dir (command) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 The command is available in the
The command is available in the




All Users :\ProgramData 12/07/2019 02:30 AM Default User :\Users\Default 12/07/2019 02:12 AM 174 desktop.ini
1 File(s) 174 bytes
2 Dir(s) 332,659,789,824 bytes free
dir , Microsoft DocsOpen source DIR implementation that comes with MS-DOS v2.0Dir command syntax and examples
{{Windows commands CP/M commands Internal DOS commands Microcomputer software Microsoft free software MSX-DOS commands OS/2 commands ReactOS commands Windows commands Windows administration
computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, e ...
, dir (directory) is a command
Command may refer to:
Computing
* Command (computing), a statement in a computer language
* COMMAND.COM, the default operating system shell and command-line interpreter for DOS
* Command key, a modifier key on Apple Macintosh computer keyboards
* ...
in various computer operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also in ...
s used for computer file
A computer file is a computer resource for recording data in a computer storage device, primarily identified by its file name. Just as words can be written to paper, so can data be written to a computer file. Files can be shared with and transfe ...
and directory
Directory may refer to:
* Directory (computing), or folder, a file system structure in which to store computer files
* Directory (OpenVMS command)
* Directory service, a software application for organizing information about a computer network's u ...
listing. It is one of the basic commands to help navigate the file system
In computing, file system or filesystem (often abbreviated to fs) is a method and data structure that the operating system uses to control how data is stored and retrieved. Without a file system, data placed in a storage medium would be one larg ...
. The command is usually implemented as an internal command in the command-line interpreter
A command-line interpreter or command-line processor uses a command-line interface (CLI) to receive commands from a user in the form of lines of text. This provides a means of setting parameters for the environment, invoking executables and pro ...
(shell
Shell may refer to:
Architecture and design
* Shell (structure), a thin structure
** Concrete shell, a thin shell of concrete, usually with no interior columns or exterior buttresses
** Thin-shell structure
Science Biology
* Seashell, a hard o ...
). On some systems, a more graphical representation of the directory structure can be displayed using the tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are ...
command.
Implementations
command-line interface
A command-line interpreter or command-line processor uses a command-line interface (CLI) to receive commands from a user in the form of lines of text. This provides a means of setting parameters for the environment, invoking executables and pro ...
(CLI) of the operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also in ...
s Digital Research
Digital Research, Inc. (DR or DRI) was a company created by Gary Kildall to market and develop his CP/M operating system and related 8-bit, 16-bit and 32-bit systems like MP/M, Concurrent DOS, FlexOS, Multiuser DOS, DOS Plus, DR DOS and ...
CP/M
CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/ 85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Inc. Initial ...
, MP/M
MP/M (Multi-Programming Monitor Control Program) is a discontinued multi-user version of the CP/M operating system, created by Digital Research developer Tom Rolander in 1979. It allowed multiple users to connect to a single computer, each us ...
, Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
ISIS-II, iRMX 86, Cromemco
Cromemco was a Mountain View, California microcomputer company known for its high-end Z80-based S-100 bus computers and peripherals in the early days of the personal computer revolution.
The company began as a partnership in 1974 between Harry ...
CDOS, MetaComCo TRIPOS
At the University of Cambridge, a Tripos (, plural 'Triposes') is any of the examinations that qualify an undergraduate for a bachelor's degree or the courses taken by a student to prepare for these. For example, an undergraduate studying mathe ...
, DOS
DOS is shorthand for the MS-DOS and IBM PC DOS family of operating systems.
DOS may also refer to:
Computing
* Data over signalling (DoS), multiplexing data onto a signalling channel
* Denial-of-service attack (DoS), an attack on a communicat ...
, IBM/Toshiba
, commonly known as Toshiba and stylized as TOSHIBA, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. Its diversified products and services include power, industrial and social infrastructure system ...
4690 OS, IBM OS/2
OS/2 (Operating System/2) is a series of computer operating systems, initially created by Microsoft and IBM under the leadership of IBM software designer Ed Iacobucci. As a result of a feud between the two companies over how to position OS/2 ...
