Dover F on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dover () is a town and major ferry port in

 Archaeological finds have shown that there were Stone Age people in the area, and that some
Archaeological finds have shown that there were Stone Age people in the area, and that some
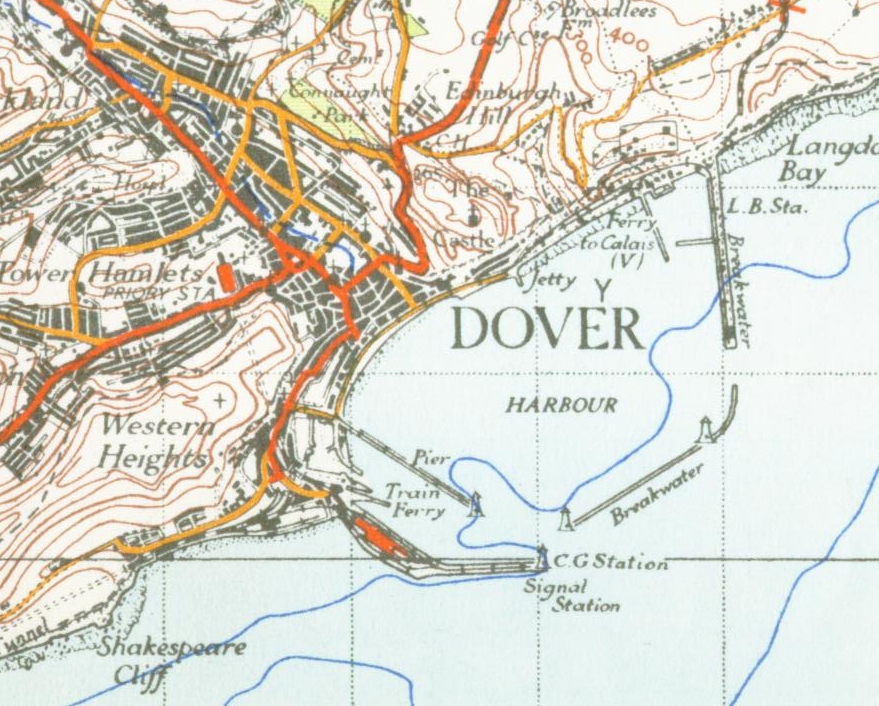 Dover is in the south-east corner of Britain. From
Dover is in the south-east corner of Britain. From
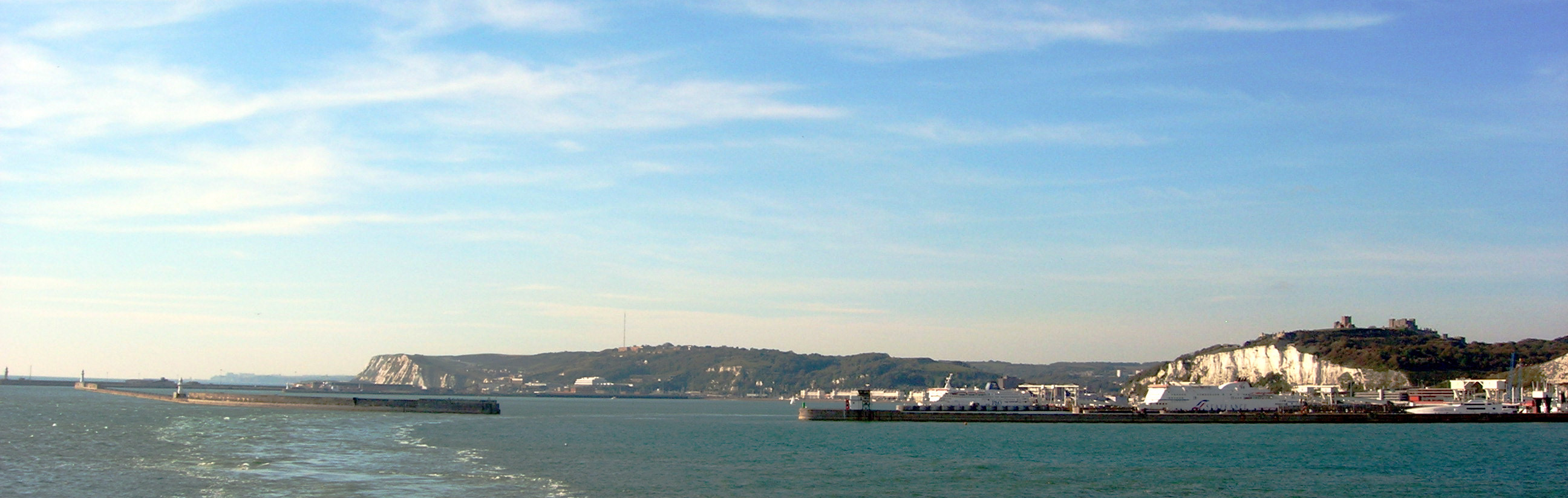 The Dover Harbour Board is the responsible authority for the running of the Port of Dover. The
The Dover Harbour Board is the responsible authority for the running of the Port of Dover. The
 * Blériot memorial: the outline of Louis Blériot's aircraft, marked with granite setts, at the exact spot where Blériot landed after the first cross-Channel flight, 1909
*
* Blériot memorial: the outline of Louis Blériot's aircraft, marked with granite setts, at the exact spot where Blériot landed after the first cross-Channel flight, 1909
*

UKHO nautical charts of Dover and approaches
The Dover War Memorial Project
* {{Authority control Towns in Kent Cinque ports Populated coastal places in Kent Dover District Market towns in Kent France–United Kingdom border crossings Beaches of Kent Civil parishes in Kent Port cities and towns in South East England
Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
, South East England
South East England is one of the nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. It consists of the counties of Buckinghamshire, East Sussex, Hampshire, the Isle of Wight, Kent, Oxfordshire, Berkshi ...
. It faces France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
at from Cap Gris Nez
Cap Gris-Nez (literally "cape grey nose"; ) is a cape on the Côte d'Opale in the Pas-de-Calais ''département'' in northern France.
