Detroit ( , ; , ) is the
largest city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metropo ...
in the
U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sover ...
of
Michigan
Michigan () is a state in the Great Lakes region of the upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the 10th-largest state by population, the 11th-largest by area, and the ...
. It is also the largest U.S. city on the
United States–Canada border
United may refer to:
Places
* United, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community
* United, West Virginia
United is an unincorporated community and coal town in Kanawha County, West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, M ...
, and the
seat of government
The seat of government is (as defined by ''Brewer's Politics'') "the building, complex of buildings or the city from which a government exercises its authority".
In most countries, the nation’s capital is also seat of its government, thus that ...
of
Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at the
2020 census,
making it the
27th-most populous city in the United States. The
metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually com ...
, known as
Metro Detroit
The Detroit metropolitan area, often referred to as Metro Detroit, is a major metropolitan area in the U.S. State of Michigan, consisting of the city of Detroit and its surrounding area. There are varied definitions of the area, including the ...
, is home to 4.3 million people, making it the second-largest in the
Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four Census Bureau Region, census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of ...
after the
Chicago metropolitan area
The Chicago metropolitan area, also colloquially referred to as Chicagoland, is a metropolitan area in the Midwestern United States. Encompassing 10,286 sq mi (28,120 km2), the metropolitan area includes the city of Chicago, its suburbs and hi ...
, and the 14th-largest in the United States. Regarded as a major cultural center, Detroit is known for its contributions to
music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect ...
, art,
architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
and design, in addition to its historical automotive background. ''
Time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, to ...
'' named Detroit as one of the fifty World's Greatest Places of 2022 to explore.
Detroit is a major port on the
Detroit River
The Detroit River flows west and south for from Lake St. Clair to Lake Erie as a strait in the Great Lakes system. The river divides the metropolitan areas of Detroit, Michigan, and Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, Ontario—an area collectively refe ...
, one of the four major
strait
A strait is an oceanic landform connecting two seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ocean channe ...
s that connect the
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
system to the
Saint Lawrence Seaway
The St. Lawrence Seaway (french: la Voie Maritime du Saint-Laurent) is a system of locks, canals, and channels in Canada and the United States that permits oceangoing vessels to travel from the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes of North Americ ...
. The City of Detroit anchors the second-largest regional economy in the
Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four Census Bureau Region, census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of ...
, behind
Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
and ahead of
Minneapolis–Saint Paul
Minneapolis–Saint Paul is a metropolitan area in the Upper Midwestern United States centered around the confluence of the Mississippi, Minnesota and St. Croix rivers in the U.S. state of Minnesota. It is commonly known as the Twin Cities ...
, and the
14th-largest in the United States. Detroit is best known as the center of the
U.S. automobile industry, and the "
Big Three" auto manufacturers
General Motors
The General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. It is the largest automaker in the United States and ...
,
Ford
Ford commonly refers to:
* Ford Motor Company, an automobile manufacturer founded by Henry Ford
* Ford (crossing), a shallow crossing on a river
Ford may also refer to:
Ford Motor Company
* Henry Ford, founder of the Ford Motor Company
* Ford F ...
, and
Stellantis North America
Stellantis North America (officially FCA US and formerly Chrysler ()) is one of the " Big Three" automobile manufacturers in the United States, headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan. It is the American subsidiary of the multinational automotiv ...
(Chrysler) are all headquartered in Metro Detroit. , the Detroit metropolitan area is the number one exporting region among 310 defined metropolitan areas in the United States.
[Why MITA will be a success]
''Michigan International Trade Association''. Retrieved on September 3, 2007. "Detroit is the most active commercial port of entry in the USA." "Greater Detroit is the number one exporting region among 310 defined metropolitan areas (CMSA) in the U.S." The
Detroit Metropolitan Airport
Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport , usually called Detroit Metro Airport, Metro Airport, or simply DTW, is a major international airport in the United States covering effective December 30, 2021. in Romulus, Michigan. It is the primar ...
is among the most important
hub airports in the United States. Detroit and its neighboring Canadian city
Windsor
Windsor may refer to:
Places Australia
* Windsor, New South Wales
** Municipality of Windsor, a former local government area
* Windsor, Queensland, a suburb of Brisbane, Queensland
**Shire of Windsor, a former local government authority around Wi ...
are connected through
a highway tunnel,
railway tunnel
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in Track (rail transport), tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the ...
, and the
Ambassador Bridge
The Ambassador Bridge is a tolled international suspension bridge across the Detroit River that connects Detroit, Michigan, United States, with Windsor, Ontario, Canada. Opened in 1929, it is the busiest international border crossing in North ...
, which is the second-busiest international crossing in North America, after
San Diego–Tijuana
San Diego–Tijuana is an international transborder agglomeration, straddling the border of the adjacent North American coastal cities of San Diego, California, United States and Tijuana, Baja California, Mexico. The 2012 population of the reg ...
. Both cities will soon be connected by a new bridge currently under construction, the
Gordie Howe International Bridge
The Gordie Howe International Bridge (french: Pont International Gordie-Howe), known during development as the Detroit River International Crossing and the New International Trade Crossing, is a cable-stayed international bridge across the Det ...
, which will provide a complete freeway-to-freeway link. The new bridge is expected to be open by 2024.
In 1701,
Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac and
Alphonse de Tonty founded
Fort Pontchartrain du Détroit
Fort Pontchartrain du Détroit or Fort Detroit (1701–1796) was a fort established on the north bank of the Detroit River by the French officer Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac and the Italian Alphonse de Tonty in 1701. In the 18th century, Fr ...
, the future city of Detroit. During the late nineteenth and early twentieth century, it became an important industrial hub at the center of the
Great Lakes region
The Great Lakes region of North America is a binational Canadian–American region that includes portions of the eight U.S. states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania and Wisconsin along with the Canadian p ...
. The city's population became the fourth-largest in the nation in 1920, after only
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
, Chicago and
Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
, with the expansion of the
auto industry
The automotive industry comprises a wide range of companies and organizations involved in the design, development, manufacturing, marketing, and selling of motor vehicles. It is one of the world's largest industries by revenue (from 16 % such ...
in the early 20th century.
[Nolan, Jenny (June 15, 1999]
How Prohibition made Detroit a bootlegger's dream town
. Michigan History, ''The Detroit News''. Retrieved on November 23, 2007. As Detroit's industrialization took off, the
Detroit River
The Detroit River flows west and south for from Lake St. Clair to Lake Erie as a strait in the Great Lakes system. The river divides the metropolitan areas of Detroit, Michigan, and Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, Ontario—an area collectively refe ...
became the busiest commercial hub in the world. The strait carried over 65 million tons of shipping commerce through Detroit to locations all over the world each year; the freight throughput was more than three times that of New York and about four times that of
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
. By the 1940s, the city's population remained the fourth-largest in the country. However, due to industrial restructuring, the loss of jobs in the auto industry, and rapid
suburbanization
Suburbanization is a population shift from central urban areas into suburbs, resulting in the formation of (sub)urban sprawl. As a consequence of the movement of households and businesses out of the city centers, low-density, peripheral urba ...
, among other reasons, Detroit entered a state of
urban decay
Urban decay (also known as urban rot, urban death or urban blight) is the sociological process by which a previously functioning city, or part of a city, falls into disrepair and decrepitude. There is no single process that leads to urban deca ...
and lost considerable population from the late 20th century to the present. Since reaching a peak of 1.85 million at the
1950 census, Detroit's population has declined by more than 65 percent.
In 2013, Detroit
became the largest U.S. city to file for bankruptcy, which it successfully exited in December 2014, when the city government regained control of Detroit's finances.
Detroit's diverse culture has had both local and international influence, particularly in
music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect ...
, with the city giving rise to the genres of
Motown
Motown Records is an American record label owned by the Universal Music Group. It was founded by Berry Gordy Jr. as Tamla Records on June 7, 1958, and incorporated as Motown Record Corporation on April 14, 1960. Its name, a portmanteau of ''moto ...
and
techno
Techno is a genre of electronic dance music (EDM) which is generally produced for use in a continuous DJ set, with tempo often varying between 120 and 150 beats per minute (bpm). The central rhythm is typically in common time (4/4) and often ch ...
, and playing an important role in the development of
jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a major ...
,
hip-hop,
rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales ...
, and
punk
Punk or punks may refer to:
Genres, subculture, and related aspects
* Punk rock, a music genre originating in the 1970s associated with various subgenres
* Punk subculture, a subculture associated with punk rock, or aspects of the subculture s ...
. The rapid growth of Detroit in its boom years resulted in a globally unique stock of
architectural monuments and
historic places. Since the 2000s,
conservation
Conservation is the preservation or efficient use of resources, or the conservation of various quantities under physical laws.
Conservation may also refer to:
Environment and natural resources
* Nature conservation, the protection and manageme ...
efforts have managed to save many architectural pieces and achieved several large-scale
revitalizations, including the restoration of several historic
theatres
Theatre or theater is a collaborative form of performing art that uses live performers, usually actor, actors or actresses, to present the experience of a real or imagined event before a live audience in a specific place, often a stage. The p ...
and entertainment venues,
high-rise renovations, new sports stadiums, and a riverfront revitalization project. More recently, the population of
Downtown Detroit
Downtown Detroit is the central business district and a residential area of the city of Detroit, Michigan, United States. Locally, downtown tends to refer to the 1.4 square mile region bordered by M-10 (Lodge Freeway) to the west, Interstate 75 ( ...
,
Midtown Detroit
Midtown Detroit is a mixed-use area consisting of a business district, cultural center, a major research university, and several residential neighborhoods; it is located along the east and west side of Woodward Avenue, north of Downtown Detroit, ...
, and various other neighborhoods have increased. An
increasingly popular tourist destination, Detroit receives 16 million visitors per year. In 2015, Detroit was named a
"City of Design" by
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
, the first U.S. city to receive that designation.
Toponymy
Detroit is named after the
Detroit River
The Detroit River flows west and south for from Lake St. Clair to Lake Erie as a strait in the Great Lakes system. The river divides the metropolitan areas of Detroit, Michigan, and Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, Ontario—an area collectively refe ...
, connecting
Lake Huron
Lake Huron ( ) is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. Hydrology, Hydrologically, it comprises the easterly portion of Lake Michigan–Huron, having the same surface elevation as Lake Michigan, to which it is connected by the , Strait ...
with
Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has t ...
. The city's name comes from the
French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
word détroit''
' meaning "strait" as the city was situated on a narrow passage of water linking two lakes. The river was known as “''le détroit du Lac Érié''," among the
French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, which meant "the strait of Lake Erie".
History
Early settlement
Paleo-Indian people inhabited areas near Detroit as early as 11,000 years ago including the culture referred to as the
Mound-builders
A number of pre-Columbian cultures are collectively termed "Mound Builders". The term does not refer to a specific people or archaeological culture, but refers to the characteristic mound earthworks erected for an extended period of more than 5 ...
.
In the 17th century, the region was inhabited by
Huron
Huron may refer to:
People
* Wyandot people (or Wendat), indigenous to North America
* Wyandot language, spoken by them
* Huron-Wendat Nation, a Huron-Wendat First Nation with a community in Wendake, Quebec
* Nottawaseppi Huron Band of Potawatomi ...
,
Odawa
The Odawa (also Ottawa or Odaawaa ), said to mean "traders", are an Indigenous American ethnic group who primarily inhabit land in the Eastern Woodlands region, commonly known as the northeastern United States and southeastern Canada. They ha ...
,
Potawatomi
The Potawatomi , also spelled Pottawatomi and Pottawatomie (among many variations), are a Native American people of the western Great Lakes region, upper Mississippi River and Great Plains. They traditionally speak the Potawatomi language, a m ...
and
Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
peoples.
The area is known by the
Anishinaabe
The Anishinaabeg (adjectival: Anishinaabe) are a group of culturally related Indigenous peoples present in the Great Lakes region of Canada and the United States. They include the Ojibwe (including Saulteaux and Oji-Cree), Odawa, Potawatomi, ...
people as ''Waawiiyaataanong'', translating to 'where the water curves around'.
The first Europeans did not penetrate into the region and reach the straits of Detroit until French missionaries and traders worked their way around the
League of the Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
, with whom they were at war and other Iroquoian tribes in the 1630s.
[
] The Huron and
Neutral people
The Neutral Confederacy (also Neutral Nation, Neutral people, or ''Attawandaron'' by neighbouring tribes) were an Iroquoian people who lived in what is now southwestern and south-central Ontario in Canada, North America. They lived throughout t ...
s held the north side of
Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has t ...
until the 1650s, when the Iroquois pushed both and the
Erie people
The Erie people (also Eriechronon, Riquéronon, Erielhonan, Eriez, Nation du Chat) were Indigenous people historically living on the south shore of Lake Erie. An Iroquoian group, they lived in what is now western New York, northwestern Pennsylvani ...
away from the lake and its
beaver
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents in the genus ''Castor'' native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. There are two extant species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers ar ...
-rich feeder streams in the
Beaver Wars
The Beaver Wars ( moh, Tsianì kayonkwere), also known as the Iroquois Wars or the French and Iroquois Wars (french: Guerres franco-iroquoises) were a series of conflicts fought intermittently during the 17th century in North America throughout t ...
of 1649–1655.
By the 1670s, the war-weakened Iroquois laid claim to as far south as the
Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illino ...
valley in northern
Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to ...
as hunting grounds,
and had absorbed many other Iroquoian peoples after defeating them in war.
For the next hundred years, virtually no British or French action was contemplated without consultation with the Iroquois or consideration of their likely response.
When the
French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
evicted the
Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. ...
from Canada, it removed one barrier to American colonists migrating west.
British negotiations with the Iroquois would both prove critical and lead to a Crown policy limiting settlements below the
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
and west of the
Alleghenies
The Allegheny Mountain Range (; also spelled Alleghany or Allegany), informally the Alleghenies, is part of the vast Appalachian Mountain Range of the Eastern United States and Canada and posed a significant barrier to land travel in less devel ...
. Many colonial American would-be migrants resented this restraint and became supporters of the
American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
. The 1778 raids and resultant 1779 decisive
Sullivan Expedition
The 1779 Sullivan Expedition (also known as the Sullivan-Clinton Expedition, the Sullivan Campaign, and the Sullivan-Clinton Genocide) was a United States military campaign during the American Revolutionary War, lasting from June to October 1779 ...
reopened the
Ohio Country to westward emigration, which began almost immediately. By 1800 white settlers were pouring westwards.
Later settlement
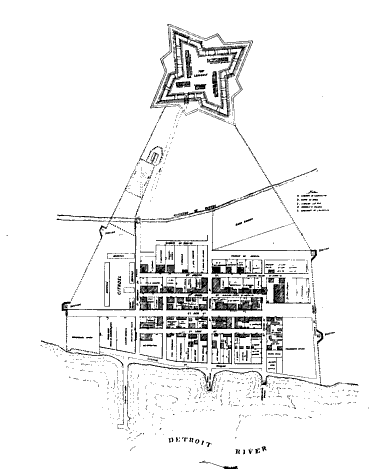
The city was named by
French colonists, referring to the
Detroit River
The Detroit River flows west and south for from Lake St. Clair to Lake Erie as a strait in the Great Lakes system. The river divides the metropolitan areas of Detroit, Michigan, and Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, Ontario—an area collectively refe ...
(french: link=no, le détroit du lac Érié, meaning ''the
strait
A strait is an oceanic landform connecting two seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ocean channe ...
of Lake Erie''), linking
Lake Huron
Lake Huron ( ) is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. Hydrology, Hydrologically, it comprises the easterly portion of Lake Michigan–Huron, having the same surface elevation as Lake Michigan, to which it is connected by the , Strait ...
and
Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has t ...
; in the historical context, the strait included the
St. Clair River
The St. Clair River (french: Rivière Sainte-Claire) is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed November 7, 2011 river in central North America which flows from Lake Huron int ...
,
Lake St. Clair
Lake St. Clair (french: Lac Sainte-Claire) is a freshwater lake that lies between the Canadian province of Ontario and the U.S. state of Michigan. It was named in 1679 by French Catholic explorers after Saint Clare of Assisi, on whose feast day ...
and the Detroit River.
On July 24, 1701, the French explorer
Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac, with his lieutenant
Alphonse de Tonty and along with more than a hundred other settlers, began constructing a small fort on the north bank of the Detroit River. Cadillac would later name the settlement
Fort Pontchartrain du Détroit
Fort Pontchartrain du Détroit or Fort Detroit (1701–1796) was a fort established on the north bank of the Detroit River by the French officer Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac and the Italian Alphonse de Tonty in 1701. In the 18th century, Fr ...
, after
Louis Phélypeaux, comte de Pontchartrain Louis may refer to:
* Louis (coin)
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name
* Louis (surname)
* Louis (singer), Serbian singer
* HMS Louis, HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy
See also
Derived or associated te ...
, Minister of Marine under
Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Vers ...
.
[, p. 56.] A church was soon founded here, and the parish was known as Sainte Anne de Détroit. France offered free land to colonists to attract families to Detroit; when it reached a population of 800 in 1765, this was the largest European settlement between
Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-most populous city in Canada and List of towns in Quebec, most populous city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian ...
and
, both also French settlements, in the former colonies of New France and La Louisiane, respectively.
By 1773, after the addition of Anglo-American settlers, the population of Detroit was 1,400. By 1778, its population reached 2,144 and it was the third-largest city in what was known as the
Province of Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirteen p ...
since the British takeover of French colonies following their victory in the
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754� ...
.
The region's economy was based on the lucrative
fur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the mos ...
, in which numerous Native American people had important roles as trappers and traders. Today the
flag of Detroit
The flag of the city of Detroit was designed in 1907 by David E. Heineman and was officially adopted as the city's flag in 1948. The flag's design has been slightly altered several times in the years since, the most recent in 2000.
Design
...
reflects its French colonial heritage. Descendants of the earliest French and
French-Canadian
French Canadians (referred to as Canadiens mainly before the twentieth century; french: Canadiens français, ; feminine form: , ), or Franco-Canadians (french: Franco-Canadiens), refers to either an ethnic group who trace their ancestry to Fr ...
settlers formed a cohesive community, who gradually were superseded as the dominant population after more
Anglo-American
Anglo-Americans are people who are English-speaking inhabitants of Anglo-America. It typically refers to the nations and ethnic groups in the Americas that speak English as a native language, making up the majority of people in the world who spe ...
settlers arrived in the early 19th century with American westward migration. Living along the shores of Lake St. Clair and south to Monroe and downriver suburbs, the ethnic French Canadians of Detroit, also known as
Muskrat French
The Muskrat French (french: Francophonie au Michigan; also known as the Mushrat French or Detroit River French Canadien) are a cultural group and dialect found in southeastern Michigan along the Detroit River and Lake St. Clair, the western and s ...
in reference to the fur trade, remain a subculture in the region in the 21st century.
During the
French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
(1754–63), the North American front of the
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754� ...
between Britain and France, British troops gained control of the settlement in 1760 and shortened its name to ''Detroit''. Several regional Native American tribes, such as the Potowatomi, Ojibwe and Huron, launched
Pontiac's War
Pontiac's War (also known as Pontiac's Conspiracy or Pontiac's Rebellion) was launched in 1763 by a loose confederation of Native Americans dissatisfied with British rule in the Great Lakes region following the French and Indian War (1754–176 ...
in 1763, and
laid siege to
Fort Detroit
Fort Pontchartrain du Détroit or Fort Detroit (1701–1796) was a fort established on the north bank of the Detroit River by the French officer Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac and the Italian Alphonse de Tonty in 1701. In the 18th century, Fre ...
, but failed to capture it. In defeat, France ceded its territory in North America east of the Mississippi to Britain following the war.
Following the
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
and the establishment of the United States as an independent country, Britain ceded Detroit along with other territories in the area under the
Jay Treaty
The Treaty of Amity, Commerce, and Navigation, Between His Britannic Majesty and the United States of America, commonly known as the Jay Treaty, and also as Jay's Treaty, was a 1794 treaty between the United States and Great Britain that averted ...
(1796), which established the northern border with its colony of Canada. The
Great Fire of 1805
The Great Fire of 1805 occurred on , in the city of Detroit, in the Michigan Territory of the United States. The fire destroyed almost everything in the city.
The motto of the city, ''Speramus meliora; resurget cineribus'' ('We hope for bett ...
destroyed most of the Detroit settlement, which had primarily buildings made of wood. One stone fort, a river warehouse, and brick chimneys of former wooden homes were the sole structures to survive. Of the 600 Detroit residents in this area, none died in the fire.
19th century
From 1805 to 1847, Detroit was the capital of Michigan as a territory and as a state.
William Hull
William Hull (June 24, 1753 – November 29, 1825) was an American soldier and politician. He fought in the American Revolutionary War and was appointed as Governor of Michigan Territory (1805–13), gaining large land cessions from several Ame ...
, the United States commander at Detroit surrendered without a fight to British troops and their Native American allies during the
War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
in the
Siege of Detroit
The siege of Detroit, also known as the surrender of Detroit or the Battle of Fort Detroit, was an early engagement in the War of 1812. A British force under Major General Isaac Brock with Native American allies under Shawnee leader Tecumseh ...
, believing his forces were vastly outnumbered. The
Battle of Frenchtown
The Battles of Frenchtown, also known as the Battle of the River Raisin and the River Raisin Massacre, were a series of conflicts in Michigan Territory that took place from January 18–23, 1813, during the War of 1812. It was fought between the ...
(January 18–23, 1813) was part of a U.S. effort to retake the city, and U.S. troops suffered their highest fatalities of any battle in the war. This battle is commemorated at
River Raisin National Battlefield Park
The River Raisin National Battlefield Park preserves the site of the Battle of Frenchtown as the only national battlefield marking a site of the War of 1812. It was established as the 393rd unit of the United States National Park Service under Ti ...
south of Detroit in
Monroe County Monroe County may refer to seventeen counties in the United States, all named for James Monroe:
* Monroe County, Alabama
*Monroe County, Arkansas
* Monroe County, Florida
* Monroe County, Georgia
*Monroe County, Illinois
*Monroe County, Indian ...
. Detroit was recaptured by the United States later that year.
The settlement was incorporated as a city in 1815.
