Djibouti Diplomacy-related Lists on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the
 The Bab-el-Mandeb region has often been considered a primary crossing point for early hominins following a southern coastal route from
The Bab-el-Mandeb region has often been considered a primary crossing point for early hominins following a southern coastal route from 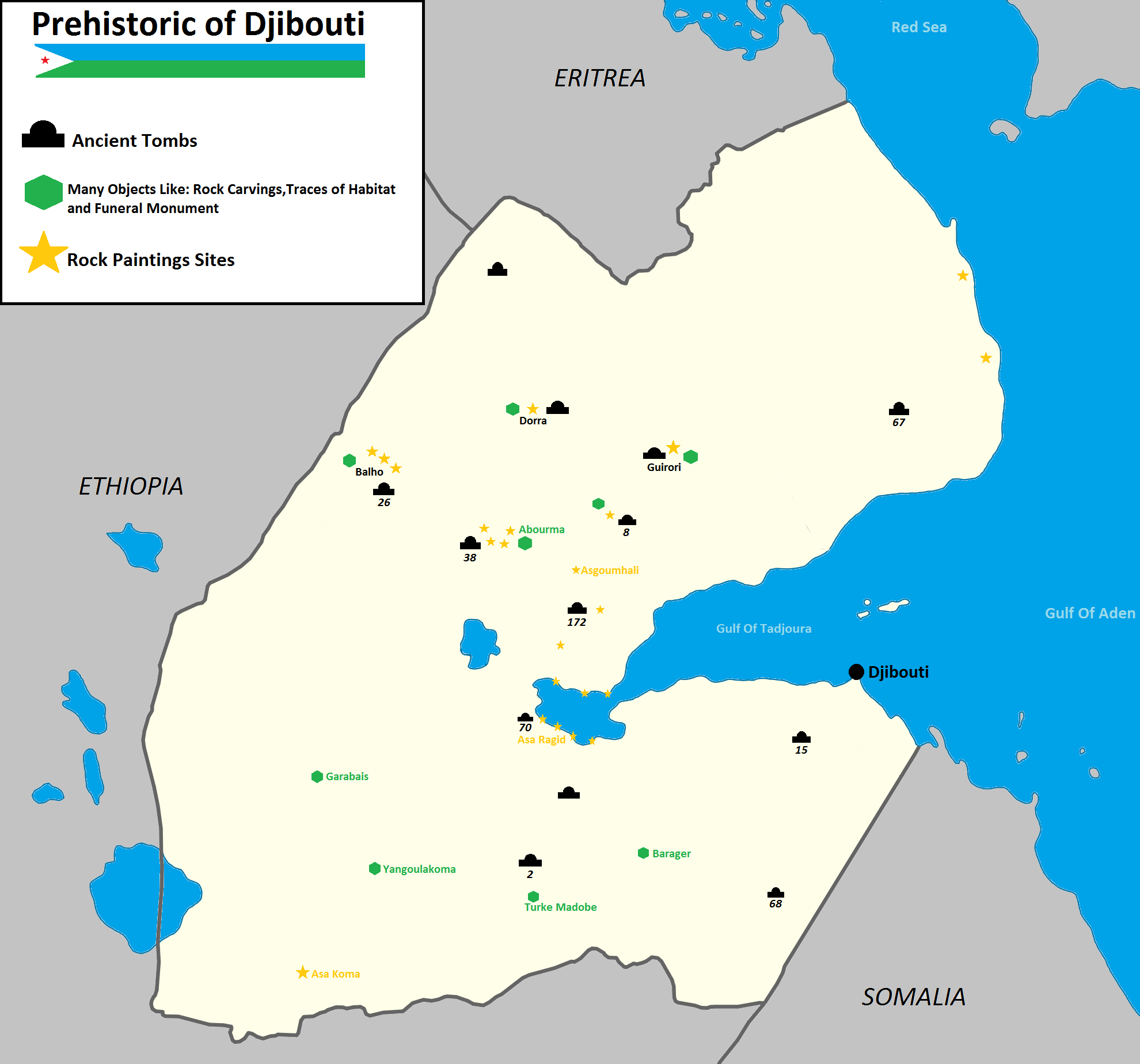 Pottery predating the mid-2nd millennium has been found at
Pottery predating the mid-2nd millennium has been found at
 Together with northern Ethiopia, Somaliland, Eritrea and the Red Sea coast of Sudan, Djibouti is considered the most likely location of the territory known to the Ancient Egyptians as '' Punt'' (or ''Ta Netjeru'', meaning "God's Land"). The first mention of the Land of Punt dates to the 25th century BC. The Puntites were a nation of people who had close relations with Ancient Egypt during the reign of the 5th dynasty Pharaoh Sahure and the 18th dynasty Queen Hatshepsut. According to the temple murals at Deir el-Bahari, the Land of Punt was ruled at that time by King Parahu and Queen Ati.
Together with northern Ethiopia, Somaliland, Eritrea and the Red Sea coast of Sudan, Djibouti is considered the most likely location of the territory known to the Ancient Egyptians as '' Punt'' (or ''Ta Netjeru'', meaning "God's Land"). The first mention of the Land of Punt dates to the 25th century BC. The Puntites were a nation of people who had close relations with Ancient Egypt during the reign of the 5th dynasty Pharaoh Sahure and the 18th dynasty Queen Hatshepsut. According to the temple murals at Deir el-Bahari, the Land of Punt was ruled at that time by King Parahu and Queen Ati.
 Through close contacts with the adjacent Arabian Peninsula for more than 1,000 years, the Somali and Afar ethnic groups in the region became among the first populations on the continent to embrace Islam. The Ifat Sultanate was a Muslim medieval kingdom in the
Through close contacts with the adjacent Arabian Peninsula for more than 1,000 years, the Somali and Afar ethnic groups in the region became among the first populations on the continent to embrace Islam. The Ifat Sultanate was a Muslim medieval kingdom in the
 According to the 16th-century explorer Leo Africanus, the Adal Sultanate's realm encompassed the geographical area between the
According to the 16th-century explorer Leo Africanus, the Adal Sultanate's realm encompassed the geographical area between the
 Although nominally part of the Ottoman Empire since 1577, between 1821 and 1841,
Although nominally part of the Ottoman Empire since 1577, between 1821 and 1841,
 Although the population fell after the completion of the railwayline to
Although the population fell after the completion of the railwayline to
''After Independence: Making and Protecting the Nation in Postcolonial and Postcommunist States''
. University of Michigan Press. p. 115. There were also allegations of widespread vote rigging. The majority of those who had voted no were Somalis who were strongly in favour of joining a united Somalia as had been proposed by Mahmoud Harbi, Vice President of the Government Council. Harbi was killed in a plane crash two years later under suspicious circumstances. In 1966, France rejected the United Nations' recommendation that it should grant French Somaliland independence. In August of the same year, an official visit to the territory by then French President, General
In 1966, France rejected the United Nations' recommendation that it should grant French Somaliland independence. In August of the same year, an official visit to the territory by then French President, General  During the 1960s, the struggle for independence was led by the
During the 1960s, the struggle for independence was led by the
 A third independence referendum was held in the French Territory of the Afars and the Issas on 8 May 1977. The previous referendums were held in
A third independence referendum was held in the French Territory of the Afars and the Issas on 8 May 1977. The previous referendums were held in
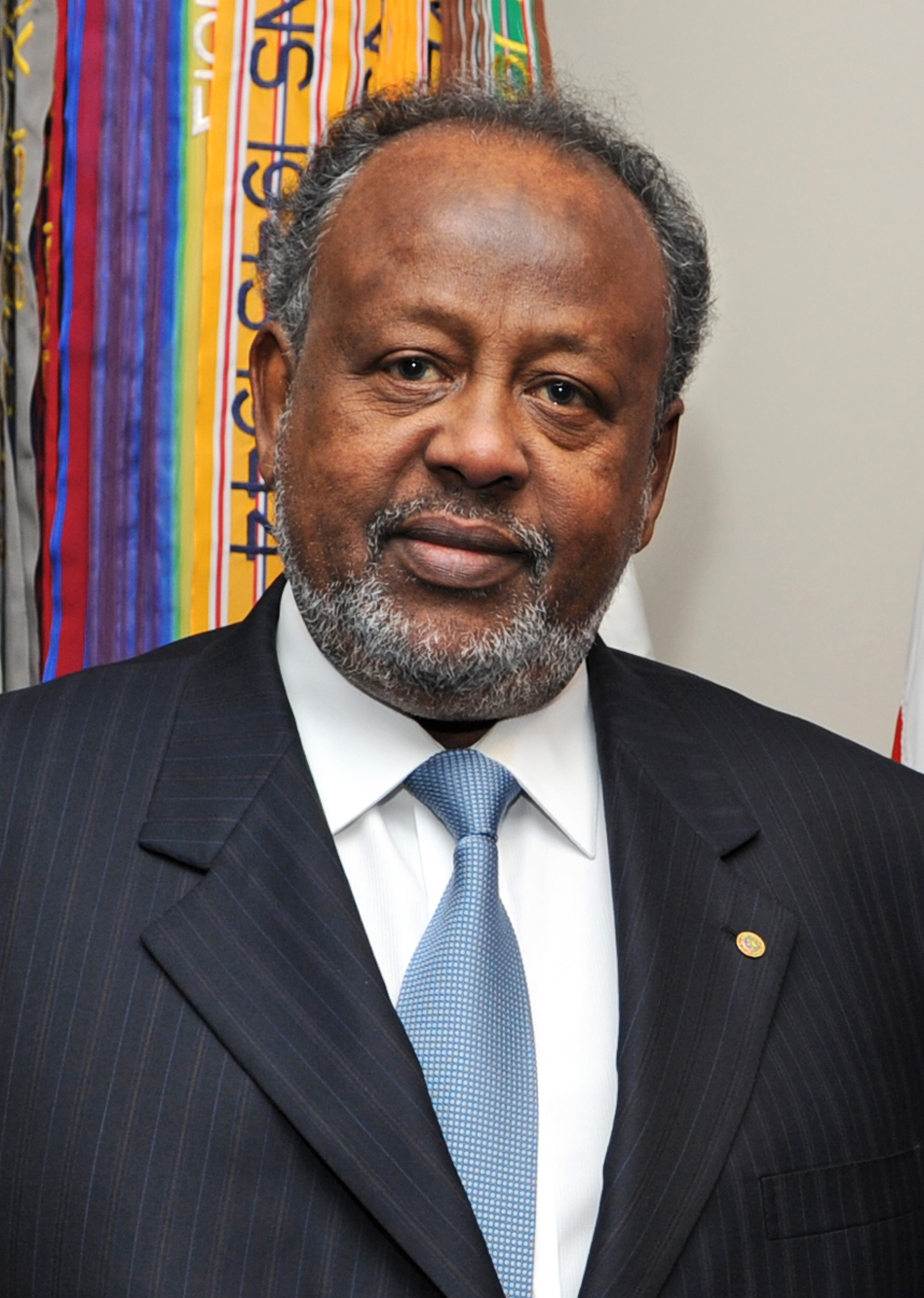 The President of Djibouti, President, Ismaïl Omar Guelleh, is the prominent figure in Djiboutian politics; the head of state and commander-in-chief. The President exercises their executive power assisted by their appointee, the Prime Minister of Djibouti, Prime Minister, Abdoulkader Kamil Mohamed. The Council of Ministers (cabinet) is responsible to and presided over by the President.
The judicial system consists of courts of first instance, a High Court of Appeal, and a Supreme Court. The legal system is a blend of Civil law (legal system), French civil law and customary law (''Xeer'') of the Somali and Afar peoples.
The National Assembly (formerly the ''Chamber of Deputies'') is the country's legislature, consisting of 65 members elected every five years. Although unicameral, the Constitution provides for the creation of a Senate.
The President of Djibouti, President, Ismaïl Omar Guelleh, is the prominent figure in Djiboutian politics; the head of state and commander-in-chief. The President exercises their executive power assisted by their appointee, the Prime Minister of Djibouti, Prime Minister, Abdoulkader Kamil Mohamed. The Council of Ministers (cabinet) is responsible to and presided over by the President.
The judicial system consists of courts of first instance, a High Court of Appeal, and a Supreme Court. The legal system is a blend of Civil law (legal system), French civil law and customary law (''Xeer'') of the Somali and Afar peoples.
The National Assembly (formerly the ''Chamber of Deputies'') is the country's legislature, consisting of 65 members elected every five years. Although unicameral, the Constitution provides for the creation of a Senate.
 The Djiboutian parliamentary election, 2018, last election was held on 23 February 2018. Djibouti has a dominant-party system, with the People's Rally for Progress (RPP) controlling the legislature and the executive since its foundation in 1979 (the party rules as a part of the Union for a Presidential Majority, which holds a supermajority of seats). Opposition parties are allowed (limited) freedom, but the main opposition party, the Union for National Salvation, boycotted the 2005 and 2008 elections, citing government control of the media and repression of the opposition candidates.
The government is dominated by the Somali Issa (clan), Issa Dir clan, who enjoy the support of the Somali clans, especially the
The Djiboutian parliamentary election, 2018, last election was held on 23 February 2018. Djibouti has a dominant-party system, with the People's Rally for Progress (RPP) controlling the legislature and the executive since its foundation in 1979 (the party rules as a part of the Union for a Presidential Majority, which holds a supermajority of seats). Opposition parties are allowed (limited) freedom, but the main opposition party, the Union for National Salvation, boycotted the 2005 and 2008 elections, citing government control of the media and repression of the opposition candidates.
The government is dominated by the Somali Issa (clan), Issa Dir clan, who enjoy the support of the Somali clans, especially the
 Foreign relations of Djibouti are managed by the Djiboutian Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation. Djibouti maintains close ties with the governments of Somalia, Ethiopia, France and the United States. It is likewise an active participant in
Foreign relations of Djibouti are managed by the Djiboutian Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation. Djibouti maintains close ties with the governments of Somalia, Ethiopia, France and the United States. It is likewise an active participant in
 The Djibouti Armed Forces, Djiboutian Armed Forces include the Djiboutian Army, which consists of the Djiboutian Navy, the Djiboutian Air Force, and the National Gendarmerie (GN). , the manpower available for military service was 170,386 males and 221,411 females aged 16 to 49. Djibouti List of countries by military expenditures, spent over US$36 million annually on its military (141st in the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, SIPRI database). After independence, Djibouti had two regiments commanded by French officers. In the early 2000s, it looked outward for a model of army organization that would best advance defensive capabilities by restructuring forces into smaller, more mobile units instead of traditional divisions.
The first war which involved the Djiboutian Armed Forces was the Djiboutian Civil War between the Djiboutian government, supported by France, and the
The Djibouti Armed Forces, Djiboutian Armed Forces include the Djiboutian Army, which consists of the Djiboutian Navy, the Djiboutian Air Force, and the National Gendarmerie (GN). , the manpower available for military service was 170,386 males and 221,411 females aged 16 to 49. Djibouti List of countries by military expenditures, spent over US$36 million annually on its military (141st in the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, SIPRI database). After independence, Djibouti had two regiments commanded by French officers. In the early 2000s, it looked outward for a model of army organization that would best advance defensive capabilities by restructuring forces into smaller, more mobile units instead of traditional divisions.
The first war which involved the Djiboutian Armed Forces was the Djiboutian Civil War between the Djiboutian government, supported by France, and the
Following the establishment of the Federal Government of Somalia in 2012, a Djibouti delegation also attended the inauguration ceremony of Somalia's new president. In recent years, Djibouti has improved its training techniques, military command and information structures and has taken steps to becoming more self-reliant in supplying its military to collaborate with the United Nations in peacekeeping missions, or to provide military help to countries that officially ask for it. Now deployed to Somalia and Sudan.
 The French Armed Forces, French Forces remained present in Djibouti when the territory gained independence, first as part of a provisional protocol of June 1977 laying down the conditions for the stationing of French forces, constituting a defense agreement. A new defence cooperation treaty between France and Djibouti was signed in Paris on 21 December 2011. It entered into force on 1 May 2014. By that treaty and its security clause, France reaffirmed its commitment to the independence and territorial integrity of the Republic of Djibouti. As well before independence, in 1962, a French Foreign Legion unit, the 13th Demi-Brigade of the Foreign Legion (13 DBLE) was transferred from Algeria to Djibouti to form the core of the French garrison there. On 31 July 2011, the (13 DBLE) left Djibouti to the United Arab Emirates.
Djibouti's strategic location by the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, which separates the
The French Armed Forces, French Forces remained present in Djibouti when the territory gained independence, first as part of a provisional protocol of June 1977 laying down the conditions for the stationing of French forces, constituting a defense agreement. A new defence cooperation treaty between France and Djibouti was signed in Paris on 21 December 2011. It entered into force on 1 May 2014. By that treaty and its security clause, France reaffirmed its commitment to the independence and territorial integrity of the Republic of Djibouti. As well before independence, in 1962, a French Foreign Legion unit, the 13th Demi-Brigade of the Foreign Legion (13 DBLE) was transferred from Algeria to Djibouti to form the core of the French garrison there. On 31 July 2011, the (13 DBLE) left Djibouti to the United Arab Emirates.
Djibouti's strategic location by the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, which separates the
 Djibouti is partitioned into six administrative regions, with Djibouti (city), Djibouti city representing one of the official regions. It is further subdivided into twenty Districts of Djibouti, districts.
Djibouti is partitioned into six administrative regions, with Djibouti (city), Djibouti city representing one of the official regions. It is further subdivided into twenty Districts of Djibouti, districts.
