Dorset Cuisine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dorset ( ;
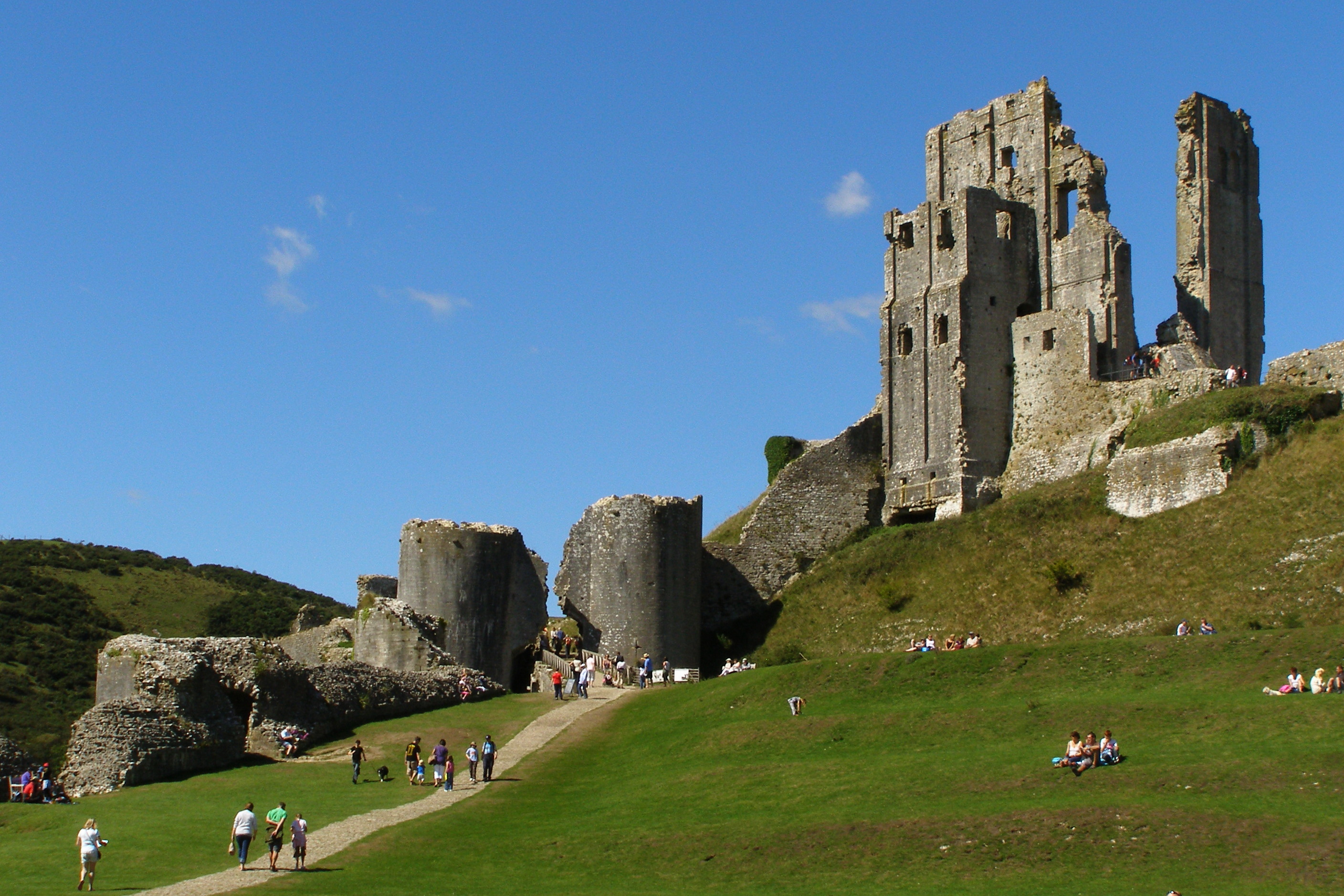 The dissolution of the monasteries (1536–1541) met little resistance in Dorset and many of the county's abbeys, including Shaftesbury, Cerne and
The dissolution of the monasteries (1536–1541) met little resistance in Dorset and many of the county's abbeys, including Shaftesbury, Cerne and
archaically
In language, an archaism (from the grc, ἀρχαϊκός, ''archaïkós'', 'old-fashioned, antiquated', ultimately , ''archaîos'', 'from the beginning, ancient') is a word, a sense of a word, or a style of speech or writing that belongs to a hi ...
: Dorsetshire , ) is a county
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
in South West England
South West England, or the South West of England, is one of nine official regions of England. It consists of the counties of Bristol, Cornwall (including the Isles of Scilly), Dorset, Devon, Gloucestershire, Somerset and Wiltshire. Cities and ...
on the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
coast. The ceremonial county
The counties and areas for the purposes of the lieutenancies, also referred to as the lieutenancy areas of England and informally known as ceremonial counties, are areas of England to which lords-lieutenant are appointed. Legally, the areas i ...
comprises the unitary authority areas of Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole and Dorset
Dorset ( ; archaically: Dorsetshire , ) is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The ceremonial county comprises the unitary authority areas of Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole and Dorset (unitary authority), Dors ...
. Covering an area of , Dorset borders Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devon is ...
to the west, Somerset
( en, All The People of Somerset)
, locator_map =
, coordinates =
, region = South West England
, established_date = Ancient
, established_by =
, preceded_by =
, origin =
, lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset
, lord_ ...
to the north-west, Wiltshire
Wiltshire (; abbreviated Wilts) is a historic and ceremonial county in South West England with an area of . It is landlocked and borders the counties of Dorset to the southwest, Somerset to the west, Hampshire to the southeast, Gloucestershire ...
to the north-east, and Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial county, ceremonial and non-metropolitan county, non-metropolitan counties of England, county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English citi ...
to the east. The county town
In the United Kingdom and Ireland, a county town is the most important town or city in a county. It is usually the location of administrative or judicial functions within a county and the place where the county's members of Parliament are elect ...
is Dorchester, in the south. After the reorganisation of local government in 1974, the county border was extended eastward to incorporate the Hampshire towns of Bournemouth and Christchurch. Around half of the population lives in the South East Dorset conurbation, while the rest of the county is largely rural with a low population density.
The county has a long history of human settlement stretching back to the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
era. The Romans conquered Dorset's indigenous Celtic tribe, and during the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
, the Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
settled the area and made Dorset a shire
Shire is a traditional term for an administrative division of land in Great Britain and some other English-speaking countries such as Australia and New Zealand. It is generally synonymous with county. It was first used in Wessex from the beginn ...
in the 7th century. The first recorded Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
raid on the British Isles occurred in Dorset during the eighth century, and the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
entered England at Melcombe Regis
Melcombe Regis is an area of Weymouth in Dorset, England.
Situated on the north shore of Weymouth Harbour and originally part of the waste of Radipole, it seems only to have developed as a significant settlement and seaport in the 13th centu ...
in 1348. Dorset has seen much civil unrest: in the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of re ...
, an uprising of vigilantes
Vigilantism () is the act of preventing, investigating and punishing perceived offenses and crimes without legal authority.
A vigilante (from Spanish, Italian and Portuguese “vigilante”, which means "sentinel" or "watcher") is a person who ...
was crushed by Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three Ki ...
's forces in a pitched battle near Shaftesbury; the doomed Monmouth Rebellion
The Monmouth Rebellion, also known as the Pitchfork Rebellion, the Revolt of the West or the West Country rebellion, was an attempt to depose James II, who in February 1685 succeeded his brother Charles II as king of England, Scotland and Ir ...
began at Lyme Regis
Lyme Regis is a town in west Dorset, England, west of Dorchester and east of Exeter. Sometimes dubbed the "Pearl of Dorset", it lies by the English Channel at the Dorset–Devon border. It has noted fossils in cliffs and beaches on the Herita ...
; and a group of farm labourers from Tolpuddle
Tolpuddle () is a village in Dorset, England, on the River Piddle from which it takes its name, east of Dorchester, the county town, and west of Poole. The estimated population in 2013 was 420.
The village was home to the Tolpuddle Martyrs, ...
were instrumental in the formation of the trade union movement
The labour movement or labor movement consists of two main wings: the trade union movement (British English) or labor union movement (American English) on the one hand, and the political labour movement on the other.
* The trade union movement ...
. During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, Dorset was heavily involved in the preparations for the invasion of Normandy
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allied operation that launched the successful invasion of German-occupied Western Europe during World War II. The operation was launched on 6 June 1944 (D-Day) with the Norm ...
, and the large harbours of Portland
Portland most commonly refers to:
* Portland, Oregon, the largest city in the state of Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States
* Portland, Maine, the largest city in the state of Maine, in the New England region of the northeas ...
and Poole
Poole () is a large coastal town and seaport in Dorset, on the south coast of England. The town is east of Dorchester and adjoins Bournemouth to the east. Since 1 April 2019, the local authority is Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole Counc ...
were two of the main embarkation points. The former was the sailing venue in the 2012 Summer Olympics
The 2012 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXX Olympiad and also known as London 2012) was an international multi-sport event held from 27 July to 12 August 2012 in London, England, United Kingdom. The first event, the ...
, and both have clubs or hire venues for sailing
Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the ''water'' (sailing ship, sailboat, raft, windsurfer, or kitesurfer), on ''ice'' (iceboat) or on ''land'' (land yacht) over a chosen cour ...
, Cornish pilot gig rowing, sea kayaking and powerboating
Power boating describes activities performed in a motorized boat. Generally, a power boat has a high power-to-weight ratio and a hull design that allows for easy planing, which allows for higher speed and improved handling. Also, the shape of ...
.
Dorset has a varied landscape featuring broad elevated chalk downs, steep limestone ridges and low-lying clay valleys. Over half the county is designated as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. Three-quarters of its coastline is part of the Jurassic Coast Natural World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
due to its geological and palaeontologic significance. It features notable landforms such as Lulworth Cove, the Isle of Portland
An isle is an island, land surrounded by water. The term is very common in British English. However, there is no clear agreement on what makes an island an isle or its difference, so they are considered synonyms.
Isle may refer to:
Geography
* Is ...
, Chesil Beach
Chesil Beach (also known as Chesil Bank) in Dorset, England is one of three major shingle beach structures in Britain.A. P. Carr and M. W. L. Blackley, "Investigations Bearing on the Age and Development of Chesil Beach, Dorset, and the Associat ...
and Durdle Door. Agriculture was traditionally the major industry of Dorset but is now in decline and tourism has become increasingly important to the economy. There are no motorways in Dorset but a network of A roads
A roads may be
*motorways or freeways, usually where the local word for motorway begins with A (for example, ''Autobahn'' in German; ''Autostrada'' in Italian).