[ As the city expanded, a geometric street plan developed by ]Augustus B. Woodward
Augustus Brevoort Woodward (born Elias Brevoort Woodward; November 1774 – June 12, 1827) was the first Chief Justice of the Michigan Territory. In that position, he played a prominent role in the reconstruction of Detroit following a d ...
was followed, featuring grand boulevards as in Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
.
Prior to the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
, the city's access to the Canada–US border made it a key stop for refugee slaves gaining freedom in the North along the Underground Railroad
The Underground Railroad was a network of clandestine routes and safe houses established in the United States during the early- to mid-19th century. It was used by enslaved African Americans primarily to escape into free states and Canada. T ...
. Many went across the Detroit River to Canada to escape pursuit by slave catchers.[ An estimated 20,000 to 30,000 African-American refugees settled in Canada. ]George DeBaptiste
George DeBaptiste ( – February 22, 1875) was a prominent African-American conductor on the Underground Railroad in southern Indiana and Detroit, Detroit, Michigan. Born free in Virginia, he moved as a young man to the free state of Indiana. In 1 ...
was considered to be the "president" of the Detroit Underground Railroad, William Lambert the "vice president" or "secretary", and Laura Haviland
Laura Smith Haviland (December 20, 1808 – April 20, 1898) was an American abolitionist, suffragette, and social reformer. She was a Quaker and an important figure in the history of the Underground Railroad.
Early years and family
Laura Sm ...
the "superintendent".
Numerous men from Detroit volunteered to fight for the Union during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
, including the 24th Michigan Infantry Regiment. It was part of the legendary Iron Brigade
The Iron Brigade, also known as The Black Hats, Black Hat Brigade, Iron Brigade of the West, and originally King's Wisconsin Brigade was an infantry brigade in the Union Army of the Potomac during the American Civil War. Although it fought enti ...
, which fought with distinction and suffered 82% casualties at the Battle of Gettysburg
The Battle of Gettysburg () was fought July 1–3, 1863, in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, by Union and Confederate forces during the American Civil War. In the battle, Union Major General George Meade's Army of the Po ...
in 1863. When the First Volunteer Infantry Regiment arrived to fortify Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, President Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
is quoted as saying, "Thank God for Michigan!" George Armstrong Custer
George Armstrong Custer (December 5, 1839 – June 25, 1876) was a United States Army officer and cavalry commander in the American Civil War and the American Indian Wars.
Custer graduated from West Point in 1861 at the bottom of his class, b ...
led the Michigan Brigade The Michigan Brigade, sometimes called the Wolverines, the Michigan Cavalry Brigade or Custer's Brigade, was a brigade of cavalry in the volunteer Union Army during the latter half of the American Civil War. Composed primarily of the 1st Michigan C ...
during the Civil War and called them the "Wolverines".
During the late 19th century, wealthy industry and shipping magnates commissioned the design and construction of several Gilded Age
In United States history, the Gilded Age was an era extending roughly from 1877 to 1900, which was sandwiched between the Reconstruction era and the Progressive Era. It was a time of rapid economic growth, especially in the Northern and Weste ...
mansions east and west of the current downtown, along the major avenues of the Woodward plan. Most notable among them was the David Whitney House
The David Whitney House is a historic mansion located at 4421 Woodward Avenue in Midtown Detroit, Michigan. The building was constructed during the 1890s as a private residence. It was restored in 1986 and is now a restaurant. The building was l ...
at 4421 Woodward Avenue
A woodward is a Game warden, warden of a wood. Woodward may also refer to:
Places
;United States
* Woodward, Iowa
* Woodward, Oklahoma
* Woodward, Pennsylvania, a census-designated place
* Woodward Avenue, a street in Tallahassee, Florida, which b ...
, and the grand avenue became a favored address for mansions. During this period, some referred to Detroit as the "Paris of the West" for its architecture, grand avenues in the Paris style, and for Washington Boulevard, recently electrified by Thomas Edison
Thomas Alva Edison (February 11, 1847October 18, 1931) was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices in fields such as electric power generation, mass communication, sound recording, and motion pictures. These inventio ...
.[ The city had grown steadily from the 1830s with the rise of shipping, shipbuilding, and manufacturing industries. Strategically located along the ]Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
waterway, Detroit emerged as a major port and transportation hub.
In 1896, a thriving carriage trade prompted Henry Ford
Henry Ford (July 30, 1863 – April 7, 1947) was an American industrialist, business magnate, founder of the Ford Motor Company, and chief developer of the assembly line technique of mass production. By creating the first automobile that mi ...
to build his first automobile in a rented workshop on Mack Avenue. During this growth period, Detroit expanded its borders by annexing all or part of several surrounding villages and townships.
20th century
In 1903, Henry Ford founded the Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company (commonly known as Ford) is an American multinational automobile manufacturer headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan, United States. It was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. The company sells automobi ...
. Ford's manufacturing—and those of automotive pioneers William C. Durant
William Crapo Durant (December 8, 1861 – March 18, 1947) was a leading pioneer of the United States automobile industry and co-founder of General Motors and Chevrolet. He created a system in which a company held multiple marques – each s ...
, the Dodge Brothers
Dodge is an American brand of automobiles and a division of Stellantis, based in Auburn Hills, Michigan, Auburn Hills, Michigan. Dodge vehicles have historically included performance cars, and for much of its existence Dodge was Chrysler's mid ...
, Packard
Packard or Packard Motor Car Company was an American luxury automobile company located in Detroit, Michigan. The first Packard automobiles were produced in 1899, and the last Packards were built in South Bend, Indiana in 1958.
One of the "Thr ...
, and Walter Chrysler
Walter Percy Chrysler (April 2, 1875 – August 18, 1940) was an American industrial pioneer in the automotive industry, American automotive industry executive and the founder and namesake of American Chrysler Corporation.
Early life
Chrysler wa ...
—established Detroit's status in the early 20th century as the world's automotive capital.[ The growth of the auto industry was reflected by changes in businesses throughout the Midwest and nation, with the development of garages to service vehicles and gas stations, as well as factories for parts and tires.
In 1907, the ]Detroit River
The Detroit River flows west and south for from Lake St. Clair to Lake Erie as a strait in the Great Lakes system. The river divides the metropolitan areas of Detroit, Michigan, and Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, Ontario—an area collectively refe ...
carried 67,292,504 tons of shipping commerce through Detroit to locations all over the world. For comparison, London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
shipped 18,727,230 tons, and New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
shipped 20,390,953 tons. The river was dubbed "the Greatest Commercial Artery on Earth" by The Detroit News
''The Detroit News'' is one of the two major newspapers in the U.S. city of Detroit, Michigan. The paper began in 1873, when it rented space in the rival ''Detroit Free Press'' building. ''The News'' absorbed the '' Detroit Tribune'' on Februa ...
in 1908.
With the rapid growth of industrial workers in the auto factories, labor unions
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and benefits ( ...
such as the American Federation of Labor
The American Federation of Labor (A.F. of L.) was a national federation of labor unions in the United States that continues today as the AFL-CIO. It was founded in Columbus, Ohio, in 1886 by an alliance of craft unions eager to provide mutu ...
and the United Auto Workers
The International Union, United Automobile, Aerospace, and Agricultural Implement Workers of America, better known as the United Auto Workers (UAW), is an American labor union that represents workers in the United States (including Puerto Rico ...
fought to organize workers to gain them better working conditions and wages. They initiated strikes and other tactics in support of improvements such as the 8-hour day/40-hour work week, increased wage
A wage is payment made by an employer to an employee for work done in a specific period of time. Some examples of wage payments include compensatory payments such as ''minimum wage'', ''prevailing wage'', and ''yearly bonuses,'' and remuner ...
s, greater benefits, and improved working conditions {{Short description, 1=Overview of and topical guide to working time and conditions
This is a list of topics on working time and conditions.
Legislation
* See :Employment law
Working time
* See :Working time
* Flextime
Working conditions
* Bios ...
. The labor activism during those years increased the influence of union leaders in the city such as Jimmy Hoffa
James Riddle Hoffa (born February 14, 1913 – disappeared July 30, 1975; declared dead July 30, 1982) was an American labor union leader who served as the president of the International Brotherhood of Teamsters (IBT) from 1957 until 1971.
F ...
of the Teamsters
The International Brotherhood of Teamsters (IBT), also known as the Teamsters Union, is a labor union in the United States and Canada. Formed in 1903 by the merger of The Team Drivers International Union and The Teamsters National Union, the u ...
and Walter Reuther
Walter Philip Reuther (; September 1, 1907 – May 9, 1970) was an American leader of Labor unions in the United States, organized labor and Civil rights movements, civil rights activist who built the United Automobile Workers (UAW) into one of ...
of the Autoworkers.
Due to the booming auto industry, Detroit became the fourth-largest city in the nation in 1920, following New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
, Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
and Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
.
The prohibition of alcohol
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic b ...
from 1920 to 1933 resulted in the Detroit River becoming a major conduit for smuggling of illegal Canadian spirits.Ku Klux Klan
The Ku Klux Klan (), commonly shortened to the KKK or the Klan, is an American white supremacist, right-wing terrorist, and hate group whose primary targets are African Americans, Jews, Latinos, Asian Americans, Native Americans, and ...
beginning in 1915. "By the 1920s the city had become a stronghold of the KKK", whose members primarily opposed Catholic and Jewish immigrants, but also practiced discrimination against Black Americans.["Detroit Race Riots 1943"](_blank)
. ''Eleanor Roosevelt'', WGBH, American Experience, PBS (June 20, 1983). Retrieved on September 5, 2013. Even after the decline of the KKK in the late 1920s, the Black Legion, a secret vigilante group, was active in the Detroit area in the 1930s. One-third of its estimated 20,000 to 30,000 members in Michigan were based in the city. It was defeated after numerous prosecutions following the kidnapping and murder in 1936 of Charles Poole, a Catholic organizer with the federal Works Progress Administration
The Works Progress Administration (WPA; renamed in 1939 as the Work Projects Administration) was an American New Deal agency that employed millions of jobseekers (mostly men who were not formally educated) to carry out public works projects, i ...
. Some 49 men of the Black Legion were convicted of numerous crimes, with many sentenced to life in prison for murder.
In the 1940s the world's "first urban depressed freeway" ever built, the Davison, was constructed in Detroit. During World War II, the government encouraged retooling of the American automobile industry in support of the Allied powers, leading to Detroit's key role in the American Arsenal of Democracy
"Arsenal of Democracy" was the central phrase used by U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt in a radio broadcast on the threat to national security, delivered on December 29, 1940—nearly a year before the United States entered the Second World ...
.[Nolan, Jenny (January 28, 1997]
Willow Run and the Arsenal of Democracy
. Michigan History, ''The Detroit News''. Retrieved on November 23, 2007.
Jobs expanded so rapidly due to the defense buildup in World War II that 400,000 people migrated to the city from 1941 to 1943, including 50,000 blacks in the second wave of the Great Migration, and 350,000 whites, many of them from the South. Whites, including ethnic Europeans, feared black competition for jobs and scarce housing. The federal government prohibited discrimination in defense work, but when in June 1943 Packard promoted three black people to work next to whites on its assembly lines, 25,000 white workers walked off the job.
The Detroit race riot of 1943 took place in June, three weeks after the Packard plant
The Packard Automotive Plant is a former automobile-manufacturing factory in Detroit, Michigan, where luxury cars were made by the Packard Motor Car Company and later by the Studebaker-Packard Corporation. In 2022, it was scheduled for demoliti ...
protest, beginning with an altercation at Belle Isle. Blacks suffered 25 deaths (of a total of 34), three-quarters of 600 wounded, and most of the losses due to property damage. Rioters moved through the city, and young whites traveled across town to attack more settled blacks in their neighborhood of Paradise Valley.[Dominic J. Capeci, Jr., and Martha Wilkerson, "The Detroit Rioters of 1943: A Reinterpretation"](_blank)
''Michigan Historical Review'', January 1990, Vol. 16 Issue 1, pp. 49–72.
Postwar era
Industrial mergers in the 1950s, especially in the automobile sector, increased oligopoly
An oligopoly (from Greek ὀλίγος, ''oligos'' "few" and πωλεῖν, ''polein'' "to sell") is a market structure in which a market or industry is dominated by a small number of large sellers or producers. Oligopolies often result from ...
in the American auto industry. Detroit manufacturers such as Packard
Packard or Packard Motor Car Company was an American luxury automobile company located in Detroit, Michigan. The first Packard automobiles were produced in 1899, and the last Packards were built in South Bend, Indiana in 1958.
One of the "Thr ...
and Hudson
Hudson may refer to:
People
* Hudson (given name)
* Hudson (surname)
* Henry Hudson, English explorer
* Hudson (footballer, born 1986), Hudson Fernando Tobias de Carvalho, Brazilian football right-back
* Hudson (footballer, born 1988), Hudso ...
merged into other companies and eventually disappeared. At its peak population of 1,849,568, in the 1950 Census, the city was the fifth-largest in the United States, after New York City, Chicago, Philadelphia and Los Angeles.
In this postwar era, the auto industry continued to create opportunities for many African Americans from the South, who continued with their Great Migration to Detroit and other northern and western cities to escape the strict Jim Crow
The Jim Crow laws were state and local laws enforcing racial segregation in the Southern United States. Other areas of the United States were affected by formal and informal policies of segregation as well, but many states outside the Sout ...
laws and racial discrimination policies of the South. Postwar Detroit was a prosperous industrial center of mass production. The auto industry comprised about 60% of all industry in the city, allowing space for a plethora of separate booming businesses including stove making, brewing, furniture building, oil refineries, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and more. The expansion of jobs created unique opportunities for black Americans, who saw novel high employment rates: there was a 103% increase in the number of blacks employed in postwar Detroit. Black Americans who immigrated to northern industrial cities from the south still faced intense racial discrimination in the employment sector. Racial discrimination kept the workforce and better jobs predominantly white, while many black Detroiters held lower-paying factory jobs. Despite changes in demographics as the city's black population expanded, Detroit's police force, fire department, and other city jobs continued to be held by predominantly white residents. This created an unbalanced racial power dynamic.redlining
In the United States, redlining is a discriminatory practice in which services (financial and otherwise) are withheld from potential customers who reside in neighborhoods classified as "hazardous" to investment; these neighborhoods have signif ...
implemented by banks and federal housing groups, which almost completely restricted the ability of blacks to improve their housing and encouraged white people to guard the racial divide that defined their neighborhoods. As a result, black people were often denied bank loans to obtain better housing, and interest rates and rents were unfairly inflated to prevent their moving into white neighborhoods. White residents and political leaders largely opposed the influx of black Detroiters to white neighborhoods, believing that their presence would lead to neighborhood deterioration (most predominantly black neighborhoods deteriorated due to local and federal governmental neglect). This perpetuated a cyclical exclusionary process that marginalized the agency of black Detroiters by trapping them in the unhealthiest, least safe areas of the city.[
As in other major American cities in the postwar era, construction of a federally subsidized, extensive highway and freeway system around Detroit, and pent-up demand for new housing stimulated suburbanization; highways made commuting by car for higher-income residents easier. However, this construction had negative implications for many lower-income urban residents. Highways were constructed through and completely demolished neighborhoods of poor residents and black communities who had less political power to oppose them. The neighborhoods were mostly low income, considered blighted, or made up of older housing where investment had been lacking due to racial redlining, so the highways were presented as a kind of urban renewal. These neighborhoods (such as Black Bottom and Paradise Valley) were extremely important to the black communities of Detroit, providing spaces for independent black businesses and social/cultural organizations. Their destruction displaced residents with little consideration of the effects of breaking up functioning neighborhoods and businesses.][
In 1956, Detroit's last heavily used electric streetcar line, which traveled along the length of Woodward Avenue, was removed and replaced with gas-powered buses. It was the last line of what had once been a 534-mile network of electric streetcars. In 1941, at peak times, a streetcar ran on ]Woodward Avenue
A woodward is a Game warden, warden of a wood. Woodward may also refer to:
Places
;United States
* Woodward, Iowa
* Woodward, Oklahoma
* Woodward, Pennsylvania, a census-designated place
* Woodward Avenue, a street in Tallahassee, Florida, which b ...
every 60 seconds.[Peter Gavrilovich & Bill McGraw (2000) ''The Detroit Almanac: 300 Years of Life in the Motor City''. p. 232]
All of these changes in the area's transportation system favored low-density, auto-oriented development rather than high-density urban development. Industry also moved to the suburbs, seeking large plots of land for single-story factories. By the 21st century, the metro Detroit area had developed as one of the most sprawling job markets in the United States; combined with poor public transport, this resulted in many new jobs being beyond the reach of urban low-income workers.
 In 1950, the city held about one-third of the state's population, anchored by its industries and workers. Over the next sixty years, the city's population declined to less than 10 percent of the state's population. During the same time period, the sprawling Detroit metropolitan area, which surrounds and includes the city, grew to contain more than half of Michigan's population.
In 1950, the city held about one-third of the state's population, anchored by its industries and workers. Over the next sixty years, the city's population declined to less than 10 percent of the state's population. During the same time period, the sprawling Detroit metropolitan area, which surrounds and includes the city, grew to contain more than half of Michigan's population.[ The shift of population and jobs eroded Detroit's tax base.
In June 1963, Rev. ]Martin Luther King Jr.
Martin Luther King Jr. (born Michael King Jr.; January 15, 1929 – April 4, 1968) was an American Baptist minister and activist, one of the most prominent leaders in the civil rights movement from 1955 until his assassination in 1968 ...
gave a major speech as part of a civil rights march in Detroit that foreshadowed his "I Have a Dream
"I Have a Dream" is a public speech that was delivered by American civil rights activist and Baptist minister, Martin Luther King Jr., during the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom on August 28, 1963. In the speech, King called ...
" speech in Washington, D.C., two months later. While the civil rights movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, Racial discrimination ...
gained significant federal civil rights laws in 1964 and 1965, longstanding inequities resulted in confrontations between the police and inner-city black youth who wanted change.
Longstanding tensions in Detroit culminated in the Twelfth Street riot in July 1967. Governor George W. Romney
George Wilcken Romney (July 8, 1907 – July 26, 1995) was an American businessman and politician. A member of the Republican Party, he served as chairman and president of American Motors Corporation from 1954 to 1962, the 43rd gover ...
ordered the Michigan National Guard into Detroit, and President Johnson sent in U.S. Army troops. The result was 43 dead, 467 injured, over 7,200 arrests, and more than 2,000 buildings destroyed, mostly in black residential and business areas. Thousands of small businesses closed permanently or relocated to safer neighborhoods. The affected district lay in ruins for decades. According to the Chicago Tribune, it was the 3rd most costly riot in the United States.
On August 18, 1970, the NAACP filed suit against Michigan state officials, including Governor William Milliken, charging ''de facto'' public school segregation. The NAACP argued that although schools were not legally segregated, the city of Detroit and its surrounding counties had enacted policies to maintain Racial segregation in the United States#Education, racial segregation in public schools. The NAACP also suggested a direct relationship between unfair housing practices and educational segregation, as the composition of students in the schools followed segregated neighborhoods.[ The subsequent Milliken v. Bradley, ''Milliken v. Bradley'' decision had nationwide influence. In a narrow decision, the US Supreme Court found schools were a subject of local control, and suburbs could not be forced to aid with the desegregation of the city's school district.
"Milliken was perhaps the greatest missed opportunity of that period", said Myron Orfield, professor of law at the University of Minnesota. "Had that gone the other way, it would have opened the door to fixing nearly all of Detroit's current problems."]["Squandered opportunities leave Detroit isolated"](_blank)
, Remapping Debate website. Retrieved on July 16, 2013. John Mogk, a professor of law and an expert in urban planning at Wayne State University in Detroit, says,
Everybody thinks that it was the riots [in 1967] that caused the white families to leave. Some people were leaving at that time but, really, it was after Milliken that you saw mass flight to the suburbs. If the case had gone the other way, it is likely that Detroit would not have experienced the steep decline in its tax base that has occurred since then.
1970s and decline
 In November 1973, the city elected Coleman Young as its first black mayor. After taking office, Young emphasized increasing racial diversity in the police department, which was predominantly white. Young also worked to improve Detroit's transportation system, but the tension between Young and his suburban counterparts over regional matters was problematic throughout his mayoral term. In 1976, the federal government offered $600 million for building a regional rapid transit system, under a single regional authority. But the inability of Detroit and its suburban neighbors to solve conflicts over transit planning resulted in the region losing the majority of funding for rapid transit.
Following the failure to reach a regional agreement over the larger system, the city moved forward with construction of the elevated downtown circulator portion of the system, which became known as the Detroit People Mover.
The gasoline crises of 1973 oil crisis, 1973 and 1979 energy crisis, 1979 also affected Detroit and the U.S. auto industry. Buyers chose smaller, more fuel-efficient cars made by foreign makers as the price of gas rose. Efforts to revive the city were stymied by the struggles of the auto industry, as their sales and market share declined. Automakers laid off thousands of employees and closed plants in the city, further eroding the tax base. To counteract this, the city used eminent domain to build two large new auto assembly plants in the city.
As mayor, Young sought to revive the city by seeking to increase investment in the city's declining downtown. The Renaissance Center, a mixed-use office and retail complex, opened in 1977. This group of skyscrapers was an attempt to keep businesses in downtown.
In November 1973, the city elected Coleman Young as its first black mayor. After taking office, Young emphasized increasing racial diversity in the police department, which was predominantly white. Young also worked to improve Detroit's transportation system, but the tension between Young and his suburban counterparts over regional matters was problematic throughout his mayoral term. In 1976, the federal government offered $600 million for building a regional rapid transit system, under a single regional authority. But the inability of Detroit and its suburban neighbors to solve conflicts over transit planning resulted in the region losing the majority of funding for rapid transit.
Following the failure to reach a regional agreement over the larger system, the city moved forward with construction of the elevated downtown circulator portion of the system, which became known as the Detroit People Mover.
The gasoline crises of 1973 oil crisis, 1973 and 1979 energy crisis, 1979 also affected Detroit and the U.S. auto industry. Buyers chose smaller, more fuel-efficient cars made by foreign makers as the price of gas rose. Efforts to revive the city were stymied by the struggles of the auto industry, as their sales and market share declined. Automakers laid off thousands of employees and closed plants in the city, further eroding the tax base. To counteract this, the city used eminent domain to build two large new auto assembly plants in the city.
