DoD Architecture Framework on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an
 The secretary of defense, appointed by the president with the advice and consent of the
The secretary of defense, appointed by the president with the advice and consent of the
 The
The
File:US Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) seal (vector).svg,
 The
The
File:United States Department of the Army Seal.svg,
File:Mark of the United States Army.svg, U.S. Army
File:Emblem of the United States Marine Corps.svg, U.S. Marine Corps
File:Emblem of the United States Navy.svg, U.S. Navy
File:Military service mark of the United States Air Force.svg, U.S. Air Force
File:United States Space Force emblem.png, U.S. Space Force
 A unified combatant command is a military command composed of personnel/equipment from at least two Military Departments, which has a broad, continuing mission. They are responsible for the operational command of forces. Almost all operational U.S. forces are under the authority of a Unified Command. The DOD Unified Command Plan lays out combatant commands' missions, geographical/functional responsibilities, and force structure.
During military operations, the chain of command runs from the president to the secretary of defense to the combatant commanders of the Combatant Commands.
, the United States has eleven Combatant Commands, organized either on a geographical basis (known as "
A unified combatant command is a military command composed of personnel/equipment from at least two Military Departments, which has a broad, continuing mission. They are responsible for the operational command of forces. Almost all operational U.S. forces are under the authority of a Unified Command. The DOD Unified Command Plan lays out combatant commands' missions, geographical/functional responsibilities, and force structure.
During military operations, the chain of command runs from the president to the secretary of defense to the combatant commanders of the Combatant Commands.
, the United States has eleven Combatant Commands, organized either on a geographical basis (known as "
 Department of Defense spending in 2017 was 3.15% of GDP and accounted for about 38% of the budgeted global military spending – more than the next 7 largest militaries combined. By 2019, the 27th secretary of defense had begun a line-by-line review of the defense budget; in 2020 the secretary identified items amounting to $5.7 billion, out of a $106 billion subtotal (the so-called "fourth estate" agencies such as missile defense, and defense intelligence, amounting to 16% of the defense budget), He will re-deploy to the modernization of hypersonics, artificial intelligence, and missile defense. Beyond 2021 the 27th secretary of defense is projecting the need for yearly budget increases of 3 to 5 percent to modernize.McLeary (6 February 2020) Flatline: SecDef Esper Says DoD Budgets Must Grow 3–5%
Department of Defense spending in 2017 was 3.15% of GDP and accounted for about 38% of the budgeted global military spending – more than the next 7 largest militaries combined. By 2019, the 27th secretary of defense had begun a line-by-line review of the defense budget; in 2020 the secretary identified items amounting to $5.7 billion, out of a $106 billion subtotal (the so-called "fourth estate" agencies such as missile defense, and defense intelligence, amounting to 16% of the defense budget), He will re-deploy to the modernization of hypersonics, artificial intelligence, and missile defense. Beyond 2021 the 27th secretary of defense is projecting the need for yearly budget increases of 3 to 5 percent to modernize.McLeary (6 February 2020) Flatline: SecDef Esper Says DoD Budgets Must Grow 3–5%
/ref> The Department of Defense accounts for the majority of federal discretionary spending. In FY 2017, the Department of Defense budgeted spending accounted for 15% of the U.S. federal budget, and 49% of federal
(2019) Overview – National Defense Budget Estimates for Fiscal Year (FY) 2019
FY 2019 PB Green Book The Department of Defense budget encompasses the majority of the National Defense Budget of approximately $716.0 billion in discretionary spending and $10.8 billion in mandatory spending for a $726.8 billion total. Of the total, $708.1 billion falls under the jurisdiction of the House Committee on Armed Services and
* Numbers may not add due to rounding
(17 January 2023) U.S. to hit debt limit Thursday: Here's what that means
*Committee for a Responsible Federal Budge
(28 Oct 2022) Q&A: Everything You Should Know About the Debt Ceiling
*Stephen Collinso
in
(30 Sep 2023) Government shutdown live updates: House passes 45-day stopgap spending bill
/ref>Clare Foran, Haley Talbot, Morgan Rimmer, Annie Grayer, Lauren Fox and Melanie Zanona, CN
/ref>Rebecca Khee
/ref>Leo Shane III ttps://www.militarytimes.com/news/pentagon-congress/2023/12/04/defense-authorization-deal-expected-this-week/ (3 Dec 2023) Defense authorization deal expected this week/ref> with passage of the NDAA on 14 December 2023.Patricia Zengerl
(7 Dec 2023) US lawmakers introduce sweeping defense bill, drop most 'culture war' issues
Patricia Zengerl
(13 Dec 2023) US Senate passes mammoth defense policy bill, next up vote in House
Bill is nearly 3100 pages, for $886 billion NDAA passed Senate 87–13; Bryant Harri
(14 Dec 2023) Congress passed the FY24 defense policy bill: Here's what's inside
passed House 310–118. The Senate will next undertake negotiations on supplemental spending for 2024.BURGESS EVERETT, ANTHONY ADRAGNA and JENNIFER HABERKOR
(14 Dec 2024) Sinema 'can see the deal' on Ukraine-border as Schumer cuts recess
/ref>Sumanti Se
$1,659 billion= $886.3 billion for defense, $772.7 billion for non-defense A government shutdown was averted on 23 March 2024 with the signing of a $1.2 trillion bill to cover FY2024.Clare Fora
/ref>Carl Huls
/ref>
Making the Grade: Access to Information Scorecard 2015
March 2015, 80 pages, Center for Effective Government, retrieved March 21, 2016
Department of Defense
on
Department of Defense
in the
Office of the Under Secretary of Defense (Comptroller)
Budget and Financial Management Policy
Death and Taxes: 2009
��A visual guide and infographic of the 2009 United States federal budget, including the Department of Defense with data provided by the Comptrollers office.
* * * {{Authority control 1947 establishments in the United States
executive department
The executive branch is the part of government which executes or enforces the law.
Function
The scope of executive power varies greatly depending on the political context in which it emerges, and it can change over time in a given country. In ...
of the U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the Army
An army, ground force or land force is an armed force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by ...
, Navy
A navy, naval force, military maritime fleet, war navy, or maritime force is the military branch, branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral z ...
