Dopamine Neurons on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Dopaminergic pathways (dopamine pathways, dopaminergic projections) in the human brain are involved in both physiological and behavioral processes including movement, cognition, executive functions, reward, motivation, and neuroendocrine control. Each pathway is a set of
Dopaminergic pathways (dopamine pathways, dopaminergic projections) in the human brain are involved in both physiological and behavioral processes including movement, cognition, executive functions, reward, motivation, and neuroendocrine control. Each pathway is a set of
 The mesocorticolimbic system (
The mesocorticolimbic system (

projection neurons
Projection, projections or projective may refer to:
Physics
* Projection (physics), the action/process of light, heat, or sound reflecting from a surface to another in a different direction
* The display of images by a projector
Optics, graphic ...
, consisting of individual dopaminergic neurons.
The four major dopaminergic pathways are the mesolimbic pathway, the mesocortical pathway, the nigrostriatal pathway, and the tuberoinfundibular pathway.The mesolimbic pathway and the mesocortical pathway form the mesocorticolimbic system. Two other dopaminergic pathways to be considered are the hypothalamospinal tract
The hypothalamospinal tract arises mainly from the paraventricular nucleus, lateral and posterior hypothalamic areas. This tract descends through the periaqueductal gray and adjacent reticular formation. The hypothalamospinal tract also connects th ...
and the incertohypothalamic pathway The incertohypothalamic pathway is a short dopaminergic pathway from the zona incerta to the hypothalamus of the brain. It has a role in modulation of fear and the integration of autonomic and neuroendocrine responses to specific sensory stimuli for ...
.
Parkinson's disease, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), substance use disorder
Substance use disorder (SUD) is the persistent use of drugs (including alcohol) despite substantial harm and adverse consequences as a result of their use. Substance use disorders are characterized by an array of mental/emotional, physical, and ...
s ( addiction), and restless legs syndrome (RLS) can be attributed to dysfunction in specific dopaminergic pathways.
The dopamine neurons of the dopaminergic pathways synthesize and release the neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neuro ...
dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine const ...
. Enzymes tyrosine hydroxylase and dopa decarboxylase are required for dopamine synthesis. These enzymes are both produced in the cell bodies
The soma (pl. ''somata'' or ''somas''), perikaryon (pl. ''perikarya''), neurocyton, or cell body is the bulbous, non-process portion of a neuron or other brain cell type, containing the cell nucleus. The word 'soma' comes from the Greek '' σῶ� ...
of dopamine neurons. Dopamine is stored in the cytoplasm and vesicles in axon terminals. Dopamine release from vesicles is triggered by action potential propagation-induced membrane depolarization. The axons of dopamine neurons extend the entire length of their designated pathway.
Pathways
Major
Six of the dopaminergic pathways are listed below.Minor
:Hypothalamospinal :* Hypothalamus → Spinal cord :Incertohypothalamic :*Zona incerta
The zona incerta (ZI) is a horizontally elongated region of gray matter in the subthalamus below the thalamus. Its connections project extensively over the brain from the cerebral cortex down into the spinal cord.
Its function is unknown, though ...
→ Hypothalamus
:* Zona incerta → Brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is cont ...
VTA → Amygdala (mesoamygdaloid pathway)
:VTA → Hippocampus
:VTA → Cingulate cortex
The cingulate cortex is a part of the brain situated in the medial aspect of the cerebral cortex. The cingulate cortex includes the entire cingulate gyrus, which lies immediately above the corpus callosum, and the continuation of this in the ci ...
:VTA → Olfactory bulb
:SNc → Subthalamic nucleus
The subthalamic nucleus (STN) is a small lens-shaped nucleus in the brain where it is, from a functional point of view, part of the basal ganglia system. In terms of anatomy, it is the major part of the subthalamus. As suggested by its name, the ...
Function
Mesocorticolimbic system
 The mesocorticolimbic system (
The mesocorticolimbic system (mesocorticolimbic circuit
The reward system (the mesocorticolimbic circuit) is a group of neural structures responsible for incentive salience (i.e., "wanting"; desire or craving for a reward and motivation), associative learning (primarily positive reinforcement and class ...