* main roads or highways, in a system where roads are graded A, B and sometimes lower c ...
cross the county and two railway main lines connect to London. Dorset has ports at Poole, Weymouth and Portland, and an international airport
An international airport is an airport with customs and border control facilities enabling passengers to travel between countries around the world. International airports are usually larger than domestic airports and they must feature longer ...
near Bournemouth. The county has a variety of museums, theatres and festivals, and is host to the Great Dorset Steam Fair
The Great Dorset Steam Fair (abbreviated GDSF, and since 2010 also known as The National Heritage Show) is an annual show featuring steam-powered vehicles and machinery. It now covers and runs for five days. This used to be from the Wednesday ...
, one of the biggest events of its kind in Europe. It is the birthplace of Thomas Hardy
Thomas Hardy (2 June 1840 – 11 January 1928) was an English novelist and poet. A Victorian realist in the tradition of George Eliot, he was influenced both in his novels and in his poetry by Romanticism, including the poetry of William Word ...
, who used the county as the principal setting of his novels, and William Barnes
William Barnes (22 February 1801 – 7 October 1886) was an English polymath, writer, poet, philologist, priest, mathematician, engraving artist and inventor. He wrote over 800 poems, some in Dorset dialect, and much other work, including a co ...
, whose poetry celebrates the ancient Dorset dialect
The Dorset dialect is the traditional dialect spoken in Dorset, a county in the West Country of England. Stemming from Old West Saxon, it is preserved in the isolated Blackmore Vale, despite it somewhat falling into disuse throughout the earlier ...
.
Toponymy
Dorset derives its name from thecounty town
In the United Kingdom and Ireland, a county town is the most important town or city in a county. It is usually the location of administrative or judicial functions within a county and the place where the county's members of Parliament are elect ...
of Dorchester. The Romans established the settlement in the 1st century and named it Durnovaria which was a Latinised version of a Common Brittonic
Common Brittonic ( cy, Brythoneg; kw, Brythonek; br, Predeneg), also known as British, Common Brythonic, or Proto-Brittonic, was a Celtic language spoken in Britain and Brittany.
It is a form of Insular Celtic, descended from Proto-Celtic, a ...
word possibly meaning "place with fist-sized pebbles". The Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
named the town ''Dornwaraceaster'' (the suffix '' -ceaster'' being the Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
name for a "Roman town"; cf. Exeter
Exeter () is a city in Devon, South West England. It is situated on the River Exe, approximately northeast of Plymouth and southwest of Bristol.
In Roman Britain, Exeter was established as the base of Legio II Augusta under the personal comm ...
and Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean to the west, east of Monmouth and east ...
) and ''Dornsæte'' came into use as the name for the inhabitants of the area from ''Dorn'' (a reduced form of ''Dornwaraceaster'') and the Old English word ''sæte'' (meaning "people"). It is first mentioned in the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of Alf ...
'' in AD 845 and in the 10th century the county's archaic name, ''Dorseteschyre'' (Dorsetshire), was first recorded.
History
Early history
The first human visitors to Dorset wereMesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
hunters, from around 8000.Putnam (p. 15)Cullingford (p. 13) The first permanent Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
settlers appeared around 3000 BC and were responsible for the creation of the Dorset Cursus
The Dorset Cursus is a Neolithic cursus monument that spans across 10 km (6¼ miles) of the chalk downland of Cranborne Chase in east Dorset, United Kingdom. Its extreme length makes it a notable example of this class of linear earthwork; it ...
, a monument for ritual or ceremonial purposes.Putnam (p. 19)Cullingford (p. 14) From 2800 BC onwards Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
farmers cleared Dorset's woodlands for agricultural use and Dorset's high chalk hills provided a location for numerous round barrows
A round barrow is a type of tumulus and is one of the most common types of archaeological monuments. Although concentrated in Europe, they are found in many parts of the world, probably because of their simple construction and universal purpose. ...
. During the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
, the British tribe known as the Durotriges established a series of hill fort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roma ...
s across the county—most notably Maiden Castle which is one of the largest in Europe.Cullingford (pp. 16–17)
The Romans arrived in Dorset during their conquest of Britain in AD 43. Maiden Castle was captured by a Roman legion
The Roman legion ( la, legiō, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of 5,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) and of 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period of ...
under the command of Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Empi ...
, and the Roman settlement of Durnovaria was established nearby. Bokerley Dyke, a large defensive ditch built by the county's post-Roman inhabitants near the border with modern-day Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial county, ceremonial and non-metropolitan county, non-metropolitan counties of England, county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English citi ...
, delayed the advance of the Saxons into Dorset for almost 150 years. It appears to have been re-fortified during this period, with the former Roman Road at Ackling Dyke
Ackling Dyke is a section of Roman road in England which runs for southwest from Old Sarum (''Sorviodunum'') to the hill fort at Badbury Rings (''Vindocladia''). Part of the road on Oakley Down has been scheduled as an ancient monument.
Much ...
also being blocked by the Britons, apparently to prevent the West Saxon advance into Dorset.
However, by the end of the 7th century, Dorset had fallen under Saxon control and been incorporated into the Kingdom of Wessex.Draper (p. 142) The precise details of this West Saxon conquest and how it took place are not clear, but it appears to have substantially taken place by the start of the reign of Caedwalla in 685. The Saxons established a diocese
In Ecclesiastical polity, church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided Roman province, pro ...
at Sherborne and Dorset was made a shire
Shire is a traditional term for an administrative division of land in Great Britain and some other English-speaking countries such as Australia and New Zealand. It is generally synonymous with county. It was first used in Wessex from the beginn ...
—an administrative district of Wessex and predecessor to the English county
The counties of England are areas used for different purposes, which include administrative, geographical, cultural and political demarcation. The term "county" is defined in several ways and can apply to similar or the same areas used by each ...
system—with borders that have changed little since. In 789 the first recorded Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
attack on the British Isles took place in Dorset on the Portland coast, and they continued to raid into the county for the next two centuries.
After the Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conque ...
in 1066, feudal
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in Middle Ages, medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a wa ...
rule was established in Dorset and the bulk of the land was divided between the Crown and ecclesiastical institutions. The Normans consolidated their control over the area by constructing castles at Corfe, Wareham and Dorchester in the early part of the 12th century. Over the next 200 years Dorset's population grew substantially and additional land was enclosed for farming to provide the extra food required.Cullingford (p. 52) The wool trade, the quarrying of Purbeck Marble
Purbeck Marble is a fossiliferous limestone found in the Isle of Purbeck, a peninsula in south-east Dorset, England. It is a variety of Purbeck stone that has been quarried since at least Roman times as a decorative building stone.
Geology
Strat ...
and the busy ports of Weymouth, Melcombe Regis
Melcombe Regis is an area of Weymouth in Dorset, England.
Situated on the north shore of Weymouth Harbour and originally part of the waste of Radipole, it seems only to have developed as a significant settlement and seaport in the 13th centu ...
, Lyme Regis
Lyme Regis is a town in west Dorset, England, west of Dorchester and east of Exeter. Sometimes dubbed the "Pearl of Dorset", it lies by the English Channel at the Dorset–Devon border. It has noted fossils in cliffs and beaches on the Herita ...
and Bridport brought prosperity to the county. However, Dorset was devastated by the bubonic plague in 1348 which arrived in Melcombe Regis on a ship from Gascony
Gascony (; french: Gascogne ; oc, Gasconha ; eu, Gaskoinia) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part o ...
. The disease, more commonly known as the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
, created an epidemic that spread rapidly and wiped out a third of the population of the country. Dorset came under the political influence of a number of different nobles during the Middle Ages. During the Wars of the Roses, for instance, Dorset came into the area influenced by Humphrey Stafford, earl of Devon
Sir Humphrey Stafford, 1st Earl of Devon, 1st Baron Stafford of Southwick (''ca.'' 143917 August 1469)Michael Hicks, ‘Stafford, Humphrey, earl of Devon (c.1439–1469)’, ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, ...
(originally of Hooke Hooke may refer to:
* Hooke, Dorset, England
** River Hooke, nearby watercourse
* Robert Hooke (1635–1703), English natural philosopher who discovered Hooke's law
* Hooke (surname), a surname
* Hooke (lunar crater)
* Hooke (Martian crater)
* ...
, Dorset) whose wider influence stretched from Cornwall to Wiltshire. After 1485, one of the most influential Dorset figures was Henry VII's chamberlain Giles Daubeney.
Modern history
 The dissolution of the monasteries (1536–1541) met little resistance in Dorset and many of the county's abbeys, including Shaftesbury, Cerne and
The dissolution of the monasteries (1536–1541) met little resistance in Dorset and many of the county's abbeys, including Shaftesbury, Cerne and Milton
Milton may refer to:
Names
* Milton (surname), a surname (and list of people with that surname)
** John Milton (1608–1674), English poet
* Milton (given name)
** Milton Friedman (1912–2006), Nobel laureate in Economics, author of '' Free t ...
, were sold to private owners. In 1642, at the commencement of the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of re ...
, the Royalists took control of the entire county apart from Poole and Lyme Regis. However, within three years their gains had been almost entirely reversed by the Parliamentarians. An uprising of Clubmen—vigilantes weary of the depredations of the war—took place in Dorset in 1645. Some 2,000 of these rebels offered battle to Lord Fairfax's Parliamentary army at Hambledon Hill
Hambledon Hill is a prehistoric hill fort in Dorset, England, situated in the Blackmore Vale five miles northwest of Blandford Forum. The hill itself is a chalk outcrop, on the southwestern corner of Cranborne Chase, separated from the Dorset ...
but they were easily routed.Cullingford (pp. 70–71) Sherborne Castle
Sherborne Castle is a 16th-century Tudor mansion southeast of Sherborne in Dorset, England, within the parish of Castleton. It stands in a park which formed a small part of the Digby estate.
Old castle
Sherborne Old Castle () is the ruin ...
was taken by Fairfax that same year and in 1646 Corfe Castle, the last remaining Royalist stronghold in Dorset, was captured after an act of betrayal: both were subsequently slighted
Slighting is the deliberate damage of high-status buildings to reduce their value as military, administrative or social structures. This destruction of property sometimes extended to the contents of buildings and the surrounding landscape. It is ...
. The Duke of Monmouth's unsuccessful attempt to overthrow James II began when he landed at Lyme Regis in 1685. A series of trials known as the Bloody Assizes
The Bloody Assizes were a series of trials started at Winchester on 25 August 1685 in the aftermath of the Battle of Sedgemoor, which ended the Monmouth Rebellion in England.
History
There were five judges: Sir William Montague (Lord Chief Bar ...
took place to punish the rebels. Over a five-day period in Dorchester, Judge Jeffreys presided over 312 cases: 74 of the accused were executed, 175 were transported
''Transported'' is an Australian convict melodrama film directed by W. J. Lincoln. It is considered a lost film.
Plot
In England, Jessie Grey is about to marry Leonard Lincoln but the evil Harold Hawk tries to force her to marry him and she wou ...
, and nine were publicly whipped. In 1686, at Charborough Park
Charborough House, also known as Charborough Park, is a Grade I listed building, the manor house of the ancient manor of Charborough. The house is between the villages of Sturminster Marshall and Bere Regis in Dorset, England.
The grounds, whic ...