The 'Cliffs of the Cape' is the closest point of France to England – from their English counterparts at ...
in France. It lies south-east of Canterbury
Canterbury (, ) is a cathedral city and UNESCO World Heritage Site, situated in the heart of the City of Canterbury local government district of Kent, England. It lies on the River Stour.
The Archbishop of Canterbury is the primate of ...
and east of Maidstone
Maidstone is the largest town in Kent, England, of which it is the county town. Maidstone is historically important and lies 32 miles (51 km) east-south-east of London. The River Medway runs through the centre of the town, linking it wi ...
. The town is the administrative centre of the Dover District and home of the Port of Dover.
Archaeological finds have revealed that the area has always been a focus for peoples entering and leaving Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
. The name derives from the River Dour
The River Dour is a chalk stream in the county of Kent, England. It flows from the villages of Temple Ewell and River between which is a neighbourhood served by a railway station, Kearsney. It is roughly long.
It originally had a wide estu ...
that flows through it.
In recent times the town has undergone transformations with a high-speed rail link to London, new retail in town with St James' area opened in 2018, and a revamped promenade and beachfront. This followed in 2019, with a new 500m Pier to the west of the Harbour, and new Marina unveiled as part of a £330m investment in the area. It has also been a point of destination for many illegal migrant crossings during the English channel migrant crisis.
The Port of Dover provides much of the town's employment, as does tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism mor ...
including to the landmark White Cliffs of Dover
The White Cliffs of Dover is the region of English coastline facing the Strait of Dover and France. The cliff face, which reaches a height of , owes its striking appearance to its composition of chalk accented by streaks of black flint, depos ...
. There were over 368,000 tourists visiting Dover castle in the year of 2019.
Dover is classified as a Large-Port Town, due to its large volumes of port traffic and low urban population .History
 Archaeological finds have shown that there were Stone Age people in the area, and that some
Archaeological finds have shown that there were Stone Age people in the area, and that some Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
finds also exist. During the Roman period, the area became part of the Roman communications network. It was connected by road to Canterbury
Canterbury (, ) is a cathedral city and UNESCO World Heritage Site, situated in the heart of the City of Canterbury local government district of Kent, England. It lies on the River Stour.
The Archbishop of Canterbury is the primate of ...
and Watling Street
Watling Street is a historic route in England that crosses the River Thames at London and which was used in Classical Antiquity, Late Antiquity, and throughout the Middle Ages. It was used by the ancient Britons and paved as one of the main ...
and it became ''Portus Dubris
Dubris, also known as Portus Dubris and Dubrae, was a port in Roman Britain on the site of present-day Dover, Kent, England.
As the closest point to continental Europe and the site of the estuary of the Dour, the site chosen for Dover was ideal ...
'', a fortified port. Dover has a partly preserved Roman lighthouse (the tallest surviving Roman structure in Britain) and the remains of a villa with preserved Roman wall paintings. Dover later figured in Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manus ...
(1086).
Forts were built above the port and lighthouses were constructed to guide passing ships. It is one of the Cinque Ports. and has served as a bastion against various attackers: notably the French during the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
and Germany during the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
.
During the Cold War, a Regional Seat of Government was located within the White Cliffs beneath Dover Castle. Curiously, this is omitted from the strategic objects appearing on the Soviet 1:10,000 city plan of Dover that was produced in 1974. The port would have served as an embarkation point for sending reinforcements to the British Army of the Rhine
There have been two formations named British Army of the Rhine (BAOR). Both were originally occupation forces in Germany, one after the First World War and the other after the Second World War. Both formations had areas of responsibility located ...
in the event of a Soviet ground invasion of Europe.
In 1974 a discovery was made at Langdon Bay off the coast near Dover. It contained bronze axes of French design and is probably the remainder of the cargo of a sunken ship. At the same time, this find also shows that trade routes across the Channel between England and France existed already in the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
, or even earlier. In 1992, the so-called Dover boat from the Bronze Age was discovered in six metres depth underwater. This is one of the oldest finds of a seaworthy boat. Using the radiocarbon method of investigation, the boat's construction was dated to approximately 1550 BC The 1550s BC was a decade lasting from January 1, 1559 BC to December 31, 1550 BC.
Events and trends
*The city of Mycenae, located in the northeast Peloponnesus, comes to dominate the rest of Achaea, giving its name to the Mycenaean civilization. ...
.
Etymology
First recorded in its Latinised form of ''Portus Dubris
Dubris, also known as Portus Dubris and Dubrae, was a port in Roman Britain on the site of present-day Dover, Kent, England.
As the closest point to continental Europe and the site of the estuary of the Dour, the site chosen for Dover was ideal ...
'', the name derives from the Brythonic word for water (''dwfr'' in Middle Welsh
Middle Welsh ( cy, Cymraeg Canol, wlm, Kymraec) is the label attached to the Welsh language of the 12th to 15th centuries, of which much more remains than for any earlier period. This form of Welsh developed directly from Old Welsh ( cy, Hen G ...
, ''dŵr'' in Modern Welsh
The history of the Welsh language (Welsh: ''Hanes yr iaith Gymraeg'') spans over 1400 years, encompassing the stages of the language known as Primitive Welsh, Old Welsh, Middle Welsh, and Modern Welsh.
Origins
Welsh evolved from British, the C ...
apart from '' 'dwfrliw' '' (Watercolour) which has retained the old Welsh spelling, ''dour'' in Breton). The same element is present in the town's French name ''Douvres'' and the name of the river, ''Dour'', which is also evident in other English towns such as Wendover
Wendover is a market town and civil parish at the foot of the Chiltern Hills in Buckinghamshire, England. It is situated at the point where the main road across the Chilterns between London and Aylesbury intersects with the once important road a ...
. However, the modern Modern Welsh
The history of the Welsh language (Welsh: ''Hanes yr iaith Gymraeg'') spans over 1400 years, encompassing the stages of the language known as Primitive Welsh, Old Welsh, Middle Welsh, and Modern Welsh.
Origins
Welsh evolved from British, the C ...
name ''Dofr'' is an adaptation of the English name ''Dover''.
