dilaceration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dilaceration is a developmental disturbance in shape of teeth. It refers to an angulation, or a sharp bend or curve, in the root or crown of a formed
Standerwick RG. A possible etiology for the dilaceration and flexion of permanent tooth roots relative to bone remodeling gradients in alveolar bone. Dent Hypotheses erial online2014 ited 2014 Mar 35:7-10. Available from: http://www.dentalhypotheses.com/text.asp?2014/5/1/7/128105 The result is that the position of the
 Pressure or pain in the jaw area can be associated with dilaceration. Checking in with a general dentist and an
Pressure or pain in the jaw area can be associated with dilaceration. Checking in with a general dentist and an
 The etiology of dilaceration is not very commonly known. However, it is thought to be related to:
* Traumatic injury that may have taken place to the deciduous teeth, also known as baby teeth.
*
The etiology of dilaceration is not very commonly known. However, it is thought to be related to:
* Traumatic injury that may have taken place to the deciduous teeth, also known as baby teeth.
*
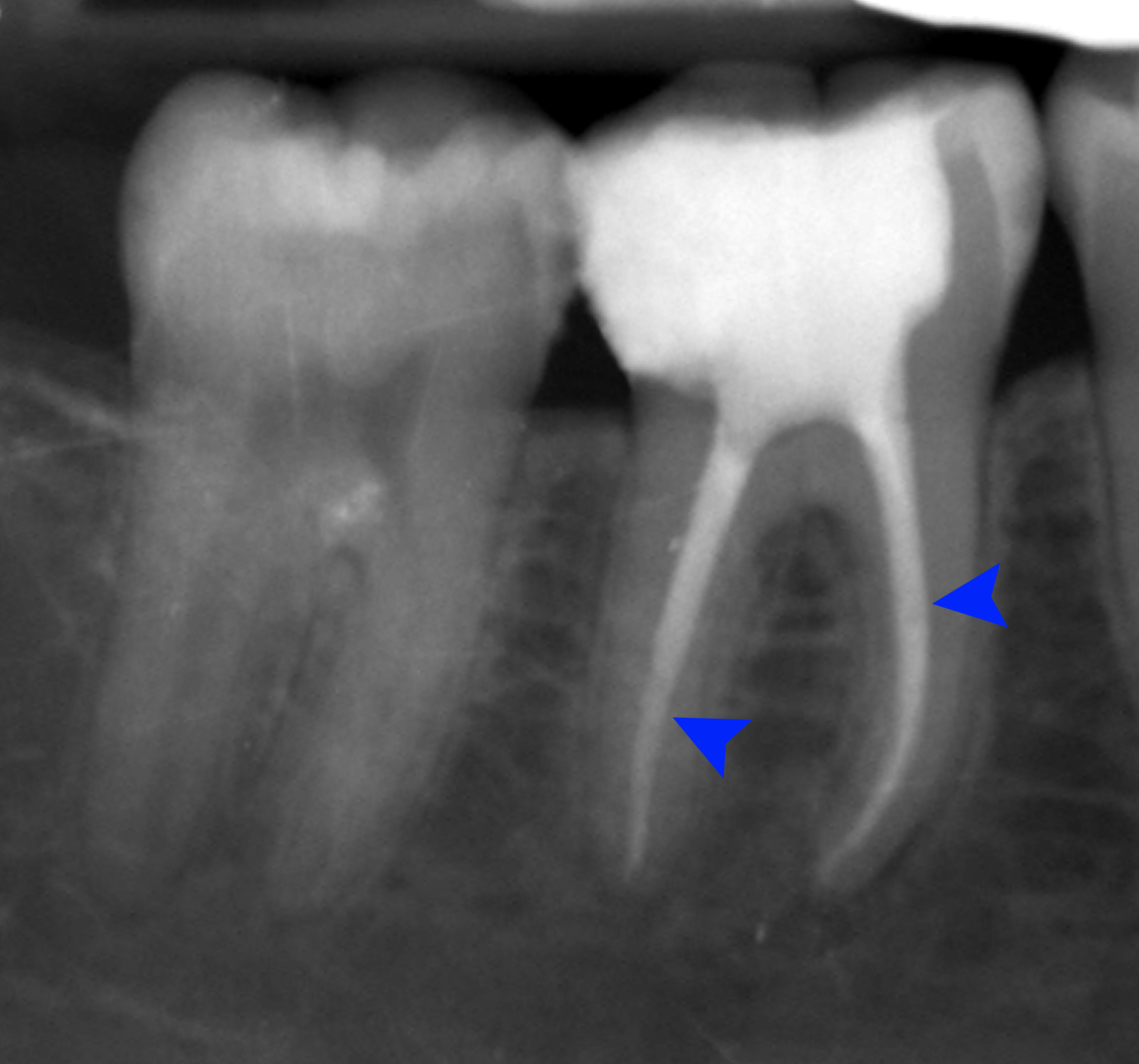 There are currently no preventative measures to be taken for dilaceration as the etiology is not well known. However, there are some treatment options that may serve to be of use. A surgical method which involves the exposing the impacted tooth to meet with normal occlusion with the help of orthodontic traction. Although this surgical method has proven to be of use in the past, it may not be the case for every patient with dilacerated teeth. Thus the degree of dilaceration is dependent on what kind of treatment can take place. In young children many cases of dilaceration occur due to some kind of trauma to the tooth, commonly causing dislocation of the tooth affecting its direction and growth. Once a trauma has occurred dilaceration can be prevented by yearly visits to the dentist and maintaining radiographic images to note any changes that may occur. If changes do occur, treatment can be done through orthodontic treatment or the tooth may be completely extracted by a dentist to prevent impaction on permanent teeth. Prevention for young children also includes avoiding injury to the mouth, especially during sporting activities, proper headgear and protective measures should be taken prior to engaging in recreational activities for the overall safety of the child. Patients with supernumerary teeth may also be candidates for teeth extraction followed by orthodontic treatment to prevent dilaceration. In some cases and