) refers to both the mesocortical
The mesocortical pathway is a dopaminergic pathway that connects the ventral tegmentum to the prefrontal cortex. It is one of the four major dopamine pathways in the brain. It is essential to the normal cognitive function of the dorsolateral pre ...
and mesolimbic
The mesolimbic pathway, sometimes referred to as the reward pathway, is a dopaminergic pathway in the brain. The pathway connects the ventral tegmentum, ventral tegmental area in the midbrain to the ventral striatum of the basal ganglia in the for ...
pathways. Both pathways originate at the ventral tegmental area (VTA). Through separate connections to the prefrontal cortex (mesocortical) and ventral striatum (mesolimbic), the mesocorticolimbic projection has a significant role in learning, motivation, reward, memory and movement. Dopamine receptor subtypes, D1 and D2 have been shown to have complementary functions in the mesocorticolimbic projection, facilitating learning in response to both positive and negative feedback. Both pathways of the mesocorticolimbic system are associated with ADHD
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by excessive amounts of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that are pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and otherwise age-inapp ...
, schizophrenia and addiction.
Mesocortical pathway
The mesocortical pathway projects from the ventral tegmental area to the prefrontal cortex ( VTA → Prefrontal cortex). This pathway is involved in cognition and the regulation of executive functions (e.g., attention, working memory, inhibitory control, planning, etc.) Dysregulation of the neurons in this pathway has been connected to ADHD.Mesolimbic pathway
Referred to as the reward pathway, mesolimbic pathway projects from the ventral tegmental area to the ventral striatum ( VTA → Ventral striatum ( nucleus accumbens andolfactory tubercle
The olfactory tubercle (OT), also known as the tuberculum olfactorium, is a multi-sensory processing center that is contained within the olfactory cortex and ventral striatum and plays a role in reward cognition. The OT has also been shown to ...
). When a reward is anticipated, the firing rate of dopamine neurons in the mesolimbic pathway increases. The mesolimbic pathway is involved with incentive salience
Motivational salience is a cognitive process and a form of attention that ''motivates'' or propels an individual's behavior towards or away from a particular stimulus (psychology), object, perceived event or outcome. Motivational salience regulat ...
, motivation
Motivation is the reason for which humans and other animals initiate, continue, or terminate a behavior at a given time. Motivational states are commonly understood as forces acting within the agent that create a disposition to engage in goal-dire ...
, reinforcement learning, fear and other cognitive processes. In animal studies, depletion of dopamine in this pathway, or lesions at its site of origin, decrease the extent to which an animal is willing to go to obtain a reward (e.g., the number of lever presses for nicotine or time searching for food). Research is ongoing to determine the role of the mesolimbic pathway in the perception of pleasure.

Nigrostriatal pathway
The nigrostriatal pathway is involved in behaviors relating to movement and motivation. The transmission of dopaminergic neurons to the dorsal striatum particularly plays a role in reward and motivation while movement is influenced by the transmission of dopaminergic neurons to the substantia nigra. The nigrostriatal pathway is associated with conditions such as Huntington's disease, Parkinson's disease, ADHD, Schizophrenia, and Tourette's Syndrome. Huntington's disease, Parkinson's disease, and Tourette's Syndrome are conditions affected by motor functioning while schizophrenia and ADHD are affected by reward and motivation functioning. This pathway also regulates associated learning such as classical conditioning and operant conditioning.