. geonames.org The Mousa Ali range is considered the country's highest mountain range, with the tallest peak on the border with Ethiopia and Eritrea. It has an elevation of . The Grand Bara desert covers parts of southern Djibouti in the Arta, Ali Sabieh and Dikhil regions. The majority of it sits at a relatively low elevation, below . Extreme geographic points include: to the north, Ras Doumera and the point at which the border with Eritrea enters the Red Sea in the Obock Region; to the east, a section of the Red Sea coast north of Ras Bir; to the south, a location on the border with Ethiopia west of the town of As Ela; and to the west, a location on the frontier with Ethiopia immediately east of the Ethiopian town of Afambo (woreda), Afambo. Most of Djibouti is part of the Ethiopian xeric grasslands and shrublands ecoregion. The exception is an eastern strip located along the Red Sea coast, which is part of the Eritrean coastal desert.
File:Djib 003.JPG, Lake Assal (Djibouti), Lake Assal
File:Traditional houses on the Mabla Mountains.jpg, Traditional houses on the Mabla Mountains
File:Lac Abbe-02.JPG, Lake Abbe
File:The mountains near Dasbiyo.png, The mountains near Dasbiyo
File:South Djibouti Beach.png, Beach south of Djibouti City, overlooking the
 Djibouti's climate is significantly warmer and has significantly less seasonal variation than the world average. The mean daily maximum temperatures range from 32 to 41 °C (90 to 106 °F), except at high elevations. In Djibouti City, for instance, average afternoon highs range from 28 to 34 °C (82 to 93 °F) in April. But at Airolaf, which ranges from 1,535 to 1,600 m (5,036 to 5,249 ft), maximum temperature is 30 °C (86 °F) in summer and minimum 9 °C (48 °F) in winter. In the wikt:upland, uplands ranges from 500 to 800 m (1,640 to 2,624 ft), are comparable and cooler to those on the coast in the hottest months of June until August. December and January is the coolest month with averages low temperatures falling as low as 15 °C (59 °F). Djibouti has either a hot semi-arid climate (BSh) or a hot desert climate (BWh), although temperatures are much moderated at the highest elevations.
Djibouti's climate ranges from arid in the northeastern coastal regions to semiarid, semi-arid in the central, northern, western and southern parts of the country. On the eastern seaboard, annual rainfall is less than 5 inches (131 mm); in the central highlands, precipitation is about 8 to 16 inches (200 to 400 mm). The hinterland is significantly less humid than the coastal regions.
Djibouti's climate is significantly warmer and has significantly less seasonal variation than the world average. The mean daily maximum temperatures range from 32 to 41 °C (90 to 106 °F), except at high elevations. In Djibouti City, for instance, average afternoon highs range from 28 to 34 °C (82 to 93 °F) in April. But at Airolaf, which ranges from 1,535 to 1,600 m (5,036 to 5,249 ft), maximum temperature is 30 °C (86 °F) in summer and minimum 9 °C (48 °F) in winter. In the wikt:upland, uplands ranges from 500 to 800 m (1,640 to 2,624 ft), are comparable and cooler to those on the coast in the hottest months of June until August. December and January is the coolest month with averages low temperatures falling as low as 15 °C (59 °F). Djibouti has either a hot semi-arid climate (BSh) or a hot desert climate (BWh), although temperatures are much moderated at the highest elevations.
Djibouti's climate ranges from arid in the northeastern coastal regions to semiarid, semi-arid in the central, northern, western and southern parts of the country. On the eastern seaboard, annual rainfall is less than 5 inches (131 mm); in the central highlands, precipitation is about 8 to 16 inches (200 to 400 mm). The hinterland is significantly less humid than the coastal regions.
 The country's flora and fauna live in a harsh landscape with forest accounting for less than one percent of the total area of the country. Wildlife is spread over three main regions, namely from the northern mountain region of the country to the volcanic plateaux in its southern and central part and culminating in the coastal region.
The country's flora and fauna live in a harsh landscape with forest accounting for less than one percent of the total area of the country. Wildlife is spread over three main regions, namely from the northern mountain region of the country to the volcanic plateaux in its southern and central part and culminating in the coastal region.
 Most species of wildlife are found in the northern part of the country, in the ecosystem of the Day Forest National Park. At an average altitude of , the area includes the Goda massif, with a peak of . It covers an area of of Juniperus procera forest, with many of the trees rising to height. This forest area is the main habitat of the endangered and endemic Djibouti francolin (a bird), and another recently noted vertebrate, ''Platyceps afarensis'' (a colubrine snake). It also contains many species of woody and herbaceous plants, including boxwood and olive trees, which account for 60% of the total identified species in the country.
According to the country profile related to biodiversity of wildlife in Djibouti, the nation contains more than 820 species of plants, 493 species of invertebrates, 455 species of fish, 40 species of reptiles, three species of amphibians, 360 species of birds and 66 species of mammals. Wildlife of Djibouti is also listed as part of
Most species of wildlife are found in the northern part of the country, in the ecosystem of the Day Forest National Park. At an average altitude of , the area includes the Goda massif, with a peak of . It covers an area of of Juniperus procera forest, with many of the trees rising to height. This forest area is the main habitat of the endangered and endemic Djibouti francolin (a bird), and another recently noted vertebrate, ''Platyceps afarensis'' (a colubrine snake). It also contains many species of woody and herbaceous plants, including boxwood and olive trees, which account for 60% of the total identified species in the country.
According to the country profile related to biodiversity of wildlife in Djibouti, the nation contains more than 820 species of plants, 493 species of invertebrates, 455 species of fish, 40 species of reptiles, three species of amphibians, 360 species of birds and 66 species of mammals. Wildlife of Djibouti is also listed as part of
 Djibouti's economy is largely concentrated in the service sector. Commercial activities revolve around the country's free trade policies and strategic location as a Red Sea transit point. Due to limited rainfall, vegetables and fruits are the principal production crops, and other food items require importation. The GDP (purchasing power parity) in 2013 was estimated at $2.505 billion, with a real growth rate of 5% annually. Per capita income is around $2,874 (PPP). The services sector constituted around 79.7% of the GDP, followed by industry at 17.3%, and agriculture at 3%.
, the container terminal at the Port of Djibouti handles the bulk of the nation's trade. About 70% of the seaport's activity consists of imports to and exports from neighboring Ethiopia, which depends on the harbour as its main maritime outlet. As of 2018, 95% of Ethiopian transit cargo was handled by the Port of Djibouti. The port also serves as an international refueling center and transshipment hub. In 2012, the Djiboutian government in collaboration with DP World started construction of the Doraleh Container Terminal, a third major seaport intended to further develop the national transit capacity. A $396 million project, it has the capacity to accommodate 1.5 million twenty foot container units annually.
Djibouti was ranked the 177th safest investment destination in the world in the March 2011 Euromoney Country Risk rankings. To improve the environment for direct foreign investment, the Djibouti authorities in conjunction with various non-profit organizations have launched a number of development projects aimed at highlighting the country's commercial potential. The government has also introduced new private sector policies targeting high interest and inflation rates, including relaxing the tax burden on enterprises and allowing exemptions on consumption tax.
Djibouti's economy is largely concentrated in the service sector. Commercial activities revolve around the country's free trade policies and strategic location as a Red Sea transit point. Due to limited rainfall, vegetables and fruits are the principal production crops, and other food items require importation. The GDP (purchasing power parity) in 2013 was estimated at $2.505 billion, with a real growth rate of 5% annually. Per capita income is around $2,874 (PPP). The services sector constituted around 79.7% of the GDP, followed by industry at 17.3%, and agriculture at 3%.
, the container terminal at the Port of Djibouti handles the bulk of the nation's trade. About 70% of the seaport's activity consists of imports to and exports from neighboring Ethiopia, which depends on the harbour as its main maritime outlet. As of 2018, 95% of Ethiopian transit cargo was handled by the Port of Djibouti. The port also serves as an international refueling center and transshipment hub. In 2012, the Djiboutian government in collaboration with DP World started construction of the Doraleh Container Terminal, a third major seaport intended to further develop the national transit capacity. A $396 million project, it has the capacity to accommodate 1.5 million twenty foot container units annually.
Djibouti was ranked the 177th safest investment destination in the world in the March 2011 Euromoney Country Risk rankings. To improve the environment for direct foreign investment, the Djibouti authorities in conjunction with various non-profit organizations have launched a number of development projects aimed at highlighting the country's commercial potential. The government has also introduced new private sector policies targeting high interest and inflation rates, including relaxing the tax burden on enterprises and allowing exemptions on consumption tax.
 Additionally, efforts have been made to lower the estimated 60% urban unemployment rate by creating more job opportunities through investment in diversified sectors. Funds have especially gone toward building telecommunications infrastructure and increasing disposable income by supporting small businesses. Owing to its growth potential, the fishing and agro-processing sector, which represents around 15% of GDP, has also enjoyed rising investment since 2008.
To expand the modest industrial sector, a 56 megawatt geothermal power plant slated to be completed by 2018 is being constructed with the help of OPEC, the World Bank and the Global Environmental Facility. The facility is expected to solve the recurring electricity shortages, decrease the nation's reliance on Ethiopia for energy, reduce costly oil imports for diesel-generated electricity, and thereby buttress the GDP and lower debt.
The Djibouti firm Salt Investment (SIS) began a large-scale operation to industrialize the plentiful salt in Djibouti's Lake Assal (Djibouti), Lake Assal region. Operating at an annual capacity of 4 million tons, the desalination project has lifted export revenues, created more job opportunities, and provided more fresh water for the area's residents. In 2012, the Djibouti government also enlisted the services of the China Harbor Engineering Company Ltd for the construction of an ore terminal. Worth $64 million, the project enabled Djibouti to export a further 5,000 tons of salt per year to markets in Southeast Asia.
Additionally, efforts have been made to lower the estimated 60% urban unemployment rate by creating more job opportunities through investment in diversified sectors. Funds have especially gone toward building telecommunications infrastructure and increasing disposable income by supporting small businesses. Owing to its growth potential, the fishing and agro-processing sector, which represents around 15% of GDP, has also enjoyed rising investment since 2008.
To expand the modest industrial sector, a 56 megawatt geothermal power plant slated to be completed by 2018 is being constructed with the help of OPEC, the World Bank and the Global Environmental Facility. The facility is expected to solve the recurring electricity shortages, decrease the nation's reliance on Ethiopia for energy, reduce costly oil imports for diesel-generated electricity, and thereby buttress the GDP and lower debt.
The Djibouti firm Salt Investment (SIS) began a large-scale operation to industrialize the plentiful salt in Djibouti's Lake Assal (Djibouti), Lake Assal region. Operating at an annual capacity of 4 million tons, the desalination project has lifted export revenues, created more job opportunities, and provided more fresh water for the area's residents. In 2012, the Djibouti government also enlisted the services of the China Harbor Engineering Company Ltd for the construction of an ore terminal. Worth $64 million, the project enabled Djibouti to export a further 5,000 tons of salt per year to markets in Southeast Asia.
 Djibouti's gross domestic product expanded by an average of more than 6 percent per year, from US$341 million in 1985 to US$1.5 billion in 2015. The Djiboutian franc is the currency of Djibouti. It is issued by the Central Bank of Djibouti, the country's monetary authority. Since the Djiboutian franc is pegged to the U.S. dollar, it is generally stable and inflation is not a problem. This has contributed to the growing interest in investment in the country.
, 10 conventional and Islamic banks operate in Djibouti. Most arrived within the past few years, including the Somali money transfer company Dahabshiil and BDCD, a subsidiary of Swiss Financial Investments. The banking system had previously been monopolized by two institutions: the Indo-Suez Bank and the Commercial and Industrial Bank (BCIMR). To assure a robust credit and deposit sector, the government requires commercial banks to maintain 30% of shares in the financial institution; a minimum of 300 million Djiboutian francs in up-front capital is mandatory for international banks. Lending has likewise been encouraged by the creation of a guarantee fund, which allows banks to issue loans to eligible small- and medium-sized businesses without first requiring a large deposit or other collateral.
Saudi investors are also reportedly exploring the possibility of linking the
Djibouti's gross domestic product expanded by an average of more than 6 percent per year, from US$341 million in 1985 to US$1.5 billion in 2015. The Djiboutian franc is the currency of Djibouti. It is issued by the Central Bank of Djibouti, the country's monetary authority. Since the Djiboutian franc is pegged to the U.S. dollar, it is generally stable and inflation is not a problem. This has contributed to the growing interest in investment in the country.
, 10 conventional and Islamic banks operate in Djibouti. Most arrived within the past few years, including the Somali money transfer company Dahabshiil and BDCD, a subsidiary of Swiss Financial Investments. The banking system had previously been monopolized by two institutions: the Indo-Suez Bank and the Commercial and Industrial Bank (BCIMR). To assure a robust credit and deposit sector, the government requires commercial banks to maintain 30% of shares in the financial institution; a minimum of 300 million Djiboutian francs in up-front capital is mandatory for international banks. Lending has likewise been encouraged by the creation of a guarantee fund, which allows banks to issue loans to eligible small- and medium-sized businesses without first requiring a large deposit or other collateral.
Saudi investors are also reportedly exploring the possibility of linking the
 The Djibouti–Ambouli International Airport in Djibouti City, the country's only international airport, serves many intercontinental routes with scheduled and chartered flights. Air Djibouti is the flag carrier of Djibouti and is the country's largest airline.
The new and electrified standard gauge Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway started operation in January 2018. Its main purpose is to facilitate freight services between the Ethiopian hinterland and the Djiboutian Port of Doraleh.
Car ferries pass the
The Djibouti–Ambouli International Airport in Djibouti City, the country's only international airport, serves many intercontinental routes with scheduled and chartered flights. Air Djibouti is the flag carrier of Djibouti and is the country's largest airline.
The new and electrified standard gauge Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway started operation in January 2018. Its main purpose is to facilitate freight services between the Ethiopian hinterland and the Djiboutian Port of Doraleh.
Car ferries pass the
 Telecommunications in Djibouti fall under the authority of the Ministry of Communication.
Djibouti Telecom is the sole provider of telecommunication services. It mostly utilizes a microwave radio relay network. A fiber-optic cable is installed in the capital, whereas rural areas are connected via wireless local loop radio systems. Mobile cellular coverage is primarily limited to the area in and around Djibouti city. , 23,000 telephone main lines and 312,000 mobile/cellular lines were in use. The SEA-ME-WE 3 (cable system), SEA-ME-WE 3 Submarine communications cable, submarine cable operates to Jeddah, Suez, Sicily, Marseille, Colombo, Singapore and beyond. Telephone satellite earth stations include 1 Intelsat (Indian Ocean) and 1 Arabsat. Medarabtel is the regional microwave radio relay telephone network.
Radio Television of Djibouti is the state-owned national broadcaster. It operates the sole terrestrial TV station, as well as the two domestic radio networks on AM broadcasting, AM 1, FM broadcasting, FM 2, and shortwave 0. Licensing and operation of broadcast media is regulated by the government. Movie theaters include the Odeon Cinema in the capital.
, there were 215 local internet service providers. Internet users comprised around 99,000 individuals (2015). The internet country top-level domain is .dj.
Telecommunications in Djibouti fall under the authority of the Ministry of Communication.
Djibouti Telecom is the sole provider of telecommunication services. It mostly utilizes a microwave radio relay network. A fiber-optic cable is installed in the capital, whereas rural areas are connected via wireless local loop radio systems. Mobile cellular coverage is primarily limited to the area in and around Djibouti city. , 23,000 telephone main lines and 312,000 mobile/cellular lines were in use. The SEA-ME-WE 3 (cable system), SEA-ME-WE 3 Submarine communications cable, submarine cable operates to Jeddah, Suez, Sicily, Marseille, Colombo, Singapore and beyond. Telephone satellite earth stations include 1 Intelsat (Indian Ocean) and 1 Arabsat. Medarabtel is the regional microwave radio relay telephone network.
Radio Television of Djibouti is the state-owned national broadcaster. It operates the sole terrestrial TV station, as well as the two domestic radio networks on AM broadcasting, AM 1, FM broadcasting, FM 2, and shortwave 0. Licensing and operation of broadcast media is regulated by the government. Movie theaters include the Odeon Cinema in the capital.
, there were 215 local internet service providers. Internet users comprised around 99,000 individuals (2015). The internet country top-level domain is .dj.
 Tourism in Djibouti is one of the growing economic sectors of the country and is an industry that generates less than 80,000 arrivals per year, mostly the family and friends of the soldiers stationed in the country's major naval bases. Although the numbers are on the rise, there are talks of the visa on arrival being stopped, which could limit tourism growth.
Infrastructure makes it difficult for tourists to travel independently and costs of private tours are high. Since the re-opening of the train line from Addis Ababa to Djibouti in January 2018, travel by land has also resumed. Djibouti's two main geological marvels, Lake Abbe and Lake Assal, are the country's top tourist destinations. The two sites draw hundreds of tourists every year looking for remote places that are not visited by many.
Tourism in Djibouti is one of the growing economic sectors of the country and is an industry that generates less than 80,000 arrivals per year, mostly the family and friends of the soldiers stationed in the country's major naval bases. Although the numbers are on the rise, there are talks of the visa on arrival being stopped, which could limit tourism growth.
Infrastructure makes it difficult for tourists to travel independently and costs of private tours are high. Since the re-opening of the train line from Addis Ababa to Djibouti in January 2018, travel by land has also resumed. Djibouti's two main geological marvels, Lake Abbe and Lake Assal, are the country's top tourist destinations. The two sites draw hundreds of tourists every year looking for remote places that are not visited by many.
 The life expectancy at birth is around 64.7 for both males and females. Fertility is at 2.35 children per woman. In Djibouti there are about 18 doctors per 100,000 persons.
