Driven element on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In an
In an
 All the elements are usually mounted on a metal beam or bracket along the antenna's central axis. Although sometimes the parasitic elements are insulated from the supporting beam, often they are clamped or welded directly to it, electrically connected to it. This doesn't affect their functioning, because the RF voltage distribution along the element is maximum at the ends and goes to zero (has a ''
All the elements are usually mounted on a metal beam or bracket along the antenna's central axis. Although sometimes the parasitic elements are insulated from the supporting beam, often they are clamped or welded directly to it, electrically connected to it. This doesn't affect their functioning, because the RF voltage distribution along the element is maximum at the ends and goes to zero (has a ''
 In an
In an antenna array
An antenna array (or array antenna) is a set of multiple connected antenna (radio), antennas which work together as a single antenna, to transmit or receive radio waves. The individual antennas (called ''elements'') are usually connected to a s ...
made of multiple conductive
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is an object or type of material that allows the flow of Electric charge, charge (electric current) in one or more directions. Materials made of metal are common electrical conductors. The flow ...
elements (typically metal rods), a driven element or active element (also called driven radiator or active radiator) is electrically connected to the receiver or transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter (often abbreviated as XMTR or TX in technical documents) is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna (radio), antenna with the purpose of sig ...
while a parasitic element (or passive radiator) is not.
Driven elements
In a multielementantenna array
An antenna array (or array antenna) is a set of multiple connected antenna (radio), antennas which work together as a single antenna, to transmit or receive radio waves. The individual antennas (called ''elements'') are usually connected to a s ...
(such as a Yagi–Uda antenna
A Yagi–Uda antenna, or simply Yagi antenna, is a directional antenna consisting of two or more parallel Antenna (radio)#Resonant antennas, resonant antenna elements in an Antenna array#Types, end-fire array; these elements are most often metal ...
), the driven element or active element is the element in the antenna (typically a metal rod) which is electrically connected to the receiver or transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter (often abbreviated as XMTR or TX in technical documents) is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna (radio), antenna with the purpose of sig ...
. In a transmitting antenna it is ''driven'' or ''excited'' by the radio frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the u ...
current from the transmitter, and is the source of the radio waves. In a receiving antenna it collects the incoming radio waves for reception, and converts them to tiny oscillating electric current
An electric current is a flow of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is defined as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface. The moving particles are called charge c ...
s, which are applied to the receiver. Multielement antennas like the Yagi typically consist of a driven element, connected to the receiver or transmitter through a feed line, and a number of other elements which are not driven, called parasitic elements. The driven element is often a dipole
In physics, a dipole () is an electromagnetic phenomenon which occurs in two ways:
* An electric dipole moment, electric dipole deals with the separation of the positive and negative electric charges found in any electromagnetic system. A simple ...
. The parasitic elements act as resonator
A resonator is a device or system that exhibits resonance or resonant behavior. That is, it naturally oscillates with greater amplitude at some frequencies, called resonant frequencies, than at other frequencies. The oscillations in a reso ...
s and couple electromagnetically with the driven element, and serve to modify the radiation pattern
In the field of antenna design the term radiation pattern (or antenna pattern or far-field pattern) refers to the ''directional'' (angular) dependence of the strength of the radio waves from the antenna or other source.Constantine A. Balanis: " ...
of the antenna, directing the radio waves in one direction, increasing the gain of the antenna.
An antenna may have more than one driven element, although the most common multielement antenna, the Yagi, usually has only one. For example, transmitting antennas for AM radio station
Radio broadcasting is the broadcasting of audio (sound), sometimes with related metadata, by radio waves to radio receivers belonging to a public audience. In terrestrial radio broadcasting the radio waves are broadcast by a land-based rad ...
s often consist of several mast radiator
A mast radiator (or radiating tower) is a radio mast or tower in which the metal structure itself is energized and functions as an antenna. This design, first used widely in the 1930s, is commonly used for transmitting antennas operating at l ...
s, each of which functions as a half-wave monopole driven element, to create a particular radiation pattern
In the field of antenna design the term radiation pattern (or antenna pattern or far-field pattern) refers to the ''directional'' (angular) dependence of the strength of the radio waves from the antenna or other source.Constantine A. Balanis: " ...