, a meeting took place to plot the downfall of James II of England
James VII and II (14 October 1633 16 September 1701) was King of England and King of Ireland as James II, and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II, on 6 February 1685. He was deposed in the Gloriou ...
. This meeting was effectively the start of the Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and ...
.
During the 18th century, much smuggling
Smuggling is the illegal transportation of objects, substances, information or people, such as out of a house or buildings, into a prison, or across an international border, in violation of applicable laws or other regulations.
There are various ...
took place along the Dorset coast; its coves, caves and sandy beaches provided opportunities for gangs such as the Hawkhursts to stealthily bring smuggled goods ashore. Poole became Dorset's busiest port and established prosperous trade links with the fisheries of Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
which supported cloth, rope and net manufacturing industries in the surrounding towns and villages. However, the industrial revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
largely bypassed Dorset which lacked coal resources and as a consequence the county remained predominantly agricultural.Cullingford (p. 105)Draper (p. 143) Farming has always been central to the economy of Dorset and the county became the birthplace of the modern trade union movement
The labour movement or labor movement consists of two main wings: the trade union movement (British English) or labor union movement (American English) on the one hand, and the political labour movement on the other.
* The trade union movement ...
when, in 1834, six farm labourers formed a union to protest against falling wages. The labourers, who are now known as the Tolpuddle Martyrs, were subsequently arrested for administering "unlawful oaths" and sentenced to transportation but they were pardoned following massive protests by the working classes.
The Dorsetshire Regiment
The Dorset Regiment was a line infantry regiment of the British Army in existence from 1881 to 1958, being the county regiment of Dorset. Until 1951, it was formally called the Dorsetshire Regiment, although usually known as "The Dorsets". In 19 ...
were the first British unit to face a gas attack during the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
(1914–1918) and they sustained particularly heavy losses at the Battle of the Somme
The Battle of the Somme ( French: Bataille de la Somme), also known as the Somme offensive, was a battle of the First World War fought by the armies of the British Empire and French Third Republic against the German Empire. It took place bet ...
. In total some 4,500 Dorset servicemen died in the war and of the county's towns and villages, only one, Langton Herring, known as a Thankful Village
Thankful Villages (also known as Blessed Villages; ) are settlements in England and Wales from which all their members of the armed forces survived World War I. The term Thankful Village was popularised by the writer Arthur Mee in the 1930s; in '' ...
, had no residents killed. During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
(1939–1945) Dorset was heavily involved in the preparations for the invasion of Normandy
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allied operation that launched the successful invasion of German-occupied Western Europe during World War II. The operation was launched on 6 June 1944 (D-Day) with the Norm ...
: beach landing exercises were carried out at Studland
Studland is a village and civil parish on the Isle of Purbeck in Dorset, England. The village is located about north of the town of Swanage, over a steep chalk ridge, and south of the South East Dorset conurbation at Sandbanks, from which it is ...
and Weymouth and the village of Tyneham was requisitioned for army training. Tens-of-thousands of troops departed Weymouth, Portland and Poole harbours during D-Day
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on Tuesday, 6 June 1944 of the Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during World War II. Codenamed Operation Neptune and often referred to as D ...
and gliders from RAF Tarrant Rushton dropped troops near Caen
Caen (, ; nrf, Kaem) is a commune in northwestern France. It is the prefecture of the department of Calvados. The city proper has 105,512 inhabitants (), while its functional urban area has 470,000,Operation Tonga. Dorset experienced an increase in holiday-makers after the war. First popularised as a tourist destination by George III's frequent visits to Weymouth, the county's coastline, seaside resorts and its sparsely populated rural areas attract millions of visitors each year. With farming declining across the country, tourism has edged ahead as the primary revenue-earning sector.
 Dorset has a number of limestone ridges which are mostly covered in either arable fields or calcareous grassland supporting sheep.Cullingford (p. 91) These limestone areas include a wide band of Cretaceous chalk which crosses the county as a range of hills from north-east to south-west, incorporating Cranborne Chase and the Dorset Downs, and a narrow band running from south-west to south-east, incorporating the Purbeck Hills.Chaffey (p. 43)Chaffey (p. 11) Between the chalk hills are large, wide River valley, vales and wide flood plains. These vales are dotted with small villages, farms and coppices, and include the Blackmore Vale (River Stour, Dorset, Stour valley) and River Frome, Dorset, Frome valley. The Blackmore Vale is composed of older Jurassic deposits, largely clays interspersed with limestones, and has traditionally been a centre for dairy agriculture. South-east Dorset, including the lower Frome valley and around Poole and Bournemouth, comprises younger Eocene deposits, mainly sands and clays of poor agricultural quality. The soils created from these deposits support a heathland habitat which sustains all six native List of reptiles of Great Britain, British reptile species. Most of the Dorset heathland has SSSI, Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) status with three areas designated as internationally important Ramsar Convention, Ramsar sites. In the far west of the county and along the coast there are frequent changes in rock strata, which appear in a less obviously sequential way compared to the landscapes of the chalk and the heath. In the west this results in a hilly landscape of diverse character that resembles that of neighbouring county
Dorset has a number of limestone ridges which are mostly covered in either arable fields or calcareous grassland supporting sheep.Cullingford (p. 91) These limestone areas include a wide band of Cretaceous chalk which crosses the county as a range of hills from north-east to south-west, incorporating Cranborne Chase and the Dorset Downs, and a narrow band running from south-west to south-east, incorporating the Purbeck Hills.Chaffey (p. 43)Chaffey (p. 11) Between the chalk hills are large, wide River valley, vales and wide flood plains. These vales are dotted with small villages, farms and coppices, and include the Blackmore Vale (River Stour, Dorset, Stour valley) and River Frome, Dorset, Frome valley. The Blackmore Vale is composed of older Jurassic deposits, largely clays interspersed with limestones, and has traditionally been a centre for dairy agriculture. South-east Dorset, including the lower Frome valley and around Poole and Bournemouth, comprises younger Eocene deposits, mainly sands and clays of poor agricultural quality. The soils created from these deposits support a heathland habitat which sustains all six native List of reptiles of Great Britain, British reptile species. Most of the Dorset heathland has SSSI, Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) status with three areas designated as internationally important Ramsar Convention, Ramsar sites. In the far west of the county and along the coast there are frequent changes in rock strata, which appear in a less obviously sequential way compared to the landscapes of the chalk and the heath. In the west this results in a hilly landscape of diverse character that resembles that of neighbouring county  Most of Dorset's coastline is part of the Jurassic Coast, a
Most of Dorset's coastline is part of the Jurassic Coast, a
 Tourism has grown in Dorset since the late 18th century and is now the predominant industry. It is estimated that 37,500 people work in Dorset's tourism sector. Some 3.2 million British and 326,000 foreign tourists visited the county in 2008, staying a total of 15.1 million nights. In addition there were 14.6 million day visitors. The combined spending of both groups was £1,458 million. Towns received 56% of Dorset's day trippers, 27% went to the coast and 17% to the countryside. A survey carried out in 1997 concluded that the primary reason tourists were drawn to Dorset was the attractiveness of the county's coast and countryside. Numbers of domestic and foreign tourists have fluctuated in recent years due to various factors including security and economic downturn, a trend reflected throughout the UK.
Manufacturing industry in Dorset provided 10.3% of employment in 2008. This was slightly above the average for Great Britain but below that of the South West region which was at 10.7% for that period. The sector is the county's fourth largest employer, but a predicted decline suggests there will be 10,200 fewer jobs in manufacturing by 2026.
Tourism has grown in Dorset since the late 18th century and is now the predominant industry. It is estimated that 37,500 people work in Dorset's tourism sector. Some 3.2 million British and 326,000 foreign tourists visited the county in 2008, staying a total of 15.1 million nights. In addition there were 14.6 million day visitors. The combined spending of both groups was £1,458 million. Towns received 56% of Dorset's day trippers, 27% went to the coast and 17% to the countryside. A survey carried out in 1997 concluded that the primary reason tourists were drawn to Dorset was the attractiveness of the county's coast and countryside. Numbers of domestic and foreign tourists have fluctuated in recent years due to various factors including security and economic downturn, a trend reflected throughout the UK.
Manufacturing industry in Dorset provided 10.3% of employment in 2008. This was slightly above the average for Great Britain but below that of the South West region which was at 10.7% for that period. The sector is the county's fourth largest employer, but a predicted decline suggests there will be 10,200 fewer jobs in manufacturing by 2026.
 As a largely rural county, Dorset has fewer major cultural institutions than larger or more densely populated areas. Major venues for concerts and theatre include Poole's The Lighthouse (Poole), Lighthouse arts centre, Bournemouth's Bournemouth International Centre, BIC, Pavilion Theatre (Bournemouth), Pavilion Theatre and O2 Academy Bournemouth, O2 Academy, and the Weymouth Pavilion, Pavilion theatre in Weymouth. One of Dorset's most noted cultural institutions is the Bournemouth Symphony Orchestra which was founded in 1893. Based in Poole, the orchestra performs over 130 concerts across southern England each year.
