Diogo De Azambuja on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Diogo de Azambuja or Diego de Azambuja (1432–1518) was a Portuguese noble and explorer.
Diogo de Azambuja or Diego de Azambuja (1432–1518) was a Portuguese noble and explorer.
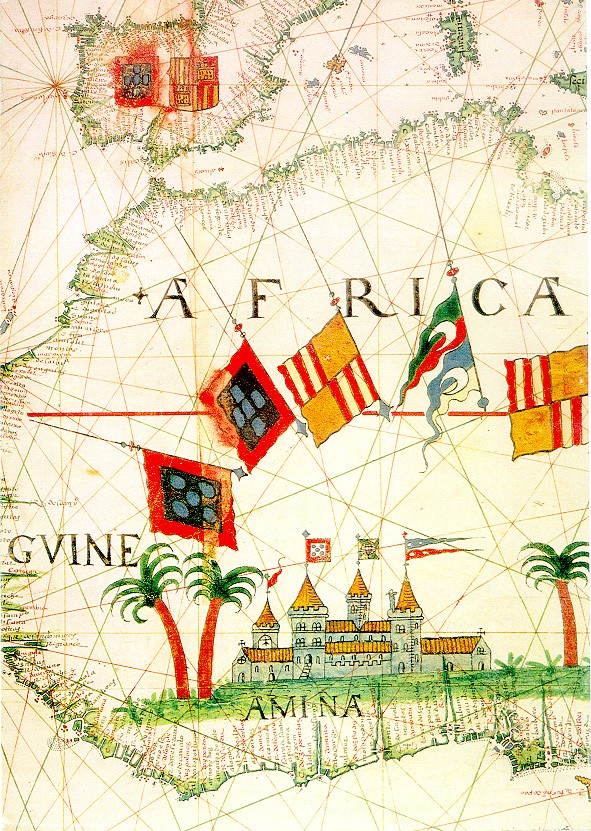
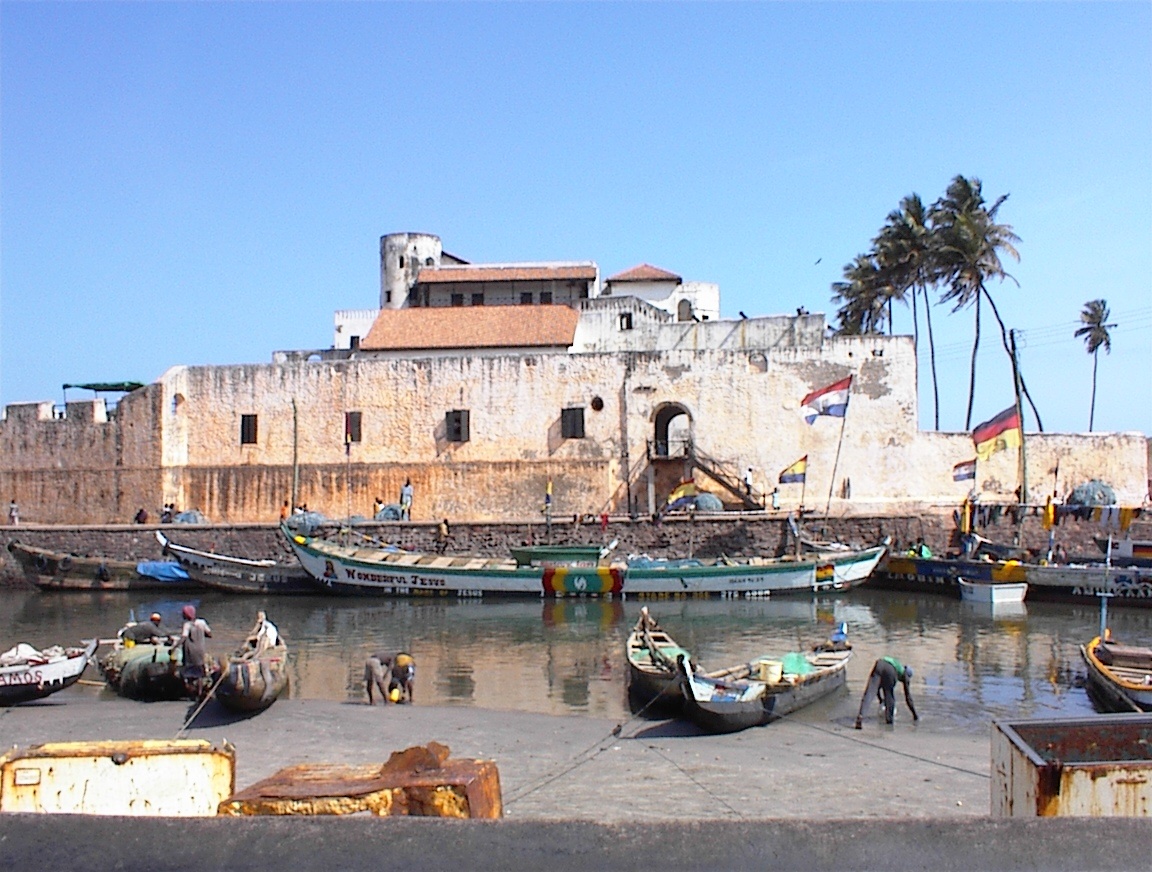 In 1481, Diogo was appointed by John II as captain of a fleet consisting of nine caravels and two ships with 600 soldiers and 100 masons and carpenters. They were sent, along with the necessary stone and other materials, to construct a fortress called São Jorge da Mina at the Gulf of Guinea in the Portuguese Gold Coast colony. This became the best-known exploit of his long life. They chose a favourable defensive position for the fort, and construction was practically complete after only 20 days, in spite of resistance from the native population.
