Detecting Earth From Distant Star-based Systems on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
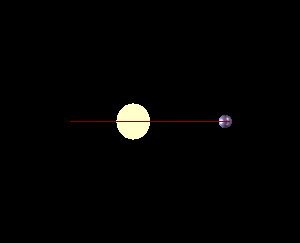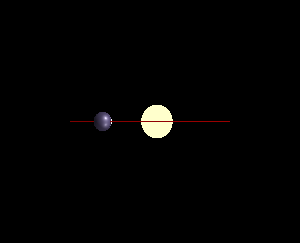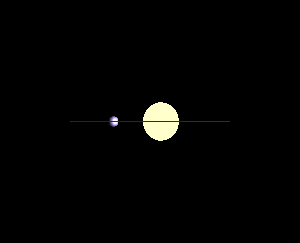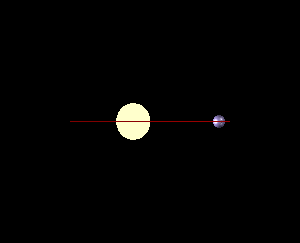 There are several methods currently used by astronomers to detect distant
There are several methods currently used by astronomers to detect distant
Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia
by the
 There are several methods currently used by astronomers to detect distant
There are several methods currently used by astronomers to detect distant exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
s from Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
. Theoretically, some of these same methods may be used to detect the Earth as an exoplanet from distant star systems.
In June 2021, astronomers identified 1,715 stars (with likely related exoplanetary systems) within 326 light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...
s (100 parsecs) that have a favorable positional vantage point—in relation to the Earth Transit Zone (ETZ)—of detecting Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
as an exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
transiting the Sun since the beginnings of human civilization (about 5,000 years ago); an additional 319 stars are expected to arrive at this special vantage point in the next 5,000 years. Seven known exoplanet hosts, including Ross 128
Ross 128 is a red dwarf in the equatorial zodiac constellation of Virgo, near β Virginis. The apparent magnitude of Ross 128 is 11.13, which is too faint to be seen with the unaided eye. Based upon parallax measurements, the distance of ...
, may be among these stars. Teegarden's Star and Trappist-1 may be expected to see the Earth in 29 and 1,642 years, respectively. Radio waves, emitted by humans, have reached over 75 of the closest stars that were studied. In June 2021, astronomers reported identifying 29 planets in habitable zones that may be capable of observing the Earth. Earlier, in October 2020, astronomers had initially identified 508 such stars within 326 light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...
s (100 parsecs) that would have a favorable positional vantage point—in relation to the Earth Transit Zone (ETZ)—of detecting Earth as an exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
transiting the Sun.
Transit method is the most popular tool used to detect exoplanets and the most common tool to spectroscopically analyze exoplanetary atmospheres. As a result, such studies, based on the transit method, will be useful in the search for life on exoplanets beyond our Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar S ...
by the SETI program, Breakthrough Listen Initiative, as well as upcoming exoplanetary TESS mission searches.
Detectability of Earth from distant star-based systems may allow for the detectability of humanity and/or analysis of Earth from distant vantage points such as via " atmospheric SETI" for the detection of atmospheric compositions explainable only by use of (artificial) technology like nitrogen dioxide air pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types ...
from e.g. transportation technologies. The easiest or most likely artificial signals from Earth to be detectable are brief pulses transmitted by anti-ballistic missile
An anti-ballistic missile (ABM) is a surface-to-air missile designed to counter ballistic missiles (missile defense). Ballistic missiles are used to deliver nuclear weapon, nuclear, Chemical weapon, chemical, Bioagent, biological, or conventiona ...
(ABM) early-warning and space-surveillance radars during the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
and later astronomical and military radars. Unlike the earliest and conventional radio- and television-broadcasting which has been claimed to be undetectable at short distances, such signals could be detected from very distant, possibly star-based, receiver stations – any single of which would detect brief episodes of powerful pulses repeating with intervals of one Earth day – and could be used to detect both Earth as well as the presence of a radar-utilizing civilization on it.
Studies have suggested that radio broadcast leakage – with the program material likely not being detectable – may be a technosignature detectable at distances of up to a hundred light years with technology equivalent to the Square Kilometer Array if the location of Earth is known. Likewise, if Earth's location can be and is known, it may be possible to use atmospheric analysis to detect life or favorable conditions for it on Earth via biosignature
A biosignature (sometimes called chemical fossil or molecular fossil) is any substance – such as an element, isotope, or molecule – or phenomenon that provides scientific evidence of past or present life. Measurable attribute ...
s, including MERMOZ instruments that may be capable of remotely detecting living matter on Earth.
See also
* *List of exoplanet search projects
The following is a list of exoplanet search projects.
Ground-based search projects
Space missions
Past and current
Planned
Proposed
* EXCEDE
* FINESSE
* Origins
* HabEx
* LUVOIR
* New Worlds Mission
* PEGASE
Canceled
* Darwin
* EChO ...
* Lists of exoplanets
These are lists of exoplanets. Most of these were discovered by the Kepler space telescope. There are an additional 2,054 potential exoplanets from Kepler's first mission yet to be confirmed, as well as 978 from its "Second Light" mission and 4 ...
*
*
*
*
References
External links
Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia
by the
Paris Observatory
The Paris Observatory (french: Observatoire de Paris ), a research institution of the Paris Sciences et Lettres University, is the foremost astronomical observatory of France, and one of the largest astronomical centers in the world. Its histor ...
{{Portal bar, Astronomy, Biology, Space
Astrobiology
Planetary science