Distributed Bragg Reflector on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
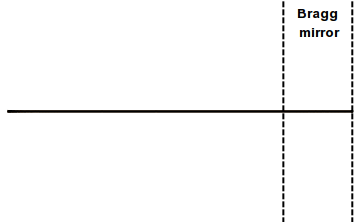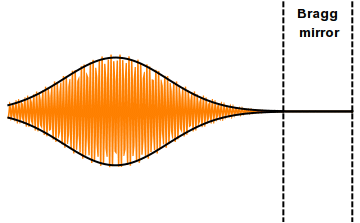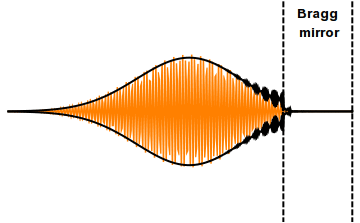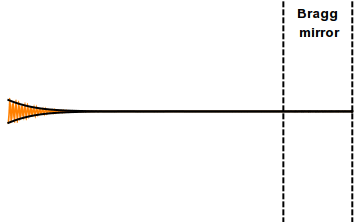 A distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) is a reflector used in waveguides, such as
A distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) is a reflector used in waveguides, such as
 This section discusses the interaction of transverse electric (TE)
and
This section discusses the interaction of transverse electric (TE)
and
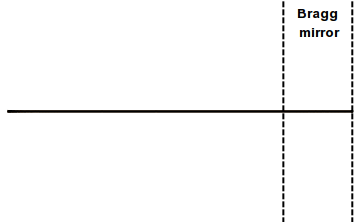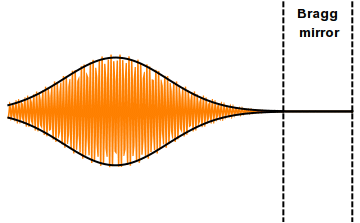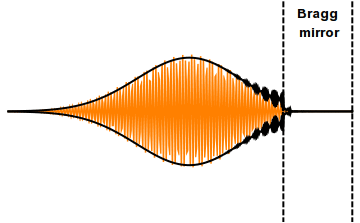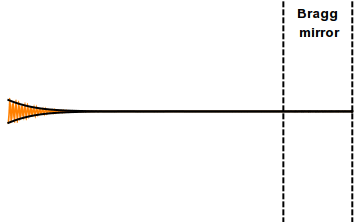 A distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) is a reflector used in waveguides, such as
A distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) is a reflector used in waveguides, such as optical fiber
An optical fiber, or optical fibre, is a flexible glass or plastic fiber that can transmit light from one end to the other. Such fibers find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at ...
s. It is a structure formed from multiple layers of alternating materials with different refractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refrac ...
, or by periodic variation of some characteristic (such as height) of a dielectric waveguide, resulting in periodic variation in the effective refractive index in the guide. Each layer boundary causes a partial reflection and refraction of an optical wave. For waves whose vacuum wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
is close to four times the optical thickness
In physics, optical depth or optical thickness is the natural logarithm of the ratio of incident to ''transmitted'' radiant power through a material.
Thus, the larger the optical depth, the smaller the amount of transmitted radiant power throu ...
of the layers, the interaction between these beams generates constructive interference
In physics, interference is a phenomenon in which two coherence (physics), coherent waves are combined by adding their intensities or displacements with due consideration for their phase (waves), phase difference. The resultant wave may have ...
, and the layers act as a high-quality reflector. The range of wavelengths that are reflected is called the photonic stopband
A stopband is a band of frequencies, between specified limits, through which a circuit, such as a filter or telephone circuit, does not allow signals to pass, or the attenuation is above the required stopband attenuation level. Depending on app ...
. Within this range of wavelengths, light is "forbidden" to propagate in the structure.
Reflectivity
The DBR'sreflectivity
The reflectance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in Reflection (physics), reflecting radiant energy. It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is reflected at the boundary. Reflectance is a component of the respon ...
, , for intensity
Intensity may refer to:
In colloquial use
* Strength (disambiguation)
*Amplitude
* Level (disambiguation)
* Magnitude (disambiguation)
In physical sciences
Physics
*Intensity (physics), power per unit area (W/m2)
*Field strength of electric, m ...
is approximately given by
:
where and are the respective refractive indices of the originating medium, the two alternating materials, and the terminating medium (i.e. backing or substrate); and is the number of repeated pairs of low/high refractive index material. This formula assumes the repeated pairs all have a quarter-wave thickness (that is , where is the refractive index of the layer, is the thickness of the layer, and is the wavelength of the light).