With the fortress finished, contacts were established with the local population to establish trade. Diogo de Azambuja sent the fleet back to
In 1481, Diogo was appointed by John II as captain of a fleet consisting of nine caravels and two ships with 600 soldiers and 100 masons and carpenters. They were sent, along with the necessary stone and other materials, to construct a fortress called São Jorge da Mina at the Gulf of Guinea in the Portuguese Gold Coast colony. This became the best-known exploit of his long life. They chose a favourable defensive position for the fort, and construction was practically complete after only 20 days, in spite of resistance from the native population.
With the fortress finished, contacts were established with the local population to establish trade. Diogo de Azambuja sent the fleet back to
 Diogo de Azambuja or Diego de Azambuja (1432–1518) was a Portuguese noble and explorer.
Diogo de Azambuja or Diego de Azambuja (1432–1518) was a Portuguese noble and explorer.
Soldier
He was born at Montemor-o-Velho, and became a knight of theOrder of Aviz
The Military Order of Saint Benedict of Aviz ( pt, Ordem Militar de São Bento de Avis, ), previously to 1910 ''Royal Military Order of Saint Benedict of Aviz'' ( pt, Real Ordem Militar de São Bento de Avis), previously to 1789 ''Knights'' (of ...
in the service of the Infante Dom Pedro, son of the Regent Infante Peter, Duke of Coimbra. After Peter's defeat and death in the battle of Alfarrobeira (1449), he accompanied his master into exile. In 1458, he fought on the side of Afonso V in the conquest of Alcácer-Ceguer
Ksar es-Seghir ( ar, القصر الصغير, ⵇⵙⴰⵔ ⵙⵖⵉⵔ, ''al-Qasr as-Seghir''), also known by numerous other spellings and names, is a small town on the Mediterranean coast in the Jebala region of northwest Morocco, between Tan ...
in Morocco. He received several honours and became a counselor of the king. During the War of the Castilian Succession, he participated in the recapture of the town of Alegrete from the Castilians. He was injured in the leg during this engagement.
Portuguese Gold Coast
 In 1481, Diogo was appointed by John II as captain of a fleet consisting of nine caravels and two ships with 600 soldiers and 100 masons and carpenters. They were sent, along with the necessary stone and other materials, to construct a fortress called São Jorge da Mina at the Gulf of Guinea in the Portuguese Gold Coast colony. This became the best-known exploit of his long life. They chose a favourable defensive position for the fort, and construction was practically complete after only 20 days, in spite of resistance from the native population.
With the fortress finished, contacts were established with the local population to establish trade. Diogo de Azambuja sent the fleet back to
In 1481, Diogo was appointed by John II as captain of a fleet consisting of nine caravels and two ships with 600 soldiers and 100 masons and carpenters. They were sent, along with the necessary stone and other materials, to construct a fortress called São Jorge da Mina at the Gulf of Guinea in the Portuguese Gold Coast colony. This became the best-known exploit of his long life. They chose a favourable defensive position for the fort, and construction was practically complete after only 20 days, in spite of resistance from the native population.
With the fortress finished, contacts were established with the local population to establish trade. Diogo de Azambuja sent the fleet back to Lisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Grande Lisboa, Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administr ...
with word that the mission has been successfully accomplished, and he remained behind as captain of the fortress with a force of 60 soldiers. He held this post until 1484. The fortress is now known as "Elmina Castle", or the "Elmina Slave Castle".
Courtier
Diogo was rewarded by the king with the post of alcaide-mor of Monsaraz, and was also named to the Privy Council. Diogo de Azambuja remained attached to the Court and the king's service for many years, in spite of his advancing age and disabled leg. He was already over the age of 70 in 1506 when Manuel I placed him in charge of building a fortress called Castelo Real atEssaouira
Essaouira ( ; ar, الصويرة, aṣ-Ṣawīra; shi, ⵜⴰⵚⵚⵓⵔⵜ, Taṣṣort, formerly ''Amegdul''), known until the 1960s as Mogador, is a port city in the western Moroccan region of Marakesh-Safi, on the Atlantic coast. It ha ...
, near Safi, in the south of Morocco, to protect Portuguese interests in the area. Diogo of Azambuja not only carried out the mission, he also took the city of Safi, where he remained as captain until 1509, at the age of 77 years. At that time he finally returned to Portugal, where he died in 1518.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Azambuja, Diogo De Captain-majors of Portuguese Gold Coast Portuguese explorers 1432 births 1518 deaths People from Montemor-o-Velho Portuguese nobility 15th century in Ghana 15th-century Portuguese people 16th-century Portuguese people 15th-century explorers of Africa 16th-century explorers