There are currently no preventative measures to be taken for dilaceration as the etiology is not well known. However, there are some treatment options that may serve to be of use. A surgical method which involves the exposing the impacted tooth to meet with normal occlusion with the help of orthodontic traction. Although this surgical method has proven to be of use in the past, it may not be the case for every patient with dilacerated teeth. Thus the degree of dilaceration is dependent on what kind of treatment can take place. In young children many cases of dilaceration occur due to some kind of trauma to the tooth, commonly causing dislocation of the tooth affecting its direction and growth. Once a trauma has occurred dilaceration can be prevented by yearly visits to the dentist and maintaining radiographic images to note any changes that may occur. If changes do occur, treatment can be done through orthodontic treatment or the tooth may be completely extracted by a dentist to prevent impaction on permanent teeth. Prevention for young children also includes avoiding injury to the mouth, especially during sporting activities, proper headgear and protective measures should be taken prior to engaging in recreational activities for the overall safety of the child. Patients with supernumerary teeth may also be candidates for teeth extraction followed by orthodontic treatment to prevent dilaceration. In some cases and
tooth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tear ...
. This disturbance is more likely to affect the maxillary incisors and occurs in permanent dentition. Although this may seem more of an aesthetics issue, an impacted maxillary incisor will cause issues related to occlusion
Occlusion may refer to:
Health and fitness
* Occlusion (dentistry), the manner in which the upper and lower teeth come together when the mouth is closed
* Occlusion miliaria, a skin condition
* Occlusive dressing, an air- and water-tight trauma ...
, phonetics
Phonetics is a branch of linguistics that studies how humans produce and perceive sounds, or in the case of sign languages, the equivalent aspects of sign. Linguists who specialize in studying the physical properties of speech are phoneticians. ...
, mastication
Chewing or mastication is the process by which food is crushed and ground by teeth. It is the first step of digestion, and it increases the surface area of foods to allow a more efficient break down by enzymes. During the mastication process, th ...