, Marines
Marines (or naval infantry) are military personnel generally trained to operate on both land and sea, with a particular focus on amphibious warfare. Historically, the main tasks undertaken by marines have included Raid (military), raiding ashor ...
, Air Force
An air force in the broadest sense is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an army aviati ...
, Space Force
A space force is a military branch of a nation's armed forces that conducts military operations in outer space and space warfare. The world's first space force was the Russian Space Forces, established in 1992 as an independent military service. ...
, the Coast Guard
A coast guard or coastguard is a Maritime Security Regimes, maritime security organization of a particular country. The term embraces wide range of responsibilities in different countries, from being a heavily armed military force with cust ...
for some purposes, and related functions and agencies. As of November 2022, the department has over 1.4 million active-duty uniformed personnel in the six armed services. It also supervises over 778,000 National Guard
National guard is the name used by a wide variety of current and historical uniformed organizations in different countries. The original National Guard was formed during the French Revolution around a cadre of defectors from the French Guards.
...
and reservist personnel, and over 747,000 civilians, bringing the total to over 2.91 million employees. Headquartered at the Pentagon
The Pentagon is the headquarters building of the United States Department of Defense, in Arlington County, Virginia, across the Potomac River from Washington, D.C. The building was constructed on an accelerated schedule during World War II. As ...
in Arlington County, Virginia
Arlington County, or simply Arlington, is a County (United States), county in the U.S. state of Virginia. The county is located in Northern Virginia on the southwestern bank of the Potomac River directly across from Washington, D.C., the nati ...
, just outside Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
, the Department of Defense's stated mission is "to provide the military forces needed to deter war and ensure our nation's security". The current Secretary of Defense is Pete Hegseth.
The Department of Defense is headed by the secretary of defense, a cabinet-level head who reports directly to the president of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal government of t ...
. The president is commander-in-chief of the U.S. armed forces. Beneath the Department of Defense are three subordinate military departments: the Department of the Army
The United States Department of the Army (DA) is one of the three military departments within the United States Department of Defense. The DA is the federal government agency within which the United States Army (U.S.) is organized. It is led ...
, the Department of the Navy, and the Department of the Air Force
The United States Department of the Air Force (DAF) is one of the three military departments within the United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense of the United States of America. The Department of the Air Force was formed on Sep ...
. In addition, four national intelligence services are subordinate to the Department of Defense: the Defense Intelligence Agency
The Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) is an intelligence agency and combat support agency of the United States Department of Defense (DoD) specializing in military intelligence.
A component of the Department of Defense and the United States In ...
, National Security Agency
The National Security Agency (NSA) is an intelligence agency of the United States Department of Defense, under the authority of the director of national intelligence (DNI). The NSA is responsible for global monitoring, collection, and proces ...
(NSA), National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency
The National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) is a combat support agency within the United States Department of Defense whose primary mission is collecting, analyzing, and distributing geospatial intelligence (GEOINT) to support national se ...
, and National Reconnaissance Office.
Other Department of Defense agencies include the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military. Originally known as the Adva ...
(DARPA), Defense Logistics Agency
The Defense Logistics Agency (DLA) is a combat support agency in the United States Department of Defense, United States Department of Defense (DoD). The agency is staffed by more than 26,000 civilian and military personnel throughout the world. ...
, Missile Defense Agency
The Missile Defense Agency (MDA) is a component of the Federal government of the United States, United States government's United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense responsible for developing a comprehensive Missile defense, defe ...
, Defense Health Agency
The Defense Health Agency (DHA) is a joint, integrated combat support agency that enables the U.S. Army, U.S. Navy, and U.S. Air Force medical services to provide a medically ready force and ready medical force to Combatant Commands in both pea ...
, Defense Threat Reduction Agency, Defense Counterintelligence and Security Agency, Space Development Agency
The Space Development Agency (SDA) is a United States Space Force direct-reporting unit tasked with deploying disruptive space technology.SDA.miAbout Us One of the technologies being worked on is space-based missile tracking using large global s ...
and Pentagon Force Protection Agency, all of which are subordinate to the secretary of defense. Additionally, the Defense Contract Management Agency is responsible for administering contracts for the Department of Defense. Military operations are managed by eleven regional or functional unified combatant commands. The Department of Defense also operates several joint services schools, including the Eisenhower School and the National War College
In the United States, the National War College (NWC) is a school within the National Defense University. It is housed in Roosevelt Hall on Fort Lesley J. McNair, Washington, D.C., the third-oldest Army post still active.
History
The National ...
.
History
Faced with rising tensions between theThirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were the British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America which broke away from the British Crown in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), and joined to form the United States of America.
The Thirteen C ...
and the British government
His Majesty's Government, abbreviated to HM Government or otherwise UK Government, is the central government, central executive authority of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
, one of the first actions taken by the First Continental Congress
The First Continental Congress was a meeting of delegates of twelve of the Thirteen Colonies held from September 5 to October 26, 1774, at Carpenters' Hall in Philadelphia at the beginning of the American Revolution. The meeting was organized b ...
in September 1774 was to recommend that the colonies begin defensive military preparations. In mid-June 1775, after the outbreak of the Revolutionary War, the Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress (1775–1781) was the meetings of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that united in support of the American Revolution and American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War, which established American independence ...
, recognizing the necessity of having a national army that could move about and fight beyond the boundaries of any particular colony, organized the Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies representing the Thirteen Colonies and later the United States during the American Revolutionary War. It was formed on June 14, 1775, by a resolution passed by the Second Continental Co ...
on 14 June 1775. Later that year, Congress would charter the Continental Navy
The Continental Navy was the navy of the United Colonies and United States from 1775 to 1785. It was founded on October 13, 1775 by the Continental Congress to fight against British forces and their allies as part of the American Revolutionary ...
on 13 October, and the Continental Marines
The Continental Marines were the Amphibious warfare, amphibious infantry of the Thirteen Colonies, American Colonies (and later the United States) during the American Revolutionary War. The Corps was formed by the Continental Congress on Novem ...
on 10 November.
