Droplet Cluster on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]




 Droplet cluster is a self-assembled levitating monolayer of microdroplets usually arranged into a hexagonally ordered structure over a locally heated thin (about 1 mm) layer of water. The droplet cluster is typologically similar to
Droplet cluster is a self-assembled levitating monolayer of microdroplets usually arranged into a hexagonally ordered structure over a locally heated thin (about 1 mm) layer of water. The droplet cluster is typologically similar to
types of levitating droplet clusters
were discovered. In a chain droplet cluster, rotating droplets may be very close to each other but viscosity of the thin gas layer between the droplets prevents them from coalescing. There is a reversible structural transition from the ordered hexagonal cluster to the chain-like structure. A hierarchical cluster is built of small groups of droplets with interactions controlled by the electrostatic force are combined into larger structures controlled by aerodynamic forces. Droplet aggregates keep continuously restructuring The droplets permanently keep rearranging, so the phenomenon is similar to the “deterministic chaos” (the
Video: Levitating clusters of droplets above heated water surface
Droplet cluster
Video: Droplet clusters
Physical phenomena Heat transfer Microfluidics





 Droplet cluster is a self-assembled levitating monolayer of microdroplets usually arranged into a hexagonally ordered structure over a locally heated thin (about 1 mm) layer of water. The droplet cluster is typologically similar to
Droplet cluster is a self-assembled levitating monolayer of microdroplets usually arranged into a hexagonally ordered structure over a locally heated thin (about 1 mm) layer of water. The droplet cluster is typologically similar to colloidal crystals A colloidal crystal is an ordered array of colloid particles and fine grained materials analogous to a standard crystal whose repeating subunits are atoms or molecules. A natural example of this phenomenon can be found in the gem opal, where sphere ...
. The phenomenon was observed for the first time in 2004, and it has been extensively studied after that.
Growing condensing droplets
A drop or droplet is a small column of liquid, bounded completely or almost completely by free surfaces. A drop may form when liquid accumulates at the lower end of a tube or other surface boundary, producing a hanging drop called a pendant d ...
with a typical diameter of 0.01 mm – 0.2 mm levitate at an equilibrium height, where their weight is equilibrated by the drag force of the ascending air-vapor jet rising over the heated spot. At the same time, the droplets are dragged towards the center of the heated spot; however, they do not merge, forming an ordered hexagonal (densest packed) pattern due to an aerodynamic repulsive pressure force from gas flow between the droplets. The spot is usually heated by a laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The fi ...
beam or another source of heat to 60 °C – 95 °C, although the phenomenon was observed also at temperatures slightly above 20 °C. The height of levitation and the distance between the droplets are of the same order as their diameters.
Due to complex nature of aerodynamic
Aerodynamics, from grc, ἀήρ ''aero'' (air) + grc, δυναμική (dynamics), is the study of the motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dyn ...
forces between the microdroplets in an ascending jet, the droplets do not coalesce but form a closed packed hexagonal structure showing similarity with various classical and newly discovered objects, where self-organization is prominent, including water breath figures, colloid and dust crystals, foams
Foams are materials formed by trapping pockets of gas in a liquid or solid.
A bath sponge and the head on a glass of beer are examples of foams. In most foams, the volume of gas is large, with thin films of liquid or solid separating the ...
, Rayleigh–Bénard cells, and to some extent, ice crystals
Ice crystals are solid ice exhibiting atomic ordering on various length scales and include hexagonal columns, hexagonal plates, dendritic crystals, and diamond dust.
Formation
The hugely symmetric shapes are due to depositional growth, n ...
. The droplets pack near the center of heated area where the temperature and the intensity of the ascending vapor jets are the highest. At the same time, there are repulsion forces of aerodynamic nature between the droplets. Consequently, the cluster packs itself in the densest packing shape (a hexagonal honeycomb
A honeycomb is a mass of hexagonal prismatic wax cells built by honey bees in their nests to contain their larvae and stores of honey and pollen.
Beekeepers may remove the entire honeycomb to harvest honey. Honey bees consume about of honey ...
structure) with a certain distance between the droplets dependent on the repulsion forces.
By controlling the temperature and temperature gradient one can control the number of droplets and their density and size. Using infrared irradiation, it is possible to suppress droplet growth and stabilize them for extended periods of time.
It has been suggested that the phenomenon, when combined with a spectrographic study of droplets content, can be used for rapid biochemical in situ analysis. Recent studies have shown that the cluster can exist at lower temperatures of about 20 °C, which makes it suitable for biochemical analysis of living objects.