, and psychology on young patients.
Description
The condition is thought to be due totrauma
Trauma most often refers to:
* Major trauma, in physical medicine, severe physical injury caused by an external source
* Psychological trauma, a type of damage to the psyche that occurs as a result of a severely distressing event
*Traumatic i ...
or possibly a delay in tooth eruption relative to bone remodeling gradients during the period in which tooth is forming.Standerwick RG. A possible etiology for the dilaceration and flexion of permanent tooth roots relative to bone remodeling gradients in alveolar bone. Dent Hypotheses erial online2014 ited 2014 Mar 35:7-10. Available from: http://www.dentalhypotheses.com/text.asp?2014/5/1/7/128105 The result is that the position of the
calcified
Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue,Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. ''Nature Mat ...
portion of the tooth is changed and the remainder of the tooth is formed at an angle
In Euclidean geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two Ray (geometry), rays, called the ''Side (plane geometry), sides'' of the angle, sharing a common endpoint, called the ''vertex (geometry), vertex'' of the angle.
Angles formed by two ...
.
The curve or bend may occur anywhere along the length of the tooth, sometimes at the cervical portion, at other times midway along the root or even just at the apex of the root, depending upon the amount of root formed when the injury occurred.
Such an injury to a permanent tooth, resulting in dilaceration, often follows traumatic injury to the deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, aft ...
predecessor in which that tooth is driven apically into the jaw.
Signs and Symptoms
 Pressure or pain in the jaw area can be associated with dilaceration. Checking in with a general dentist and an
Pressure or pain in the jaw area can be associated with dilaceration. Checking in with a general dentist and an endodontist
Endodontics (from the Greek roots ''endo-'' "inside" and ''odont-'' "tooth") is the dental specialty concerned with the study and treatment of the dental pulp.
Overview
Endodontics encompasses the study (practice) of the basic and clinical ...
should be done if a patient feels these symptoms. Signs in radiographic imaging will indicate an bend in the tooth's root as opposed to a straight growth. Dilaceration of the crown
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, partic ...
, the top part of the teeth that we see when we smile, can be visually seen for diagnosis. Crown dilaceration will present itself as a tooth that is angled to face outward or inward. It will be a non axial displacement and more of a longitudinal displacement.
Cause
 The etiology of dilaceration is not very commonly known. However, it is thought to be related to:
* Traumatic injury that may have taken place to the deciduous teeth, also known as baby teeth.
*
The etiology of dilaceration is not very commonly known. However, it is thought to be related to:
* Traumatic injury that may have taken place to the deciduous teeth, also known as baby teeth.
* Idiopathic
An idiopathic disease is any disease with an unknown cause or mechanism of apparent wikt:spontaneous, spontaneous origin. From Ancient Greek, Greek ἴδιος ''idios'' "one's own" and πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", ''idiopathy'' means approxi ...
developmental disturbance, meaning it is unknown
* An ankylosed deciduous tooth, meaning a baby tooth that is permanently attached to the jaw bone
* And the presence of supernumerary teeth, meaning an individual that is born with extra teeth
* Smith-Magenis syndrome
* Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome
* Cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and cell division, division compared with the nearby Biological tissue, tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of Cell (biology), cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which ...
s
* Tumors
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
Mechanism/ Pathophysiology
During the developmental stages, the permanent tooth germ, specifically of the maxillary incisor lies superior to the apex of the primary incisor. If there is damage to the primary incisor, this will cause an impact on the permanent incisor as well as there is only about a 3mm space of thickness between the primary and permanent teeth. In the human mouth, once the permanent teeth begin to develop, they remain underneath the primary teeth. Once they are ready to erupt they push upward eventually causing the primary teeth to fall out. There is essentially a small space between the permanent andprimary teeth
Deciduous teeth or primary teeth, also informally known as baby teeth, milk teeth, or temporary teeth,Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy, Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach, Elsevier, 2011, page 255 are the first set of teeth in the ...