The current name was in use at least by the time of Shakespeare's ''King Lear
''King Lear'' is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare.
It is based on the mythological Leir of Britain. King Lear, in preparation for his old age, divides his power and land between two of his daughters. He becomes destitute and insane ...
'' (between 1603 and 1606), in which the town and its cliffs play a prominent role.
The Siege of Dover (1216)
Louis VIII of France
Louis VIII (5 September 1187 – 8 November 1226), nicknamed The Lion (french: Le Lion), was King of France from 1223 to 1226. As prince, he invaded England on 21 May 1216 and was excommunicated by a papal legate on 29 May 1216. On 2 June 1216 ...
landed his army, seeking to depose King Henry III, on Dover's mainland beach. Henry III ambushed Louis' army with approximately 400 bowmen atop The White Cliffs of Dover and his cavalry attacking the invaders on the beach. However, the French slaughtered the English cavalry and made their way up the cliffs to disperse the bowmen. Louis' army seized Dover village, forcing the English back to Canterbury. French control of Dover lasted for three months after which English troops pushed back, forcing the French to surrender and return home.
Geography and climate
 Dover is in the south-east corner of Britain. From
Dover is in the south-east corner of Britain. From South Foreland
South Foreland is a chalk headland on the Kent coast of southeast England. It presents a bold cliff to the sea, and commands views over the Strait of Dover. It is centred northeast of Dover and 15 miles south of North Foreland. It includes ...
, the nearest point to the European mainland, Cap Gris Nez
Cap Gris-Nez (literally "cape grey nose"; ) is a cape on the Côte d'Opale in the Pas-de-Calais ''département'' in northern France.
The 'Cliffs of the Cape' is the closest point of France to England – from their English counterparts at ...
is away across the Strait of Dover.
The site of its original settlement lies in the valley of the River Dour
The River Dour is a chalk stream in the county of Kent, England. It flows from the villages of Temple Ewell and River between which is a neighbourhood served by a railway station, Kearsney. It is roughly long.
It originally had a wide estu ...
, sheltering from the prevailing south-westerly winds. This has led to the silting up of the river mouth by the action of longshore drift. The town has been forced into making artificial breakwaters to keep the port in being. These breakwaters have been extended and adapted so that the port lies almost entirely on reclaimed land.
The higher land on either side of the valley – the Western Heights and the eastern high point on which Dover Castle
Dover Castle is a medieval castle in Dover, Kent, England and is Grade I listed. It was founded in the 11th century and has been described as the "Key to England" due to its defensive significance throughout history. Some sources say it is the ...
stands – has been adapted to perform the function of protection against invaders. The town has gradually extended up the river valley, encompassing several villages in doing so. Little growth is possible along the coast, since the cliffs are on the sea's edge. The railway, being tunnelled and embanked, skirts the foot of the cliffs.
Dover has an oceanic climate (Köppen classification ''Cfb'') similar to the rest of the United Kingdom with mild temperatures year-round and a light amount of rainfall each month. The warmest recorded temperature was , recorded at Langdon Bay on 25 July 2019. The temperature is usually between and . There is evidence that the sea is coldest in February; the warmest recorded temperature for February was only , compared with in January.
Demography
In 1800, the year before Britain's first national census,Edward Hasted
Edward Hasted (20 December 1732 OS (31 December 1732 NS) – 14 January 1812) was an English antiquarian and pioneering historian of his ancestral home county of Kent. As such, he was the author of a major county history, ''The History and T ...
(1732–1812) reported that the town had a population of almost 10,000 people.
At the 2001 census, the town of Dover had 28,156 inhabitants, while the population of the whole urban area of Dover, as calculated by the Office for National Statistics
The Office for National Statistics (ONS; cy, Swyddfa Ystadegau Gwladol) is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department which reports directly to the UK Parliament.
Overview
The ONS is responsible for t ...
, was 39,078 inhabitants.
With the expansion of Dover, many of the outlying ancient villages have been incorporated into the town. Originally the parishes of Dover St. Mary's and Dover St. James, since 1836 Buckland and Charlton have become part Dover, and Maxton (a hamlet to the west), River
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of w ...
, Kearsney, Temple Ewell
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
, and Whitfield, all to the north of the town centre, are within its conurbation.
Economy
Retail
The town's main shopping streets are the High Street, Biggin Street, Market Square, Cannon Street, Pencester Road and Castle Street. The Castleton Retail Park is to the north-west of the town centre. The new St James' Retail and Leisure Park opened in 2018 and is a southern extension of the town centre and consists of shops, restaurants, a Travelodge Hotel and a Cineworld Cinema.Shipping
English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
, here at its narrowest point in the Straits of Dover, is the busiest shipping lane in the world. Ferries crossing between here and the Continent have to negotiate their way through the constant stream of shipping crossing their path. The ''Dover Strait Traffic Separation Scheme'' allots ships separate lanes when passing through the Strait. The Scheme is controlled by the Channel Navigation Information Service based at Maritime Rescue Co-ordination Centre Dover. MRCC Dover is also charged with co-ordination of civil maritime search and rescue within these waters.
The Port of Dover is also used by cruise ships. The old Dover Marine railway station building houses one passenger terminal, together with a car park. A second, purpose-built, terminal is located further out along the pier.
The ferry lines using the port are (number of daily sailings in parentheses):
* to Calais: P&O Ferries (25), DFDS Seaways
DFDS Seaways is a Danish shipping company that operates passenger and freight services across northern Europe. Following the acquisition of Norfolkline in 2010, DFDS restructured its other shipping divisions ( DFDS Tor Line and DFDS Lisco) ...
(10).
* to Dunkirk: DFDS Seaways
DFDS Seaways is a Danish shipping company that operates passenger and freight services across northern Europe. Following the acquisition of Norfolkline in 2010, DFDS restructured its other shipping divisions ( DFDS Tor Line and DFDS Lisco) ...
(11).
