Distal Hereditary Motor Neuropathy Type V on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Distal hereditary motor neuropathy type V is a particular type of neuropathic disorder. In general,
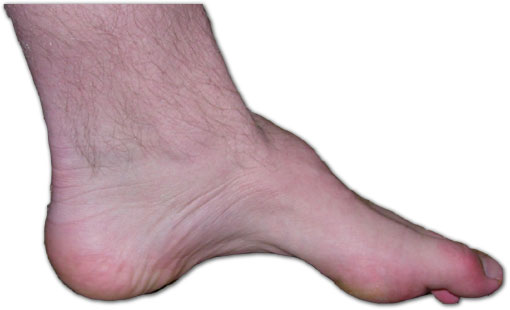 High arch of the foot (
High arch of the foot (
distal hereditary motor neuropathies Distal hereditary motor neuronopathies (distal HMN, dHMN), sometimes also called distal hereditary motor neuropathies, are a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of motor neuron diseases that result from genetic mutations in various genes ...
affect the axons of distal motor neurons and are characterized by progressive weakness and atrophy of muscles of the extremities. It is common for them to be called "spinal forms of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT)", because the diseases are closely related in symptoms and genetic cause. The diagnostic difference in these diseases is the presence of sensory loss in the extremities. There are seven classifications of dHMNs, each defined by patterns of inheritance, age of onset, severity, and muscle groups involved. Type V (sometimes notated as Type 5) is a disorder characterized by autosomal dominance
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ...
, weakness of the upper limbs that is progressive and symmetrical, and atrophy of the small muscles of the hands.
Signs and symptoms
Onset usually occurs within the first two decades of life, commonly in the teenage years or the twenties. Life expectancy is normal. High arch of the foot (
High arch of the foot (pes cavus
Pes cavus, also known as high arch, is a human foot type in which the sole of the foot is distinctly hollow when bearing weight. That is, there is a fixed plantar flexion of the foot. A high arch is the opposite of a flat foot and is somewhat ...
) is common. Patients also have trouble controlling their hands, due to muscle loss on the thumb side of the index finger and palm below the thumb. It is rare for a person with this disorder to lose the ability to walk, though changes in gait may occur later in life.
Frequency of this disorder is unknown.
Genetics
dHMN V has a pattern ofautosomal dominance
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ...
, meaning that only one copy of the gene is needed for the development of the disease. However, there is incomplete penetrance of this disorder, meaning that some individuals with the disease-causing mutations will not display any symptoms. Mutations on chromosome 7
Chromosome 7 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans, who normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 7 spans about 159 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 5 and 5.5 percent of the total D ...
have been linked to this disease. It is allelic (i.e., caused by mutations on the same gene) with Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease and with Silver’s Syndrome, a disorder also characterized by small muscle atrophy in the hands.
Another rare form of dHMN V is associated with a splicing mutation in REEP-1, a gene often associated with hereditary spastic neuroplegia.Diagnosis
In an individual with dHMN V, electromyography will show pure motor neuropathy, patterns of weakness without upper motor neuron damage, in the hands. Tendon reflexes will also appear normal. Clinical, electrophysiological, and pathological testing will show a lack of damage to sensory neurons, differentiating this disease from CMT.Treatment
Physical therapy is the predominant treatment of symptoms. Orthopedic shoes and foot surgery can be used to manage foot problems.References
External links
{{Medical resources , OMIM = 600794 Genetic diseases and disorders