, Microsoft Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for serv ...
, Singularity, Datalight
Datalight was a privately held software company specializing in power failsafe and high performance software for preserving data integrity in embedded systems. The company was founded in 1983 by Roy Sherrill, and is headquartered in Bothell, Was ...
ROM-DOS
Datalight was a privately held software company specializing in power failsafe and high performance software for preserving data integrity in embedded systems. The company was founded in 1983 by Roy Sherrill, and is headquartered in Bothell, Was ...
, ReactOS
ReactOS is a free and open-source operating system for amd64/i686 personal computers intended to be binary-compatible with computer programs and device drivers made for Windows Server 2003 and later versions of Windows. ReactOS has been noted a ...
, GNU
GNU () is an extensive collection of free software (383 packages as of January 2022), which can be used as an operating system or can be used in parts with other operating systems. The use of the completed GNU tools led to the family of operat ...
, AROS Aros may refer to:
*Aros (Middle-earth), a river in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium
* Aros, Mull, the location of Aros Castle, a ruined 13th-century castle on the Isle of Mull, Scotland
*AROS Research Operating System, a free software i ...
and in the DCL command-line interface used on DEC VMS, RT-11
RT-11 (Real-time 11) is a discontinued small, low-end, single-user real-time operating system for the full line of Digital Equipment Corporation PDP-11 16-bit computers. RT-11 was first implemented in 1970. It was widely used for real-time computin ...
and RSX-11
RSX-11 is a discontinued family of multi-user real-time operating systems for PDP-11 computers created by Digital Equipment Corporation. In widespread use through the late 1970s and early 1980s, RSX-11 was influential in the development of later ...
. It is also supplied with OS/8
OS/8 is the primary operating system used on the Digital Equipment Corporation's PDP-8 minicomputer.
PDP-8 operating systems which precede OS/8 include:
* R-L Monitor, also referred to as MS/8.
* P?S/8, requiring only 4K of memory.
* PDP-8 4K ...
as a CUSP (Commonly-Used System Program).
The dir command is supported by Tim Paterson
Tim Paterson (born 1 June 1956) is an American computer programmer, best known for creating 86-DOS, an operating system for the Intel 8086. This system emulated the application programming interface (API) of CP/M, which was created by Gary Kild ...
's SCP
SCP may refer to:
Organizations Political parties
* Soviet Communist Party, the leading political party in the former Soviet Union
* Syrian Communist Party
* Sudanese Communist Party
* Scottish Christian Party
Companies
* Seattle Computer Produ ...
86-DOS
86-DOS (known internally as QDOS, for Quick and Dirty Operating System) is a discontinued operating system developed and marketed by Seattle Computer Products (SCP) for its Intel 8086-based computer kit.
86-DOS shared a few of its commands wit ...
. On MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few ope ...
, the command is available in versions 1 and later. It is also available in the open source
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open-source model is a decentralized sof ...
MS-DOS emulator
In computing, an emulator is Computer hardware, hardware or software that enables one computer system (called the ''host'') to behave like another computer system (called the ''guest''). An emulator typically enables the host system to run so ...
DOSBox
DOSBox is a free and open-source emulator which runs software for MS-DOS compatible disk operating systems—primarily video games. It was first released in 2002, when DOS technology was becoming obsolete. Its adoption for running DOS games i ...
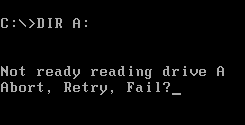
. MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few ope ...
prompts " Abort, Retry, Fail?" after being commanded to list a directory
Directory may refer to:
* Directory (computing), or folder, a file system structure in which to store computer files
* Directory (OpenVMS command)
* Directory service, a software application for organizing information about a computer network's u ...
with no diskette
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, or a diskette) is an obsolescent type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined w ...
in the drive.