War Department and Navy Department
Upon the seating of the 1st U.S. Congress on 4 March 1789, legislation to create a military defense force stagnated as they focused on other concerns relevant to setting up the new government. PresidentGeorge Washington
George Washington (, 1799) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the first president of the United States, serving from 1789 to 1797. As commander of the Continental Army, Washington led Patriot (American Revoluti ...
went to Congress to remind them of their duty to establish a military twice during this time. Finally, on the last day of the session, 29 September 1789, Congress created the War Department. The War Department handled naval affairs until Congress created the Navy Department in 1798. The secretaries of each department reported directly to the president as cabinet-level advisors until 1949, when all military departments became subordinate to the Secretary of Defense.
National Military Establishment
After the end ofWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, President Harry Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. As the 34th vice president in 1945, he assumed the presidency upon the death of Franklin D. Roosevelt that year. Subsequen ...
proposed the creation of a unified department of national defense. In a special message to the Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
on 19 December 1945, the president cited wasteful military spending and interdepartmental conflicts. Deliberations in Congress went on for months focusing heavily on the role of the military in society and the threat of granting too much military power to the executive. On 26 July 1947, Truman signed the National Security Act of 1947
The National Security Act of 1947 (Act of Congress, Pub.L.]80-253 61 United States Statutes at Large, Stat.]495 enacted July 26, 1947) was a law enacting major restructuring of the Federal government of the United States, United States governmen ...
, which established the National Military Establishment (NME) and created the United States National Security Council, National Security Council, National Security Resources Board, United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Air force, air service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is one of the six United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Tracing its ori ...
, and the Joint Chiefs of Staff
The Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) is the body of the most senior uniformed leaders within the United States Department of Defense, which advises the president of the United States, the secretary of defense, the Homeland Security Council and ...
. The NME was placed under the control of the new post of secretary of defense.
The National Military Establishment formally began operations on 18 September, the day after the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
confirmed James V. Forrestal as the first secretary of defense. The National Military Establishment was renamed the "Department of Defense" on 10 August 1949, and absorbed the three cabinet-level military departments, in an amendment to the original 1947 law. The renaming is alleged to be due to the Establishment's abbreviation, NME, being pronounced "enemy."
Under the Department of Defense Reorganization Act of 1958 (), channels of authority within the department were streamlined while still maintaining the ordinary jurisdiction of the Military Departments to organize, train, and equip their associated forces. The Act clarified the overall decision-making authority of the secretary of defense concerning these subordinate military departments. It more clearly defined the operational chain of command over U.S. military forces (created by the military departments) as running from the president to the secretary of defense, the service chief of the unified combatant commander(s), and then to the unified combatant commander(s). Also provided in this legislation was a centralized research authority, the Advanced Research Projects Agency, eventually known as DARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military. Originally known as the Adva ...
. The act was written and promoted by the Eisenhower administration and was signed into law on 6 August 1958.
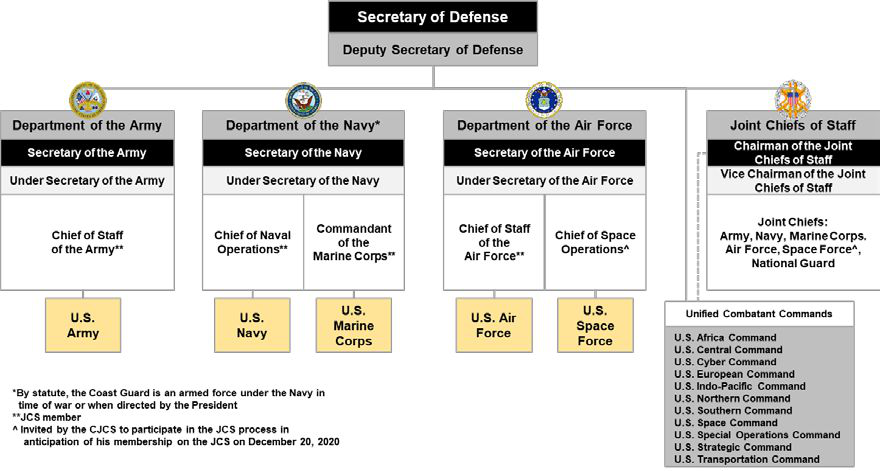
Organizational structure

 The secretary of defense, appointed by the president with the advice and consent of the
The secretary of defense, appointed by the president with the advice and consent of the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
, is by federal law () the head of the Department of Defense, "the principal assistant to the President in all matters relating to Department of Defense", and has "authority, direction, and control over the Department of Defense". Because the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these pri ...
vests all military authority in Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
and the president, the statutory authority of the secretary of defense is derived from their constitutional authority. Since it is impractical for either Congress or the president to participate in every piece of Department of Defense affairs, the secretary of defense and the secretary's subordinate officials generally exercise military authority.
The Department of Defense is composed of the Office of the Secretary of Defense
The Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD) is a headquarters-level staff of the United States Department of Defense. It is the principal civilian staff element of the U.S. Secretary of Defense, and it assists the Secretary in carrying out au ...
, Joint Chiefs of Staff
The Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) is the body of the most senior uniformed leaders within the United States Department of Defense, which advises the president of the United States, the secretary of defense, the Homeland Security Council and ...
and Joint Staff
The Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) is the body of the most senior uniformed leaders within the United States Department of Defense, which advises the president of the United States, the United States Secretary of Defense, secretary of defense, ...
, Office of the Inspector General
In the United States, Office of Inspector General (OIG) is a generic term for the oversight division of a List of federal agencies in the United States, federal or state agency aimed at preventing inefficient or unlawful operations within their p ...
, Combatant Commands, Military Departments (Department of the Army
The United States Department of the Army (DA) is one of the three military departments within the United States Department of Defense. The DA is the federal government agency within which the United States Army (U.S.) is organized. It is led ...
, Department of the Navy and Department of the Air Force
The United States Department of the Air Force (DAF) is one of the three military departments within the United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense of the United States of America. The Department of the Air Force was formed on Sep ...
), Defense Agencies and Department of Defense Field Activities, National Guard Bureau, and such other offices, agencies, activities, organizations, and commands established or designated by law, or by the president or by the secretary of defense. Department of Defense Directive 5100.01 describes the organizational relationships within the department and is the foundational issuance for delineating the major functions of the department. The latest version, signed by former secretary of defense Robert Gates
Robert Michael Gates (born September 25, 1943) is an American intelligence analyst and university president who served as the 22nd United States secretary of defense from 2006 to 2011. He was appointed by President George W. Bush and retained b ...
in December 2010, is the first major re-write since 1987.