Tuberoinfundibular pathway
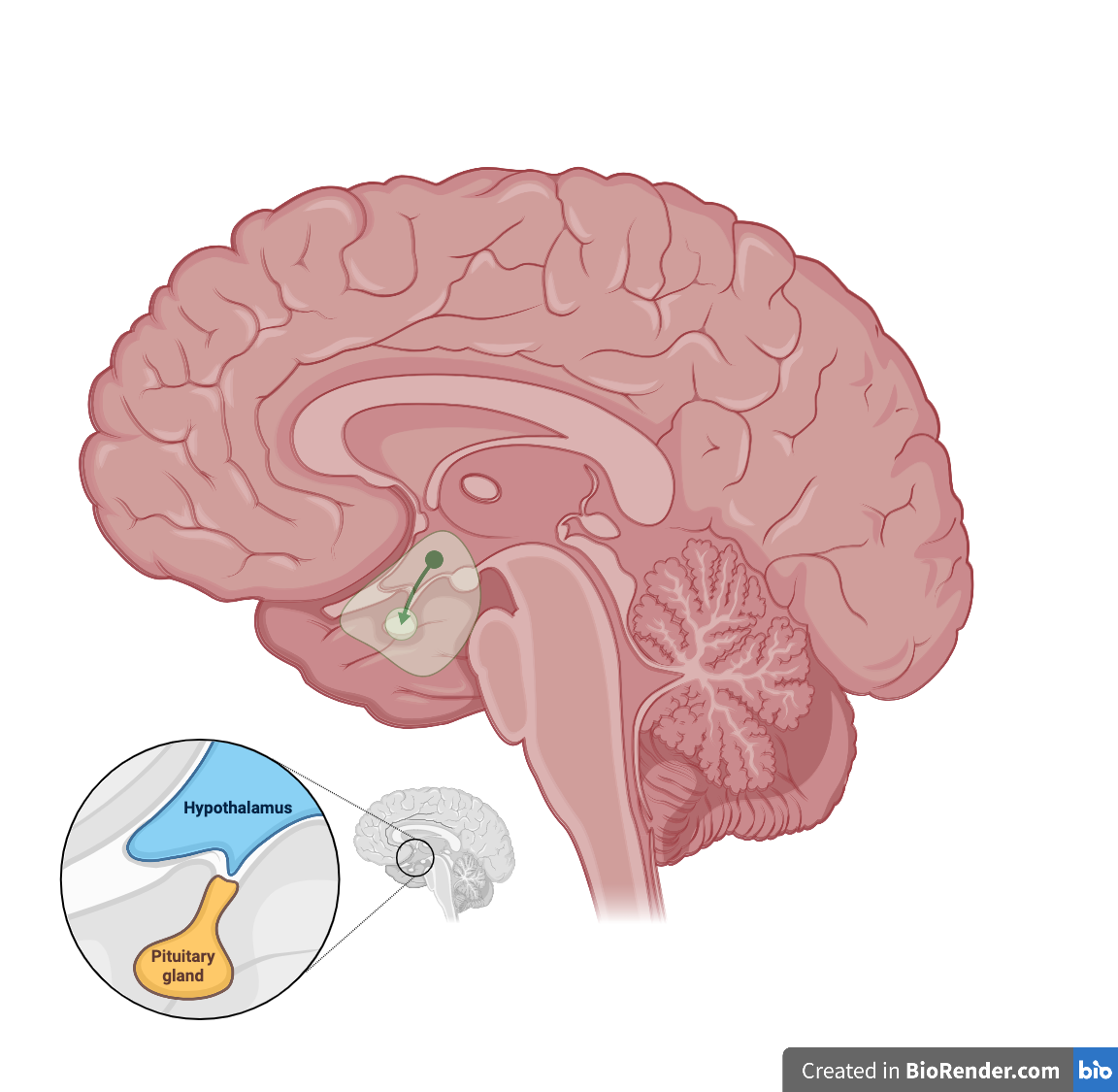
The tuberoinfundibular pathway transmits dopamine the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland. This pathway also regulates the secretion of prolactin from the pituitary gland, which is responsible for breast milk production in females. Hyperprolactinemia is an associated condition caused by an excessive amount of prolactin production that is common in pregnant women.Cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop
The dopaminergic pathways that project from thesubstantia nigra pars compacta
The pars compacta (SNpc) is a portion of the ''substantia nigra'', located in the midbrain. It is formed by dopaminergic neurons and located medial to the pars reticulata. Parkinson's disease is characterized by the death of dopaminergic neurons ...
(SNc) and ventral tegmental area (VTA) into the striatum
The striatum, or corpus striatum (also called the striate nucleus), is a nucleus (a cluster of neurons) in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamate ...