These services have been cut in recent years:
* P&O Ferries sailings to Boulogne (5 daily) were withdrawn in 1993 and Zeebrugge
Zeebrugge (, from: ''Brugge aan zee'' meaning "Bruges at Sea", french: Zeebruges) is a village on the coast of Belgium and a subdivision of Bruges, for which it is the modern port. Zeebrugge serves as both the international port of Bruges-Zee ...
(4 daily) in 2002.
* SNCF withdrew their three train ferry
A train ferry is a ship (ferry) designed to carry railway vehicles. Typically, one level of the ship is fitted with railway tracks, and the vessel has a door at the front and/or rear to give access to the wharves. In the United States, train ...
sailings on the opening of the Channel Tunnel.
* Regie voor Maritiem Transport
Regie voor Maritiem Transport (RMT) was the Belgium, Belgian state-owned ferry service and operated ferries on the Ostend-Dover route under the name Oostende Lines. For the last few years until its demise in February 1997, the ferries from Osten ...
moved their Ostend
Ostend ( nl, Oostende, ; french: link=no, Ostende ; german: link=no, Ostende ; vls, Ostende) is a coastal city and municipality, located in the province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It comprises the boroughs of Mariakerk ...
service of three sailings daily to Ramsgate in 1994; this route was operated by TransEuropa Ferries until April 2013.
* Stena Line merged their 20 Calais sailings into the current P&O operation in 1998.
* Hoverspeed
Hoverspeed was a ferry company that operated on the English Channel from 1981 until 2005. It was formed in 1981 by the merger of Seaspeed and Hoverlloyd. Its last owners were Sea Containers; the company ran a small fleet of two high-speed Sea ...
ceased operations in 2005 and withdrew their 8 daily sailings.
* SpeedFerries ceased operations in 2008 and withdrew their 5 daily sailings.
* LD Lines
LD Lines was a French shipping company, with both roro freight and passenger ferry operations. It was a subsidiary of Louis Dreyfus Armateurs (LDA), which engages in building, owning, operating, and managing vessels. LD Lines operated fer ...
ceased the Dover-Dieppe
Dieppe (; Norman: ''Dgieppe'') is a coastal commune in the Seine-Maritime department in the Normandy region of northern France.
Dieppe is a seaport on the English Channel at the mouth of the river Arques. A regular ferry service runs to N ...
service on 29 June 2009 and Dover-Boulogne 5 September 2010.
* SeaFrance ceased operations in 2012 of their Dover- Calais service which was their only service.

Main sights
Dover Castle
Dover Castle is a medieval castle in Dover, Kent, England and is Grade I listed. It was founded in the 11th century and has been described as the "Key to England" due to its defensive significance throughout history. Some sources say it is the ...
* White Cliffs of Dover
The White Cliffs of Dover is the region of English coastline facing the Strait of Dover and France. The cliff face, which reaches a height of , owes its striking appearance to its composition of chalk accented by streaks of black flint, depos ...
* Dover Western Heights
* Dover Museum
Dover Museum is a museum in Dover, Kent, in south-east England.
History
Founded in February 1836 by the town's mayor Edward Pett Thompson, it was initially housed in the old Guildhall and run by the Dover Philosophical Institute. The Town Co ...
* Dover Marina
* Dover Pier
* Roman Painted House Museum
* Maison Dieu, Dover
* Samphire Hoe
Samphire Hoe is a country park situated west of Dover in Kent in southeast England. The park was created by using 4.9 million cubic metres of chalk marl from the Channel Tunnel excavations and is found at the bottom of a section of the White Cl ...
* South Foreland Lighthouse
South Foreland Lighthouses are a pair of Victorian lighthouses on the South Foreland in St. Margaret's Bay, Dover, Kent, England, used to warn ships approaching the nearby Goodwin Sands. There has been a pair of lighthouses at South Forelan ...
* Pines Garden
Pines Garden is a house and large garden, located on the winding beach road from St Margaret's at Cliffe village down to the beach at St Margeret's Bay, near Dover.
History
Fred Cleary
Frederick Ernest Cleary (1905-1984) CBE, was originally a ...
* St Edmund's Chapel
* St Mary's Church
* St James' Church: preserved as a "tidy ruin"
* St Paul's Church
Transport
Road
Dover's main communications artery, the A2 road replicates two former routes, connecting the town with Canterbury. The Roman road was followed for centuries until, in the late 18th century, it became atoll road
A toll road, also known as a turnpike or tollway, is a public or private road (almost always a controlled-access highway in the present day) for which a fee (or ''Toll (fee), toll'') is assessed for passage. It is a form of road pricing typically ...
. Stagecoaches were operating: one description stated that the journey took all day to reach London, from 4am to being "in time for supper".
The other main roads, travelling west and east, are the A20 to Folkestone and thence the M20 to London, and the A258 through Deal to Sandwich.
In December 2020, a long line of freight trucks formed due to sudden border closures with France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, because of new strains of COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease quickly ...
within the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
.
Rail
The railway reached Dover from two directions: the South Eastern Railway's main line connected with Folkestone in 1844, and theLondon, Chatham & Dover Railway
The London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR or LC&DR) was a railway company in south-eastern England created on 1 August 1859, when the East Kent Railway was given parliamentary approval to change its name. Its lines ran through London and no ...
opened its line from Canterbury in 1861. Southeastern
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each se ...
trains run from Dover Priory
The Priory of St. Mary the Virgin and St. Martin of the New Work, or Newark, commonly called Dover Priory, was a priory at Dover in southeast England. It was variously independent in rule, then occupied by canons regular of the Augustinian r ...
to London Charing Cross, London Victoria
Victoria station, also known as London Victoria, is a central London railway terminus and connected London Underground station in Victoria, in the City of Westminster, managed by Network Rail. Named after the nearby Victoria Street (not the Q ...
or London St Pancras International
St Pancras railway station (), also known as London St Pancras or St Pancras International and officially since 2007 as London St Pancras International, is a central London railway terminus on Euston Road in the London Borough of Camden. It i ...
stations in London, and Ramsgate or Sandwich
A sandwich is a food typically consisting of vegetables, sliced cheese or meat, placed on or between slices of bread, or more generally any dish wherein bread serves as a container or wrapper for another food type. The sandwich began as a po ...
in Kent. London is reached in 55 minutes by train from Dover.