Office of the Secretary of Defense
 The
The Office of the Secretary of Defense
The Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD) is a headquarters-level staff of the United States Department of Defense. It is the principal civilian staff element of the U.S. Secretary of Defense, and it assists the Secretary in carrying out au ...
(OSD) is the secretary and their deputies, including predominantly civilian staff. OSD is the principal staff element of the Secretary of Defense in the exercise of policy development, planning, resource management, fiscal and program evaluation and oversight, and interface and exchange with other U.S. federal government departments and agencies, foreign governments, and international organizations, through formal and informal processes. OSD also performs oversight and management of the Defense Agencies, Department of Defense Field Activities, and specialized Cross Functional Teams.
Defense agencies
OSD is a parent agency of the following defense agencies:National intelligence agencies
Several defense agencies are members of theUnited States Intelligence Community
The United States Intelligence Community (IC) is a group of separate US federal government, U.S. federal government intelligence agencies and subordinate organizations that work to conduct Intelligence assessment, intelligence activities which ...
. These are national-level intelligence services that operate under the Department of Defense jurisdiction but simultaneously fall under the authorities of the Office of the Director of National Intelligence
The director of national intelligence (DNI) is a cabinet-level United States government intelligence and security official. The position is required by the Intelligence Reform and Terrorism Prevention Act of 2004 to serve as executive head o ...
. They fulfill the requirements of national policymakers and war planners, serve as Combat Support Agencies, and also assist and deploy alongside non-Department of Defense intelligence or law enforcement services such as the Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA; ) is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States tasked with advancing national security through collecting and analyzing intelligence from around the world and ...
and the Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic Intelligence agency, intelligence and Security agency, security service of the United States and Federal law enforcement in the United States, its principal federal law enforcement ag ...
. The military services each have their intelligence elements that are distinct from but subject to coordination by national intelligence agencies under the Department of Defense. Department of Defense manages the nation's coordinating authorities and assets in disciplines of signals intelligence
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is the act and field of intelligence-gathering by interception of ''signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly u ...
, geospatial intelligence, and measurement and signature intelligence
Measurement and signature intelligence (MASINT) is a technical branch of intelligence gathering, which serves to detect, track, identify or describe the distinctive characteristics (signatures) of fixed or dynamic target sources. This often inc ...
, and also builds, launches, and operates the Intelligence Community's satellite assets. Department of Defense also has its own human intelligence
Human intelligence is the Intellect, intellectual capability of humans, which is marked by complex Cognition, cognitive feats and high levels of motivation and self-awareness. Using their intelligence, humans are able to learning, learn, Concept ...
service
Service may refer to:
Activities
* Administrative service, a required part of the workload of university faculty
* Civil service, the body of employees of a government
* Community service, volunteer service for the benefit of a community or a ...
, which contributes to the CIA's human intelligence efforts while also focusing on military human intelligence priorities. These agencies are directly overseen by the under secretary of defense for intelligence and security.
Defense Intelligence Agency
The Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) is an intelligence agency and combat support agency of the United States Department of Defense (DoD) specializing in military intelligence.
A component of the Department of Defense and the United States In ...
File:US-NationalGeospatialIntelligenceAgency-2008Seal.svg, National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency
The National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) is a combat support agency within the United States Department of Defense whose primary mission is collecting, analyzing, and distributing geospatial intelligence (GEOINT) to support national se ...
File:US-NationalReconnaissanceOffice-Seal.svg, National Reconnaissance Office
File:National Security Agency.svg, National Security Agency
The National Security Agency (NSA) is an intelligence agency of the United States Department of Defense, under the authority of the director of national intelligence (DNI). The NSA is responsible for global monitoring, collection, and proces ...
Joint Chiefs of Staff
 The
The Joint Chiefs of Staff
The Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) is the body of the most senior uniformed leaders within the United States Department of Defense, which advises the president of the United States, the secretary of defense, the Homeland Security Council and ...
is a body of senior uniformed leaders in the Department of Defense who advise the secretary of defense, the Homeland Security Council, the United States National Security Council, National Security Council and the president on military matters. The composition of the Joint Chiefs of Staff is defined by statute and consists of the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
The chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (CJCS) is the presiding officer of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS). The chairman is the highest-ranking and most senior military officer in the United States Armed Forces Chairman: appointment; gra ...
, vice chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
The vice chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (VJCS) is, by U.S. law, the second highest-ranking military officer in the United States Armed Forces, - Vice Chairman ranking just below the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff. The vice chairman ...
, senior enlisted advisor to the chairman, the Military Service chiefs from the Army
An army, ground force or land force is an armed force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by ...
, Marine Corps, Navy
A navy, naval force, military maritime fleet, war navy, or maritime force is the military branch, branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral z ...
, Air Force
An air force in the broadest sense is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an army aviati ...
, and Space Force
A space force is a military branch of a nation's armed forces that conducts military operations in outer space and space warfare. The world's first space force was the Russian Space Forces, established in 1992 as an independent military service. ...
, in addition to the chief of National Guard Bureau, all appointed by the president following U.S. Senate confirmation. Each of the individual military service chiefs, outside their Joint Chiefs of Staff obligations, works directly for the secretary of the military department concerned: the secretary of the Army
The secretary of the Army (SA or SECARMY) is a senior civilian official within the United States Department of Defense, with statutory responsibility for all matters relating to the United States Army: manpower, personnel, reserve affairs, insta ...
, secretary of the Navy
The Secretary of the Navy (SECNAV) is a statutory officer () and the head (chief executive officer) of the Department of the Navy, a military department within the United States Department of Defense. On March 25, 2025, John Phelan was confirm ...
, and secretary of the Air Force.