(i.e., the nigrostriatal and mesolimbic pathways, respectively) form one component of a sequence of pathways known as the cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop. The nigrostriatal component of the loop consists of the SNc, giving rise to both inhibitory and excitatory pathways that run from the striatum into the globus pallidus
The globus pallidus (GP), also known as paleostriatum or dorsal pallidum, is a subcortical structure of the brain. It consists of two adjacent segments, one external, known in rodents simply as the globus pallidus, and one internal, known in rod ...
, before carrying on to the thalamus, or into the subthalamic nucleus
The subthalamic nucleus (STN) is a small lens-shaped nucleus in the brain where it is, from a functional point of view, part of the basal ganglia system. In terms of anatomy, it is the major part of the subthalamus. As suggested by its name, the ...
before heading into the thalamus. The dopaminergic neurons in this circuit increase the magnitude of phasic firing in response to positive reward error, that is when the reward exceeds the expected reward. These neurons do not decrease phasic firing during a negative reward prediction (less reward than expected), leading to hypothesis that serotonergic, rather than dopaminergic neurons encode reward loss (source?). Dopamine phasic activity also increases during cues that signal negative events, however dopaminergic neuron stimulation still induces place preference, indicating its main role in evaluating a positive stimulus. From these findings, two hypotheses have developed, as to the role of the basal ganglia and nigrostiatal dopamine circuits in action selection. The first model suggests a "critic" which encodes value, and an actor which encodes responses to stimuli based on perceived value. However, the second model proposes that the actions do not originate in the basal ganglia, and instead originate in the cortex and are selected by the basal ganglia. This model proposes that the direct pathway controls appropriate behavior and the indirect suppresses actions not suitable for the situation. This model proposes that tonic dopaminergic firing increases the activity of the direct pathway, causing a bias towards executing actions faster.
These models of the basal ganglia are thought to be relevant to the study of OCD, ADHD
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by excessive amounts of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that are pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and otherwise age-inapp ...
, Tourette syndrome, Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, and addiction. For example, Parkinson's disease is hypothesized to be a result of excessive inhibitory pathway activity, which explains the slow movement and cognitive deficits, while Tourettes is proposed to be a result of excessive excitatory activity resulting in the tics characteristic of Tourettes.
Regulation
The ventral tegmental area andsubstantia nigra pars compacta
The pars compacta (SNpc) is a portion of the ''substantia nigra'', located in the midbrain. It is formed by dopaminergic neurons and located medial to the pars reticulata. Parkinson's disease is characterized by the death of dopaminergic neurons ...
receive inputs from other neurotransmitters systems, including glutaminergic inputs, GABAergic
In molecular biology and physiology, something is GABAergic or GABAnergic if it pertains to or affects the neurotransmitter GABA. For example, a synapse is GABAergic if it uses GABA as its neurotransmitter, and a GABAergic neuron produces GABA. A ...
inputs, cholinergic inputs, and inputs from other monoaminergic nuclei. The VTA contains 5-HT1A receptors that exert a biphasic effects on firing, with low doses of 5-HT1A receptor agonists eliciting an increase in firing rate, and higher doses suppressing activity. The 5-HT2A receptors expressed on dopaminergic neurons increase activity, while 5-HT2C receptors elicit a decrease in activity. The mesolimbic pathway, which projects from the VTA to the nucleus accumbens, is also regulated by muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. In particular, the activation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 and muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4 inhibits dopamine release, while muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1 activation increases dopamine release. GABAergic inputs from the striatum decrease dopaminergic neuronal activity, and glutaminergic inputs from many cortical and subcortical areas increase the firing rate of dopaminergic neurons. Endocannabinoids also appear to have a modulatory effect on dopamine release from neurons that project out of the VTA and SNc. Noradrenergic inputs deriving from the locus coeruleus
The locus coeruleus () (LC), also spelled locus caeruleus or locus ceruleus, is a nucleus in the pons of the brainstem involved with physiological responses to stress and panic. It is a part of the reticular activating system.
The locus coerule ...
have excitatory and inhibitory effects on the dopaminergic neurons that project out of the VTA and SNc. The excitatory orexinergic inputs to the VTA originate in the lateral hypothalamus and may regulate the baseline firing of VTA dopaminergic neurons.
See also
* Dopaminergic cell groupsNotes
References
{{Neurotransmitter systems Central nervous system pathways Dopamine