As mayor, Young sought to revive the city by seeking to increase investment in the city's declining downtown. The Renaissance Center, a mixed-use office and retail complex, opened in 1977. This group of skyscrapers was an attempt to keep businesses in downtown.[Bailey, Ruby L.(August 22, 2007). "The D is a draw: Most suburbanites are repeat visitors", ''Detroit Free Press''. Quote: A Local 4 poll conducted by Selzer and Co., finds, "nearly two-thirds of residents of suburban Wayne, Oakland, and Macomb counties say they at least occasionally dine, attend cultural events or take in professional games in Detroit."] Young also gave city support to other large developments to attract middle and upper-class residents back to the city. Despite the Renaissance Center and other projects, the downtown area continued to lose businesses to the Automobile dependency, automobile-dependent suburbs. Major stores and hotels closed, and many large office buildings went vacant. Young was criticized for being too focused on downtown development and not doing enough to lower the city's high crime rate and improve city services to residents.
High unemployment was compounded by middle-class flight to the suburbs, and some residents leaving the state to find work. The result for the city was a higher proportion of poor in its population, reduced tax base, depressed property values, abandoned buildings, abandoned neighborhoods, high crime rates, and a pronounced demographic imbalance.
1980s
On August 16, 1987, Northwest Airlines Flight 255 crashed near Detroit Metro airport, killing all but one of the 155 people on board, as well as two people on the ground.
1990s & 2000s
In 1993, Young retired as Detroit's longest-serving mayor, deciding not to seek a sixth term. That year the city elected Dennis Archer, a former Michigan Supreme Court justice. Archer prioritized downtown development and easing tensions with Detroit's suburban neighbors. A referendum to allow casino gambling in the city passed in 1996; several temporary casino facilities opened in 1999, and permanent downtown casinos with hotels opened in 2007–08.
Campus Martius Park, Campus Martius, a reconfiguration of downtown's main intersection as a new park, was opened in 2004. The park has been cited as one of the best public spaces in the United States. The city's Detroit International Riverfront, riverfront on the Detroit River has been the focus of redevelopment, following successful examples of other older industrial cities. In 2001, the first portion of the Detroit International Riverfront, International Riverfront was completed as a part of the city's 300th-anniversary celebration.
2010s
In September 2008, Mayor Kwame Kilpatrick (who had served for six years) resigned following felony convictions. In 2013, Kilpatrick was convicted on 24 federal felony counts, including mail fraud, wire fraud, and Racket (crime), racketeering, In the 2010s, several initiatives were taken by Detroit's citizens and new residents to improve the cityscape by renovating and revitalizing neighborhoods. Such projects include volunteer renovation groups and various Urban agriculture, urban gardening movements. Miles of associated parks and landscaping have been completed in recent years. In 2011, the Port Authority Passenger Terminal opened, with the riverwalk connecting Hart Plaza to the Renaissance Center.
In the 2010s, several initiatives were taken by Detroit's citizens and new residents to improve the cityscape by renovating and revitalizing neighborhoods. Such projects include volunteer renovation groups and various Urban agriculture, urban gardening movements. Miles of associated parks and landscaping have been completed in recent years. In 2011, the Port Authority Passenger Terminal opened, with the riverwalk connecting Hart Plaza to the Renaissance Center.
Geography

Metropolitan area
Detroit is the center of a three-county urban area (with a population of 3,734,090 within an area of according to the 2010 United States Census), six-county metropolitan statistical area (population of 4,296,250 in an area of as of the 2010 census), and a nine-county Combined Statistical Area (population of 5.3 million within ).
Topography
According to the United States Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , of which is land and is water.Metro Detroit
The Detroit metropolitan area, often referred to as Metro Detroit, is a major metropolitan area in the U.S. State of Michigan, consisting of the city of Detroit and its surrounding area. There are varied definitions of the area, including the ...
and Southeast Michigan. It is situated in the Midwestern United States and the Great Lakes region
The Great Lakes region of North America is a binational Canadian–American region that includes portions of the eight U.S. states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania and Wisconsin along with the Canadian p ...
.
The Detroit River International Wildlife Refuge is the only international wildlife preserve in North America, and is uniquely located in the heart of a major metropolitan area. The Refuge includes islands, coastal wetlands, marshes, shoals, and waterfront lands along of the Detroit River
The Detroit River flows west and south for from Lake St. Clair to Lake Erie as a strait in the Great Lakes system. The river divides the metropolitan areas of Detroit, Michigan, and Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, Ontario—an area collectively refe ...
and Western Lake Erie shoreline.
The city slopes gently from the northwest to southeast on a till plain composed largely of glacial and lake clay. The most notable topographical feature in the city is the Detroit Moraine, a broad clay ridge on which the older portions of Detroit and Windsor are located, rising approximately above the river at its highest point. The highest elevation in the city is directly north of Gorham Playground on the northwest side approximately three blocks south of M-102 (Michigan highway), 8 Mile Road, at a height of . Detroit's lowest elevation is along the Detroit River, at a surface height of .
Belle Isle Park is a island park in the Detroit River
The Detroit River flows west and south for from Lake St. Clair to Lake Erie as a strait in the Great Lakes system. The river divides the metropolitan areas of Detroit, Michigan, and Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, Ontario—an area collectively refe ...
, between Detroit and Windsor, Ontario. It is connected to the mainland by the MacArthur Bridge (Detroit), MacArthur Bridge in Detroit. Belle Isle Park contains such attractions as the James Scott Memorial Fountain, the Belle Isle Conservatory, the Detroit Yacht Club on an adjacent island, a half-mile (800 m) beach, a golf course, a nature center, monuments, and gardens. Both the Detroit and Windsor
Windsor may refer to:
Places Australia
* Windsor, New South Wales
** Municipality of Windsor, a former local government area
* Windsor, Queensland, a suburb of Brisbane, Queensland
**Shire of Windsor, a former local government authority around Wi ...
skylines can be viewed at the island’s Sunset Point.
Three road systems cross the city: the original French template, with avenues radiating from the waterfront, and true Mile Road System (Detroit), north–south roads based on the Northwest Ordinance township system. The city is north of Windsor, Ontario. Detroit is the only major city along the Canada–U.S. border in which one travels south in order to cross into Canada.
Detroit has four border crossings: the Ambassador Bridge
The Ambassador Bridge is a tolled international suspension bridge across the Detroit River that connects Detroit, Michigan, United States, with Windsor, Ontario, Canada. Opened in 1929, it is the busiest international border crossing in North ...
and the Detroit–Windsor Tunnel provide motor vehicle thoroughfares, with the Michigan Central Railway Tunnel providing railroad access to and from Canada. The fourth border crossing is the Detroit–Windsor Truck Ferry, near the Windsor Salt Mine and Zug Island. Near Zug Island, the southwest part of the city was developed over a salt mine that is below the surface. The Detroit salt mine run by the Detroit Salt Company has over of roads within.
Climate
Detroit and the rest of southeastern Michigan have a hot-summer humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification, Köppen: ''Dfa'') which is influenced by the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
like other places in the Michigan, state; the city and close-in suburbs are part of USDA Hardiness zone 6b, while the more distant northern and western suburbs generally are included in zone 6a. Winters are cold, with moderate snowfall and temperatures not rising above freezing on an average 44 days annually, while dropping to or below on an average 4.4 days a year; summers are warm to hot with temperatures exceeding on 12 days.
Cityscape
Architecture
 Seen in panorama, Detroit's waterfront shows a variety of architectural styles. The Post-modern architecture, post modern Neo-Gothic spires of the One Detroit Center (1993) were designed to refer to the city's Art Deco skyscrapers. Together with the Renaissance Center, these buildings form a distinctive and recognizable skyline. Examples of the Art Deco style include the Guardian Building and Penobscot Building downtown, as well as the Fisher Building and Cadillac Place in the New Center, Detroit, New Center area near Wayne State University. Among the city's prominent structures are United States' largest Fox Theatre (Detroit), Fox Theatre, the Detroit Opera House, and the Detroit Institute of Arts, all built in the early 20th century.
Seen in panorama, Detroit's waterfront shows a variety of architectural styles. The Post-modern architecture, post modern Neo-Gothic spires of the One Detroit Center (1993) were designed to refer to the city's Art Deco skyscrapers. Together with the Renaissance Center, these buildings form a distinctive and recognizable skyline. Examples of the Art Deco style include the Guardian Building and Penobscot Building downtown, as well as the Fisher Building and Cadillac Place in the New Center, Detroit, New Center area near Wayne State University. Among the city's prominent structures are United States' largest Fox Theatre (Detroit), Fox Theatre, the Detroit Opera House, and the Detroit Institute of Arts, all built in the early 20th century.[ Architecturally significant churches and cathedrals in the city include St. Joseph Roman Catholic Church, Detroit, St. Joseph's, Old St. Mary Roman Catholic Church (Detroit), St. Mary's, the Sweetest Heart of Mary Roman Catholic Church, Sweetest Heart of Mary, and the Cathedral of the Most Blessed Sacrament.][ Little Caesars Arena, a new home for the Detroit Red Wings and the Detroit Pistons, with attached residential, hotel, and retail use, opened on September 5, 2017.]Ambassador Bridge
The Ambassador Bridge is a tolled international suspension bridge across the Detroit River that connects Detroit, Michigan, United States, with Windsor, Ontario, Canada. Opened in 1929, it is the busiest international border crossing in North ...
for a total of of parkway from bridge to bridge. Civic planners envision the pedestrian parks will stimulate residential redevelopment of riverfront properties condemned under eminent domain.
Other major parks include River Rouge Park, River Rouge (in the southwest side), the largest park in Detroit; Palmer (north of Highland Park, Michigan, Highland Park) and Chene Park (on the east river downtown).
Neighborhoods
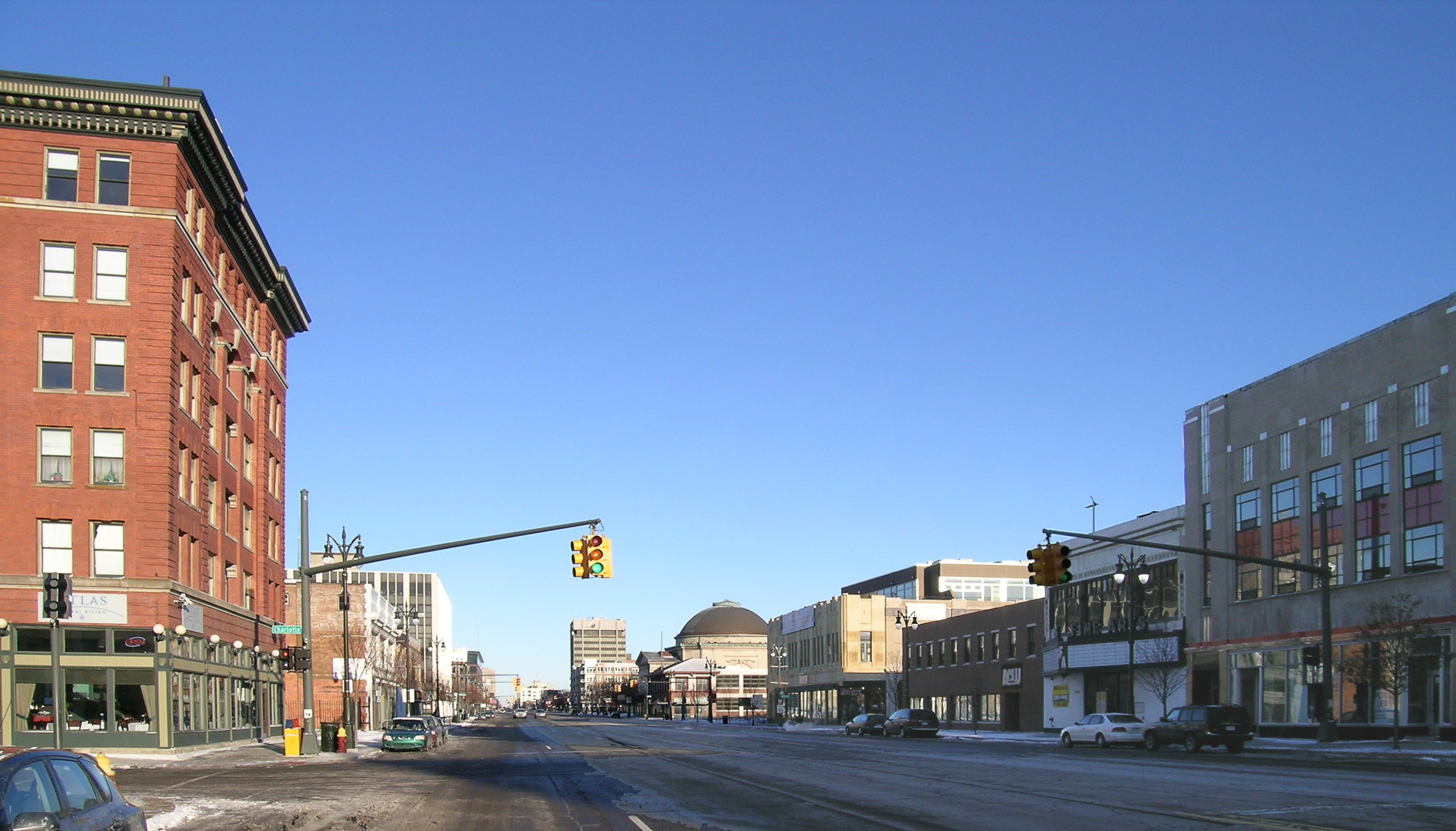


 Detroit has a variety of neighborhood types. The revitalized Downtown, Midtown Detroit, Midtown, Corktown, New Center, Detroit, New Center areas feature many historic buildings and are high density, while further out, particularly in the northeast and on the fringes,
Detroit has a variety of neighborhood types. The revitalized Downtown, Midtown Detroit, Midtown, Corktown, New Center, Detroit, New Center areas feature many historic buildings and are high density, while further out, particularly in the northeast and on the fringes,[ high vacancy levels are problematic, for which a number of solutions have been proposed. In 2007, ]Downtown Detroit
Downtown Detroit is the central business district and a residential area of the city of Detroit, Michigan, United States. Locally, downtown tends to refer to the 1.4 square mile region bordered by M-10 (Lodge Freeway) to the west, Interstate 75 ( ...
was recognized as the best city neighborhood in which to retire among the United States' largest metro areas by CNNMoney editors.
Lafayette Park, Detroit, Lafayette Park is a Planning and development in Detroit, revitalized neighborhood on the city's East Jefferson Avenue Residential TR, east side, part of the Ludwig Mies van der Rohe residential district.[Vitullo-Martin, Julio, (December 22, 2007)]
"The Biggest Mies Collection: His Lafayette Park residential development thrives in Detroit"
''The Wall Street Journal''. Retrieved July 5, 2012. The development was originally called the Gratiot Park. Planned by Mies van der Rohe, Ludwig Hilberseimer and Alfred Caldwell it includes a landscaped, park with no through traffic, in which these and other low-rise apartment buildings are situated.[ Immigrants have contributed to the city's neighborhood revitalization, especially in southwest Detroit.][Williams, Corey (February 28, 2008]
New Latino Wave Helps Revitalize Detroit
''USA Today''. Retrieved July 5, 2012.
The city has numerous neighborhoods consisting of vacant properties resulting in low inhabited density in those areas, stretching city services and infrastructure. These neighborhoods are concentrated in the northeast and on the city's fringes.[ A 2009 parcel survey found about a quarter of residential lots in the city to be undeveloped or vacant, and about 10% of the city's housing to be unoccupied.][Detroit Parcel Survey]
Retrieved on July 23, 2011.[Associated Press (February 10, 2010)]
''Mlive.com''. Retrieved July 5, 2012.[Kavanaugh, Kelli B. (March 2, 2010]
Intensive property survey captures state of Detroit housing, vacancy
''Model D''. Retrieved July 5, 2012.
To deal with vacancy issues, the city has begun demolishing the derelict houses, razing 3,000 of the total 10,000 in 2010, but the resulting low density creates a strain on the city's infrastructure. To remedy this, a number of solutions have been proposed including resident relocation from more sparsely populated neighborhoods and converting unused space to urban agricultural use, including Hantz Woodlands, though the city expects to be in the planning stages for up to another two years.[. ''City of Detroit''. Retrieved July 5, 2012.]
Public funding and private investment have also been made with promises to rehabilitate neighborhoods. In April 2008, the city announced a $300-million stimulus plan to create jobs and revitalize neighborhoods, financed by city bonds and paid for by earmarking about 15% of the wagering tax.[ Private organizations have pledged substantial funding to the efforts.][. ''DEGA''. Retrieved on January 2, 2009.][Detroit Neighborhood Fund]
. ''Community Foundation for Southeast Michigan''. Retrieved January 2, 2009. Additionally, the city has cleared a section of land for large-scale neighborhood construction, which the city is calling the ''Far Eastside Plan''.[Rose, Judy (May 11, 2003)]
Detroit to revive 1 neighborhood at a time
''Chicago Tribune''. Retrieved November 29, 2011. In 2011, Mayor Dave Bing announced a plan to categorize neighborhoods by their needs and prioritize the most needed services for those neighborhoods.
Demographics
In the 2020 United States census, 2020 United States Census, the city had 639,111 residents, ranking it the List of United States cities by population, 27th most populous city in the United States.
2020 census
''Note: the US Census treats Hispanic/Latino as an ethnic category. This table excludes Latinos from the racial categories and assigns them to a separate category. Hispanics/Latinos can be of any race.''
Of the large shrinking cities in the United States, Detroit has had the most dramatic decline in the population of the past 70 years (down 1,210,457) and the second-largest percentage decline (down 65.4%). While the drop in Detroit's population has been ongoing since 1950, the most dramatic period was the significant 25% decline between the 2000 United States Census, 2000 and 2010 Census.
Religion
According to a 2014 study, 67% of the population of the city identified themselves as Christians, with 49% professing attendance at Protestant churches, and 16% professing Roman Catholic beliefs, while 24% claim Irreligion, no religious affiliation. Other religions collectively make up about 8% of the population.
Income and employment
The loss of industrial and working-class jobs in the city has resulted in high rates of poverty and associated problems.[Hopkins, Carol (March 28, 2010]
Oakland still ranks among the nation's wealthiest counties
. ''Daily Tribune''. Retrieved November 27, 2011. Detroit dominates Wayne County, which has an average household income of about $38,000, compared to Oakland County's $62,000.
Race and ethnicity
 Beginning with the rise of the automobile industry, Detroit's population increased more than sixfold during the first half of the 20th century as an influx of European, Middle Eastern (Lebanese Americans, Lebanese, Assyrian Americans, Assyrian/Chaldean), and Southern migrants brought their families to the city.
Beginning with the rise of the automobile industry, Detroit's population increased more than sixfold during the first half of the 20th century as an influx of European, Middle Eastern (Lebanese Americans, Lebanese, Assyrian Americans, Assyrian/Chaldean), and Southern migrants brought their families to the city.[Baulch, Vivian M. (September 4, 1999)]
Michigan's greatest treasure – Its people
. Michigan History, ''The Detroit News''. Retrieved on October 22, 2007. With this economic boom following World War I, the African American population grew from a mere 6,000 in 1910 to more than 120,000 by 1930. This influx of thousands of African Americans in the 20th century became known as the Great Migration. Perhaps one of the most overt examples of neighborhood discrimination occurred in 1925 when African American physician Ossian Sweet found his home surrounded by an angry mob of his hostile white neighbors violently protesting his new move into a traditionally white neighborhood. Ossian Sweet, Sweet and ten of his family members and friends were put on trial for murder as one of the mob members throwing rocks at the newly purchased house was shot and killed by someone firing out of a second-floor window. Many middle-class families experienced the same kind of hostility as they sought the security of homeownership and the potential for upward mobility.
Detroit has a relatively large Mexican-American population. In the early 20th century, thousands of Mexicans came to Detroit to work in agricultural, automotive, and steel jobs. During the Mexican Repatriation of the 1930s many Mexicans in Detroit were willingly repatriated or forced to repatriate. By the 1940s much of the Mexican community began to settle what is now Mexicantown, Detroit, Mexicantown.
 After World War II, many people from Appalachia also settled in Detroit. Appalachians formed communities and their children acquired southern accents. Many Lithuanians also settled in Detroit during the World War II era, especially on the city's Southwest side in the West Vernor-Junction Historic District, West Vernor area, where the renovated Lithuanian Hall reopened in 2006.
By 1940, 80% of Detroit deeds contained restrictive covenants prohibiting African Americans from buying houses they could afford. These discriminatory tactics were successful as a majority of black people in Detroit resorted to living in all-black neighborhoods such as Black Bottom, Detroit, Black Bottom and Paradise Valley. At this time, white people still made up about 90.4% of the city's population.
After World War II, many people from Appalachia also settled in Detroit. Appalachians formed communities and their children acquired southern accents. Many Lithuanians also settled in Detroit during the World War II era, especially on the city's Southwest side in the West Vernor-Junction Historic District, West Vernor area, where the renovated Lithuanian Hall reopened in 2006.
By 1940, 80% of Detroit deeds contained restrictive covenants prohibiting African Americans from buying houses they could afford. These discriminatory tactics were successful as a majority of black people in Detroit resorted to living in all-black neighborhoods such as Black Bottom, Detroit, Black Bottom and Paradise Valley. At this time, white people still made up about 90.4% of the city's population.redlining
In the United States, redlining is a discriminatory practice in which services (financial and otherwise) are withheld from potential customers who reside in neighborhoods classified as "hazardous" to investment; these neighborhoods have signif ...
).suburbanization
Suburbanization is a population shift from central urban areas into suburbs, resulting in the formation of (sub)urban sprawl. As a consequence of the movement of households and businesses out of the city centers, low-density, peripheral urba ...
" led to a complete population shift.
The Detroit riot of 1967 is considered to be one of the greatest racial turning points in the history of the city. The ramifications of the uprising were widespread as there were many allegations of white police brutality towards Black Americans and over $36 million of insured property was lost. Discrimination and deindustrialization in tandem with racial tensions that had been intensifying in the previous years boiled over and led to an event considered to be the most damaging in Detroit's history.