Following the Goldwater–Nichols Act
The Goldwater–Nichols Department of Defense Reorganization Act of October 4, 1986 (; signed by President Ronald Reagan) made the most sweeping changes to the United States Department of Defense since the department was established in the Na ...
in 1986, the Joint Chiefs of Staff
The Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) is the body of the most senior uniformed leaders within the United States Department of Defense, which advises the president of the United States, the secretary of defense, the Homeland Security Council and ...
no longer maintained operational command authority individually or collectively. The act designated the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (CJCS) as the "principal military adviser to the president, the National Security Council, the Homeland Security Council, and the Secretary of Defense". The remaining Joint Chiefs of Staff may only have their advice relayed to the president, National Security Council, the Homeland Security Council, or the secretary of defense after submitting it to the CJCS. By law, the chairman has to present that advice whenever he is presenting his own. The chain of command goes from the president
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
to the secretary of defense to the commanders of the Combatant Commands. Goldwater–Nichols also created the office of vice-chairman, and the chairman is now designated as the ''principal military adviser'' to the secretary of defense, the Homeland Security Council, the National Security Council and to the president.
The Joint Staff is a headquarters staff at the Pentagon
In geometry, a pentagon () is any five-sided polygon or 5-gon. The sum of the internal angles in a simple polygon, simple pentagon is 540°.
A pentagon may be simple or list of self-intersecting polygons, self-intersecting. A self-intersecting ...
made up of personnel from all five services that assist the chairman and vice chairman in discharging their duties. It is managed by the director of the Joint Staff who is a lieutenant general
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the battlefield, who was norma ...
or vice admiral
Vice admiral is a senior naval flag officer rank, usually equivalent to lieutenant general and air marshal. A vice admiral is typically senior to a rear admiral and junior to an admiral.
Australia
In the Royal Australian Navy, the rank of Vice ...
.
Military departments and services
There are three military departments within the Department of Defense: # theDepartment of the Army
The United States Department of the Army (DA) is one of the three military departments within the United States Department of Defense. The DA is the federal government agency within which the United States Army (U.S.) is organized. It is led ...
, within which the United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary Land warfare, land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of th ...
is organized.
# the Department of the Navy, within which the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
and the United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines or simply the Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is responsible for conducting expeditionar ...
are organized.
# the Department of the Air Force
The United States Department of the Air Force (DAF) is one of the three military departments within the United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense of the United States of America. The Department of the Air Force was formed on Sep ...
, within which the United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Air force, air service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is one of the six United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Tracing its ori ...
and United States Space Force
The United States Space Force (USSF) is the space force branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is one of the six United States Armed Forces, armed forces of the United States and one of the eight uniformed services of the Unite ...
are organized.
The military departments are each headed by their secretary (i.e., Secretary of the Army
The secretary of the Army (SA or SECARMY) is a senior civilian official within the United States Department of Defense, with statutory responsibility for all matters relating to the United States Army: manpower, personnel, reserve affairs, insta ...
, Secretary of the Navy
The Secretary of the Navy (SECNAV) is a statutory officer () and the head (chief executive officer) of the Department of the Navy, a military department within the United States Department of Defense. On March 25, 2025, John Phelan was confirm ...
and Secretary of the Air Force), appointed by the president, with the advice and consent of the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
. They have the legal authority under Title 10 of the United States Code
Title 10 of the United States Code outlines the role of United States Armed Forces.
It provides the legal basis for the roles, missions and organization of each of the services as well as the United States Department of Defense. Each of the fi ...
to conduct all the affairs of their respective departments within which the military services are organized. The secretaries of the military departments are (by law) subordinate to the secretary of defense and (by SecDef delegation) to the deputy secretary of defense
The deputy secretary of defense (acronym: DepSecDef) is a statutory office () and the second-highest-ranking official in the Department of Defense of the United States of America.
The deputy secretary is the principal civilian deputy to the s ...
.
Secretaries of military departments, in turn, normally exercise authority over their forces by delegation through their respective service chiefs (i.e., Chief of Staff of the Army, Commandant of the Marine Corps Commandant of the Marine Corps may refer to:
* Commandant of the Marine Corps (Indonesia)
* Commandant of the Netherlands Marine Corps
* Commandant of the Philippine Marine Corps
* Commandant of the Republic of Korea Marine Corps
* Commandant of th ...
, Chief of Naval Operations
The chief of naval operations (CNO) is the highest-ranking officer of the United States Navy. The position is a statutory office () held by an Admiral (United States), admiral who is a military adviser and deputy to the United States Secretary ...
, Chief of Staff of the Air Force, and Chief of Space Operations) over forces not assigned to a Combatant Command.
Military departments are tasked solely with "the training, provision of equipment, and administration of troops." The Defense Reorganization Act of 1958 removed the power of command over troops from secretaries of military departments and service chiefs.
Department of the Army
The United States Department of the Army (DA) is one of the three military departments within the United States Department of Defense. The DA is the federal government agency within which the United States Army (U.S.) is organized. It is led ...
File:United States Department of the Navy Seal.svg, Department of the Navy
File:Seal of the US Air Force.svg, Department of the Air Force
The United States Department of the Air Force (DAF) is one of the three military departments within the United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense of the United States of America. The Department of the Air Force was formed on Sep ...
Unified Combatant Commands
 A unified combatant command is a military command composed of personnel/equipment from at least two Military Departments, which has a broad, continuing mission. They are responsible for the operational command of forces. Almost all operational U.S. forces are under the authority of a Unified Command. The DOD Unified Command Plan lays out combatant commands' missions, geographical/functional responsibilities, and force structure.
During military operations, the chain of command runs from the president to the secretary of defense to the combatant commanders of the Combatant Commands.
, the United States has eleven Combatant Commands, organized either on a geographical basis (known as "
A unified combatant command is a military command composed of personnel/equipment from at least two Military Departments, which has a broad, continuing mission. They are responsible for the operational command of forces. Almost all operational U.S. forces are under the authority of a Unified Command. The DOD Unified Command Plan lays out combatant commands' missions, geographical/functional responsibilities, and force structure.
During military operations, the chain of command runs from the president to the secretary of defense to the combatant commanders of the Combatant Commands.
, the United States has eleven Combatant Commands, organized either on a geographical basis (known as "area of responsibility
Area of responsibility (AOR) is a pre-defined geographic region assigned to Combatant commanders of the Unified Command Plan (UCP), that are used to define an area with specific geographic boundaries where they have the authority to plan and c ...
", AOR) or on a global, functional basis:
* U.S. Northern Command (USNORTHCOM)
*U.S. Southern Command
The United States Southern Command (USSOUTHCOM), located in Doral in Greater Miami, Florida, is one of the eleven unified combatant commands in the United States Department of Defense. It is responsible for providing contingency planning, ope ...