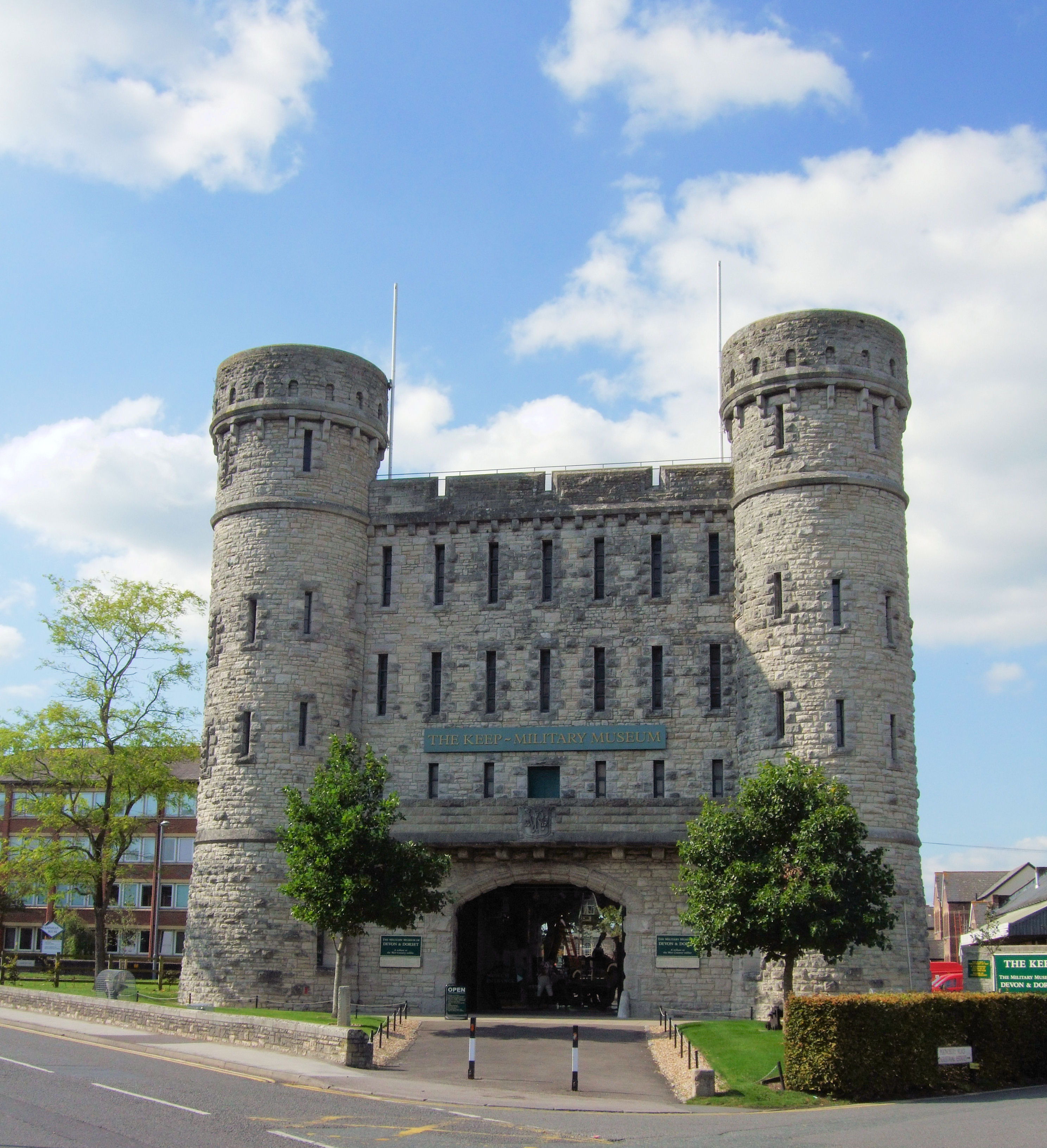
Dorset has more than 30 general and specialist museums. The Dorset County Museum in Dorchester was founded in 1846 and contains an extensive collection of exhibits covering the county's history and environment. The Tank Museum at Bovington contains more than 300 tanks and armoured vehicles from 30 nations. The museum is the largest in Dorset and its collection has been Designation Scheme, designated of national importance. Other museums which reflect the cultural heritage of the county include The Keep, Dorchester, The Keep Military Museum in Dorchester, the Russell-Cotes Museum in Bournemouth, the Charmouth Heritage Coast Centre, Poole Museum, Portland Museum, Dorset, Portland Museum and Wareham Town Museum.
Dorset contains 190 conservation area (United Kingdom), conservation areas, more than 1,500 scheduled monuments, over 30 registered parks and gardens and 12,850 listed buildings. Grade I listed buildings include: Portland Castle, a coastal fort commissioned by Henry VIII; a castle with more than a 1,000 years of history at Corfe Castle (village), Corfe; a Roman Town House, Dorchester, Roman ruin described by Historic England as the "only Roman town house visible in Britain"; Athelhampton, a Tudor dynasty, Tudor manor house; Forde Abbey, a stately home and former Cistercian monastery; Christchurch Priory, the longest church in England; and St Edwold's Church, Stockwood, St Edwold's church, one of the smallest.
As a largely rural county, Dorset has fewer major cultural institutions than larger or more densely populated areas. Major venues for concerts and theatre include Poole's The Lighthouse (Poole), Lighthouse arts centre, Bournemouth's Bournemouth International Centre, BIC, Pavilion Theatre (Bournemouth), Pavilion Theatre and O2 Academy Bournemouth, O2 Academy, and the Weymouth Pavilion, Pavilion theatre in Weymouth. One of Dorset's most noted cultural institutions is the Bournemouth Symphony Orchestra which was founded in 1893. Based in Poole, the orchestra performs over 130 concerts across southern England each year.
Dorset has more than 30 general and specialist museums. The Dorset County Museum in Dorchester was founded in 1846 and contains an extensive collection of exhibits covering the county's history and environment. The Tank Museum at Bovington contains more than 300 tanks and armoured vehicles from 30 nations. The museum is the largest in Dorset and its collection has been Designation Scheme, designated of national importance. Other museums which reflect the cultural heritage of the county include The Keep, Dorchester, The Keep Military Museum in Dorchester, the Russell-Cotes Museum in Bournemouth, the Charmouth Heritage Coast Centre, Poole Museum, Portland Museum, Dorset, Portland Museum and Wareham Town Museum.
Dorset contains 190 conservation area (United Kingdom), conservation areas, more than 1,500 scheduled monuments, over 30 registered parks and gardens and 12,850 listed buildings. Grade I listed buildings include: Portland Castle, a coastal fort commissioned by Henry VIII; a castle with more than a 1,000 years of history at Corfe Castle (village), Corfe; a Roman Town House, Dorchester, Roman ruin described by Historic England as the "only Roman town house visible in Britain"; Athelhampton, a Tudor dynasty, Tudor manor house; Forde Abbey, a stately home and former Cistercian monastery; Christchurch Priory, the longest church in England; and St Edwold's Church, Stockwood, St Edwold's church, one of the smallest.
 Dorset hosts a number of annual festivals, fairs and events including the
Dorset hosts a number of annual festivals, fairs and events including the 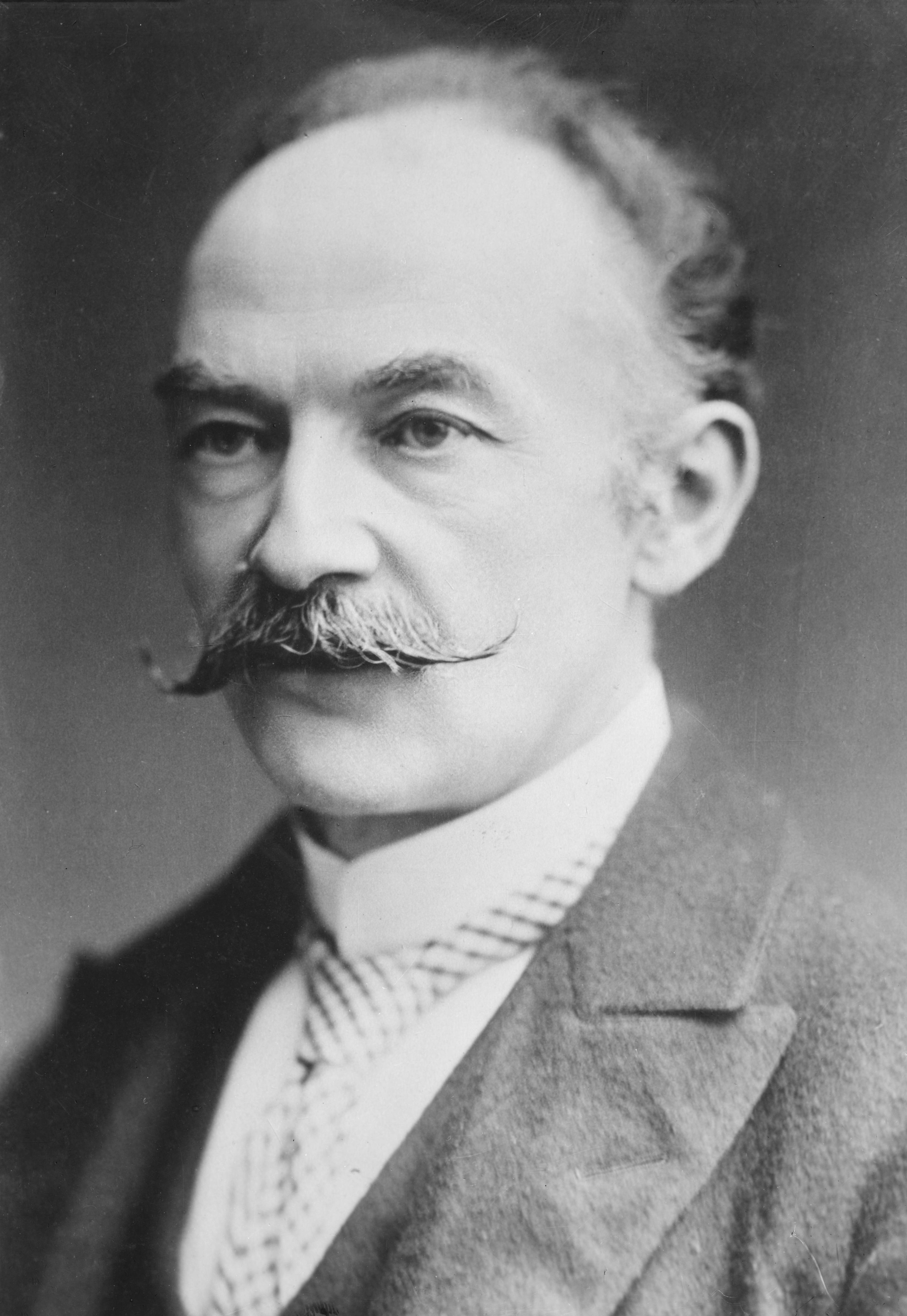 Dorset is famed in literature for being the native county of author and poet
Dorset is famed in literature for being the native county of author and poet
 Unlike all of its neighbouring counties, Dorset does not have a cathedral. Over 95% of the county falls within the Church of England Diocese of Salisbury. A small section to the west comes under the Diocese of Bath and Wells and to the east Christchurch and much of Bournemouth—both historically part of Hampshire—belong to the Diocese of Winchester. The Roman Catholic Diocese of Plymouth incorporates most of Dorset with the exception of Christchurch and a portion of Bournemouth which belongs to the Roman Catholic Diocese of Portsmouth, Diocese of Portsmouth. Few purpose-built places of worship exist in Dorset for faiths other than Christianity. In 2008 a Hindu temple was constructed in Blandford Forum for the Queen's Gurkha Signals, Gurkhas based at the town's military camp. Bournemouth, which contains a higher proportion of Jewish residents than the national average, has three synagogues besides an Islamic Centre and a mosque for Muslims.
Christianity was introduced to Dorset by the Romans. A 4th century Hinton St Mary Mosaic, Roman mosaic discovered near Hinton St Mary contains what is generally accepted to be an image of Christ. Christianity became firmly established in the county during the Saxon period although there are few surviving Saxon churches; the most complete is St Martin's Church, Wareham, St. Martin's in Wareham which has features from the early 11th century. Mediaeval churches are more prevalent in Dorset; most are 15th century and are of a Perpendicular Gothic, Perpendicular style. Sherborne Abbey, one of the county's largest, is noted for its broad fan vaulting added during an extensive 15th century rebuild. Founded in AD 705 by Aldhelm, the Abbey contained the Cathedra, chair of the Bishop of Sherborne and was granted cathedral status until 1075 when the diocese was transferred to Old Sarum. Wimborne Minster (church), Wimborne Minster features a chained library and a 14th-century astronomical clock; Christchurch Priory is renowned for its Christchurch Priory#Miraculous beam, miraculous beam which, according to legend, was installed by Christ; and the 15th century roof spanning the nave at St John the Baptist Church in Bere Regis is described by architectural historian Nikolaus Pevsner as the "finest timber roof of Dorset". Church of St Candida and Holy Cross, St Candida and Holy Cross at Whitchurch Canonicorum is the only church in the country, besides Westminster Abbey, to have a shrine that contains the relics of a saint.
