ...
of total body calcium but this is not suitable for paediatric subjects and studies have been carried out on paediatric-sized animals.
Body composition measurement
 DXA scans can also be used to measure total
DXA scans can also be used to measure total body composition
In physical fitness, body composition is used to describe the percentages of fat, bone, water, and muscle in human bodies. Because muscular tissue takes up less space in the body than fat tissue, body composition, as well as weight, determines ...
and fat content with a high degree of accuracy comparable to hydrostatic weighing
Hydrostatic weighing, also referred to as underwater weighing, hydrostatic body composition analysis and hydrodensitometry, is a technique for measuring the density of a living person's body. It is a direct application of Archimedes' principle, t ...
with a few important caveats. From the DXA scans, a low resolution "fat shadow" image can also be generated, which gives an overall impression of fat distribution throughout the body It has been suggested that, while very accurately measuring minerals and lean soft tissue (LST), DXA may provide skewed results due to its method of indirectly calculating fat mass by subtracting it from the LST and/or body cell mass (BCM) that DXA actually measures.
DXA scans have been suggested as useful tools to diagnose conditions with an abnormal fat distribution, such as familial partial lipodystrophy. They are also used to assess adiposity in children, especially to conduct clinical research.

Radiation exposure
DXA uses X-rays to measure bone mineral density. The radiation dose of current DEXA systems is small, as low as 0.001 mSv, much less than a standard chest or dental x-ray. However, the dose delivered by older DEXA radiation sources (that usedradioisotope
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferr ...
s rather than x-ray generator
An X-ray generator is a device that produces X-rays. Together with an X-ray detector, it is commonly used in a variety of applications including medicine, X-ray fluorescence, electronic assembly inspection, and measurement of material thicknes ...
s) could be as high as 35 mGy, considered a significant dose by radiological health standards.
Regulation
United States
The quality of DXA operators varies widely. DXA is not regulated like other radiation-based imaging techniques because of its low dosage. Each US state has a different policy as to what certifications are needed to operate a DXA machine.California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
, for example, requires coursework and a state-run test, whereas Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
has no requirements for DXA technicians. Many states require a training course and certificate from the International Society of Clinical Densitometry (ISCD).
Australia
In Australia, regulation differs according to the applicable state or territory. For example, in Victoria, an individual performing DXA scans is required to completed a recognised course in safe use of bone mineral densitometers. In NSW and QLD a DXA technician only requires prior study in science, nursing or other related undergraduate study. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees licensing of technicians, however, this is far from rigorous and regulation is non-existent.References
External links
Non-invasive testing of bone density explained
from RSNA
Bone Densitometry explained
{{DEFAULTSORT:Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Radiology Medical imaging es:Densitometría osea