, roughly less than 3mm of spacing. If a young child is to experience trauma to the mouth, this can cause developmental disorders to the permanent tooth that is still developing and lying direction underneath it. The impact from the primary tooth will be transferred to the permanent tooth that may have its roots formed, thus causing a bend or curvature of the permanent tooth root. It is noted that rather than the force of the impact, the direction in which the impact occurs has a more significant effect on dilaceration formation. Cysts or tumors
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
can cause dilaceration as well. As a tumor or cyst forms it may cause impaction on the growth and development of the permanent teeth as well. This may cause crown or root dilaceration as the tooth tries to grow around the cysts or tumor causing dramatic angulation. Similarly, patients present with supernumerary teeth, may have impacted the growth of underlying permanent teeth causing the abnormal root curvature growth. An ankylosed deciduous tooth will not allow for proper growth the permanent tooth. Thus, the tooth may look for another path to erupt. This may cause dilaceration of root or may potentially impact neighboring teeth causing dilaceration to those teeth.
Diagnosis
Dilaceration can be diagnosed with a simple radiograph of the affected teeth. However, if the bends are more lingual or facially present, more advance imaging techniques may be necessary. In some cases a cone-bean CT scan may be useful to create a three dimensional view.Prevention/ Treatment
 There are currently no preventative measures to be taken for dilaceration as the etiology is not well known. However, there are some treatment options that may serve to be of use. A surgical method which involves the exposing the impacted tooth to meet with normal occlusion with the help of orthodontic traction. Although this surgical method has proven to be of use in the past, it may not be the case for every patient with dilacerated teeth. Thus the degree of dilaceration is dependent on what kind of treatment can take place. In young children many cases of dilaceration occur due to some kind of trauma to the tooth, commonly causing dislocation of the tooth affecting its direction and growth. Once a trauma has occurred dilaceration can be prevented by yearly visits to the dentist and maintaining radiographic images to note any changes that may occur. If changes do occur, treatment can be done through orthodontic treatment or the tooth may be completely extracted by a dentist to prevent impaction on permanent teeth. Prevention for young children also includes avoiding injury to the mouth, especially during sporting activities, proper headgear and protective measures should be taken prior to engaging in recreational activities for the overall safety of the child. Patients with supernumerary teeth may also be candidates for teeth extraction followed by orthodontic treatment to prevent dilaceration. In some cases and
There are currently no preventative measures to be taken for dilaceration as the etiology is not well known. However, there are some treatment options that may serve to be of use. A surgical method which involves the exposing the impacted tooth to meet with normal occlusion with the help of orthodontic traction. Although this surgical method has proven to be of use in the past, it may not be the case for every patient with dilacerated teeth. Thus the degree of dilaceration is dependent on what kind of treatment can take place. In young children many cases of dilaceration occur due to some kind of trauma to the tooth, commonly causing dislocation of the tooth affecting its direction and growth. Once a trauma has occurred dilaceration can be prevented by yearly visits to the dentist and maintaining radiographic images to note any changes that may occur. If changes do occur, treatment can be done through orthodontic treatment or the tooth may be completely extracted by a dentist to prevent impaction on permanent teeth. Prevention for young children also includes avoiding injury to the mouth, especially during sporting activities, proper headgear and protective measures should be taken prior to engaging in recreational activities for the overall safety of the child. Patients with supernumerary teeth may also be candidates for teeth extraction followed by orthodontic treatment to prevent dilaceration. In some cases and Endodontist
Endodontics (from the Greek roots ''endo-'' "inside" and ''odont-'' "tooth") is the dental specialty concerned with the study and treatment of the dental pulp.
Overview
Endodontics encompasses the study (practice) of the basic and clinical ...
, a tooth root specialist, may be involved in treatment of dilaceration. Using radiographs to determine the extent of dilaceration, the endodontist may recommend a root canal treatment
Root canal treatment (also known as endodontic therapy, endodontic treatment, or root canal therapy) is a treatment sequence for the infected pulp of a tooth which is intended to result in the elimination of infection and the protection of ...