Monastic foundations were once abundant in Dorset, but all ceased to exist at the Dissolution of the monasteries. The English Reformation, Reformation and the political and religious turmoil that ensued largely checked the building of new churches until the turn of the 18th century.Draper (p. 82) Notable examples of Georgian architecture, Early Georgian churches include the Bastard brothers' Church of St. Peter and St. Paul in Blandford Forum, and St George's Church, Portland, St George's Church on the Isle of Portland, which has a steeple and tower inspired by the works of Christopher Wren. From the late 18th century onwards, churches in Dorset tended towards a Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic Revival style. A notable exception to this trend, however, is the Church of St Mary in East Lulworth—the first freestanding Roman Catholic church built in England after the Reformation.Lehane (p. 59) George III gave permission to erect the building on the condition that it resembled a garden mausoleum rather than a church. It was completed in 1789. Bournemouth, founded in 1810, has a wealth of 19th-century churches including St Peter's Church, Bournemouth, St Peter's and St Stephen's Church, Bournemouth, St Stephen's. St Dunstan's Church (formerly St Osmund's) in Poole is one of a small number of 20th-century churches in Dorset. The final major work of Edward Schroeder Prior, it is one of the last examples of the Byzantine Revival architecture, Neo Byzantine style. The Church of St Nicholas and St Magnus in Moreton, Dorset, Moreton is noted for its elaborate engraved glass windows designed by Laurence Whistler. Severely damaged by a stray German bomb in 1940, the church subsequently underwent extensive renovation and Whistler had replaced every window by 1984.
Unlike all of its neighbouring counties, Dorset does not have a cathedral. Over 95% of the county falls within the Church of England Diocese of Salisbury. A small section to the west comes under the Diocese of Bath and Wells and to the east Christchurch and much of Bournemouth—both historically part of Hampshire—belong to the Diocese of Winchester. The Roman Catholic Diocese of Plymouth incorporates most of Dorset with the exception of Christchurch and a portion of Bournemouth which belongs to the Roman Catholic Diocese of Portsmouth, Diocese of Portsmouth. Few purpose-built places of worship exist in Dorset for faiths other than Christianity. In 2008 a Hindu temple was constructed in Blandford Forum for the Queen's Gurkha Signals, Gurkhas based at the town's military camp. Bournemouth, which contains a higher proportion of Jewish residents than the national average, has three synagogues besides an Islamic Centre and a mosque for Muslims.
Christianity was introduced to Dorset by the Romans. A 4th century Hinton St Mary Mosaic, Roman mosaic discovered near Hinton St Mary contains what is generally accepted to be an image of Christ. Christianity became firmly established in the county during the Saxon period although there are few surviving Saxon churches; the most complete is St Martin's Church, Wareham, St. Martin's in Wareham which has features from the early 11th century. Mediaeval churches are more prevalent in Dorset; most are 15th century and are of a Perpendicular Gothic, Perpendicular style. Sherborne Abbey, one of the county's largest, is noted for its broad fan vaulting added during an extensive 15th century rebuild. Founded in AD 705 by Aldhelm, the Abbey contained the Cathedra, chair of the Bishop of Sherborne and was granted cathedral status until 1075 when the diocese was transferred to Old Sarum. Wimborne Minster (church), Wimborne Minster features a chained library and a 14th-century astronomical clock; Christchurch Priory is renowned for its Christchurch Priory#Miraculous beam, miraculous beam which, according to legend, was installed by Christ; and the 15th century roof spanning the nave at St John the Baptist Church in Bere Regis is described by architectural historian Nikolaus Pevsner as the "finest timber roof of Dorset". Church of St Candida and Holy Cross, St Candida and Holy Cross at Whitchurch Canonicorum is the only church in the country, besides Westminster Abbey, to have a shrine that contains the relics of a saint.
Monastic foundations were once abundant in Dorset, but all ceased to exist at the Dissolution of the monasteries. The English Reformation, Reformation and the political and religious turmoil that ensued largely checked the building of new churches until the turn of the 18th century.Draper (p. 82) Notable examples of Georgian architecture, Early Georgian churches include the Bastard brothers' Church of St. Peter and St. Paul in Blandford Forum, and St George's Church, Portland, St George's Church on the Isle of Portland, which has a steeple and tower inspired by the works of Christopher Wren. From the late 18th century onwards, churches in Dorset tended towards a Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic Revival style. A notable exception to this trend, however, is the Church of St Mary in East Lulworth—the first freestanding Roman Catholic church built in England after the Reformation.Lehane (p. 59) George III gave permission to erect the building on the condition that it resembled a garden mausoleum rather than a church. It was completed in 1789. Bournemouth, founded in 1810, has a wealth of 19th-century churches including St Peter's Church, Bournemouth, St Peter's and St Stephen's Church, Bournemouth, St Stephen's. St Dunstan's Church (formerly St Osmund's) in Poole is one of a small number of 20th-century churches in Dorset. The final major work of Edward Schroeder Prior, it is one of the last examples of the Byzantine Revival architecture, Neo Byzantine style. The Church of St Nicholas and St Magnus in Moreton, Dorset, Moreton is noted for its elaborate engraved glass windows designed by Laurence Whistler. Severely damaged by a stray German bomb in 1940, the church subsequently underwent extensive renovation and Whistler had replaced every window by 1984.
Dorset County Museum
Images of Dorset
at the English Heritage Archive
Dorset AONB
{{Authority control Dorset, Non-metropolitan counties Counties of England established in antiquity Counties in South West England
Settlements
Dorset is largely rural with many small villages, few large towns and no cities. The only major urban area is the South East Dorset conurbation, which is situated at the south-eastern end of the county and is atypical of the county as a whole. It consists of theseaside resort
A seaside resort is a resort town, town, village, or hotel that serves as a Resort, vacation resort and is located on a coast. Sometimes the concept includes an aspect of official accreditation based on the satisfaction of certain requirements, suc ...
of Bournemouth, the historic port and borough
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle Ag ...
of Poole, the towns of Christchurch and Ferndown plus many surrounding villages. Bournemouth, the most populous town in the conurbation, was established in the Georgian era when sea bathing became popular. Poole, the second largest settlement (once the largest town in the county), adjoins Bournemouth to the west and contains the suburb of Sandbanks which has some of the highest land values by area in the world.
The other two major settlements in the county are Dorchester, which has been the county town since at least 1305, and Weymouth, a major seaside resort since the 18th century. Blandford Forum, Sherborne, Gillingham, Dorset, Gillingham, Shaftesbury and Sturminster Newton are historic market towns which serve the farms and villages of the Blackmore Vale in north Dorset. Beaminster and Bridport are situated in the west of the county; Verwood and the historic Saxon market towns of Wareham, Dorset, Wareham and Wimborne Minster are located to the east. Lyme Regis and Swanage are small coastal towns popular with tourists. Under construction on the western edge of Dorchester is the experimental new town of Poundbury commissioned and co-designed by Charles III of the United Kingdom, Prince Charles. The suburb, which is expected to be fully completed by 2025, was designed to integrate residential and retail buildings and counter the growth of dormitory towns and car-oriented development.
Physical geography
Dorset covers an area of and contains considerable variety in its underlying geology, which is partly responsible for the diversity of landscape.Draper (p. 136) A large percentage (66%) of the county comprises either chalk, clay or mixed sand and gravels. The remainder is less straightforward and includes Portland stone, Portland and Purbeck Group, Purbeck stone, other limestones, calcareous clays and shales. Draper (pp. 136–137) Portland and Purbeck stone are of national importance as a building material and for restoring some of Britain's most famous landmarks. Almost every type of rock known from the Early Jurassic to the Eocene epochs can be found in the county. Dorset has a number of limestone ridges which are mostly covered in either arable fields or calcareous grassland supporting sheep.Cullingford (p. 91) These limestone areas include a wide band of Cretaceous chalk which crosses the county as a range of hills from north-east to south-west, incorporating Cranborne Chase and the Dorset Downs, and a narrow band running from south-west to south-east, incorporating the Purbeck Hills.Chaffey (p. 43)Chaffey (p. 11) Between the chalk hills are large, wide River valley, vales and wide flood plains. These vales are dotted with small villages, farms and coppices, and include the Blackmore Vale (River Stour, Dorset, Stour valley) and River Frome, Dorset, Frome valley. The Blackmore Vale is composed of older Jurassic deposits, largely clays interspersed with limestones, and has traditionally been a centre for dairy agriculture. South-east Dorset, including the lower Frome valley and around Poole and Bournemouth, comprises younger Eocene deposits, mainly sands and clays of poor agricultural quality. The soils created from these deposits support a heathland habitat which sustains all six native List of reptiles of Great Britain, British reptile species. Most of the Dorset heathland has SSSI, Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) status with three areas designated as internationally important Ramsar Convention, Ramsar sites. In the far west of the county and along the coast there are frequent changes in rock strata, which appear in a less obviously sequential way compared to the landscapes of the chalk and the heath. In the west this results in a hilly landscape of diverse character that resembles that of neighbouring county
Dorset has a number of limestone ridges which are mostly covered in either arable fields or calcareous grassland supporting sheep.Cullingford (p. 91) These limestone areas include a wide band of Cretaceous chalk which crosses the county as a range of hills from north-east to south-west, incorporating Cranborne Chase and the Dorset Downs, and a narrow band running from south-west to south-east, incorporating the Purbeck Hills.Chaffey (p. 43)Chaffey (p. 11) Between the chalk hills are large, wide River valley, vales and wide flood plains. These vales are dotted with small villages, farms and coppices, and include the Blackmore Vale (River Stour, Dorset, Stour valley) and River Frome, Dorset, Frome valley. The Blackmore Vale is composed of older Jurassic deposits, largely clays interspersed with limestones, and has traditionally been a centre for dairy agriculture. South-east Dorset, including the lower Frome valley and around Poole and Bournemouth, comprises younger Eocene deposits, mainly sands and clays of poor agricultural quality. The soils created from these deposits support a heathland habitat which sustains all six native List of reptiles of Great Britain, British reptile species. Most of the Dorset heathland has SSSI, Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) status with three areas designated as internationally important Ramsar Convention, Ramsar sites. In the far west of the county and along the coast there are frequent changes in rock strata, which appear in a less obviously sequential way compared to the landscapes of the chalk and the heath. In the west this results in a hilly landscape of diverse character that resembles that of neighbouring county Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devon is ...
. Marshwood Vale, a valley of Lower Lias clay at the western tip of the county, lies to the south of the two highest points in Dorset: Lewesdon Hill at and Pilsdon Pen at .
A former river valley flooded by rising sea levels 6,000 years ago, Poole Harbour is one of the largest natural harbours in the world.