The population of Latinos significantly increased in the 1990s due to immigration from Jalisco. By 2010 Detroit had 48,679 Hispanics, including 36,452 Mexicans: a 70% increase from 1990.[Denvir, Daniel]
"The Paradox of Mexicantown: Detroit's Uncomfortable Relationship With the Immigrants it Desperately Needs"
Archive
''The Atlantic Cities''. September 24, 2012. Retrieved on January 15, 2013. While African Americans previously comprised only 13% of Michigan's population, by 2010 they made up nearly 82% of Detroit's population. The next largest population groups were white people, at 10%, and Hispanics, at 6%. In 2001, 103,000 Jews, or about 1.9% of the population, were living in the Detroit area, in both Detroit and Ann Arbor, Michigan, Ann Arbor.
According to the 2010 census, segregation in Detroit has decreased in absolute and relative terms and in the first decade of the 21st century, about two-thirds of the total black population in the metropolitan area resided within the city limits of Detroit.[Wisely, John]
"Number of whites living in Detroit goes up for first time in 60 years"
''Detroit Free Press'' at KSDK. September 29, 2010. Retrieved on January 7, 2013. Gentrification in Detroit has become a rather controversial issue as reinvestment will hopefully lead to economic growth and an increase in population; however, it has already forced many black families to relocate to the suburbs. Despite revitalization efforts, Detroit remains one of the most Racial segregation in the United States, racially segregated cities in the United States.
Asians and Asian Americans
 As of 2002, of all of the municipalities in the Wayne County-Oakland County, Michigan, Oakland County-Macomb County, Michigan, Macomb County area, Detroit had the second-largest Asian population. As of that year, Detroit's percentage of Asians was 1%, far lower than the 13.3% of Troy, Michigan, Troy.
As of 2002, of all of the municipalities in the Wayne County-Oakland County, Michigan, Oakland County-Macomb County, Michigan, Macomb County area, Detroit had the second-largest Asian population. As of that year, Detroit's percentage of Asians was 1%, far lower than the 13.3% of Troy, Michigan, Troy.[Metzger, Kurt and Jason Booza]
"Asians in the United States, Michigan and Metropolitan Detroit"
Center for Urban Studies, Wayne State University. January 2002 Working Paper Series, No. 7. p. 8. Retrieved on November 6, 2013. By 2000 Troy had the largest Asian American population in the tri-county area, surpassing Detroit.[Metzger, Kurt and Jason Booza]
"Asians in the United States, Michigan and Metropolitan Detroit"
Center for Urban Studies, Wayne State University. January 2002 Working Paper Series, No. 7. p. 10. Retrieved on November 6, 2013.
There are four areas in Detroit with significant Asian and Asian American populations. Northeast Detroit has a population of Hmong American, Hmong with a smaller group of Lao American, Lao people. A portion of Detroit next to eastern Hamtramck includes Bangladeshi Americans, Indian Americans, and Pakistani Americans; nearly all of the Bangladeshi population in Detroit lives in that area. Many of those residents own small businesses or work in blue-collar jobs, and the population is mostly Muslim. The area north of Downtown Detroit
Downtown Detroit is the central business district and a residential area of the city of Detroit, Michigan, United States. Locally, downtown tends to refer to the 1.4 square mile region bordered by M-10 (Lodge Freeway) to the west, Interstate 75 ( ...
, including the region around the Henry Ford Hospital, the Detroit Medical Center, and Wayne State University, has transient Asian national origin residents who are university students or hospital workers. Few of them have permanent residency after schooling ends. They are mostly Chinese and Indian but the population also includes Filipinos, Koreans, and Pakistanis. In Southwest Detroit and western Detroit there are smaller, scattered Asian communities including an area in the westside adjacent to Dearborn, Michigan, Dearborn and Redford Township that has a mostly Indian Asian population, and a community of Vietnamese and Laotians in Southwest Detroit.[
, the city has one of the U.S.'s largest concentrations of Hmong Americans.][Archambault, Dennis]
"Young and Asian in Detroit"
Archive
''Model D Media''. Issue Media Group, LLC. Tuesday November 14, 2006. Retrieved on November 5, 2012.
Crime
Detroit has gained notoriety for its high amount of crime, having struggled with it for decades. The number of homicides peaked in 1974 at 714 and again in 1991 with 615. The murder rate for the city has gone up and down throughout the years averaging over 400 murders with a population of over 1,000,000 residents. The crime rate, however, has been above the national average since the 1970s.
Crime has since decreased and, in 2014, the murder rate was 43.4 per 100,000, lower than in St. Louis.
The city's downtown typically has lower crime than national and state averages.[Booza, Jason C. (July 23, 2008]
Reality v. Perceptions: An Analysis of Crime and Safety in Downtown Detroit
Archive
Michigan Metropolitan Information Center, ''Wayne State University Center for Urban Studies''. Retrieved August 14, 2011. According to a 2007 analysis, Detroit officials note about 65 to 70 percent of homicides in the city were drug related,[
Although the rate of violent crime dropped 11% in 2008, violent crime in Detroit has not declined as much as the national average from 2007 to 2011.]Michigan
Michigan () is a state in the Great Lakes region of the upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the 10th-largest state by population, the 11th-largest by area, and the ...
in 2015 occurred in Detroit. Annual statistics released by the Detroit Police Department for 2016 indicate that while the city's overall crime rate declined that year, the murder rate rose from 2015.[Williams, Corey (January 3, 2017)]
"Crime in Detroit is down overall in 2016; homicide up by 7"
''Detroit Free Press''. Retrieved January 13, 2017. In 2016 there were 302 homicides in Detroit, a 2.37% increase in the number of murder victims from the preceding year.Detroit River
The Detroit River flows west and south for from Lake St. Clair to Lake Erie as a strait in the Great Lakes system. The river divides the metropolitan areas of Detroit, Michigan, and Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, Ontario—an area collectively refe ...
are also patrolled by the United States Border Patrol.
Economy
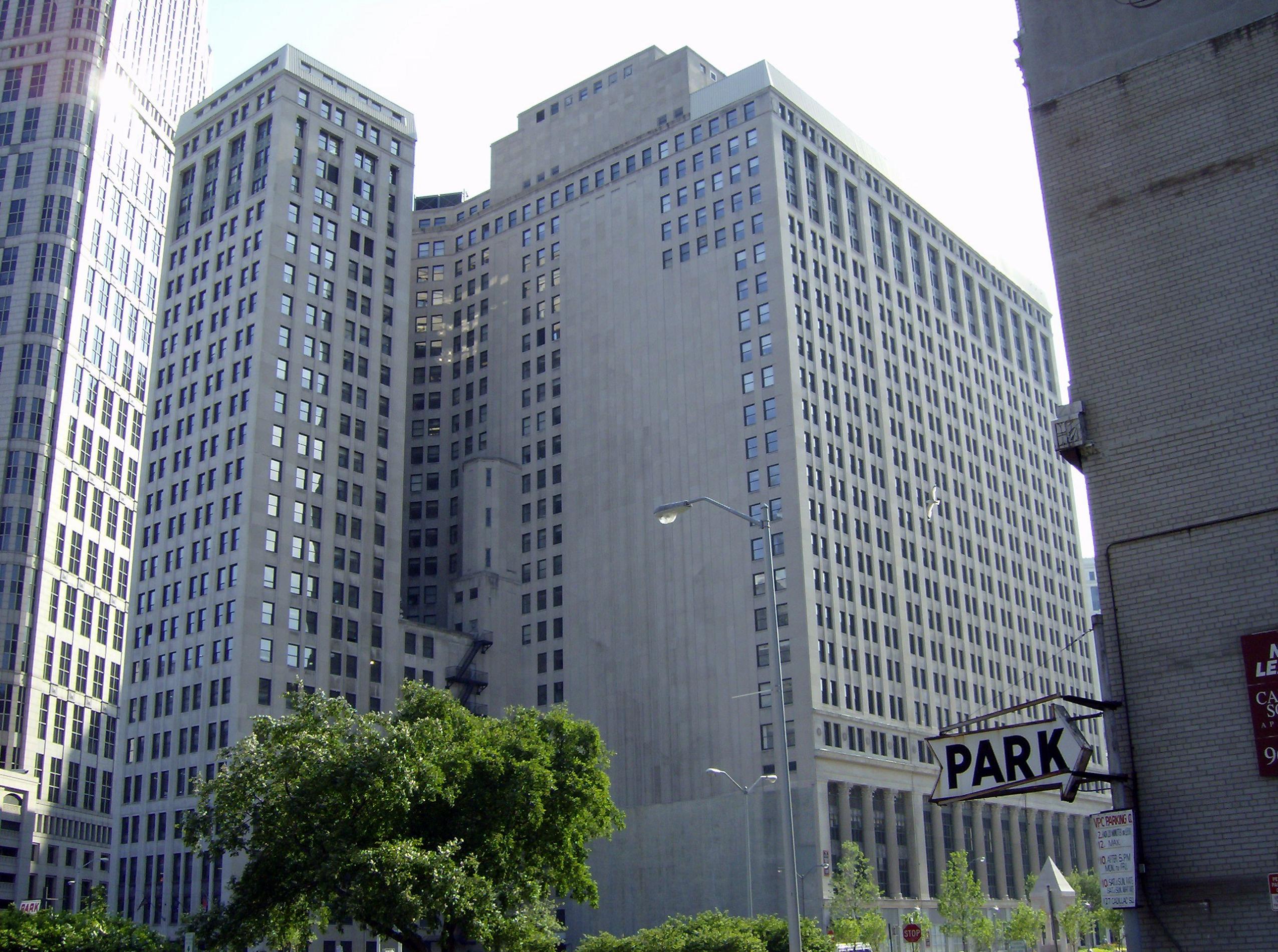

 Several major corporations are based in the city, including three Fortune 500 companies. The most heavily represented sectors are manufacturing (particularly automotive), finance, technology, and health care. The most significant companies based in Detroit include
Several major corporations are based in the city, including three Fortune 500 companies. The most heavily represented sectors are manufacturing (particularly automotive), finance, technology, and health care. The most significant companies based in Detroit include General Motors
The General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. It is the largest automaker in the United States and ...
, Quicken Loans, Ally Financial, Compuware, Shinola Detroit, Shinola, American Axle, Little Caesars, DTE Energy, Lowe Campbell Ewald, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan, and Rossetti Architects.
About 80,500 people work in downtown Detroit, comprising one-fifth of the city's employment base.[The Urban Markets Initiative, Brookings Institution Metropolitan Policy Program, The Social Compact Inc., University of Michigan Graduate Real Estate Program, (October 2006]
Downtown Detroit in Focus: A Profile of Market Opportunity
. ''Detroit Economic Growth Corporation'' and ''Downtown Detroit Partnership''. Retrieved on June 14, 2008. Aside from the numerous Detroit-based companies listed above, downtown contains large offices for Comerica, Chrysler, Fifth Third Bank, HP Enterprise Services, HP Enterprise, Deloitte, PricewaterhouseCoopers, KPMG, and Ernst & Young. Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company (commonly known as Ford) is an American multinational automobile manufacturer headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan, United States. It was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. The company sells automobi ...
is in the adjacent city of Dearborn, Michigan, Dearborn.
Thousands of more employees work in Midtown, north of the central business district. Midtown's anchors are the city's largest single employer Detroit Medical Center, Wayne State University, and the Henry Ford Health System in New Center. Midtown is also home to watchmaker Shinola Detroit, Shinola and an array of small and startup company, startup companies. New Center, Detroit, New Center bases Tech Town (Detroit), TechTown, a research and business incubator hub that is part of the WSU system. Like downtown, Corktown, Detroit, Corktown Is experiencing growth with the new Ford Corktown Campus under development.
Midtown also has a fast-growing retailing and restaurant scene.
A number of the city's downtown employers are relatively new, as there has been a marked trend of companies moving from satellite suburbs around Metropolitan Detroit into the downtown core. Compuware completed its Compuware World Headquarters, world headquarters in downtown in 2003. OnStar, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan, Blue Cross Blue Shield, and HP Enterprise Services are at the Renaissance Center. PricewaterhouseCoopers Plaza offices are adjacent to Ford Field, and Ernst & Young completed its office building at One Kennedy Square in 2006. Perhaps most prominently, in 2010, Quicken Loans, one of the largest mortgage lenders, relocated its world headquarters and 4,000 employees to downtown Detroit, consolidating its suburban offices.[Howes, Daniel (November 12, 2007)]
Quicken moving to downtown Detroit
''The Detroit News''. Retrieved on November 12, 2007. In July 2012, the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office opened its Elijah J. McCoy Satellite Office in the Rivertown/Warehouse District as its first location outside Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
's metropolitan area.
In April 2014, the United States Department of Labor reported the city's unemployment rate at 14.5%.[Morice, Zach (September 21, 2007]
Planting community in fallow fields
. American Institute of Architects. Retrieved on December 23, 2009. even though it has struggled with finances, the city issued bonds in 2008 to provide funding for ongoing work to demolish blighted properties.[The Urban Markets Initiative, Brookings Institution Metropolitan Policy Program The Social Compact, Inc. University of Michigan Graduate Real Estate Program (October 2006]
. Downtown Detroit Partnership. Retrieved on July 10, 2010.
Despite the city's recent financial issues, many developers remain unfazed by Detroit's problems. Midtown is one of the most successful areas within Detroit to have a residential occupancy rate of 96%. Numerous Planning and development in Detroit, developments have been recently completed or are in various stages of construction. These include the $82 million reconstruction of downtown's David Whitney Building (now an Aloft Hotel and luxury residences), the Woodward Garden Block Development in Midtown, the residential conversion of the David Broderick Tower in downtown, the rehabilitation of the Book Cadillac Hotel (now a Westin and luxury condos) and Fort Shelby Hotel (now Doubletree) also in downtown, and various smaller projects.[ A study in 2007 found out that Downtown's new residents are predominantly young professionals (57% are ages 25 to 34, 45% have bachelor's degrees, and 34% have a master's or professional degree),][ a trend which has hastened over the last decade. Since 2006, $9 billion has been invested in downtown and surrounding neighborhoods; $5.2 billion of which has come in 2013 and 2014. Construction activity, particularly rehabilitation of historic downtown buildings, has increased markedly. The number of vacant downtown buildings has dropped from nearly 50 to around 13.]
Arts and culture

 In the central portions of Detroit, the population of young professionals, artists, and other transplants is growing and retail is expanding.
In the central portions of Detroit, the population of young professionals, artists, and other transplants is growing and retail is expanding.[Harrison, Sheena (June 25, 2007)]
DEGA enlists help to spur Detroit retail
. ''Crain's Detroit Business''. Retrieved on November 28, 2007. "New downtown residents are largely young professionals according to Social Compact". This dynamic is luring additional new residents, and former residents returning from other cities, to the city's Downtown Detroit, Downtown along with the revitalized Midtown Detroit, Midtown and New Center, Detroit, New Center areas.[Reppert, Joe (October 2007]
Detroit Neighborhood Market Drill Down
. ''Social Compact''. Retrieved on July 10, 2010.
A desire to be closer to the urban scene has also attracted some young professionals to reside in inner ring suburbs such as Ferndale, Michigan, Ferndale and Royal Oak, Michigan, Royal Oak, Michigan. Detroit's proximity to Windsor, Ontario, provides for views and nightlife, along with Ontario's minimum drinking age of 19.[Bailey, Ruby L (August 22, 2007). The D is a draw: Most suburbanites are repeat visitors. ''Detroit Free Press''. New Detroit Free Press-Local 4 poll conducted by Selzer and Co., finds, "nearly two-thirds of residents of suburban Wayne, Oakland, and Macomb counties say they at least occasionally dine, attend cultural events or take in professional games in Detroit."]
Nicknames
Known as the world's automotive center, "Detroit" is a Metonymy, metonym for Automotive industry in the United States, that industry.Arsenal of Democracy
"Arsenal of Democracy" was the central phrase used by U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt in a radio broadcast on the threat to national security, delivered on December 29, 1940—nearly a year before the United States entered the Second World ...
" supporting the Allied powers during World War II.Motown
Motown Records is an American record label owned by the Universal Music Group. It was founded by Berry Gordy Jr. as Tamla Records on June 7, 1958, and incorporated as Motown Record Corporation on April 14, 1960. Its name, a portmanteau of ''moto ...
''. Other nicknames arose in the 20th century, including ''City of Champions'', beginning in the 1930s for its successes in individual and team sport;[ ''The D''; ''Hockeytown'' (a trademark owned by the city's National Hockey League, NHL club, the Detroit Red Wings, Red Wings); ''Rock City'' (after the Kiss (band), Kiss song "Detroit Rock City"); and ''The Area code 313, 313'' (its telephone area code).][
]
Music


 Live music has been a prominent feature of Detroit's nightlife since the late 1940s, bringing the city recognition under the nickname "Motown". The metropolitan area has many nationally prominent Theatre in Detroit, live music venues. Concerts hosted by Live Nation perform throughout the Detroit area. Large concerts are held at DTE Energy Music Theatre. The city's Theatre in Detroit, theatre venue circuit is the United States' second largest and hosts Broadway theatre, Broadway performances.
The city of Detroit has a rich musical heritage and has contributed to a number of different genres over the decades leading into the new millennium.
Live music has been a prominent feature of Detroit's nightlife since the late 1940s, bringing the city recognition under the nickname "Motown". The metropolitan area has many nationally prominent Theatre in Detroit, live music venues. Concerts hosted by Live Nation perform throughout the Detroit area. Large concerts are held at DTE Energy Music Theatre. The city's Theatre in Detroit, theatre venue circuit is the United States' second largest and hosts Broadway theatre, Broadway performances.
The city of Detroit has a rich musical heritage and has contributed to a number of different genres over the decades leading into the new millennium.[ Important music events in the city include the Detroit International Jazz Festival, the Detroit Electronic Music Festival, the Motor City Music Conference (MC2), the Urban Organic Music Conference, the Concert of Colors, and the hip-hop Summer Jamz festival.][
In the 1940s, Detroit blues artist John Lee Hooker became a long-term resident in the city's southwest Delray, Detroit, Delray neighborhood. Hooker, among other important blues musicians, migrated from his home in Mississippi, bringing the Delta blues to northern cities like Detroit. Hooker recorded for Fortune Records, the biggest pre-Motown blues/soul label. During the 1950s, the city became a center for jazz, with stars performing in the Black Bottom, Detroit, Black Bottom neighborhood.][ Prominent emerging jazz musicians included trumpeter Donald Byrd, who attended Cass Tech and performed with Art Blakey and the Jazz Messengers early in his career, and saxophonist Pepper Adams, who enjoyed a solo career and accompanied Byrd on several albums. The Graystone International Jazz Museum documents jazz in Detroit.
Other prominent Motor City R&B stars in the 1950s and early 1960s were Nolan Strong, Andre Williams (musician), Andre Williams and Nathaniel Mayer – who all scored local and national hits on the Fortune Records label. According to Smokey Robinson, Strong was a primary influence on his voice as a teenager. The Fortune label, a family-operated label on Third Avenue in Detroit, was owned by the husband-and-wife team of Jack Brown and Devora Brown. Fortune, which also released country, gospel and rockabilly LPs and 45s, laid the groundwork for Motown, which became Detroit's most legendary record label.][
Local artists and bands rose to prominence in the 1960s and '70s, including the MC5, Glenn Frey, The Stooges, Bob Seger, Amboy Dukes featuring Ted Nugent, Mitch Ryder and The Detroit Wheels, Rare Earth (band), Rare Earth, Alice Cooper, and Suzi Quatro. The group Kiss (band), Kiss emphasized the city's connection with rock in the song "Detroit Rock City" and the movie produced in 1999. In the 1980s, Detroit was an important center of the hardcore punk rock underground with many nationally known bands coming out of the city and its suburbs, such as The Necros, The Meatmen, and Negative Approach.][
Detroit is cited as the birthplace of techno music in the early 1980s.]
Entertainment and performing arts
 Major theaters in Detroit include the Fox Theatre (Detroit), Fox Theatre (5,174 seats), Music Hall Center for the Performing Arts (1,770 seats), the Gem Theatre (451 seats), Detroit Masonic Temple, Masonic Temple Theatre (4,404 seats), the Detroit Opera House (2,765 seats), the Fisher Theatre (2,089 seats), The Fillmore Detroit (2,200 seats), Saint Andrew's Hall, the Majestic Theater (Detroit, Michigan), Majestic Theater, and Orchestra Hall (Detroit), Orchestra Hall (2,286 seats), which hosts the renowned Detroit Symphony Orchestra. The Nederlander Organization, the largest controller of Broadway productions in New York City, originated with the purchase of the Detroit Opera House in 1922 by the Nederlander family.
Major theaters in Detroit include the Fox Theatre (Detroit), Fox Theatre (5,174 seats), Music Hall Center for the Performing Arts (1,770 seats), the Gem Theatre (451 seats), Detroit Masonic Temple, Masonic Temple Theatre (4,404 seats), the Detroit Opera House (2,765 seats), the Fisher Theatre (2,089 seats), The Fillmore Detroit (2,200 seats), Saint Andrew's Hall, the Majestic Theater (Detroit, Michigan), Majestic Theater, and Orchestra Hall (Detroit), Orchestra Hall (2,286 seats), which hosts the renowned Detroit Symphony Orchestra. The Nederlander Organization, the largest controller of Broadway productions in New York City, originated with the purchase of the Detroit Opera House in 1922 by the Nederlander family.
Tourism
 Because of its Culture of Detroit, unique culture, Architecture of metropolitan Detroit, distinctive architecture, and Planning and development in Detroit, revitalization and urban renewal efforts in the 21st century, Detroit has enjoyed increased prominence as a tourist destination in recent years. ''The New York Times'' listed Detroit as the ninth-best destination in its list of ''52 Places to Go in 2017'',
Because of its Culture of Detroit, unique culture, Architecture of metropolitan Detroit, distinctive architecture, and Planning and development in Detroit, revitalization and urban renewal efforts in the 21st century, Detroit has enjoyed increased prominence as a tourist destination in recent years. ''The New York Times'' listed Detroit as the ninth-best destination in its list of ''52 Places to Go in 2017'',["52 Places to Go in 2017"](_blank)
NYT Travel, ''The New York Times''. January 4, 2017. Retrieved on February 7, 2018. while travel guide publisher ''Lonely Planet'' named Detroit the second-best city in the world to visit in 2018.["Top 10 cities to visit in 2018"](_blank)
Lonely Planet. Retrieved on February 7, 2018.