The 2010 maternal mortality rate per 100,000 births for Djibouti is 300. This is compared with 461.6 in 2008 and 606.5 in 1990. The under 5 mortality rate per 1,000 births is 95 and the neonatal mortality as a percentage of under 5's mortality are 37. In Djibouti the number of midwives per 1,000 live births is 6 and the lifetime risk of death for pregnant women 1 in 93.
About 93.1% of Djibouti's women and girls have undergone female genital mutilation (FGM, sometimes referred to as 'female circumcision'), a pre-marital custom mainly endemic to Northeast Africa and parts of the Near East.Bodman, Herbert L. and Tohidi, Nayereh Esfahlani (1998
The life expectancy at birth is around 64.7 for both males and females. Fertility is at 2.35 children per woman. In Djibouti there are about 18 doctors per 100,000 persons.
The 2010 maternal mortality rate per 100,000 births for Djibouti is 300. This is compared with 461.6 in 2008 and 606.5 in 1990. The under 5 mortality rate per 1,000 births is 95 and the neonatal mortality as a percentage of under 5's mortality are 37. In Djibouti the number of midwives per 1,000 live births is 6 and the lifetime risk of death for pregnant women 1 in 93.
About 93.1% of Djibouti's women and girls have undergone female genital mutilation (FGM, sometimes referred to as 'female circumcision'), a pre-marital custom mainly endemic to Northeast Africa and parts of the Near East.Bodman, Herbert L. and Tohidi, Nayereh Esfahlani (1998
''Women in Muslim societies: diversity within unity''
. Lynne Rienner Publishers. p. 41. . Although legally proscribed in 1994, the procedure is still widely practiced, as it is deeply ingrained in the local culture. Encouraged and performed by women in the community, FGM is primarily intended to deter promiscuity and to offer protection from assault.Suzanne G. Frayser, Thomas J. Whitby
Studies in human sexuality: a selected guide
, (Libraries Unlimited: 1995), p. 257 . About 94% of Djibouti's male population have also reportedly undergone Circumcision, male circumcision, a figure in line with adherence to Islam, which requires this.
ICT in Education in Djibouti
, World Bank The Djiboutian educational system was initially formulated to cater to a limited pupil base. As such, the schooling framework was largely elitist and drew considerably from the French colonial paradigm, which was ill-suited to local circumstances and needs.
In the late 1990s, the Djiboutian authorities revised the national educational strategy and launched a broad-based consultative process involving administrative officials, teachers, parents, national assembly members and NGOs. The initiative identified areas in need of attention and produced concrete recommendations on how to go about improving them. The government subsequently prepared a comprehensive reform plan aimed at modernizing the educational sector over the 2000–10 period. In August 2000, it passed an official Education Planning Act and drafted a medium-term development plan for the next five years. The fundamental academic system was significantly restructured and made compulsory; it now consists of five years of primary school and four years of middle school. Secondary schools also require a Certificate of Fundamental Education for admission. In addition, the new law introduced secondary-level vocational instruction and established university facilities in the country.
As a result of the Education Planning Act and the medium-term action strategy, substantial progress has been registered throughout the educational sector. In particular, school enrollment, attendance, and retention rates have all steadily increased, with some regional variation. From 2004 to 2005 to 2007–08, net enrollments of girls in primary school rose by 18.6%; for boys, it increased 8.0%. Net enrollments in middle school over the same period rose by 72.4% for girls and 52.2% for boys. At the secondary level, the rate of increase in net enrollments was 49.8% for girls and 56.1% for boys.Djibouti Assistance to Education Evaluation
The Djiboutian educational system was initially formulated to cater to a limited pupil base. As such, the schooling framework was largely elitist and drew considerably from the French colonial paradigm, which was ill-suited to local circumstances and needs.
In the late 1990s, the Djiboutian authorities revised the national educational strategy and launched a broad-based consultative process involving administrative officials, teachers, parents, national assembly members and NGOs. The initiative identified areas in need of attention and produced concrete recommendations on how to go about improving them. The government subsequently prepared a comprehensive reform plan aimed at modernizing the educational sector over the 2000–10 period. In August 2000, it passed an official Education Planning Act and drafted a medium-term development plan for the next five years. The fundamental academic system was significantly restructured and made compulsory; it now consists of five years of primary school and four years of middle school. Secondary schools also require a Certificate of Fundamental Education for admission. In addition, the new law introduced secondary-level vocational instruction and established university facilities in the country.
As a result of the Education Planning Act and the medium-term action strategy, substantial progress has been registered throughout the educational sector. In particular, school enrollment, attendance, and retention rates have all steadily increased, with some regional variation. From 2004 to 2005 to 2007–08, net enrollments of girls in primary school rose by 18.6%; for boys, it increased 8.0%. Net enrollments in middle school over the same period rose by 72.4% for girls and 52.2% for boys. At the secondary level, the rate of increase in net enrollments was 49.8% for girls and 56.1% for boys.Djibouti Assistance to Education Evaluation
. USAID (April 2009) The Djiboutian government has especially focused on developing and improving institutional infrastructure and teaching materials, including constructing new classrooms and supplying textbooks. At the post-secondary level, emphasis has also been placed on producing qualified instructors and encouraging out-of-school youngsters to pursue vocational training. , the literacy rate in Djibouti was estimated at 70%. Institutions of higher learning in the country include the University of Djibouti.
 Djiboutian attire reflects the region's hot and arid climate. When not dressed in Western clothing such as jeans and T-shirts, men typically wear the , which is a traditional sarong-like garment worn around the waist. Many nomadic people wear a loosely wrapped white cotton robe called a ''tobe'' that goes down to about the knee, with the end thrown over the shoulder (much like a Roman toga).
Women typically wear the ''dirac'', which is a long, light, diaphanous voile dress made of cotton or polyester that is worn over a full-length Slip (clothing), half-slip and a bra. Married women tend to sport head-scarves referred to as ''shash'' and often cover their upper body with a shawl known as ''garbasaar''. Unmarried or young women, however, do not always cover their heads. Traditional Arabian garb such as the male jellabiya (''jellabiyaad'' in Somali) and the female jilbāb is also commonly worn. For some occasions such as festivals, women may adorn themselves with specialized jewelry and head-dresses similar to those worn by the Berber people, Berber tribes of the Maghreb.
A lot of Djibouti's original art is passed on and preserved orally, mainly through song. Many examples of Islamic, Ottoman, and French influences can also be noted in the local buildings, which contain plasterwork, carefully constructed Motif (visual arts), motifs, and calligraphy.
Djiboutian attire reflects the region's hot and arid climate. When not dressed in Western clothing such as jeans and T-shirts, men typically wear the , which is a traditional sarong-like garment worn around the waist. Many nomadic people wear a loosely wrapped white cotton robe called a ''tobe'' that goes down to about the knee, with the end thrown over the shoulder (much like a Roman toga).
Women typically wear the ''dirac'', which is a long, light, diaphanous voile dress made of cotton or polyester that is worn over a full-length Slip (clothing), half-slip and a bra. Married women tend to sport head-scarves referred to as ''shash'' and often cover their upper body with a shawl known as ''garbasaar''. Unmarried or young women, however, do not always cover their heads. Traditional Arabian garb such as the male jellabiya (''jellabiyaad'' in Somali) and the female jilbāb is also commonly worn. For some occasions such as festivals, women may adorn themselves with specialized jewelry and head-dresses similar to those worn by the Berber people, Berber tribes of the Maghreb.
A lot of Djibouti's original art is passed on and preserved orally, mainly through song. Many examples of Islamic, Ottoman, and French influences can also be noted in the local buildings, which contain plasterwork, carefully constructed Motif (visual arts), motifs, and calligraphy.
 Somalis have a rich musical heritage centered on traditional Somali folklore. Most Somali songs are Pentatonic scale, pentatonic. That is, they only use five Pitch (music), pitches per octave in contrast to a Heptatonic scale, heptatonic (seven note) scale such as the major scale. At first listen, Somali music might be mistaken for the sounds of nearby regions such as Ethiopia, Sudan or the Arabian Peninsula, but it is ultimately recognizable by its own unique tunes and styles. Somali songs are usually the product of collaboration between lyricists (), songwriters () and singers ( or "voice"). Balwo is a Somali musical style centered on love themes that is popular in Djibouti.
Traditional Afar music resembles the folk music of other parts of the
Somalis have a rich musical heritage centered on traditional Somali folklore. Most Somali songs are Pentatonic scale, pentatonic. That is, they only use five Pitch (music), pitches per octave in contrast to a Heptatonic scale, heptatonic (seven note) scale such as the major scale. At first listen, Somali music might be mistaken for the sounds of nearby regions such as Ethiopia, Sudan or the Arabian Peninsula, but it is ultimately recognizable by its own unique tunes and styles. Somali songs are usually the product of collaboration between lyricists (), songwriters () and singers ( or "voice"). Balwo is a Somali musical style centered on love themes that is popular in Djibouti.
Traditional Afar music resembles the folk music of other parts of the
 Football is the most popular sport amongst Djiboutians. The country became a member of FIFA in 1994, but has only taken part in the qualifying rounds for the African Cup of Nations as well as the FIFA World Cup in the mid-2000s. In November 2007, the Djibouti national football team beat Somalia national football team, Somalia's national squad 1–0 in the qualification rounds for the 2010 FIFA World Cup, marking its first ever World Cup-related win.
Recently, the World Archery Federation has helped to implement the Djibouti Archery Federation, and an international archery training center is being created in Arta, Djibouti, Arta to support archery development in East Africa and Red Sea area.
Football is the most popular sport amongst Djiboutians. The country became a member of FIFA in 1994, but has only taken part in the qualifying rounds for the African Cup of Nations as well as the FIFA World Cup in the mid-2000s. In November 2007, the Djibouti national football team beat Somalia national football team, Somalia's national squad 1–0 in the qualification rounds for the 2010 FIFA World Cup, marking its first ever World Cup-related win.
Recently, the World Archery Federation has helped to implement the Djibouti Archery Federation, and an international archery training center is being created in Arta, Djibouti, Arta to support archery development in East Africa and Red Sea area.
 Djiboutian cuisine is a mixture of Somali cuisine, Somali,
Djiboutian cuisine is a mixture of Somali cuisine, Somali,
Djibouti
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Djibouti profile
from the BBC News. * * ; Others
The State of the World's Midwifery – Djibouti Country Profile
from UNFPA
Key Development Forecasts for Djibouti
from International Futures. * * {{Authority control Djibouti, 1977 establishments in Djibouti Arabic-speaking countries and territories Countries in Africa East African countries Former French colonies French-speaking countries and territories Gulf of Aden Horn African countries Least developed countries Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie Member states of the African Union Member states of the Arab League Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation Member states of the United Nations Republics Somali-speaking countries and territories States and territories established in 1977
Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia ...
in the north, and the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden
The Gulf of Aden ( ar, خليج عدن, so, Gacanka Cadmeed 𐒅𐒖𐒐𐒕𐒌 𐒋𐒖𐒆𐒗𐒒) is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channe ...
to the east. The country has an area of .
In antiquity, the territory, together with Ethiopia, Eritrea and Somaliland, was part of the Land of Punt. Nearby Zeila, now in Somaliland, was the seat of the medieval Adal and Ifat Sultanates. In the late 19th century, the colony of French Somaliland
French Somaliland (french: Côte française des Somalis, lit= French Coast of the Somalis so, Xeebta Soomaaliyeed ee Faransiiska) was a French colony in the Horn of Africa. It existed between 1884 and 1967, at which time it became the French Ter ...
was established following treaties signed by the ruling Dir Somali sultans with the French, and its railroad to Dire Dawa
Dire Dawa ( am, ድሬዳዋ, om, Dirree Dhawaa, 3=Place of Remedy; so, Diridhaba, meaning "where Dir hit his spear into the ground" or "The true Dir", ar, ديري داوا,) is a city in eastern Ethiopia near the Oromia and Somali Re ...
(and later Addis Ababa) allowed it to quickly supersede Zeila as the port for southern Ethiopia and the Ogaden
Ogaden (pronounced and often spelled ''Ogadēn''; so, Ogaadeen, am, ውጋዴ/ውጋዴን) is one of the historical names given to the modern Somali Region, the territory comprising the eastern portion of Ethiopia formerly part of the Harargh ...
. It was renamed the French Territory of the Afars and the Issas in 1967. A decade later, the Djiboutian people voted for independence. This officially marked the establishment of the ''Republic of Djibouti'', named after its capital city. The new state joined the United Nations. In the early 1990s, tensions over government representation led to armed conflict
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular ...
, which ended in a power-sharing agreement in 2000 between the ruling party and the opposition.
Djibouti is a multi-ethnic nation with a population of over 920,000 ( the smallest in mainland Africa). French and Arabic are the country's two official languages, Afar and Somali are national languages. About 94% adhere to Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
, which is the official religion and has been predominant in the region for more than a thousand years. The Somalis and Afar
Afar may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Afar language, an East Cushitic language
*Afar people, an ethnic group of Djibouti, Eritrea, and Ethiopia
Places Horn of Africa
*Afar Desert or Danakil Desert, a desert in Ethiopia
*Afar Region, a region ...
make up the two largest ethnic groups, with the former comprising the majority of the population. Both speak a language of the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages.
Djibouti is near some of the world's busiest shipping lanes, controlling access to the Red Sea and Indian Ocean. It serves as a key refuelling and transshipment center, and the principal maritime port for imports from and exports to neighboring Ethiopia. A burgeoning commercial hub, the nation is the site of various foreign military bases. The Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD) regional body also has its headquarters in Djibouti City.
Name and etymology
''Djibouti'' is officially known as the ''Republic of Djibouti''. In local languages it is known as ''Yibuuti'' (inAfar
Afar may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Afar language, an East Cushitic language
*Afar people, an ethnic group of Djibouti, Eritrea, and Ethiopia
Places Horn of Africa
*Afar Desert or Danakil Desert, a desert in Ethiopia
*Afar Region, a region ...
) and ''Jabuuti'' (in Somali).
The country is named for its capital, the City of Djibouti
Djibouti (also called Djibouti City and in many early English texts and on many early maps, Jibuti; so, Magaalada Jabuuti, french: link=no, Ville de Djibouti, ar, مدينة جيبوتي, aa, Gabuutî Magaala) is the eponymous capital of Dji ...
. The etymology of the name is disputed. Several theories and legends exist regarding its origin, varying based on ethnicity. One theory derives it from the Afar
Afar may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Afar language, an East Cushitic language
*Afar people, an ethnic group of Djibouti, Eritrea, and Ethiopia
Places Horn of Africa
*Afar Desert or Danakil Desert, a desert in Ethiopia
*Afar Region, a region ...
word , meaning "plate", possibly referring to the geographical features of the area. Another connects it to ''gabood'', meaning "upland/plateau". Djibouti could also mean "Land of ''Tehuti''" or "Land of Thoth (Egyptian
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
: ''Djehuti''/ ''Djehuty'')", after the Egyptian
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
Moon God.
From 1862 until 1894, the land to the north of the Gulf of Tadjoura
The Gulf of Tadjoura (; ) is a gulf or basin of the Indian Ocean in the Horn of Africa. It lies south of the straits of Bab-el-Mandeb, or the entrance to the Red Sea, at . The gulf has many fishing grounds, extensive coral reefs, and abundant pea ...
was called "Obock
Obock (also Obok, aa, Hayyú) is a small port town in Djibouti. It is located on the northern shore of the Gulf of Tadjoura, where it opens out into the Gulf of Aden. The town is home to an airstrip and has ferries to Djibouti City. The French ...
". Under French administration, from 1883 to 1967 the area was known as French Somaliland
French Somaliland (french: Côte française des Somalis, lit= French Coast of the Somalis so, Xeebta Soomaaliyeed ee Faransiiska) was a French colony in the Horn of Africa. It existed between 1884 and 1967, at which time it became the French Ter ...
(French: ''Côte française des Somalis''), and from 1967 to 1977 as the French Territory of the Afars and the Issas (French: ''Territoire français des Afars et des Issas'').
History
Prehistory
East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historical ...
to South
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
and Southeast Asia.
The Djibouti area has been inhabited since the Neolithic. According to linguists, the first Afroasiatic-speaking populations arrived in the region during this period from the family's proposed urheimat ("original homeland") in the Nile Valley
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest rive ...
, or the Near East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
. Other scholars propose that the Afroasiatic family developed in situ in the Horn, with its speakers subsequently dispersing from there.
Cut stones dated about 3 million years old have been collected in the area of Lake Abbe. In the Gobaad plain (between Dikhil and Lake Abbe), the remains of a Palaeoloxodon recki elephant were also discovered, visibly butchered using basalt tools found nearby. These remains would date from 1.4 million years BCE. Subsequently, other similar sites were identified as probably the work of Homo ergaster. An Acheulean site (from 800,000 to 400,000 years BCE), where stone was cut, was excavated in the 1990s, in Gombourta, between Damerdjog and Loyada
Loyada ( ar, لويعدا , so, Lowyacadde) is a small town in Djibouti. Located in the Arta Region, it is the only official border crossing from Djibouti into Somaliland. It is situated on the west coast of Gulf of Aden, from the capital, Djib ...
, 15 km south of Djibouti City. Finally, in Gobaad, a Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor' ...
jaw was found, dating from 100,000 BCE. On Devil's Island
The penal colony of Cayenne ( French: ''Bagne de Cayenne''), commonly known as Devil's Island (''Île du Diable''), was a French penal colony that operated for 100 years, from 1852 to 1952, and officially closed in 1953 in the Salvation Islands ...