The harbour is very shallow in places and contains a number of islands, notably Brownsea Island, the birthplace of the Scouting movement and one of the few remaining sanctuaries for indigenous red squirrels in England. The harbour, and the chalk and limestone hills of the Isle of Purbeck to the south, lie atop Western Europe's largest onshore oil field. The field, operated by Perenco from Wytch Farm, has the world's oldest continuously pumping well at Kimmeridge Oil Field, Kimmeridge which has been producing oil since the early 1960s.Cullingford (p. 122)
Dorset's diverse geography ensures it has an assortment of rivers, although a moderate annual rainfall coupled with rolling hills, means most are typically lowland in nature.Wright (p. 7) Much of the county drains into three rivers, the Frome, River Piddle, Piddle and Stour which all flow to the sea in a south-easterly direction. The Frome and Piddle are chalk streams but the Stour, which rises in Wiltshire to the north, has its origins in clay soil. The Hampshire Avon, River Avon, which flows mainly through Wiltshire and Hampshire, enters Dorset towards the end of its journey at Christchurch Harbour. The rivers River Axe (Lyme Bay), Axe and River Yeo (South Somerset), Yeo, which principally drain the counties of Devon and Somerset
( en, All The People of Somerset)
, locator_map =
, coordinates =
, region = South West England
, established_date = Ancient
, established_by =
, preceded_by =
, origin =
, lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset
, lord_ ...
respectively, have their sources in the north-west of the county. In the south-west, a number of small rivers run into the sea along the Dorset coastline; most notable of these are the River Char, Char, River Brit, Brit, River Bride, Dorset, Bride and River Wey, Dorset, Wey.Wright (pp. 6, 17)
 Most of Dorset's coastline is part of the Jurassic Coast, a
Most of Dorset's coastline is part of the Jurassic Coast, a World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
, which stretches for between Studland and Exmouth in Devon. This coast documents the entire Mesozoic era, from Triassic to Cretaceous, and is noted for its geological landforms. The Dorset section has yielded important fossils, including Petrified wood, Jurassic trees and the first complete Ichthyosaur, discovered near Lyme Regis in 1811 by Mary Anning. The county features some notable coastal landforms, including examples of a cove ( Lulworth Cove), a natural arch ( Durdle Door) and chalk Stack (geology), stacks (Old Harry Rocks). Jutting out into the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
at roughly the midpoint of the Dorset coastline is the Isle of Portland
An isle is an island, land surrounded by water. The term is very common in British English. However, there is no clear agreement on what makes an island an isle or its difference, so they are considered synonyms.
Isle may refer to:
Geography
* Is ...
, a limestone island that is connected to the mainland by Chesil Beach
Chesil Beach (also known as Chesil Bank) in Dorset, England is one of three major shingle beach structures in Britain.A. P. Carr and M. W. L. Blackley, "Investigations Bearing on the Age and Development of Chesil Beach, Dorset, and the Associat ...
, a long Shingle beach, shingle Shoal, barrier beach protecting Chesil Beach#The Fleet Lagoon, Britain's largest tidal lagoon.
The county has one of the highest proportions of conservation areas in England—and two AONB, Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB) covering 53% of the administrative county. It has two Heritage Coasts totalling and Sites of Special Scientific Interest covering . The South West Coast Path, National Trail, begins at South Haven Point at the entrance to Poole Harbour. There are also substantial areas of Green belt (United Kingdom), green belt surrounding the South East Dorset conurbation, filling in the area between this and the Cranborne Chase and the West Wiltshire Downs AONB.
Climate
Dorset's climate of warm summers and mild winters is partly due to its position on Britain's south coast. The third most southerly county in the UK, Dorset is less affected by the more intense Atlantic winds than Cornwall and Devon. Dorset, along with the entire South West England, south-west, has higher winter temperatures, average , than the rest of the United Kingdom. However, Dorset maintains higher summer temperatures than Devon and Cornwall, with average highs of . Excluding hills such as the Dorset Downs, the average annual temperature of the county is . The south coast counties of Dorset, Hampshire, West Sussex, East Sussex and Kent enjoy more sunshine than anywhere else in the United Kingdom, receiving 1,541–1,885 hours a year. Average annual rainfall varies across the county—southern and eastern coastal areas receive per year; the Dorset Downs receive between per year; less than much of Devon and Cornwall to the west but more than counties to the east.Demography
The United Kingdom Census 2011, 2011 Census records Dorset's population as 744,041. This consisted of 412,905 for the non-metropolitan county (not including Bournemouth and Poole), 183,491 for the unitary authority of Bournemouth and 147,645 for the unitary authority of Poole. In 2013 it was estimated that the population had risen by around 1.4% to 754,460: 416,720 in the non-metropolitan county and 188,730 and 149,010 in Bournemouth and Poole respectively. More than half of the county's residents live in the Bournemouth, Poole and Christchurch conurbation. Dorset's population has a high proportion of older people and a lower than average proportion of young people: According to 2013 mid-year estimates, 23.6% are over 65 years of age, higher than the England and Wales average of 17.4%, and 18.6% are less than 17 years old, lower than the England and Wales average of 21.3%. The working age population (females and males between 16 and 64) is lower than England and Wales average, 60% compared to 64%. Data collected between 2010 and 2012 shows that average life expectancy at birth in the county is 85.3 years for females and 81.2 years for males. This compares favourably with the averages for England and Wales of 82.9 and 79.1 years respectively. Around 95.2% of Dorset's population are of white ethnicity, 60.9% of the population are Christianity in the United Kingdom, Christian and 28.5% say they are not religious. More than 33% of the county's population possess a level 4 qualification or above, such as a Higher National Diploma, Degree or a Higher Degree; while nearly 6.3% have no qualifications at all. Almost 43.7% are employed in a professional or technical capacity (Standard Occupational Classification 2010, groups 1–3), just over 10.3% are administrators or secretaries (group 4), around 12.8% have a skilled trade (group 5), over 18% are employed at a low-level in the care, leisure, sales or customer relations sector (groups 6 and 7) and 14.8% are operatives or in elementary occupations (groups 8 and 9).Politics
Local government
Local government in England, Local government in Dorset consists of two unitary authorities (UA); Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole Council, Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole (BCP) Council, which governs the major conurbation comprising the three towns, and Dorset Council (UK), Dorset Council which serves the more rural remainder of the county. For the BCP council, voters choose 76 councillors from 33 wards, with ten wards returning three candidates apiece and 23 wards, two. Dorset elects 82 councillors representing six three-councillor wards, 18 two-councillor wards and 28 single-councillor wards - 52 wards in total. In both authorities, elections for the entire council occur every four years. The two authorities came into existence on 1 April 2019, when Bournemouth Borough Council, Bournemouth and Poole Borough Council, Poole merged with Christchurch, one of six second-tier Non-metropolitan district, districts previously governed by Dorset County Council, leaving the other five districts - Weymouth and Portland, West Dorset, North Dorset, Purbeck District, Purbeck and East Dorset - to form a second UA. Dorset County Council was first formed in 1888 by Local Government Act 1888, an act of government to govern the newly created Administrative counties of England, administrative county of Dorset which had been based largely on the historic county borders. Dorset became a two-tier non-metropolitan county after a reorganisation of local government in 1974 and its border was extended eastwards to incorporate the former Hampshire towns of Bournemouth and Christchurch. Following a review by the Local Government Commission for England (1992), Local Government Commission for England, Bournemouth and Poole each became administratively independent single-tier unitary authorities in 1997.National representation
For representation in Parliament of the United Kingdom, Parliament Dorset is divided into eight Parliamentary constituencies—five county constituencies and three borough constituencies. At the 2017 United Kingdom general election, 2017 general election, the Conservative Party was dominant, taking all eight seats. The borough constituencies of Bournemouth East (UK Parliament constituency), Bournemouth East, Bournemouth West (UK Parliament constituency), Bournemouth West and Poole (UK Parliament constituency), Poole are traditionally Conservative safe seats and are all represented by Conservative members of parliament. The county constituencies of North Dorset (UK Parliament constituency), North Dorset and Christchurch (UK Parliament constituency), Christchurch are also represented by Conservative MPs. Between 1997 and 2019, West Dorset (UK Parliament constituency), West Dorset was represented by Conservative MP Oliver Letwin who was the Cabinet Office, Minister of State at the Cabinet Office in David Cameron's government. The seat was won by Chris Loder in the 2019 United Kingdom general election, 2019 general election. The marginal seat of South Dorset (UK Parliament constituency), South Dorset is represented by Richard Drax, who gained the seat from Labour Party (UK), Labour representative, Jim Knight, in 2010. Drax retained the seat in 2015 and 2017. The Mid Dorset and North Poole (UK Parliament constituency), Mid Dorset and North Poole constituency has been represented by the Conservative MP, Michael Tomlinson since 2015. In the 2019 general election, the Conservative Party (UK), Conservatives held all eight constituencies in Dorset.Economy and industry
In 2003 the gross value added (GVA) for the non-metropolitan county was £4,673 million, with an additional £4,705 million for Poole and Bournemouth. The primary sector produced 2.03% of GVA, the secondary sector produced 22.44% and 75.53% came from the tertiary sector. The average GVA for the 16 regions of South West England was £4,693 million. The principal industry (economics), industry in Dorset was once agriculture. It has not, however, been the largest employer since the mid 19th century as mechanisation substantially reduced the number of workers required.Draper (pp. 105, 143) Agriculture has become less profitable and the industry has declined further. Within the administrative county between 1995 and 2003, GVA for primary industry (largely agriculture, fishing and quarrying) declined from £229 million to £188 million—7.1% to 4.0%. In 2007, of the county was in agricultural use, up from in 1989, although this was due to an increase in permanent grass, and land set aside. By contrast, in the same period, arable land decreased from . Excluding fowl, sheep are the most common animal stock in the county; between 1989 and 2006 their numbers fell from 252,189 to 193,500. Cattle and pig farming has declined similarly; during the same period the number of cattle fell from 240,413 to 170,700, and pigs from 169,636 to 72,700. In 2009 there were 2,340 armed forces personnel stationed in Dorset including the Royal Armoured Corps at Bovington Camp, Bovington, Royal Corps of Signals, Royal Signals at Blandford Camp, Blandford and the Royal Marines at RM Poole, Poole. The military presence has had a mixed effect on the local economy, bringing additional employment for civilians, but on occasion having a negative impact on the tourist trade, particularly when popular areas are closed for military manoeuvres. Other major employers in the county include: BAE Systems, Sunseeker International, J.P. Morgan Chase, J.P. Morgan, Cobham plc and Bournemouth University. Dorset's three ports, Poole, Weymouth Harbour, Dorset, Weymouth andPortland
Portland most commonly refers to:
* Portland, Oregon, the largest city in the state of Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States
* Portland, Maine, the largest city in the state of Maine, in the New England region of the northeas ...