Many of the area's prominent museums are in the historic Detroit Cultural Center, cultural center neighborhood around Wayne State University and the College for Creative Studies. These museums include the Detroit Institute of Arts, the Detroit Historical Museum, Charles H. Wright Museum of African American History, the Detroit Science Center, as well as the main branch of the Detroit Public Library. Other cultural highlights include Hitsville U.S.A., Motown Historical Museum, the Ford Piquette Avenue Plant museum, the Pewabic Pottery studio and school, the Tuskegee Airmen Museum, Fort Wayne (Detroit), Fort Wayne, the Dossin Great Lakes Museum, the Museum of Contemporary Art Detroit (MOCAD), the Contemporary Art Institute of Detroit (CAID), and the Belle Isle Conservatory.
In 2010, the G.R. N'Namdi Gallery opened in a complex in Midtown. Important history of America and the Detroit area are exhibited at The Henry Ford in Dearborn, Michigan, Dearborn, the United States' largest indoor-outdoor museum complex. The Detroit Historical Society provides information about tours of area churches, skyscrapers, and mansions. Inside Detroit, meanwhile, hosts tours, educational programming, and a downtown welcome center. Other sites of interest are the Detroit Zoo in Royal Oak, Michigan, Royal Oak, the Cranbrook Art Museum in Bloomfield Hills, Michigan, Bloomfield Hills, the Anna Scripps Whitcomb Conservatory on Belle Isle Park, Belle Isle, and Walter P. Chrysler Museum in Auburn Hills, Michigan, Auburn Hills.[
The city's Greektown Historic District, Greektown and three downtown casino resort hotels serve as part of an entertainment hub. The Eastern Market Historic District, Eastern Market farmer's distribution center is the largest open-air flowerbed market in the United States and has more than 150 foods and specialty businesses. On Saturdays, about 45,000 people shop the city's historic Eastern Market Historic District, Eastern Market.][. ''Model D Media'' (April 5, 2008). Retrieved January 24, 2011.] The Midtown, Detroit, Midtown and the New Center area are centered on Wayne State University and Henry Ford Hospital. Midtown has about 50,000 residents and attracts millions of visitors each year to its museums and cultural centers;[. ''Model D Media'' (April 4, 2008). Retrieved on January 24, 2011.] for example, the Detroit Festival of the Arts in Midtown draws about 350,000 people.[
] Annual summer events include the Detroit Electronic Music Festival, Electronic Music Festival, Detroit International Jazz Festival, International Jazz Festival, the Woodward Dream Cruise, the African World Festival, the country music Hoedown, Noel Night, and Dally in the Alley. Within downtown, Campus Martius Park hosts large events, including the annual Motown Winter Blast. As the world's traditional automotive center, the city hosts the North American International Auto Show. Held since 1924, America's Thanksgiving Parade is one of the nation's largest. River Days, a five-day summer festival on the Detroit International Riverfront, International Riverfront lead up to the Windsor–Detroit International Freedom Festival fireworks, which draw super sized-crowds ranging from hundreds of thousands to over three million people.
Annual summer events include the Detroit Electronic Music Festival, Electronic Music Festival, Detroit International Jazz Festival, International Jazz Festival, the Woodward Dream Cruise, the African World Festival, the country music Hoedown, Noel Night, and Dally in the Alley. Within downtown, Campus Martius Park hosts large events, including the annual Motown Winter Blast. As the world's traditional automotive center, the city hosts the North American International Auto Show. Held since 1924, America's Thanksgiving Parade is one of the nation's largest. River Days, a five-day summer festival on the Detroit International Riverfront, International Riverfront lead up to the Windsor–Detroit International Freedom Festival fireworks, which draw super sized-crowds ranging from hundreds of thousands to over three million people.[Fifth Third Bank rocks the Winter Blast. ''Michigan Chronicle''. (March 14, 2006).]
An important civic sculpture in Detroit is ''The Spirit of Detroit'' by Marshall Fredericks at the Coleman Young Municipal Center. The image is often used as a symbol of Detroit and the statue itself is occasionally dressed in sports jerseys to celebrate when a Detroit team is doing well. A Monument to Joe Louis, memorial to Joe Louis at the intersection of Jefferson and Woodward Avenues was dedicated on October 1, 1986. The sculpture, commissioned by ''Sports Illustrated'' and executed by Robert Graham (sculptor), Robert Graham, is a long arm with a fisted hand suspended by a pyramidal framework.
Artist Tyree Guyton created the controversial street art exhibit known as the Heidelberg Project in 1986, using found objects including cars, clothing and shoes found in the neighborhood near and on Heidelberg Street on the near East Side of Detroit.[
''Time'' named Detroit as one of the fifty World's Greatest Places of 2022 to explore.]
Sports
Detroit is one of 13 U.S. metropolitan areas that are home to professional teams representing the four major sports in North America. Since 2017, all of these teams play in the city limits of Detroit itself, a distinction shared with only three other U.S. cities. Detroit is the only U.S. city to have its four major sports teams play within its downtown district.
There are three active major sports venues in the city: Comerica Park (home of the Major League Baseball team Detroit Tigers), Ford Field (home of the National Football League, NFL's Detroit Lions), and Little Caesars Arena (home of the National Hockey League, NHL's Detroit Red Wings and the National Basketball Association, NBA's Detroit Pistons). A 1996 marketing campaign promoted the nickname "Hockeytown".[
] The Detroit Tigers have won four World Series titles (1935 World Series, 1935, 1945 World Series, 1945, 1968 World Series, 1968, and 1984 World Series, 1984). The Detroit Red Wings have won 11 Stanley Cups (1936 Stanley Cup Finals, 1935–36, 1937 Stanley Cup Finals, 1936–37, 1943 Stanley Cup Finals, 1942–43, 1950 Stanley Cup Finals, 1949–50, 1952 Stanley Cup Finals, 1951–52, 1954 Stanley Cup Finals, 1953–54, 1955 Stanley Cup Finals, 1954–55, 1997 Stanley Cup Finals, 1996–97, 1998 Stanley Cup Finals, 1997–98, 2002 Stanley Cup Finals, 2001–02, 2008 Stanley Cup Finals, 2007–08) (the most by an American NHL franchise). The Detroit Lions have won 4 NFL titles (1935 NFL Championship Game, 1935, 1952 NFL Championship Game, 1952, 1953 NFL Championship Game, 1953, 1957 NFL Championship Game, 1957) . The Detroit Pistons have won three NBA titles (1989 NBA Finals, 1989, 1990 NBA Finals, 1990, 2004 NBA Finals, 2004).
The Detroit Tigers have won four World Series titles (1935 World Series, 1935, 1945 World Series, 1945, 1968 World Series, 1968, and 1984 World Series, 1984). The Detroit Red Wings have won 11 Stanley Cups (1936 Stanley Cup Finals, 1935–36, 1937 Stanley Cup Finals, 1936–37, 1943 Stanley Cup Finals, 1942–43, 1950 Stanley Cup Finals, 1949–50, 1952 Stanley Cup Finals, 1951–52, 1954 Stanley Cup Finals, 1953–54, 1955 Stanley Cup Finals, 1954–55, 1997 Stanley Cup Finals, 1996–97, 1998 Stanley Cup Finals, 1997–98, 2002 Stanley Cup Finals, 2001–02, 2008 Stanley Cup Finals, 2007–08) (the most by an American NHL franchise). The Detroit Lions have won 4 NFL titles (1935 NFL Championship Game, 1935, 1952 NFL Championship Game, 1952, 1953 NFL Championship Game, 1953, 1957 NFL Championship Game, 1957) . The Detroit Pistons have won three NBA titles (1989 NBA Finals, 1989, 1990 NBA Finals, 1990, 2004 NBA Finals, 2004).[ With the Pistons' first of three NBA titles in 1989, the city of Detroit has won titles in all four of the major professional sports leagues. Two new downtown stadiums for the Detroit Tigers and Detroit Lions opened in 2000 and 2002, respectively, returning the Lions to the city proper.
In college sports, Detroit's central location within the Mid-American Conference has made it a frequent site for the league's championship events. While the MAC Basketball Tournament moved permanently to Cleveland, Ohio, Cleveland starting in 2000, the MAC Football Championship Game has been played at Ford Field in Detroit since 2004, and annually attracts 25,000 to 30,000 fans. The University of Detroit Mercy has an NCAA Division I program, and Wayne State University has both NCAA Division I and NCAA Division II, II programs. The NCAA football Quick Lane Bowl is held at Ford Field each December.
Detroit's professional soccer team is Detroit City FC. Founded in 2012 as a semi-professional soccer club, the team now plays professional soccer in the USL Championship (USLC). Nicknamed, ''Le Rouge'', the club are two-time champions of NISA since joining in 2020. They play their home matches in Keyworth Stadium, which is located in the Detroit enclave of Hamtramck.
The city hosted the 2005 MLB All-Star Game, 2006 Super Bowl XL, both the 2006 World Series, 2006 and 2012 World Series, WrestleMania 23 in 2007, and the NCAA Final Four (college basketball), Final Four in April 2009.
The city hosted the Detroit Indy Grand Prix on Belle Isle Park (Michigan), Belle Isle Park from 1989 to 2001, 2007 to 2008, and 2012 and beyond. In 2007, open-wheel racing returned to Belle Isle with both Indy Racing League and American Le Mans Series Racing.][
]
Government
 The city is governed pursuant to the ''home rule Charter of the City of Detroit''. The government of Detroit is run by a mayor, the nine-member Detroit City Council, the eleven-member Detroit Board of Police Commissioners, Board of Police Commissioners, and a clerk. All of these officers are elected on a nonpartisan ballot, with the exception of four of the police commissioners, who are appointed by the mayor. Detroit has a "Mayor–council government, strong mayoral" system, with the mayor approving departmental appointments. The council approves budgets, but the mayor is not obligated to adhere to any earmarking. The city clerk supervises elections and is formally charged with the maintenance of municipal records. City ordinances and substantially large contracts must be approved by the council.
The city is governed pursuant to the ''home rule Charter of the City of Detroit''. The government of Detroit is run by a mayor, the nine-member Detroit City Council, the eleven-member Detroit Board of Police Commissioners, Board of Police Commissioners, and a clerk. All of these officers are elected on a nonpartisan ballot, with the exception of four of the police commissioners, who are appointed by the mayor. Detroit has a "Mayor–council government, strong mayoral" system, with the mayor approving departmental appointments. The council approves budgets, but the mayor is not obligated to adhere to any earmarking. The city clerk supervises elections and is formally charged with the maintenance of municipal records. City ordinances and substantially large contracts must be approved by the council.[Ward, George E. (July 1993)]
Detroit Charter Revision – A Brief History
. ''Citizens Research Council of Michigan'' (pdf file). The ''Detroit City Code'' is the codification (law), codification of Detroit's local ordinances.
The city clerk supervises elections and is formally charged with the maintenance of municipal records. Municipal elections for mayor, city council and city clerk are held at four-year intervals, in the year after presidential elections.[Nelson, Gabe (November 3, 2009]
Voters overwhelmingly approve Detroit Proposal D
''Crains Detroit Business''. Retrieved on December 23, 2009.
Detroit's courts are state-administered and elections are nonpartisan. The Probate Court for Wayne County is in the Coleman A. Young Municipal Center in downtown Detroit. The Circuit Court is across Gratiot Avenue in the Frank Murphy Hall of Justice, in downtown Detroit. The city is home to the Thirty-Sixth District Court, as well as the First District of the Michigan Court of Appeals and the United States District Court for the Eastern District of Michigan. The city provides law enforcement through the Detroit Police Department and emergency services through the Detroit Fire Department.
Politics
Beginning with its incorporation in 1802, Detroit has had a total of List of mayors of Detroit, Michigan, 74 mayors. Detroit's last mayor from the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party was Louis Miriani, who served from 1957 to 1962. In 1973, the city elected its first black mayor, Coleman Young. Despite development efforts, his combative style during his five terms in office was not well received by many suburban residents. Mayor Dennis Archer, a former Michigan Supreme Court Justice, refocused the city's attention on redevelopment with a plan to permit three casinos downtown. By 2008, three major casino resort hotels established operations in the city.
In 2000, the city requested an investigation by the United States Justice Department into the Detroit Police Department which was concluded in 2003 over allegations regarding its use of force and civil rights violations. The city proceeded with a major reorganization of the Detroit Police Department.
In 2013, felony bribery charges were brought against seven building inspectors. In 2016, further corruption charges were brought against 12 principals, a former school superintendent and supply vendor for a $12 million kickback scheme. However, law professor Peter Henning argues Detroit's corruption is not unusual for a city its size, especially when compared with Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
.
Detroit is sometimes referred to as a sanctuary city because it has "anti-profiling ordinances that generally prohibit local police from asking about the immigration status of people who are not suspected of any crime".
The city in recent years has been a stronghold for the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, with around 94% of votes in the city going to Joe Biden, the Democratic candidate in the 2020 United States presidential election, 2020 Presidential election.
Public finances
Detroit's protracted decline has resulted in severe urban decay, with thousands of empty buildings around the city, referred to as greyfield land, greyfield. Some parts of Detroit are so sparsely populated the city has difficulty providing municipal services. The city has demolished abandoned homes and buildings, planting grass and trees, and considered removing street lighting from large portions of the city, in order to encourage the small population in certain areas to move to more populated areas.
Education
Colleges and universities
 Detroit is home to several institutions of higher learning including Wayne State University, a national research university with medical and Wayne State University Law School, law schools in the Midtown, Detroit, Midtown area offering hundreds of academic degrees and programs. The University of Detroit Mercy, in Northwest Detroit in the University District, Detroit, University District, is a prominent Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Mixed-sex education, co-educational university affiliated with the Society of Jesus (the Jesuits) and the Sisters of Mercy. The University of Detroit Mercy offers more than a hundred academic degrees and programs of study including business, dentistry, law school, law, engineering, architecture, nursing and allied health professions. The University of Detroit Mercy School of Law is Downtown Detroit, Downtown across from the Renaissance Center.
Grand Valley State University's Detroit Center host workshops, seminars, professional development, and other large gatherings in the building. Located in the heart of downtown next to Comerica Park and the Detroit Athletic Club, the center has become a key component for educational activity in the city.
Detroit is home to several institutions of higher learning including Wayne State University, a national research university with medical and Wayne State University Law School, law schools in the Midtown, Detroit, Midtown area offering hundreds of academic degrees and programs. The University of Detroit Mercy, in Northwest Detroit in the University District, Detroit, University District, is a prominent Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Mixed-sex education, co-educational university affiliated with the Society of Jesus (the Jesuits) and the Sisters of Mercy. The University of Detroit Mercy offers more than a hundred academic degrees and programs of study including business, dentistry, law school, law, engineering, architecture, nursing and allied health professions. The University of Detroit Mercy School of Law is Downtown Detroit, Downtown across from the Renaissance Center.
Grand Valley State University's Detroit Center host workshops, seminars, professional development, and other large gatherings in the building. Located in the heart of downtown next to Comerica Park and the Detroit Athletic Club, the center has become a key component for educational activity in the city.
 Sacred Heart Major Seminary, founded in 1919, is affiliated with Pontifical University of Saint Thomas Aquinas, ''Angelicum'' in Rome and offers pontifical degrees as well as civil undergraduate and graduate degrees. Sacred Heart Major Seminary offers a variety of academic programs for both clerical and lay students. Other institutions in the city include the College for Creative Studies and Wayne County Community College. Marygrove College was a Catholic institution formerly based in Detroit before it closed in 2019. In June 2009, the Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine which is based in East Lansing, Michigan, East Lansing opened a satellite campus at the Detroit Medical Center. The University of Michigan was established in 1817 in Detroit and later moved to Ann Arbor, Michigan, Ann Arbor in 1837.
Sacred Heart Major Seminary, founded in 1919, is affiliated with Pontifical University of Saint Thomas Aquinas, ''Angelicum'' in Rome and offers pontifical degrees as well as civil undergraduate and graduate degrees. Sacred Heart Major Seminary offers a variety of academic programs for both clerical and lay students. Other institutions in the city include the College for Creative Studies and Wayne County Community College. Marygrove College was a Catholic institution formerly based in Detroit before it closed in 2019. In June 2009, the Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine which is based in East Lansing, Michigan, East Lansing opened a satellite campus at the Detroit Medical Center. The University of Michigan was established in 1817 in Detroit and later moved to Ann Arbor, Michigan, Ann Arbor in 1837.
Primary and secondary schools
many K-12 students in Detroit frequently change schools, with some children having been enrolled in seven schools before finishing their K-12 careers. There is a concentration of senior high schools and charter schools in the Downtown Detroit
Downtown Detroit is the central business district and a residential area of the city of Detroit, Michigan, United States. Locally, downtown tends to refer to the 1.4 square mile region bordered by M-10 (Lodge Freeway) to the west, Interstate 75 ( ...
area, which had wealthier residents and more gentrification relative to other parts of Detroit: Downtown, northwest Detroit, and northeast Detroit have 1,894, 3,742, and 6,018 students of high school age each, respectively, while they have 11, three, and two high schools each, respectively.[
]
Public schools and charter schools

 With about 66,000 public school students (2011–12), the Detroit Public Schools (DPS) district is the largest school district in Michigan. Detroit has an additional 56,000 charter school students for a combined enrollment of about 122,000 students.
With about 66,000 public school students (2011–12), the Detroit Public Schools (DPS) district is the largest school district in Michigan. Detroit has an additional 56,000 charter school students for a combined enrollment of about 122,000 students.[Dawsey, Chastity Pratt (October 20, 2011). Detroit Public Schools hits enrollment goal. ''Detroit Free Press''] there are about as many students in charter schools as there are in district schools. DPS continues to have the majority of the special education pupils. In addition, some Detroit students, as of 2016, attend public schools in other municipalities.[
In 1999, the Michigan Legislature removed the locally elected board of education amid allegations of mismanagement and replaced it with a reform board appointed by the mayor and governor. The elected board of education was re-established following a city referendum in 2005. The first election of the new 11-member board of education occurred on November 8, 2005.
Due to growing Detroit charter schools enrollment as well as a continued exodus of population, the city planned to close many public schools.][Hing, Julianne (March 17, 2010]
Where Have All The Students Gone?
. ''Color Lines.com''. Retrieved on August 19, 2010. State officials report a 68% graduation rate for Detroit's public schools adjusted for those who change schools.[Detroit Public Schools news](_blank)
(June 15, 2007). Retrieved February 13, 2017. Traditional public and charter school students in the city have performed poorly on standardized tests. Circa 2009 and 2011, while Detroit traditional public schools scored a record low on national tests, the publicly funded charter schools did even worse than the traditional public schools. there were 30,000 excess openings in Detroit traditional public and charter schools, bearing in mind the number of K-12-aged children in the city. In 2016, Kate Zernike of ''The New York Times'' stated school performance did not improve despite the proliferation of charters, describing the situation as "lots of choice, with no good choice".[
Detroit public schools students scored the lowest on tests of reading and writing of all major cities in the United States in 2015. Among eighth-graders, only 27% showed basic proficiency in math and 44% in reading. Nearly half of Detroit's adults are Functional illiteracy, functionally illiterate.
]
Private schools
Detroit is served by various private schools, as well as parochial Roman Catholic schools operated by the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Detroit, Archdiocese of Detroit. there are four Catholic grade schools and three Catholic high schools in the City of Detroit, with all of them in the city's west side.[Detroit area's Catholic schools shrink, but tradition endures]
Archive
. ''Detroit Free Press''. February 1, 2013. Retrieved on September 13, 2014. The Archdiocese of Detroit lists a number of primary and secondary schools in the metro area as Catholic education has emigrated to the suburbs. Of the three Catholic high schools in the city, two are operated by the Society of Jesus and the third is co-sponsored by the Sisters, Servants of the Immaculate Heart of Mary and the Congregation of St. Basil.[
]
Media
 The ''Detroit Free Press'' and ''
The ''Detroit Free Press'' and ''The Detroit News
''The Detroit News'' is one of the two major newspapers in the U.S. city of Detroit, Michigan. The paper began in 1873, when it rented space in the rival ''Detroit Free Press'' building. ''The News'' absorbed the '' Detroit Tribune'' on Februa ...
'' are the major daily newspapers, both broadsheet publications published together under a joint operating agreement called the Detroit Newspaper Partnership. Media philanthropy includes the ''Detroit Free Press'' high school journalism program and the Old Newsboys' Goodfellow Fund of Detroit. In March 2009, the two newspapers reduced home delivery to three days a week, print reduced newsstand issues of the papers on non-delivery days and focus resources on Internet-based news delivery. The ''Metro Times'', founded in 1980, is a weekly publication, covering news, arts & entertainment.
Also founded in 1935 and based in Detroit, the ''Michigan Chronicle'' is one of the oldest and most respected African-American weekly newspapers in America, covering politics, entertainment, sports and community events. The Detroit television market is the 11th largest in the United States;[Nielsen Media Research Local Universe Estimates (September 24, 2005)]
''The Nielson Company'' according to estimates that do not include audiences in large areas of Ontario, Canada (Windsor
Windsor may refer to:
Places Australia
* Windsor, New South Wales
** Municipality of Windsor, a former local government area
* Windsor, Queensland, a suburb of Brisbane, Queensland
**Shire of Windsor, a former local government authority around Wi ...
and its surrounding area on broadcast and cable TV, as well as several other cable markets in Ontario, such as the city of Ottawa) which receive and watch Detroit television stations.[
Detroit has the 11th largest radio market in the United States,][ Nearby Canadian stations such as Windsor's CKLW (whose jingles formerly proclaimed "CKLW-the Motor City") are popular in Detroit.
]
Infrastructure

Health systems
Within the city of Detroit, there are over a dozen major hospitals, which include the Detroit Medical Center (DMC), Henry Ford Hospital, Henry Ford Health System, St. John Health, St. John Health System, and the John D. Dingell VA Medical Center. The DMC, a regional Level I trauma center, consists of Detroit Receiving Hospital and University Health Center, Children's Hospital of Michigan, Harper University Hospital, Hutzel Women's Hospital, Kresge Eye Institute, Rehabilitation Institute of Michigan, Sinai-Grace Hospital, and the Karmanos Cancer Institute. The DMC has more than 2,000 licensed beds and 3,000 affiliated physicians. It is the largest private employer in the City of Detroit.[ ''Wayne State University'' Retrieved January 24, 2011.] The center is staffed by physicians from the Wayne State University School of Medicine, the largest single-campus medical school in the United States, and the United States' fourth largest medical school overall.[
] Detroit Medical Center formally became a part of Vanguard Health Systems on December 30, 2010, as a for-profit corporation. Vanguard has agreed to invest nearly $1.5 B in the Detroit Medical Center complex, which will include $417 M to retire debts, at least $350 M in capital expenditures and an additional $500 M for new capital investment.
