Double Balloon Enteroscopy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Double-balloon enteroscopy, also known as push-and-pull enteroscopy, is an endoscopic technique for visualization of the small bowel. It was developed by Hironori Yamamoto in 2001. It is novel in the field of diagnostic gastroenterology as it is the first endoscopic technique that allows for the entire
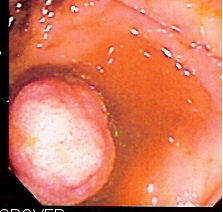 Double-balloon enteroscopy offers a number of advantages to other small bowel image techniques, including
Double-balloon enteroscopy offers a number of advantages to other small bowel image techniques, including
gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive syste ...
to be visualized in real time.
Technique
The technique involves the use of a balloon at the end of a special enteroscope camera and an overtube, which is a tube that fits over the endoscope, and which is also fitted with a balloon. The procedure is usually done under generalanesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), ...
, but may be done with the use of conscious sedation. The enteroscope and overtube are inserted through the mouth
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on ...
and passed in conventional fashion (that is, as with gastroscopy) into the small bowel. Following this, the endoscope is advanced a small distance in front of the overtube and the balloon at the end is inflated. Using the assistance of friction at the interface of the enteroscope and intestinal wall, the small bowel is accordioned back to the overtube. The overtube balloon is then deployed, and the enteroscope balloon is deflated. The process is then continued until the entire small bowel is visualized.
The double-balloon enteroscope can also be passed in retrograde fashion, through the colon and into the ileum to visualize the end of the small bowel.
Indications
Double-balloon enteroscopy has found a niche application in the following settings: * Bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract of obscure cause * Iron deficiency anemia with normalcolonoscopy
Colonoscopy () or coloscopy () is the endoscopic examination of the large bowel and the distal part of the small bowel with a CCD camera or a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube passed through the anus. It can provide a visual diagnosis (''e. ...
and gastroscopy
* Visualization and therapeutic intervention on abnormalities seen on traditional small bowel imaging
* Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) in post-surgical patients with long afferent limbs
Advantages
 Double-balloon enteroscopy offers a number of advantages to other small bowel image techniques, including
Double-balloon enteroscopy offers a number of advantages to other small bowel image techniques, including barium
Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in group 2 and is a soft, silvery alkaline earth metal. Because of its high chemical reactivity, barium is never found in nature as a free element.
Th ...
imaging, wireless capsule endoscopy
Capsule endoscopy is a medical procedure used to record internal images of the gastrointestinal tract for use in disease diagnosis. Newer developments are also able to take biopsies and release medication at specific locations of the entire ...
and push enteroscopy:
* It allows for visualization of the entire small bowel to the terminal ileum.
* It allows for the application of therapeutics.
* It allows for the sampling or biopsying of small bowel mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is ...
, for the resection of polyps of the small bowel, and in the placement of stents or dilatation
Dilation (or dilatation) may refer to:
Physiology or medicine
* Cervical dilation, the widening of the cervix in childbirth, miscarriage etc.
* Coronary dilation, or coronary reflex
* Dilation and curettage, the opening of the cervix and surgic ...
of strictures of the small bowel.
* It allows for access to the papilla in patients with long afferent limbs after Billroth II antrectomy.
Disadvantages
The key disadvantage of double-balloon enteroscopy is the time required to visualize the small bowel; this can exceed three hours, and may require that patients be admitted to hospital for the procedure. There have also been case reports of acute pancreatitis (at a rate of 0.3%-0.4%, when the oral route is used) and intestinal necrosis associated with the technique. A 2015 study in the ''World Journal of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy'' reported that: "Due to prolonged procedure and air insufflation, abdominal pain can be observed in up to 20% patients." Depending on whether the oral or rectal approach was used, a patient may experience a sore throat (following use of the oral route), upset stomach, vomiting, and painful bloating, cramping, or abdominal discomfort in reaction to the gas in the intestines.References
{{Reflist Gastroenterology Endoscopy