The Chatham Main Line into Priory was electrified under British Railways in 1959 as part of Stage 1 of Kent Coast Electrification, under the BR 1955 Modernisation Plan
Events January
* January 3 – José Ramón Guizado becomes president of Panama.
* January 17 – , the first nuclear-powered submarine, puts to sea for the first time, from Groton, Connecticut.
* January 18– 20 – Battle of Yijian ...
. The line up to Ramsgate, via Deal, was subsequently electrified under stage two of Kent Coast electrification in January 1961. The line from Folkestone into Priory was electrified in June 1961.
A tram system
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are ...
operated in the town from 1897 to 1936.
Walking
Dover has two long distance footpaths: theSaxon Shore Way
The Saxon Shore Way is a long-distance footpath in England. It starts at Gravesend, Kent, and traces the coast of South-East England as it was in Roman times as far as Hastings, East Sussex, in total. This means that around Romney Marsh the ...
and the North Downs Way
The North Downs Way National Trail is a long-distance path in southern England, opened in 1978. It runs from Farnham to Dover, past Guildford, Dorking, Merstham, Otford and Rochester, along the Surrey Hills Area of Outstanding Natural Be ...
. The National Trust
The National Trust, formally the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, is a charity and membership organisation for heritage conservation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. In Scotland, there is a separate and ...
White Cliffs can be reached by foot from the town centre, with pathways to South Foreland Lighthouse
South Foreland Lighthouses are a pair of Victorian lighthouses on the South Foreland in St. Margaret's Bay, Dover, Kent, England, used to warn ships approaching the nearby Goodwin Sands. There has been a pair of lighthouses at South Forelan ...
, and St Margarets Bay along the cliff top . The walking routes from Dover pass the National Trust
The National Trust, formally the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, is a charity and membership organisation for heritage conservation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. In Scotland, there is a separate and ...
visitor centre on the landmark chalk cliffs overlooking the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
with views of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
visible on a clear day.
Cycling
TwoNational Cycle Network
The National Cycle Network (NCN) is the national cycling route network of the United Kingdom, which was established to encourage cycling and walking throughout Britain, as well as for the purposes of bicycle touring. It was created by the cha ...
routes begin their journey at the town. Route one goes from Dover to Canterbury.
This route links with National Cycle Route 2
When complete, the route will be long.
Route
The route has several sections.
# Dover to Hastings. The route follows the Chalk and Channel Way along the cliff tops to Folkestone and crosses Romney Marsh to Lydd. From Rye it follows the coast ...
from Dover to St Austell, Regional route 16, and Regional route 17 in Dover. It passes three castles. Firstly from Dover on the steap incline past Dover Castle. ThenSouth Foreland Lighthouse
South Foreland Lighthouses are a pair of Victorian lighthouses on the South Foreland in St. Margaret's Bay, Dover, Kent, England, used to warn ships approaching the nearby Goodwin Sands. There has been a pair of lighthouses at South Forelan ...
is visible from the route. Mostly traffic-free along the east coast from Kingsdown to Deal, passing Walmer Castle
Walmer Castle is an artillery fort originally constructed by Henry VIII in Walmer, Kent, between 1539 and 1540. It formed part of the King's Device programme to protect against invasion from France and the Holy Roman Empire, and defended the s ...
and Deal Castle
Deal Castle is an artillery fort constructed by Henry VIII in Deal, Kent, between 1539 and 1540. It formed part of the King's Device programme to protect against invasion from France and the Holy Roman Empire, and defended the strategically i ...
. Follows toll road (free to cyclists) through the Royal Cinque Ports Golf Club to the town of Sandwich. In Sandwich the route links with Regional route 15.
Dover town centre is cycle friendly: There are dedicated cycle lanes along the seafront, cycle routes through the town's pedestrianised High Street area.
Ferry
The Port of Dover is a 20-minute walk fromDover Priory railway station
Dover Priory railway station is the southern terminus of the South Eastern Main Line in England, and is the main station serving the town of Dover, Kent, the other open station being , on the outskirts. It is down the line from London Victoria ...
.
The Dover to Dunkirk ferry route was originally operated by ferry operator Norfolkline
Norfolkline was a European ferry operator and logistics company owned by Maersk. It provided freight ferry services on the English channel, Irish Sea, and the North Sea; and passenger ferry services on the English channel and Irish Sea; and l ...
. This company was later acquired by the pan European operator DFDS Seaways
DFDS Seaways is a Danish shipping company that operates passenger and freight services across northern Europe. Following the acquisition of Norfolkline in 2010, DFDS restructured its other shipping divisions ( DFDS Tor Line and DFDS Lisco) ...
in July 2010. The crossing time is approximately two hours. Due to this route not being as well known as Dover to Calais, prices are often cheaper. The location of Dunkirk is also more convenient for those travelling by road transport on to countries in Northern Europe including Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
, the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, Germany and further afield.
Bus
Stagecoach in East Kent provide local bus services. Dover is on the Stagecoach Diamond network providing links toCanterbury
Canterbury (, ) is a cathedral city and UNESCO World Heritage Site, situated in the heart of the City of Canterbury local government district of Kent, England. It lies on the River Stour.
The Archbishop of Canterbury is the primate of ...
and Deal
A deal, or deals may refer to:
Places United States
* Deal, New Jersey, a borough
* Deal, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community
* Deal Lake, New Jersey
Elsewhere
* Deal Island (Tasmania), Australia
* Deal, Kent, a town in England
* Deal, ...
. The Western Docks at the port of Dover are served from the town centre as well as Canterbury and Deal. Dover is the start of The Wave network to New Romney via Folkestone, Hythe
Hythe, from Anglo-Saxon ''hȳð'', may refer to a landing-place, port or haven, either as an element in a toponym, such as Rotherhithe in London, or to:
Places Australia
* Hythe, Tasmania
Canada
*Hythe, Alberta, a village in Canada
England
* T ...
and Dymchurch
Dymchurch is a village and civil parish in the Folkestone and Hythe district of Kent, England. The village is located on the coast five miles (8 km) south-west of Hythe, and on the Romney Marsh.