Detroit Medical Center formally became a part of Vanguard Health Systems on December 30, 2010, as a for-profit corporation. Vanguard has agreed to invest nearly $1.5 B in the Detroit Medical Center complex, which will include $417 M to retire debts, at least $350 M in capital expenditures and an additional $500 M for new capital investment.[Anstett, Patricia (March 20, 2010]
$1.5 billion for new DMC
''Detroit Free Press''. DMC.org. Retrieved on June 12, 2010. Vanguard has agreed to assume all debts and pension obligations.[Greene, Jay (April 5, 2010]
Henry Ford Health System plans $500 million expansion
''Crains Detroit Business''. Retrieved on June 12, 2010.
In 2012, two major construction projects were begun in New Center, Detroit, New Center. The Henry Ford Health System started the first phase of a $500 million, 300-acre revitalization project, with the construction of a new $30 million, 275,000-square-foot, ''Medical Distribution Center'' for Cardinal Health, Inc. and Wayne State University started construction on a new $93 million, 207,000-square-foot, Integrative Biosciences Center (IBio).[Henderson, Tom (April 15, 2012]
WSU to build $93M biotech hub
''Crains Detroit Business''. Retrieved on March 15, 2015. As many as 500 researchers and staff will work out of the IBio Center.
Transportation
With its proximity to Canada and its facilities, ports, major highways, rail connections and international airports, Detroit is an important transportation hub. The city has three international border crossings, the Ambassador Bridge
The Ambassador Bridge is a tolled international suspension bridge across the Detroit River that connects Detroit, Michigan, United States, with Windsor, Ontario, Canada. Opened in 1929, it is the busiest international border crossing in North ...
, Detroit–Windsor Tunnel and Michigan Central Railway Tunnel, linking Detroit to Windsor, Ontario. The Ambassador Bridge is the single busiest border crossing in North America, carrying 27% of the total trade between the U.S. and Canada.
On February 18, 2015, Canadian Transport Minister Lisa Raitt announced Canada has agreed to pay the entire cost to build a $250 million U.S. Customs plaza adjacent to the planned new Detroit–Windsor bridge, now the Gordie Howe International Bridge
The Gordie Howe International Bridge (french: Pont International Gordie-Howe), known during development as the Detroit River International Crossing and the New International Trade Crossing, is a cable-stayed international bridge across the Det ...
. Canada had already planned to pay for 95% of the bridge, which will cost $2.1 billion, and is expected to open in 2024. "This allows Canada and Michigan to move the project forward immediately to its next steps which include further design work and property acquisition on the U.S. side of the border", Raitt said in a statement issued after she spoke in the House of Commons.
Transit systems
 Mass transit in the region is provided by bus services. The Detroit Department of Transportation (DDOT) provides service within city limits up to the outer edges of the city. From there, the Suburban Mobility Authority for Regional Transportation, Suburban Mobility Authority for Regional Transportation (SMART) provides service to the suburbs and the city regionally with local routes and SMART's FAST service. FAST is a new service provided by SMART which offers limited stops along major corridors throughout the Detroit metropolitan area connecting the suburbs to downtown. The new high-frequency service travels along three of Detroit's busiest corridors, Gratiot, Woodward, and Michigan, and only stops at designated FAST stops. Cross border service between the downtown areas of Windsor and Detroit is provided by Transit Windsor via the Tunnel Bus.
Mass transit in the region is provided by bus services. The Detroit Department of Transportation (DDOT) provides service within city limits up to the outer edges of the city. From there, the Suburban Mobility Authority for Regional Transportation, Suburban Mobility Authority for Regional Transportation (SMART) provides service to the suburbs and the city regionally with local routes and SMART's FAST service. FAST is a new service provided by SMART which offers limited stops along major corridors throughout the Detroit metropolitan area connecting the suburbs to downtown. The new high-frequency service travels along three of Detroit's busiest corridors, Gratiot, Woodward, and Michigan, and only stops at designated FAST stops. Cross border service between the downtown areas of Windsor and Detroit is provided by Transit Windsor via the Tunnel Bus. An elevated rail system known as the Detroit People Mover, People Mover, completed in 1987, provides daily service around a loop downtown. The QLINE serves as a link between the Detroit People Mover and Detroit (Amtrak station), Detroit Amtrak station via Woodward Avenue. The SEMCOG Commuter Rail line will extend from Detroit's New Center, Detroit, New Center, connecting to Ann Arbor, Michigan, Ann Arbor via Dearborn, Michigan, Dearborn, Wayne, Michigan, Wayne, and Ypsilanti, Michigan, Ypsilanti when it is opened.
An elevated rail system known as the Detroit People Mover, People Mover, completed in 1987, provides daily service around a loop downtown. The QLINE serves as a link between the Detroit People Mover and Detroit (Amtrak station), Detroit Amtrak station via Woodward Avenue. The SEMCOG Commuter Rail line will extend from Detroit's New Center, Detroit, New Center, connecting to Ann Arbor, Michigan, Ann Arbor via Dearborn, Michigan, Dearborn, Wayne, Michigan, Wayne, and Ypsilanti, Michigan, Ypsilanti when it is opened.[Ann Arbor – Detroit Regional Rail Project]
''SEMCOG''. Retrieved on February 4, 2010.
The Regional Transit Authority of Southeast Michigan, Regional Transit Authority (RTA) was established by an act of the Michigan legislature in December 2012 to oversee and coordinate all existing regional mass transit operations, and to develop new transit services in the region. The RTA's first project was the introduction of RelfeX, a limited-stop, cross-county bus service connecting downtown and midtown Detroit with Oakland county via Woodward avenue.
Amtrak provides service to Detroit, operating its ''Wolverine (Amtrak train), Wolverine'' service between Chicago and Pontiac, Michigan, Pontiac. The Amtrak station is in New Center north of downtown. The ''J. W. Westcott II'', which delivers mail to lake freighters on the Detroit River, is a floating post office.
Car ownership
The city of Detroit has a higher than average percentage of households without a car. In 2016, 24.7 percent of Detroit households lacked a car, much higher than the national average of 8.7. Detroit averaged 1.15 cars per household in 2016, compared to a national average of 1.8.
Freight railroads
Freight railroad operations in the city of Detroit are provided by Canadian National Railway, Canadian Pacific Railway, Conrail Shared Assets, CSX Transportation and Norfolk Southern Railway, each of which have local yards within the city. Detroit is also served by the Delray Connecting Railroad and Detroit Connecting Railroad shortlines.
Airports
 Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport (DTW), the principal airport serving Detroit, is in nearby Romulus, Michigan, Romulus. DTW is a primary hub for Delta Air Lines (following its acquisition of Northwest Airlines), and a secondary hub for Spirit Airlines. The airport is connected to
Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport (DTW), the principal airport serving Detroit, is in nearby Romulus, Michigan, Romulus. DTW is a primary hub for Delta Air Lines (following its acquisition of Northwest Airlines), and a secondary hub for Spirit Airlines. The airport is connected to Downtown Detroit
Downtown Detroit is the central business district and a residential area of the city of Detroit, Michigan, United States. Locally, downtown tends to refer to the 1.4 square mile region bordered by M-10 (Lodge Freeway) to the west, Interstate 75 ( ...
by the Suburban Mobility Authority for Regional Transportation, Suburban Mobility Authority for Regional Transportation (SMART) FAST Michigan route.
Coleman A. Young International Airport (DET), previously called Detroit City Airport, is on Detroit's northeast side; the airport now maintains only charter service and general aviation. Willow Run Airport, in far-western Wayne County near Ypsilanti, Michigan, Ypsilanti, is a general aviation and cargo airport.
Freeways
Metro Detroit has an extensive toll-free network of freeways administered by the Michigan Department of Transportation. Four major Interstate Highway System, Interstate Highways surround the city. Detroit is connected via Interstate 75 in Michigan, Interstate 75 (I-75) and Interstate 96, I-96 to Ontario Highway 401, Kings Highway 401 and to major Southern Ontario cities such as London, Ontario and the Greater Toronto Area. I-75 (Chrysler and Fisher freeways) is the region's main north–south route, serving Flint, Michigan, Flint, Pontiac, Michigan, Pontiac, Troy, Michigan, Troy, and Detroit, before continuing south (as the Detroit–Toledo and Seaway Freeways) to serve many of the communities along the shore of Lake Erie.Henry Ford
Henry Ford (July 30, 1863 – April 7, 1947) was an American industrialist, business magnate, founder of the Ford Motor Company, and chief developer of the assembly line technique of mass production. By creating the first automobile that mi ...
built it to link the factories at Willow Run and Dearborn during World War II. A portion was known as the Willow Run Expressway. The Interstate 96 in Michigan, I-96 freeway runs northwest–southeast through Livingston, Oakland and Wayne counties and (as the Jeffries Freeway through Wayne County) has its eastern terminus in downtown Detroit.
Floating post office
 Detroit has a floating post office, the ''J. W. Westcott II'', which serves lake freighters along the Detroit River. Its ZIP Code is 48222. The ZIP Code is used exclusively for the ''J. W. Westcott II'', which makes is the only floating ZIP Code in the United States. It has a land-based office at 12 24th Street, just south of the Ambassador Bridge. The J.W. Westcott Company was established in 1874 by Captain John Ward Westcott as a maritime reporting agency to inform other vessels about port conditions, and the ''J. W. Westcott II'' vessel began service in 1949 and is still in operation today.
Detroit has a floating post office, the ''J. W. Westcott II'', which serves lake freighters along the Detroit River. Its ZIP Code is 48222. The ZIP Code is used exclusively for the ''J. W. Westcott II'', which makes is the only floating ZIP Code in the United States. It has a land-based office at 12 24th Street, just south of the Ambassador Bridge. The J.W. Westcott Company was established in 1874 by Captain John Ward Westcott as a maritime reporting agency to inform other vessels about port conditions, and the ''J. W. Westcott II'' vessel began service in 1949 and is still in operation today.
Notable people
Sister cities
Detroit's Sister city, sister cities are:
* Chongqing, China
* Dubai, United Arab Emirates
* Kitwe, Zambia
* Minsk, Belarus
* Nassau, Bahamas, Nassau, Bahamas
* Toyota, Aichi, Toyota, Japan
* Turin, Italy
Notes
References
Further reading
*
*
*
* Barrow, Heather B. ''Henry Ford's Plan for the American Suburb: Dearborn and Detroit''. DeKalb, IL: Northern Illinois University Press, 2015.
* Bates, Beth Tompkins. ''The Making of Black Detroit in the Age of Henry Ford''. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Press, 2012.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Farmer, Silas. (1884) (July 1969) ''The history of Detroit and Michigan, or, The metropolis illustrated: a chronological cyclopaedia of the past and present: including a full record of territorial days in Michigan, and the annuals of Wayne County'', in various formats at
Open Library.
*
*
* Galster, George. (2012). ''Driving Detroit: The Quest for Respect in the Motor City'' University of Pennsylvania Press
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Philp, Drew (2017).
A $500 house in Detroit: rebuilding an abandoned home and an American city.
' Scribner.
*
*
*
* Powell, L. P (1901). "Detroit, the Queen City", ''Historic Towns of the Western States'' (New York).
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Primary sources
* Moon, Elaine Latzman. ''Untold tales, unsung heroes: an oral history of Detroit's African American community, 1918-1967'' (1994
online
External links
Municipal government and local Chamber of Commerce
Official website
Detroit Metro Convention & Visitors Bureau
Detroit Regional Chamber
*
Historical research and current events
Labor, Urban Affairs and Detroit History archival collections
at the Walter P. Reuther Library
Virtual Motor City Collection
at Wayne State University Library, contains over 30,000 images of Detroit from 1890 to 1980
"In Energized Detroit, Savoring an Architectural Legacy"
''The New York Times''. March 26, 2018.
{{Portal bar, Michigan, France, North America, History, United States, Cities
Detroit,
Cities in Wayne County, Michigan
County seats in Michigan
Detroit River
Michigan populated places on the Detroit River
Former state capitals in the United States, Michigan
Government units that have filed for Chapter 9 bankruptcy
Inland port cities and towns of the United States
Metro Detroit
Michigan Neighborhood Enterprise Zone
Populated places established in 1701
Populated places on the Underground Railroad
1701 establishments in New France
 The city was named by French colonists, referring to the
The city was named by French colonists, referring to the  In 1950, the city held about one-third of the state's population, anchored by its industries and workers. Over the next sixty years, the city's population declined to less than 10 percent of the state's population. During the same time period, the sprawling Detroit metropolitan area, which surrounds and includes the city, grew to contain more than half of Michigan's population. The shift of population and jobs eroded Detroit's tax base.
In June 1963, Rev.
In 1950, the city held about one-third of the state's population, anchored by its industries and workers. Over the next sixty years, the city's population declined to less than 10 percent of the state's population. During the same time period, the sprawling Detroit metropolitan area, which surrounds and includes the city, grew to contain more than half of Michigan's population. The shift of population and jobs eroded Detroit's tax base.
In June 1963, Rev.  In November 1973, the city elected Coleman Young as its first black mayor. After taking office, Young emphasized increasing racial diversity in the police department, which was predominantly white. Young also worked to improve Detroit's transportation system, but the tension between Young and his suburban counterparts over regional matters was problematic throughout his mayoral term. In 1976, the federal government offered $600 million for building a regional rapid transit system, under a single regional authority. But the inability of Detroit and its suburban neighbors to solve conflicts over transit planning resulted in the region losing the majority of funding for rapid transit.
Following the failure to reach a regional agreement over the larger system, the city moved forward with construction of the elevated downtown circulator portion of the system, which became known as the Detroit People Mover.
The gasoline crises of 1973 oil crisis, 1973 and 1979 energy crisis, 1979 also affected Detroit and the U.S. auto industry. Buyers chose smaller, more fuel-efficient cars made by foreign makers as the price of gas rose. Efforts to revive the city were stymied by the struggles of the auto industry, as their sales and market share declined. Automakers laid off thousands of employees and closed plants in the city, further eroding the tax base. To counteract this, the city used eminent domain to build two large new auto assembly plants in the city.
As mayor, Young sought to revive the city by seeking to increase investment in the city's declining downtown. The Renaissance Center, a mixed-use office and retail complex, opened in 1977. This group of skyscrapers was an attempt to keep businesses in downtown.Bailey, Ruby L.(August 22, 2007). "The D is a draw: Most suburbanites are repeat visitors", ''Detroit Free Press''. Quote: A Local 4 poll conducted by Selzer and Co., finds, "nearly two-thirds of residents of suburban Wayne, Oakland, and Macomb counties say they at least occasionally dine, attend cultural events or take in professional games in Detroit." Young also gave city support to other large developments to attract middle and upper-class residents back to the city. Despite the Renaissance Center and other projects, the downtown area continued to lose businesses to the Automobile dependency, automobile-dependent suburbs. Major stores and hotels closed, and many large office buildings went vacant. Young was criticized for being too focused on downtown development and not doing enough to lower the city's high crime rate and improve city services to residents.
High unemployment was compounded by middle-class flight to the suburbs, and some residents leaving the state to find work. The result for the city was a higher proportion of poor in its population, reduced tax base, depressed property values, abandoned buildings, abandoned neighborhoods, high crime rates, and a pronounced demographic imbalance.
In November 1973, the city elected Coleman Young as its first black mayor. After taking office, Young emphasized increasing racial diversity in the police department, which was predominantly white. Young also worked to improve Detroit's transportation system, but the tension between Young and his suburban counterparts over regional matters was problematic throughout his mayoral term. In 1976, the federal government offered $600 million for building a regional rapid transit system, under a single regional authority. But the inability of Detroit and its suburban neighbors to solve conflicts over transit planning resulted in the region losing the majority of funding for rapid transit.
Following the failure to reach a regional agreement over the larger system, the city moved forward with construction of the elevated downtown circulator portion of the system, which became known as the Detroit People Mover.
The gasoline crises of 1973 oil crisis, 1973 and 1979 energy crisis, 1979 also affected Detroit and the U.S. auto industry. Buyers chose smaller, more fuel-efficient cars made by foreign makers as the price of gas rose. Efforts to revive the city were stymied by the struggles of the auto industry, as their sales and market share declined. Automakers laid off thousands of employees and closed plants in the city, further eroding the tax base. To counteract this, the city used eminent domain to build two large new auto assembly plants in the city.
As mayor, Young sought to revive the city by seeking to increase investment in the city's declining downtown. The Renaissance Center, a mixed-use office and retail complex, opened in 1977. This group of skyscrapers was an attempt to keep businesses in downtown.Bailey, Ruby L.(August 22, 2007). "The D is a draw: Most suburbanites are repeat visitors", ''Detroit Free Press''. Quote: A Local 4 poll conducted by Selzer and Co., finds, "nearly two-thirds of residents of suburban Wayne, Oakland, and Macomb counties say they at least occasionally dine, attend cultural events or take in professional games in Detroit." Young also gave city support to other large developments to attract middle and upper-class residents back to the city. Despite the Renaissance Center and other projects, the downtown area continued to lose businesses to the Automobile dependency, automobile-dependent suburbs. Major stores and hotels closed, and many large office buildings went vacant. Young was criticized for being too focused on downtown development and not doing enough to lower the city's high crime rate and improve city services to residents.
High unemployment was compounded by middle-class flight to the suburbs, and some residents leaving the state to find work. The result for the city was a higher proportion of poor in its population, reduced tax base, depressed property values, abandoned buildings, abandoned neighborhoods, high crime rates, and a pronounced demographic imbalance.
 In the 2010s, several initiatives were taken by Detroit's citizens and new residents to improve the cityscape by renovating and revitalizing neighborhoods. Such projects include volunteer renovation groups and various Urban agriculture, urban gardening movements. Miles of associated parks and landscaping have been completed in recent years. In 2011, the Port Authority Passenger Terminal opened, with the riverwalk connecting Hart Plaza to the Renaissance Center.
One symbol of the city's decades-long decline, the Michigan Central Station, was long vacant. The city renovated it with new windows, elevators and facilities, completing the work in December 2015. In 2018, Ford Motor Company purchased the building and plans to use it for mobility testing with a potential return of train service. Several other landmark buildings have been privately renovated and adapted as condominiums, hotels, offices, or for cultural uses. Detroit is mentioned as a city of renaissance and has reversed many of the trends of the prior decades.
The city has also seen a rise in gentrification. In downtown, for example, the construction of Little Caesars Arena brought with it new, high class shops and restaurants up and down Woodward Ave. Office tower and condominium construction has led to an influx of wealthy families, but also a displacement of long-time residents and culture.
Areas outside of downtown and other recently revived areas have an average household income of about 25% less than the gentrified areas, a gap that is continuing to grow. Rents and cost of living in these gentrified areas rise every year, pushing minorities and the poor out, causing more and more racial disparity and separation in the city. In 2019, the cost of a one-bedroom loft in Rivertown reached $300,000, with a five-year sale price change of over 500% and average income rising by 18%.
In the 2010s, several initiatives were taken by Detroit's citizens and new residents to improve the cityscape by renovating and revitalizing neighborhoods. Such projects include volunteer renovation groups and various Urban agriculture, urban gardening movements. Miles of associated parks and landscaping have been completed in recent years. In 2011, the Port Authority Passenger Terminal opened, with the riverwalk connecting Hart Plaza to the Renaissance Center.
One symbol of the city's decades-long decline, the Michigan Central Station, was long vacant. The city renovated it with new windows, elevators and facilities, completing the work in December 2015. In 2018, Ford Motor Company purchased the building and plans to use it for mobility testing with a potential return of train service. Several other landmark buildings have been privately renovated and adapted as condominiums, hotels, offices, or for cultural uses. Detroit is mentioned as a city of renaissance and has reversed many of the trends of the prior decades.
The city has also seen a rise in gentrification. In downtown, for example, the construction of Little Caesars Arena brought with it new, high class shops and restaurants up and down Woodward Ave. Office tower and condominium construction has led to an influx of wealthy families, but also a displacement of long-time residents and culture.
Areas outside of downtown and other recently revived areas have an average household income of about 25% less than the gentrified areas, a gap that is continuing to grow. Rents and cost of living in these gentrified areas rise every year, pushing minorities and the poor out, causing more and more racial disparity and separation in the city. In 2019, the cost of a one-bedroom loft in Rivertown reached $300,000, with a five-year sale price change of over 500% and average income rising by 18%.

 Seen in panorama, Detroit's waterfront shows a variety of architectural styles. The Post-modern architecture, post modern Neo-Gothic spires of the One Detroit Center (1993) were designed to refer to the city's Art Deco skyscrapers. Together with the Renaissance Center, these buildings form a distinctive and recognizable skyline. Examples of the Art Deco style include the Guardian Building and Penobscot Building downtown, as well as the Fisher Building and Cadillac Place in the New Center, Detroit, New Center area near Wayne State University. Among the city's prominent structures are United States' largest Fox Theatre (Detroit), Fox Theatre, the Detroit Opera House, and the Detroit Institute of Arts, all built in the early 20th century.
While the Downtown Detroit, Downtown and New Center areas contain high-rise buildings, the majority of the surrounding city consists of low-rise structures and single-family homes. Outside of the city's core, residential high-rises are found in upper-class neighborhoods such as the East Riverfront, extending toward Grosse Pointe, and the Palmer Park Apartment Building Historic District, Palmer Park neighborhood just west of Woodward. The University Commons-Palmer Park district in northwest Detroit, near the University of Detroit Mercy and Marygrove College, anchors historic neighborhoods including Palmer Woods, Sherwood Forest, Detroit, Sherwood Forest, and the University District, Detroit, University District.