(USSOUTHCOM)
* U.S. Central Command (USCENTCOM)
* U.S. European Command (USEUCOM)
* U.S. Indo-Pacific Command (USINDOPACOM)
*U.S. Africa Command
The United States Africa Command (USAFRICOM, U.S. AFRICOM, and AFRICOM) is one of the eleven unified combatant commands of the United States Department of Defense, headquartered at Kelley Barracks, Stuttgart, Germany. It is responsible for U. ...
(USAFRICOM)
* U.S. Strategic Command (USSTRATCOM)
* U.S. Special Operations Command (USSOCOM)
* U.S. Transportation Command (USTRANSCOM)
* U.S. Cyber Command (USCYBERCOM)
* U.S. Space Command (USSPACECOM)
Budget

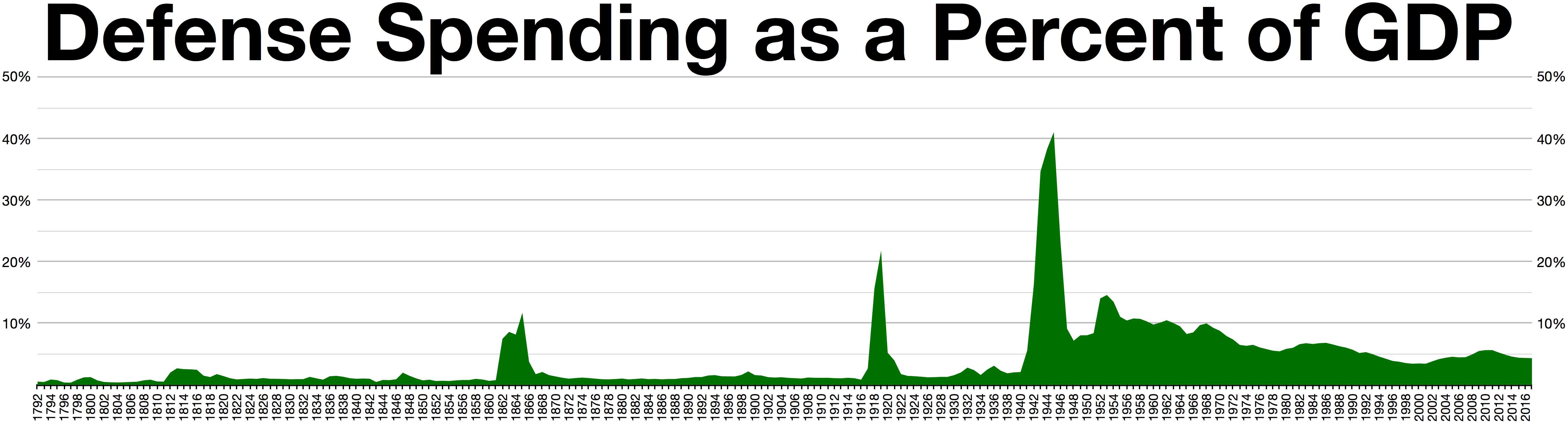
 Department of Defense spending in 2017 was 3.15% of GDP and accounted for about 38% of the budgeted global military spending – more than the next 7 largest militaries combined. By 2019, the 27th secretary of defense had begun a line-by-line review of the defense budget; in 2020 the secretary identified items amounting to $5.7 billion, out of a $106 billion subtotal (the so-called "fourth estate" agencies such as missile defense, and defense intelligence, amounting to 16% of the defense budget), He will re-deploy to the modernization of hypersonics, artificial intelligence, and missile defense. Beyond 2021 the 27th secretary of defense is projecting the need for yearly budget increases of 3 to 5 percent to modernize.McLeary (6 February 2020) Flatline: SecDef Esper Says DoD Budgets Must Grow 3–5%
Department of Defense spending in 2017 was 3.15% of GDP and accounted for about 38% of the budgeted global military spending – more than the next 7 largest militaries combined. By 2019, the 27th secretary of defense had begun a line-by-line review of the defense budget; in 2020 the secretary identified items amounting to $5.7 billion, out of a $106 billion subtotal (the so-called "fourth estate" agencies such as missile defense, and defense intelligence, amounting to 16% of the defense budget), He will re-deploy to the modernization of hypersonics, artificial intelligence, and missile defense. Beyond 2021 the 27th secretary of defense is projecting the need for yearly budget increases of 3 to 5 percent to modernize.McLeary (6 February 2020) Flatline: SecDef Esper Says DoD Budgets Must Grow 3–5%/ref> The Department of Defense accounts for the majority of federal discretionary spending. In FY 2017, the Department of Defense budgeted spending accounted for 15% of the U.S. federal budget, and 49% of federal
discretionary spending
In United States, American public finance, discretionary spending is government spending implemented through an Appropriations bill (United States), appropriations bill. This spending is an optional part of fiscal policy, in contrast to social ...
, which represents funds not accounted for by pre-existing obligations. However, this does not include many military-related items that are outside the Department of Defense budget, such as nuclear weapons research, maintenance, cleanup, and production, which is in the Department of Energy budget, Veterans Affairs, the Treasury Department's payments in pensions to military retirees and widows and their families, interest on debt incurred in past wars, or State Department financing of foreign arms sales and militarily-related development assistance. Neither does it include defense spending that is not military, such as the Department of Homeland Security, counter-terrorism spending by the FBI, and intelligence-gathering spending by the NSA.
In the 2010 United States federal budget
The United States Federal Budget for Fiscal Year 2010, titled A New Era of Responsibility: Renewing America's Promise, is a spending request by President Barack Obama to fund government operations for October 2009–September 2010. Figu ...
, the Department of Defense was allocated a base budget of $533.7 billion, with a further $75.5 billion adjustment in respect of 2009, and $130 billion for overseas contingencies. The subsequent 2010 Department of Defense Financial Report shows the total budgetary resources for fiscal year
A fiscal year (also known as a financial year, or sometimes budget year) is used in government accounting, which varies between countries, and for budget purposes. It is also used for financial reporting by businesses and other organizations. La ...
