Double Bubble (radiology) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
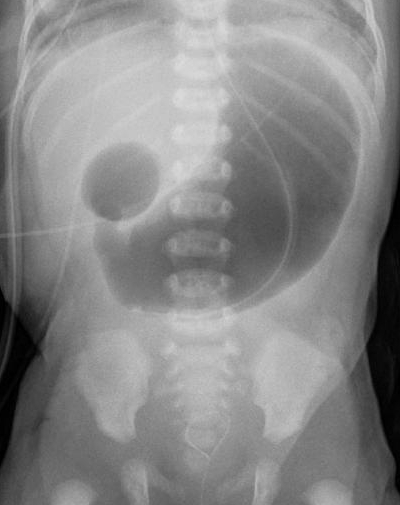 In
In
 In
In radiology
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiat ...
, the double bubble sign is a feature of pediatric imaging seen on radiographs or prenatal
Prenatal development () includes the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal devel ...
ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequency, frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing range, hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hea ...
in which two air filled bubbles are seen in the abdomen, representing two discontiguous loops of bowel in a proximal, or 'high,' small bowel obstruction. The finding is typically pathologic, and implies either duodenal atresia
Duodenal atresia is the congenital absence or complete closure of a portion of the lumen of the duodenum. It causes increased levels of amniotic fluid during pregnancy ( polyhydramnios) and intestinal obstruction in newborn babies. Newborns pres ...
, duodenal web
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine ...
, annular pancreas
Annular pancreas is a rare condition in which the second part of the duodenum is surrounded by a ring of pancreatic tissue continuous with the head of the pancreas. This portion of the pancreas can constrict the duodenum and block or impair the fl ...
, and on occasion midgut volvulus
A volvulus is when a loop of intestine twists around itself and the mesentery that supports it, resulting in a bowel obstruction. Symptoms include abdominal pain, abdominal bloating, vomiting, constipation, and bloody stool. Onset of symptoms ma ...
, a distinction that requires close clinical correlation and, in most cases, surgical intervention.
Distal gas is more often seen with midgut volvulus, duodenal stenosis and duodenal web, though this not always present. In such cases, distinguishing the diagnoses depends on clinical presentation.
Follow up imaging
Afluoroscopic
Fluoroscopy () is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope () allows a physician to see the internal anatomy, structure and ...
study known as an upper gastrointestinal series is often the next step in management in patients that are not critically ill, though if volvulus is suspected, emergent surgical intervention is mandated. If clinical findings are equivocal, caution with non water-soluble contrast is needed, as the usage of barium
Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in group 2 and is a soft, silvery alkaline earth metal. Because of its high chemical reactivity, barium is never found in nature as a free element.
Th ...
can impede surgical revision and lead to increased post operative complications. Non ionic water-soluble contrast should be used, as the hyperosmolar agents, if aspirated, can result in life-threatening pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema, also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive edema, liquid accumulation in the parenchyma, tissue and pulmonary alveolus, air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. It leads to impaired gas exchange and may cause hypoxemia an ...
. When reflective of duodenal atresia, associations with Down syndrome
Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is usually associated with physical growth delays, mild to moderate intellectual dis ...
and VACTERL sequence abnormalities are often seen.
Mimics
Certain rare anatomic anomalies, such as congenital duodenal duplication and pyloric atresia can causefalse positives
A false positive is an error in binary classification in which a test result incorrectly indicates the presence of a condition (such as a disease when the disease is not present), while a false negative is the opposite error, where the test result ...
for the sign on radiographs. Congenital pyloric atresia usually causes a single bubble on radiographs without distal gas, though an intermittent double bubble sign is occasionally seen. Duodenal atresia, while typically without distal gas, has been reported with an absent double bubble, though this variant is quite rare. On neonatal ultrasound, a double bubble can also be caused by a choledochal cyst, omental cyst, or enteric duplication cyst Enteric duplication cysts, sometimes simply called duplication cysts, are rare congenital malformations of the gastrointestinal tract. They most frequently occur in the small intestine, particularly the ileum, but can occur anywhere along the gastro ...
.
References
{{Radiologic signs Radiologic signs