History
The history of Dymchurch began with ...
. There are services to Lydd
Lydd is a town and electoral ward in Kent, England, lying on Romney Marsh. It is one of the larger settlements on the marsh, and the most southerly town in Kent. Lydd reached the height of its prosperity during the 13th century, when it was a c ...
via Lydd Airport
London Ashford Airport is east of the town of Lydd and south of Ashford in the district of Folkestone and Hythe, in Kent, England. Originally named Lydd Ferryfield, it is now also known as London Ashford Airport, despite being from Lond ...
, with one continuing from Lydd on to Hastings
Hastings () is a large seaside town and borough in East Sussex on the south coast of England,
east to the county town of Lewes and south east of London. The town gives its name to the Battle of Hastings, which took place to the north-west ...
via Camber
Camber may refer to a variety of curvatures and angles:
* Camber angle, the angle made by the wheels of a vehicle
* Camber beam, an upward curvature of a joist to compensate for load deflection due in buildings
* Camber thrust in bike technology
* ...
and Rye. There is a link to Sandwich
A sandwich is a food typically consisting of vegetables, sliced cheese or meat, placed on or between slices of bread, or more generally any dish wherein bread serves as a container or wrapper for another food type. The sandwich began as a po ...
. Buses run from Dover to Elvington via Eythorne
Eythorne is a civil parish and small village located 7.3 miles north-northwest of Dover in Kent, with a combined population of approximately 2,500 residents including nearby villages Barfrestone and Elvington. Although not classed as one of the ...
.
National Express
National Express Group is a British multinational public transport company headquartered in Birmingham, England. It operates bus, coach, train and tram services in the United Kingdom, Ireland (National Express operates Eurolines in conjunction ...
runs coaches from Dover to other towns in Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
including Canterbury, Folkestone, Ashford, Kent, Maidstone
Maidstone is the largest town in Kent, England, of which it is the county town. Maidstone is historically important and lies 32 miles (51 km) east-south-east of London. The River Medway runs through the centre of the town, linking it wi ...
, Gillingham at Hempsted Valley shopping centre and Greenhithe
Greenhithe is a village in the Borough of Dartford in Kent, England, and the civil parish of Swanscombe and Greenhithe. It is located east of Dartford and west of Gravesend.
Area
In the past, Greenhithe's waterfront on the estuary of the ri ...
at Bluewater Shopping Centre
Bluewater Shopping Centre (commonly referred to as Bluewater) is an out-of-town shopping centre in Stone (postally Greenhithe), Kent, England, outside the M25 motorway, east south east of London's centre. Opened on 16 March 1999 in a former chal ...
for Dartford to London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
including Bexleyheath, Eltham
Eltham ( ) is a district of southeast London, England, within the Royal Borough of Greenwich. It is east-southeast of Charing Cross, and is identified in the London Plan as one of 35 major centres in Greater London. The three wards of E ...
, Walworth
Walworth () is a district of south London, England, within the London Borough of Southwark. It adjoins Camberwell to the south and Elephant and Castle to the north, and is south-east of Charing Cross.
Major streets in Walworth include the Old ...
, Canary Wharf
Canary Wharf is an area of London, England, located near the Isle of Dogs in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. Canary Wharf is defined by the Greater London Authority as being part of London's central business district, alongside Central Lon ...
, Elephant & Castle
The Elephant and Castle is an area around a major road junction in London, England, in the London Borough of Southwark. The name also informally refers to much of Walworth and Newington, due to the proximity of the London Underground stati ...
, The City (The City of London
The City of London is a city, ceremonial county and local government district that contains the historic centre and constitutes, alongside Canary Wharf, the primary central business district (CBD) of London. It constituted most of London from ...
) and to Victoria Coach Station
Victoria Coach Station is the largest coach station in London, located in the central district of Victoria in the City of Westminster. It serves as a terminus for many medium- and long-distance coach services in the United Kingdom, and is al ...
.
RNLI
The Dover lifeboat is aSevern class lifeboat
The Severn class is the largest lifeboat operated by the Royal National Lifeboat Institution (RNLI). The class, which is long, was introduced in to service in 1996. It is named after the River Severn, the longest river in Great Britain. The l ...
based in the Western Docks.
Dover Lifeboat station is based at crosswall quay in Dover Harbour. There is a Severn-class lifeboat
The Severn class is the largest lifeboat operated by the Royal National Lifeboat Institution (RNLI). The class, which is long, was introduced in to service in 1996. It is named after the River Severn, the longest river in Great Britain. The l ...
, which is the biggest in the fleet. It belongs to the RNLI which covers all of Great Britain. The lifeboat number is 17-09 and has a lot of emergencies in the Channel. The Severn class is designed to lay afloat. Built from fibre reinforced composite (FRC) the boat is lightweight yet very strong and is designed to right itself in the event of a capsize.
Education
There are seven secondary level schools serving Dover. Public schools *Dover College
, motto_translation = I cannot refuse the task
, established =
, closed =
, type = Public SchoolIndependent day and boarding
, religion = Church of England
, headmaster = Simon Fisher
, r_head_label =
, r_head ...
Dover College
, motto_translation = I cannot refuse the task
, established =
, closed =
, type = Public SchoolIndependent day and boarding
, religion = Church of England
, headmaster = Simon Fisher
, r_head_label =
, r_head ...
is a mixed public school founded in 1871 by a group of local business men.
Selective secondary schools
There are 2 single-sex grammar school
A grammar school is one of several different types of school in the history of education in the United Kingdom and other English-speaking countries, originally a school teaching Latin, but more recently an academically oriented secondary school ...
s and a mixed military school.
* Dover Grammar School for Boys
Dover Grammar School for Boys (DGSB) is a selective secondary school located in Dover, United Kingdom, whose origins can be traced back to the Education Act (the 'Balfour Act') of 1902. Originally founded as the Dover County School for Boys a ...