Forty-two significant structures or sites are listed on the List of Registered Historic Places in Detroit, Michigan, National Register of Historic Places. Neighborhoods constructed prior to World War II feature the architecture of the times, with wood-frame and brick houses in the working-class neighborhoods, larger brick homes in middle-class neighborhoods, and ornate mansions in upper-class neighborhoods such as Brush Park, Woodbridge, Detroit, Woodbridge, Indian Village, Detroit, Indian Village, Palmer Woods, Boston-Edison Historic District, Boston-Edison, and others.
Some of the oldest neighborhoods are along the major Woodward and East Jefferson Avenue Residential TR, East Jefferson corridors, which formed spines of the city. Some newer residential construction may also be found along the Woodward corridor and in the far west and northeast. The oldest extant neighborhoods include West Canfield Historic District, West Canfield and Brush Park. There have been multi-million dollar restorations of existing homes and construction of new homes and condominiums here.
The city has one of the United States' largest surviving collections of late 19th- and early 20th-century buildings. Architecturally significant churches and cathedrals in the city include St. Joseph Roman Catholic Church, Detroit, St. Joseph's, Old St. Mary Roman Catholic Church (Detroit), St. Mary's, the Sweetest Heart of Mary Roman Catholic Church, Sweetest Heart of Mary, and the Cathedral of the Most Blessed Sacrament.
The city has substantial activity in urban design, historic preservation, and architecture. A number of downtown redevelopment projects—of which Campus Martius Park is one of the most notable—have revitalized parts of the city. Grand Circus Park Historic District, Grand Circus Park and historic district is near the Detroit Theatre District, city's theater district; Ford Field, home of the Detroit Lions, and Comerica Park, home of the Detroit Tigers. Little Caesars Arena, a new home for the Detroit Red Wings and the Detroit Pistons, with attached residential, hotel, and retail use, opened on September 5, 2017. The plans for the project call for mixed-use residential on the blocks surrounding the arena and the renovation of the vacant 14-story Eddystone Hotel. It will be a part of The District Detroit, a group of places owned by Olympia Entertainment, Olympia Entertainment Inc., including Comerica Park and the Detroit Opera House, among others.
The Detroit International Riverfront includes a partially completed three-and-one-half-mile riverfront promenade with a combination of parks, residential buildings, and commercial areas. It extends from Hart Plaza to the MacArthur Bridge, which connects to Belle Isle Park, the largest island park in a U.S. city. The riverfront includes Tri-Centennial State Park and Harbor, Michigan's first urban state park. The second phase is a extension from Hart Plaza to the
Seen in panorama, Detroit's waterfront shows a variety of architectural styles. The Post-modern architecture, post modern Neo-Gothic spires of the One Detroit Center (1993) were designed to refer to the city's Art Deco skyscrapers. Together with the Renaissance Center, these buildings form a distinctive and recognizable skyline. Examples of the Art Deco style include the Guardian Building and Penobscot Building downtown, as well as the Fisher Building and Cadillac Place in the New Center, Detroit, New Center area near Wayne State University. Among the city's prominent structures are United States' largest Fox Theatre (Detroit), Fox Theatre, the Detroit Opera House, and the Detroit Institute of Arts, all built in the early 20th century.
While the Downtown Detroit, Downtown and New Center areas contain high-rise buildings, the majority of the surrounding city consists of low-rise structures and single-family homes. Outside of the city's core, residential high-rises are found in upper-class neighborhoods such as the East Riverfront, extending toward Grosse Pointe, and the Palmer Park Apartment Building Historic District, Palmer Park neighborhood just west of Woodward. The University Commons-Palmer Park district in northwest Detroit, near the University of Detroit Mercy and Marygrove College, anchors historic neighborhoods including Palmer Woods, Sherwood Forest, Detroit, Sherwood Forest, and the University District, Detroit, University District.
Forty-two significant structures or sites are listed on the List of Registered Historic Places in Detroit, Michigan, National Register of Historic Places. Neighborhoods constructed prior to World War II feature the architecture of the times, with wood-frame and brick houses in the working-class neighborhoods, larger brick homes in middle-class neighborhoods, and ornate mansions in upper-class neighborhoods such as Brush Park, Woodbridge, Detroit, Woodbridge, Indian Village, Detroit, Indian Village, Palmer Woods, Boston-Edison Historic District, Boston-Edison, and others.
Some of the oldest neighborhoods are along the major Woodward and East Jefferson Avenue Residential TR, East Jefferson corridors, which formed spines of the city. Some newer residential construction may also be found along the Woodward corridor and in the far west and northeast. The oldest extant neighborhoods include West Canfield Historic District, West Canfield and Brush Park. There have been multi-million dollar restorations of existing homes and construction of new homes and condominiums here.
The city has one of the United States' largest surviving collections of late 19th- and early 20th-century buildings. Architecturally significant churches and cathedrals in the city include St. Joseph Roman Catholic Church, Detroit, St. Joseph's, Old St. Mary Roman Catholic Church (Detroit), St. Mary's, the Sweetest Heart of Mary Roman Catholic Church, Sweetest Heart of Mary, and the Cathedral of the Most Blessed Sacrament.
The city has substantial activity in urban design, historic preservation, and architecture. A number of downtown redevelopment projects—of which Campus Martius Park is one of the most notable—have revitalized parts of the city. Grand Circus Park Historic District, Grand Circus Park and historic district is near the Detroit Theatre District, city's theater district; Ford Field, home of the Detroit Lions, and Comerica Park, home of the Detroit Tigers. Little Caesars Arena, a new home for the Detroit Red Wings and the Detroit Pistons, with attached residential, hotel, and retail use, opened on September 5, 2017. The plans for the project call for mixed-use residential on the blocks surrounding the arena and the renovation of the vacant 14-story Eddystone Hotel. It will be a part of The District Detroit, a group of places owned by Olympia Entertainment, Olympia Entertainment Inc., including Comerica Park and the Detroit Opera House, among others.
The Detroit International Riverfront includes a partially completed three-and-one-half-mile riverfront promenade with a combination of parks, residential buildings, and commercial areas. It extends from Hart Plaza to the MacArthur Bridge, which connects to Belle Isle Park, the largest island park in a U.S. city. The riverfront includes Tri-Centennial State Park and Harbor, Michigan's first urban state park. The second phase is a extension from Hart Plaza to the 

 Detroit has a variety of neighborhood types. The revitalized Downtown, Midtown Detroit, Midtown, Corktown, New Center, Detroit, New Center areas feature many historic buildings and are high density, while further out, particularly in the northeast and on the fringes, high vacancy levels are problematic, for which a number of solutions have been proposed. In 2007,
Detroit has a variety of neighborhood types. The revitalized Downtown, Midtown Detroit, Midtown, Corktown, New Center, Detroit, New Center areas feature many historic buildings and are high density, while further out, particularly in the northeast and on the fringes, high vacancy levels are problematic, for which a number of solutions have been proposed. In 2007,  Beginning with the rise of the automobile industry, Detroit's population increased more than sixfold during the first half of the 20th century as an influx of European, Middle Eastern (Lebanese Americans, Lebanese, Assyrian Americans, Assyrian/Chaldean), and Southern migrants brought their families to the city.Baulch, Vivian M. (September 4, 1999)
Beginning with the rise of the automobile industry, Detroit's population increased more than sixfold during the first half of the 20th century as an influx of European, Middle Eastern (Lebanese Americans, Lebanese, Assyrian Americans, Assyrian/Chaldean), and Southern migrants brought their families to the city.Baulch, Vivian M. (September 4, 1999) After World War II, many people from Appalachia also settled in Detroit. Appalachians formed communities and their children acquired southern accents. Many Lithuanians also settled in Detroit during the World War II era, especially on the city's Southwest side in the West Vernor-Junction Historic District, West Vernor area, where the renovated Lithuanian Hall reopened in 2006.
By 1940, 80% of Detroit deeds contained restrictive covenants prohibiting African Americans from buying houses they could afford. These discriminatory tactics were successful as a majority of black people in Detroit resorted to living in all-black neighborhoods such as Black Bottom, Detroit, Black Bottom and Paradise Valley. At this time, white people still made up about 90.4% of the city's population. From the Second Great Migration (African American), 1940s to the 1970s a second wave of black people moved to Detroit in search of employment and with the desire to escape the Jim Crow laws enforcing segregation in the south. However, they soon found themselves once again excluded from many opportunities in Detroit—through Racially motivated crime, violence and policy perpetuating economic discrimination (e.g.,
After World War II, many people from Appalachia also settled in Detroit. Appalachians formed communities and their children acquired southern accents. Many Lithuanians also settled in Detroit during the World War II era, especially on the city's Southwest side in the West Vernor-Junction Historic District, West Vernor area, where the renovated Lithuanian Hall reopened in 2006.
By 1940, 80% of Detroit deeds contained restrictive covenants prohibiting African Americans from buying houses they could afford. These discriminatory tactics were successful as a majority of black people in Detroit resorted to living in all-black neighborhoods such as Black Bottom, Detroit, Black Bottom and Paradise Valley. At this time, white people still made up about 90.4% of the city's population. From the Second Great Migration (African American), 1940s to the 1970s a second wave of black people moved to Detroit in search of employment and with the desire to escape the Jim Crow laws enforcing segregation in the south. However, they soon found themselves once again excluded from many opportunities in Detroit—through Racially motivated crime, violence and policy perpetuating economic discrimination (e.g., 
 Several major corporations are based in the city, including three Fortune 500 companies. The most heavily represented sectors are manufacturing (particularly automotive), finance, technology, and health care. The most significant companies based in Detroit include
Several major corporations are based in the city, including three Fortune 500 companies. The most heavily represented sectors are manufacturing (particularly automotive), finance, technology, and health care. The most significant companies based in Detroit include 
 In the central portions of Detroit, the population of young professionals, artists, and other transplants is growing and retail is expanding.Harrison, Sheena (June 25, 2007)
In the central portions of Detroit, the population of young professionals, artists, and other transplants is growing and retail is expanding.Harrison, Sheena (June 25, 2007)
 Live music has been a prominent feature of Detroit's nightlife since the late 1940s, bringing the city recognition under the nickname "Motown". The metropolitan area has many nationally prominent Theatre in Detroit, live music venues. Concerts hosted by Live Nation perform throughout the Detroit area. Large concerts are held at DTE Energy Music Theatre. The city's Theatre in Detroit, theatre venue circuit is the United States' second largest and hosts Broadway theatre, Broadway performances.
The city of Detroit has a rich musical heritage and has contributed to a number of different genres over the decades leading into the new millennium. Important music events in the city include the Detroit International Jazz Festival, the Detroit Electronic Music Festival, the Motor City Music Conference (MC2), the Urban Organic Music Conference, the Concert of Colors, and the hip-hop Summer Jamz festival.
In the 1940s, Detroit blues artist John Lee Hooker became a long-term resident in the city's southwest Delray, Detroit, Delray neighborhood. Hooker, among other important blues musicians, migrated from his home in Mississippi, bringing the Delta blues to northern cities like Detroit. Hooker recorded for Fortune Records, the biggest pre-Motown blues/soul label. During the 1950s, the city became a center for jazz, with stars performing in the Black Bottom, Detroit, Black Bottom neighborhood. Prominent emerging jazz musicians included trumpeter Donald Byrd, who attended Cass Tech and performed with Art Blakey and the Jazz Messengers early in his career, and saxophonist Pepper Adams, who enjoyed a solo career and accompanied Byrd on several albums. The Graystone International Jazz Museum documents jazz in Detroit.
Other prominent Motor City R&B stars in the 1950s and early 1960s were Nolan Strong, Andre Williams (musician), Andre Williams and Nathaniel Mayer – who all scored local and national hits on the Fortune Records label. According to Smokey Robinson, Strong was a primary influence on his voice as a teenager. The Fortune label, a family-operated label on Third Avenue in Detroit, was owned by the husband-and-wife team of Jack Brown and Devora Brown. Fortune, which also released country, gospel and rockabilly LPs and 45s, laid the groundwork for Motown, which became Detroit's most legendary record label.
Berry Gordy, Jr. founded Motown Records, which rose to prominence during the 1960s and early 1970s with acts such as Stevie Wonder, The Temptations, The Four Tops, Smokey Robinson & The Miracles, Diana Ross & The Supremes, the The Jackson 5, Jackson 5, Martha and the Vandellas, The Spinners (American R&B group), The Spinners, Gladys Knight & the Pips, The Marvelettes, The Elgins, The Monitors (American band), The Monitors, The Velvelettes and Marvin Gaye. Artists were backed by in-house vocalists The Andantes and The Funk Brothers, the Motown house band that was featured in Paul Justman's 2002 documentary film ''Standing in the Shadows of Motown'', based on Allan Slutsky's book of the same name.
The Motown Sound played an important role in the crossover appeal with popular music, since it was the first African American–owned record label to primarily feature African-American artists. Gordy moved Motown to Los Angeles in 1972 to pursue film production, but the company has since returned to Detroit. Aretha Franklin, another Detroit R&B star, carried the Motown Sound; however, she did not record with Berry's Motown label.
Local artists and bands rose to prominence in the 1960s and '70s, including the MC5, Glenn Frey, The Stooges, Bob Seger, Amboy Dukes featuring Ted Nugent, Mitch Ryder and The Detroit Wheels, Rare Earth (band), Rare Earth, Alice Cooper, and Suzi Quatro. The group Kiss (band), Kiss emphasized the city's connection with rock in the song "Detroit Rock City" and the movie produced in 1999. In the 1980s, Detroit was an important center of the hardcore punk rock underground with many nationally known bands coming out of the city and its suburbs, such as The Necros, The Meatmen, and Negative Approach.
In the 1990s and the new millennium, the city has produced a number of influential hip hop music, hip hop artists, including Eminem, the hip-hop artist with the highest cumulative sales, his rap group D12, hip-hop rapper and producer Royce da 5'9", hip-hop producer Denaun Porter, hip-hop producer J Dilla, rapper and musician Kid Rock and rappers Big Sean and Danny Brown (rapper), Danny Brown. The band Sponge (band), Sponge toured and produced music. The city also has an active garage rock scene that has generated national attention with acts such as The White Stripes, The Von Bondies, The Detroit Cobras, The Dirtbombs, Electric Six, and The Hard Lessons.
Detroit is cited as the birthplace of techno music in the early 1980s. The city also lends its name to an early and pioneering genre of electronic dance music, "Detroit techno". Featuring science fiction imagery and robotic themes, its futuristic style was greatly influenced by the geography of Detroit's urban decline and its industrial past. Prominent Detroit techno artists include Juan Atkins, Derrick May (musician), Derrick May, Kevin Saunderson, and Jeff Mills. The Detroit Electronic Music Festival, now known as Movement, occurs annually in late May on Memorial Day Weekend, and takes place in Hart Plaza. In the early years (2000–2002), this was a landmark event, boasting over a million estimated attendees annually, coming from all over the world to celebrate techno music in the city of its birth.
Live music has been a prominent feature of Detroit's nightlife since the late 1940s, bringing the city recognition under the nickname "Motown". The metropolitan area has many nationally prominent Theatre in Detroit, live music venues. Concerts hosted by Live Nation perform throughout the Detroit area. Large concerts are held at DTE Energy Music Theatre. The city's Theatre in Detroit, theatre venue circuit is the United States' second largest and hosts Broadway theatre, Broadway performances.
The city of Detroit has a rich musical heritage and has contributed to a number of different genres over the decades leading into the new millennium. Important music events in the city include the Detroit International Jazz Festival, the Detroit Electronic Music Festival, the Motor City Music Conference (MC2), the Urban Organic Music Conference, the Concert of Colors, and the hip-hop Summer Jamz festival.
In the 1940s, Detroit blues artist John Lee Hooker became a long-term resident in the city's southwest Delray, Detroit, Delray neighborhood. Hooker, among other important blues musicians, migrated from his home in Mississippi, bringing the Delta blues to northern cities like Detroit. Hooker recorded for Fortune Records, the biggest pre-Motown blues/soul label. During the 1950s, the city became a center for jazz, with stars performing in the Black Bottom, Detroit, Black Bottom neighborhood. Prominent emerging jazz musicians included trumpeter Donald Byrd, who attended Cass Tech and performed with Art Blakey and the Jazz Messengers early in his career, and saxophonist Pepper Adams, who enjoyed a solo career and accompanied Byrd on several albums. The Graystone International Jazz Museum documents jazz in Detroit.
Other prominent Motor City R&B stars in the 1950s and early 1960s were Nolan Strong, Andre Williams (musician), Andre Williams and Nathaniel Mayer – who all scored local and national hits on the Fortune Records label. According to Smokey Robinson, Strong was a primary influence on his voice as a teenager. The Fortune label, a family-operated label on Third Avenue in Detroit, was owned by the husband-and-wife team of Jack Brown and Devora Brown. Fortune, which also released country, gospel and rockabilly LPs and 45s, laid the groundwork for Motown, which became Detroit's most legendary record label.
Berry Gordy, Jr. founded Motown Records, which rose to prominence during the 1960s and early 1970s with acts such as Stevie Wonder, The Temptations, The Four Tops, Smokey Robinson & The Miracles, Diana Ross & The Supremes, the The Jackson 5, Jackson 5, Martha and the Vandellas, The Spinners (American R&B group), The Spinners, Gladys Knight & the Pips, The Marvelettes, The Elgins, The Monitors (American band), The Monitors, The Velvelettes and Marvin Gaye. Artists were backed by in-house vocalists The Andantes and The Funk Brothers, the Motown house band that was featured in Paul Justman's 2002 documentary film ''Standing in the Shadows of Motown'', based on Allan Slutsky's book of the same name.
The Motown Sound played an important role in the crossover appeal with popular music, since it was the first African American–owned record label to primarily feature African-American artists. Gordy moved Motown to Los Angeles in 1972 to pursue film production, but the company has since returned to Detroit. Aretha Franklin, another Detroit R&B star, carried the Motown Sound; however, she did not record with Berry's Motown label.
Local artists and bands rose to prominence in the 1960s and '70s, including the MC5, Glenn Frey, The Stooges, Bob Seger, Amboy Dukes featuring Ted Nugent, Mitch Ryder and The Detroit Wheels, Rare Earth (band), Rare Earth, Alice Cooper, and Suzi Quatro. The group Kiss (band), Kiss emphasized the city's connection with rock in the song "Detroit Rock City" and the movie produced in 1999. In the 1980s, Detroit was an important center of the hardcore punk rock underground with many nationally known bands coming out of the city and its suburbs, such as The Necros, The Meatmen, and Negative Approach.
In the 1990s and the new millennium, the city has produced a number of influential hip hop music, hip hop artists, including Eminem, the hip-hop artist with the highest cumulative sales, his rap group D12, hip-hop rapper and producer Royce da 5'9", hip-hop producer Denaun Porter, hip-hop producer J Dilla, rapper and musician Kid Rock and rappers Big Sean and Danny Brown (rapper), Danny Brown. The band Sponge (band), Sponge toured and produced music. The city also has an active garage rock scene that has generated national attention with acts such as The White Stripes, The Von Bondies, The Detroit Cobras, The Dirtbombs, Electric Six, and The Hard Lessons.
Detroit is cited as the birthplace of techno music in the early 1980s. The city also lends its name to an early and pioneering genre of electronic dance music, "Detroit techno". Featuring science fiction imagery and robotic themes, its futuristic style was greatly influenced by the geography of Detroit's urban decline and its industrial past. Prominent Detroit techno artists include Juan Atkins, Derrick May (musician), Derrick May, Kevin Saunderson, and Jeff Mills. The Detroit Electronic Music Festival, now known as Movement, occurs annually in late May on Memorial Day Weekend, and takes place in Hart Plaza. In the early years (2000–2002), this was a landmark event, boasting over a million estimated attendees annually, coming from all over the world to celebrate techno music in the city of its birth.
 Major theaters in Detroit include the Fox Theatre (Detroit), Fox Theatre (5,174 seats), Music Hall Center for the Performing Arts (1,770 seats), the Gem Theatre (451 seats), Detroit Masonic Temple, Masonic Temple Theatre (4,404 seats), the Detroit Opera House (2,765 seats), the Fisher Theatre (2,089 seats), The Fillmore Detroit (2,200 seats), Saint Andrew's Hall, the Majestic Theater (Detroit, Michigan), Majestic Theater, and Orchestra Hall (Detroit), Orchestra Hall (2,286 seats), which hosts the renowned Detroit Symphony Orchestra. The Nederlander Organization, the largest controller of Broadway productions in New York City, originated with the purchase of the Detroit Opera House in 1922 by the Nederlander family.
Motown Motion Picture Studios with produces movies in Detroit and the surrounding area based at the Pontiac Centerpoint Business Campus for a film industry expected to employ over 4,000 people in the metro area.
Major theaters in Detroit include the Fox Theatre (Detroit), Fox Theatre (5,174 seats), Music Hall Center for the Performing Arts (1,770 seats), the Gem Theatre (451 seats), Detroit Masonic Temple, Masonic Temple Theatre (4,404 seats), the Detroit Opera House (2,765 seats), the Fisher Theatre (2,089 seats), The Fillmore Detroit (2,200 seats), Saint Andrew's Hall, the Majestic Theater (Detroit, Michigan), Majestic Theater, and Orchestra Hall (Detroit), Orchestra Hall (2,286 seats), which hosts the renowned Detroit Symphony Orchestra. The Nederlander Organization, the largest controller of Broadway productions in New York City, originated with the purchase of the Detroit Opera House in 1922 by the Nederlander family.
Motown Motion Picture Studios with produces movies in Detroit and the surrounding area based at the Pontiac Centerpoint Business Campus for a film industry expected to employ over 4,000 people in the metro area.