, tools dating back 6,000 years have been found, which were used to open shells. In the area at the bottom of Goubet (Dankalélo, not far from Devil's Island), circular stone structures and fragments of painted pottery have also been discovered. Previous investigators have also reported a fragmentary maxilla, attributed to an older form of Homo sapiens and dated to ~250 Ka, from the valley of the Dagadlé Wadi.
 Pottery predating the mid-2nd millennium has been found at
Pottery predating the mid-2nd millennium has been found at Asa Koma
Asa Koma ("Red Hill") is an archaeological site in Djibouti.
Overview
Asa Koma is an inland lake area on the Gobaad Plain. The site of Wakrita is a small Neolithic establishment located on a wadi in the tectonic depression of Gobaad in Djibouti ...
, an inland lake area on the Gobaad Plain. The site's ware is characterized by punctate and incision geometric designs, which bear a similarity to the Sabir culture phase 1 ceramics from Ma'layba in Southern Arabia. Long-horned humpless cattle bones have likewise been discovered at Asa Koma, suggesting that domesticated cattle were present by around 3,500 years ago. Rock art of what appear to be antelopes and a giraffe are also found at Dorra
Dorra ( ar, درة) is a village in Djibouti in the mid-north of Tadjoura Region, the largest region. It is about 237 kilometers north-west of Djibouti City and 65 km (40 mi) south of the border with Eritrea and east of the border wit ...
and Balho
Balho ( ar, بالهو) is a town located in the Tadjourah region of Djibouti. It is situated on the RN-11 highway. It is situated about 32 kilometres (20 miles) west of Dorra and 6 km (4 mi) east of the Ethiopian border.
History
In Balho ar ...
. Handoga
Handoga is located 14 km to the west of Dikhil, Djibouti. During the first excavations in 1970, archaeologists discovered foundations of stone houses and the walls of a stone edifice with a recess that faces Mecca.
History
In 1986, the surve ...
, dated to the fourth millennium BCE, has in turn yielded obsidian microliths and plain ceramics used by early nomadic pastoralists with domesticated cattle.
The site of Wakrita is a small Neolithic establishment located on a wadi in the tectonic depression of Gobaad in Djibouti in the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
. The 2005 excavations yielded abundant ceramics that enabled us to define one Neolithic cultural facies of this region, which was also identified at the nearby site of Asa Koma
Asa Koma ("Red Hill") is an archaeological site in Djibouti.
Overview
Asa Koma is an inland lake area on the Gobaad Plain. The site of Wakrita is a small Neolithic establishment located on a wadi in the tectonic depression of Gobaad in Djibouti ...
. The faunal remains confirm the importance of fishing in Neolithic settlements close to Lake Abbé, but also the importance of bovine husbandry and, for the first time in this area, evidence for caprine herding practices. Radiocarbon dating places this occupation at the beginning of the 2nd millennium BCE, similar in range to Asa Koma. These two sites represent the oldest evidence of herding in the region, and they provide a better understanding of the development of Neolithic societies in this region.
Up to 4000 years BCE, the region benefited from a climate very different from the one it knows today and probably close to the Mediterranean climate. The water resources were numerous with lakes in Gobaad, lakes Assal and Abbé larger and resembling real bodies of water. The humans therefore lived by gathering, fishing and hunting. The region was populated by a very rich fauna: felines
The Felinae are a subfamily of the family Felidae. This subfamily comprises the small cats having a bony hyoid, because of which they are able to purr but not roar.
Other authors have proposed an alternative definition for this subfamily: as c ...
, buffaloes, elephants, rhinos, etc., as evidenced, for example, by the bestiary of cave paintings at Balho
Balho ( ar, بالهو) is a town located in the Tadjourah region of Djibouti. It is situated on the RN-11 highway. It is situated about 32 kilometres (20 miles) west of Dorra and 6 km (4 mi) east of the Ethiopian border.
History
In Balho ar ...
. In the 3rd and 2nd millennia BCE, few nomads settled around the lakes and practiced fishing and cattle breeding. The burial of an 18-year-old woman, dating from this period, as well as the bones of hunted animals, bone tools and small jewels have been unearthed. By about 1500 BCE, the climate was already beginning to change, with sources of fresh water becoming more scarce. Engravings show dromedaries (animal of arid zones), some of which are ridden by armed warriors. The sedentary people now returned to a , nomadic life. Stone tumuli of various shapes and sheltering graves dating from this period have been unearthed all over the territory.
Punt (2,500 BCE)
 Together with northern Ethiopia, Somaliland, Eritrea and the Red Sea coast of Sudan, Djibouti is considered the most likely location of the territory known to the Ancient Egyptians as '' Punt'' (or ''Ta Netjeru'', meaning "God's Land"). The first mention of the Land of Punt dates to the 25th century BC. The Puntites were a nation of people who had close relations with Ancient Egypt during the reign of the 5th dynasty Pharaoh Sahure and the 18th dynasty Queen Hatshepsut. According to the temple murals at Deir el-Bahari, the Land of Punt was ruled at that time by King Parahu and Queen Ati.
Together with northern Ethiopia, Somaliland, Eritrea and the Red Sea coast of Sudan, Djibouti is considered the most likely location of the territory known to the Ancient Egyptians as '' Punt'' (or ''Ta Netjeru'', meaning "God's Land"). The first mention of the Land of Punt dates to the 25th century BC. The Puntites were a nation of people who had close relations with Ancient Egypt during the reign of the 5th dynasty Pharaoh Sahure and the 18th dynasty Queen Hatshepsut. According to the temple murals at Deir el-Bahari, the Land of Punt was ruled at that time by King Parahu and Queen Ati.
Macrobians (247 BCE)
The Macrobians (Μακροβίοι) were a legendary people and kingdom positioned in theHorn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
mentioned by Herodotus. Later authors (so Pliny on the authority of Ctesias' ''Indika
Indika may refer to:
* An alternate name of Megasthenes' ''Indica''
People
* Indika Anuruddha, Sri Lankan politician
* Indika Bandaranayake (b. 1972), Sri Lankan politician
* Indika Basnayake (b. 1979), Sri Lankan cricketer
* Indika Batuwitara ...
'') place them in India instead. It is one of the legendary peoples postulated at the extremity of the known world (from the perspective of the Greeks), in this case in the extreme south, contrasting with the Hyperboreans in the extreme east. Their name is due to their legendary longevity
The word " longevity" is sometimes used as a synonym for "life expectancy" in demography. However, the term ''longevity'' is sometimes meant to refer only to especially long-lived members of a population, whereas ''life expectancy'' is always d ...
, an average person supposedly living to the age of 120. They were said to be the "tallest and handsomest of all men".Wheeler pg 526 According to Herodotus' account, the Persian Emperor Cambyses II
Cambyses II ( peo, 𐎣𐎲𐎢𐎪𐎡𐎹 ''Kabūjiya'') was the second King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 530 to 522 BC. He was the son and successor of Cyrus the Great () and his mother was Cassandane.
Before his accession, Cambyses ...
upon his conquest of Egypt (525 BC) sent ambassadors to Macrobia, bringing luxury gifts for the Macrobian king to entice his submission. The Macrobian ruler, who was elected based at least in part on stature, replied instead with a challenge for his Persian counterpart in the form of an unstrung bow: if the Persians could manage to string it, they would have the right to invade his country; but until then, they should thank the gods that the Macrobians never decided to invade their empire.John Kitto, James Taylor, ''The popular cyclopædia of Biblical literature: condensed from the larger work'', (Gould and Lincoln: 1856), p.302.

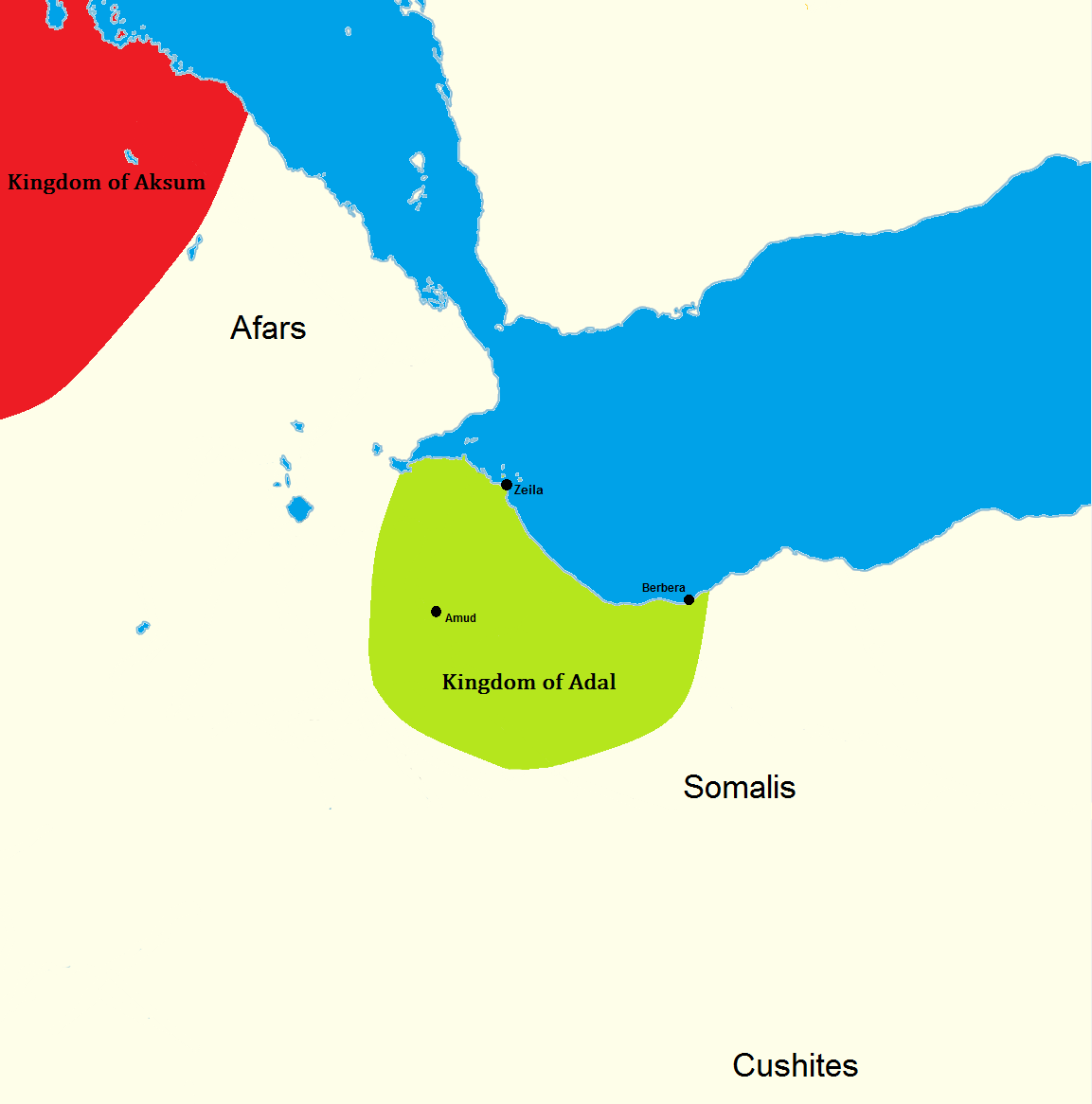
Kingdom of Adal (900–1285)
The ''Kingdom of Adal'' (also ''Awdal'', ''Adl'', or ''Adel'')Mohamed Haji Mukhtar, ''Historical Dictionary of Somalia'', new edn, African Historical Dictionary Series, 87 (Lanham, MD: Scarecrow Press, 2003), s.v. ''Awdal'' . 44 was centered around Zeila, its capital. It was established by the local Somali tribes in the early 9th century. Zeila attracted merchants from around the world, contributing to the wealth of the city. Zeila is an ancient city and it was one of the earliest cities in the world to embraceIslam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
, shortly after the hijra. Zeila's two-mihrab
Mihrab ( ar, محراب, ', pl. ') is a niche in the wall of a mosque that indicates the ''qibla'', the direction of the Kaaba in Mecca towards which Muslims should face when praying. The wall in which a ''mihrab'' appears is thus the "qibla w ...
Masjid al-Qiblatayn
The Masjid al-Qiblatayn ( ar, مسجد القبلتين, lit=Mosque of the Two Qiblas), also spelt Masjid al-Qiblatain, is a mosque in Medina believed by Muslims to be the place where the final Islamic prophet, Muhammad, received the command to ...
dates to the 7th century, and is the oldest mosque.
In the late 9th century, Al-Yaqubi, an Armenian Muslim scholar and traveler, wrote that the Kingdom of Adal was a small wealthy kingdom and that Zeila served as the headquarters for the kingdom, which dated back to the beginning of the century.
Ifat Sultanate (1285–1415)
 Through close contacts with the adjacent Arabian Peninsula for more than 1,000 years, the Somali and Afar ethnic groups in the region became among the first populations on the continent to embrace Islam. The Ifat Sultanate was a Muslim medieval kingdom in the
Through close contacts with the adjacent Arabian Peninsula for more than 1,000 years, the Somali and Afar ethnic groups in the region became among the first populations on the continent to embrace Islam. The Ifat Sultanate was a Muslim medieval kingdom in the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
. Founded in 1285 by the Walashma dynasty, it was centered in Zeila. Ifat established bases in Djibouti and Somaliland, and from there expanded southward to the Ahmar Mountains
The Ahmar Mountains is a mountain range of the Ethiopian Highlands, located in the eastern Oromia Region of Ethiopia.
The range has an average elevation of above sea level.
The mountain range is located approximately south of Dire Dawa, fro ...
. Its Sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it ...
Umar Walashma (or his son Ali, according to another source) is recorded as having conquered the Sultanate of Shewa
The Makhzumi dynasty also known as Sultanate of Shewa or Shewa Sultanate, was a Muslim kingdom in present-day Ethiopia. Its capital Walale was situated in northern Hararghe in Harla country. Its territory extended possibly to some areas west of th ...
in 1285. Taddesse Tamrat explains Sultan Umar's military expedition as an effort to consolidate the Muslim territories in the Horn, in much the same way as Emperor Yekuno Amlak was attempting to unite the Christian territories in the highlands during the same period. These two states inevitably came into conflict over Shewa and territories further south. A lengthy war ensued, but the Muslim sultanates of the time were not strongly unified. Ifat was finally defeated by Emperor Amda Seyon I of Ethiopia in 1332, and withdrew from Shewa.
Adal Sultanate (1415–1577)
Bab el Mandeb
The Bab-el-Mandeb (Arabic: , , ) is a strait between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula, and Djibouti and Eritrea in the Horn of Africa. It connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden.
Name
The strait derives its name from the dangers attendin ...
and Cape Guardafui. It was therefore flanked to the south by the Ajuran Empire (Kingdom of Ajuuran) and to the west by the Abyssinian Empire
The Ethiopian Empire (), also formerly known by the exonym Abyssinia, or just simply known as Ethiopia (; Amharic and Tigrinya: ኢትዮጵያ , , Oromo: Itoophiyaa, Somali: Itoobiya, Afar: ''Itiyoophiyaa''), was an empire that historical ...
(Abassin Empire). Adal is mentioned by name in the 14th century in the context of the battles between the Muslims of the Somali and Afar seaboard and the Abyssinian King Amda Seyon I's Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
troops. Adal originally had its capital in the port city of Zeila, situated in the western Awdal region. The polity at the time was an Emirate in the larger Ifat Sultanate ruled by the Walashma dynasty.
According to I.M. Lewis, the polity was governed by local dynasties consisting of Afarized Arabs or Arabized Somalis, who also ruled over the similarly established Sultanate of Mogadishu in the Benadir region to the south. Adal's history from this founding period forth would be characterized by a succession of battles with neighbouring Abyssinia. At its height, the Adal kingdom controlled large parts of modern-day Djibouti, Somaliland
Somaliland,; ar, صوماليلاند ', ' officially the Republic of Somaliland,, ar, جمهورية صوماليلاند, link=no ''Jumhūrīyat Ṣūmālīlānd'' is a ''de facto'' sovereign state in the Horn of Africa, still conside ...
, Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia ...
and Ethiopia. Between Djibouti City and Loyada
Loyada ( ar, لويعدا , so, Lowyacadde) is a small town in Djibouti. Located in the Arta Region, it is the only official border crossing from Djibouti into Somaliland. It is situated on the west coast of Gulf of Aden, from the capital, Djib ...
are a number of anthropomorphic and phallic stelae. The structures are associated with graves of rectangular shape flanked by vertical slabs, as also found in Tiya
Tiya is a town in central Ethiopia. It is situated in the Gurage Zone of the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples Region south of Addis Ababa. It is also the location of the Tiya archaeological site, famous for its unique stelae.
Demogra ...
, central Ethiopia. The Djibouti-Loyada stelae are of uncertain age, and some of them are adorned with a T-shaped symbol. Additionally, archaeological excavations at Tiya have yielded tombs. As of 1997, 118 stelae were reported in the area. Along with the stelae in the Hadiya Zone
Hadiya (also transliterated Hadiyya) is a zone in the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region of Ethiopia. This zone is named after the Hadiya of the Hadiya Kingdom, whose homeland covers part of the administrative division. Hadiya ...
, the structures are identified by local residents as ''Yegragn Dingay'' or "Gran's stone", in reference to Imam Ahmad ibn Ibrahim al-Ghazi (Ahmad "Gurey" or "Gran"), ruler of the Adal Sultanate.
