Dichloro(1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane)nickel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dichloro ,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propaneickel a
coordination complex
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many ...
with the formula NiCl2(dppp); where dppp is the diphosphine
Diphosphane, or diphosphine, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula P2H4. This colourless liquid is one of several binary phosphorus hydrides. It is the impurity that typically causes samples of phosphine to ignite in air.
Propert ...
1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane
1,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)propane (dppp) is an organophosphorus compound with the formula PhP(CH)PPh. The compound is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is slightly air-sensitive, degrading in air to the phosphine oxide. It i ...
. It is used as a catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
in organic synthesis. The compound is a bright orange-red crystalline powder.
Structure and properties
While the electronic and solid-state structure of the chloride congener is not known (due to low solubility in common analytical solvents), several studies have been carried out on the bromo and iodo derivatives. The complexes display a temperature-dependent interconversion between square-planar and tetrahedral geometries (diamagnetic and paramagnetic) in polar organic solvents (Keq between 1-3.68, depending on the solvent and temperature). In contrast, dichloro(1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane)nickel adopts a static square-planar (diamagnetic) structure in solution.Preparation
NiCl2(dppp) is prepared by combining equal molar portions ofnickel(II) chloride
Nickel(II) chloride (or just nickel chloride) is the chemical compound NiCl2. The anhydrous salt is yellow, but the more familiar hydrate NiCl2·6H2O is green. Nickel(II) chloride, in various forms, is the most important source of nickel for chemi ...
hexahydrate with 1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane
1,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)propane (dppp) is an organophosphorus compound with the formula PhP(CH)PPh. The compound is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is slightly air-sensitive, degrading in air to the phosphine oxide. It i ...
in 2-propanol.
:Ni(H2O)6Cl2 + dppp → NiCl2(dppp) + 6 H2O
Reactions
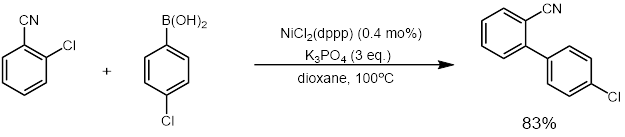
NiCl2(dppp) in an effective catalyst forcoupling reaction A coupling reaction in organic chemistry is a general term for a variety of reactions where two fragments are joined together with the aid of a metal catalyst. In one important reaction type, a main group organometallic compound of the type R-M (R = ...
s such as the Kumada coupling
In organic chemistry, the Kumada coupling is a type of cross coupling reaction, useful for generating carbon–carbon bonds by the reaction of a Grignard reagent and an organic halide. The procedure uses transition metal catalysts, typically n ...
and Suzuki reaction
The Suzuki reaction is an organic reaction, classified as a cross-coupling reaction, where the coupling partners are a boronic acid and an organohalide and the catalyst is a palladium(0) complex. It was first published in 1979 by Akira Suzuki, ...
s (example below). It also catalyzes other reactions that convert enol ether
In organic chemistry an enol ether is an alkene with an alkoxy substituent. The general structure is R2C=CR-OR where R = H, alkyl or aryl. A common subfamily of enol ethers are vinyl ethers, with the formula ROCH=CH2. Important enol ethers include ...
s, dithioacetal
In organosulfur chemistry, thioacetals are the sulfur (''thio-'') analogues of acetals (). There are two classes: the less-common monothioacetals, with the formula , and the dithioacetals, with the formula (symmetric dithioacetals) or (asym ...
s, and vinyl sulfides to olefins
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond.
Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, an ...
.

References
{{Reflist, 1 Nickel complexes Phosphine complexes Chloro complexes