. A two-element array with the elements spaced a quarter wavelength apart has a distinct cardioid
In geometry, a cardioid () is a plane curve traced by a point on the perimeter of a circle that is rolling around a fixed circle of the same radius. It can also be defined as an epicycloid having a single cusp. It is also a type of sinusoidal ...
radiation pattern
In the field of antenna design the term radiation pattern (or antenna pattern or far-field pattern) refers to the ''directional'' (angular) dependence of the strength of the radio waves from the antenna or other source.Constantine A. Balanis: " ...
when the second element is driven with a source −90° out of phase
Phase or phases may refer to:
Science
*State of matter, or phase, one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist
*Phase (matter), a region of space throughout which all physical properties are essentially uniform
*Phase space, a mathematica ...
relative to the first element. A log-periodic antenna
A log-periodic antenna (LP), also known as a log-periodic array or log-periodic aerial, is a multi-element, directional antenna designed to operate over a wide band of frequencies. It was invented by John Dunlavy in 1952.
The most common form ...
(LPDA) consists of many dipole
In physics, a dipole () is an electromagnetic phenomenon which occurs in two ways:
* An electric dipole moment, electric dipole deals with the separation of the positive and negative electric charges found in any electromagnetic system. A simple ...
elements of decreasing length, all of which are driven. However, because they are different lengths, only one of the many dipoles is resonant at a given frequency, so only one is driven at a time. The dipole that is driven depends on the frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
of the signal
A signal is both the process and the result of transmission of data over some media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processing, information theory and biology.
In ...
. Phased array
In antenna (radio), antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled Antenna array, array of antennas which creates a radio beam, beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point ...
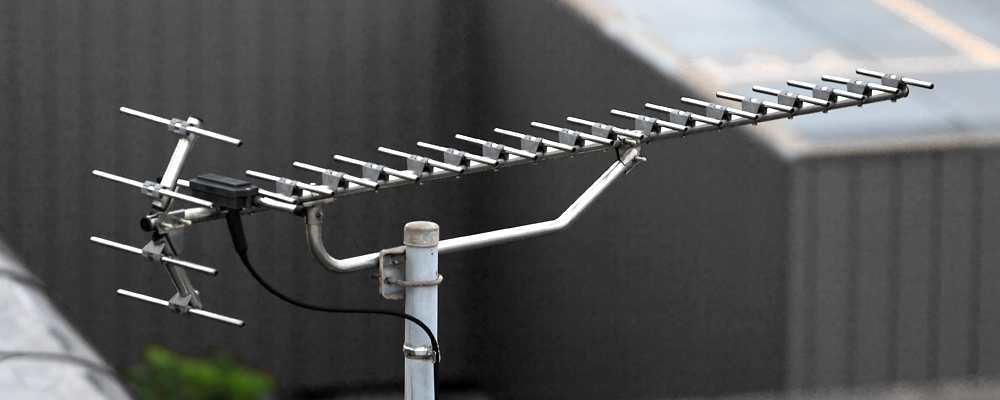
s may have hundreds of driven elements. Household multiband television antenna
A television antenna, also called a television aerial (in British English), is an antenna specifically designed for use with a television receiver (TV) to receive terrestrial over-the-air (OTA) broadcast television signals from a television s ...
s generally consist of a hybrid between a UHF Yagi with one driven dipole and a log-periodic for VHF behind that with alternating active elements. The driven elements between the UHF and VHF are then coupled and often matched for a 75 Ω coaxial downlead to the receiver.
When a "driven element" is referred to in an antenna array, it is often assumed that other elements are not driven (i.e. passive radiator) and that the array is tightly coupled (spacing far below a wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
).
Parasitic elements
In aradio antenna
In radio-frequency engineering, an antenna (American English) or aerial (British English) is an electronic device that converts an alternating electric current into radio waves (transmitting), or radio waves into an electric current (receivi ...
, a parasitic element or passive radiator is a conductive element, typically a metal rod, which is not electrically connected to anything else.