Ottoman Eyalet (1577–1867)
 Although nominally part of the Ottoman Empire since 1577, between 1821 and 1841,
Although nominally part of the Ottoman Empire since 1577, between 1821 and 1841, Muhammad Ali
Muhammad Ali (; born Cassius Marcellus Clay Jr.; January 17, 1942 – June 3, 2016) was an American professional boxer and activist. Nicknamed "The Greatest", he is regarded as one of the most significant sports figures of the 20th century, a ...
, Pasha of Egypt, came to control Yemen, Harar, Gulf of Tadjoura
The Gulf of Tadjoura (; ) is a gulf or basin of the Indian Ocean in the Horn of Africa. It lies south of the straits of Bab-el-Mandeb, or the entrance to the Red Sea, at . The gulf has many fishing grounds, extensive coral reefs, and abundant pea ...
with Zeila and Berbera included. The Governor Abou Baker ordered the Egyptian garrison at Sagallo to retire to Zeila. The cruiser Seignelay reached Sagallo shortly after the Egyptians had departed. French troops occupied the fort despite protests from the British Agent in Aden
Aden ( ar, عدن ' Yemeni: ) is a city, and since 2015, the temporary capital of Yemen, near the eastern approach to the Red Sea (the Gulf of Aden), some east of the strait Bab-el-Mandeb. Its population is approximately 800,000 people. ...
, Major Frederick Mercer Hunter, who dispatched troops to safeguard British and Egyptian interests in Zeila and prevent further extension of French influence in that direction. FRENCH SOMALI COAST Timeline
On 14 April 1884 the Commander of the patrol sloop L'Inferent reported on the Egyptian occupation in the Gulf of Tadjoura. The Commander of the patrol sloop Le Vaudreuil reported that the Egyptians were occupying the interior between Obock
Obock (also Obok, aa, Hayyú) is a small port town in Djibouti. It is located on the northern shore of the Gulf of Tadjoura, where it opens out into the Gulf of Aden. The town is home to an airstrip and has ferries to Djibouti City. The French ...
and Tadjoura. Emperor Yohannes IV of Ethiopia signed an accord with Great Britain to cease fighting the Egyptians and to allow the evacuation of Egyptian forces from Ethiopia and the Somaliland littoral. The Egyptian garrison was withdrawn from Tadjoura. Léonce Lagarde deployed a patrol sloop to Tadjoura the following night.
French rule (1883–1977)
The boundaries of the present-day Djibouti state were established as the first French establishment in theHorn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
during the Scramble for Africa
The Scramble for Africa, also called the Partition of Africa, or Conquest of Africa, was the invasion, annexation, division, and colonisation of Africa, colonization of most of Africa by seven Western Europe, Western European powers during a ...
. The March 11, 1862, agreement the Afar
Afar may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Afar language, an East Cushitic language
*Afar people, an ethnic group of Djibouti, Eritrea, and Ethiopia
Places Horn of Africa
*Afar Desert or Danakil Desert, a desert in Ethiopia
*Afar Region, a region ...
sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it ...
, Raieta Dini Ahmet, signed in Paris was a treaty where the Afars sold lands surrounding in Obock
Obock (also Obok, aa, Hayyú) is a small port town in Djibouti. It is located on the northern shore of the Gulf of Tadjoura, where it opens out into the Gulf of Aden. The town is home to an airstrip and has ferries to Djibouti City. The French ...
. The French were interested in having a coaling station for steamship
A steamship, often referred to as a steamer, is a type of steam-powered vessel, typically ocean-faring and seaworthy, that is propelled by one or more steam engines that typically move (turn) propellers or paddlewheels. The first steamships ...
s, which would become especially important upon the opening of the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
in 1869. (Up to that time French ships had to buy coal at the British port of Aden
Aden ( ar, عدن ' Yemeni: ) is a city, and since 2015, the temporary capital of Yemen, near the eastern approach to the Red Sea (the Gulf of Aden), some east of the strait Bab-el-Mandeb. Its population is approximately 800,000 people. ...
across the gulf, an unwise dependency in case of war.) Later on, that treaty was used by the captain of the Fleuriot de Langle to colonize the south of the Gulf of Tadjoura
The Gulf of Tadjoura (; ) is a gulf or basin of the Indian Ocean in the Horn of Africa. It lies south of the straits of Bab-el-Mandeb, or the entrance to the Red Sea, at . The gulf has many fishing grounds, extensive coral reefs, and abundant pea ...
. On March 26, 1885, the French signed another treaty with the Issas where the latter would become a protectorate under the French, no monetary exchange occurred and Issa clan
The Issa (also Eesah, Esa, Aysa) ( so, Ciise, '', ar, عيسى)'' is a northern Somali clan, a sub-division of the Dir clan family.'
Overview
As a Dir sub-clan, the Issa have immediate lineal ties with the Gadabuursi, the Surre (Abdalle a ...
did not sign away any of their rights to the land, the agreement was to kick the Gadebuursi, who were against the French, and the Isaaq from the country with the help of the French. It was established between 1883 and 1887, after the ruling Somalis and Afar
Afar may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Afar language, an East Cushitic language
*Afar people, an ethnic group of Djibouti, Eritrea, and Ethiopia
Places Horn of Africa
*Afar Desert or Danakil Desert, a desert in Ethiopia
*Afar Region, a region ...
sultans each signed a treaty with the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
.Raph Uwechue, ''Africa year book and who's who'', (Africa Journal Ltd.: 1977), p. 209 .''A Political Chronology of Africa'', (Taylor & Francis: 2001), p. 132 . An attempt by Nikolay Ivanovitch Achinov
Sagallo (russian: Сагалло; ar, ساغلو; french: Sagallou) was a short-lived settlement established in 1889 by a Russian monk and adventurer on the Gulf of Tadjoura in French Somaliland (modern-day Djibouti). It was located some west ...
, a Russian adventurer, to establish a settlement at Sagallo in 1889 was promptly thwarted by French forces after just one month. In 1894, Léonce Lagarde established a permanent French administration in the city of Djibouti
Djibouti (also called Djibouti City and in many early English texts and on many early maps, Jibuti; so, Magaalada Jabuuti, french: link=no, Ville de Djibouti, ar, مدينة جيبوتي, aa, Gabuutî Magaala) is the eponymous capital of Dji ...
and named the region French Somaliland
French Somaliland (french: Côte française des Somalis, lit= French Coast of the Somalis so, Xeebta Soomaaliyeed ee Faransiiska) was a French colony in the Horn of Africa. It existed between 1884 and 1967, at which time it became the French Ter ...
. As is shown in "Morin" (2005), this name has been proposed by Mohamed Haji Dide of the Mahad 'Ase branch of the Gadabuursi
The Gadabuursi ( Somali: ''Gadabuursi'', Arabic: جادابورسي), also known as ''Samaroon'' (Arabic: ''قبيلة سَمَرُون)'', is a northern Somali clan, a sub-division of the Dir clan family.
The Gadabuursi are geographically s ...
. It lasted from 1896 until 1967, when it was renamed the ''Territoire Français des Afars et des Issas'' (TFAI) (" French Territory of the Afars and the Issas"), after France, the colonial power, has empowered the Issas clan at the expense of the Gadabuursi
The Gadabuursi ( Somali: ''Gadabuursi'', Arabic: جادابورسي), also known as ''Samaroon'' (Arabic: ''قبيلة سَمَرُون)'', is a northern Somali clan, a sub-division of the Dir clan family.
The Gadabuursi are geographically s ...
.
The construction of the Imperial Ethiopian Railway
The Ethio-Djibouti Railway (french: Chemin de Fer Djibouto-Éthiopien, C.D.E.; ) is a metre gauge railway in the Horn of Africa that once connected Addis Ababa to the port city of Djibouti. The operating company was also known as the Ethio-Dji ...
west into Ethiopia turned the port of Djibouti
The Port of Djibouti is a port in Djibouti, the capital of Djibouti. It is strategically located at the crossroads of one of the busiest shipping routes in the world, linking Europe, the Far East, the Horn of Africa and the Persian Gulf. The por ...
into a boomtown of 15,000" at a time when Harar was the only city in Ethiopia to exceed that.
 Although the population fell after the completion of the railwayline to
Although the population fell after the completion of the railwayline to Dire Dawa
Dire Dawa ( am, ድሬዳዋ, om, Dirree Dhawaa, 3=Place of Remedy; so, Diridhaba, meaning "where Dir hit his spear into the ground" or "The true Dir", ar, ديري داوا,) is a city in eastern Ethiopia near the Oromia and Somali Re ...
and the original company failed and required a government bail-out, the rail link allowed the territory to quickly supersede the caravan-based trade carried on at Zeila (then in the British area of Somaliland
Somaliland,; ar, صوماليلاند ', ' officially the Republic of Somaliland,, ar, جمهورية صوماليلاند, link=no ''Jumhūrīyat Ṣūmālīlānd'' is a ''de facto'' sovereign state in the Horn of Africa, still conside ...
) and become the premier port for coffee and other goods leaving southern Ethiopia and the Ogaden
Ogaden (pronounced and often spelled ''Ogadēn''; so, Ogaadeen, am, ውጋዴ/ውጋዴን) is one of the historical names given to the modern Somali Region, the territory comprising the eastern portion of Ethiopia formerly part of the Harargh ...
through Harar.
After the Italian invasion and occupation of Ethiopia in the mid-1930s, constant border skirmishes occurred between French forces in French Somaliland and Italian forces in Italian East Africa. In June 1940, during the early stages of World War II, France fell and the colony was then ruled by the pro- Axis Vichy (French) government.
British and Commonwealth forces fought the neighboring Italians during the East African Campaign. In 1941, the Italians were defeated and the Vichy forces in French Somaliland were isolated. The Vichy French administration continued to hold out in the colony for over a year after the Italian collapse. In response, the British blockaded the port of Djibouti City but it could not prevent local French from providing information on the passing ship convoys. In 1942, about 4,000 British troops occupied the city. A local battalion from French Somaliland participated in the Liberation of Paris
The liberation of Paris (french: Libération de Paris) was a military battle that took place during World War II from 19 August 1944 until the German garrison surrendered the French capital on 25 August 1944. Paris had been occupied by Nazi Germ ...
in 1944.
In 1958, on the eve of neighboring Somalia's independence in 1960, a referendum was held in Djibouti to decide whether to remain with France or to be an independent country. The referendum turned out in favour of a continued association with France, partly due to a combined yes vote by the sizable Afar ethnic group and resident French.Barrington, Lowell (2006''After Independence: Making and Protecting the Nation in Postcolonial and Postcommunist States''
. University of Michigan Press. p. 115. There were also allegations of widespread vote rigging. The majority of those who had voted no were Somalis who were strongly in favour of joining a united Somalia as had been proposed by Mahmoud Harbi, Vice President of the Government Council. Harbi was killed in a plane crash two years later under suspicious circumstances.
 In 1966, France rejected the United Nations' recommendation that it should grant French Somaliland independence. In August of the same year, an official visit to the territory by then French President, General
In 1966, France rejected the United Nations' recommendation that it should grant French Somaliland independence. In August of the same year, an official visit to the territory by then French President, General Charles de Gaulle
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle (; ; (commonly abbreviated as CDG) 22 November 18909 November 1970) was a French army officer and statesman who led Free France against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Government ...
, was also met with demonstrations and rioting.''Newsweek'', Volume 81, (Newsweek: 1973), p.254. In response to the protests, de Gaulle ordered another referendum.
In 1967, a second plebiscite was held to determine the fate of the territory. Initial results supported a continued but looser relationship with France. Voting was also divided along ethnic lines, with the resident Somalis generally voting for independence, with the goal of eventual union with Somalia, and the Afars largely opting to remain associated with France. The referendum was again marred by reports of vote rigging on the part of the French authorities.American Universities Field Staff (1968) ''Northeast Africa series'', Volume 15, Issue 1, p. 3. Shortly after the plebiscite was held, the former ''Côte française des Somalis'' (French Somaliland) was renamed to ''Territoire français des Afars et des Issas''. Announcement of the plebiscite results sparked civil unrest, including several deaths. France also increased its military force along the frontier.Alvin J. Cottrell, Robert Michael Burrell, Georgetown University. Center for Strategic and International Studies, ''The Indian Ocean: its political, economic, and military importance'', (Praeger: 1972), p.166.
 During the 1960s, the struggle for independence was led by the
During the 1960s, the struggle for independence was led by the Front for the Liberation of the Somali Coast
Front may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''The Front'' (1943 film), a 1943 Soviet drama film
* '' The Front'', 1976 film
Music
*The Front (band), an American rock band signed to Columbia Records and active in the 1980s and e ...
(FLCS), who waged an armed struggle for independence with much of its violence aimed at French personnel. FLCS used to initiate few mounting cross-border operations into French Somaliland
French Somaliland (french: Côte française des Somalis, lit= French Coast of the Somalis so, Xeebta Soomaaliyeed ee Faransiiska) was a French colony in the Horn of Africa. It existed between 1884 and 1967, at which time it became the French Ter ...
from Somalia and Ethiopia to attacks on French targets. On March 24, 1975, the Front de Libération de la Côte des Somalis kidnapped the French Ambassador to Somalia, Jean Guery, to be exchanged against two activists of FLCS members who were both serving life terms in mainland France. He was exchanged for the two FLCS members in Aden
Aden ( ar, عدن ' Yemeni: ) is a city, and since 2015, the temporary capital of Yemen, near the eastern approach to the Red Sea (the Gulf of Aden), some east of the strait Bab-el-Mandeb. Its population is approximately 800,000 people. ...
, South Yemen
South Yemen ( ar, اليمن الجنوبي, al-Yaman al-Janubiyy), officially the People's Democratic Republic of Yemen (, ), also referred to as Democratic Yemen (, ) or Yemen (Aden) (, ), was a communist state that existed from 1967 to 19 ...
. The FLCS was recognized as a national liberation movement by the Organization of African Unity (OAU), which participated in its financing. The FLCS evolved its demands between the request of integration in a possible "Greater Somalia
Greater Somalia ( so, Soomaaliweyn, ar, الصومال الكبرى ''As-Sūmal al-Kubra'') is a concept to unite all ethnic Somalis comprising the regions in or near the Horn of Africa in which ethnic Somalis live and have historically inhabited ...
" influenced by the Somali government or the simple independence of the territory. In 1975 the African People's League for the Independence (LPAI) and FLCS met in Kampala, Uganda with several meeting later they finally opted for independence path, causing tensions with Somalia.
In 1976, members of the Front de Libération de la Côte des Somalis
''Front de Libération de la Côte des Somalis'' (English: ''Front for the Liberation of the Somali Coast'') was a nationalist organization, and later a guerrilla group, in the French Territory of the Afars and the Issas in present-day Djibouti. It ...
which sought Djibouti's independence from France, also clashed with the Gendarmerie Nationale Intervention Group over a bus hijacking en route to Loyada
Loyada ( ar, لويعدا , so, Lowyacadde) is a small town in Djibouti. Located in the Arta Region, it is the only official border crossing from Djibouti into Somaliland. It is situated on the west coast of Gulf of Aden, from the capital, Djib ...
. This event, by showing the difficulties of maintaining the French colonial presence in Djibouti, was an important step in the independence of the territory. The likelihood of a third referendum appearing successful for the French had grown even dimmer. The prohibitive cost of maintaining the colony, France's last outpost on the continent, was another factor that compelled observers to doubt that the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
would attempt to hold on to the territory.
Djibouti Republic
 A third independence referendum was held in the French Territory of the Afars and the Issas on 8 May 1977. The previous referendums were held in
A third independence referendum was held in the French Territory of the Afars and the Issas on 8 May 1977. The previous referendums were held in 1958
Events
January
* January 1 – The European Economic Community (EEC) comes into being.
* January 3 – The West Indies Federation is formed.
* January 4
** Edmund Hillary's Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition completes the third ...
and 1967
Events
January
* January 1 – Canada begins a year-long celebration of the 100th anniversary of Confederation, featuring the Expo 67 World's Fair.
* January 5
** Spain and Romania sign an agreement in Paris, establishing full consular and ...
,Kevin Shillington, ''Encyclopedia of African history'', (CRC Press: 2005), p.360. which rejected independence. This referendum backed independence from France. A landslide 98.8% of the electorate supported disengagement from France, officially marking Djibouti's independence. Hassan Gouled Aptidon
Hassan Gouled Aptidon ( so, Xasan Guuleed Abtidoon; ar, حسن جوليد أبتيدون) (October 15, 1916 – November 21, 2006) was the first President of Djibouti from 1977 to 1999.
Biography
He was born in the small village of Gerisa in th ...
, an Issa (ethnic Somali) politician who had campaigned for a yes vote in the referendum of 1958, became the nation's first president (1977–1999).
During its first year, Djibouti joined the Organization of African Unity (now the African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the Africa ...
), the Arab League
The Arab League ( ar, الجامعة العربية, ' ), formally the League of Arab States ( ar, جامعة الدول العربية, '), is a regional organization in the Arab world, which is located in Northern Africa, Western Africa, E ...
and United Nations. In 1986, the nascent republic was also among the founding members of the Intergovernmental Authority on Development regional development organization. During the Ogaden War
The Ogaden War, or the Ethio-Somali War (, am, የኢትዮጵያ ሶማሊያ ጦርነት, ye’ītiyop’iya somalīya t’orineti), was a military conflict fought between Somalia and Ethiopia from July 1977 to March 1978 over the Ethiopi ...
, influential Issa politicians envisioned a Greater Djibouti or "Issa-land", where Djibouti's borders would extend from the Red Sea to Dire Dawa
Dire Dawa ( am, ድሬዳዋ, om, Dirree Dhawaa, 3=Place of Remedy; so, Diridhaba, meaning "where Dir hit his spear into the ground" or "The true Dir", ar, ديري داوا,) is a city in eastern Ethiopia near the Oromia and Somali Re ...