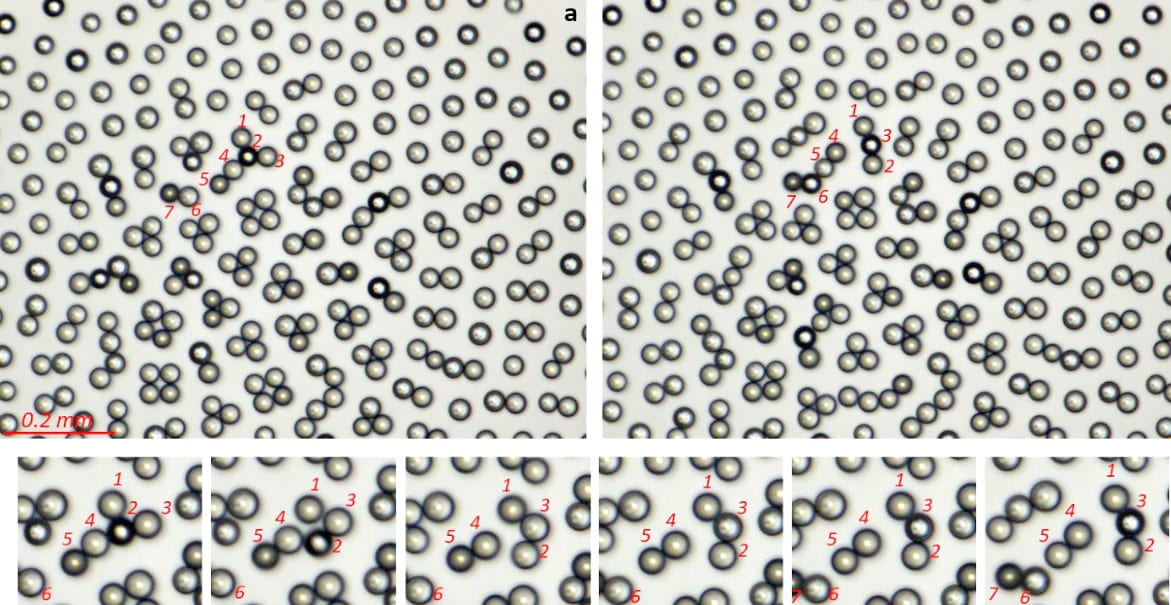
Clusters with an arbitrary small number of droplets can be created. Unlike the clusters with a large number of droplets, small clusters cannot always form a hexagonally symmetric structure. Instead, they produce various more or less symmetric configurations depending on the number of droplets. Tracing individual droplets in small clusters is crucial for potential applications. The symmetry, orderliness, and stability of these configurations can be studied with such a measure of self-organization as the Voronoi entropy.
Since the most common hexagonal (honeycomb shaped) droplet cluster was observed for the first time in 2004, new types otypes of levitating droplet clusters
were discovered. In a chain droplet cluster, rotating droplets may be very close to each other but viscosity of the thin gas layer between the droplets prevents them from coalescing. There is a reversible structural transition from the ordered hexagonal cluster to the chain-like structure. A hierarchical cluster is built of small groups of droplets with interactions controlled by the electrostatic force are combined into larger structures controlled by aerodynamic forces. Droplet aggregates keep continuously restructuring The droplets permanently keep rearranging, so the phenomenon is similar to the “deterministic chaos” (the
Lorenz attractor
The Lorenz system is a system of ordinary differential equations first studied by mathematician and meteorologist Edward Lorenz. It is notable for having chaotic solutions for certain parameter values and initial conditions. In particular, the Lo ...
). In the absence of the surfactant suppressing the thermocapillary (TC) flow at the surface of the water layer, a ring-shaped cluster is formed. Small clusters may demonstrate 4-fold, 5-fold, and 7-fold symmetry which is absent from large drolet clusters and colloidal crystals. The symmetry properties of small cluster configurations are universal, i.e., they do not depend on the size of the droplets and details of the interactions between the droplets. It was hypothesized that the symmetries in small clusters may be related to the ADE classification
In mathematics, the ADE classification (originally ''A-D-E'' classifications) is a situation where certain kinds of objects are in correspondence with simply laced Dynkin diagrams. The question of giving a common origin to these classifications, r ...
or to the simply-laced Dynkin diagrams
In the mathematical field of Lie theory, a Dynkin diagram, named for Eugene Dynkin, is a type of graph with some edges doubled or tripled (drawn as a double or triple line). Dynkin diagrams arise in the classification of semisimple Lie algebras ...
.
The phenomenon of the droplet cluster is different from the Leidenfrost effect
The Leidenfrost effect is a physical phenomenon in which a liquid, close to a surface that is significantly hotter than the liquid's boiling point, produces an insulating vapor layer that keeps the liquid from boiling rapidly. Because of this re ...
because the latter occurs at much higher temperatures over a solid surface, while the droplet cluster forms at lower temperatures over a liquid surface. The phenomenon has also been observed with liquids other than water.
See also
*Leidenfrost effect
The Leidenfrost effect is a physical phenomenon in which a liquid, close to a surface that is significantly hotter than the liquid's boiling point, produces an insulating vapor layer that keeps the liquid from boiling rapidly. Because of this re ...
* Rayleigh–Bénard convection
In fluid thermodynamics, Rayleigh–Bénard convection is a type of natural convection, occurring in a planar horizontal layer of fluid heated from below, in which the fluid develops a regular pattern of convection cells known as Bénard cells. ...
* Self assembly
Self-assembly is a process in which a disordered system of pre-existing components forms an organized structure or pattern as a consequence of specific, local interactions among the components themselves, without external direction. When the ...
References
{{ReflistExternal links
Video: Levitating clusters of droplets above heated water surface
Droplet cluster
Video: Droplet clusters
Physical phenomena Heat transfer Microfluidics