, which is essentially cleaning out the nerve of the tooth and placing material inside the tooth to help maintain its structure. Since at this point the tooth with no nerve is essentially dead, further treatment from a general dentist to crown the tooth will be necessary. Crowning the tooth will prevent breakage of the tooth while still allowing functionality of the tooth. In order to achieve the best possible results, treatment should begin as soon as possible.
Prognosis
The prognosis will vary from each patients case to case. In less severe cases, patients may face minor issues with aesthetics which orthodontic treatment can resolve. In more severe cases which are not as easily treatable patients may face more severe issues with occlusions and phonetics. In some cases young children may face psychological issues. There is no death sentence associated with dilaceration. However, patients may face some difficulties as time progresses and if they are left untreated. Other teeth may become impacted and cause pain and soreness.Epidemiology
Most commonly affects patients in their permanentdentition
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiolo ...
. It may also appear in primary teeth however, its incidence rate is significantly lower. Some studies indicate that dilaceration is not more common in any gender however, other studies indicate that incidence rate is more common in females than males with a ratio of 1:6. There are reports of a 0.53% for this to occur on the two front teeth of the upper jaw. In a study conducted on the adult population in Croatia, the most common teeth to experience dilaceration were the lower jaw's 3rd molars with a whopping 24.1%. Next was the upper jaw's first, second and third molars at 15.3%,11.4% and 8.1% incidence rate respectively.
Research Directions
Although this disease is rare there has been a significant amount of research done on this. * A 2016 study was done to find reasoning behind dilacerated crowns and treatment options for different types of crown dilacerations. Researchers found that dental trauma should not be taken lightly as it is one of the most common caused for dilaceration. Researchers also concluded that if trauma has occurred to primary teeth, it should be followed up with the dentist on a regular basis due to the future complications that may arise. The main focus of treatment in this research was root canal therapy over surgical methods as it was less invasive and more conservative. * A research review published in 2016 indicated that a multidisciplinary approach was more favorable in diagnosing and treatment of dilaceration. Researchers presented that although dilaceration of permanent teeth is rare, it can pose many issues. Therefore, rather than just simply having clinical follow ups and standard imaging conducted, to reach a proper diagnosis imaging tools such as a CBCT should be used. Additionally, treatment requires patient compliance as well as early treatment wherever possible. Treatment options may include exposure of the tooth followed by orthodontic treatment to bring the tooth to a corrected positioning. * A 2014 case report indicated a young patient approached the pediatric dental department complaining of upper teeth that had still not come in yet. It was found that the patient had experienced a trauma, thus had completed extractions 6 years prior. Panoramic radiographs showed the tooth was impacted and potentially had a dilacerated root. A cone beam CT scan was done to gain a better idea of the relationship of the teeth. Treatment consisted of extractions followed by orthodontic bonding and extrusion of the tooth. This allowed for other teeth to come into better places as well. *A research study conducted from 2005-2010 was conducted in South Iran to check for the presence of dilacerations. Records were compiled from the endodontic and periodontal departments of Shiraz University of Medical Science's dental school. All patients were Caucasian ranging from 12–75 years if age. Researchers found dilaceration in 0.3% of teeth among 7.2% of patients. Distribution was equal between the lower and upper jaw. Researchers concluded that root dilacerations mainly occur in posterior teeth.See also
*Tooth enamel
Tooth enamel is one of the four major Tissue (biology), tissues that make up the tooth in humans and many other animals, including some species of fish. It makes up the normally visible part of the tooth, covering the Crown (tooth), crown. The ...
*Turner's hypoplasia
Enamel hypoplasia is a defect of the teeth in which the enamel is deficient in quantity, caused by defective enamel matrix formation during enamel development, as a result of inherited and acquired systemic condition(s). It can be identified as m ...
References
External links
{{Tooth disease Developmental tooth disorders