. That dream however was dashed towards the end of the war as Somali forces were routed from Ethiopia.
In the early 1990s, tensions over government representation led to armed conflict
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular ...
between Djibouti's ruling People's Rally for Progress (PRP) party and the Front for the Restoration of Unity and Democracy
The Front for the Restoration of Unity and Democracy (french: Front pour la Restauration de l'Unité et de la Démocratie, ar, الجبهة من أجل استعادة الوحدة والديمقراطية) is a political party in Djibouti. It is ...
(FRUD) opposition group. The impasse ended in a power-sharing agreement in 2000.
In April 2021, Ismael Guelleh, the second President of Djibouti
This is a list of presidents of Djibouti. Since the establishment of the office of president in 1977, there have been two presidents. The president is both head of state and head of government of Djibouti and the commander-in-chief of the Djibo ...
since independence from France in 1977, was re-elected for his fifth term.
Politics
Djibouti is a Unitary state, unitary Presidential system, presidential republic, with executive power resting in the presidency, which is by turn dominant over the cabinet, and legislative power in both the government and the National Assembly (Djibouti), National Assembly.Governance
 The President of Djibouti, President, Ismaïl Omar Guelleh, is the prominent figure in Djiboutian politics; the head of state and commander-in-chief. The President exercises their executive power assisted by their appointee, the Prime Minister of Djibouti, Prime Minister, Abdoulkader Kamil Mohamed. The Council of Ministers (cabinet) is responsible to and presided over by the President.
The judicial system consists of courts of first instance, a High Court of Appeal, and a Supreme Court. The legal system is a blend of Civil law (legal system), French civil law and customary law (''Xeer'') of the Somali and Afar peoples.
The National Assembly (formerly the ''Chamber of Deputies'') is the country's legislature, consisting of 65 members elected every five years. Although unicameral, the Constitution provides for the creation of a Senate.
The President of Djibouti, President, Ismaïl Omar Guelleh, is the prominent figure in Djiboutian politics; the head of state and commander-in-chief. The President exercises their executive power assisted by their appointee, the Prime Minister of Djibouti, Prime Minister, Abdoulkader Kamil Mohamed. The Council of Ministers (cabinet) is responsible to and presided over by the President.
The judicial system consists of courts of first instance, a High Court of Appeal, and a Supreme Court. The legal system is a blend of Civil law (legal system), French civil law and customary law (''Xeer'') of the Somali and Afar peoples.
The National Assembly (formerly the ''Chamber of Deputies'') is the country's legislature, consisting of 65 members elected every five years. Although unicameral, the Constitution provides for the creation of a Senate.
 The Djiboutian parliamentary election, 2018, last election was held on 23 February 2018. Djibouti has a dominant-party system, with the People's Rally for Progress (RPP) controlling the legislature and the executive since its foundation in 1979 (the party rules as a part of the Union for a Presidential Majority, which holds a supermajority of seats). Opposition parties are allowed (limited) freedom, but the main opposition party, the Union for National Salvation, boycotted the 2005 and 2008 elections, citing government control of the media and repression of the opposition candidates.
The government is dominated by the Somali Issa (clan), Issa Dir clan, who enjoy the support of the Somali clans, especially the
The Djiboutian parliamentary election, 2018, last election was held on 23 February 2018. Djibouti has a dominant-party system, with the People's Rally for Progress (RPP) controlling the legislature and the executive since its foundation in 1979 (the party rules as a part of the Union for a Presidential Majority, which holds a supermajority of seats). Opposition parties are allowed (limited) freedom, but the main opposition party, the Union for National Salvation, boycotted the 2005 and 2008 elections, citing government control of the media and repression of the opposition candidates.
The government is dominated by the Somali Issa (clan), Issa Dir clan, who enjoy the support of the Somali clans, especially the Gadabuursi
The Gadabuursi ( Somali: ''Gadabuursi'', Arabic: جادابورسي), also known as ''Samaroon'' (Arabic: ''قبيلة سَمَرُون)'', is a northern Somali clan, a sub-division of the Dir clan family.
The Gadabuursi are geographically s ...
Dir clan. The country emerged from a decade-long Djiboutian Civil War, civil war at the end of the 1990s, with the government and the Front for the Restoration of Unity and Democracy
The Front for the Restoration of Unity and Democracy (french: Front pour la Restauration de l'Unité et de la Démocratie, ar, الجبهة من أجل استعادة الوحدة والديمقراطية) is a political party in Djibouti. It is ...
(FRUD) signing a peace treaty in 2000. Two FRUD members subsequently joined the cabinet, and beginning with Djiboutian presidential election, 1999, the presidential elections of 1999, the FRUD has campaigned in support of the RPP.
Djibouti's president, Guelleh, succeeded Hassan Gouled Aptidon
Hassan Gouled Aptidon ( so, Xasan Guuleed Abtidoon; ar, حسن جوليد أبتيدون) (October 15, 1916 – November 21, 2006) was the first President of Djibouti from 1977 to 1999.
Biography
He was born in the small village of Gerisa in th ...
in office in 1999. Guelleh was sworn in for his second six-year term after a Djiboutian presidential election, 2005, one-man election on 8 April 2005. He took 100% of the votes in a 78.9% turnout. In early 2011, the Djiboutian citizenry took part in a 2011 Djiboutian protests, series of protests against the long-serving government, which were associated with the larger Arab Spring demonstrations. Guelleh was Djiboutian presidential election, 2011, re-elected to a third term later that year, with 80.63% of the vote in a 75% turnout. Although opposition groups boycotted the ballot over changes to the constitution permitting Guelleh to run again for office, international observers from the African Union generally described the election as free and fair.
On 31 March 2013, Guelleh replaced long-serving Prime Minister Dilleita Mohamed Dilleita with former president of the Union for a Presidential Majority (UMP) Abdoulkader Kamil Mohamed. In December 2014, the ruling Union for the Presidential Majority also signed a framework agreement with the Union of National Salvation coalition, which paves the way for opposition legislators to enter parliament and for reformation of the national electoral agency.
Foreign relations
African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the Africa ...
, United Nations, Non-Aligned Movement, Organisation of Islamic Cooperation and Arab League
The Arab League ( ar, الجامعة العربية, ' ), formally the League of Arab States ( ar, جامعة الدول العربية, '), is a regional organization in the Arab world, which is located in Northern Africa, Western Africa, E ...
affairs. Since the 2000s, Djiboutian authorities have also strengthened relations with Turkey.
Military
 The Djibouti Armed Forces, Djiboutian Armed Forces include the Djiboutian Army, which consists of the Djiboutian Navy, the Djiboutian Air Force, and the National Gendarmerie (GN). , the manpower available for military service was 170,386 males and 221,411 females aged 16 to 49. Djibouti List of countries by military expenditures, spent over US$36 million annually on its military (141st in the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, SIPRI database). After independence, Djibouti had two regiments commanded by French officers. In the early 2000s, it looked outward for a model of army organization that would best advance defensive capabilities by restructuring forces into smaller, more mobile units instead of traditional divisions.
The first war which involved the Djiboutian Armed Forces was the Djiboutian Civil War between the Djiboutian government, supported by France, and the
The Djibouti Armed Forces, Djiboutian Armed Forces include the Djiboutian Army, which consists of the Djiboutian Navy, the Djiboutian Air Force, and the National Gendarmerie (GN). , the manpower available for military service was 170,386 males and 221,411 females aged 16 to 49. Djibouti List of countries by military expenditures, spent over US$36 million annually on its military (141st in the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, SIPRI database). After independence, Djibouti had two regiments commanded by French officers. In the early 2000s, it looked outward for a model of army organization that would best advance defensive capabilities by restructuring forces into smaller, more mobile units instead of traditional divisions.
The first war which involved the Djiboutian Armed Forces was the Djiboutian Civil War between the Djiboutian government, supported by France, and the Front for the Restoration of Unity and Democracy
The Front for the Restoration of Unity and Democracy (french: Front pour la Restauration de l'Unité et de la Démocratie, ar, الجبهة من أجل استعادة الوحدة والديمقراطية) is a political party in Djibouti. It is ...
(''FRUD''). The war lasted from 1991 to 2001, although most of the hostilities ended when the moderate factions of FRUD signed a peace treaty with the government after suffering an extensive military setback when the government forces captured most of the rebel-held territory. A radical group continued to fight the government, but signed its own peace treaty in 2001. The war ended in a government victory, and FRUD became a political party.
As the headquarters of the IGAD regional body, Djibouti has been an active participant in the Somali peace process, hosting the Arta, Djibouti, Arta conference in 2000.The Rise and Fall of the Somalia Airforce: A Diary ReflectionFollowing the establishment of the Federal Government of Somalia in 2012, a Djibouti delegation also attended the inauguration ceremony of Somalia's new president. In recent years, Djibouti has improved its training techniques, military command and information structures and has taken steps to becoming more self-reliant in supplying its military to collaborate with the United Nations in peacekeeping missions, or to provide military help to countries that officially ask for it. Now deployed to Somalia and Sudan.
Foreign military presence
 The French Armed Forces, French Forces remained present in Djibouti when the territory gained independence, first as part of a provisional protocol of June 1977 laying down the conditions for the stationing of French forces, constituting a defense agreement. A new defence cooperation treaty between France and Djibouti was signed in Paris on 21 December 2011. It entered into force on 1 May 2014. By that treaty and its security clause, France reaffirmed its commitment to the independence and territorial integrity of the Republic of Djibouti. As well before independence, in 1962, a French Foreign Legion unit, the 13th Demi-Brigade of the Foreign Legion (13 DBLE) was transferred from Algeria to Djibouti to form the core of the French garrison there. On 31 July 2011, the (13 DBLE) left Djibouti to the United Arab Emirates.
Djibouti's strategic location by the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, which separates the
The French Armed Forces, French Forces remained present in Djibouti when the territory gained independence, first as part of a provisional protocol of June 1977 laying down the conditions for the stationing of French forces, constituting a defense agreement. A new defence cooperation treaty between France and Djibouti was signed in Paris on 21 December 2011. It entered into force on 1 May 2014. By that treaty and its security clause, France reaffirmed its commitment to the independence and territorial integrity of the Republic of Djibouti. As well before independence, in 1962, a French Foreign Legion unit, the 13th Demi-Brigade of the Foreign Legion (13 DBLE) was transferred from Algeria to Djibouti to form the core of the French garrison there. On 31 July 2011, the (13 DBLE) left Djibouti to the United Arab Emirates.
Djibouti's strategic location by the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, which separates the Gulf of Aden
The Gulf of Aden ( ar, خليج عدن, so, Gacanka Cadmeed 𐒅𐒖𐒐𐒕𐒌 𐒋𐒖𐒆𐒗𐒒) is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channe ...
from the Red Sea and controls the approaches to the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
, has made it a desirable location for foreign military bases. Camp Lemonnier was abandoned by the French and later leased to the United States Central Command in September 2002. The lease was renewed in 2014 for another 20 years. The country also hosts the only overseas Chinese People's Liberation Army Support Base in Djibouti, Chinese support base and the only overseas Japan Self-Defense Force Base Djibouti, Japanese military base. The Italian National Support Military Base is also located in Djibouti.
The hosting of foreign military bases is an important part of Djibouti's economy. The United States pays $63 million a year to rent Camp Lemonnier, France and Japan each pay about $30 million a year, and China pays $20 million a year. The lease payments added up to more than 5% of Djibouti's GDP of in 2017.
China has, in recent times, stepped up its military presence in Africa, with ongoing plans to secure an even greater military presence in Djibouti specifically. China's presence in Djibouti is tied to strategic ports to ensure the security of Chinese assets. Djibouti's strategic location makes the country prime for an increased military presence.
Human rights
In its 2011 Freedom in the World report, Freedom House ranked Djibouti as "Not Free", a downgrading from its former status as "Partly Free". The US State Department Country Report on Human Rights Practices for 2019 points out that Djibouti's significant human rights issues included: unlawful or arbitrary killings by government agents; arbitrary detention by government agents; harsh and life-threatening prison conditions; arbitrary or unlawful interference with privacy; unjustified arrests or prosecutions of journalists; criminal libel; substantial interference with the rights of peaceful assembly and freedom of association; significant acts of corruption; and violence against women and girls with inadequate government action for prosecution and accountability, including female genital mutilation/cutting. It states also that impunity was a problem, with the government seldom taking steps to identify and punish officials who committed abuses, whether in the security services or elsewhere in the government.Administrative divisions
 Djibouti is partitioned into six administrative regions, with Djibouti (city), Djibouti city representing one of the official regions. It is further subdivided into twenty Districts of Djibouti, districts.
Djibouti is partitioned into six administrative regions, with Djibouti (city), Djibouti city representing one of the official regions. It is further subdivided into twenty Districts of Djibouti, districts.
Geography
Location and habitat
Djibouti is situated in theHorn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
on the Gulf of Aden
The Gulf of Aden ( ar, خليج عدن, so, Gacanka Cadmeed 𐒅𐒖𐒐𐒕𐒌 𐒋𐒖𐒆𐒗𐒒) is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channe ...
and the Bab-el-Mandeb, at the southern entrance to the Red Sea. It lies between latitudes 11° and 14°N and longitudes 41° and 44°E, at the northernmost point of the Great Rift Valley. It is here in Djibouti that the rift between the African Plate and the Somali Plate meet the Arabian Plate, forming a geologic tripoint. The tectonic interaction at this tripoint has created the Extreme points of Africa, lowest elevation of any place in Africa at Lake Assal (Djibouti), Lake Assal, and indeed, the second lowest depression on dry land found anywhere on earth (surpassed only by the depression along the border of Jordan and Israel).
The country's coastline stretches , with terrain consisting mainly of plateau, plains and highlands. Djibouti has a total area of . Its borders extend , of which are shared with Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia ...
, with Ethiopia, and with Somaliland
Somaliland,; ar, صوماليلاند ', ' officially the Republic of Somaliland,, ar, جمهورية صوماليلاند, link=no ''Jumhūrīyat Ṣūmālīlānd'' is a ''de facto'' sovereign state in the Horn of Africa, still conside ...
. Djibouti is the southernmost Arabian Plate country, country on the Arabian Plate.
Djibouti has eight mountain ranges with peaks of over .Highest Mountains in Djibouti. geonames.org The Mousa Ali range is considered the country's highest mountain range, with the tallest peak on the border with Ethiopia and Eritrea. It has an elevation of . The Grand Bara desert covers parts of southern Djibouti in the Arta, Ali Sabieh and Dikhil regions. The majority of it sits at a relatively low elevation, below . Extreme geographic points include: to the north, Ras Doumera and the point at which the border with Eritrea enters the Red Sea in the Obock Region; to the east, a section of the Red Sea coast north of Ras Bir; to the south, a location on the border with Ethiopia west of the town of As Ela; and to the west, a location on the frontier with Ethiopia immediately east of the Ethiopian town of Afambo (woreda), Afambo. Most of Djibouti is part of the Ethiopian xeric grasslands and shrublands ecoregion. The exception is an eastern strip located along the Red Sea coast, which is part of the Eritrean coastal desert.
Gulf of Aden
The Gulf of Aden ( ar, خليج عدن, so, Gacanka Cadmeed 𐒅𐒖𐒐𐒕𐒌 𐒋𐒖𐒆𐒗𐒒) is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channe ...
Climate
 Djibouti's climate is significantly warmer and has significantly less seasonal variation than the world average. The mean daily maximum temperatures range from 32 to 41 °C (90 to 106 °F), except at high elevations. In Djibouti City, for instance, average afternoon highs range from 28 to 34 °C (82 to 93 °F) in April. But at Airolaf, which ranges from 1,535 to 1,600 m (5,036 to 5,249 ft), maximum temperature is 30 °C (86 °F) in summer and minimum 9 °C (48 °F) in winter. In the wikt:upland, uplands ranges from 500 to 800 m (1,640 to 2,624 ft), are comparable and cooler to those on the coast in the hottest months of June until August. December and January is the coolest month with averages low temperatures falling as low as 15 °C (59 °F). Djibouti has either a hot semi-arid climate (BSh) or a hot desert climate (BWh), although temperatures are much moderated at the highest elevations.
Djibouti's climate ranges from arid in the northeastern coastal regions to semiarid, semi-arid in the central, northern, western and southern parts of the country. On the eastern seaboard, annual rainfall is less than 5 inches (131 mm); in the central highlands, precipitation is about 8 to 16 inches (200 to 400 mm). The hinterland is significantly less humid than the coastal regions.
Djibouti's climate is significantly warmer and has significantly less seasonal variation than the world average. The mean daily maximum temperatures range from 32 to 41 °C (90 to 106 °F), except at high elevations. In Djibouti City, for instance, average afternoon highs range from 28 to 34 °C (82 to 93 °F) in April. But at Airolaf, which ranges from 1,535 to 1,600 m (5,036 to 5,249 ft), maximum temperature is 30 °C (86 °F) in summer and minimum 9 °C (48 °F) in winter. In the wikt:upland, uplands ranges from 500 to 800 m (1,640 to 2,624 ft), are comparable and cooler to those on the coast in the hottest months of June until August. December and January is the coolest month with averages low temperatures falling as low as 15 °C (59 °F). Djibouti has either a hot semi-arid climate (BSh) or a hot desert climate (BWh), although temperatures are much moderated at the highest elevations.