, and the smaller harbours of Christchurch, Swanage, Lyme Regis, Wareham and West Bay generate a substantial amount of international trade and tourism. Around 230 fishing vessels that predominantly catch crab and lobster are based in Dorset's ports. When the waters around Weymouth and Portland were chosen for the sailing events in the 2012 Summer Olympics, 2012 Summer Olympic Games, the area underwent an increased investment in infrastructure and a growth in the marine leisure sector. It is expected that this will continue to have a positive effect on local businesses and tourism.
Culture
 As a largely rural county, Dorset has fewer major cultural institutions than larger or more densely populated areas. Major venues for concerts and theatre include Poole's The Lighthouse (Poole), Lighthouse arts centre, Bournemouth's Bournemouth International Centre, BIC, Pavilion Theatre (Bournemouth), Pavilion Theatre and O2 Academy Bournemouth, O2 Academy, and the Weymouth Pavilion, Pavilion theatre in Weymouth. One of Dorset's most noted cultural institutions is the Bournemouth Symphony Orchestra which was founded in 1893. Based in Poole, the orchestra performs over 130 concerts across southern England each year.
Dorset has more than 30 general and specialist museums. The Dorset County Museum in Dorchester was founded in 1846 and contains an extensive collection of exhibits covering the county's history and environment. The Tank Museum at Bovington contains more than 300 tanks and armoured vehicles from 30 nations. The museum is the largest in Dorset and its collection has been Designation Scheme, designated of national importance. Other museums which reflect the cultural heritage of the county include The Keep, Dorchester, The Keep Military Museum in Dorchester, the Russell-Cotes Museum in Bournemouth, the Charmouth Heritage Coast Centre, Poole Museum, Portland Museum, Dorset, Portland Museum and Wareham Town Museum.
Dorset contains 190 conservation area (United Kingdom), conservation areas, more than 1,500 scheduled monuments, over 30 registered parks and gardens and 12,850 listed buildings. Grade I listed buildings include: Portland Castle, a coastal fort commissioned by Henry VIII; a castle with more than a 1,000 years of history at Corfe Castle (village), Corfe; a Roman Town House, Dorchester, Roman ruin described by Historic England as the "only Roman town house visible in Britain"; Athelhampton, a Tudor dynasty, Tudor manor house; Forde Abbey, a stately home and former Cistercian monastery; Christchurch Priory, the longest church in England; and St Edwold's Church, Stockwood, St Edwold's church, one of the smallest.
As a largely rural county, Dorset has fewer major cultural institutions than larger or more densely populated areas. Major venues for concerts and theatre include Poole's The Lighthouse (Poole), Lighthouse arts centre, Bournemouth's Bournemouth International Centre, BIC, Pavilion Theatre (Bournemouth), Pavilion Theatre and O2 Academy Bournemouth, O2 Academy, and the Weymouth Pavilion, Pavilion theatre in Weymouth. One of Dorset's most noted cultural institutions is the Bournemouth Symphony Orchestra which was founded in 1893. Based in Poole, the orchestra performs over 130 concerts across southern England each year.
Dorset has more than 30 general and specialist museums. The Dorset County Museum in Dorchester was founded in 1846 and contains an extensive collection of exhibits covering the county's history and environment. The Tank Museum at Bovington contains more than 300 tanks and armoured vehicles from 30 nations. The museum is the largest in Dorset and its collection has been Designation Scheme, designated of national importance. Other museums which reflect the cultural heritage of the county include The Keep, Dorchester, The Keep Military Museum in Dorchester, the Russell-Cotes Museum in Bournemouth, the Charmouth Heritage Coast Centre, Poole Museum, Portland Museum, Dorset, Portland Museum and Wareham Town Museum.
Dorset contains 190 conservation area (United Kingdom), conservation areas, more than 1,500 scheduled monuments, over 30 registered parks and gardens and 12,850 listed buildings. Grade I listed buildings include: Portland Castle, a coastal fort commissioned by Henry VIII; a castle with more than a 1,000 years of history at Corfe Castle (village), Corfe; a Roman Town House, Dorchester, Roman ruin described by Historic England as the "only Roman town house visible in Britain"; Athelhampton, a Tudor dynasty, Tudor manor house; Forde Abbey, a stately home and former Cistercian monastery; Christchurch Priory, the longest church in England; and St Edwold's Church, Stockwood, St Edwold's church, one of the smallest.
 Dorset hosts a number of annual festivals, fairs and events including the
Dorset hosts a number of annual festivals, fairs and events including the Great Dorset Steam Fair
The Great Dorset Steam Fair (abbreviated GDSF, and since 2010 also known as The National Heritage Show) is an annual show featuring steam-powered vehicles and machinery. It now covers and runs for five days. This used to be from the Wednesday ...
near Blandford, one of the largest events of its kind in Europe, and the Bournemouth Air Festival, a free air show that attracted 1.3 million visitors in 2009. The Spirit of the Seas is a maritime festival held in Weymouth and Portland. Launched in 2008, the festival features sporting activities, cultural events and local entertainers. The Dorset County Show, which was first held in 1841, is a celebration of Dorset's agriculture. The two-day event exhibits local produce and livestock and attracts some 55,000 people. Inside Out Dorset is an outdoor arts festival that takes place every two years in rural and urban locations across Dorset. In addition to the smaller folk festivals held in towns such as Christchurch and Wimborne Folk Festival, Wimborne, Dorset holds several larger musical events such as Camp Bestival, End Of The Road Festival, End of the Road and the Larmer Tree Festival.
Dorset's only professional football club is AFC Bournemouth, which plays in the Premier League— the highest division in the English football league system. Non-League football, Non-League semi-professional teams in the county include Southern Football League, Southern Premier Division teams Dorchester Town F.C., Poole Town F.C. and Weymouth F.C. Dorset County Cricket Club competes in the Minor Counties Cricket Championship and is based at Dean Park Cricket Ground in Bournemouth. Poole Stadium hosts regular greyhound racing and is the home to top-flight speedway team Poole Pirates. The county's coastline, on the English Channel, is noted for its watersports (particularly sailing, gig racing, windsurfing, power boating and kayaking) which take advantage of the sheltered waters in the bays of Weymouth Bay, Weymouth and Poole Bay, Poole, and the harbours of Poole and Portland. Dorset hosted the sailing events at the 2012 Summer Olympics and 2012 Summer Paralympics at the Weymouth and Portland National Sailing Academy. The venue was completed in May 2009 and was used by international sailing teams in preparation for the Games. In motorsport, Dorset hosts the Extreme E Jurassic X Prix at Bovington Camp.
 Dorset is famed in literature for being the native county of author and poet
Dorset is famed in literature for being the native county of author and poet Thomas Hardy
Thomas Hardy (2 June 1840 – 11 January 1928) was an English novelist and poet. A Victorian realist in the tradition of George Eliot, he was influenced both in his novels and in his poetry by Romanticism, including the poetry of William Word ...
, and many of the places he describes in his novels in the fictional Thomas Hardy's Wessex, Wessex are in Dorset, which he renamed ''South Wessex''. The National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, National Trust owns Thomas Hardy's Cottage, in Higher Bockhampton, east of Dorchester; and Max Gate, his former house in Dorchester. Several other writers have called Dorset home, including Douglas Adams, who wrote much of ''The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy'' while he lived in Stalbridge; John le Carré, author of espionage novels, was born in Poole; Tom Sharpe of ''Wilt (novel), Wilt'' fame lived in Bridport; John Fowles (''The French Lieutenant's Woman'') lived in Lyme Regis before he died in late 2005; T.F. Powys lived in Chaldon Herring for over 20 years and used it as inspiration for the fictitious village of Folly Down in his novel ''Mr. Weston's Good Wine''; John Cowper Powys, his elder brother, also set a number of his works in Dorset, such as the novels ''Maiden Castle (novel), Maiden Castle'' and ''Weymouth Sands''. Children's author Enid Blyton drew inspiration for many of her works from Dorset. The 19th-century poet William Barnes
William Barnes (22 February 1801 – 7 October 1886) was an English polymath, writer, poet, philologist, priest, mathematician, engraving artist and inventor. He wrote over 800 poems, some in Dorset dialect, and much other work, including a co ...
was born in Bagber and wrote many poems in his native West Country dialect, Dorset dialect. Originating from the ancient Proto-Norse language, Norse and Old Saxon, Saxon languages, the dialect was prevalent across the Blackmore Vale but has fallen into disuse.
Flag of Dorset, Dorset's flag, which is known as the Dorset Cross or St Wite's Cross, was adopted in 2008 following a public competition organised by Dorset County Council. The winning design, which features a white cross with a red border on a golden background, attracted 54% of the vote. All three colours are used in Dorset County Council's coat of arms and the red and white was used in recognition of the Flag of England, English flag. The golden colour represents Dorset's sandy beaches and the Dorset landmarks of Golden Cap and Gold Hill, Shaftesbury, Gold Hill. It is also a reference to the Wessex#Wyvern or dragon, Wessex Dragon, a symbol of the Wessex, Saxon Kingdom which Dorset once belonged to, and the gold wreath featured on the badge of the Dorset Regiment.
Transport
Dorset is connected to London by two main line railways. The West of England Main Line runs through the north of the county at Gillingham and Sherborne. Running west from London Waterloo station, London Waterloo to Exeter St Davids railway station, Exeter St Davids in Devon, it provides a service for those who live in the western districts of Dorset. The South West Main Line runs through the south at Bournemouth, Poole, Dorchester and the terminus at Weymouth. Additionally, the Heart of Wessex Line runs north from Weymouth to Bristol and the Swanage Railway, a Heritage railway, heritage steam and diesel railway, runs the between Norden railway station (Dorset), Norden and Swanage. Dorset is one of the few counties in England not to have a motorway. The A303 road, A303, A35 road, A35 and A31 road, A31 trunk roads run through the county. The A303, which connects the West Country to London via the M3 motorway (Great Britain), M3, clips the north-west of the county. The A35 crosses the county in a west–east direction from Honiton in Devon, via Bridport, Dorchester, Poole, Bournemouth and Christchurch, to Southampton in Hampshire. The A31 connects to the A35 at Bere Regis, and passes east through Wimborne and Ferndown to Hampshire, where it later becomes the M27 motorway (England), M27. Other main roads in the county include the A338, A354, A37 road (England), A37 and A350 road, A350. The A338 heads north from Bournemouth to Ringwood, Hampshire, Ringwood (Hampshire) and on to Salisbury (Wiltshire) and beyond. The A354 also connects to Salisbury after travelling north-east from Weymouth in the south of the county. The A37 travels north-west from Dorchester to Yeovil in Somerset. The A350 also leads north, from Poole through Blandford and Shaftesbury, to Warminster in Wiltshire. A passenger sea port and an international airport are situated in the county. Brittany Ferries and Condor Ferries, operate out of Poole Harbour; Brittany Ferries provide access to Cherbourg in France and Condor Ferries sail a seasonal service to the Channel Islands and St Malo, France. Poole, since the dredging of the main channel in 2008, and Portland harbours are capable of taking cruise liners. Bournemouth Airport, which is situated on the edge of Hurn village north of Bournemouth, has flights to 36 destinations and serves some 600,000 passengers a year. In August 2007 work began on a £32 million expansion programme which includes enlargement of the terminal building and an increase in parking. Go South Coast, Morebus and Damory provide a county wide bus network with frequent services linking major towns, including Bournemouth, Poole and Wimborne, and a varied service in further rural locations. The First Hampshire & Dorset, First Group operate buses in the Weymouth and Bridport area, including: a regular route along the A35 from Weymouth to Axminster, which helps to compensate for the missing rail link west of Dorchester; and the Jurassic Coast service, one of the longest bus routes in the UK, which provides through travel from Poole to Exeter, exploiting a popular tourist route. Yellow Buses provided bus services within Bournemouth and outlying areas until they ceased operating in 2022.Religious sites
 Unlike all of its neighbouring counties, Dorset does not have a cathedral. Over 95% of the county falls within the Church of England Diocese of Salisbury. A small section to the west comes under the Diocese of Bath and Wells and to the east Christchurch and much of Bournemouth—both historically part of Hampshire—belong to the Diocese of Winchester. The Roman Catholic Diocese of Plymouth incorporates most of Dorset with the exception of Christchurch and a portion of Bournemouth which belongs to the Roman Catholic Diocese of Portsmouth, Diocese of Portsmouth. Few purpose-built places of worship exist in Dorset for faiths other than Christianity. In 2008 a Hindu temple was constructed in Blandford Forum for the Queen's Gurkha Signals, Gurkhas based at the town's military camp. Bournemouth, which contains a higher proportion of Jewish residents than the national average, has three synagogues besides an Islamic Centre and a mosque for Muslims.