(DGSB)
* Dover Grammar School for Girls (DGGS)
Both grammar schools require the Dover Test or the Kent Test for admission to Year 7.
* Duke of York's Royal Military School
The Duke of York's Royal Military School, more commonly called the Duke of York's, is a co-educational academy (for students aged 11 to 18) with military traditions in Guston, Kent. Since becoming an academy in 2010, the school is now sponsor ...
Duke of York's Royal Military School
The Duke of York's Royal Military School, more commonly called the Duke of York's, is a co-educational academy (for students aged 11 to 18) with military traditions in Guston, Kent. Since becoming an academy in 2010, the school is now sponsor ...
is a selective secondary school with academy status and England's only military boarding school for children of service personnel (co-education ages 11–18), located next to the former site of Connaught Barracks.
Non-selective secondary schools
There are 3 ex-secondary modern
A secondary modern school is a type of secondary school that existed throughout England, Wales and Northern Ireland from 1944 until the 1970s under the Tripartite System. Schools of this type continue in Northern Ireland, where they are usuall ...
mixed schools, all with academy status.
* Astor Secondary School
Astor Secondary School federated with St Radigunds Primary School (then renamed White Cliffs Primary College for the Arts) to form the Dover Federation for the Arts (DFA). Subsequently, Barton Junior School and Shatterlocks Nursery and Infant School joined the DFA. In 2014 the DFA was warned by the Department for Education about "unacceptably low standards of performance of pupils ".
* St Edmund's Catholic School
St Edmund's Catholic School federated with St Richards Catholic Primary School to form the Dover Federation of Catholic Schools.
* Dover Christ Church Academy
The Dover Christ Church Academy, previously known as Archers Court Secondary School is a coeducational secondary school and sixth form located in Whitfield, Kent, 4 miles north of Dover. It has academy status and sponsored by Canterbury Chr ...
Dover Christ Church Academy
The Dover Christ Church Academy, previously known as Archers Court Secondary School is a coeducational secondary school and sixth form located in Whitfield, Kent, 4 miles north of Dover. It has academy status and sponsored by Canterbury Chr ...
is located in Whitfield, 4 miles north of Dover.
Technical College
Dover Technical College is part of the East Kent College
East Kent College is a further education college (although also provides higher education courses) located in Broadstairs, Kent on the southeast coast of the United Kingdom.
The main campus is located on Ramsgate Road, Broadstairs. In Septembe ...
(EKC) group.
In addition, 16 primary schools and 2 special schools add to the educational offering.
Public services
Dover has one hospital,Buckland Hospital
Buckland Hospital is a community hospital at Dover in Kent, England. It is managed by East Kent Hospitals University NHS Foundation Trust.
History
The hospital has its origins in the Dover Union Workhouse Infirmary which was completed in 1836. T ...
. Earlier hospitals included the Royal Victoria Hospital, the Isolation Hospital and the Eye Hospital.
Local media
Television
Dover was the home to television studios and production offices of Southern Television Ltd, the company which operated the ITV franchise for South and South East England from 1958–1981. The studios were located on Russell Street and were home to programmes like 'Scene South East', 'Scene Midweek', 'Southern News', 'Farm Progress' and the nightly epilogue, 'Guideline'. The studios were operated by TVS in 1982 and home to 'Coast to Coast', however they closed a year later when the company moved their operations to the newly complete Television Centre inMaidstone
Maidstone is the largest town in Kent, England, of which it is the county town. Maidstone is historically important and lies 32 miles (51 km) east-south-east of London. The River Medway runs through the centre of the town, linking it wi ...
.
Newspapers
Dover has two paid for newspapers, the ''Dover Express'' (published by Kent Regional News and Media) and the '' Dover Mercury'' (published by theKM Group
KM Media Group is a multimedia company in the county of Kent, England which originated as the publisher of the Kent Messenger. The Group now produces local newspapers, radio stations and websites throughout the county. Iliffe Media acquired KM ...
). Free newspapers for the town previously included the ''Dover and Deal Extra'', part of the KM Group; and ''yourdover'', part of KOS Media
KOS Media was a multimedia company based in the county of Kent in South East England. The company operated local newspapers and internet sites throughout the county.
History
KOS Media's first newspaper, the '' Kent on Sunday'' was launched as a ...
.
Radio
Dover has one local commercial radio station,KMFM Shepway and White Cliffs Country
KMFM Shepway and White Cliffs Country is an Independent Local Radio station serving the districts of Dover and Folkestone and Hythe (previously known as Shepway) and the surrounding areas in Kent, South East England. It is the South Kent region ...
, broadcasting to Dover on 106.8FM. The station was founded in Dover as Neptune Radio in September 1997 but moved to Folkestone in 2003 and was consequently rebranded after a takeover by the KM Group. Dover is also served by the county-wide stations Heart South
Heart South is a regional radio station owned and operated by Global as part of the Heart network. It broadcasts to the south and south east of England from studios in Fareham, Hampshire.
The station launched on 3 June 2019 as a result of a me ...
, Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
and BBC Radio Kent
BBC Radio Kent is the BBC's local radio station serving the county of Kent.
It broadcasts on FM, DAB, digital TV and via BBC Sounds from studios at The Great Hall in Tunbridge Wells.
According to RAJAR, the station has a weekly audience of ...
.
The Gateway Hospital Broadcasting Service, in Buckland Hospital radio, closed at the end of 2006. It was the oldest hospital radio station in East Kent being founded in 1968.
DCR 104.9FM (Dover Community Radio) started broadcasting on 104.9FM in May 2022 and is Dover and White Cliffs Country's community radio station. The online station of the same name launched on 30 July 2011 offering local programmes, music and news for Dover and district. Prior to this DCR was an online podcasting service since 2010. . Dover Community Radio was awarded a community radio licence by OFCOM on 12 May 2020.
As of November 2021, BFBS Gurkha Radio has been broadcasting on 90.8FM in Dover and can be picked up within 1 mile of its transmission site at the Dover Community Centre located at Burgoyne Heights. This is part of a trial broadcast of small scale FM services by OFCOM due to end in September 2022 but it maybe extended to serve the Gurkha community living at Burgoyne Heights.