Djibouti's climate ranges from arid in the northeastern coastal regions to semiarid, semi-arid in the central, northern, western and southern parts of the country. On the eastern seaboard, annual rainfall is less than 5 inches (131 mm); in the central highlands, precipitation is about 8 to 16 inches (200 to 400 mm). The hinterland is significantly less humid than the coastal regions.
Wildlife
 Most species of wildlife are found in the northern part of the country, in the ecosystem of the Day Forest National Park. At an average altitude of , the area includes the Goda massif, with a peak of . It covers an area of of Juniperus procera forest, with many of the trees rising to height. This forest area is the main habitat of the endangered and endemic Djibouti francolin (a bird), and another recently noted vertebrate, ''Platyceps afarensis'' (a colubrine snake). It also contains many species of woody and herbaceous plants, including boxwood and olive trees, which account for 60% of the total identified species in the country.
According to the country profile related to biodiversity of wildlife in Djibouti, the nation contains more than 820 species of plants, 493 species of invertebrates, 455 species of fish, 40 species of reptiles, three species of amphibians, 360 species of birds and 66 species of mammals. Wildlife of Djibouti is also listed as part of
Most species of wildlife are found in the northern part of the country, in the ecosystem of the Day Forest National Park. At an average altitude of , the area includes the Goda massif, with a peak of . It covers an area of of Juniperus procera forest, with many of the trees rising to height. This forest area is the main habitat of the endangered and endemic Djibouti francolin (a bird), and another recently noted vertebrate, ''Platyceps afarensis'' (a colubrine snake). It also contains many species of woody and herbaceous plants, including boxwood and olive trees, which account for 60% of the total identified species in the country.
According to the country profile related to biodiversity of wildlife in Djibouti, the nation contains more than 820 species of plants, 493 species of invertebrates, 455 species of fish, 40 species of reptiles, three species of amphibians, 360 species of birds and 66 species of mammals. Wildlife of Djibouti is also listed as part of Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
biodiversity hotspot and the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden
The Gulf of Aden ( ar, خليج عدن, so, Gacanka Cadmeed 𐒅𐒖𐒐𐒕𐒌 𐒋𐒖𐒆𐒗𐒒) is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channe ...
coral reef hotspot. Mammals include several species of antelope, such as Soemmerring's gazelle and Pelzeln's gazelle. As a result of the hunting ban imposed since early 1970 these species are well conserved now. Other characteristic mammals are Grevy's zebra, hamadryas baboon and Hunter's antelope. The warthog, a vulnerable species, is also found in the Day National park. The coastal waters have dugongs and Abyssinian genet; the latter needs confirmation by further studies. Green turtles and hawksbill turtles are in the coastal waters where nestling also takes place. The Northeast African cheetah ''Acinonyx jubatus soemmeringii'' is thought to be extinct in Djibouti.
Economy
 Djibouti's economy is largely concentrated in the service sector. Commercial activities revolve around the country's free trade policies and strategic location as a Red Sea transit point. Due to limited rainfall, vegetables and fruits are the principal production crops, and other food items require importation. The GDP (purchasing power parity) in 2013 was estimated at $2.505 billion, with a real growth rate of 5% annually. Per capita income is around $2,874 (PPP). The services sector constituted around 79.7% of the GDP, followed by industry at 17.3%, and agriculture at 3%.
, the container terminal at the Port of Djibouti handles the bulk of the nation's trade. About 70% of the seaport's activity consists of imports to and exports from neighboring Ethiopia, which depends on the harbour as its main maritime outlet. As of 2018, 95% of Ethiopian transit cargo was handled by the Port of Djibouti. The port also serves as an international refueling center and transshipment hub. In 2012, the Djiboutian government in collaboration with DP World started construction of the Doraleh Container Terminal, a third major seaport intended to further develop the national transit capacity. A $396 million project, it has the capacity to accommodate 1.5 million twenty foot container units annually.
Djibouti was ranked the 177th safest investment destination in the world in the March 2011 Euromoney Country Risk rankings. To improve the environment for direct foreign investment, the Djibouti authorities in conjunction with various non-profit organizations have launched a number of development projects aimed at highlighting the country's commercial potential. The government has also introduced new private sector policies targeting high interest and inflation rates, including relaxing the tax burden on enterprises and allowing exemptions on consumption tax.
Djibouti's economy is largely concentrated in the service sector. Commercial activities revolve around the country's free trade policies and strategic location as a Red Sea transit point. Due to limited rainfall, vegetables and fruits are the principal production crops, and other food items require importation. The GDP (purchasing power parity) in 2013 was estimated at $2.505 billion, with a real growth rate of 5% annually. Per capita income is around $2,874 (PPP). The services sector constituted around 79.7% of the GDP, followed by industry at 17.3%, and agriculture at 3%.
, the container terminal at the Port of Djibouti handles the bulk of the nation's trade. About 70% of the seaport's activity consists of imports to and exports from neighboring Ethiopia, which depends on the harbour as its main maritime outlet. As of 2018, 95% of Ethiopian transit cargo was handled by the Port of Djibouti. The port also serves as an international refueling center and transshipment hub. In 2012, the Djiboutian government in collaboration with DP World started construction of the Doraleh Container Terminal, a third major seaport intended to further develop the national transit capacity. A $396 million project, it has the capacity to accommodate 1.5 million twenty foot container units annually.
Djibouti was ranked the 177th safest investment destination in the world in the March 2011 Euromoney Country Risk rankings. To improve the environment for direct foreign investment, the Djibouti authorities in conjunction with various non-profit organizations have launched a number of development projects aimed at highlighting the country's commercial potential. The government has also introduced new private sector policies targeting high interest and inflation rates, including relaxing the tax burden on enterprises and allowing exemptions on consumption tax.
 Additionally, efforts have been made to lower the estimated 60% urban unemployment rate by creating more job opportunities through investment in diversified sectors. Funds have especially gone toward building telecommunications infrastructure and increasing disposable income by supporting small businesses. Owing to its growth potential, the fishing and agro-processing sector, which represents around 15% of GDP, has also enjoyed rising investment since 2008.
To expand the modest industrial sector, a 56 megawatt geothermal power plant slated to be completed by 2018 is being constructed with the help of OPEC, the World Bank and the Global Environmental Facility. The facility is expected to solve the recurring electricity shortages, decrease the nation's reliance on Ethiopia for energy, reduce costly oil imports for diesel-generated electricity, and thereby buttress the GDP and lower debt.
The Djibouti firm Salt Investment (SIS) began a large-scale operation to industrialize the plentiful salt in Djibouti's Lake Assal (Djibouti), Lake Assal region. Operating at an annual capacity of 4 million tons, the desalination project has lifted export revenues, created more job opportunities, and provided more fresh water for the area's residents. In 2012, the Djibouti government also enlisted the services of the China Harbor Engineering Company Ltd for the construction of an ore terminal. Worth $64 million, the project enabled Djibouti to export a further 5,000 tons of salt per year to markets in Southeast Asia.
Additionally, efforts have been made to lower the estimated 60% urban unemployment rate by creating more job opportunities through investment in diversified sectors. Funds have especially gone toward building telecommunications infrastructure and increasing disposable income by supporting small businesses. Owing to its growth potential, the fishing and agro-processing sector, which represents around 15% of GDP, has also enjoyed rising investment since 2008.
To expand the modest industrial sector, a 56 megawatt geothermal power plant slated to be completed by 2018 is being constructed with the help of OPEC, the World Bank and the Global Environmental Facility. The facility is expected to solve the recurring electricity shortages, decrease the nation's reliance on Ethiopia for energy, reduce costly oil imports for diesel-generated electricity, and thereby buttress the GDP and lower debt.
The Djibouti firm Salt Investment (SIS) began a large-scale operation to industrialize the plentiful salt in Djibouti's Lake Assal (Djibouti), Lake Assal region. Operating at an annual capacity of 4 million tons, the desalination project has lifted export revenues, created more job opportunities, and provided more fresh water for the area's residents. In 2012, the Djibouti government also enlisted the services of the China Harbor Engineering Company Ltd for the construction of an ore terminal. Worth $64 million, the project enabled Djibouti to export a further 5,000 tons of salt per year to markets in Southeast Asia.
 Djibouti's gross domestic product expanded by an average of more than 6 percent per year, from US$341 million in 1985 to US$1.5 billion in 2015. The Djiboutian franc is the currency of Djibouti. It is issued by the Central Bank of Djibouti, the country's monetary authority. Since the Djiboutian franc is pegged to the U.S. dollar, it is generally stable and inflation is not a problem. This has contributed to the growing interest in investment in the country.
, 10 conventional and Islamic banks operate in Djibouti. Most arrived within the past few years, including the Somali money transfer company Dahabshiil and BDCD, a subsidiary of Swiss Financial Investments. The banking system had previously been monopolized by two institutions: the Indo-Suez Bank and the Commercial and Industrial Bank (BCIMR). To assure a robust credit and deposit sector, the government requires commercial banks to maintain 30% of shares in the financial institution; a minimum of 300 million Djiboutian francs in up-front capital is mandatory for international banks. Lending has likewise been encouraged by the creation of a guarantee fund, which allows banks to issue loans to eligible small- and medium-sized businesses without first requiring a large deposit or other collateral.
Saudi investors are also reportedly exploring the possibility of linking the
Djibouti's gross domestic product expanded by an average of more than 6 percent per year, from US$341 million in 1985 to US$1.5 billion in 2015. The Djiboutian franc is the currency of Djibouti. It is issued by the Central Bank of Djibouti, the country's monetary authority. Since the Djiboutian franc is pegged to the U.S. dollar, it is generally stable and inflation is not a problem. This has contributed to the growing interest in investment in the country.
, 10 conventional and Islamic banks operate in Djibouti. Most arrived within the past few years, including the Somali money transfer company Dahabshiil and BDCD, a subsidiary of Swiss Financial Investments. The banking system had previously been monopolized by two institutions: the Indo-Suez Bank and the Commercial and Industrial Bank (BCIMR). To assure a robust credit and deposit sector, the government requires commercial banks to maintain 30% of shares in the financial institution; a minimum of 300 million Djiboutian francs in up-front capital is mandatory for international banks. Lending has likewise been encouraged by the creation of a guarantee fund, which allows banks to issue loans to eligible small- and medium-sized businesses without first requiring a large deposit or other collateral.
Saudi investors are also reportedly exploring the possibility of linking the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
with the Arabian Peninsula via a oversea bridge through Djibouti, referred to as the Bridge of the Horns. The investor Tarek bin Laden has been linked to the project. However, it was announced in June 2010 that Phase I of the project had been delayed.
Transport
 The Djibouti–Ambouli International Airport in Djibouti City, the country's only international airport, serves many intercontinental routes with scheduled and chartered flights. Air Djibouti is the flag carrier of Djibouti and is the country's largest airline.
The new and electrified standard gauge Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway started operation in January 2018. Its main purpose is to facilitate freight services between the Ethiopian hinterland and the Djiboutian Port of Doraleh.
Car ferries pass the
The Djibouti–Ambouli International Airport in Djibouti City, the country's only international airport, serves many intercontinental routes with scheduled and chartered flights. Air Djibouti is the flag carrier of Djibouti and is the country's largest airline.
The new and electrified standard gauge Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway started operation in January 2018. Its main purpose is to facilitate freight services between the Ethiopian hinterland and the Djiboutian Port of Doraleh.
Car ferries pass the Gulf of Tadjoura
The Gulf of Tadjoura (; ) is a gulf or basin of the Indian Ocean in the Horn of Africa. It lies south of the straits of Bab-el-Mandeb, or the entrance to the Red Sea, at . The gulf has many fishing grounds, extensive coral reefs, and abundant pea ...
from Djibouti City to Tadjoura. There is the Port of Doraleh west of Djibouti City, which is the main port of Djibouti. The Port of Doraleh is the terminal of the new Addis Ababa–Djibouti Railway. In addition to the Port of Doraleh, which handles general cargo and oil imports, Djibouti (2018) has three other major ports for the import and export of bulk goods and livestock, the Tadjoura, Port of Tadjourah (potash), the Damerjog, Damerjog Port (livestock) and the Port of Goubet (salt). Almost 95% of Ethiopia's imports and exports move through Djiboutian ports.
The Djiboutian highway system is named according to the road classification. Roads that are considered primary roads are those that are fully asphalted (throughout their entire length) and in general they carry traffic between all the major towns in Djibouti.
Djibouti is part of the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road that runs from the Chinese coast to the Upper Adriatic region with its connections to Central and Eastern Europe.
Media and telecommunications
 Telecommunications in Djibouti fall under the authority of the Ministry of Communication.
Djibouti Telecom is the sole provider of telecommunication services. It mostly utilizes a microwave radio relay network. A fiber-optic cable is installed in the capital, whereas rural areas are connected via wireless local loop radio systems. Mobile cellular coverage is primarily limited to the area in and around Djibouti city. , 23,000 telephone main lines and 312,000 mobile/cellular lines were in use. The SEA-ME-WE 3 (cable system), SEA-ME-WE 3 Submarine communications cable, submarine cable operates to Jeddah, Suez, Sicily, Marseille, Colombo, Singapore and beyond. Telephone satellite earth stations include 1 Intelsat (Indian Ocean) and 1 Arabsat. Medarabtel is the regional microwave radio relay telephone network.
Radio Television of Djibouti is the state-owned national broadcaster. It operates the sole terrestrial TV station, as well as the two domestic radio networks on AM broadcasting, AM 1, FM broadcasting, FM 2, and shortwave 0. Licensing and operation of broadcast media is regulated by the government. Movie theaters include the Odeon Cinema in the capital.
, there were 215 local internet service providers. Internet users comprised around 99,000 individuals (2015). The internet country top-level domain is .dj.
Telecommunications in Djibouti fall under the authority of the Ministry of Communication.
Djibouti Telecom is the sole provider of telecommunication services. It mostly utilizes a microwave radio relay network. A fiber-optic cable is installed in the capital, whereas rural areas are connected via wireless local loop radio systems. Mobile cellular coverage is primarily limited to the area in and around Djibouti city. , 23,000 telephone main lines and 312,000 mobile/cellular lines were in use. The SEA-ME-WE 3 (cable system), SEA-ME-WE 3 Submarine communications cable, submarine cable operates to Jeddah, Suez, Sicily, Marseille, Colombo, Singapore and beyond. Telephone satellite earth stations include 1 Intelsat (Indian Ocean) and 1 Arabsat. Medarabtel is the regional microwave radio relay telephone network.
Radio Television of Djibouti is the state-owned national broadcaster. It operates the sole terrestrial TV station, as well as the two domestic radio networks on AM broadcasting, AM 1, FM broadcasting, FM 2, and shortwave 0. Licensing and operation of broadcast media is regulated by the government. Movie theaters include the Odeon Cinema in the capital.
, there were 215 local internet service providers. Internet users comprised around 99,000 individuals (2015). The internet country top-level domain is .dj.
Tourism
 Tourism in Djibouti is one of the growing economic sectors of the country and is an industry that generates less than 80,000 arrivals per year, mostly the family and friends of the soldiers stationed in the country's major naval bases. Although the numbers are on the rise, there are talks of the visa on arrival being stopped, which could limit tourism growth.
Infrastructure makes it difficult for tourists to travel independently and costs of private tours are high. Since the re-opening of the train line from Addis Ababa to Djibouti in January 2018, travel by land has also resumed. Djibouti's two main geological marvels, Lake Abbe and Lake Assal, are the country's top tourist destinations. The two sites draw hundreds of tourists every year looking for remote places that are not visited by many.
Tourism in Djibouti is one of the growing economic sectors of the country and is an industry that generates less than 80,000 arrivals per year, mostly the family and friends of the soldiers stationed in the country's major naval bases. Although the numbers are on the rise, there are talks of the visa on arrival being stopped, which could limit tourism growth.
Infrastructure makes it difficult for tourists to travel independently and costs of private tours are high. Since the re-opening of the train line from Addis Ababa to Djibouti in January 2018, travel by land has also resumed. Djibouti's two main geological marvels, Lake Abbe and Lake Assal, are the country's top tourist destinations. The two sites draw hundreds of tourists every year looking for remote places that are not visited by many.
Energy
Djibouti has an installed electrical power generating capacity of 126 MW from fuel oil and diesel plants. In 2002 electrical power output was put at 232 GWh, with consumption at 216 GWh. At 2015, per capita annual electricity consumption is about 330 kilowatt-hours (kWh); moreover, about 45% of the population does not have access to electricity, and the level of unmet demand in the country's power sector is significant. Increased hydropower imports from Ethiopia, which satisfies 65% of Djibouti's demand, will play a significant role in boosting the country's renewable energy supply. The geothermal potential has generated particular interest in Japan, with 13 potential sites; they have already started the construction on one site near Lake Assal. The construction of the photovoltaic power station (solar farms) in Grand Bara will generate 50 MW capacity.Demographics
Djibouti has a population of about 921,804 inhabitants. It is a multiethnic country. The local population grew rapidly during the latter half of the 20th century, increasing from about 69,589 in 1955 to around 869,099 by 2015. The two largest ethnic groups native to Djibouti are the Somalis (60%) and theAfar
Afar may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Afar language, an East Cushitic language
*Afar people, an ethnic group of Djibouti, Eritrea, and Ethiopia
Places Horn of Africa
*Afar Desert or Danakil Desert, a desert in Ethiopia
*Afar Region, a region ...
(35%). The Somali clan component is mainly composed of the Issa (clan), Issa, followed by the Gadabuursi
The Gadabuursi ( Somali: ''Gadabuursi'', Arabic: جادابورسي), also known as ''Samaroon'' (Arabic: ''قبيلة سَمَرُون)'', is a northern Somali clan, a sub-division of the Dir clan family.