The frequency bandwidth
Bandwidth commonly refers to:
* Bandwidth (signal processing) or ''analog bandwidth'', ''frequency bandwidth'', or ''radio bandwidth'', a measure of the width of a frequency range
* Bandwidth (computing), the rate of data transfer, bit rate or thr ...
of the photonic stop-band can be calculated by
:
where is the central frequency of the band. This configuration gives the largest possible ratio that can be achieved with these two values of the refractive index.
Increasing the number of pairs in a DBR increases the mirror reflectivity and increasing the refractive index contrast between the materials in the Bragg pairs increases both the reflectivity and the bandwidth. A common choice of materials for the stack is titanium dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound derived from titanium with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or Colour Index Internationa ...
(''n'' ≈ 2.5) and silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant f ...
(''n'' ≈ 1.5). Substituting into the formula above gives a bandwidth of about 200 nm for 630 nm light.
Distributed Bragg reflectors are critical components in vertical cavity surface emitting laser
The vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL ) is a type of semiconductor laser diode with laser beam emission perpendicular from the top surface, contrary to conventional edge-emitting semiconductor lasers (also called ''in-plane'' lasers ...
s and other types of narrow-linewidth laser diode
file:Laser diode chip.jpg, The laser diode chip removed and placed on the eye of a needle for scale
A laser diode (LD, also injection laser diode or ILD or semiconductor laser or diode laser) is a semiconductor device similar to a light-emittin ...
s such as distributed feedback (DFB) lasers and distributed bragg reflector (DBR) lasers. They are also used to form the cavity resonator
A microwave cavity or radio frequency cavity (RF cavity) is a special type of resonator, consisting of a closed (or largely closed) metal structure that confines electromagnetic fields in the microwave or radio frequency, RF region of the spect ...
(or optical cavity
An optical cavity, resonating cavity or optical resonator is an arrangement of mirrors or other optical elements that confines light waves similarly to how a cavity resonator confines microwaves. Optical cavities are a major component of lasers, ...
) in fiber laser
A fiber laser (or fibre laser in Commonwealth English) is a laser in which the active gain medium is an optical fiber doped with rare-earth elements such as erbium, ytterbium, neodymium, dysprosium, praseodymium, thulium and holmium. They ar ...
s and free electron laser
A free-electron laser (FEL) is a fourth generation light source producing extremely brilliant and short pulses of radiation. An FEL functions much as a laser but employs relativistic electrons as a gain medium instead of using stimulated emission ...
s.
TE and TM mode reflectivity
 This section discusses the interaction of transverse electric (TE)
and
This section discusses the interaction of transverse electric (TE)
and transverse magnetic
A transverse mode of electromagnetic radiation is a particular electromagnetic field pattern of the radiation in the plane perpendicular (i.e., transverse) to the radiation's Wave propagation, propagation direction. Transverse modes occur in rad ...
(TM) polarized light with the DBR structure, over several
wavelengths and incidence angles. This reflectivity of the DBR structure (described below)
was calculated using the transfer-matrix method (TMM), where
the TE mode alone is highly reflected by this stack, while the TM modes are passed
through. This also shows the DBR acting as a polarizer
A polarizer or polariser is an optical filter that lets light waves of a specific polarization (waves), polarization pass through while attenuation, blocking light waves of other polarizations. It can filter a beam of light of undefined or mixed ...
.
For TE and TM incidence we have the reflection spectra of a DBR stack, corresponding
to a 6 layer stack of dielectric contrast of 11.5, between an air and dielectric layers.
The thicknesses of the air and dielectric layers are 0.8 and 0.2 of the period, respectively.
The wavelength in the figures below, corresponds to multiples of the cell period.
This DBR is also a simple example of a 1D photonic crystal
A photonic crystal is an optical nanostructure in which the refractive index changes periodically. This affects the propagation of light in the same way that the structure of Crystal structure, natural crystals gives rise to X-ray crystallograp ...
. It has a complete TE band gap, but only a pseudo TM band gap.
Bio-inspired Bragg reflectors
Bio-inspired Bragg reflectors are 1D photonic crystals inspired by nature. Reflection of light from such a nanostructured matter results instructural colouration
Structural coloration in animals, and a few plants, is the production of colour by microscopically structured surfaces fine enough to interfere with visible light instead of pigments, although some structural coloration occurs in combination wi ...
. When designed from mesoporous metal-oxides or polymers, these devices can be used as low-cost vapor/solvents sensors. For example, colour of this porous multi-layered structures will change when the matter filling up the pores is replaced by another, e.g. replacing air with water.
See also
* * * ** * * * * * * Photonic crystal sensorReferences
{{Reflist Optical devices Fiber optics