Dielectric Mirrors on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
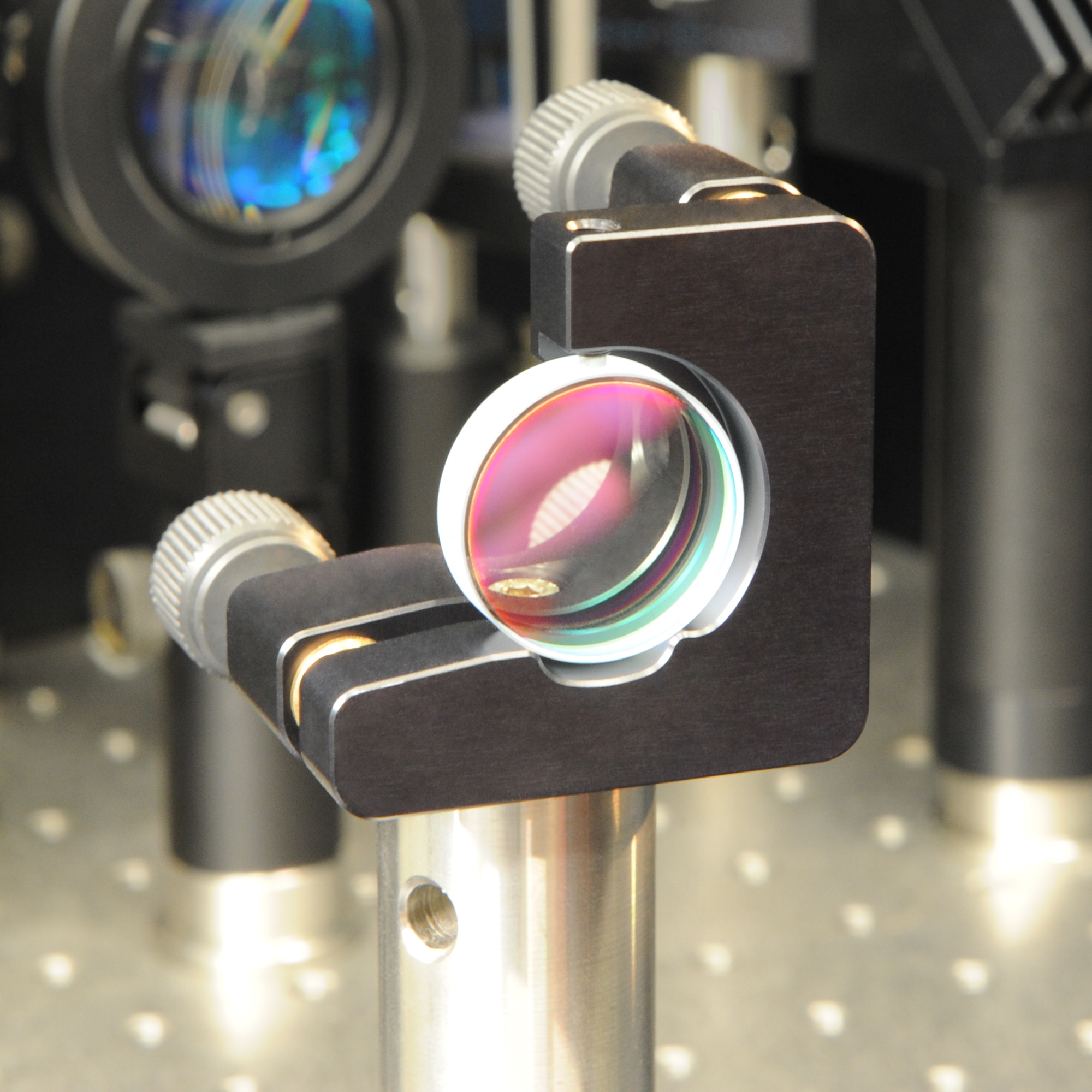 A dielectric mirror, also known as a Bragg mirror, is a type of
A dielectric mirror, also known as a Bragg mirror, is a type of
 Other designs have a more complicated structure generally produced by
Other designs have a more complicated structure generally produced by
Fast code for computation of dielectric mirror reflectivity and dispersion
Optical filters Mirrors ja:ダイクロイックミラー
 A dielectric mirror, also known as a Bragg mirror, is a type of
A dielectric mirror, also known as a Bragg mirror, is a type of mirror
A mirror or looking glass is an object that Reflection (physics), reflects an image. Light that bounces off a mirror will show an image of whatever is in front of it, when focused through the lens of the eye or a camera. Mirrors reverse the ...
composed of multiple thin layers of dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the mate ...
material, typically deposited on a substrate of glass
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of ...
or some other optical material. By careful choice of the type and thickness of the dielectric layers, one can design an optical coating
An optical coating is one or more thin layers of material deposited on an optical component such as a lens, prism or mirror, which alters the way in which the optic reflects and transmits light. These coatings have become a key technology in th ...
with specified reflectivity at different wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tro ...
s of light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 tera ...