Christianity was introduced to Dorset by the Romans. A 4th century Hinton St Mary Mosaic, Roman mosaic discovered near Hinton St Mary contains what is generally accepted to be an image of Christ. Christianity became firmly established in the county during the Saxon period although there are few surviving Saxon churches; the most complete is St Martin's Church, Wareham, St. Martin's in Wareham which has features from the early 11th century. Mediaeval churches are more prevalent in Dorset; most are 15th century and are of a Perpendicular Gothic, Perpendicular style. Sherborne Abbey, one of the county's largest, is noted for its broad fan vaulting added during an extensive 15th century rebuild. Founded in AD 705 by Aldhelm, the Abbey contained the Cathedra, chair of the Bishop of Sherborne and was granted cathedral status until 1075 when the diocese was transferred to Old Sarum. Wimborne Minster (church), Wimborne Minster features a chained library and a 14th-century astronomical clock; Christchurch Priory is renowned for its Christchurch Priory#Miraculous beam, miraculous beam which, according to legend, was installed by Christ; and the 15th century roof spanning the nave at St John the Baptist Church in Bere Regis is described by architectural historian Nikolaus Pevsner as the "finest timber roof of Dorset". Church of St Candida and Holy Cross, St Candida and Holy Cross at Whitchurch Canonicorum is the only church in the country, besides Westminster Abbey, to have a shrine that contains the relics of a saint.
Monastic foundations were once abundant in Dorset, but all ceased to exist at the Dissolution of the monasteries. The English Reformation, Reformation and the political and religious turmoil that ensued largely checked the building of new churches until the turn of the 18th century.Draper (p. 82) Notable examples of Georgian architecture, Early Georgian churches include the Bastard brothers' Church of St. Peter and St. Paul in Blandford Forum, and St George's Church, Portland, St George's Church on the Isle of Portland, which has a steeple and tower inspired by the works of Christopher Wren. From the late 18th century onwards, churches in Dorset tended towards a Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic Revival style. A notable exception to this trend, however, is the Church of St Mary in East Lulworth—the first freestanding Roman Catholic church built in England after the Reformation.Lehane (p. 59) George III gave permission to erect the building on the condition that it resembled a garden mausoleum rather than a church. It was completed in 1789. Bournemouth, founded in 1810, has a wealth of 19th-century churches including St Peter's Church, Bournemouth, St Peter's and St Stephen's Church, Bournemouth, St Stephen's. St Dunstan's Church (formerly St Osmund's) in Poole is one of a small number of 20th-century churches in Dorset. The final major work of Edward Schroeder Prior, it is one of the last examples of the Byzantine Revival architecture, Neo Byzantine style. The Church of St Nicholas and St Magnus in Moreton, Dorset, Moreton is noted for its elaborate engraved glass windows designed by Laurence Whistler. Severely damaged by a stray German bomb in 1940, the church subsequently underwent extensive renovation and Whistler had replaced every window by 1984.
Unlike all of its neighbouring counties, Dorset does not have a cathedral. Over 95% of the county falls within the Church of England Diocese of Salisbury. A small section to the west comes under the Diocese of Bath and Wells and to the east Christchurch and much of Bournemouth—both historically part of Hampshire—belong to the Diocese of Winchester. The Roman Catholic Diocese of Plymouth incorporates most of Dorset with the exception of Christchurch and a portion of Bournemouth which belongs to the Roman Catholic Diocese of Portsmouth, Diocese of Portsmouth. Few purpose-built places of worship exist in Dorset for faiths other than Christianity. In 2008 a Hindu temple was constructed in Blandford Forum for the Queen's Gurkha Signals, Gurkhas based at the town's military camp. Bournemouth, which contains a higher proportion of Jewish residents than the national average, has three synagogues besides an Islamic Centre and a mosque for Muslims.
Christianity was introduced to Dorset by the Romans. A 4th century Hinton St Mary Mosaic, Roman mosaic discovered near Hinton St Mary contains what is generally accepted to be an image of Christ. Christianity became firmly established in the county during the Saxon period although there are few surviving Saxon churches; the most complete is St Martin's Church, Wareham, St. Martin's in Wareham which has features from the early 11th century. Mediaeval churches are more prevalent in Dorset; most are 15th century and are of a Perpendicular Gothic, Perpendicular style. Sherborne Abbey, one of the county's largest, is noted for its broad fan vaulting added during an extensive 15th century rebuild. Founded in AD 705 by Aldhelm, the Abbey contained the Cathedra, chair of the Bishop of Sherborne and was granted cathedral status until 1075 when the diocese was transferred to Old Sarum. Wimborne Minster (church), Wimborne Minster features a chained library and a 14th-century astronomical clock; Christchurch Priory is renowned for its Christchurch Priory#Miraculous beam, miraculous beam which, according to legend, was installed by Christ; and the 15th century roof spanning the nave at St John the Baptist Church in Bere Regis is described by architectural historian Nikolaus Pevsner as the "finest timber roof of Dorset". Church of St Candida and Holy Cross, St Candida and Holy Cross at Whitchurch Canonicorum is the only church in the country, besides Westminster Abbey, to have a shrine that contains the relics of a saint.
Monastic foundations were once abundant in Dorset, but all ceased to exist at the Dissolution of the monasteries. The English Reformation, Reformation and the political and religious turmoil that ensued largely checked the building of new churches until the turn of the 18th century.Draper (p. 82) Notable examples of Georgian architecture, Early Georgian churches include the Bastard brothers' Church of St. Peter and St. Paul in Blandford Forum, and St George's Church, Portland, St George's Church on the Isle of Portland, which has a steeple and tower inspired by the works of Christopher Wren. From the late 18th century onwards, churches in Dorset tended towards a Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic Revival style. A notable exception to this trend, however, is the Church of St Mary in East Lulworth—the first freestanding Roman Catholic church built in England after the Reformation.Lehane (p. 59) George III gave permission to erect the building on the condition that it resembled a garden mausoleum rather than a church. It was completed in 1789. Bournemouth, founded in 1810, has a wealth of 19th-century churches including St Peter's Church, Bournemouth, St Peter's and St Stephen's Church, Bournemouth, St Stephen's. St Dunstan's Church (formerly St Osmund's) in Poole is one of a small number of 20th-century churches in Dorset. The final major work of Edward Schroeder Prior, it is one of the last examples of the Byzantine Revival architecture, Neo Byzantine style. The Church of St Nicholas and St Magnus in Moreton, Dorset, Moreton is noted for its elaborate engraved glass windows designed by Laurence Whistler. Severely damaged by a stray German bomb in 1940, the church subsequently underwent extensive renovation and Whistler had replaced every window by 1984.
Education
Responsibility for state schools in Dorset is divided between two local education authority, local education authorities: Dorset Council, which covers the majority of the county, and Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole (BCP) Council. Most of the Dorset Council area operates a two-tier Comprehensive school, comprehensive system whereby pupils attend a primary school before completing their education at secondary school but Corfe Mullen, Dorchester, Ferndown and West Moors maintain a Three-tier education, three-tier system (first school, first, middle school, middle and high school). Bournemouth operates a two-tier system; Poole operates two and three-tier systems. BCP is one of the few local authorities in England to maintain selective education, containing four Single-sex education, single-sex grammar schools which select pupils on the basis of an eleven-plus examination. Some of the county's schools are Academy (English school), academies—self-governing state schools which have become independent of their local education authority and are maintained directly by the Department for Education. In 2017, the Progress 8 benchmark, Progress 8 score for schools in the Dorset Council area was ranked below average, and 39.6% of pupils gained at least Grade 5 or above in English and maths GCSEs matching the national average of 39.6%. Poole recorded an above average Progress 8 score and 54% of pupils achieved Grade 5 or above in English and maths GCSEs. Bournemouth was ranked as average and 47.8% of pupils achieved Grade 5 or above in English and maths GCSEs. Dorset contains a range of privately funded independent schools. Many are boarding schools which also take Day school, day pupils, such as the co-educational Canford School which is built around a 19th-century Grade I listed manor house; and Sherborne School, a boys' school founded in the 16th century. Four of the county's five largest towns contain a further education college: Weymouth College, Kingston Maurward College in Dorchester and Bournemouth and Poole College which is one of the largest in the UK. Dorset has two higher education establishments situated in the heart of the county's south east conurbation. Bournemouth University has facilities across Bournemouth and Poole and over 17,000 students. Previously named Bournemouth Polytechnic, it was granted university status as a result of the Further and Higher Education Act 1992. The Arts University Bournemouth is situated between the border of Poole and Bournemouth. It became a higher education institute in 2001 and was given degree-awarding powers in 2008. It was granted full university status in 2012.See also
*Custos Rotulorum of Dorset—list of keepers of the rolls for Dorset *Dorset (UK Parliament constituency), Dorset—list of MPs for the abolished Dorset county constituency *High Sheriff of Dorset, List of High Sheriffs of Dorset *List of hills of Dorset *Dorset Police *Dorset Police and Crime Commissioner *Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole Council - Unitary council replacing the 3 previous councils in 2019 *Dorset heraldryFootnotes
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * *Hinton, David A. (1998). ''Saxons & Vikings''. Wimborne, Dorset: Dovecote Press. ISBN 1-874336-50-4 * * * * * * * * * * *External links
*Dorset County Museum
Images of Dorset
at the English Heritage Archive
Dorset AONB
{{Authority control Dorset, Non-metropolitan counties Counties of England established in antiquity Counties in South West England