2010 were $1.2 trillion. Of these resources, $1.1 trillion were obligated and $994 billion were disbursed, with the remaining resources relating to multi-year modernization projects requiring additional time to procure. After over a decade of non-compliance, as part of the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2010, Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
established a deadline of Fiscal year
A fiscal year (also known as a financial year, or sometimes budget year) is used in government accounting, which varies between countries, and for budget purposes. It is also used for financial reporting by businesses and other organizations. La ...
2017 for the Department of Defense to achieve audit readiness, although this did not end up occurring.
In 2015 the allocation for the Department of Defense was $585 billion, the highest level of budgetary resources among all federal agencies, and this amounts to more than one-half of the annual federal expenditures in the United States federal budget discretionary budget.
On 28 September 2018, President Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who is the 47th president of the United States. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served as the 45 ...
signed the Department of Defense and Labor, Health and Human Services, and Education Appropriations Act, 2019, and Continuing Appropriations Act, 2019 (H.R.6157) into law. On 30 September 2018, the FY2018 Budget expired and the FY2019 budget came into effect.
FY2019
The FY2019 Budget for the Department of Defense is approximately $686,074,048,000 (Including Base + Overseas Contingency Operations + Emergency Funds) in discretionary spending and $8,992,000,000 in mandatory spending totaling $695,066,000,000 Undersecretary of Defense (Comptroller) David L. Norquist said in a hearing regarding the FY 2019 budget: "The overall number you often hear is $716 billion. That is the amount of funding for national defense, the accounting code is 050 and includes more than simply the Department of Defense. It includes, for example, the Department of Energy and others. That large a number, if you back out the $30 billion for non-defense agencies, you get to $686 billion. That is the funding for the Department of Defense, split between $617 billion in base and $69 billion in overseas contingency".DoD Comptrolle(2019) Overview – National Defense Budget Estimates for Fiscal Year (FY) 2019
FY 2019 PB Green Book The Department of Defense budget encompasses the majority of the National Defense Budget of approximately $716.0 billion in discretionary spending and $10.8 billion in mandatory spending for a $726.8 billion total. Of the total, $708.1 billion falls under the jurisdiction of the House Committee on Armed Services and
Senate Armed Services Committee
The Committee on Armed Services, sometimes abbreviated SASC for Senate Armed Services Committee, is a committee of the United States Senate empowered with legislative oversight of the nation's military, including the Department of Defen ...
and is subject to authorization by the annual National Defense Authorization Act
The National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) is any of a series of United States federal laws specifying the annual budget and expenditures of the U.S. Department of Defense. The first NDAA was passed in 1961. The U.S. Congress oversees the de ...
(NDAA). The remaining $7.9 billion falls under the jurisdiction of other congressional committees.
The Department of Defense is unique because it is one of the few federal entities where the majority of its funding falls into the discretionary category. The majority of the entire federal budget is mandatory, and much of the discretionary funding in the budget consists of DoD dollars.
Budget overview
FY2024
As of 10 March 2023 thefiscal year
A fiscal year (also known as a financial year, or sometimes budget year) is used in government accounting, which varies between countries, and for budget purposes. It is also used for financial reporting by businesses and other organizations. La ...
2024 (FY2024) presidential budget request was $842billion. In January 2023, Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen
Janet Louise Yellen (born August 13, 1946) is an American economist who served as the 78th United States secretary of the treasury from 2021 to 2025. She also served as chair of the Federal Reserve from 2014 to 2018. She was the first woman to h ...
announced the US government would hit its $31.4trillion debt ceiling on 19 January 2023; the date on which the US government would no longer be able to use extraordinary measures such as issuance of Treasury securities is estimated to be in June 2023.Victor Reklaiti(17 January 2023) U.S. to hit debt limit Thursday: Here's what that means
*Committee for a Responsible Federal Budge
(28 Oct 2022) Q&A: Everything You Should Know About the Debt Ceiling
*Stephen Collinso
in
power projection
Power projection (or force projection or strength projection) in international relations is the capacity of a state to deploy and sustain forces outside its territory. The ability of a state to project its power into an area may serve as an eff ...
in light of the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
On 3 June 2023, the debt ceiling was suspended until 2025. Fiscal Responsibility Act of 2023
On January 19, 2023, the United States hit its United States debt ceiling, debt ceiling, leading to a debt-ceiling crisis, part of an ongoing political debate within United States Congress, Congress about United States federal budget, federal ...
The $886billion National Defense Authorization Act
The National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) is any of a series of United States federal laws specifying the annual budget and expenditures of the U.S. Department of Defense. The first NDAA was passed in 1961. The U.S. Congress oversees the de ...
is facing reconciliation of the House
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air c ...
and Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
bills after passing both houses 27 July 2023; the conferees have to be chosen, next. As of September 2023, a Continuing resolution is needed to prevent a Government shutdown
A government shutdown occurs when the legislative branch does not pass key bills which fund or authorize the operations of the executive branch, resulting in the cessation of some or all operations of a government.
Government shutdowns in the U ...
.
* A shutdown was avoided on 30 September for 45 days (until 17 November 2023),Alexandra Hutzler and Nadine El-Bawa(30 Sep 2023) Government shutdown live updates: House passes 45-day stopgap spending bill
/ref>Clare Foran, Haley Talbot, Morgan Rimmer, Annie Grayer, Lauren Fox and Melanie Zanona, CN
/ref>Rebecca Khee
/ref>Leo Shane III ttps://www.militarytimes.com/news/pentagon-congress/2023/12/04/defense-authorization-deal-expected-this-week/ (3 Dec 2023) Defense authorization deal expected this week/ref> with passage of the NDAA on 14 December 2023.Patricia Zengerl
(7 Dec 2023) US lawmakers introduce sweeping defense bill, drop most 'culture war' issues
Patricia Zengerl
(13 Dec 2023) US Senate passes mammoth defense policy bill, next up vote in House
Bill is nearly 3100 pages, for $886 billion NDAA passed Senate 87–13; Bryant Harri
(14 Dec 2023) Congress passed the FY24 defense policy bill: Here's what's inside
passed House 310–118. The Senate will next undertake negotiations on supplemental spending for 2024.BURGESS EVERETT, ANTHONY ADRAGNA and JENNIFER HABERKOR
(14 Dec 2024) Sinema 'can see the deal' on Ukraine-border as Schumer cuts recess
/ref>Sumanti Se
$1,659 billion= $886.3 billion for defense, $772.7 billion for non-defense A government shutdown was averted on 23 March 2024 with the signing of a $1.2 trillion bill to cover FY2024.Clare Fora
/ref>Carl Huls
/ref>
Criticism of finances
A 2013 ''Reuters'' investigation concluded thatDefense Finance and Accounting Service
The Defense Finance and Accounting Service (DFAS) is an agency of the United States Department of Defense (DOD), headquartered in Indianapolis, Indiana. The DFAS was established in 1991 under the authority, direction, and control of the Under S ...