The numerical computing environments MATLAB
MATLAB (an abbreviation of "MATrix LABoratory") is a proprietary multi-paradigm programming language and numeric computing environment developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation ...
and GNU Octave
GNU Octave is a high-level programming language primarily intended for scientific computing and numerical computation. Octave helps in solving linear and nonlinear problems numerically, and for performing other numerical experiments using a langu ...
include a dir
function with similar functionality.
Examples



DOS, Windows, ReactOS
List all files and directories in the currentworking directory
In computing, the working directory of a process is a directory of a hierarchical file system, if any, dynamically associated with each process. It is sometimes called the current working directory (CWD), e.g. the BSD getcwd function, or just cur ...
.
dir
List any text file
A text file (sometimes spelled textfile; an old alternative name is flatfile) is a kind of computer file that is structured as a sequence of lines of electronic text. A text file exists stored as data within a computer file system. In operating ...
s and batch file
Batch may refer to:
Food and drink
* Batch (alcohol), an alcoholic fruit beverage
* Batch loaf, a type of bread popular in Ireland
* A dialect term for a bread roll used in North Warwickshire, Nuneaton and Coventry, as well as on the Wirral ...
s (filename extension
A filename extension, file name extension or file extension is a suffix to the name of a computer file (e.g., .txt, .docx, .md). The extension indicates a characteristic of the file contents or its intended use. A filename extension is typically d ...
".txt" or ".bat").
dir *.txt *.bat
Recursively
Recursion (adjective: ''recursive'') occurs when a thing is defined in terms of itself or of its type. Recursion is used in a variety of disciplines ranging from linguistics to logic. The most common application of recursion is in mathematics ...
list all files and directories in the specified directory and any subdirectories, in wide format, pausing after each screen of output. The directory name is enclosed in double-quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted is as two separate command-line option
A command-line interpreter or command-line processor uses a command-line interface (CLI) to receive commands from a user in the form of lines of text. This provides a means of setting parameters for the environment, invoking executables and pro ...
s because it contains a whitespace character
In computer programming, whitespace is any character or series of characters that represent horizontal or vertical space in typography. When rendered, a whitespace character does not correspond to a visible mark, but typically does occupy an area ...
.
dir /s /w /p "C:\My Documents"
List any NTFS junction point
The NTFS file system defines various ways to redirect files and folders, e.g., to make a file point to another file or its contents without making a copy of it. The object being pointed to is called the target. Such file is called a hard or symbo ...
s:
C:\Users>dir /ash
Volume in drive C is OS.
Volume Serial Number is xxxx-xxxx
Directory of C:\Users
12/07/2019 02:30 AM Unices
dir is not a Unix
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and ot ...
command; Unix has the analogous ls command instead. The GNU operating system
GNU () is an extensive collection of free software (383 packages as of January 2022), which can be used as an operating system or can be used in parts with other operating systems. The use of the completed GNU tools led to the family of operat ...
, however, has a dir command that "is equivalent to ls -C -b; that is, by default files are listed in columns, sorted vertically, and special characters are represented by backslash escape sequences". /www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/manual/html_node/dir-invocation.html dir invocation(GNU coreutils) at www.gnu.org Actually, for compatibility reasons, ls produces device-dependent output. The dir instruction, unlike ls -Cb, produces device-independent output.
See also
*Directory (OpenVMS command)
In computer software, specifically the DCL command-line interface of the OpenVMS operating system, the DIRECTORY command (often abbreviated as DIR) is used to list the files inside a directory. It is analogous to the DOS dir and Unix ls command ...
*List of DOS commands
This article presents a list of commands used by DOS operating systems, especially as used on x86-based IBM PC compatibles (PCs). Other DOS operating systems are not part of the scope of this list.
In DOS, many standard system commands were pro ...
* ls (corresponding command for *nix systems)
References
Further reading
* * *External links
dir , Microsoft Docs
{{Windows commands CP/M commands Internal DOS commands Microcomputer software Microsoft free software MSX-DOS commands OS/2 commands ReactOS commands Windows commands Windows administration