. Dielectric mirrors are also used to produce ultra-high reflectivity mirrors: values of 99.999% or better over a narrow range of wavelengths can be produced using special techniques. Alternatively, they can be made to reflect a broad spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors i ...
of light, such as the entire visible range or the spectrum of the Ti-sapphire laser. Mirrors of this type are very common in optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviole ...
experiments, due to improved techniques that allow inexpensive manufacture of high-quality mirrors. Examples of their applications include laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The fir ...
cavity
Cavity may refer to:
Biology and healthcare
*Body cavity, a fluid-filled space in many animals where organs typically develop
**Gastrovascular cavity, the primary organ of digestion and circulation in cnidarians and flatworms
*Dental cavity or too ...
end mirrors, hot
Hot or the acronym HOT may refer to:
Food and drink
*Pungency, in food, a spicy or hot quality
*Hot, a wine tasting descriptor
Places
* Hot district, a district of Chiang Mai province, Thailand
**Hot subdistrict, a sub-district of Hot Distric ...
and cold mirrors, thin-film beamsplitters, high damage threshold mirrors, and the coatings on modern mirrorshades and some binoculars roof prism systems.
Mechanism
image:Dielectric mirror diagram.svg, Diagram of a dielectric mirror. Thin layers with a high refractive index ''n''1 are interleaved with thicker layers with a lower refractive index ''n''2. The path lengths ''l''A and ''l''B differ by exactly one wavelength, which leads to constructive interference. Dielectric mirrors function based on the Interference (wave propagation), interference of light reflected from the different layers of dielectric stack. This is the same principle used in multi-layer anti-reflection coatings, which are dielectric stacks which have been designed to minimize rather than maximize reflectivity. Simple dielectric mirrors function like one-dimensional photonic crystals, consisting of a stack of layers with a highrefractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or ...
interleaved with layers of a low refractive index (see diagram). The thicknesses of the layers are chosen such that the path-length differences for reflections from different high-index layers are integer multiples of the wavelength for which the mirror is designed. The reflections from the low-index layers have exactly half a wavelength in path length difference, but there is a 180-degree difference in phase shift at a low-to-high index boundary, compared to a high-to-low index boundary, which means that these reflections are also in phase. In the case of a mirror at normal incidence, the layers have a thickness of a quarter wavelength.
 Other designs have a more complicated structure generally produced by
Other designs have a more complicated structure generally produced by numerical optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criterion, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfi ...
. In the latter case, the phase dispersion of the reflected light can also be controlled (see Chirped mirror). In the design of dielectric mirrors, an optical transfer-matrix method can be used. A well-designed multilayer dielectric coating can provide a reflectivity
The reflectance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in reflecting radiant energy. It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is reflected at the boundary. Reflectance is a component of the response of the electronic ...
of over 99% across the visible light spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called ''visible light'' or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wav ...
.
Dielectric mirrors exhibit retardance as a function of angle of incidence and mirror design.
Manufacturing
The manufacturing techniques for dielectric mirrors are based on thin-film deposition methods. Common techniques are physical vapor deposition (which includesevaporative deposition
Evaporation is a common method of thin-film deposition. The source material is evaporated in a vacuum. The vacuum allows vapor particles to travel directly to the target object (substrate), where they condense back to a solid state. Evaporation ...
and ion beam assisted deposition
Ion beam assisted deposition or IBAD or IAD (not to be confused with ion beam induced deposition, IBID) is a materials engineering technique which combines ion implantation with simultaneous sputtering or another physical vapor deposition techniq ...
), chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high quality, and high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films.
In typical CVD, the wafer (substra ...
, ion beam deposition, molecular beam epitaxy
Molecular-beam epitaxy (MBE) is an epitaxy method for thin-film deposition of single crystals. MBE is widely used in the manufacture of semiconductor devices, including transistors, and it is considered one of the fundamental tools for the devel ...
, and sputter deposition
Sputter deposition is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) method of thin film deposition by the phenomenon of sputtering. This involves ejecting material from a "target" that is a source onto a "substrate" such as a silicon wafer. Resputtering is re ...
. Common materials are magnesium fluoride , silicon dioxide
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one ...
, tantalum pentoxide
Tantalum pentoxide, also known as tantalum(V) oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a white solid that is insoluble in all solvents but is attacked by strong bases and hydrofluoric acid. is an inert material with a high refract ...
, zinc sulfide
Zinc sulfide (or zinc sulphide) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula of ZnS. This is the main form of zinc found in nature, where it mainly occurs as the mineral sphalerite. Although this mineral is usually black because of various i ...
, and titanium dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or CI 77891. It is a white solid that is insolubl ...
.
Polymeric dielectric mirrors are fabricated industrially via co-extrusion of melt polymers, and by spin-coating or dip-coating
image:Dip coating.svg, A schematic of the continuous dip coating process.
Roll of coarse cloth
Cloth
Bath
Liquid material
Rollers
Oven
Scrapers
Excess liquid falls back
A coating remains on the fabric cloth.
Dip coating is an industrial ...
on smaller scale.
See also
* Distributed Bragg reflector *Dichroic filter
A dichroic filter, thin-film filter, or interference filter is a color filter used to selectively pass light of a small range of colors while reflecting other colors. By comparison, dichroic mirrors and dichroic reflectors tend to be characteriz ...
* Perfect mirror A perfect mirror is a mirror that reflects light (and electromagnetic radiation in general) perfectly, and does not transmit or absorb it.
General
Domestic mirrors are not perfect mirrors as they absorb a significant portion of the light which fal ...
* Rugate filter
A rugate filter, also known as a gradient-index filter, is an optical filter based on a dielectric mirror that selectively reflects specific wavelength ranges of light. This effect is achieved by a periodic, continuous change of the refractive ind ...
References
External links
{{Commons category, Dielectric mirrorsFast code for computation of dielectric mirror reflectivity and dispersion
Optical filters Mirrors ja:ダイクロイックミラー