, the Department of Defense's primary financial management arm, implements monthly "unsubstantiated change actions"—illegal, inaccurate "plugs"—that forcibly make DoD's books match Treasury's books. Reuters
Reuters ( ) is a news agency owned by Thomson Reuters. It employs around 2,500 journalists and 600 photojournalists in about 200 locations worldwide writing in 16 languages. Reuters is one of the largest news agencies in the world.
The agency ...
reported that the Pentagon
The Pentagon is the headquarters building of the United States Department of Defense, in Arlington County, Virginia, across the Potomac River from Washington, D.C. The building was constructed on an accelerated schedule during World War II. As ...
was the only federal agency that had not released annual audits as required by a 1992 law. According to Reuters, the Pentagon "annually reports to Congress that its books are in such disarray that an audit is impossible".
In 2015, a Pentagon consulting firm performed an audit on the Department of Defense's budget. It found that there was $125 billion in wasteful spending that could be saved over the next five years without layoffs or reduction in military personnel. In 2016, ''The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'', locally known as ''The'' ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'' or ''WP'', is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C., the national capital. It is the most widely circulated newspaper in the Washington m ...
'' uncovered that rather than taking the advice of the auditing firm, senior defense officials suppressed and hid the report from the public to avoid political scrutiny. In June 2016, the Office of the Inspector General
In the United States, Office of Inspector General (OIG) is a generic term for the oversight division of a List of federal agencies in the United States, federal or state agency aimed at preventing inefficient or unlawful operations within their p ...
released a report stating that the Army made $6.5 trillion in wrongful adjustments to its accounting entries in 2015. The Department of Defense failed its fifth audit in 2022, and could not account for more than 60% of its $3.5 trillion in assets.
In the latest Center for Effective Government analysis of 15 federal agencies which receive the most Freedom of Information Act requests, published in 2015 (using 2012 and 2013 data, the most recent years available), the DoD earned 61 out of a possible 100 points, a D− grade. While it had improved from a failing grade in 2013, it still had low scores in processing requests (55%) and disclosure rules (42%).March 2015, 80 pages, Center for Effective Government, retrieved March 21, 2016
Related legislation
The organization and functions of the Department of Defense are inTitle 10 of the United States Code
Title 10 of the United States Code outlines the role of United States Armed Forces.
It provides the legal basis for the roles, missions and organization of each of the services as well as the United States Department of Defense. Each of the fi ...
.
Other significant legislation related to the Department of Defense includes:
*1947: National Security Act of 1947
The National Security Act of 1947 (Act of Congress, Pub.L.]80-253 61 United States Statutes at Large, Stat.]495 enacted July 26, 1947) was a law enacting major restructuring of the Federal government of the United States, United States governmen ...
*1958: Department of Defense Reorganization Act,
*1963: Department of Defense Appropriations Act,
*1963: Military Construction Authorization Act,
*1967: Supplemental Defense Appropriations Act,
*1984: Department of Defense Authorization Act,
*1986: Goldwater-Nichols Act of 1986 (Department of Defense Reorganization Act),
*1996: Antiterrorism and Effective Death Penalty Act,
See also
* Arms industry * Energy usage of the United States military *Global Command and Control System
Global Command and Control System (GCCS) is the United States' armed forces DoD joint command and control (C2) system used to provide accurate, complete, and timely information for the operational command hierarchy, chain of command for U.S. armed ...
* JADE (planning system)
*List of United States defense contractors
The Top 100 Contractors Report on the Federal Procurement Data System lists the top 100 defense contractors by sales to the United States Armed Forces and Department of Defense. ('DoD 9700' worksheet). The Department of Defense
The United ...
* List of United States military bases
*Military–industrial complex
The expression military–industrial complex (MIC) describes the relationship between a country's military and the Arms industry, defense industry that supplies it, seen together as a vested interest which influences public policy. A driving fac ...
*Nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear exp ...
s
* Private military company
* Title 32 of the Code of Federal Regulations
*United States Department of Homeland Security
The United States Department of Homeland Security (DHS) is the U.S. United States federal executive departments, federal executive department responsible for public security, roughly comparable to the Interior minister, interior, Home Secretary ...
*United States Department of Justice
The United States Department of Justice (DOJ), also known as the Justice Department, is a United States federal executive departments, federal executive department of the U.S. government that oversees the domestic enforcement of Law of the Unite ...
*United States Department of Veterans Affairs
The United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is a Cabinet-level executive branch department of the federal government charged with providing lifelong healthcare services to eligible military veterans at the 170 VA medical centers an ...
*Warrior Games
The Warrior Games is a multi-sport event for wounded, injured or ill service personnel and veterans organized by the United States Department of Defense.
History 2010–2014
The Warrior Games have taken place annually since 2010 except ...
Notes
References
* *External links
*Department of Defense
on
USAspending.gov
USAspending.gov is a database of spending by the United States federal government.
History
Around the time of the Federal Funding Accountability and Transparency Act of 2006's passage, OMB Watch, a government watchdog group, was developing a ...
Department of Defense
in the
Federal Register
The ''Federal Register'' (FR or sometimes Fed. Reg.) is the government gazette, official journal of the federal government of the United States that contains government agency rules, proposed rules, and public notices. It is published every wee ...
Office of the Under Secretary of Defense (Comptroller)
Budget and Financial Management Policy
Death and Taxes: 2009
��A visual guide and infographic of the 2009 United States federal budget, including the Department of Defense with data provided by the Comptrollers office.
* * * {{Authority control 1947 establishments in the United States
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
Government agencies established in 1947
NATO defence ministries
Nuclear weapons infrastructure of the United States
Defense
Defense or defence may refer to:
Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups
* Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare
* Civil defense, the organizing of civilians to deal with emergencies or enemy attacks
* Defense industr ...