Multielement antennas such as the Yagi–Uda antenna
A Yagi–Uda antenna, or simply Yagi antenna, is a directional antenna consisting of two or more parallel Antenna (radio)#Resonant antennas, resonant antenna elements in an Antenna array#Types, end-fire array; these elements are most often metal ...
typically consist of a "''driven element''" which is connected to the radio receiver
In radio communications, a radio receiver, also known as a receiver, a wireless, or simply a radio, is an electronic device that receives radio waves and converts the information carried by them to a usable form. It is used with an antenna. ...
or transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter (often abbreviated as XMTR or TX in technical documents) is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna (radio), antenna with the purpose of sig ...
through a feed line, and parasitic elements, which are not. The purpose of the parasitic elements is to modify the radiation pattern
In the field of antenna design the term radiation pattern (or antenna pattern or far-field pattern) refers to the ''directional'' (angular) dependence of the strength of the radio waves from the antenna or other source.Constantine A. Balanis: " ...
of the radio waves emitted by the driven element, directing them in a beam in one direction, increasing the antenna's directivity
In electromagnetics, directivity is a parameter of an antenna or optical system which measures the degree to which the radiation emitted is concentrated in a single direction. It is the ratio of the radiation intensity in a given direction f ...
( gain). A parasitic element does this by acting as a passive resonator
A resonator is a device or system that exhibits resonance or resonant behavior. That is, it naturally oscillates with greater amplitude at some frequencies, called resonant frequencies, than at other frequencies. The oscillations in a reso ...
, something like a guitar's sound box, absorbing the radio waves from the nearby driven element and re-radiating them again with a different phase
Phase or phases may refer to:
Science
*State of matter, or phase, one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist
*Phase (matter), a region of space throughout which all physical properties are essentially uniform
*Phase space, a mathematica ...
. The waves from the different antenna elements interfere, strengthening the antenna's radiation in the desired direction, and cancelling out the waves in undesired directions.
The parasitic elements in a Yagi antenna are mounted parallel to the driven element, with all the elements usually in a line perpendicular to the direction of radiation of the antenna. What effect a parasitic element has on the radiation pattern depends both on its separation from the next element, and on its length. The driven element of the antenna is usually a half-wave dipole
In physics, a dipole () is an electromagnetic phenomenon which occurs in two ways:
* An electric dipole moment, electric dipole deals with the separation of the positive and negative electric charges found in any electromagnetic system. A simple ...
, its length half a wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
of the radio waves used. The parasitic elements are of two types. A "''reflector''" is slightly longer (around 5%) than a half-wavelength. It serves to reflect the radio waves in the opposite direction. A "''director''" is slightly shorter than a half-wavelength; it serves to increase the radiation in a given direction. A Yagi antenna may have a reflector on one side of the driven element, and one or more directors on the other side. If all the elements are in a plane, usually only one reflector is used, because additional ones give little improvement in gain, but sometimes additional reflectors are mounted above and below the plane of the antenna on a vertical bracket at the end.
node
In general, a node is a localized swelling (a "knot") or a point of intersection (a vertex).
Node may refer to:
In mathematics
* Vertex (graph theory), a vertex in a mathematical graph
*Vertex (geometry), a point where two or more curves, lines ...
'') at the midpoint where the grounded beam is attached.
The addition of parasitic elements gives a diminishing improvement in the antenna's gain.
Adding a reflector to a dipole, to make a 2 element Yagi, increases the gain by about 5 dB over the dipole. Adding a director to this, to give a 3 element Yagi, gives a gain of about 7 dB over a dipole. As a rule of thumb, each additional parasitic element beyond this adds about 1 dB of gain.
In an example of a parasitic element that is not rod-shaped, a parasitic microstrip patch antenna is sometimes mounted above another driven patch antenna. This antenna combination resonates at a slightly lower frequency than the original element. However, the main effect is to greatly increase the impedance bandwidth of the antenna. In some cases the bandwidth can be increased by a factor of 10.
Not all types of thin conductor multielement antennas have parasitic elements. The log periodic antenna
A log-periodic antenna (LP), also known as a log-periodic array or log-periodic aerial, is a multi-element, directional antenna designed to operate over a wide band of Frequency, frequencies. It was invented by John Dunlavy in 1952.
The most c ...
is similar in appearance to a Yagi, but all of its elements are driven elements, connected to the transmitter or receiver.
References
Further reading
* {{cite book , title=ARRL Antenna Book , year=2015 , edition=23 , at=Subsection 11.1 , place=Newington, CT , publisher=American Radio Relay League
The American Radio Relay League (ARRL) is the largest membership association of amateur radio enthusiasts in the United States. ARRL is a non-profit organization and was co-founded on April 6, 1914, by Hiram Percy Maxim and Clarence D. Tuska of ...
, isbn=978-1625950444
Antennas (radio)