 Because of its Culture of Detroit, unique culture, Architecture of metropolitan Detroit, distinctive architecture, and Planning and development in Detroit, revitalization and urban renewal efforts in the 21st century, Detroit has enjoyed increased prominence as a tourist destination in recent years. ''The New York Times'' listed Detroit as the ninth-best destination in its list of ''52 Places to Go in 2017'',"52 Places to Go in 2017"
Because of its Culture of Detroit, unique culture, Architecture of metropolitan Detroit, distinctive architecture, and Planning and development in Detroit, revitalization and urban renewal efforts in the 21st century, Detroit has enjoyed increased prominence as a tourist destination in recent years. ''The New York Times'' listed Detroit as the ninth-best destination in its list of ''52 Places to Go in 2017'',"52 Places to Go in 2017" Annual summer events include the Detroit Electronic Music Festival, Electronic Music Festival, Detroit International Jazz Festival, International Jazz Festival, the Woodward Dream Cruise, the African World Festival, the country music Hoedown, Noel Night, and Dally in the Alley. Within downtown, Campus Martius Park hosts large events, including the annual Motown Winter Blast. As the world's traditional automotive center, the city hosts the North American International Auto Show. Held since 1924, America's Thanksgiving Parade is one of the nation's largest. River Days, a five-day summer festival on the Detroit International Riverfront, International Riverfront lead up to the Windsor–Detroit International Freedom Festival fireworks, which draw super sized-crowds ranging from hundreds of thousands to over three million people.Fifth Third Bank rocks the Winter Blast. ''Michigan Chronicle''. (March 14, 2006).
An important civic sculpture in Detroit is ''The Spirit of Detroit'' by Marshall Fredericks at the Coleman Young Municipal Center. The image is often used as a symbol of Detroit and the statue itself is occasionally dressed in sports jerseys to celebrate when a Detroit team is doing well. A Monument to Joe Louis, memorial to Joe Louis at the intersection of Jefferson and Woodward Avenues was dedicated on October 1, 1986. The sculpture, commissioned by ''Sports Illustrated'' and executed by Robert Graham (sculptor), Robert Graham, is a long arm with a fisted hand suspended by a pyramidal framework.
Artist Tyree Guyton created the controversial street art exhibit known as the Heidelberg Project in 1986, using found objects including cars, clothing and shoes found in the neighborhood near and on Heidelberg Street on the near East Side of Detroit.
''Time'' named Detroit as one of the fifty World's Greatest Places of 2022 to explore.
Annual summer events include the Detroit Electronic Music Festival, Electronic Music Festival, Detroit International Jazz Festival, International Jazz Festival, the Woodward Dream Cruise, the African World Festival, the country music Hoedown, Noel Night, and Dally in the Alley. Within downtown, Campus Martius Park hosts large events, including the annual Motown Winter Blast. As the world's traditional automotive center, the city hosts the North American International Auto Show. Held since 1924, America's Thanksgiving Parade is one of the nation's largest. River Days, a five-day summer festival on the Detroit International Riverfront, International Riverfront lead up to the Windsor–Detroit International Freedom Festival fireworks, which draw super sized-crowds ranging from hundreds of thousands to over three million people.Fifth Third Bank rocks the Winter Blast. ''Michigan Chronicle''. (March 14, 2006).
An important civic sculpture in Detroit is ''The Spirit of Detroit'' by Marshall Fredericks at the Coleman Young Municipal Center. The image is often used as a symbol of Detroit and the statue itself is occasionally dressed in sports jerseys to celebrate when a Detroit team is doing well. A Monument to Joe Louis, memorial to Joe Louis at the intersection of Jefferson and Woodward Avenues was dedicated on October 1, 1986. The sculpture, commissioned by ''Sports Illustrated'' and executed by Robert Graham (sculptor), Robert Graham, is a long arm with a fisted hand suspended by a pyramidal framework.
Artist Tyree Guyton created the controversial street art exhibit known as the Heidelberg Project in 1986, using found objects including cars, clothing and shoes found in the neighborhood near and on Heidelberg Street on the near East Side of Detroit.
''Time'' named Detroit as one of the fifty World's Greatest Places of 2022 to explore.
 The Detroit Tigers have won four World Series titles (1935 World Series, 1935, 1945 World Series, 1945, 1968 World Series, 1968, and 1984 World Series, 1984). The Detroit Red Wings have won 11 Stanley Cups (1936 Stanley Cup Finals, 1935–36, 1937 Stanley Cup Finals, 1936–37, 1943 Stanley Cup Finals, 1942–43, 1950 Stanley Cup Finals, 1949–50, 1952 Stanley Cup Finals, 1951–52, 1954 Stanley Cup Finals, 1953–54, 1955 Stanley Cup Finals, 1954–55, 1997 Stanley Cup Finals, 1996–97, 1998 Stanley Cup Finals, 1997–98, 2002 Stanley Cup Finals, 2001–02, 2008 Stanley Cup Finals, 2007–08) (the most by an American NHL franchise). The Detroit Lions have won 4 NFL titles (1935 NFL Championship Game, 1935, 1952 NFL Championship Game, 1952, 1953 NFL Championship Game, 1953, 1957 NFL Championship Game, 1957) . The Detroit Pistons have won three NBA titles (1989 NBA Finals, 1989, 1990 NBA Finals, 1990, 2004 NBA Finals, 2004). With the Pistons' first of three NBA titles in 1989, the city of Detroit has won titles in all four of the major professional sports leagues. Two new downtown stadiums for the Detroit Tigers and Detroit Lions opened in 2000 and 2002, respectively, returning the Lions to the city proper.
In college sports, Detroit's central location within the Mid-American Conference has made it a frequent site for the league's championship events. While the MAC Basketball Tournament moved permanently to Cleveland, Ohio, Cleveland starting in 2000, the MAC Football Championship Game has been played at Ford Field in Detroit since 2004, and annually attracts 25,000 to 30,000 fans. The University of Detroit Mercy has an NCAA Division I program, and Wayne State University has both NCAA Division I and NCAA Division II, II programs. The NCAA football Quick Lane Bowl is held at Ford Field each December.
Detroit's professional soccer team is Detroit City FC. Founded in 2012 as a semi-professional soccer club, the team now plays professional soccer in the USL Championship (USLC). Nicknamed, ''Le Rouge'', the club are two-time champions of NISA since joining in 2020. They play their home matches in Keyworth Stadium, which is located in the Detroit enclave of Hamtramck.
The city hosted the 2005 MLB All-Star Game, 2006 Super Bowl XL, both the 2006 World Series, 2006 and 2012 World Series, WrestleMania 23 in 2007, and the NCAA Final Four (college basketball), Final Four in April 2009.
The city hosted the Detroit Indy Grand Prix on Belle Isle Park (Michigan), Belle Isle Park from 1989 to 2001, 2007 to 2008, and 2012 and beyond. In 2007, open-wheel racing returned to Belle Isle with both Indy Racing League and American Le Mans Series Racing. From 1982 to 1988, Detroit held the Detroit Grand Prix, at the Detroit street circuit.
Detroit is one of eight American cities to have won titles in all four major leagues (MLB, NFL, NHL and NBA), though of the eight it is the only one to have not won a Super Bowl title (all of the Lions' titles came prior to the start of the Super Bowl era). In the years following the mid-1930s, Detroit was referred to as the "City of Champions" after the Tigers, Lions, and Red Wings captured the three major professional sports championships in existence at the time in a seven-month period of time (the Tigers won the World Series in October 1935; the Lions won the NFL championship in December 1935; the Red Wings won the Stanley Cup in April 1936). In 1932, Eddie "The Midnight Express" Tolan from Detroit won the 100- and 200-meter races and two gold medals at the 1932 Summer Olympics. Joe Louis won the heavyweight championship of the world in 1937.
Detroit has made the most bids to host the Summer Olympics without ever being awarded the games, with seven unsuccessful bids for the 1944 Summer Olympics, 1944, 1952 Summer Olympics, 1952, 1956 Summer Olympics, 1956, 1960 Summer Olympics, 1960, 1964 Summer Olympics, 1964, 1968 Summer Olympics, 1968, and 1972 Summer Olympics, 1972 summer games.
The Detroit Tigers have won four World Series titles (1935 World Series, 1935, 1945 World Series, 1945, 1968 World Series, 1968, and 1984 World Series, 1984). The Detroit Red Wings have won 11 Stanley Cups (1936 Stanley Cup Finals, 1935–36, 1937 Stanley Cup Finals, 1936–37, 1943 Stanley Cup Finals, 1942–43, 1950 Stanley Cup Finals, 1949–50, 1952 Stanley Cup Finals, 1951–52, 1954 Stanley Cup Finals, 1953–54, 1955 Stanley Cup Finals, 1954–55, 1997 Stanley Cup Finals, 1996–97, 1998 Stanley Cup Finals, 1997–98, 2002 Stanley Cup Finals, 2001–02, 2008 Stanley Cup Finals, 2007–08) (the most by an American NHL franchise). The Detroit Lions have won 4 NFL titles (1935 NFL Championship Game, 1935, 1952 NFL Championship Game, 1952, 1953 NFL Championship Game, 1953, 1957 NFL Championship Game, 1957) . The Detroit Pistons have won three NBA titles (1989 NBA Finals, 1989, 1990 NBA Finals, 1990, 2004 NBA Finals, 2004). With the Pistons' first of three NBA titles in 1989, the city of Detroit has won titles in all four of the major professional sports leagues. Two new downtown stadiums for the Detroit Tigers and Detroit Lions opened in 2000 and 2002, respectively, returning the Lions to the city proper.
In college sports, Detroit's central location within the Mid-American Conference has made it a frequent site for the league's championship events. While the MAC Basketball Tournament moved permanently to Cleveland, Ohio, Cleveland starting in 2000, the MAC Football Championship Game has been played at Ford Field in Detroit since 2004, and annually attracts 25,000 to 30,000 fans. The University of Detroit Mercy has an NCAA Division I program, and Wayne State University has both NCAA Division I and NCAA Division II, II programs. The NCAA football Quick Lane Bowl is held at Ford Field each December.
Detroit's professional soccer team is Detroit City FC. Founded in 2012 as a semi-professional soccer club, the team now plays professional soccer in the USL Championship (USLC). Nicknamed, ''Le Rouge'', the club are two-time champions of NISA since joining in 2020. They play their home matches in Keyworth Stadium, which is located in the Detroit enclave of Hamtramck.
The city hosted the 2005 MLB All-Star Game, 2006 Super Bowl XL, both the 2006 World Series, 2006 and 2012 World Series, WrestleMania 23 in 2007, and the NCAA Final Four (college basketball), Final Four in April 2009.
The city hosted the Detroit Indy Grand Prix on Belle Isle Park (Michigan), Belle Isle Park from 1989 to 2001, 2007 to 2008, and 2012 and beyond. In 2007, open-wheel racing returned to Belle Isle with both Indy Racing League and American Le Mans Series Racing. From 1982 to 1988, Detroit held the Detroit Grand Prix, at the Detroit street circuit.
Detroit is one of eight American cities to have won titles in all four major leagues (MLB, NFL, NHL and NBA), though of the eight it is the only one to have not won a Super Bowl title (all of the Lions' titles came prior to the start of the Super Bowl era). In the years following the mid-1930s, Detroit was referred to as the "City of Champions" after the Tigers, Lions, and Red Wings captured the three major professional sports championships in existence at the time in a seven-month period of time (the Tigers won the World Series in October 1935; the Lions won the NFL championship in December 1935; the Red Wings won the Stanley Cup in April 1936). In 1932, Eddie "The Midnight Express" Tolan from Detroit won the 100- and 200-meter races and two gold medals at the 1932 Summer Olympics. Joe Louis won the heavyweight championship of the world in 1937.
Detroit has made the most bids to host the Summer Olympics without ever being awarded the games, with seven unsuccessful bids for the 1944 Summer Olympics, 1944, 1952 Summer Olympics, 1952, 1956 Summer Olympics, 1956, 1960 Summer Olympics, 1960, 1964 Summer Olympics, 1964, 1968 Summer Olympics, 1968, and 1972 Summer Olympics, 1972 summer games.
 The city is governed pursuant to the ''home rule Charter of the City of Detroit''. The government of Detroit is run by a mayor, the nine-member Detroit City Council, the eleven-member Detroit Board of Police Commissioners, Board of Police Commissioners, and a clerk. All of these officers are elected on a nonpartisan ballot, with the exception of four of the police commissioners, who are appointed by the mayor. Detroit has a "Mayor–council government, strong mayoral" system, with the mayor approving departmental appointments. The council approves budgets, but the mayor is not obligated to adhere to any earmarking. The city clerk supervises elections and is formally charged with the maintenance of municipal records. City ordinances and substantially large contracts must be approved by the council.Ward, George E. (July 1993)
The city is governed pursuant to the ''home rule Charter of the City of Detroit''. The government of Detroit is run by a mayor, the nine-member Detroit City Council, the eleven-member Detroit Board of Police Commissioners, Board of Police Commissioners, and a clerk. All of these officers are elected on a nonpartisan ballot, with the exception of four of the police commissioners, who are appointed by the mayor. Detroit has a "Mayor–council government, strong mayoral" system, with the mayor approving departmental appointments. The council approves budgets, but the mayor is not obligated to adhere to any earmarking. The city clerk supervises elections and is formally charged with the maintenance of municipal records. City ordinances and substantially large contracts must be approved by the council.Ward, George E. (July 1993) Detroit is home to several institutions of higher learning including Wayne State University, a national research university with medical and Wayne State University Law School, law schools in the Midtown, Detroit, Midtown area offering hundreds of academic degrees and programs. The University of Detroit Mercy, in Northwest Detroit in the University District, Detroit, University District, is a prominent Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Mixed-sex education, co-educational university affiliated with the Society of Jesus (the Jesuits) and the Sisters of Mercy. The University of Detroit Mercy offers more than a hundred academic degrees and programs of study including business, dentistry, law school, law, engineering, architecture, nursing and allied health professions. The University of Detroit Mercy School of Law is Downtown Detroit, Downtown across from the Renaissance Center.
Grand Valley State University's Detroit Center host workshops, seminars, professional development, and other large gatherings in the building. Located in the heart of downtown next to Comerica Park and the Detroit Athletic Club, the center has become a key component for educational activity in the city.
Detroit is home to several institutions of higher learning including Wayne State University, a national research university with medical and Wayne State University Law School, law schools in the Midtown, Detroit, Midtown area offering hundreds of academic degrees and programs. The University of Detroit Mercy, in Northwest Detroit in the University District, Detroit, University District, is a prominent Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Mixed-sex education, co-educational university affiliated with the Society of Jesus (the Jesuits) and the Sisters of Mercy. The University of Detroit Mercy offers more than a hundred academic degrees and programs of study including business, dentistry, law school, law, engineering, architecture, nursing and allied health professions. The University of Detroit Mercy School of Law is Downtown Detroit, Downtown across from the Renaissance Center.
Grand Valley State University's Detroit Center host workshops, seminars, professional development, and other large gatherings in the building. Located in the heart of downtown next to Comerica Park and the Detroit Athletic Club, the center has become a key component for educational activity in the city.
 Sacred Heart Major Seminary, founded in 1919, is affiliated with Pontifical University of Saint Thomas Aquinas, ''Angelicum'' in Rome and offers pontifical degrees as well as civil undergraduate and graduate degrees. Sacred Heart Major Seminary offers a variety of academic programs for both clerical and lay students. Other institutions in the city include the College for Creative Studies and Wayne County Community College. Marygrove College was a Catholic institution formerly based in Detroit before it closed in 2019. In June 2009, the Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine which is based in East Lansing, Michigan, East Lansing opened a satellite campus at the Detroit Medical Center. The University of Michigan was established in 1817 in Detroit and later moved to Ann Arbor, Michigan, Ann Arbor in 1837.
Sacred Heart Major Seminary, founded in 1919, is affiliated with Pontifical University of Saint Thomas Aquinas, ''Angelicum'' in Rome and offers pontifical degrees as well as civil undergraduate and graduate degrees. Sacred Heart Major Seminary offers a variety of academic programs for both clerical and lay students. Other institutions in the city include the College for Creative Studies and Wayne County Community College. Marygrove College was a Catholic institution formerly based in Detroit before it closed in 2019. In June 2009, the Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine which is based in East Lansing, Michigan, East Lansing opened a satellite campus at the Detroit Medical Center. The University of Michigan was established in 1817 in Detroit and later moved to Ann Arbor, Michigan, Ann Arbor in 1837.

 With about 66,000 public school students (2011–12), the Detroit Public Schools (DPS) district is the largest school district in Michigan. Detroit has an additional 56,000 charter school students for a combined enrollment of about 122,000 students.Dawsey, Chastity Pratt (October 20, 2011). Detroit Public Schools hits enrollment goal. ''Detroit Free Press'' there are about as many students in charter schools as there are in district schools. DPS continues to have the majority of the special education pupils. In addition, some Detroit students, as of 2016, attend public schools in other municipalities.
In 1999, the Michigan Legislature removed the locally elected board of education amid allegations of mismanagement and replaced it with a reform board appointed by the mayor and governor. The elected board of education was re-established following a city referendum in 2005. The first election of the new 11-member board of education occurred on November 8, 2005.
Due to growing Detroit charter schools enrollment as well as a continued exodus of population, the city planned to close many public schools.Hing, Julianne (March 17, 2010
With about 66,000 public school students (2011–12), the Detroit Public Schools (DPS) district is the largest school district in Michigan. Detroit has an additional 56,000 charter school students for a combined enrollment of about 122,000 students.Dawsey, Chastity Pratt (October 20, 2011). Detroit Public Schools hits enrollment goal. ''Detroit Free Press'' there are about as many students in charter schools as there are in district schools. DPS continues to have the majority of the special education pupils. In addition, some Detroit students, as of 2016, attend public schools in other municipalities.
In 1999, the Michigan Legislature removed the locally elected board of education amid allegations of mismanagement and replaced it with a reform board appointed by the mayor and governor. The elected board of education was re-established following a city referendum in 2005. The first election of the new 11-member board of education occurred on November 8, 2005.
Due to growing Detroit charter schools enrollment as well as a continued exodus of population, the city planned to close many public schools.Hing, Julianne (March 17, 2010 The ''Detroit Free Press'' and ''
The ''Detroit Free Press'' and ''
 Detroit Medical Center formally became a part of Vanguard Health Systems on December 30, 2010, as a for-profit corporation. Vanguard has agreed to invest nearly $1.5 B in the Detroit Medical Center complex, which will include $417 M to retire debts, at least $350 M in capital expenditures and an additional $500 M for new capital investment.Anstett, Patricia (March 20, 2010
Detroit Medical Center formally became a part of Vanguard Health Systems on December 30, 2010, as a for-profit corporation. Vanguard has agreed to invest nearly $1.5 B in the Detroit Medical Center complex, which will include $417 M to retire debts, at least $350 M in capital expenditures and an additional $500 M for new capital investment.Anstett, Patricia (March 20, 2010
 Mass transit in the region is provided by bus services. The Detroit Department of Transportation (DDOT) provides service within city limits up to the outer edges of the city. From there, the Suburban Mobility Authority for Regional Transportation, Suburban Mobility Authority for Regional Transportation (SMART) provides service to the suburbs and the city regionally with local routes and SMART's FAST service. FAST is a new service provided by SMART which offers limited stops along major corridors throughout the Detroit metropolitan area connecting the suburbs to downtown. The new high-frequency service travels along three of Detroit's busiest corridors, Gratiot, Woodward, and Michigan, and only stops at designated FAST stops. Cross border service between the downtown areas of Windsor and Detroit is provided by Transit Windsor via the Tunnel Bus.
Mass transit in the region is provided by bus services. The Detroit Department of Transportation (DDOT) provides service within city limits up to the outer edges of the city. From there, the Suburban Mobility Authority for Regional Transportation, Suburban Mobility Authority for Regional Transportation (SMART) provides service to the suburbs and the city regionally with local routes and SMART's FAST service. FAST is a new service provided by SMART which offers limited stops along major corridors throughout the Detroit metropolitan area connecting the suburbs to downtown. The new high-frequency service travels along three of Detroit's busiest corridors, Gratiot, Woodward, and Michigan, and only stops at designated FAST stops. Cross border service between the downtown areas of Windsor and Detroit is provided by Transit Windsor via the Tunnel Bus.
 An elevated rail system known as the Detroit People Mover, People Mover, completed in 1987, provides daily service around a loop downtown. The QLINE serves as a link between the Detroit People Mover and Detroit (Amtrak station), Detroit Amtrak station via Woodward Avenue. The SEMCOG Commuter Rail line will extend from Detroit's New Center, Detroit, New Center, connecting to Ann Arbor, Michigan, Ann Arbor via Dearborn, Michigan, Dearborn, Wayne, Michigan, Wayne, and Ypsilanti, Michigan, Ypsilanti when it is opened.Ann Arbor – Detroit Regional Rail Project
An elevated rail system known as the Detroit People Mover, People Mover, completed in 1987, provides daily service around a loop downtown. The QLINE serves as a link between the Detroit People Mover and Detroit (Amtrak station), Detroit Amtrak station via Woodward Avenue. The SEMCOG Commuter Rail line will extend from Detroit's New Center, Detroit, New Center, connecting to Ann Arbor, Michigan, Ann Arbor via Dearborn, Michigan, Dearborn, Wayne, Michigan, Wayne, and Ypsilanti, Michigan, Ypsilanti when it is opened.Ann Arbor – Detroit Regional Rail Project Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport (DTW), the principal airport serving Detroit, is in nearby Romulus, Michigan, Romulus. DTW is a primary hub for Delta Air Lines (following its acquisition of Northwest Airlines), and a secondary hub for Spirit Airlines. The airport is connected to
Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport (DTW), the principal airport serving Detroit, is in nearby Romulus, Michigan, Romulus. DTW is a primary hub for Delta Air Lines (following its acquisition of Northwest Airlines), and a secondary hub for Spirit Airlines. The airport is connected to  Detroit has a floating post office, the ''J. W. Westcott II'', which serves lake freighters along the Detroit River. Its ZIP Code is 48222. The ZIP Code is used exclusively for the ''J. W. Westcott II'', which makes is the only floating ZIP Code in the United States. It has a land-based office at 12 24th Street, just south of the Ambassador Bridge. The J.W. Westcott Company was established in 1874 by Captain John Ward Westcott as a maritime reporting agency to inform other vessels about port conditions, and the ''J. W. Westcott II'' vessel began service in 1949 and is still in operation today.
Detroit has a floating post office, the ''J. W. Westcott II'', which serves lake freighters along the Detroit River. Its ZIP Code is 48222. The ZIP Code is used exclusively for the ''J. W. Westcott II'', which makes is the only floating ZIP Code in the United States. It has a land-based office at 12 24th Street, just south of the Ambassador Bridge. The J.W. Westcott Company was established in 1874 by Captain John Ward Westcott as a maritime reporting agency to inform other vessels about port conditions, and the ''J. W. Westcott II'' vessel began service in 1949 and is still in operation today.