Culture
There are three museums: the mainDover Museum
Dover Museum is a museum in Dover, Kent, in south-east England.
History
Founded in February 1836 by the town's mayor Edward Pett Thompson, it was initially housed in the old Guildhall and run by the Dover Philosophical Institute. The Town Co ...
, the Dover Transport Museum and the Roman Painted House. The town has two cinemas, the Silver Screen Cinema located at the Dover Museum and the Cineworld Cinema opened in 2018 as part of the St James' Retail and Leisure complex. The Discovery Centre located off the Market Square houses Dover's library, Dover Museum, Silver Screen Cinema, the Roundhouse Community Theatre as well as adult education facilities. The Charlton Shopping Centre off the High Street has retail units, the Dover Local community hub, leisure facilities and the studios of Dover Community Radio. The White Cliffs Theatre opened in 2001 is based at Astor College. There is also a community theatre based at St Edmund's Catholic School
Twin towns
* Calais, France * Huber Heights,Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, United States
* Split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, entertai ...
, Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
*Dover, Christ Church, Barbados
The parish of Christ Church is one of eleven historic political divisions of Barbados. It has a land area of and is found at the southern end of the island. Christ Church has survived by name as one of the original six parishes created in 1629 b ...
Sports
Dover District Leisure Centre operated by Places Leisure located in Whitfield opened in March 2019 replacing the previous facility on Townwall Street, which was operated by Your Leisure, a not for profit charitable trust, which caters for sports and includes a swimming pool. There are sports clubs, amongst themDover Athletic F.C.
Dover Athletic Football Club is a semi-professional association football club based in the town of Dover, Kent, England. The club currently competes in the National League South, the sixth tier of English football. The club was formed in 198 ...
, who play in the National League
The National League of Professional Baseball Clubs, known simply as the National League (NL), is the older of two leagues constituting Major League Baseball (MLB) in the United States and Canada, and the world's oldest extant professional team ...
; rugby; swimming; water polo and netball (Dover and District Netball League).
Dover Rowing Club is the oldest coastal rowing club in Britain and has a rich history, at one time becoming the best club on the south coast. More information can be found on the history page of the club's website.
One event which gets media attention is that of swimming the English Channel.
Sea fishing, from the beach, pier or out at sea, is carried out here. The so-called Dover sole (''solea solea'') is found all over European waters.
Dover is now the host of a variety of watersports; such as paddle-boarding and kayaking.
Notable people
In literature
* M.R. James located part of his 1911 ghost story "Casting the Runes
"Casting the Runes" is a short story written by the English writer M.R. James. It was first published in 1911 as the fourth story in ''More Ghost Stories'', which was James' second collection of ghost story, ghost stories.
Plot summary
Mr. Edward ...
", from '' More Ghost Stories'', in the town's Lord Warden Hotel
* Matthew Arnold
Matthew Arnold (24 December 1822 – 15 April 1888) was an English poet and cultural critic who worked as an inspector of schools. He was the son of Thomas Arnold, the celebrated headmaster of Rugby School, and brother to both Tom Arnold, lit ...
used the setting of Dover in his 19th-century
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium.
The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolis ...
poem, ''Dover Beach''.
* Dover feature several times in ''A Tale of Two Cities
''A Tale of Two Cities'' is a historical novel published in 1859 by Charles Dickens, set in London and Paris before and during the French Revolution. The novel tells the story of the French Doctor Manette, his 18-year-long imprisonment in ...
'' by Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian e ...
.
* Russell Hoban
Russell Conwell Hoban (February 4, 1925 – December 13, 2011) was an American expatriate writer. His works span many genres, including fantasy, science fiction, mainstream fiction, magical realism, poetry, and children's books.
He lived in ...
repurposed Dover as "Do It Over" in his 1980, post apocalyptic novel ''Riddley Walker
''Riddley Walker'' is a science fiction novel by American writer Russell Hoban, first published in 1980. It won the John W. Campbell Memorial Award for best science fiction novel in 1982, as well as an Australian Science Fiction Achievement Awa ...
''. Wye became "How"; Canterbury
Canterbury (, ) is a cathedral city and UNESCO World Heritage Site, situated in the heart of the City of Canterbury local government district of Kent, England. It lies on the River Stour.
The Archbishop of Canterbury is the primate of ...
, "Cambry", and Ashford, "Bernt Arse".
In song
* " (There'll Be Bluebirds Over) The White Cliffs of Dover" byVera Lynn
Dame Vera Margaret Lynn (; 20 March 191718 June 2020) was an English singer and entertainer whose musical recordings and performances were very popular during World War II. She is honorifically known as the " Forces' Sweetheart", having giv ...
, recorded in 1942.
* "Clover Over Dover" by British band Blur is track 12 on their 1994 album ''Parklife
''Parklife'' is the third studio album by the English rock band Blur, released on 25 April 1994 on Food Records. After disappointing sales for their previous album '' Modern Life Is Rubbish'' (1993), ''Parklife'' returned Blur to prominence i ...
''.
* "Calais to Dover" by American band Bright Eyes is track 13 on their 2020 album '' Down in the Weeds, Where the World Once Was''.
* "Dover Beach" by Baby Queen is on her 2021 album ''The Yearbook''. She wrote the song following a visit to Dover, taking inspiration from Matthew Arnold
Matthew Arnold (24 December 1822 – 15 April 1888) was an English poet and cultural critic who worked as an inspector of schools. He was the son of Thomas Arnold, the celebrated headmaster of Rugby School, and brother to both Tom Arnold, lit ...
's poem of the same name, and filmed an accompanying music video at Samphire Hoe.
See also
* Strait of DoverReferences
Bibliography
* *External links
UKHO nautical charts of Dover and approaches
The Dover War Memorial Project
* {{Authority control Towns in Kent Cinque ports Populated coastal places in Kent Dover District Market towns in Kent France–United Kingdom border crossings Beaches of Kent Civil parishes in Kent Port cities and towns in South East England