The Gadabuursi are geographically s ...
and the Isaaq. The remaining 5% of Djibouti's population primarily consists of Yemenis, Yemeni Arabs, People of Ethiopia, Ethiopians and Europeans (French people, French and Italians). Approximately 76% of local residents are urban dwellers; the remainder are Pastoralism, pastoralists. Djibouti also hosts a number of immigrants and refugees from neighboring states, with Djibouti City nicknamed the "French Hong Kong in the Red Sea" due to its cosmopolitan urbanism. Djibouti's location on the eastern coast of Africa makes it a hub of regional Human migration, migration, with Somalis, Yemenis, and Ethiopians traveling through the country en route to the Arab states of the Persian Gulf, Gulf and North Africa, northern Africa. Djibouti has received a massive influx of migrants from Yemen.
Languages
Djibouti is a multilingual nation. The majority of local residents speak Somali (524,000 speakers) andAfar
Afar may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Afar language, an East Cushitic language
*Afar people, an ethnic group of Djibouti, Eritrea, and Ethiopia
Places Horn of Africa
*Afar Desert or Danakil Desert, a desert in Ethiopia
*Afar Region, a region ...
(306,000 speakers) as first languages. These idioms are the mother tongues of the Somali and Afar ethnic groups, respectively. Both languages belong to the larger Afroasiatic Cushitic family. Northern Somali is the main dialect spoken in the country and in neighbouring Somaliland, in contrast to Benadiri Somali which is the main dialect spoken in Somalia. There are two official languages in Djibouti: Arabic language, Arabic and French language, French.
Arabic is of religious importance. In formal settings, it consists of Modern Standard Arabic. Colloquially, about 59,000 local residents speak the Ta'izzi-Adeni Arabic dialect, also known as ''Djibouti Arabic''. French serves as a statutory national language. It was inherited from the colonial period, and is the primary language of instruction. Around 17,000 Djiboutians speak it as a first language. Immigrant languages include Omani Arabic (38,900 speakers), Amharic (1,400 speakers), and Greek language, Greek (1,000 speakers).
Religion
Djibouti's population is predominantly Muslim.Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
is observed by around 98% of the nation's population (approximately 891,000 ). , 94% of the population was Muslim whereas the remaining 6% of residents are Christian adherents.
Islam entered the region very early on, as a group of persecuted Muslims had sought refuge across the Red Sea in the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
at the urging of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. In 1900, during the early part of the colonial era, there were virtually no Christians in the territories, with only about 100–300 followers coming from the schools and orphanages of the few Catholic missions in the French Somaliland
French Somaliland (french: Côte française des Somalis, lit= French Coast of the Somalis so, Xeebta Soomaaliyeed ee Faransiiska) was a French colony in the Horn of Africa. It existed between 1884 and 1967, at which time it became the French Ter ...
. The Constitution of Djibouti names Islam as the sole state religion, and also provides for the equality of citizens of all faiths (Article 1) and freedom of religious practice (Article 11). Most local Muslims adhere to the Sunni Islam, Sunni denomination, following the Shafi'i school. The non-denominational Muslims largely belong to Sufism, Sufi orders of varying schools. According to the International Religious Freedom Report 2008, while Muslim Djiboutians have the legal right to convert to or marry someone from another faith, converts may encounter negative reactions from their family and clan or from society at large, and they often face pressure to go back to Islam.
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Djibouti, Diocese of Djibouti serves the small local Catholicism, Catholic population, which it estimates numbered around 7,000 individuals in 2006.
Largest cities
Health
 The life expectancy at birth is around 64.7 for both males and females. Fertility is at 2.35 children per woman. In Djibouti there are about 18 doctors per 100,000 persons.
The 2010 maternal mortality rate per 100,000 births for Djibouti is 300. This is compared with 461.6 in 2008 and 606.5 in 1990. The under 5 mortality rate per 1,000 births is 95 and the neonatal mortality as a percentage of under 5's mortality are 37. In Djibouti the number of midwives per 1,000 live births is 6 and the lifetime risk of death for pregnant women 1 in 93.
About 93.1% of Djibouti's women and girls have undergone female genital mutilation (FGM, sometimes referred to as 'female circumcision'), a pre-marital custom mainly endemic to Northeast Africa and parts of the Near East.Bodman, Herbert L. and Tohidi, Nayereh Esfahlani (1998
The life expectancy at birth is around 64.7 for both males and females. Fertility is at 2.35 children per woman. In Djibouti there are about 18 doctors per 100,000 persons.
The 2010 maternal mortality rate per 100,000 births for Djibouti is 300. This is compared with 461.6 in 2008 and 606.5 in 1990. The under 5 mortality rate per 1,000 births is 95 and the neonatal mortality as a percentage of under 5's mortality are 37. In Djibouti the number of midwives per 1,000 live births is 6 and the lifetime risk of death for pregnant women 1 in 93.
About 93.1% of Djibouti's women and girls have undergone female genital mutilation (FGM, sometimes referred to as 'female circumcision'), a pre-marital custom mainly endemic to Northeast Africa and parts of the Near East.Bodman, Herbert L. and Tohidi, Nayereh Esfahlani (1998''Women in Muslim societies: diversity within unity''
. Lynne Rienner Publishers. p. 41. . Although legally proscribed in 1994, the procedure is still widely practiced, as it is deeply ingrained in the local culture. Encouraged and performed by women in the community, FGM is primarily intended to deter promiscuity and to offer protection from assault.Suzanne G. Frayser, Thomas J. Whitby
Studies in human sexuality: a selected guide
, (Libraries Unlimited: 1995), p. 257 . About 94% of Djibouti's male population have also reportedly undergone Circumcision, male circumcision, a figure in line with adherence to Islam, which requires this.
Education
Education is a priority for the government of Djibouti. , it allocates 20.5% of its annual budget to scholastic instruction.Hare, Harry (2007ICT in Education in Djibouti
, World Bank
 The Djiboutian educational system was initially formulated to cater to a limited pupil base. As such, the schooling framework was largely elitist and drew considerably from the French colonial paradigm, which was ill-suited to local circumstances and needs.
In the late 1990s, the Djiboutian authorities revised the national educational strategy and launched a broad-based consultative process involving administrative officials, teachers, parents, national assembly members and NGOs. The initiative identified areas in need of attention and produced concrete recommendations on how to go about improving them. The government subsequently prepared a comprehensive reform plan aimed at modernizing the educational sector over the 2000–10 period. In August 2000, it passed an official Education Planning Act and drafted a medium-term development plan for the next five years. The fundamental academic system was significantly restructured and made compulsory; it now consists of five years of primary school and four years of middle school. Secondary schools also require a Certificate of Fundamental Education for admission. In addition, the new law introduced secondary-level vocational instruction and established university facilities in the country.
As a result of the Education Planning Act and the medium-term action strategy, substantial progress has been registered throughout the educational sector. In particular, school enrollment, attendance, and retention rates have all steadily increased, with some regional variation. From 2004 to 2005 to 2007–08, net enrollments of girls in primary school rose by 18.6%; for boys, it increased 8.0%. Net enrollments in middle school over the same period rose by 72.4% for girls and 52.2% for boys. At the secondary level, the rate of increase in net enrollments was 49.8% for girls and 56.1% for boys.Djibouti Assistance to Education Evaluation
The Djiboutian educational system was initially formulated to cater to a limited pupil base. As such, the schooling framework was largely elitist and drew considerably from the French colonial paradigm, which was ill-suited to local circumstances and needs.
In the late 1990s, the Djiboutian authorities revised the national educational strategy and launched a broad-based consultative process involving administrative officials, teachers, parents, national assembly members and NGOs. The initiative identified areas in need of attention and produced concrete recommendations on how to go about improving them. The government subsequently prepared a comprehensive reform plan aimed at modernizing the educational sector over the 2000–10 period. In August 2000, it passed an official Education Planning Act and drafted a medium-term development plan for the next five years. The fundamental academic system was significantly restructured and made compulsory; it now consists of five years of primary school and four years of middle school. Secondary schools also require a Certificate of Fundamental Education for admission. In addition, the new law introduced secondary-level vocational instruction and established university facilities in the country.
As a result of the Education Planning Act and the medium-term action strategy, substantial progress has been registered throughout the educational sector. In particular, school enrollment, attendance, and retention rates have all steadily increased, with some regional variation. From 2004 to 2005 to 2007–08, net enrollments of girls in primary school rose by 18.6%; for boys, it increased 8.0%. Net enrollments in middle school over the same period rose by 72.4% for girls and 52.2% for boys. At the secondary level, the rate of increase in net enrollments was 49.8% for girls and 56.1% for boys.Djibouti Assistance to Education Evaluation. USAID (April 2009) The Djiboutian government has especially focused on developing and improving institutional infrastructure and teaching materials, including constructing new classrooms and supplying textbooks. At the post-secondary level, emphasis has also been placed on producing qualified instructors and encouraging out-of-school youngsters to pursue vocational training. , the literacy rate in Djibouti was estimated at 70%. Institutions of higher learning in the country include the University of Djibouti.
Culture
 Djiboutian attire reflects the region's hot and arid climate. When not dressed in Western clothing such as jeans and T-shirts, men typically wear the , which is a traditional sarong-like garment worn around the waist. Many nomadic people wear a loosely wrapped white cotton robe called a ''tobe'' that goes down to about the knee, with the end thrown over the shoulder (much like a Roman toga).
Women typically wear the ''dirac'', which is a long, light, diaphanous voile dress made of cotton or polyester that is worn over a full-length Slip (clothing), half-slip and a bra. Married women tend to sport head-scarves referred to as ''shash'' and often cover their upper body with a shawl known as ''garbasaar''. Unmarried or young women, however, do not always cover their heads. Traditional Arabian garb such as the male jellabiya (''jellabiyaad'' in Somali) and the female jilbāb is also commonly worn. For some occasions such as festivals, women may adorn themselves with specialized jewelry and head-dresses similar to those worn by the Berber people, Berber tribes of the Maghreb.
A lot of Djibouti's original art is passed on and preserved orally, mainly through song. Many examples of Islamic, Ottoman, and French influences can also be noted in the local buildings, which contain plasterwork, carefully constructed Motif (visual arts), motifs, and calligraphy.
Djiboutian attire reflects the region's hot and arid climate. When not dressed in Western clothing such as jeans and T-shirts, men typically wear the , which is a traditional sarong-like garment worn around the waist. Many nomadic people wear a loosely wrapped white cotton robe called a ''tobe'' that goes down to about the knee, with the end thrown over the shoulder (much like a Roman toga).
Women typically wear the ''dirac'', which is a long, light, diaphanous voile dress made of cotton or polyester that is worn over a full-length Slip (clothing), half-slip and a bra. Married women tend to sport head-scarves referred to as ''shash'' and often cover their upper body with a shawl known as ''garbasaar''. Unmarried or young women, however, do not always cover their heads. Traditional Arabian garb such as the male jellabiya (''jellabiyaad'' in Somali) and the female jilbāb is also commonly worn. For some occasions such as festivals, women may adorn themselves with specialized jewelry and head-dresses similar to those worn by the Berber people, Berber tribes of the Maghreb.
A lot of Djibouti's original art is passed on and preserved orally, mainly through song. Many examples of Islamic, Ottoman, and French influences can also be noted in the local buildings, which contain plasterwork, carefully constructed Motif (visual arts), motifs, and calligraphy.
Music
 Somalis have a rich musical heritage centered on traditional Somali folklore. Most Somali songs are Pentatonic scale, pentatonic. That is, they only use five Pitch (music), pitches per octave in contrast to a Heptatonic scale, heptatonic (seven note) scale such as the major scale. At first listen, Somali music might be mistaken for the sounds of nearby regions such as Ethiopia, Sudan or the Arabian Peninsula, but it is ultimately recognizable by its own unique tunes and styles. Somali songs are usually the product of collaboration between lyricists (), songwriters () and singers ( or "voice"). Balwo is a Somali musical style centered on love themes that is popular in Djibouti.
Traditional Afar music resembles the folk music of other parts of the
Somalis have a rich musical heritage centered on traditional Somali folklore. Most Somali songs are Pentatonic scale, pentatonic. That is, they only use five Pitch (music), pitches per octave in contrast to a Heptatonic scale, heptatonic (seven note) scale such as the major scale. At first listen, Somali music might be mistaken for the sounds of nearby regions such as Ethiopia, Sudan or the Arabian Peninsula, but it is ultimately recognizable by its own unique tunes and styles. Somali songs are usually the product of collaboration between lyricists (), songwriters () and singers ( or "voice"). Balwo is a Somali musical style centered on love themes that is popular in Djibouti.
Traditional Afar music resembles the folk music of other parts of the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
such as Music of Ethiopia, Ethiopia; it also contains elements of Arabic music. The history of Djibouti is recorded in the poetry and songs of its nomadic people, and goes back thousands of years to a time when the peoples of Djibouti traded hides and skins for the perfumes and spices of ancient Egypt, India and China. Afar oral literature is also quite musical. It comes in many varieties, including songs for weddings, war, praise and boasting. – ''Website no longer exists; link is to Internet Archive''
Literature
Djibouti has a long tradition of poetry. Several well-developed Somali forms of verse include the , , , , , , and . The (epic poem) has the most complex length and meter, often exceeding 100 lines. It is considered the mark of poetic attainment when a young poet is able to compose such verse, and is regarded as the height of poetry. Groups of memorizers and reciters () traditionally propagated the well-developed art form. Poems revolve around several main themes, including (elegy), (praise), (romance), (diatribe), (gloating) and (guidance). The baroorodiiq is composed to commemorate the death of a prominent poet or figure.Abdullahi, Mohamed Diriye (2001) ''Culture and Customs of Somalia'', Greenwood Press. pp. 75–76. The Afar are familiar with the , a kind of warrior-poet and diviner, and have a rich oral tradition of folk stories. They also have an extensive repertoire of battle songs.Phillips, Matt and Carillet, Jean-Bernard (2006) ''Lonely Planet Ethiopia and Eritrea'', Lonely Planet. p. 301. Additionally, Djibouti has a long tradition of Islamic literature. Among the most prominent historical works is the medieval ''Futuh Al-Habash'' by Shihāb al-Dīn, which chronicles the Adal Sultanate army's Ethiopian-Adal War, conquest of Abyssinia during the 16th century. In recent years, a number of politicians and intellectuals have also penned memoirs or reflections on the country.Sport
 Football is the most popular sport amongst Djiboutians. The country became a member of FIFA in 1994, but has only taken part in the qualifying rounds for the African Cup of Nations as well as the FIFA World Cup in the mid-2000s. In November 2007, the Djibouti national football team beat Somalia national football team, Somalia's national squad 1–0 in the qualification rounds for the 2010 FIFA World Cup, marking its first ever World Cup-related win.
Recently, the World Archery Federation has helped to implement the Djibouti Archery Federation, and an international archery training center is being created in Arta, Djibouti, Arta to support archery development in East Africa and Red Sea area.
Football is the most popular sport amongst Djiboutians. The country became a member of FIFA in 1994, but has only taken part in the qualifying rounds for the African Cup of Nations as well as the FIFA World Cup in the mid-2000s. In November 2007, the Djibouti national football team beat Somalia national football team, Somalia's national squad 1–0 in the qualification rounds for the 2010 FIFA World Cup, marking its first ever World Cup-related win.
Recently, the World Archery Federation has helped to implement the Djibouti Archery Federation, and an international archery training center is being created in Arta, Djibouti, Arta to support archery development in East Africa and Red Sea area.
Cuisine
 Djiboutian cuisine is a mixture of Somali cuisine, Somali,
Djiboutian cuisine is a mixture of Somali cuisine, Somali, Afar
Afar may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Afar language, an East Cushitic language
*Afar people, an ethnic group of Djibouti, Eritrea, and Ethiopia
Places Horn of Africa
*Afar Desert or Danakil Desert, a desert in Ethiopia
*Afar Region, a region ...
, Yemeni cuisine, Yemeni, and French cuisine, with some additional South Asian cuisine, South Asian (especially Indian cuisine, Indian) culinary influences. Local dishes are commonly prepared using a lot of Middle Eastern spices, ranging from saffron to cinnamon. Grilled Yemeni fish, opened in half and often cooked in tandoori style ovens, are a local delicacy. Spicy dishes come in many variations, from the traditional ''Fah-fah'' or "''Soupe Djiboutienne''" (spicy boiled beef soup), to the (spicy mixed vegetable stew). (pronounced "halwo") or halva is a popular confection eaten during festive occasions, such as Eid ul-Fitr, Eid celebrations or wedding receptions. Halva is made from sugar, corn starch, cardamom powder, nutmeg powder and ghee. Peanuts are sometimes added to enhance texture and flavor.Ali, Barlin (2007) ''Somali Cuisine''. AuthorHouse. p. 79. After meals, homes are traditionally perfumed using incense () or frankincense (), which is prepared inside an incense burner referred to as a ''dabqaad''.
See also
* Index of Djibouti-related articles * Outline of DjiboutiNotes
References
Online sources
*External links
; Government * * ; ProfileDjibouti
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Djibouti profile
from the BBC News. * * ; Others
The State of the World's Midwifery – Djibouti Country Profile
from UNFPA
Key Development Forecasts for Djibouti
from International Futures. * * {{Authority control Djibouti, 1977 establishments in Djibouti Arabic-speaking countries and territories Countries in Africa East African countries Former French colonies French-speaking countries and territories Gulf of Aden Horn African countries Least developed countries Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie Member states of the African Union Member states of the Arab League Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation Member states of the United Nations Republics Somali-speaking countries and territories States and territories established in 1977